Overview of Immunology and Serology Concepts
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
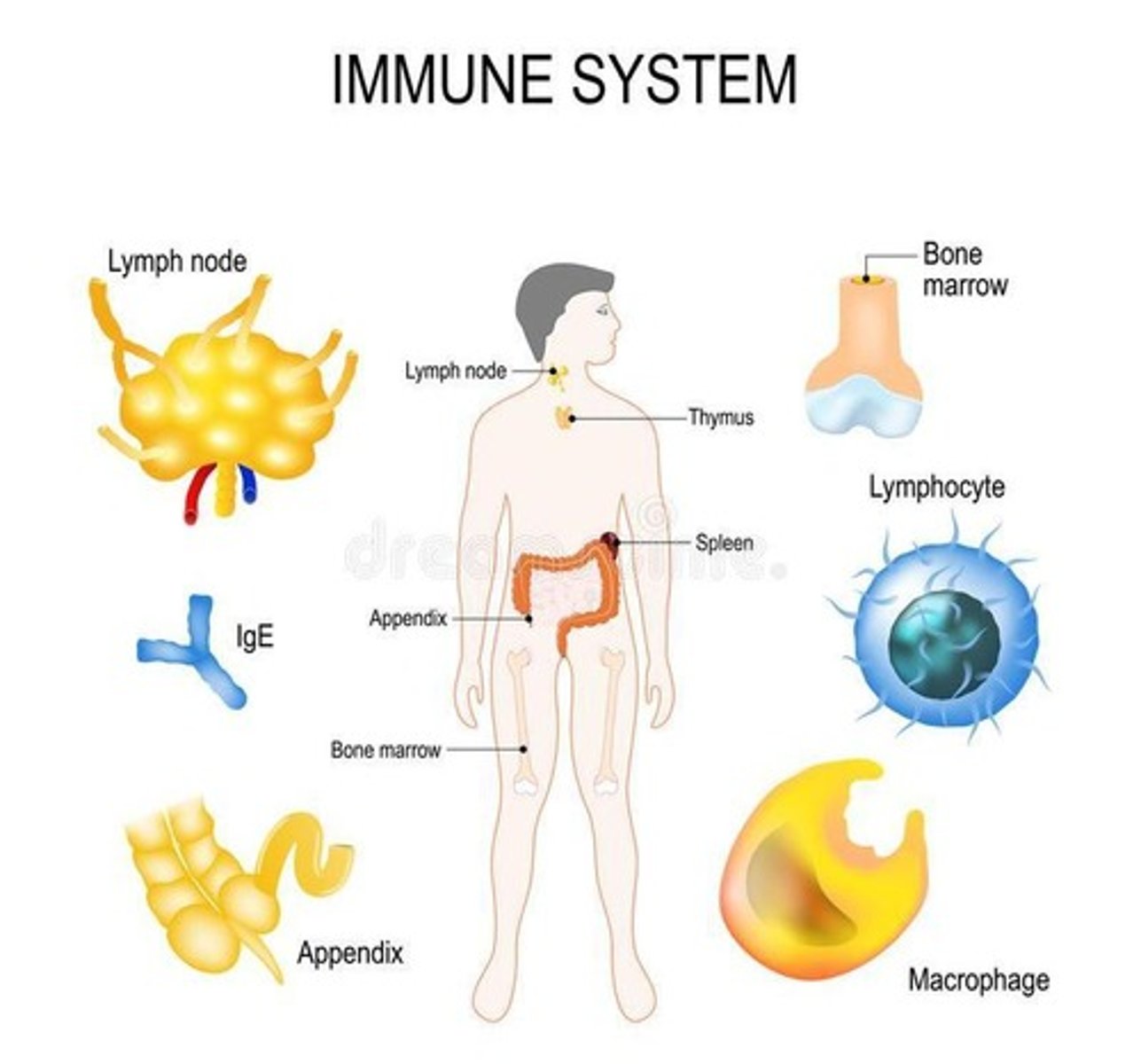
Immunology
Study of organisms' defense against infections.
Serology
Study of blood serum and immune responses.
Immunochemistry
Chemical processes in immune responses.
Immunobiology
Biological aspects of immune system functions.
Immunogenetics
Genetic basis of immune responses.
Immunopathology
Study of diseases related to immune dysfunction.
Immunohematology
Study of blood-related immune responses.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells including T and B cells.
T cells
Lymphocytes that mediate cellular immunity.
B cells
Lymphocytes that produce antibodies.
Antigen presenting cells
Cells that display antigens to T cells.
Dendritic cells
APCs that activate T cells.
Macrophages
Phagocytic cells in immune response.
Follicular dendritic cells
Display antigens to B cells.
Anatomical Barriers
Physical barriers preventing pathogen entry.
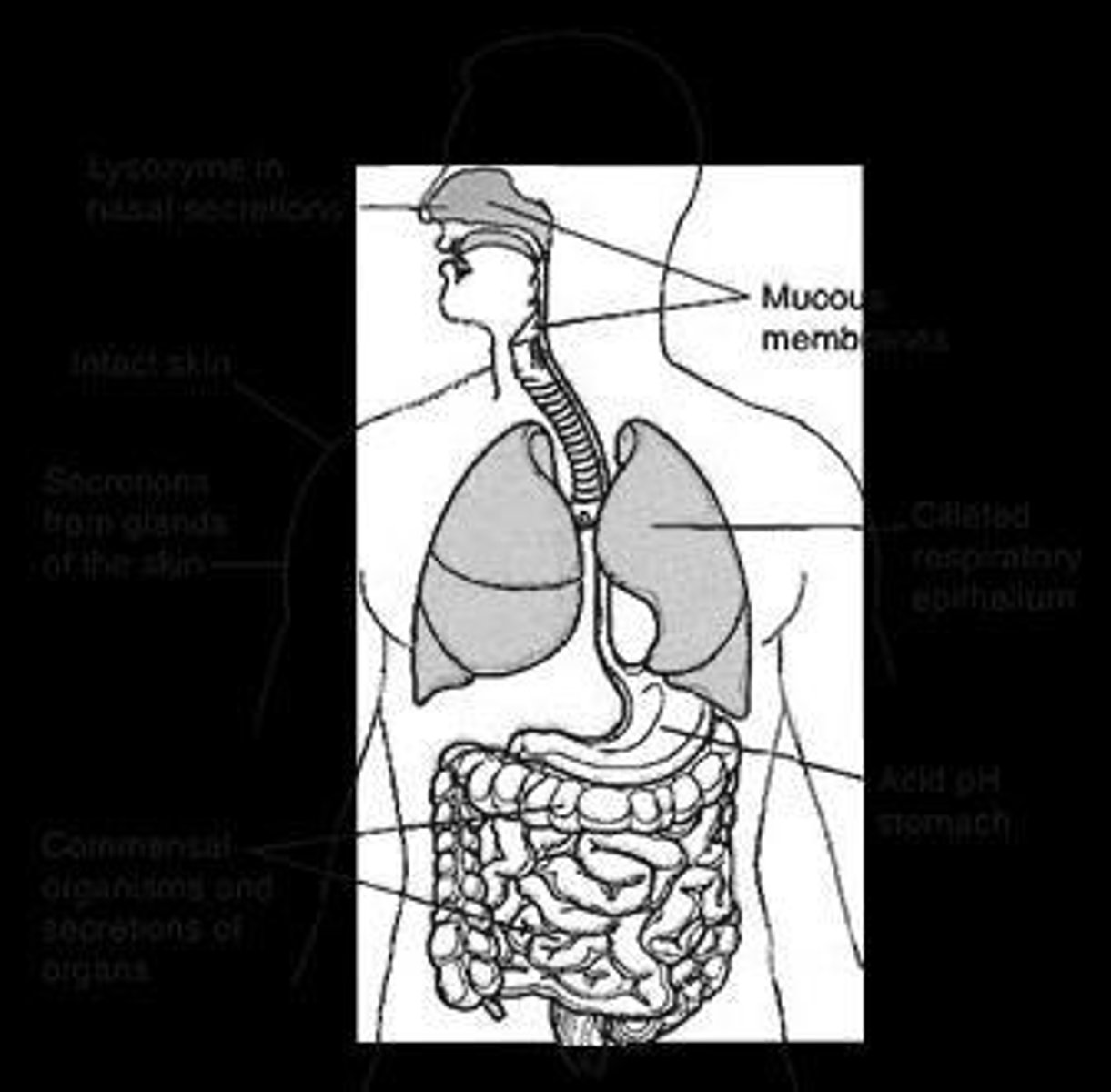
Mechanical Factors
Physical processes like skin and mucus.
Chemical Factors
Substances like lysozymes and fatty acids.
Biological Factors
Living cells contributing to immune defense.
Innate Immunity
Non-specific first line of defense.
Adaptive Immunity
Specific immune response to pathogens.
Complement system
Group of proteins enhancing immune response.
Type I Interferons
Cytokines augmenting NK cell activity.
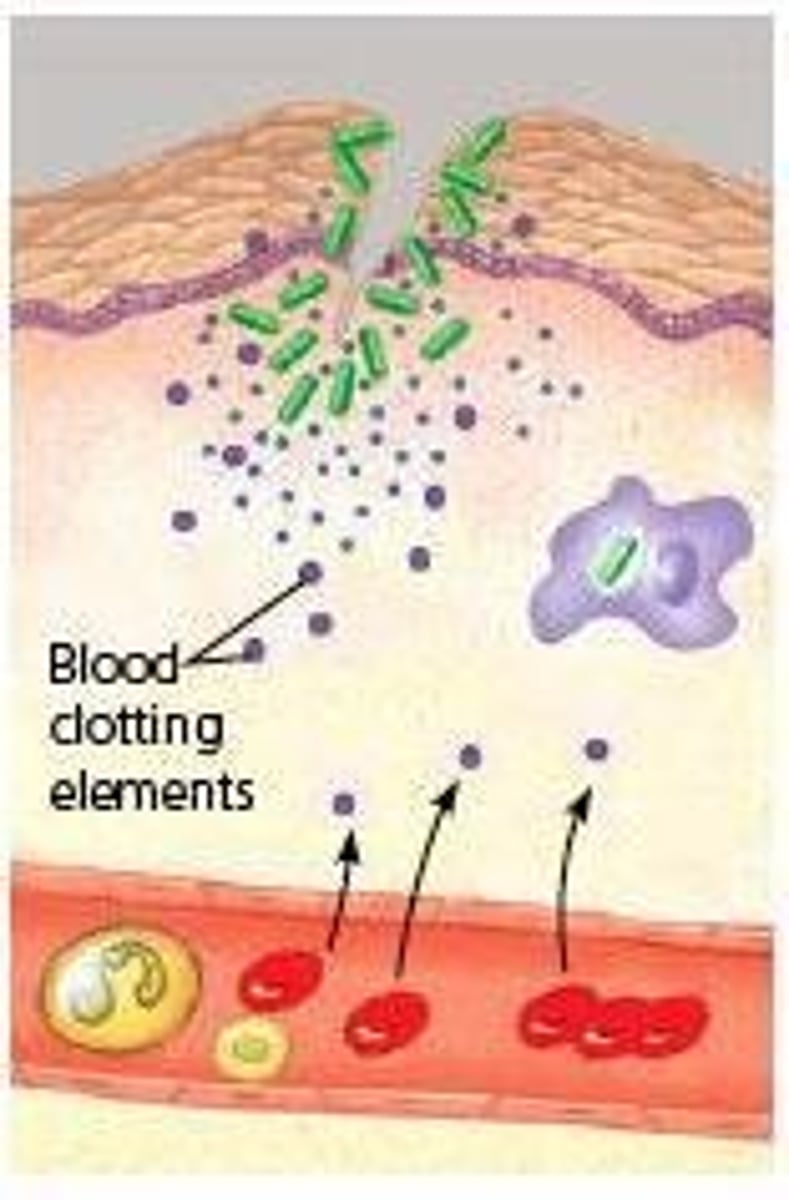
Coagulation system
Blood clotting factors aiding immune defense.
TNF
Mediates inflammatory response to infections.
TNF α (cachectin)
Cytotoxic to tumor cells directly.
TNF β (lymphotoxin)
Involved in killing and endothelial activation.
Beta-lysin
Protein from platelets that lyses Gram positive bacteria.
Lactoferrin
Binds iron, limiting bacterial growth.
Transferrin
Iron-binding protein, restricts bacterial access to iron.
Lysozyme
Enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls.
Interferons
Proteins that limit viral replication in cells.
Interleukin-1 (IL-1)
Regulates immune responses and inflammatory reactions.
Interleukin-2 (IL-2)
Activates cytotoxic T cells.
Interleukin-3 (IL-3)
Induces hematopoiesis.
Interleukin-4 (IL-4)
Stimulates B cell activation and growth.
Interleukin-5 (IL-5)
Promotes eosinophil growth and activation.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
Involved in B-cell differentiation and inflammation.
Interleukin-7 (IL-7)
Growth factor for early lymphoid cells.
Interleukin-8 (IL-8)
Activates neutrophils, promotes chemotaxis and phagocytosis.
Interleukin-9 (IL-9)
Supports growth of helper T-cells.
Interleukin-10 (IL-10)
Inhibits antigen presentation and Th2 cell activity.
Interleukin-11 (IL-11)
Stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and inhibits epithelial proliferation.
Interleukin-24 (IL-24)
Involved in tumor suppression and wound healing.
Interleukin-27 (IL-27)
Regulates B and T lymphocyte activity.
Interleukin-28 (IL-28)
Role in immune defense against viruses.
Acute phase reactants (APR)
Serum proteins that change during inflammation.
Interleukin-12
Stimulates Th1 responses against intracellular pathogens.
Th1 Cellular Immune Response
Defensive mechanism against intracellular infections.
Interleukin-15
Promotes proliferation of NK cells.
Interleukin-17
Proinflammatory cytokine from activated memory T cells.
Interleukin-19
Regulates immune responses, synergistic with IL-2.
Interleukin-20
Regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation.
TGF-β
Suppresses autoimmune responses and Th1 activity.
Macrophages
Phagocytose and kill microorganisms intracellularly.
Resident Macrophages
Main defense in non-specific immune system.
Transient Macrophages
Temporary macrophages responding to infection.
Neutrophils
Phagocytose and kill invading organisms intracellularly.
Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
Antimicrobial enzyme in neutrophil granules.
Lactoferrin
Iron-binding glycoprotein inhibiting microbial growth.
Azurophilic Granules
Contain antimicrobial products like defensins.
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
Non-specifically kill virus-infected and tumor cells.
Lymphokine Activated Killer (LAK) Cells
Enhanced NK cells targeting infected or cancerous cells.
Eosinophils
Kill parasites and involved in allergic reactions.
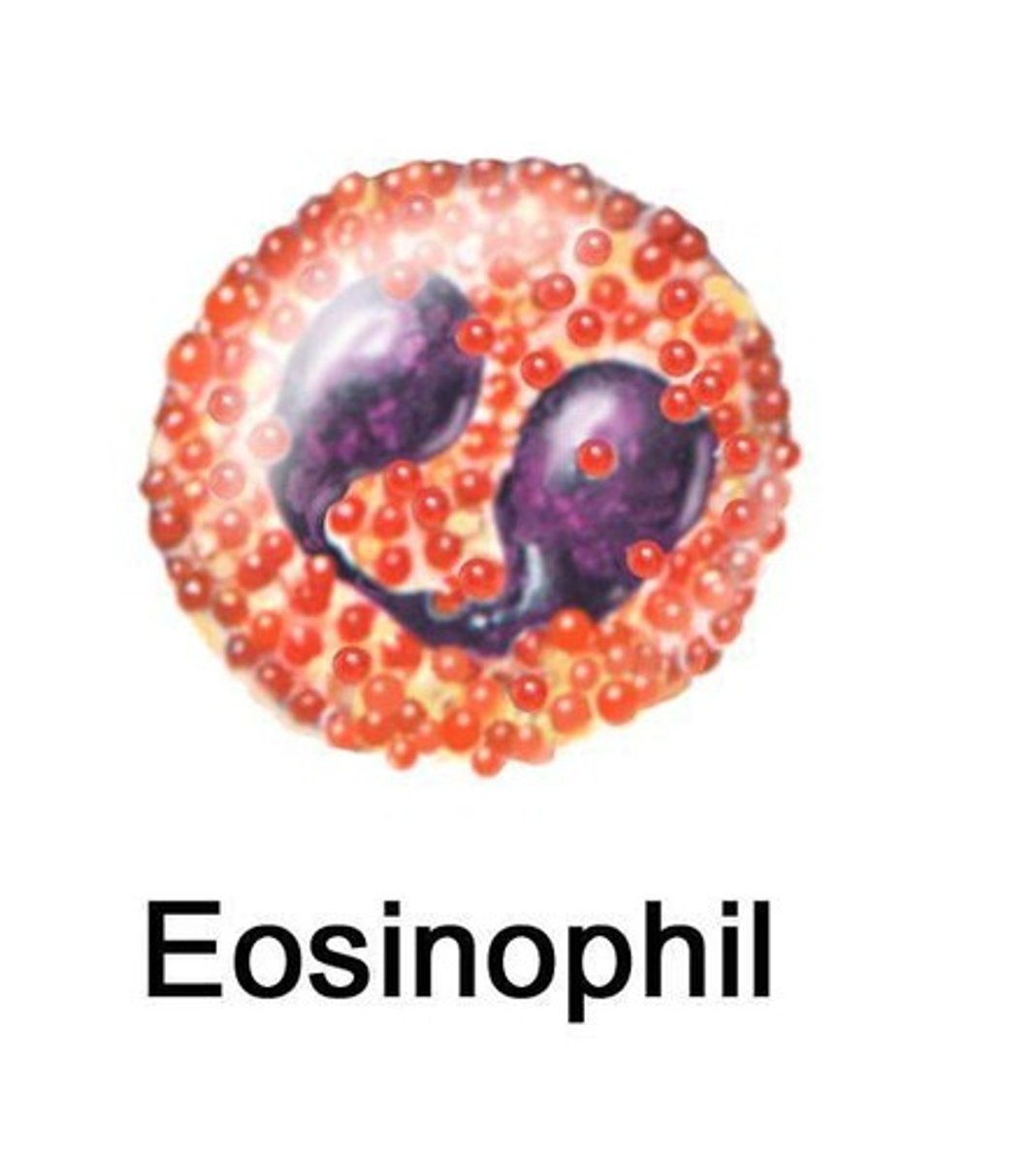
Eosinophil Granules
Contain neurotoxins and proteins for parasite killing.
Dendritic Cells
APCs that present antigens to T helper cells.
Langerhans Cells
Skin-resident dendritic cells for immune surveillance.
Interdigitating Dendritic Cells
Found in thymus and secondary lymphoid tissues.
Basophils
Involved in immediate hypersensitivity and allergies.
Mast Cells
Tissue-based basophils releasing histamine.
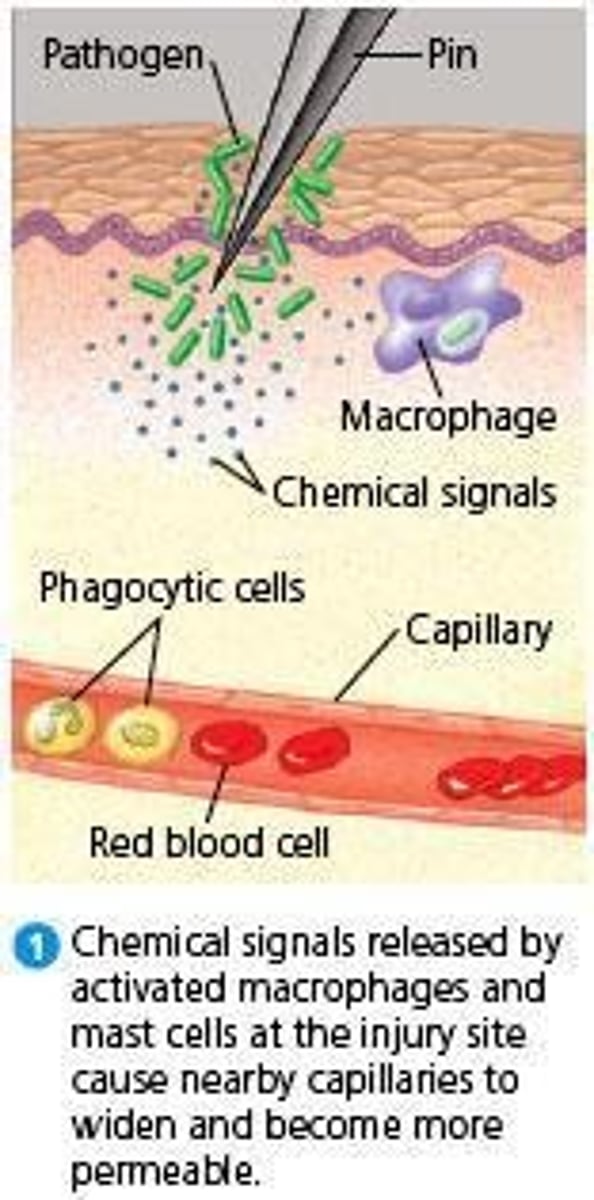
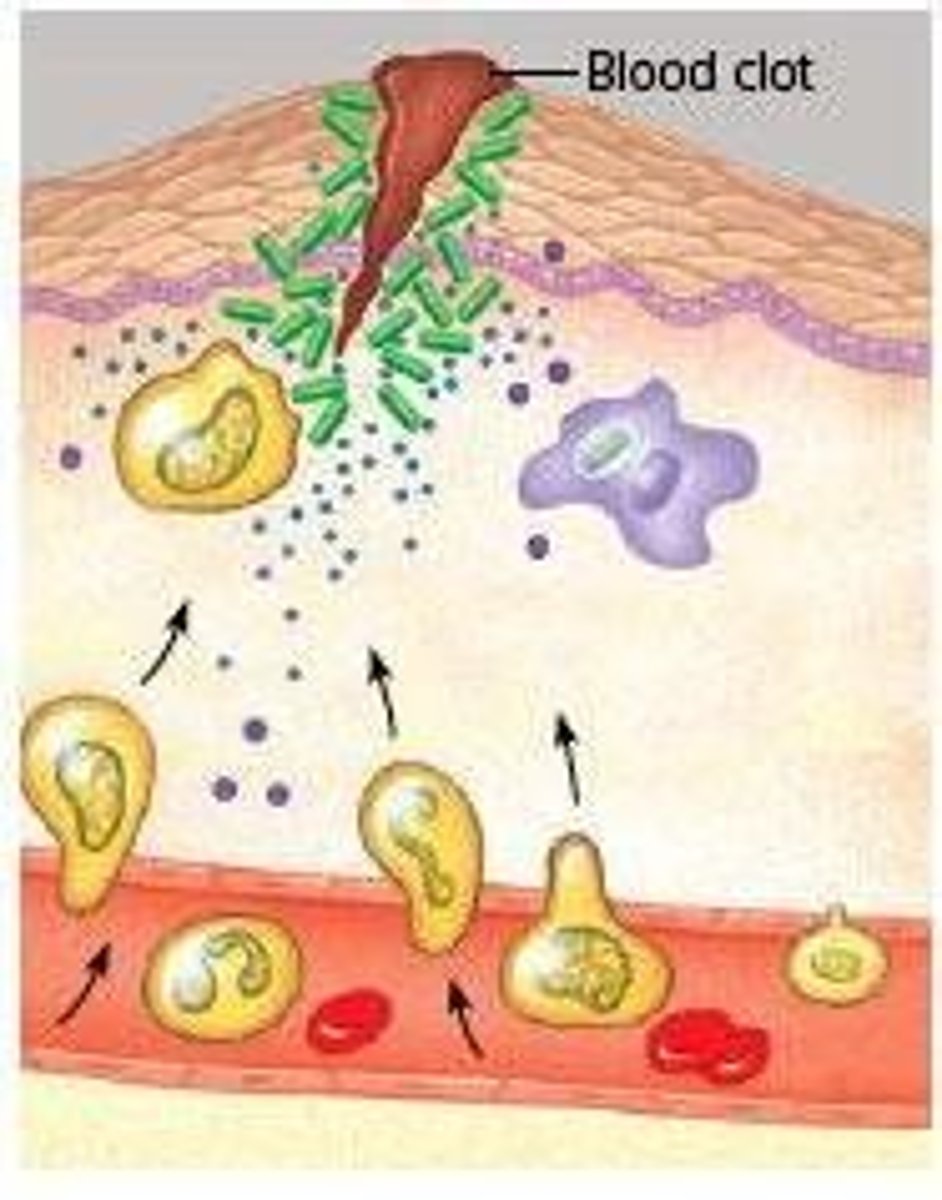
Inflammation
Body's response to injury or infection.
Vascular response
Dilation of capillaries increases blood flow.
Capillary permeability
Increased permeability allows fluid and cells to enter.
White blood cells (WBCs)
Cells that migrate to injured tissue.
Neutrophils
First responders in inflammation, migrate quickly.
Natural Killer cells
Attack infected or cancerous cells.
Macrophages
Engulf pathogens and debris in tissue.
Pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs)
Detect pathogens and initiate immune response.
Mannose receptors
Recognize carbohydrates in bacterial cell walls.
Alpha-helical receptors
Bind lipids, chemokines, and peptides.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Recognize specific microbial components.
Histamine
Chemical that causes vasodilation during inflammation.
Kinins
Mediators that promote vasodilation.
Prostaglandins
Intensify effects of kinins and histamine.
Leukotrienes
Promote phagocytic attachment to pathogens.
Preformed molecules
Existing mediators like serotonin and histamine.
Newly synthesized molecules
Mediators produced during inflammation, e.g., cytokines.
Neutrophil mobilization
Occurs within 30 to 60 minutes post-injury.
Monocyte migration
Starts 4 hours after injury, peaks at 16-48 hours.
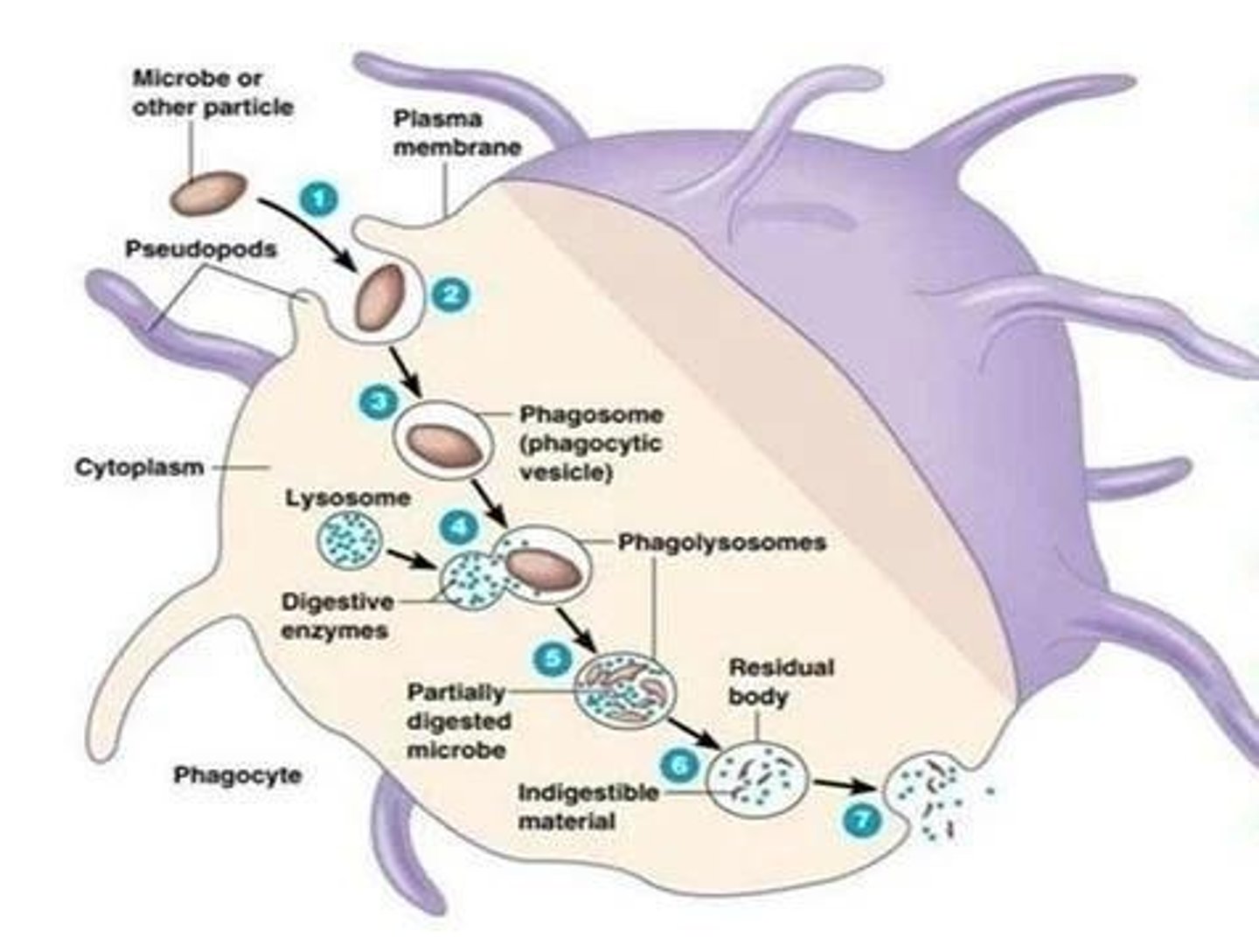
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing and digesting pathogens.
Chemotaxis
Movement of cells toward chemical signals.
Opsonization
Coating of pathogens to enhance phagocytosis.
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
Molecular signatures recognized by immune cells.
CSF
Colony Stimulating Factor, regulates blood cell production.
EPO
Erythropoietin, stimulates red blood cell formation.
G-CSF (Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor)
promotes granulocyte production.
M-CSF (Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor)
enhances macrophage development.
GM-CSF
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor, stimulates both cell types.
TGF (Transforming Growth Factor)
involved in cell growth regulation.
SCF
Stem Cell Factor, supports hematopoietic stem cell survival.
IFN
Interferon, antiviral cytokine produced by immune cells.