Unit 3: Heat, Temperature, and Energy Transfer
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is thermal energy?
The energy of all the particles in an object related to its temperature, essentially heat energy.
What are some advantages and disadvantages of using an open fire for heating?
Advantages: very warm; Disadvantages: hard to control, dangerous, messy.
How does a modern stove differ from an open fire?
easy to control and safe to use, while an open fire requires more work and is less controlled.
What is a pioneer stove used for?
To heat homes and cook food.
What are the benefits of a modern fireplace?
Convenient (flip a switch), no mess, consistent heat, but it costs money (natural gas/electricity) and is not as hot as an open fire.
What are some examples of devices that use heat energy?
Hair dryers, clothes dryers, whistling kettles, hot tubs, microwaves, saunas, hair straighteners, portable heaters.
What is the purpose of a thermometer?
To measure temperature using mechanical or electrical devices.
Who invented the early thermometer?
Galileo.

What is the Celsius scale and who invented it?
A temperature system commonly used in Canada and other parts of the world, invented by Anders Celsius.
What temperatures correspond to the freezing and boiling points of water on the Celsius scale?
Freezing point: 0 degrees Celsius; Boiling point: 100 degrees Celsius.
What factors can affect the boiling and freezing points of water?
The purity of water and pressure.
What is absolute zero and who invented the Kelvin scale?
Absolute zero is 0 K or -273.15 degrees Celsius, and the Kelvin scale was developed by William Thomson (Lord Kelvin).
What are the freezing and boiling points of water on the Kelvin scale?
Freezing point: 273 K; Boiling point: 373 K.
What are the three main components of a thermometer?
1) Sensor: detects changes in temperature; 2) Signal: provides information about temperature; 3) Responder: indicates the temperature using a pointer, light, or other mechanism.
What is a thermocouple?
A device made of two different metals twisted together to generate a small electrical current that varies with temperature.
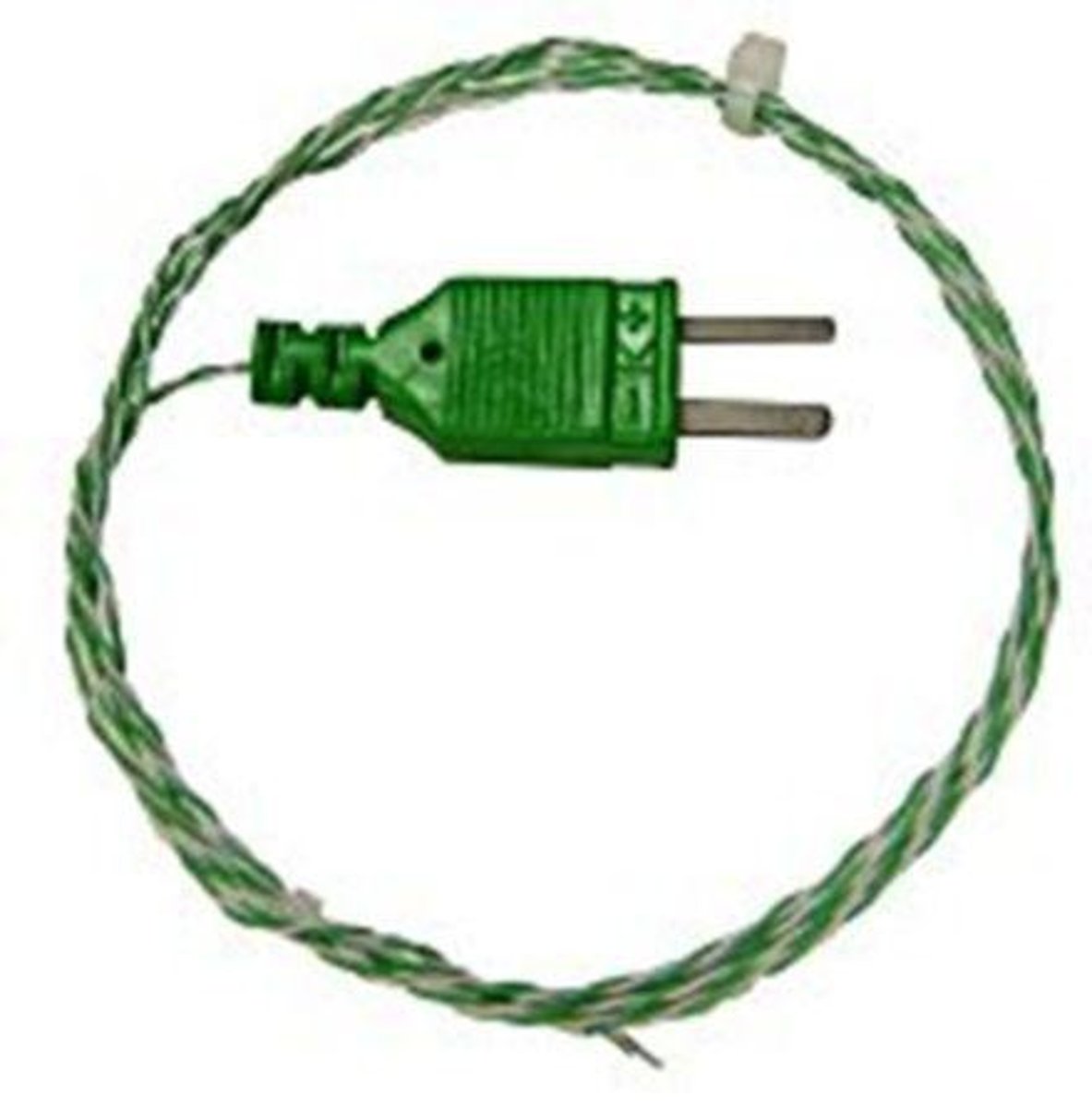

What are some applications of thermocouples?
Used in flame sensors for gas-powered appliances and for temperature measurements in engines and kilns.
How can you save energy in your daily life?
By using energy-efficient appliances and practices, such as turning off devices when not in use.
What is the significance of the temperature scale?
It provides a standardized way to measure and communicate temperature.
Why does water boil at different temperatures at high altitudes?
Because the weight of air above is less at high altitudes, leading to lower boiling temperatures.
What is the estimated value of absolute zero in Celsius?
-273.15 degrees Celsius.
What is the importance of the Kelvin scale in scientific experiments?
It provides a scale for measuring temperatures that is absolute and does not go below zero.
What are some new inventions or technologies that use heat energy?
Examples include microwaves, hair dryers, and modern stoves.
What is the role of the responder in a thermometer?
To indicate the temperature using a pointer, light, or other mechanism.
What is the relationship between temperature and the energy of particles in an object?
Higher temperatures correspond to higher thermal energy, meaning the particles are moving more vigorously.
How does temperature affect the strength of the current?
The strength of the current depends on temperature.
What is a thermocouple used for?
can be used for temperature measurements in engines and kilns.
What is a bimetallic strip and how does it work?
consists of two different metals joined together; when heated, one metal expands more than the other, causing the strip to curl up, commonly used in thermostats.
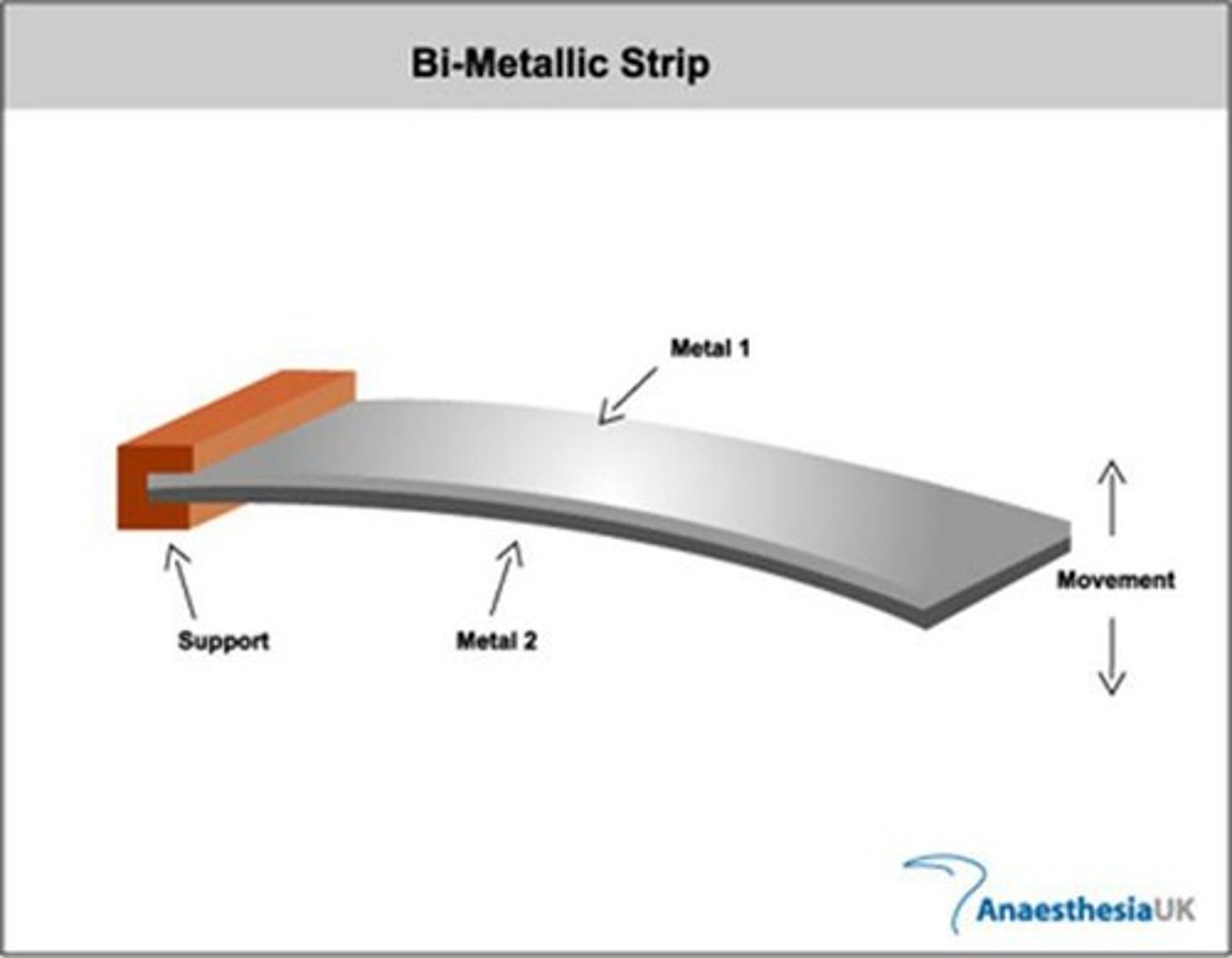
What is a recording thermometer?
a bimettic strip connected to a writing device and paper that records temperature fluctuations over time.
What instrument works similarly to a recording thermometer?
An infrared thermogram works similarly by recording infrared radiation as different colors according to their temperature.
What are the three main points of the Particle Model?
1) All substances are made of tiny particles too small to be seen. 2) Particles are always in motion. 3) Particles have spaces between them.
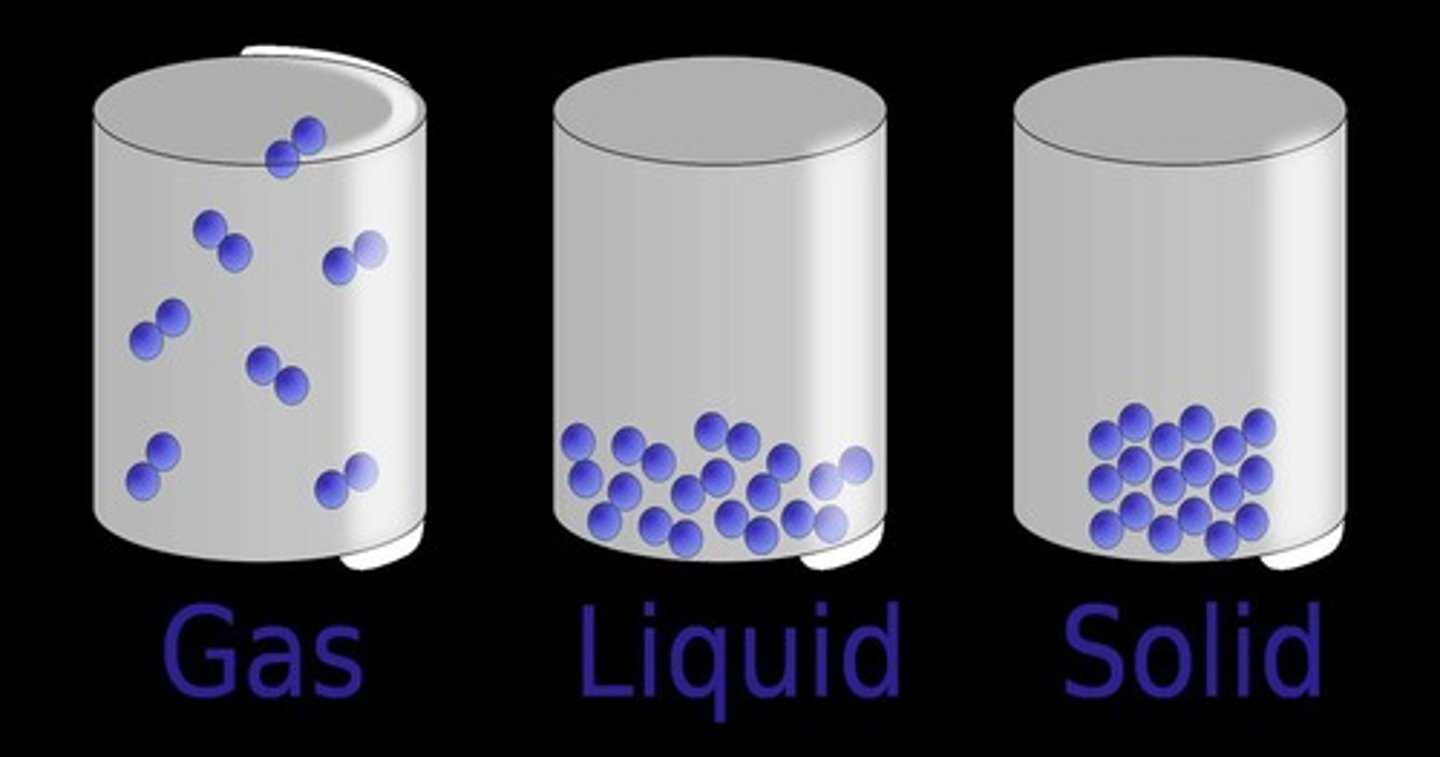
How does temperature relate to the motion of particles?
The motion of particles increases as temperature increases and decreases as temperature decreases; therefore, temperature indicates the average speed of particle motion in a substance.
Define energy in the context of physics.
measure of something's ability to do work, move, or cause change.
What are the two principles that apply whenever change occurs?
1) Changes happen when there is a difference in energy. 2) Energy is always transferred from a high-energy source to something with a low-energy source.
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one type to another or passed from one object to another.
What happens to materials as they are heated?
As materials are heated, their particles move faster and spread out, causing them to expand.
What happens to particles when they are cooled?
Cooled particles slow down and contract.
Describe the size and shape of solids.
Solids have a definite size and shape and a fixed volume, making them incompressible.
Describe the size and shape of liquids.
Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape, making them almost incompressible.
Describe the size and shape of gases.
Gases have no definite shape and their volume changes, making them compressible.
How do solids expand and contract compared to gases?
Solids expand and contract but not very much, while gases expand and contract much more when temperature changes.
What are heat capacity and specific heat capacity?
Heat capacity is the amount of thermal energy that warms or cools an object by one degree Celsius, depending on mass and material. Specific heat capacity is the amount of thermal energy that warms or cools one gram of a material by one degree Celsius, depending on the material.
What is the relationship between temperature changes and the expansion and contraction of substances?
Temperature changes cause substances to expand and contract.
What is the significance of the particle model in understanding states of matter?
The particle model explains how the arrangement and motion of particles determine the size, shape, and behavior of solids, liquids, and gases.
What happens to the energy of particles in solids, liquids, and gases?
Gases have the most energy, followed by liquids, while solids have the least energy.
What is the effect of temperature on the speed of particles?
As temperature increases, the speed of particles increases; as temperature decreases, the speed of particles decreases.
What is the process called when a solid turns into a liquid?
Melting.
What is the term for the transition from a liquid to a solid?
Freezing.
What do we call the change from a liquid to a gas?
Vaporization.
What is the term for the transition from a gas to a liquid?
Condensation.
What is sublimation?
The process of a solid turning directly into a gas.
What is deposition in terms of phase transitions?
The process of a gas turning directly into a solid.
What energy change occurs when gas turns into a solid?
It releases energy.
What energy change occurs when a solid turns into a gas?
It requires energy.
What is evaporative cooling?
A process where faster-moving particles escape from a liquid, lowering its average temperature.
What happens to the average temperature during a phase change?
It does not change.
What is hidden heat or latent heat?
The energy change associated with the arrangement of particles during a phase change, which is not detected by thermometers.
What are the three ways energy can be transferred?
Radiation, conduction, and convection.
What is radiation?
The transfer of energy without any movement of matter.
What are three characteristics of radiant energy?
It behaves like waves, can be absorbed and reflected, and travels at high speed (300,000 km/s).
What is conduction?
The process of transferring thermal energy through direct collisions between particles.
What is a heat insulator?
A material that is not efficient at transferring thermal energy, such as wood.
What is a conductor?
A material that is efficient at transferring thermal energy, typically metals.
What is convection?
The movement of a warm fluid (gas or liquid) that carries thermal energy with it.
What is a convection current?
A moving fluid that rises when warm (less dense) and falls when cool (more dense).
What are the five characteristics of an energy transfer system?
Energy source, direction of energy transfer, control system, transformed energy, waste heat.
What is the role of an energy source in an energy transfer system?
It supplies energy to the system.
What happens to energy in an energy transfer system?
Energy is transformed from one form to another and can be lost as waste heat.
At which point in an energy transfer diagram is energy most concentrated?
At the energy source.
What are the five common characteristics of Energy Transfer Systems?
1) Energy Source, 2) Direction of Transfer Energy, 3) Transformations, 4) Waste Heat, 5) Control Systems.
What is the direction of energy transfer in Energy Transfer Systems?
Energy transfers away from concentrated sources.
What happens to energy during transformations in Energy Transfer Systems?
Energy can change forms as it is transferred.
What is waste heat in the context of Energy Transfer Systems?
Waste heat is energy transferred to the surroundings.
What are two examples of things warmed by waste heat from a volleyball spike?
Examples are the volleyball itself and the player's body.
What is chemical energy and where is it found?
Chemical energy is used by our body (food) and is found in batteries and wood.
How do hydro-electric dams generate electricity?
They change the energy of gravitational water into electricity.
What are the disadvantages of hydro-electric dams?
They can cause environmental damage and disrupt ecosystems.
What are thermo-electric generating stations?
They are fuel-burning electrical generating stations that produce heat as a byproduct.
How do mechanical forces produce thermal energy?
Mechanical forces caused by friction (e.g., brakes, hammer and nail) often release thermal energy.
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is harnessed from the Earth's interior, using hot water and steam from volcanoes.
What is a significant advantage of geothermal energy?
It is a renewable energy source.
What are the two types of solar energy?
1) Passive Solar: uses materials to absorb and store solar energy; 2) Active Solar: uses mechanical devices to distribute thermal energy.
What is wind energy?
Wind energy is the energy of moving air harnessed using wind turbines.
What are fossil fuels?
Fossil fuels are chemicals made from decomposed plants and animals preserved underground.
What are some problems associated with fossil fuels?
Pollution and they are non-renewable.
What is global warming?
Global warming occurs when CO2 concentrations increase from burning fossil fuels, trapping heat in the atmosphere.
What is thermal pollution?
Thermal pollution is the accidental warming of the environment from sources like vehicle engines and furnaces.
What is cogeneration?
Cogeneration is the use of waste heat to heat needed areas, generate electricity, and perform other useful tasks.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is stored energy, such as gravitational energy (a rock on a counter) or elastic energy (pulled back).
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion present in a moving object.
How can we conserve fossil fuel resources?
By insulating homes, reducing energy use, installing programmable thermostats, and carpooling.
What are some concerns regarding thermal energy?
Concerns include forest fires, burns from hot objects, and pollution from storing fossil fuels.
What are some harmful by-products of thermal energy use?
1) Carbon Dioxide: a greenhouse gas contributing to global warming; 2) Sulfur Dioxide: irritates respiratory systems; 3) Carbon Monoxide: a colorless, odorless, lethal gas.