IOA2 Exam 3 - Visual Pathway Pt 2
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
What is the shape of the optic chiasm?
Rectangular
What is the width of the optic chiasm?
15mm
What is the anterior to posterior diameter of the optic chiasm?
8mm
What is the height of the optic chiasm?
4mm
What is the optic chiasm surrounded by?
-Meningeal sheaths
-Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Where is the optic chiasm located?
Within the circle of Willis
What is the circle of Willis?
Anastomotic group of anterior and posterior arteries that join the anterior circulation of the internal carotid arteries with the posterior circulation of the basilar artery
The circle of Willis is an anastomotic group of anterior and posterior arteries that join the anterior circulation of the ________ with the posterior circulation of the _________.
internal carotid arteries; basilar artery
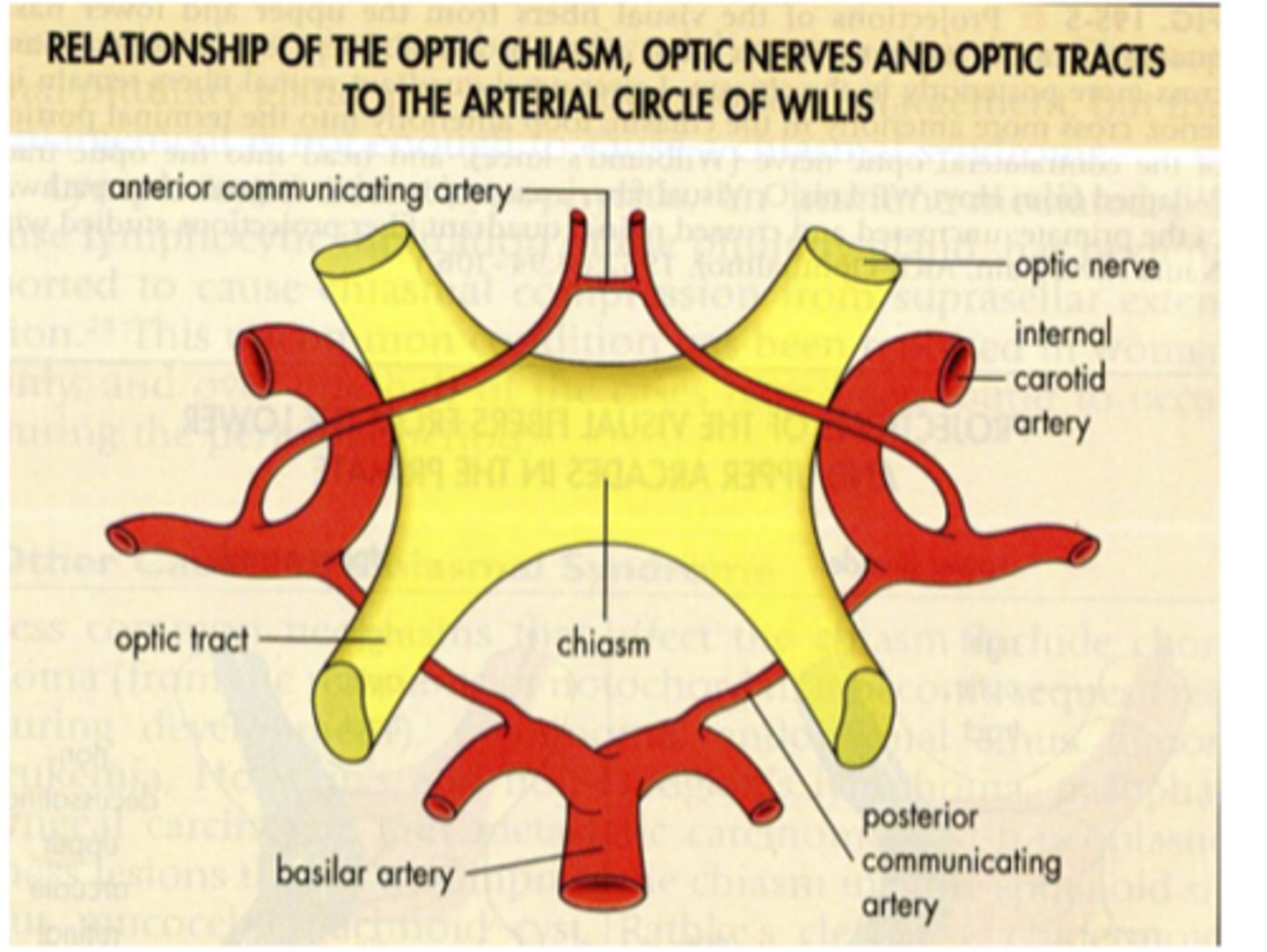
A: Anterior communicating artery
B: Optic tract
C: Basilar artery
D: Chiasm
E: Optic nerve
F: Internal carotid artery
G: Posterior communicating artery
Name each structure
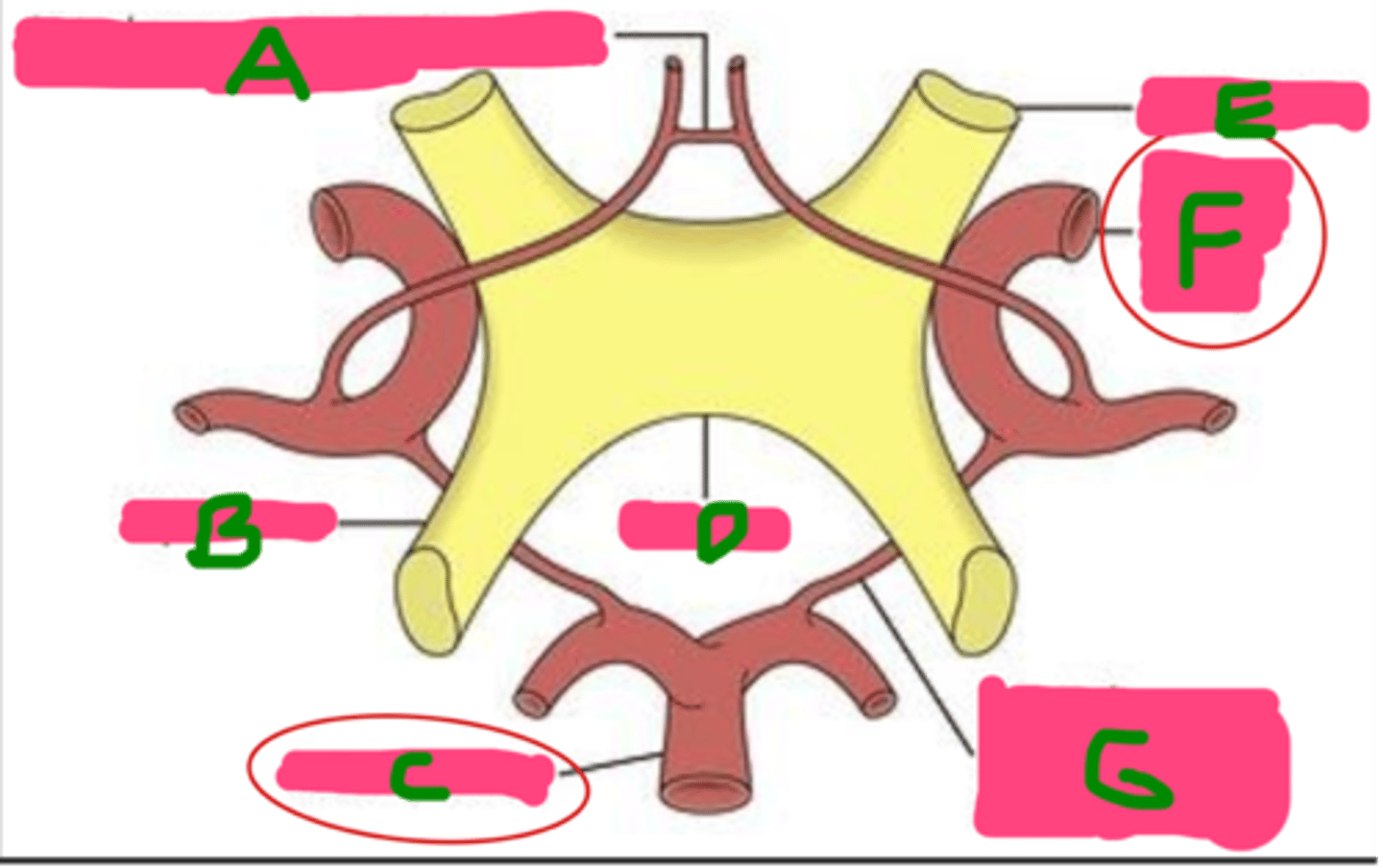
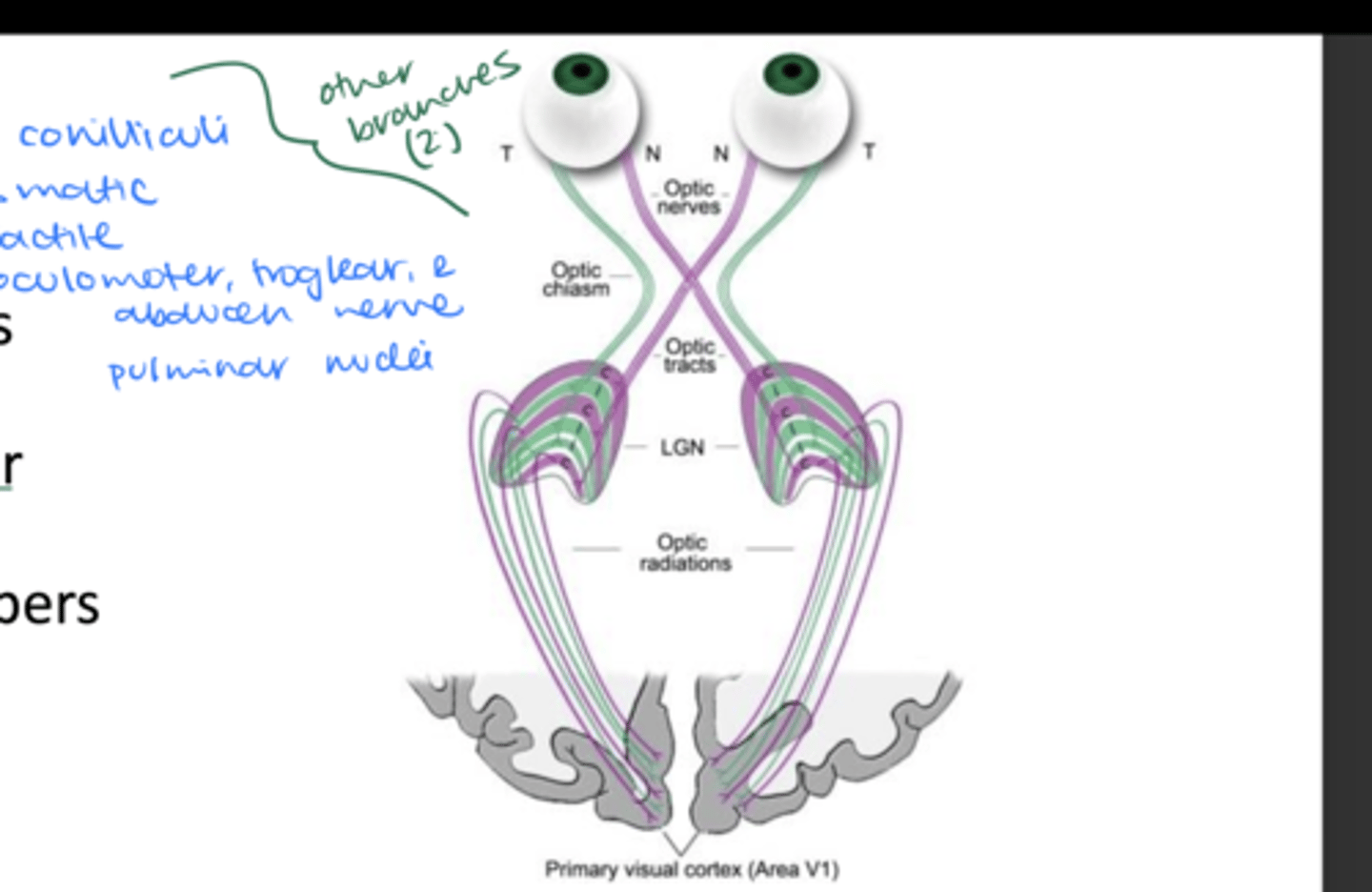
A: Olfactory tract
B: Pituitary gland
C: Mesencephalon
D: Eye
E: Olfactory bulb
F: OPTIC NERVE (N II)
G: Optic chiasm
H: Optic tract
I: LGN (in thalamus)
J: Optic projection fibers
K: Visual cortex (in occipital lobes)
Name each structure
SLIDE 3 PICTURE
ok
SLIDE 4 PICTURE
ok
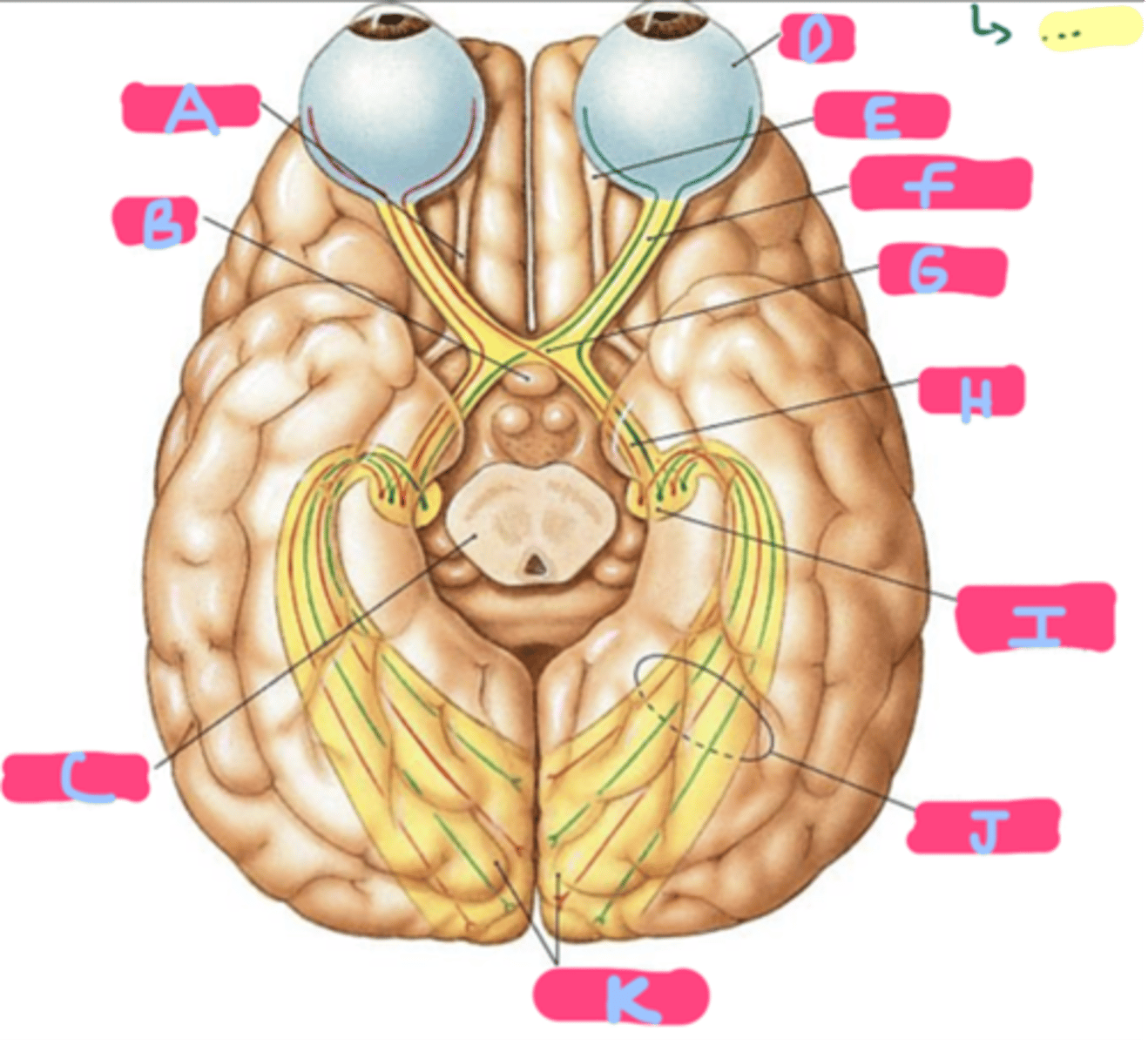
What is above the optic chiasm?
Floor of the third ventricle
What lies 1 cm below the optic chiasm?
-Pituitary gland
-Anterior and posterior clinoid processes of sphenoid (sella turcica)
What is located laterally to the optic chiasm?
-Internal carotid artery (ICA)
-Cavernous sinus (CS)
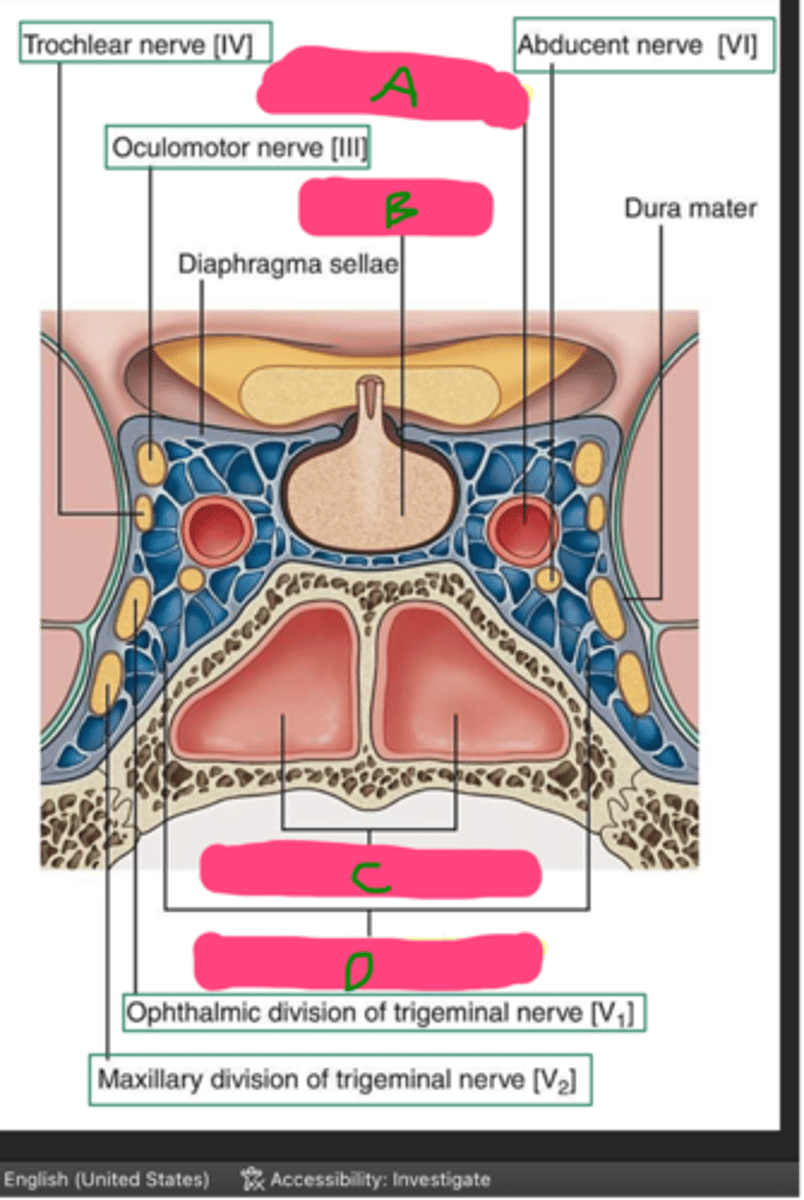
A: Optic chiasm
B: Anterior lobe
C: Pituitary gland
D: Posterior lobe
E: Sella turcica
Name each structure!
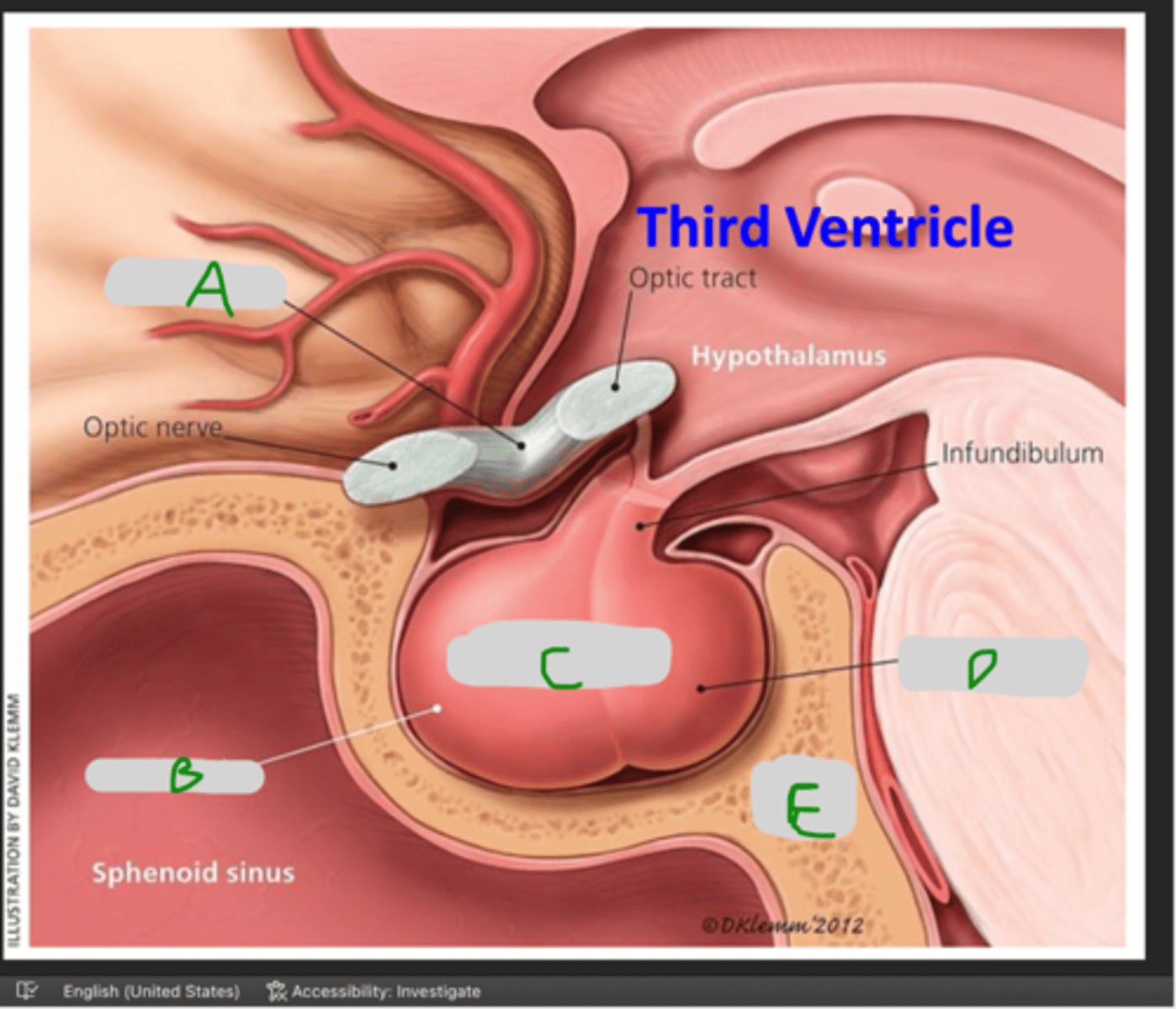
A: Internal carotid artery
B: Pituitary gland
C: Spenoid (paranasal) sinus
D: Cavernous (venous) sinus
Name each structure
What is the shape of the optic tract?
Cylindrical, flattened band of fibers
What is the height of the optic tract?
3.5 mm
What is the length of the optic tract?
5.1 mm
What structures does the optic tract connect?
Connects optic chiasm to the LGN
What are the subtypes of nerve fibers in the optic tract?
-Magnocellular fibers
-Contralateral parvocellular fibers
-Ipsilateral parvocellular fibers
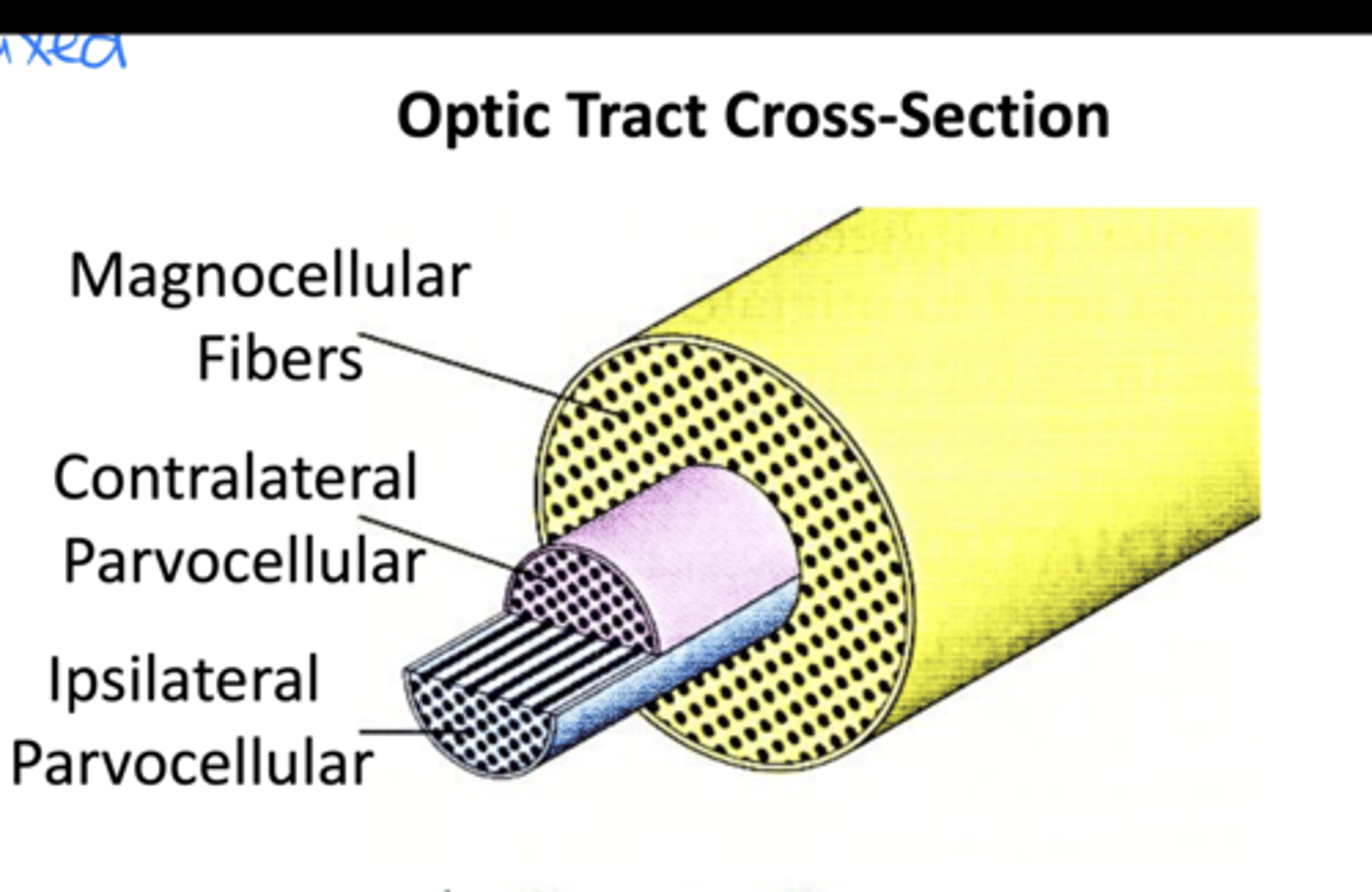
How do magnocellular fibers run?
Peripherally
How do contralateral parvocellular fibers run?
Centrally
How do ipsilateral parvocellular fibers run?
Centrally
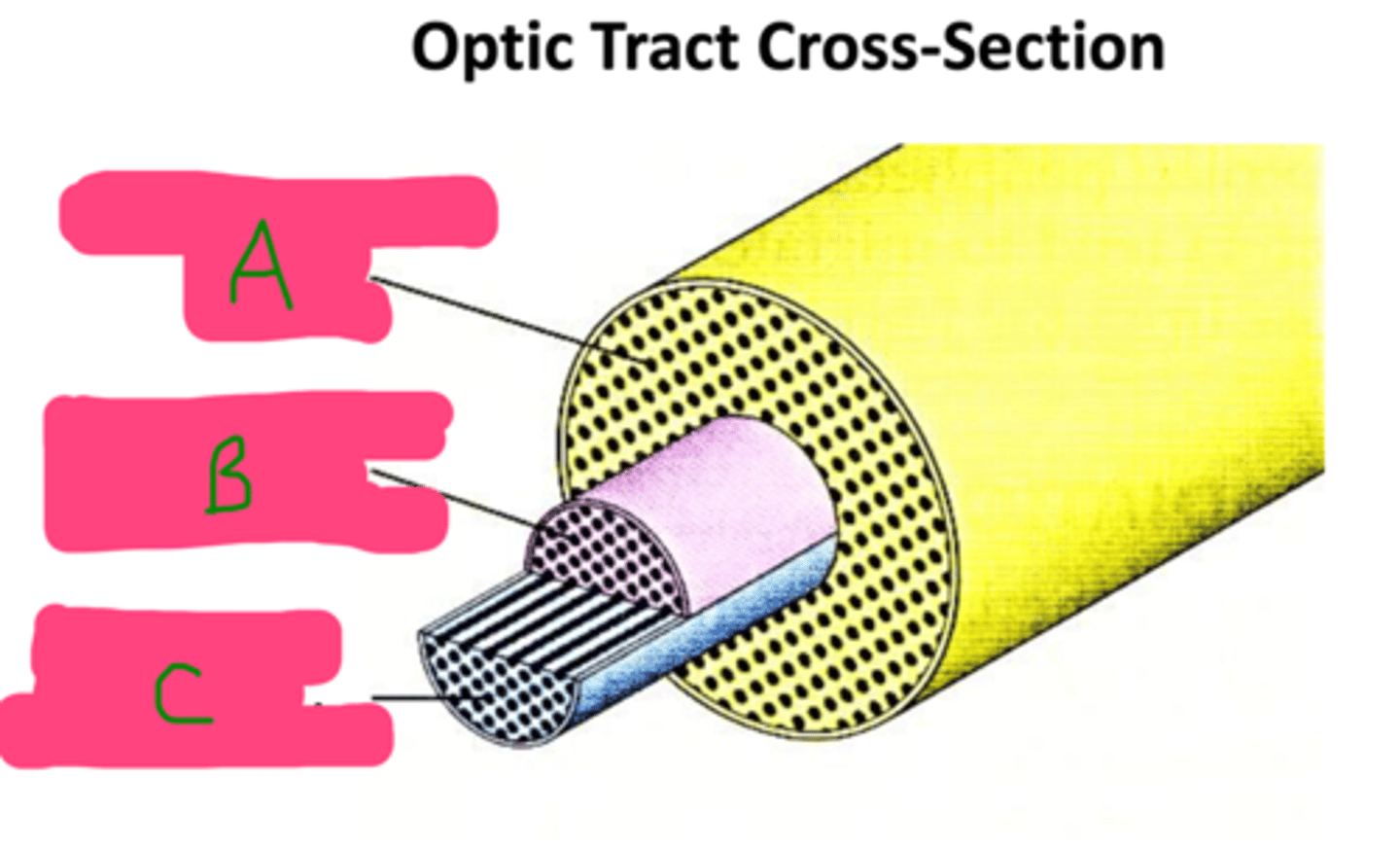
A: Magnocellular
B: Contralateral parvocellular
C: Ipsilateral parvocellular
Label each of the nerve fiber subtypes in the optic tract
What is the function of the LGN?
Visual information is processed in the LGN and then relayed to higher cortical centers
Where is the LGN located?
Dorsolateral thalamus
What is the shape of the LGN?
Asymmetric cone shape
What synapses at the LGN, and what does this lead to?
Retinal axons synapse here, and optic radiations exit towards the VC (visual cortex)
Where do most of the fibers that leave the LGN project to?
Visual cortex
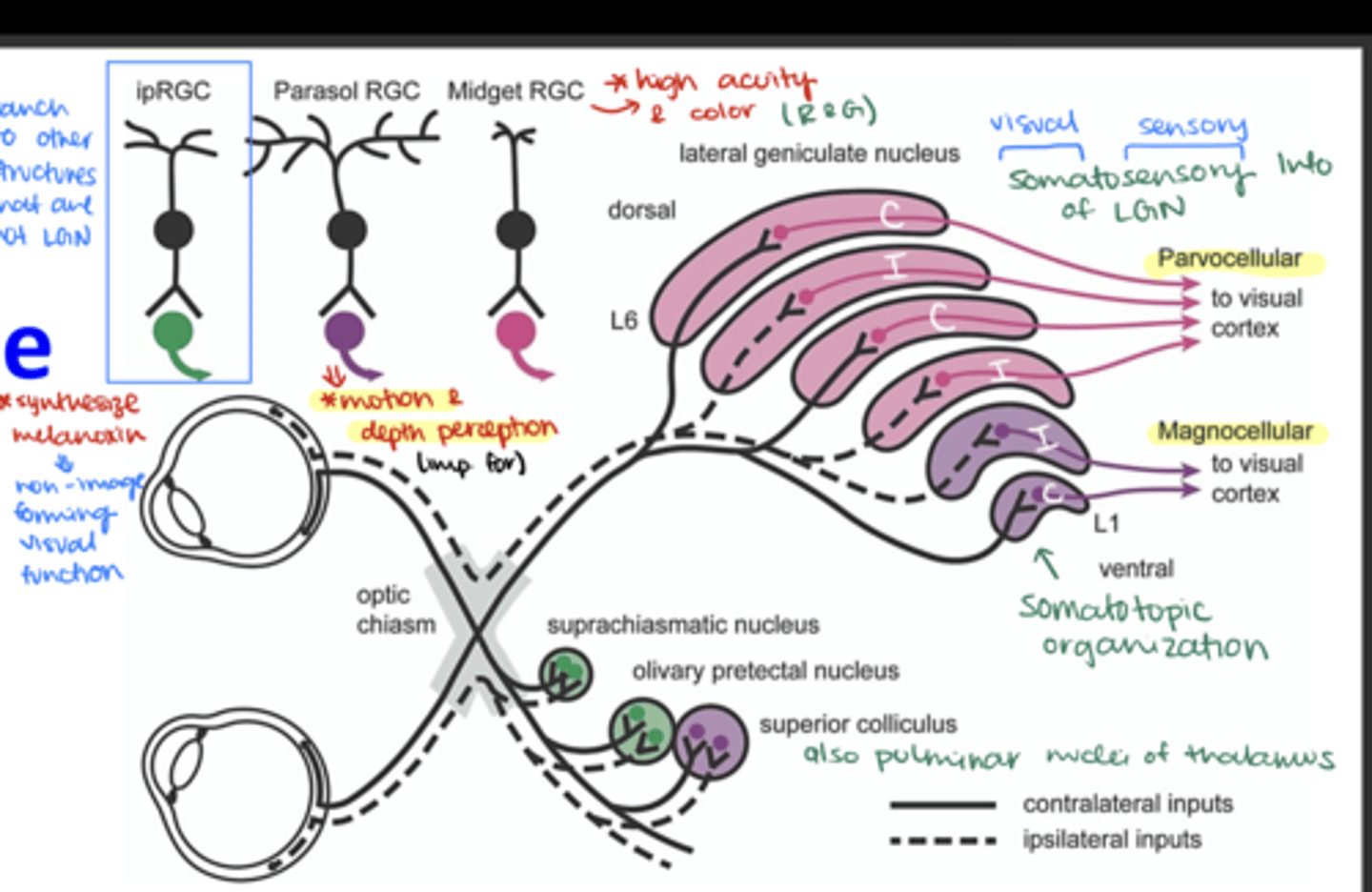
Known to have roles in non-image-forming visual functions, such as regulating circadian rhythms and the pupillary light reflex
ipRGC (intrinsically photosensitive RCGs)
These are part of the magnocellular pathway, primarily concerned with motion and depth perception
Parasol RCG
These cells are part of the parvocellular pathway, largely responsible for processing color and fine detail
Midget RGC
Which layers of the LGN are innervated by ganglion cell axons from the contralateral side?
Layers 1, 4, and 6
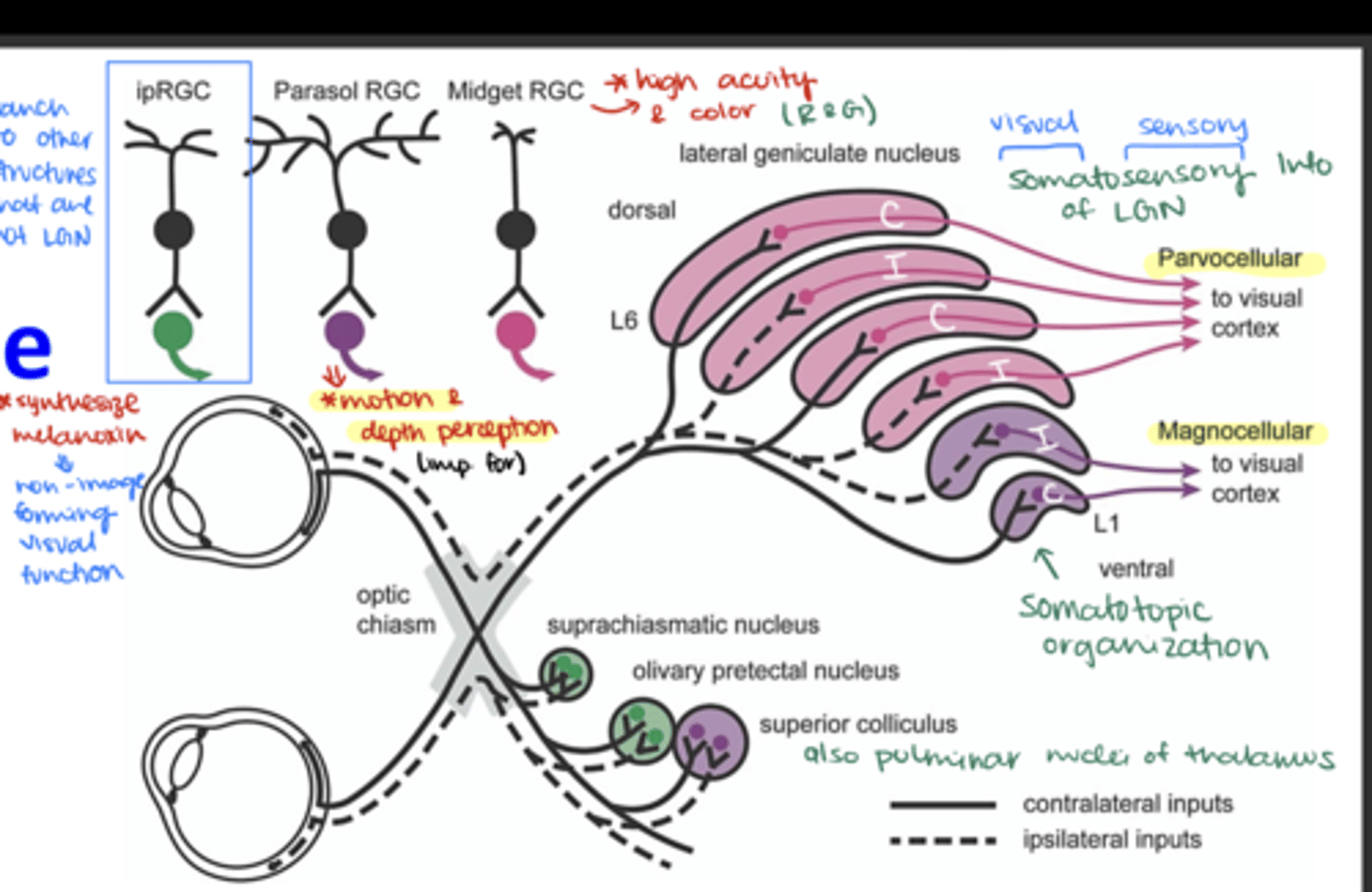
Which layers of the LGN are innervated by ganglion cell axons from the ipsilateral side?
Layers 2, 3, and 5
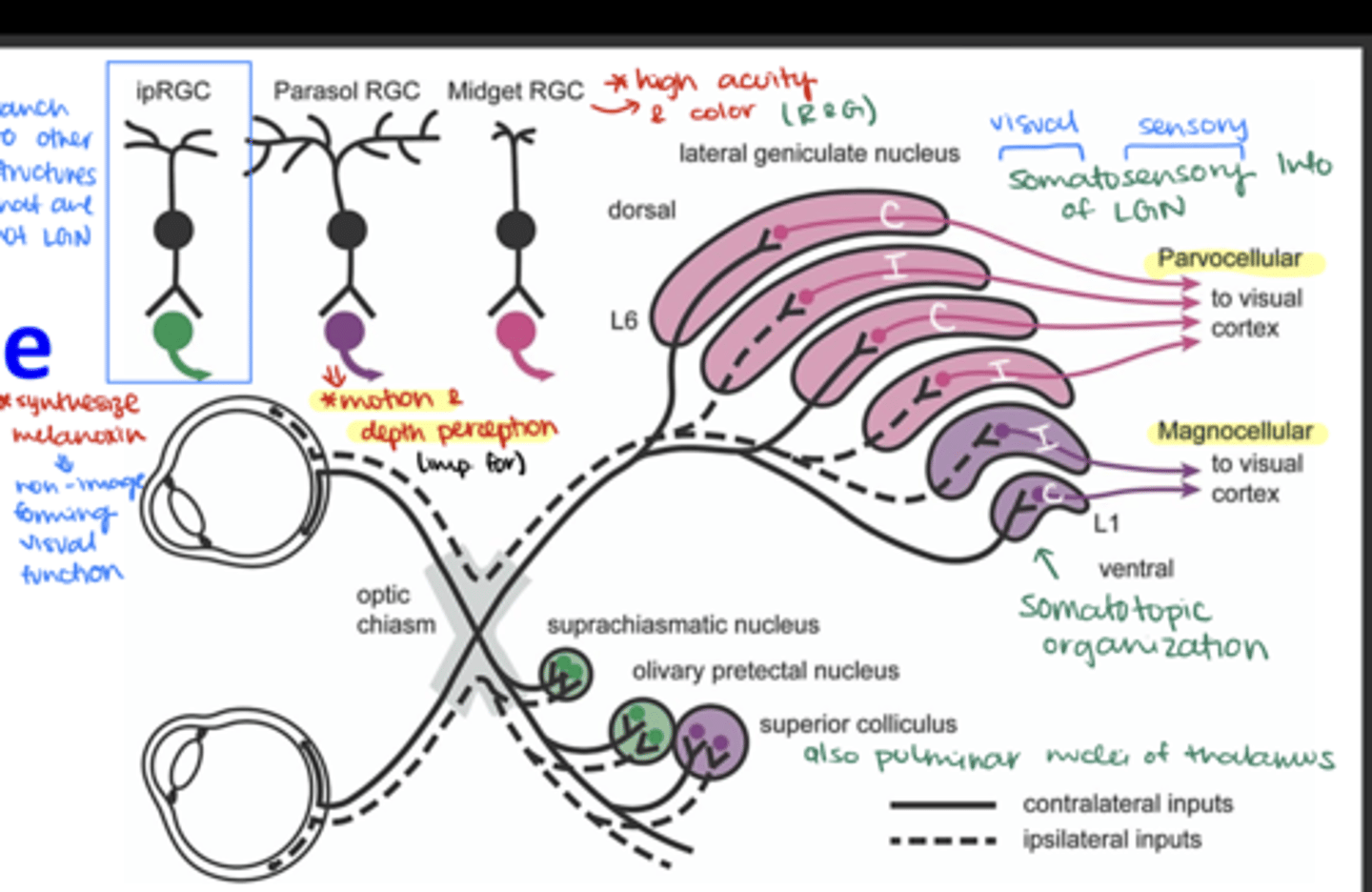
Where do M (magnocellular) ganglion cells terminate in the LGN?
in the magnocellular layers
Where do P (parvocellular) ganglion cells terminate in the LGN?
in the parvocellular layers
Where do non-M, non-P ganglion cells terminate?
Onto the koniocellular cells
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 1 of the LGN?
Contralateral M parasol ganglion cells
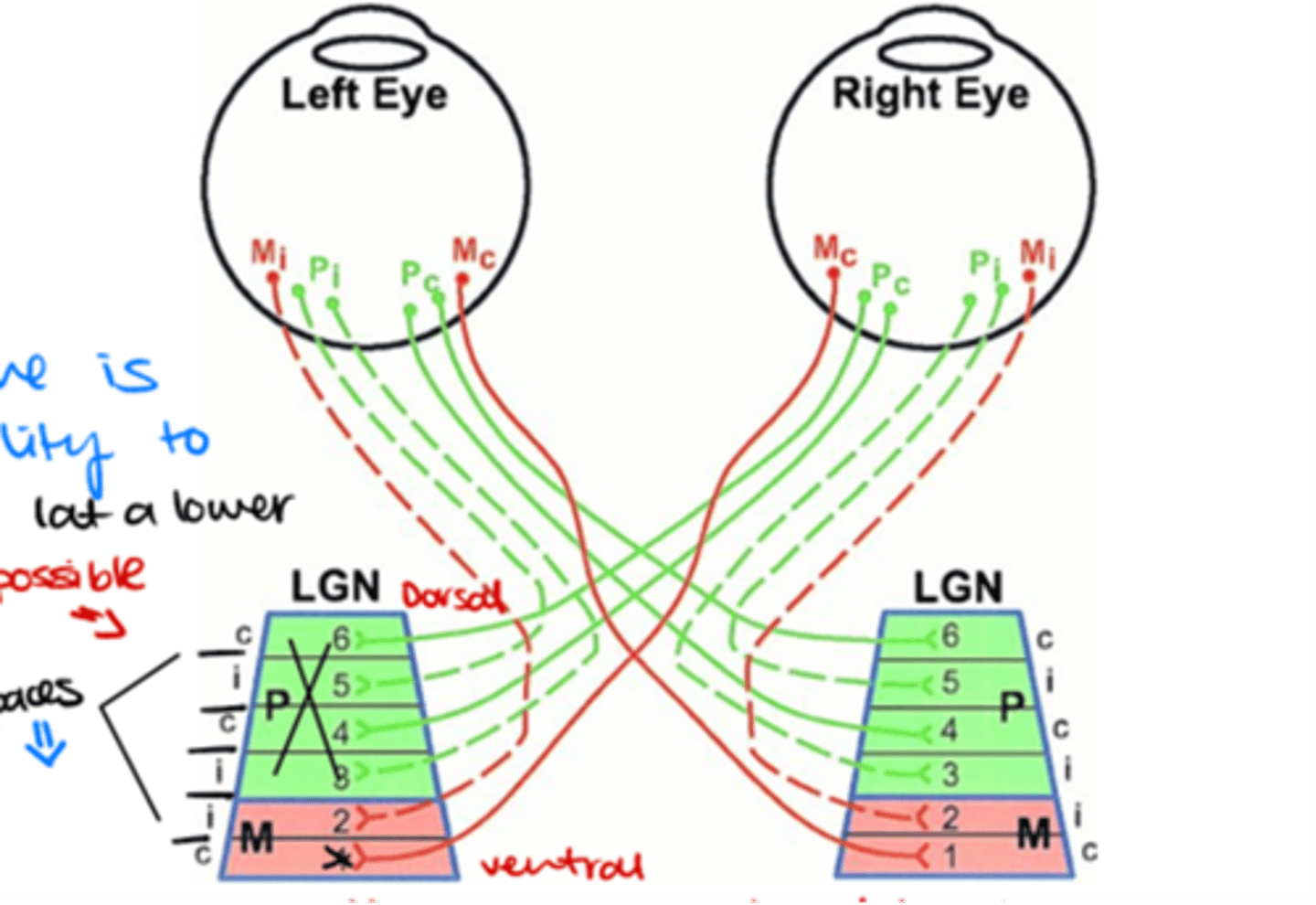
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 2 of the LGN?
Ipsilateral M parasol ganglion cells
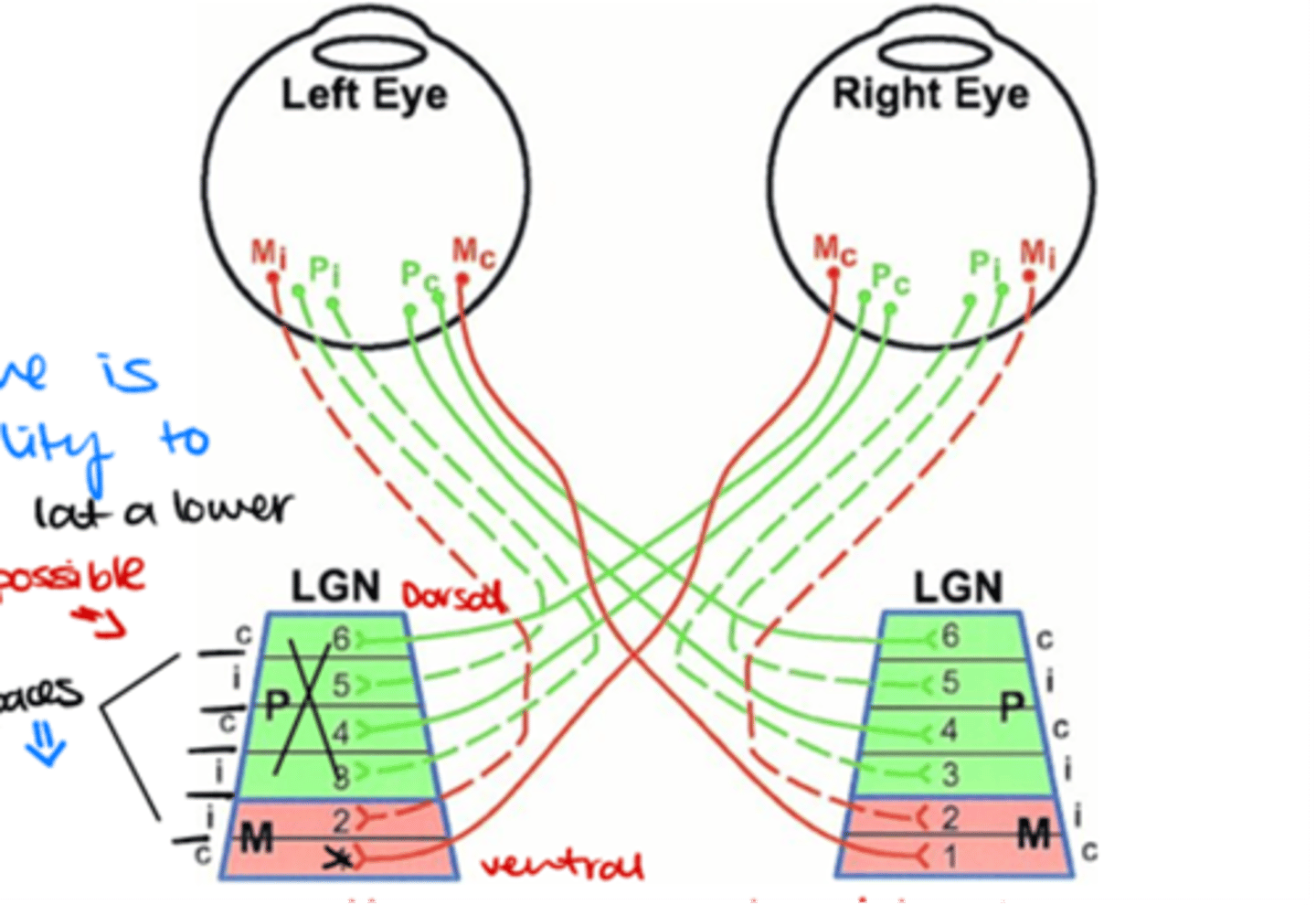
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 3 of the LGN?
Ipsilateral P midget ganglion cells
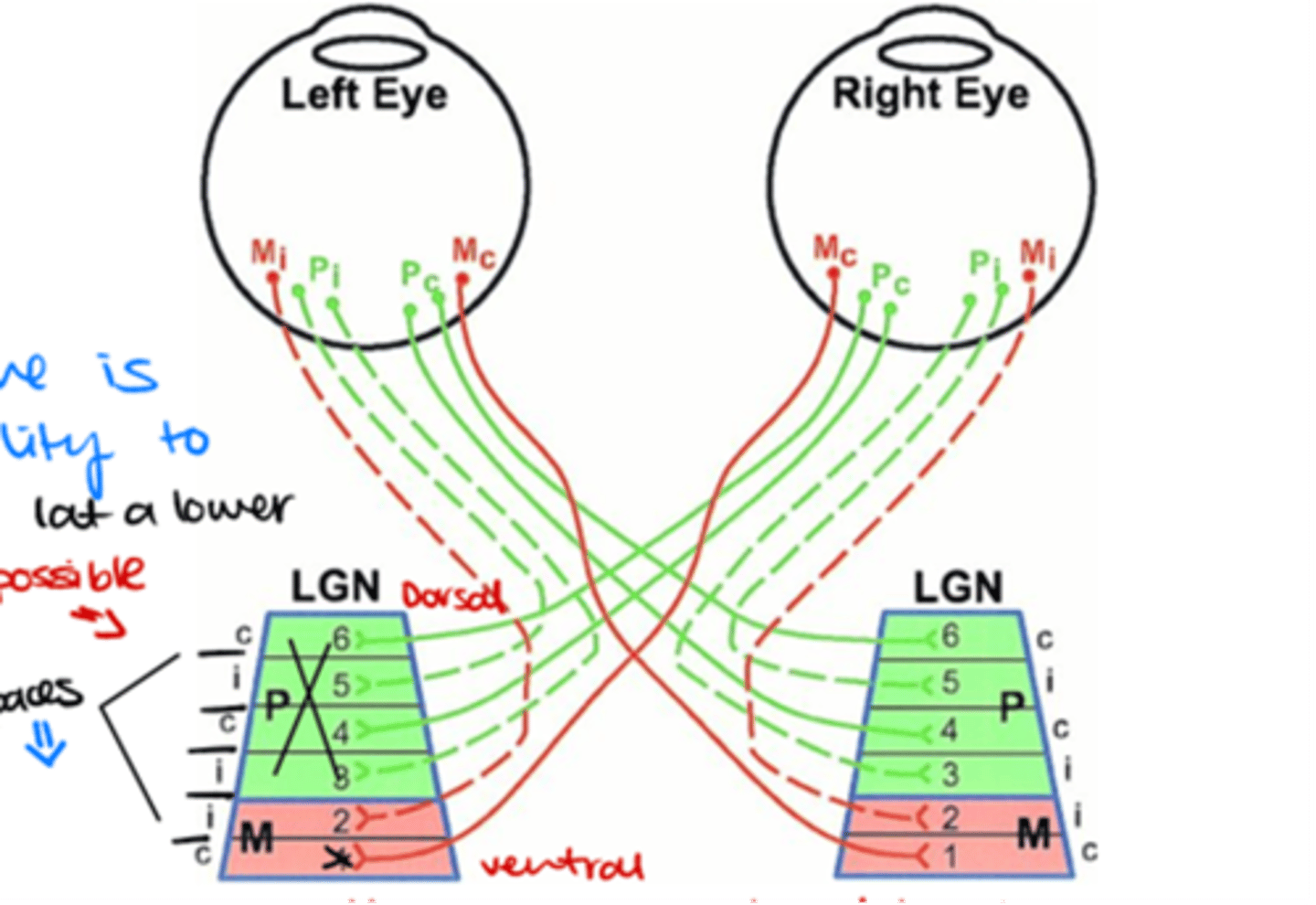
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 4 of the LGN?
Contralateral P midget ganglion cells
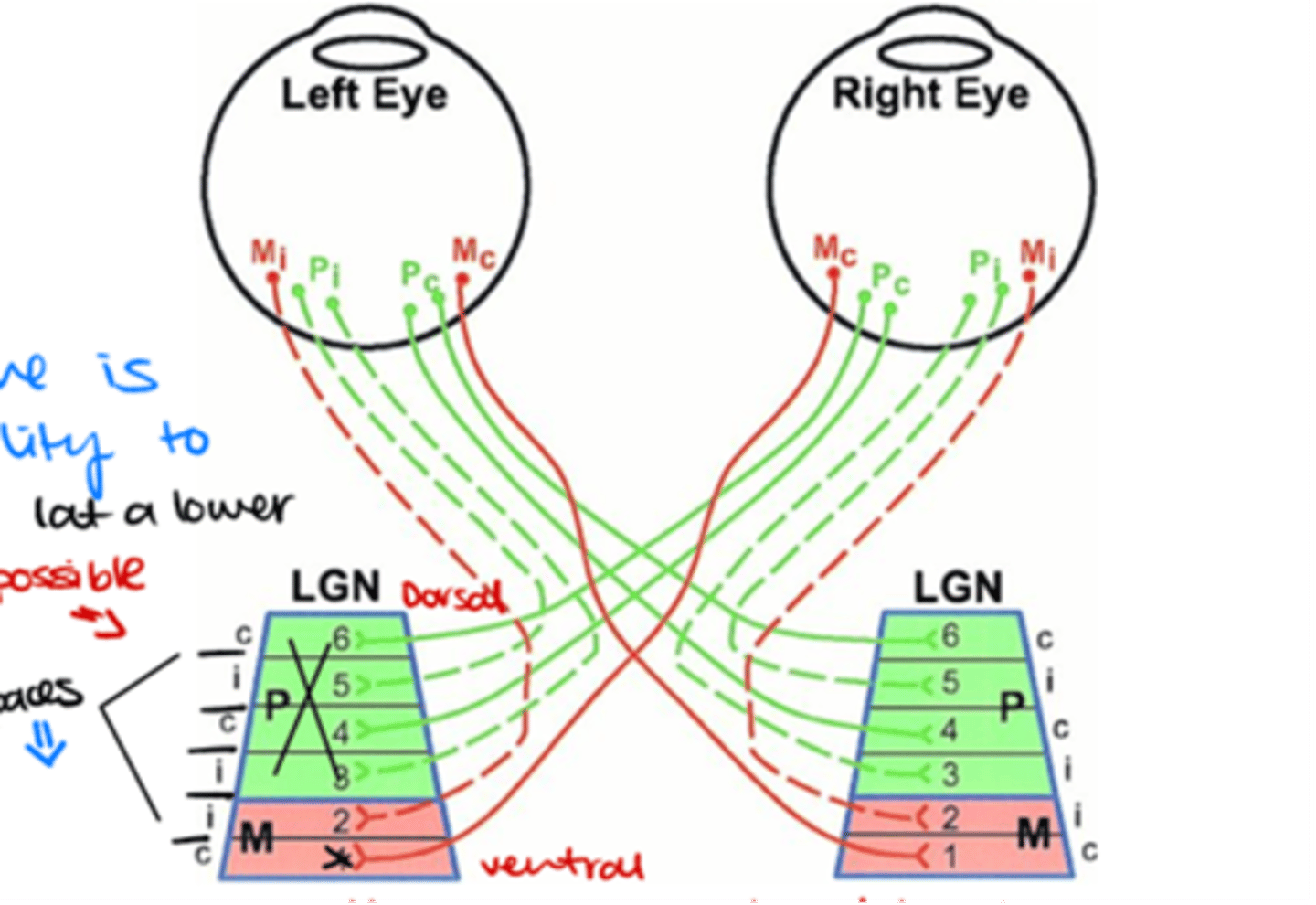
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 5 of the LGN?
Ipsilateral P midget ganglion cells
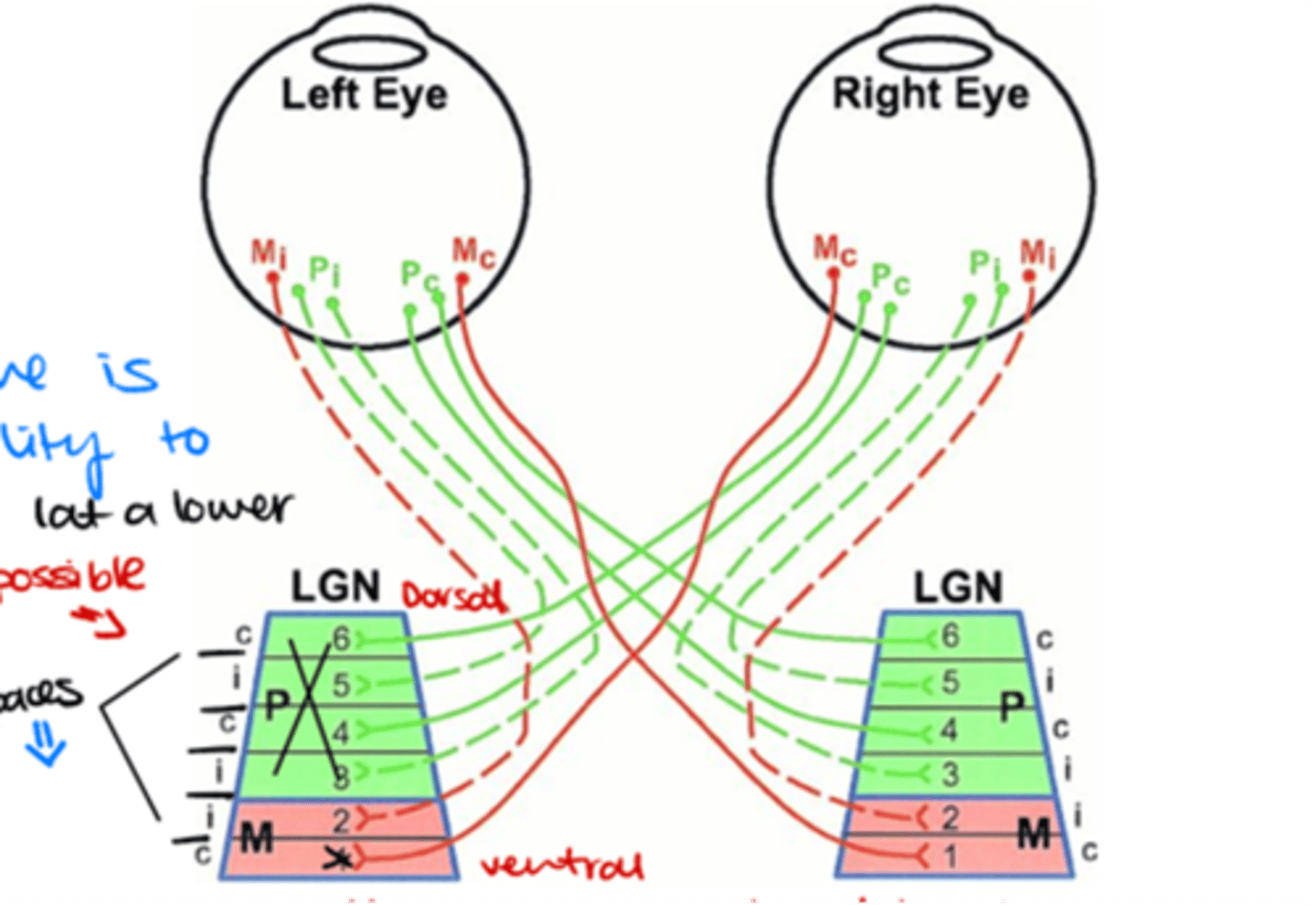
Which ganglion cells terminate in layer 6 of the LGN?
Contralateral P midget ganglion cells
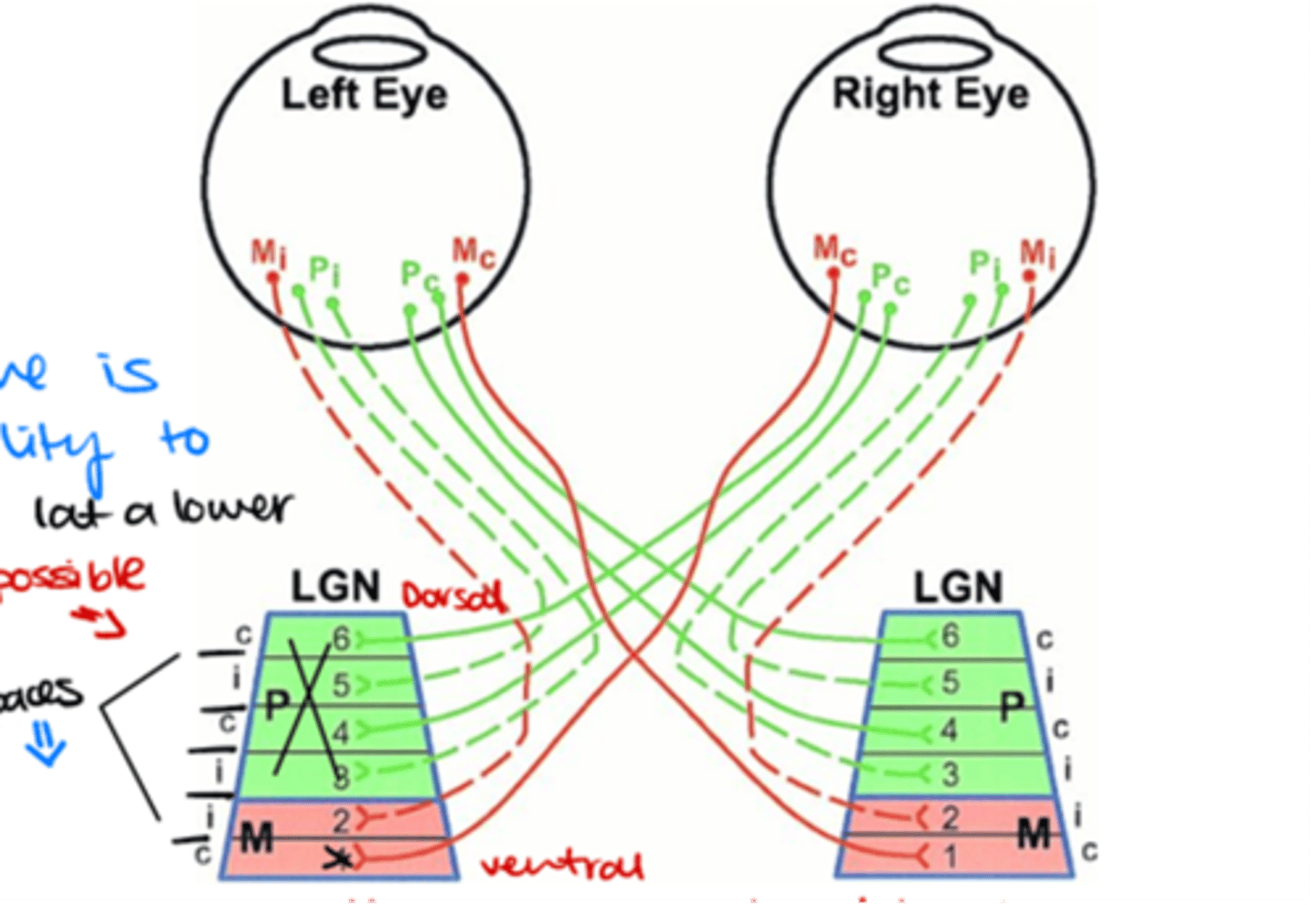
Which pathway carries visual information from the LGN to the primary visual cortex (V1)?
Optic radiations (Geniculocalcarine tract)
How do nerve fibers spread out as they leave the LGN?
In a fan-like manner (fanwise)
Where do the nerve fibers travel once they leave the LGN by spreading fanwise?
Deep in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres from all 6 LGN layers
How do the nerve fibers sweep around the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle?
-Laterally
-Superiorly
-Inferiorly
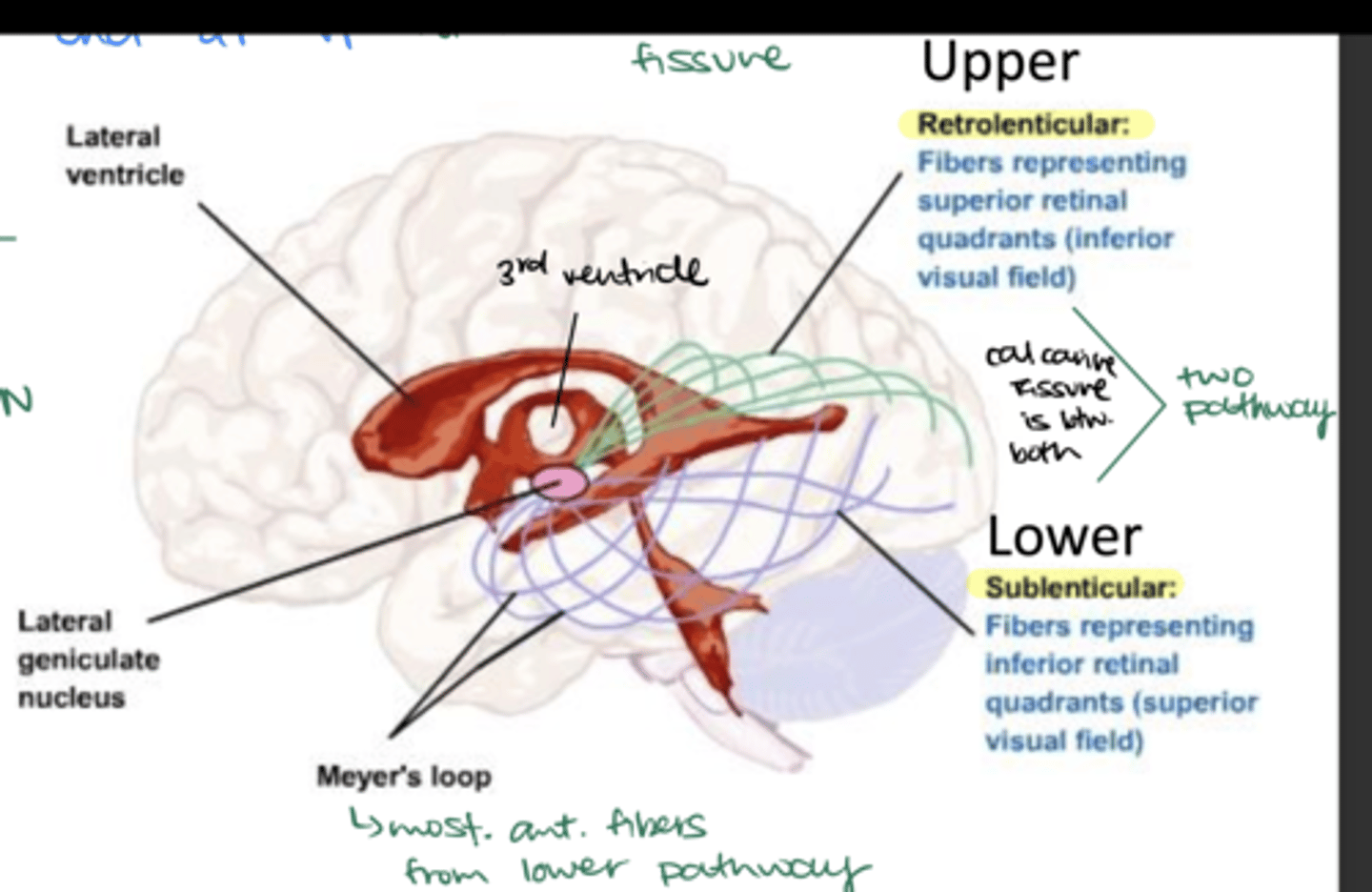
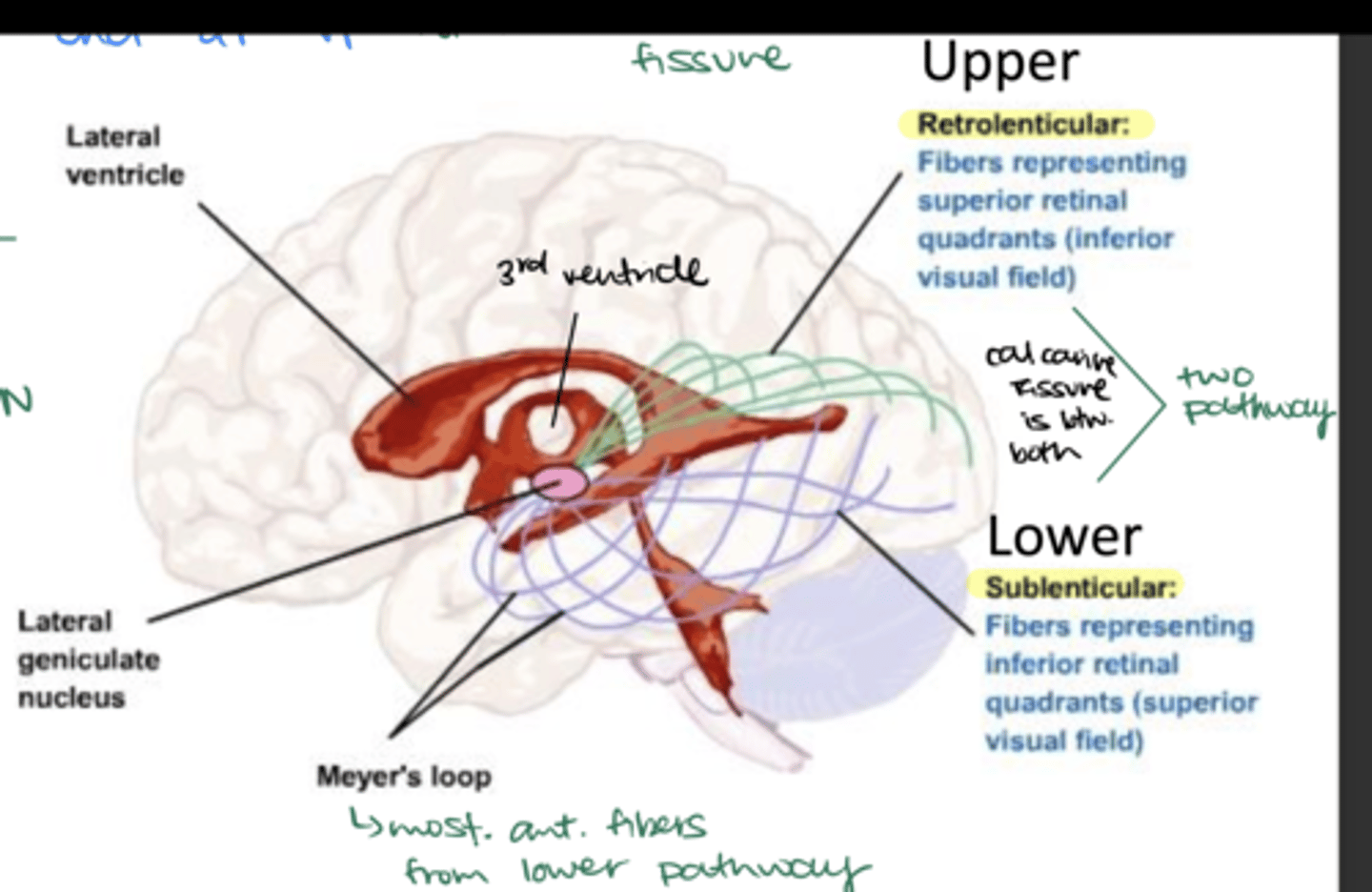
What is Meyer's Loop?
Part of the lower sublenticular pathway (most anterior segment)
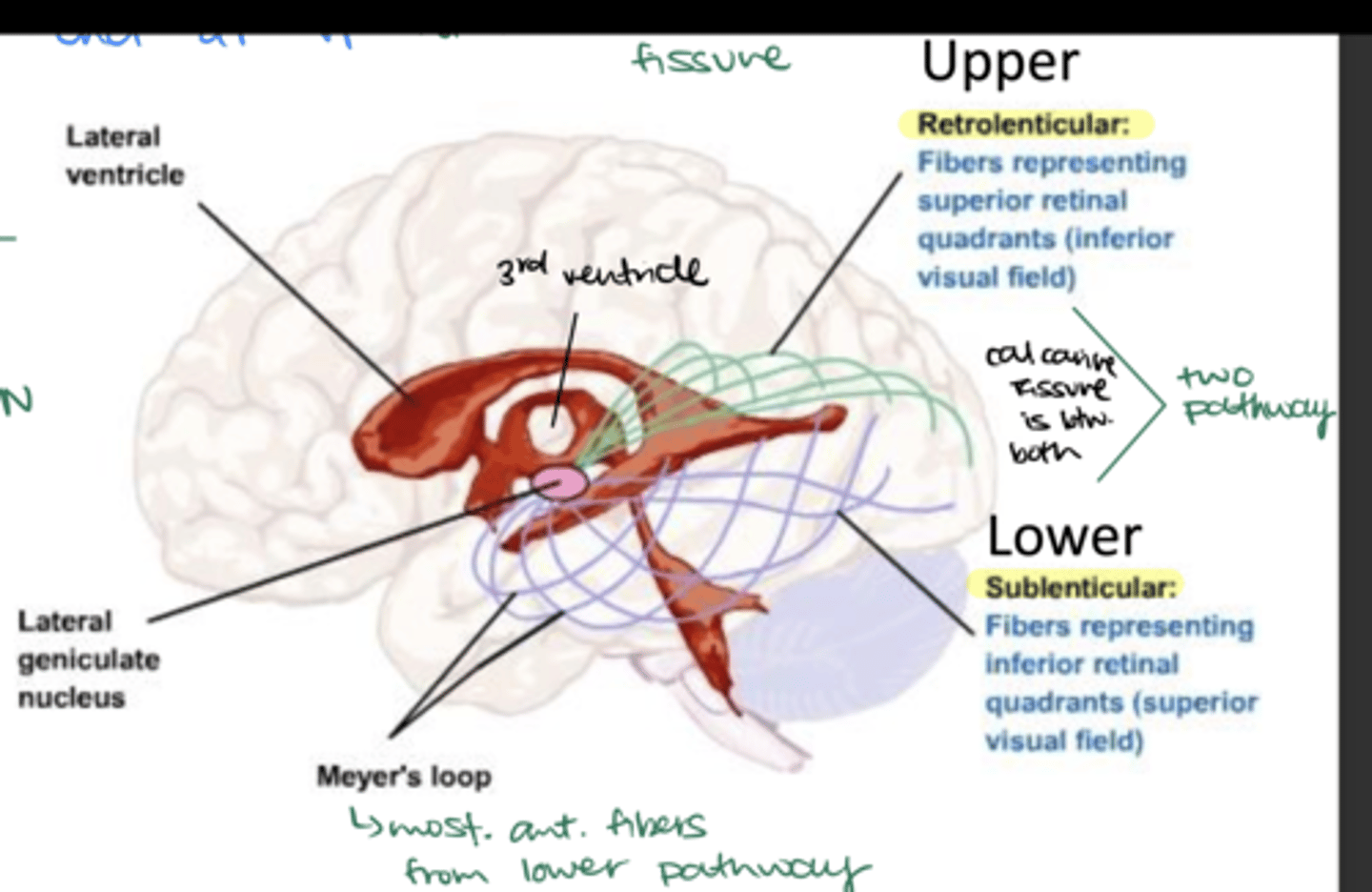
What visual defect can damage to Meyer's loop cause?
Contralateral superior quadrantanopia
What retinal quadrants do the retrolenticular fibers represent? What visual field?
Upper or superior retinal quadrants; inferior visual field
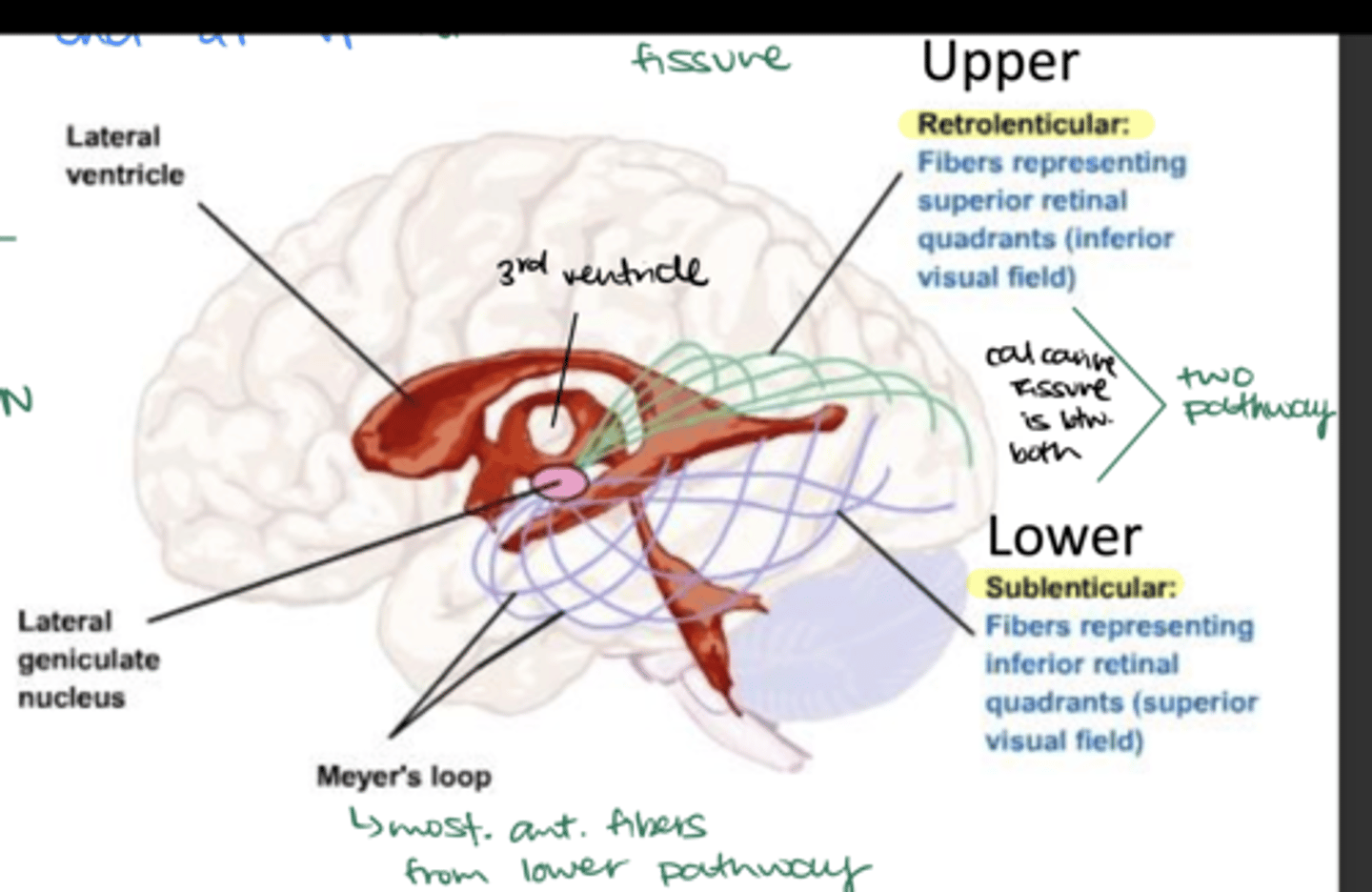
What retinal quadrants do the sublenticular fibers represent? What visual field?
Lower or inferior retinal quadrants; superior visual field
Where is the primary visual cortex (V1) located?
Lies on the medial surface of each occipital lobe, specifcally in the interhemispheric fissure (medial aspect of occipital lobe)
What is the primary visual cortex aka?
-V1
-Striate cortex
What Brodmann area number corresponds to the primary visual cortex?
Broadmann area 17
The calcarine fissure extends from the ________ to the _________, dividing the visual cortex into an upper portion and lower portion.
Parieto-occipital sulcus --> posterior pole
What does the calcarine fissure divide the visual cortex into?
-upper portion
-lower portion
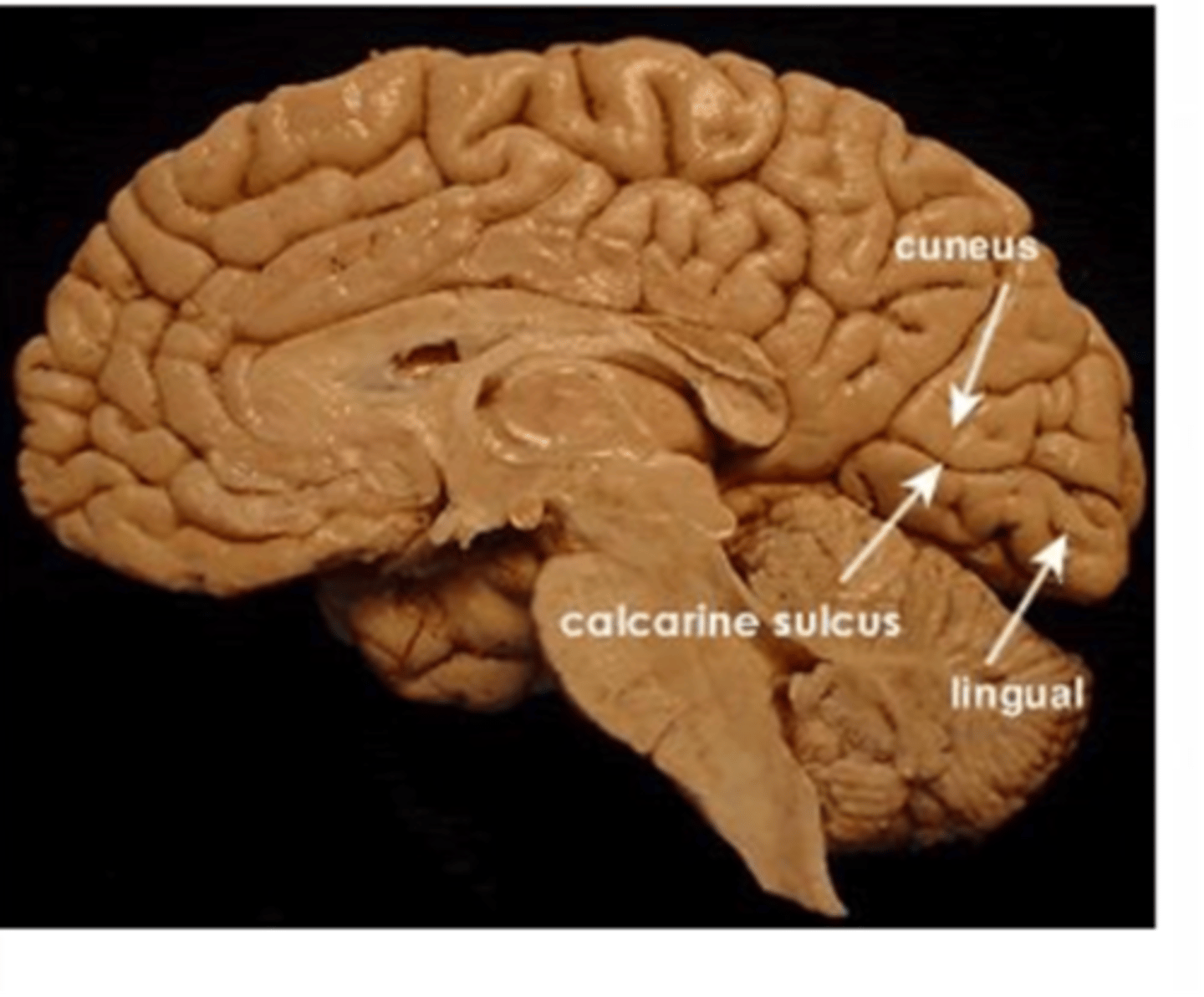
What is the upper portion of the visual cortex called?
Cuneus gyrus
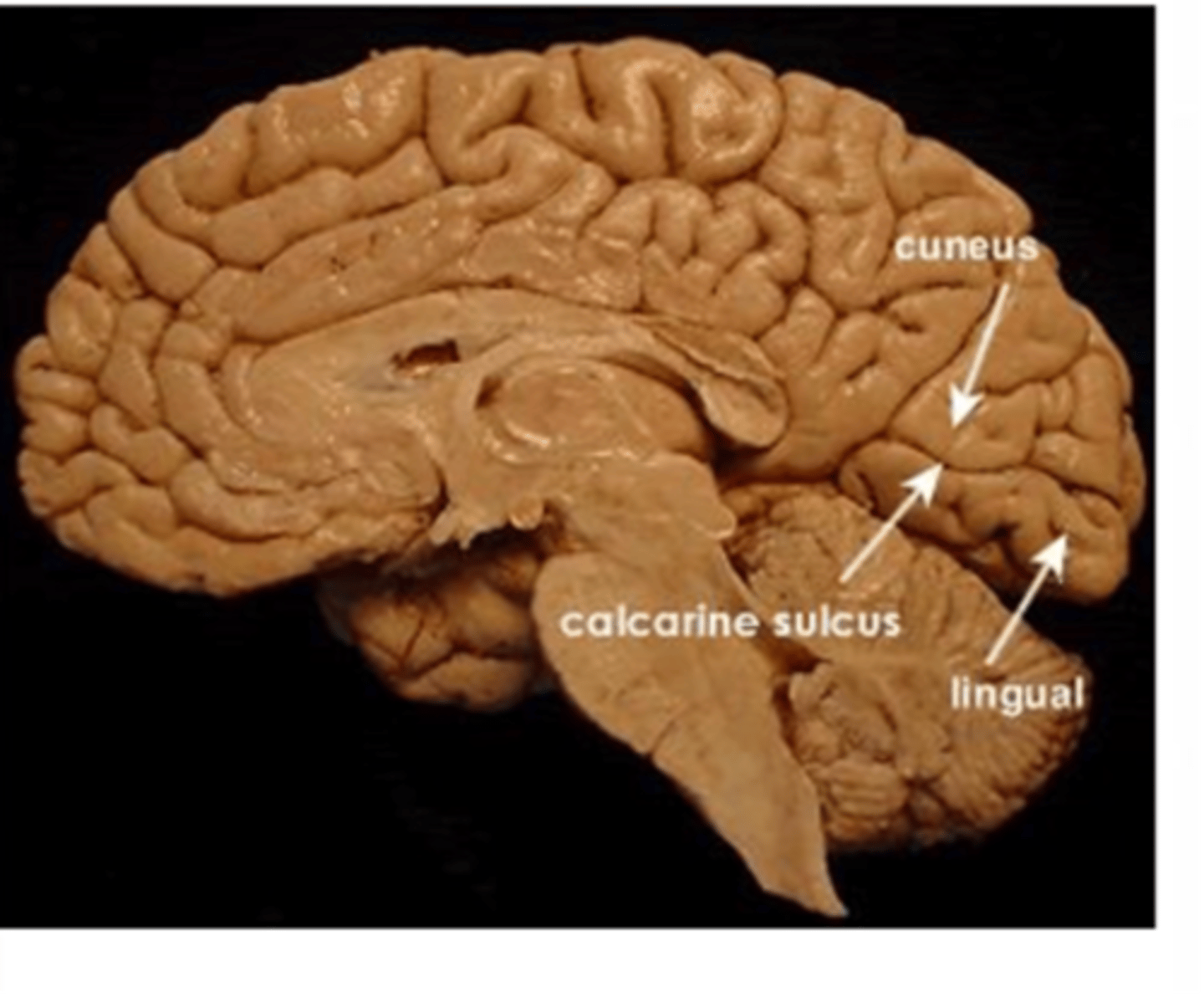
What is the lower portion of the visual cortex called?
Lingual gyrus
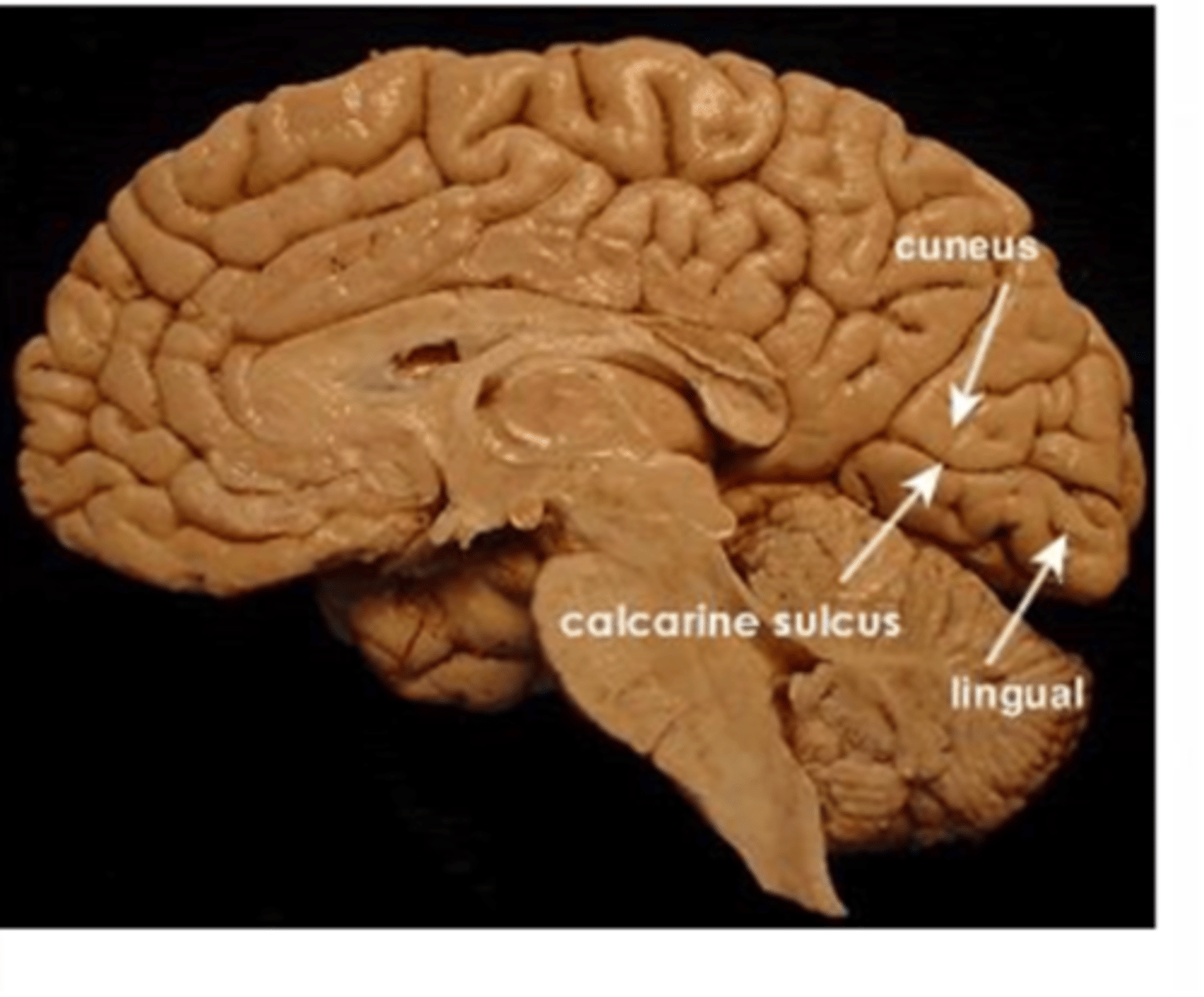
What part of the brain does the V1 receive visual input from?
The retina, via the LGN of the thalamus
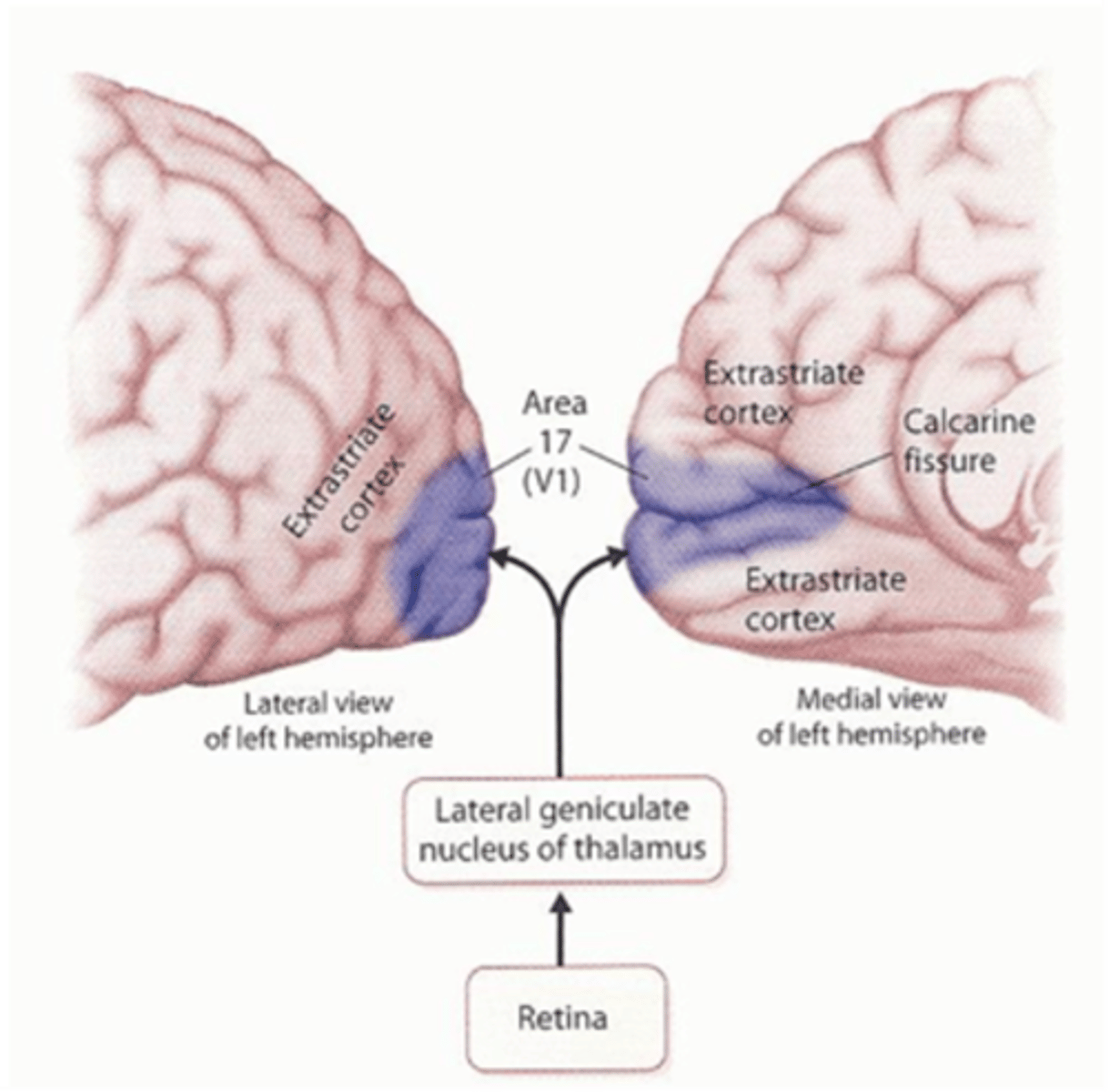
AGAIN, the primary visual cortex is divided by the calcarine fissure (calcarine sulcus) into:
-upper portion (Cuneus gyrus)
-lower portion (Lingual gyrus)
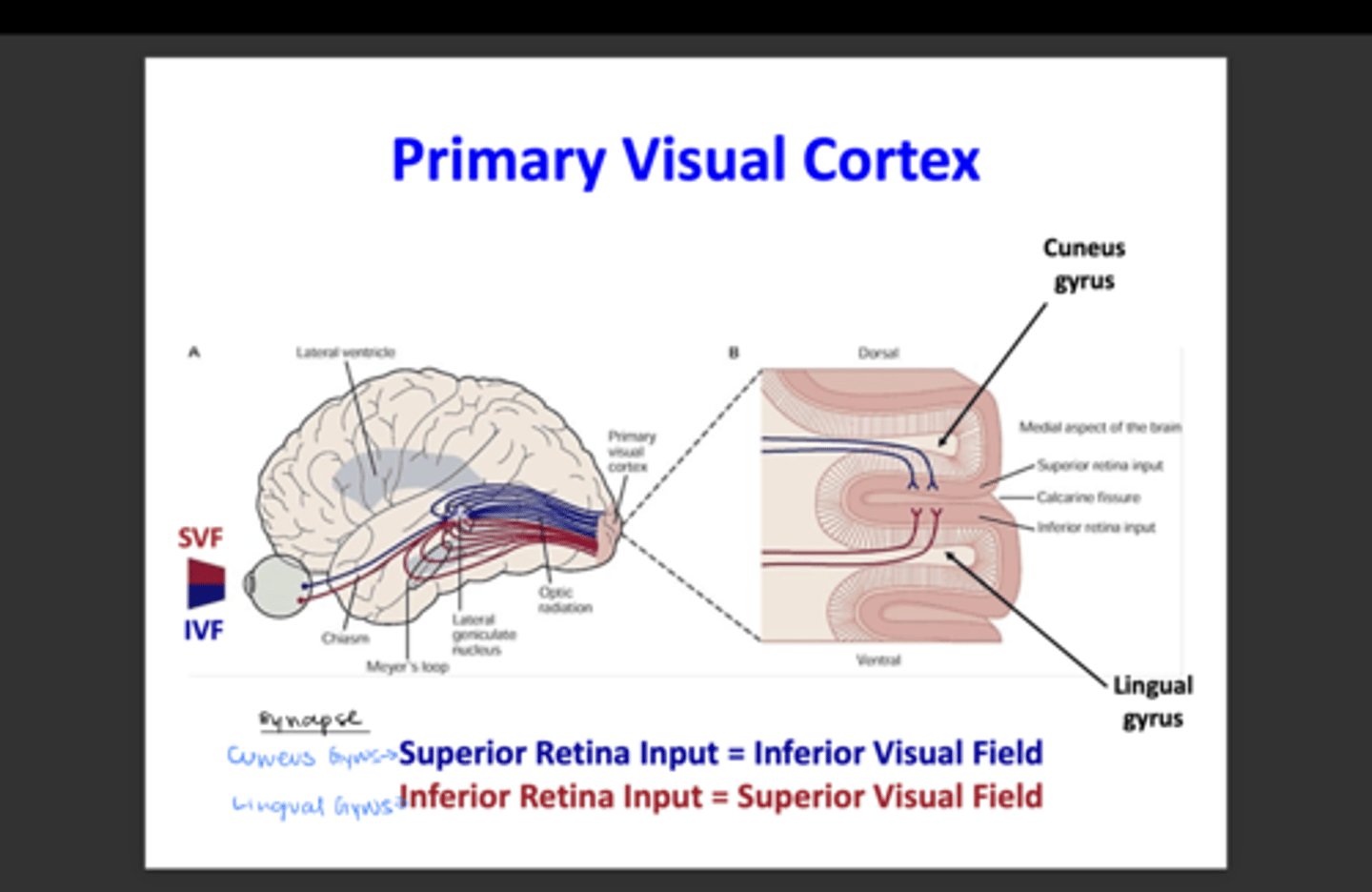
What is the main function of the striate cortex?
To combine and analyze visual information from the LGN and transmit it to higher visual association areas for further processing
What are the higher visual association areas called?
Extrastriate cortex- Broadmann areas 18 and 19
Which specialized cortical areas are found in the extrastriate cortex?
-V2
-V3
-V4
-V5 (MT)
What is the function of V1?
Segregates pattern vision from motion signals
What is the function of V2?
-3D vision
-Seeing camouflage
-More complex patterns
What is the function of V3?
Shape perception
What is the function of V4?
Color area and shape perception
What is the function of V5?
Motion area
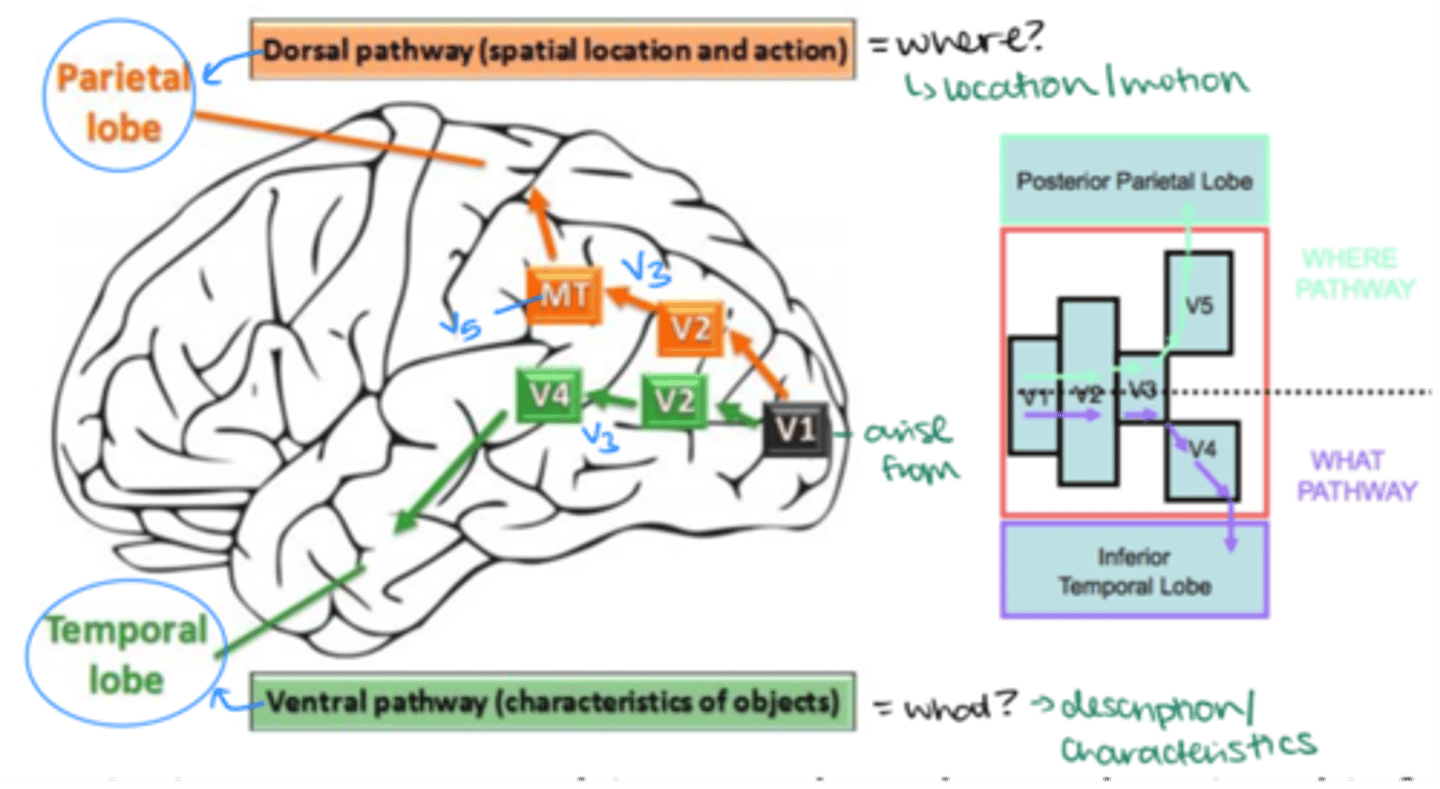
Visual information traveling to the posterior parietal lobe takes which pathway?
V1 --> V2 --> V3 --> V5 --> Parietal lobe (Dorsal Pathway)
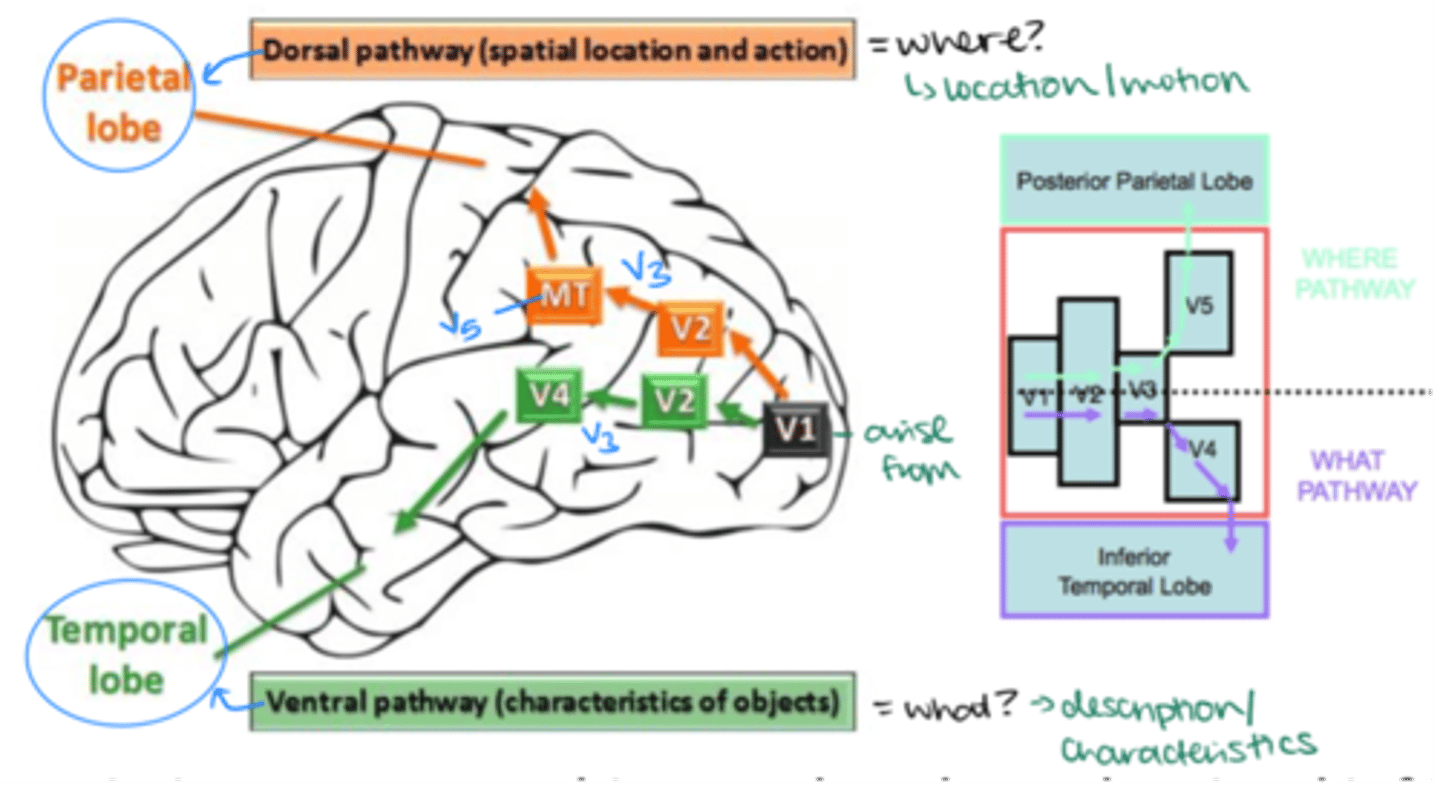
What is the dorsal pathway responsible for?
Processing spatial location and action ("where")
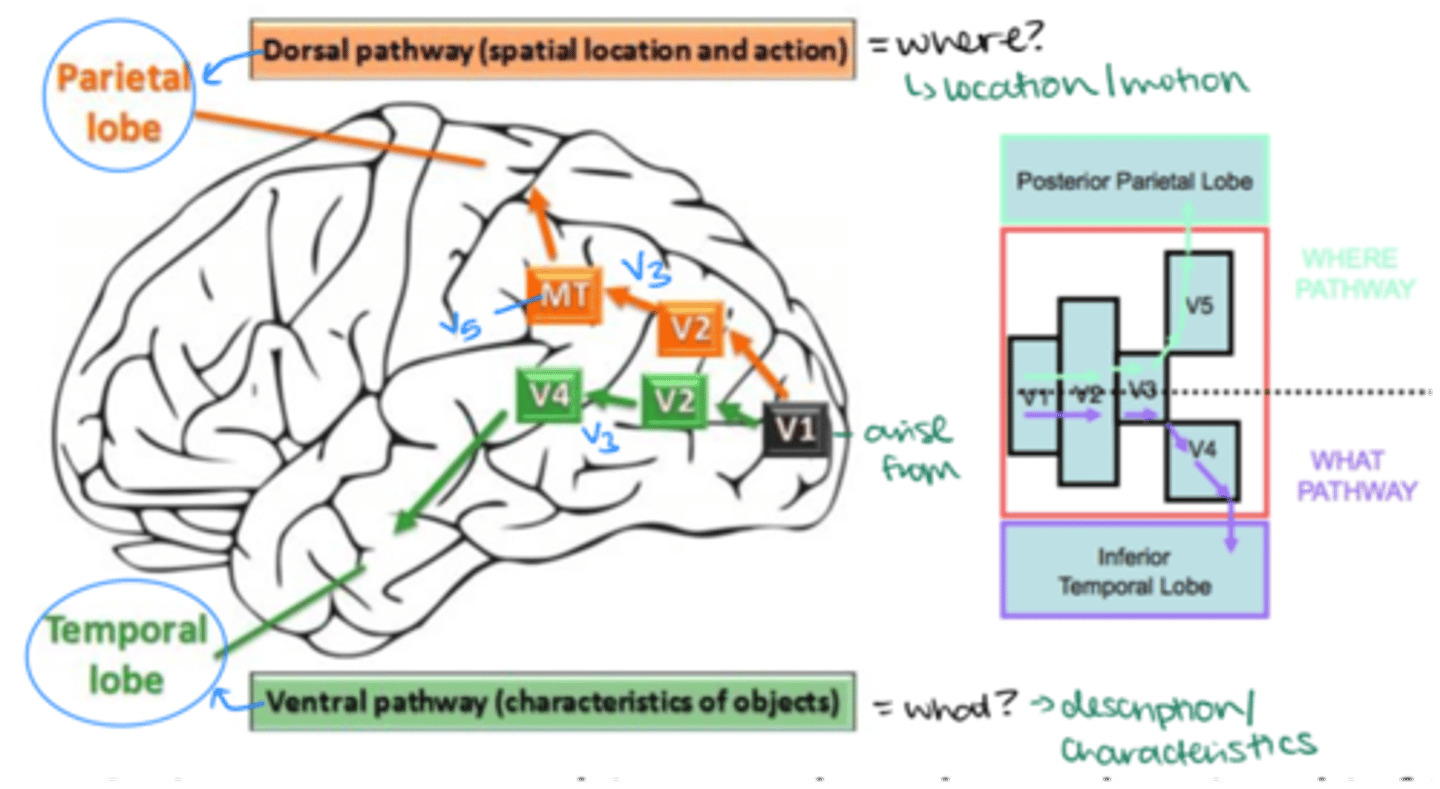
Visual information traveling to the inferior temporal lobe takes which pathway?
V1 --> V2 --> V3 --> V4 --> Temporal lobe (Ventral Pathway)
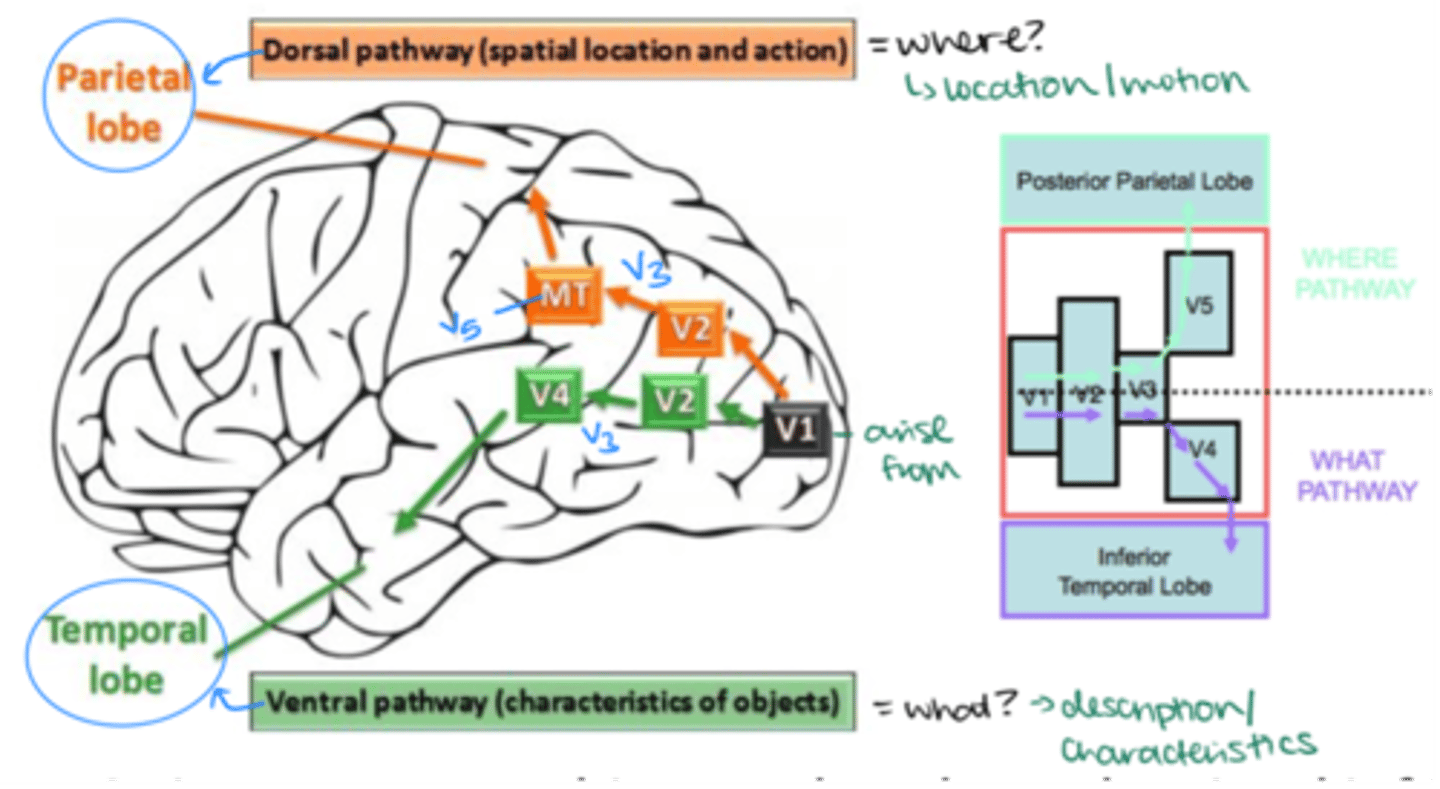
What is the ventral pathway responsible for?
Processing object recognition ("what")
What is the term for the remapping of the retinal image onto the cortical surface?
Retinotopy
How is the visual field represented on the surface of V1?
Each point of the visual field maps onto a local group of neurons in V1
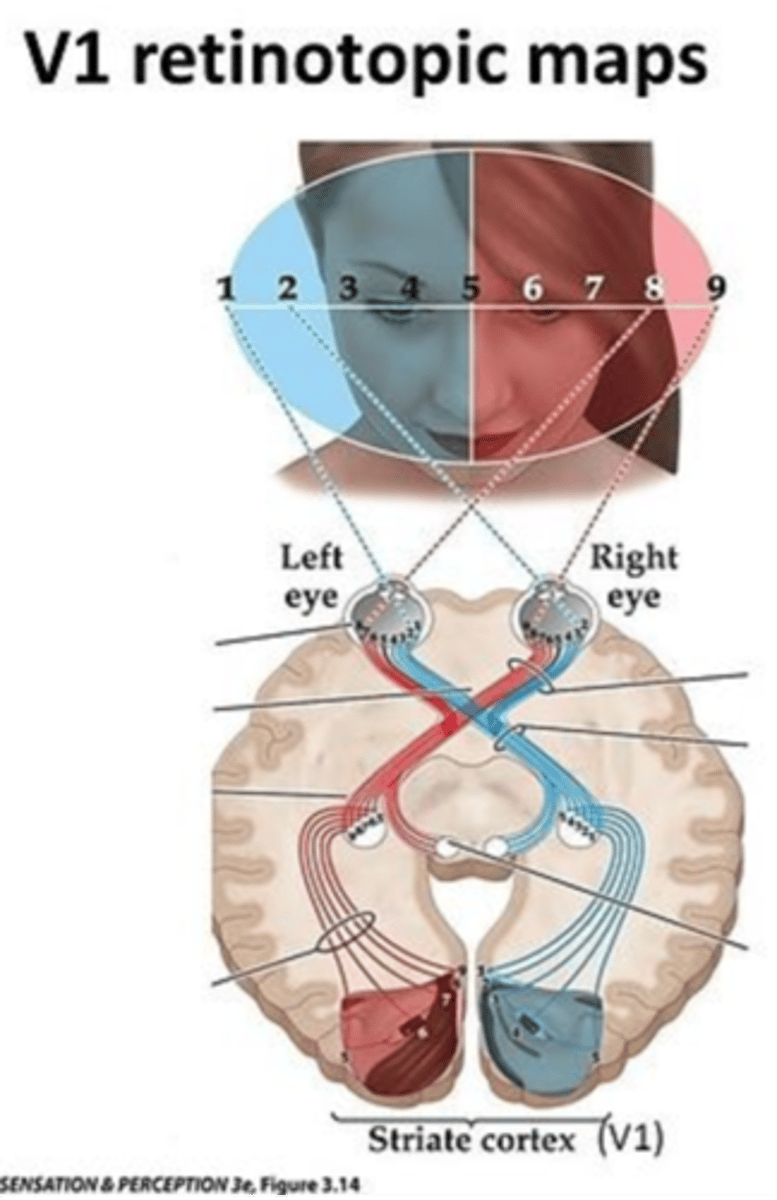
Which region uses more V1 (has a greater magnification factor) compared to peripheral regions of the retina?
Foveal region
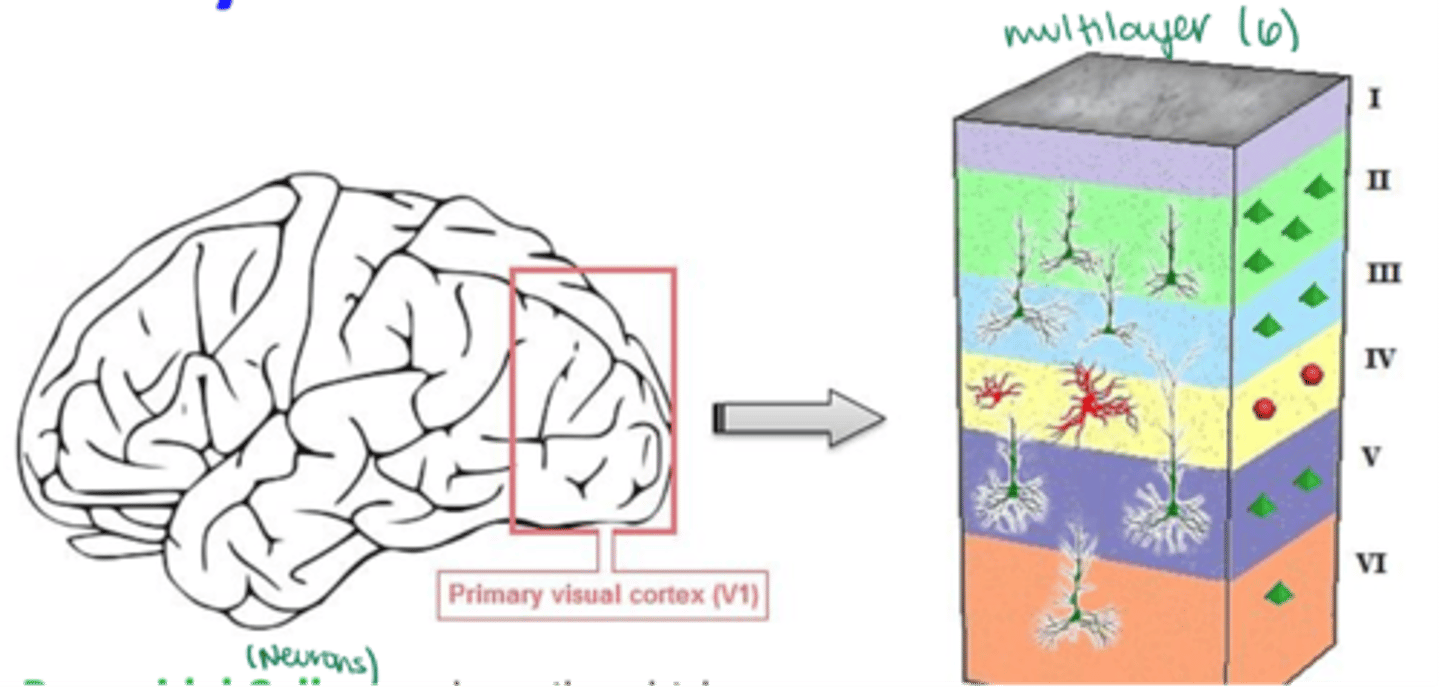
What are the 2 main types of neurons found in primary visual cortex (V1)?
-Pyramidal cells
-Stellate interneurons
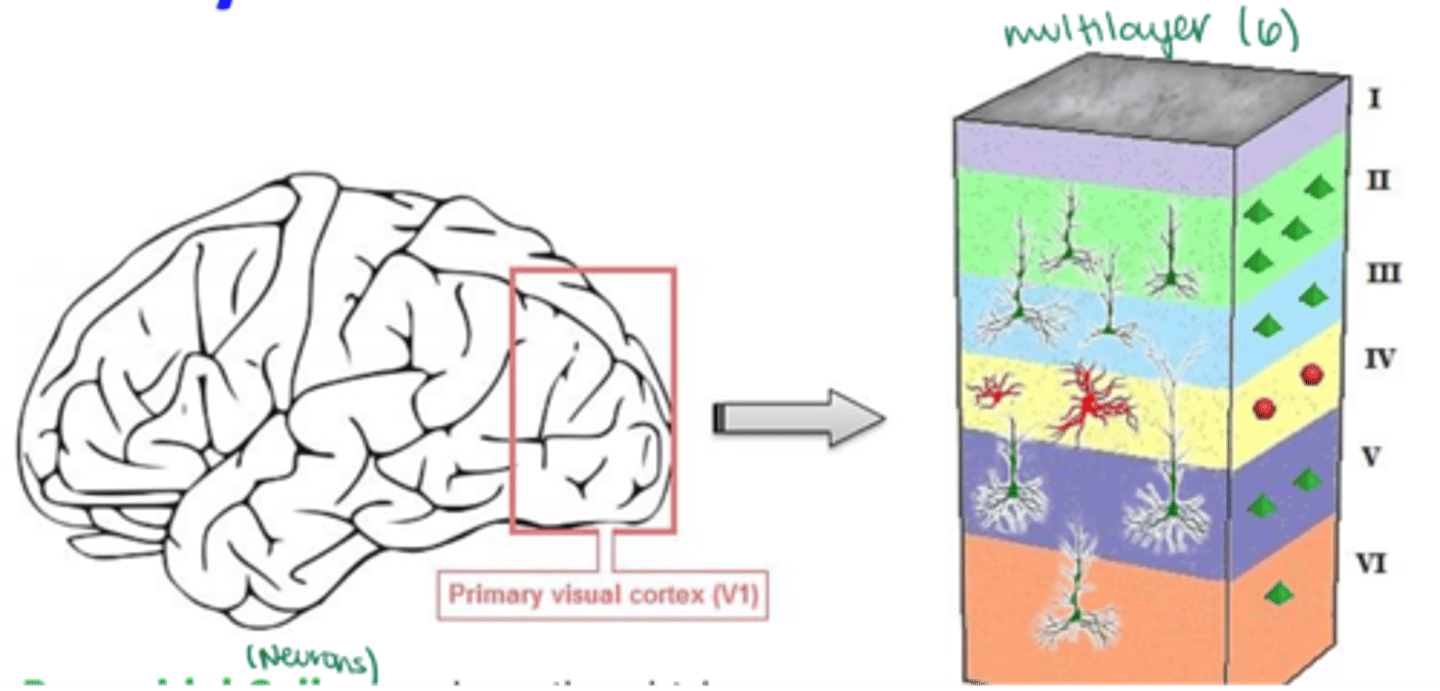
What is the shape of a pyramidal cell's cell body?
Triangular or pyramid-shaped
Are pyramidal cells excitatory or inhibitory, and where do they project to?
Excitatory; project onto other brain regions
What is the spike pattern of pyramidal cells?
Regular spike with a slower ascending slope
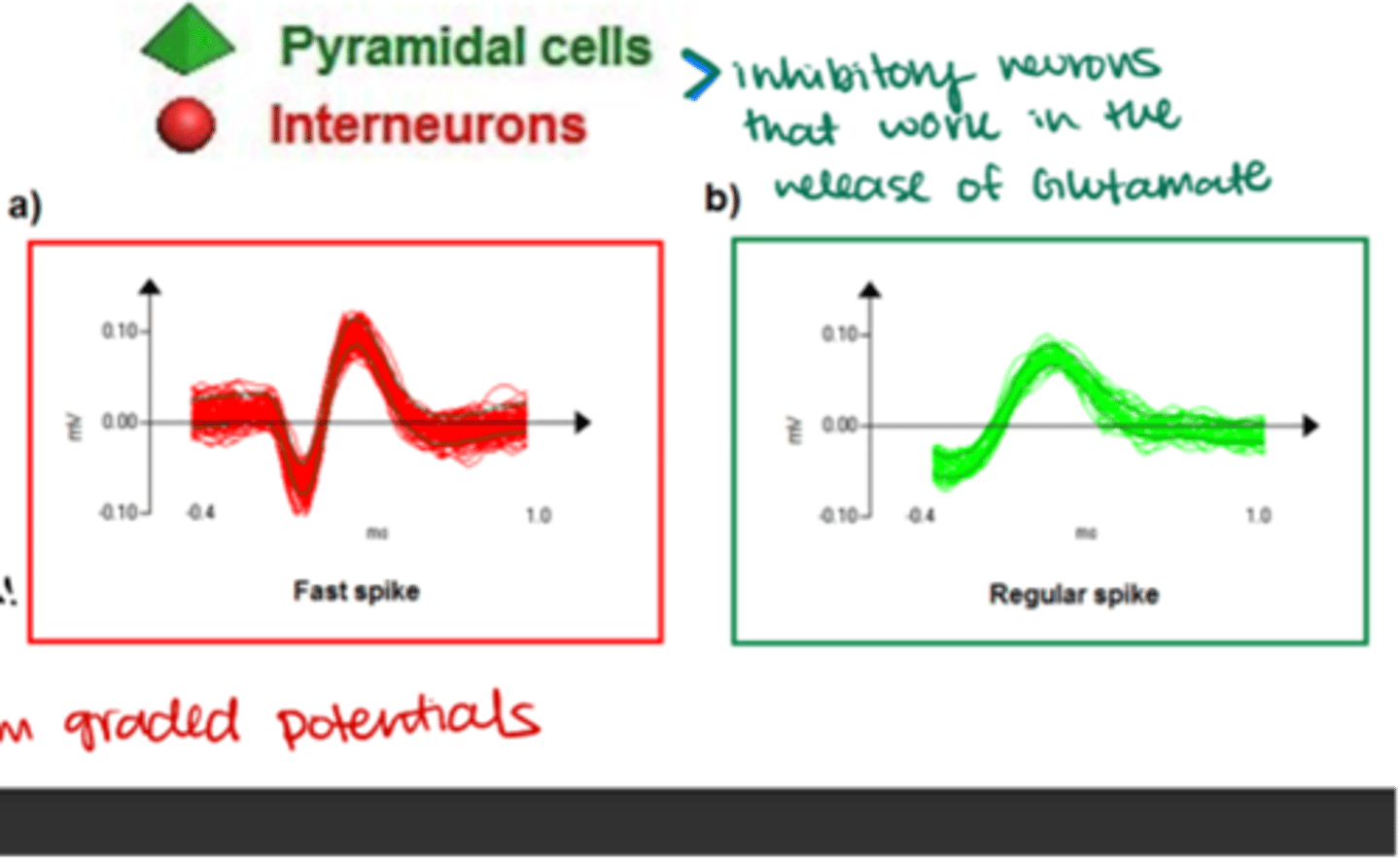
What cortical layers are pyramidal cells found in?
Multiple cortical layers
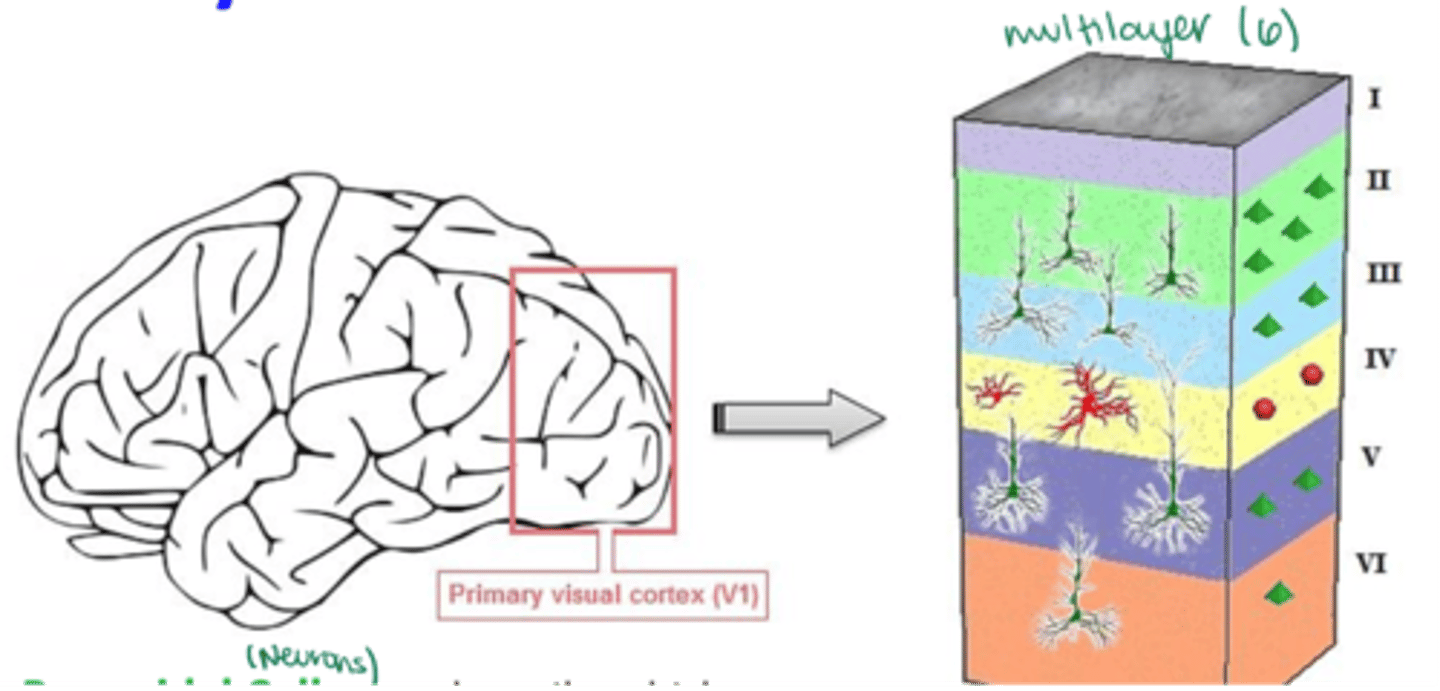
What is the shape of a stellate interneurons' cell body?
"Spiny"
Are stellate interneurons excitatory or inhibitory?
Exhibitory (although some can be inhibitory towards the cerebellum)
What is the spike pattern of stellate interneurons?
Fast spike with a steeper ascending slope
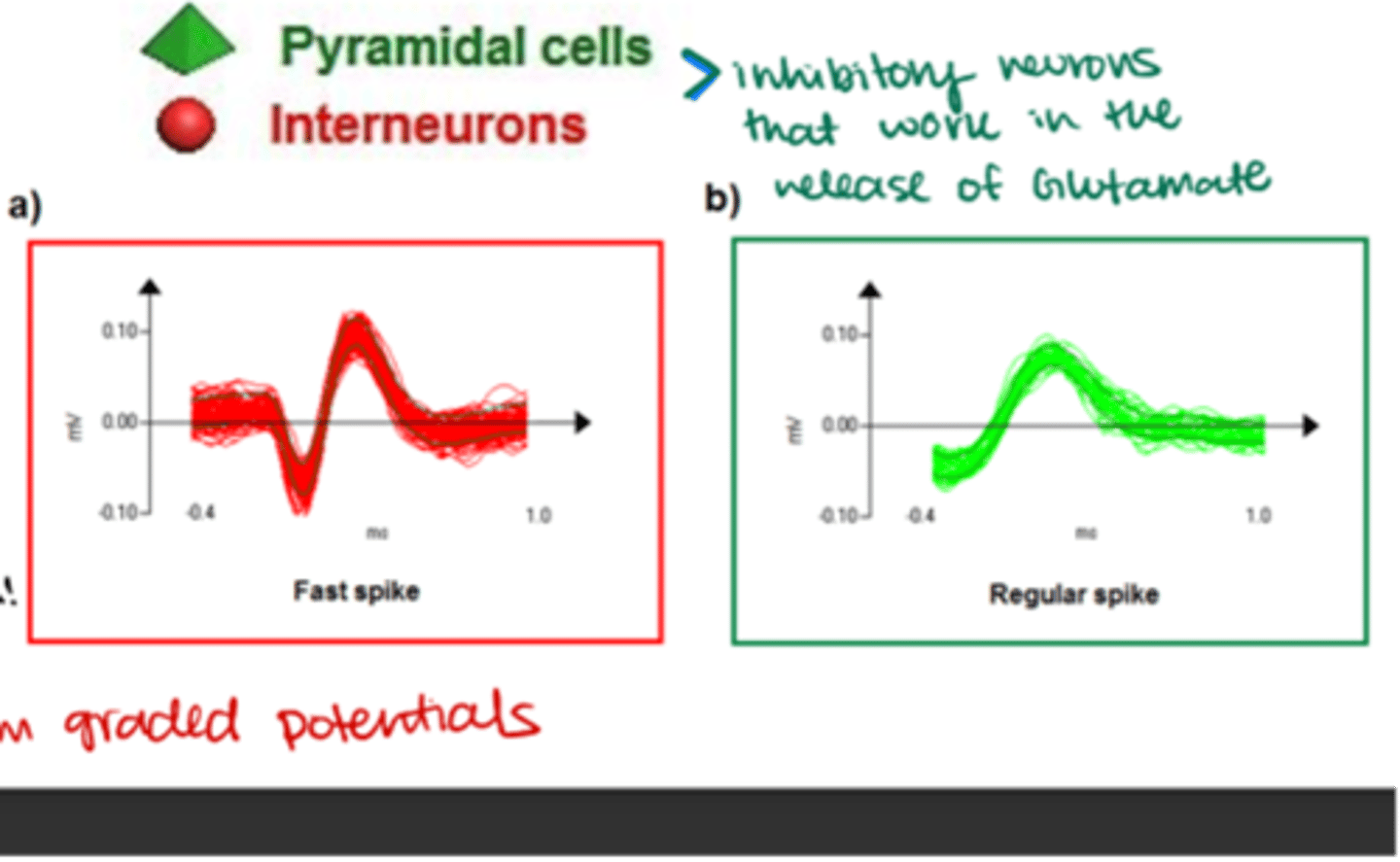
Where do stellate interneurons receive visual input from?
LGN
Which cortical layers are stellate interneurons found in?
ONLY V4
What supplies blood to the outer retinal layers?
Choroid
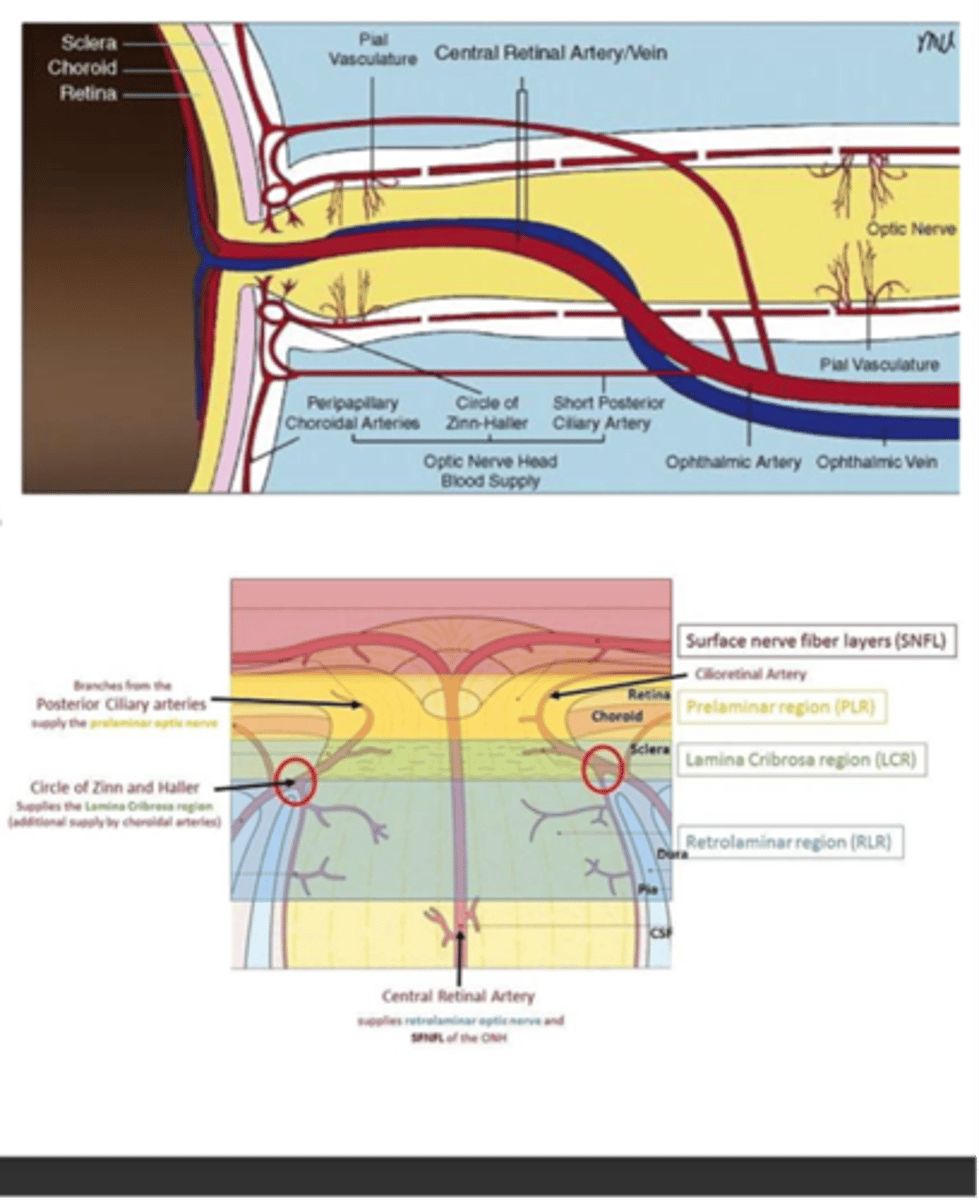
What supplies blood to and drains blood from the inner retina?
CRA/V
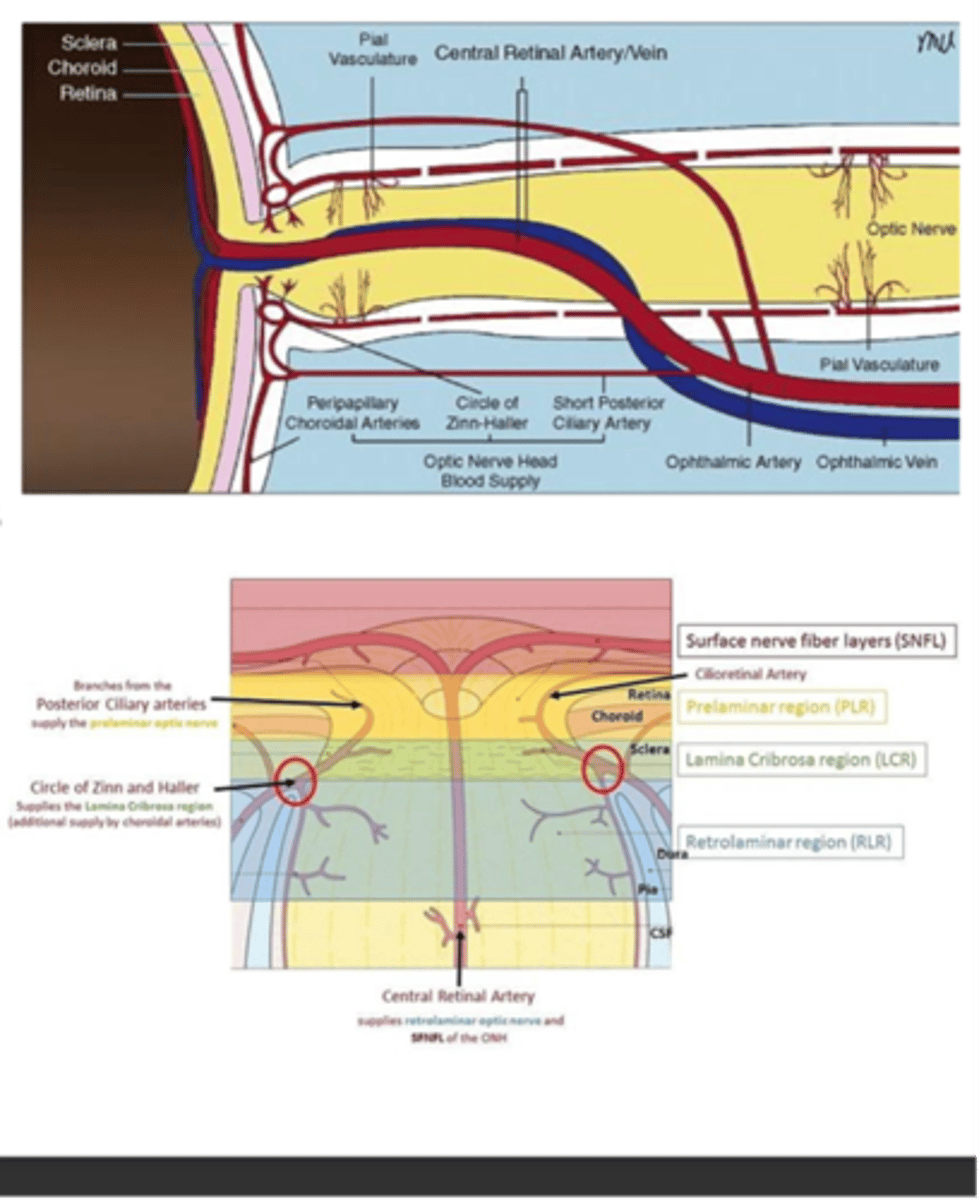
What supplies blood to the ONH?
-Circle of Zinn-Haller
-SPCA
-Peripapillary vessels
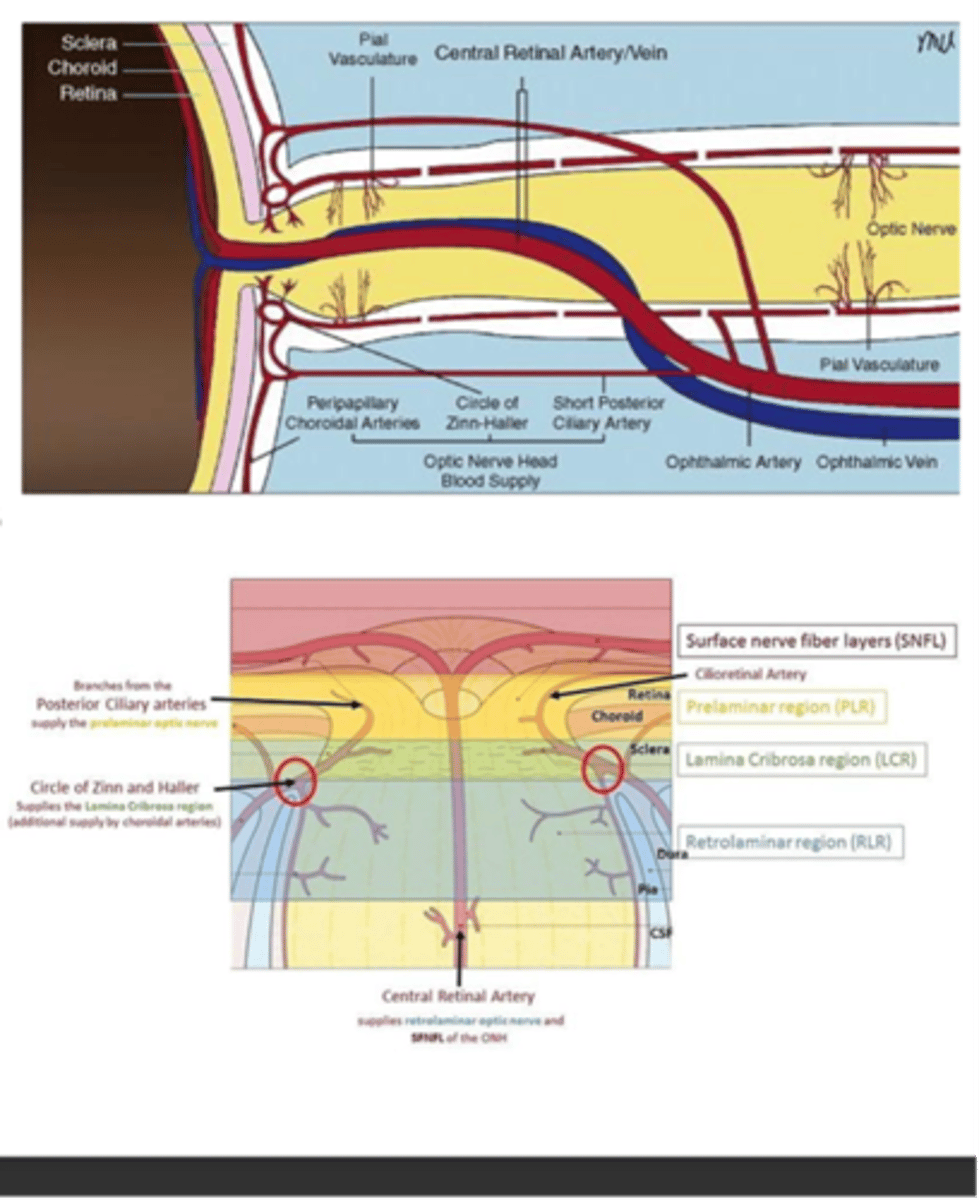
What supplies the intraorbital portion of the ONH?
Pial vessels (branches of the ophthalmic artery)
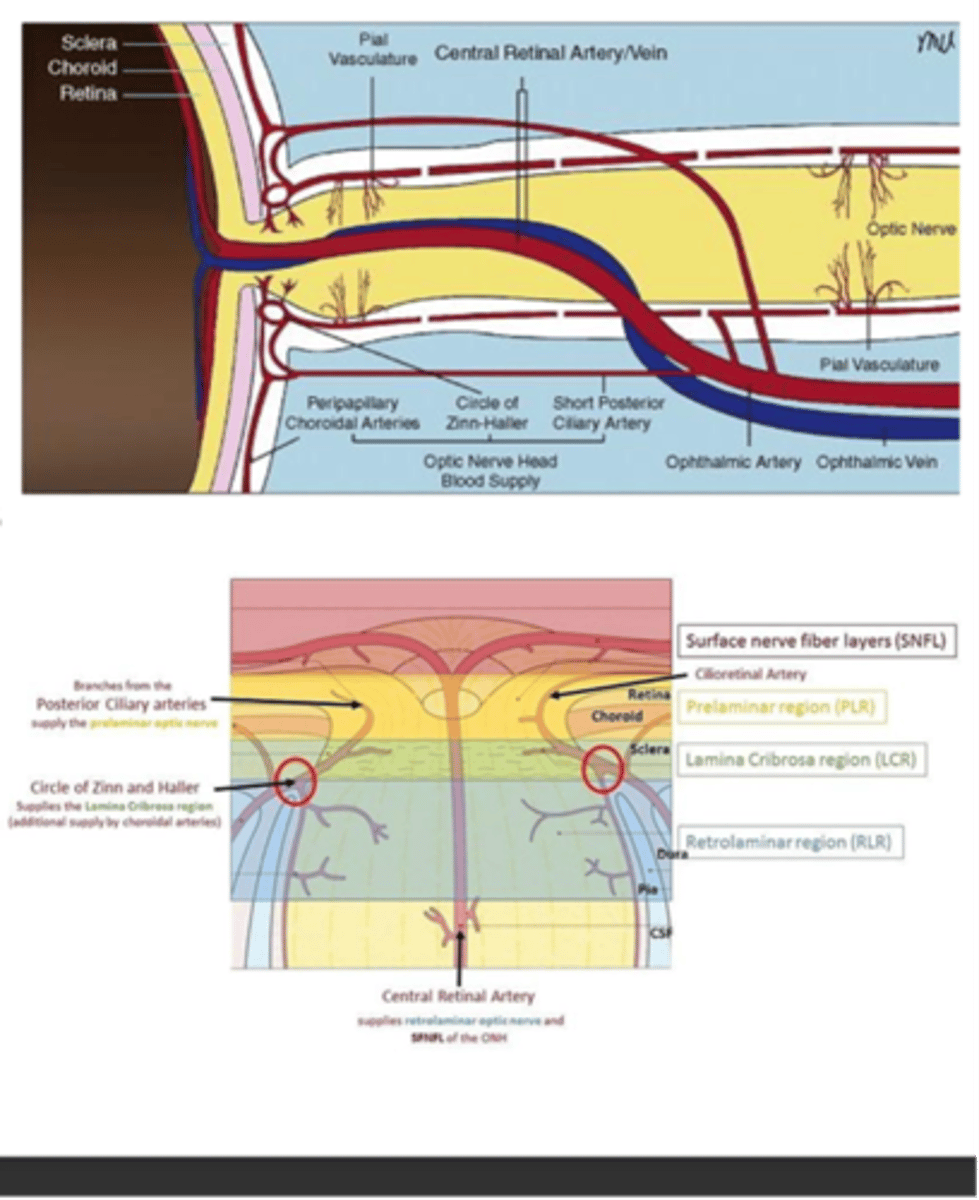
What supplies the posterior intaorbital portion of the ONH?
Hypophyseal branches of the ICS (internal carotid system)
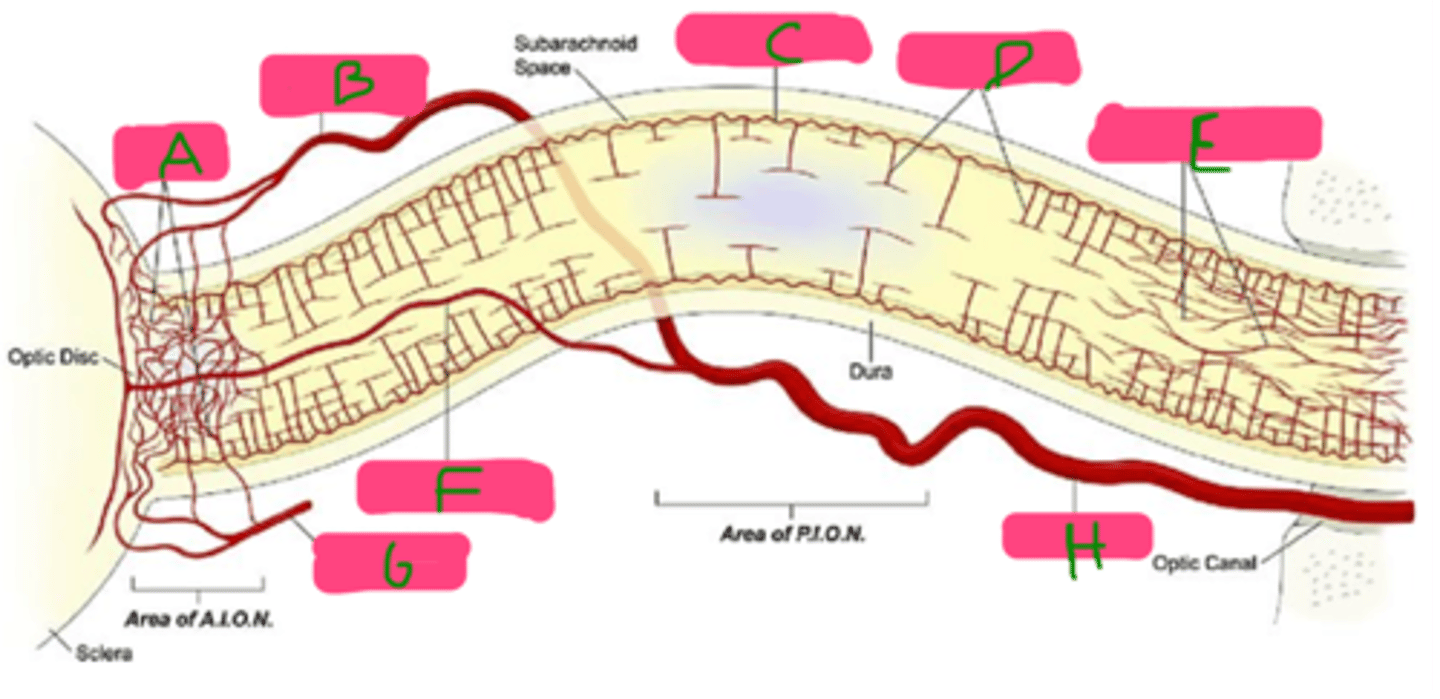
Which arteries supply blood to the intracranial optic nerve?
branches of the:
-Ophthalmic
-Anterior cerebral
-Anterior communicating
-Internal carotid
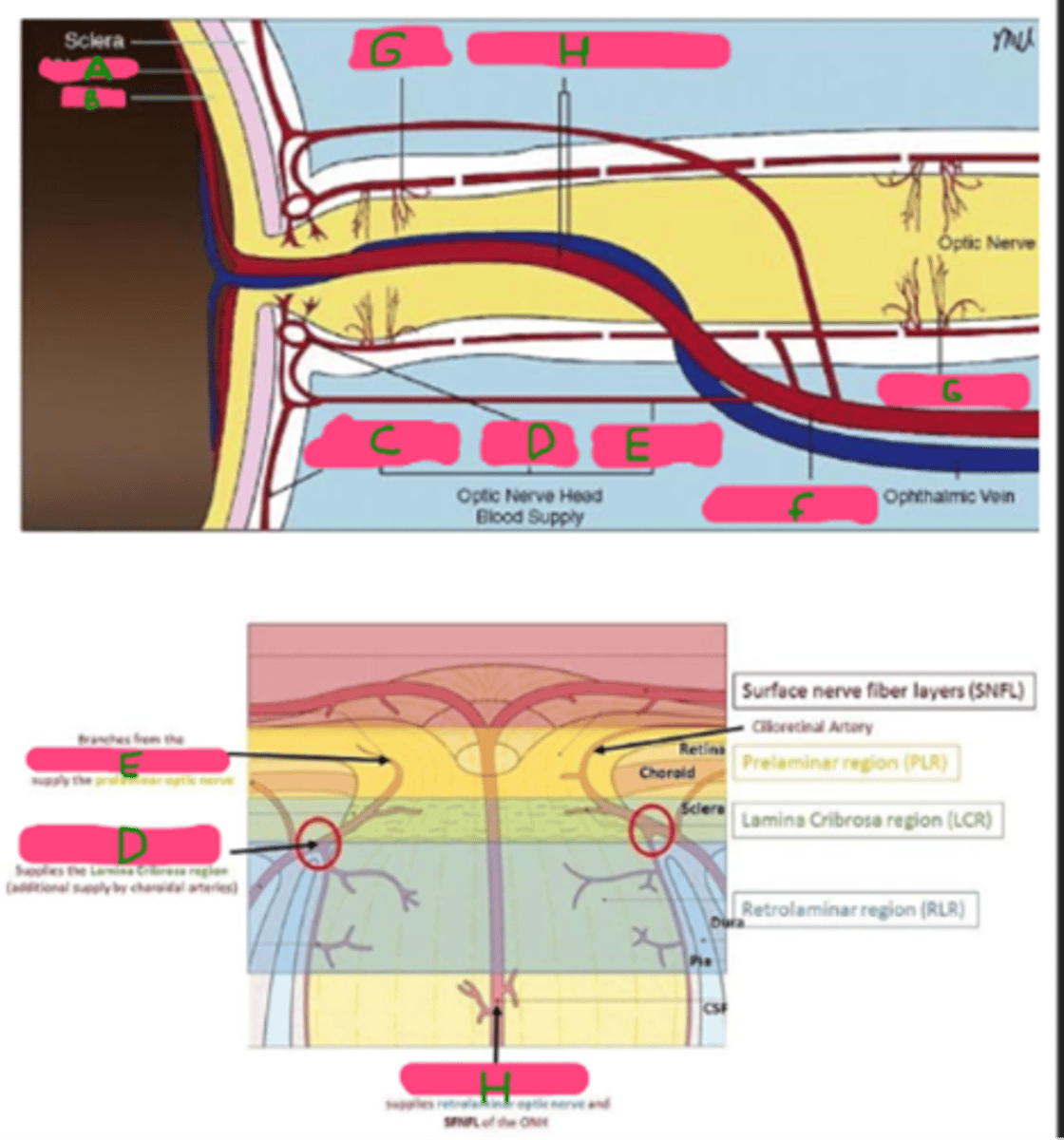
A: Choroid
B: Retina
C: Peripapillary choroidal arteries
D: Circle of Zinn-Haller
E: SPCA
F: Ophthalmic artery
G: Pial vasculature
H: CRA/V
Label A-H.
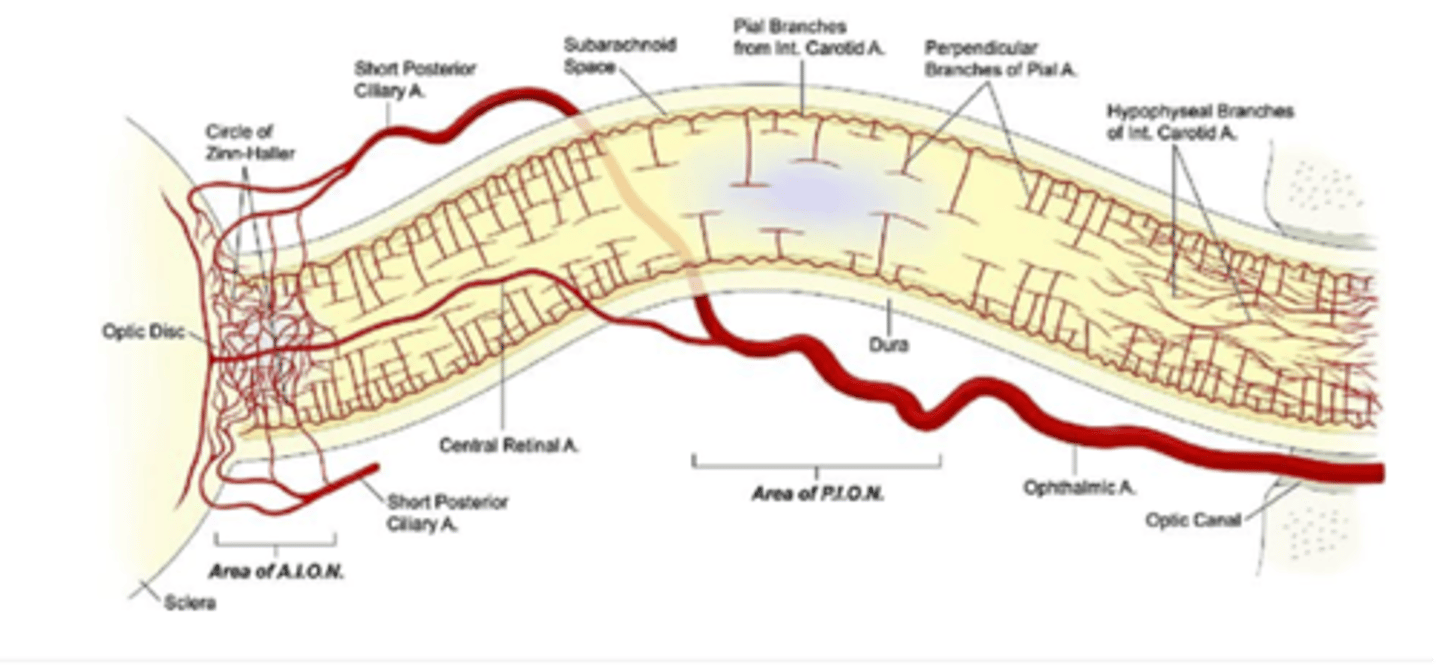
A: Circle of Zinn-Haller
B: SPCA
C: Pial branches from Int carotid a.
D: Perpendicular branches of pial a.
E: Hypophyseal branches of int. carotid a.
F: CRA
G: SPCA
H: Ophthalmic artery
Label A-H
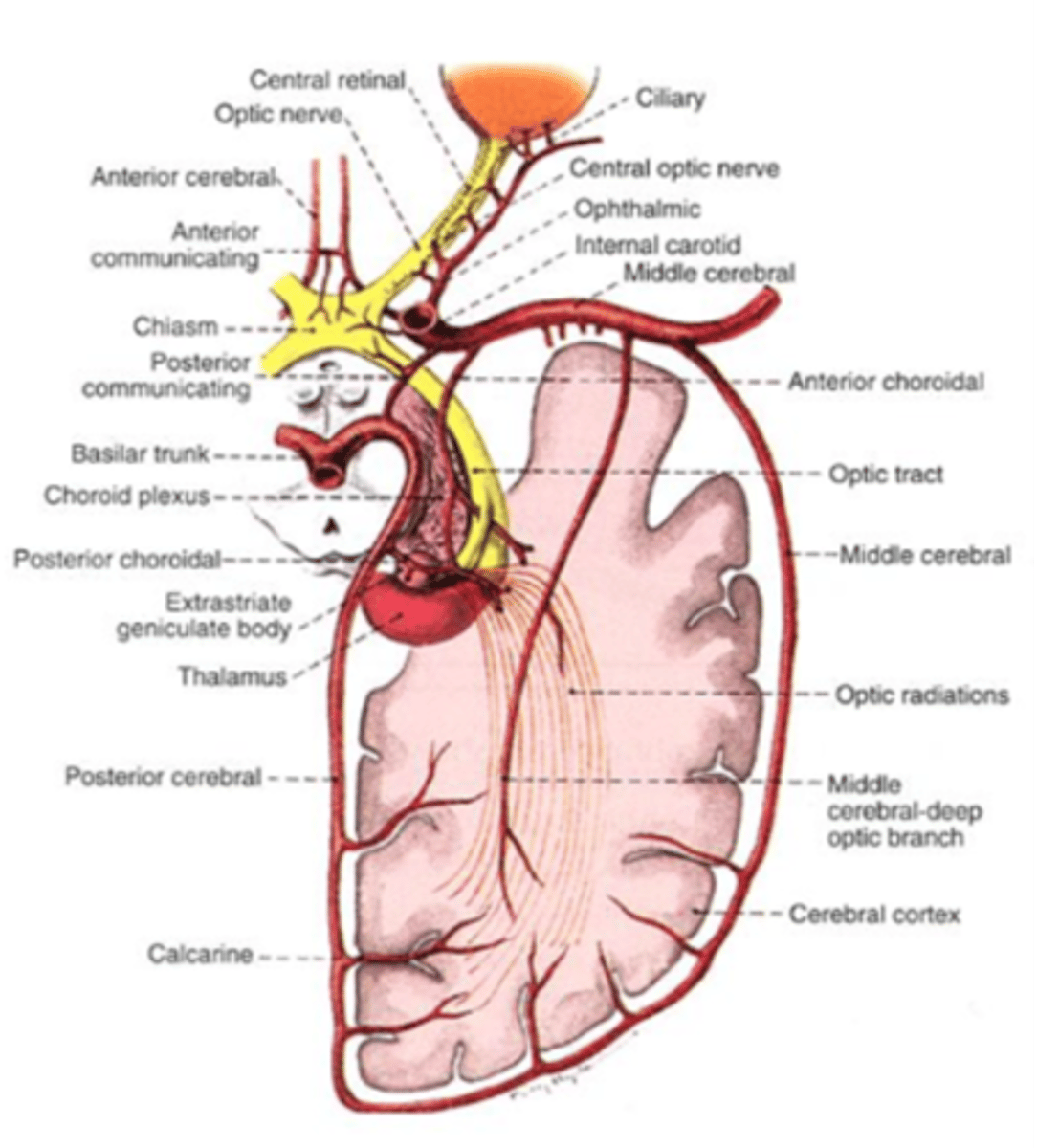
A: Anterior cerebral artery
B: Anterior communicating artery
C: Ophthalmic artery
D: Internal carotid artery
Label each structure which supplies blood to the intracranial optic nerve.

What structure supplies blood to the optic chiasm?
Arterioles (branches) from Circle of Willis
What arteries make up the superior network supplying the optic chiasm?
-Anterior cerebral
-Anterior communicating
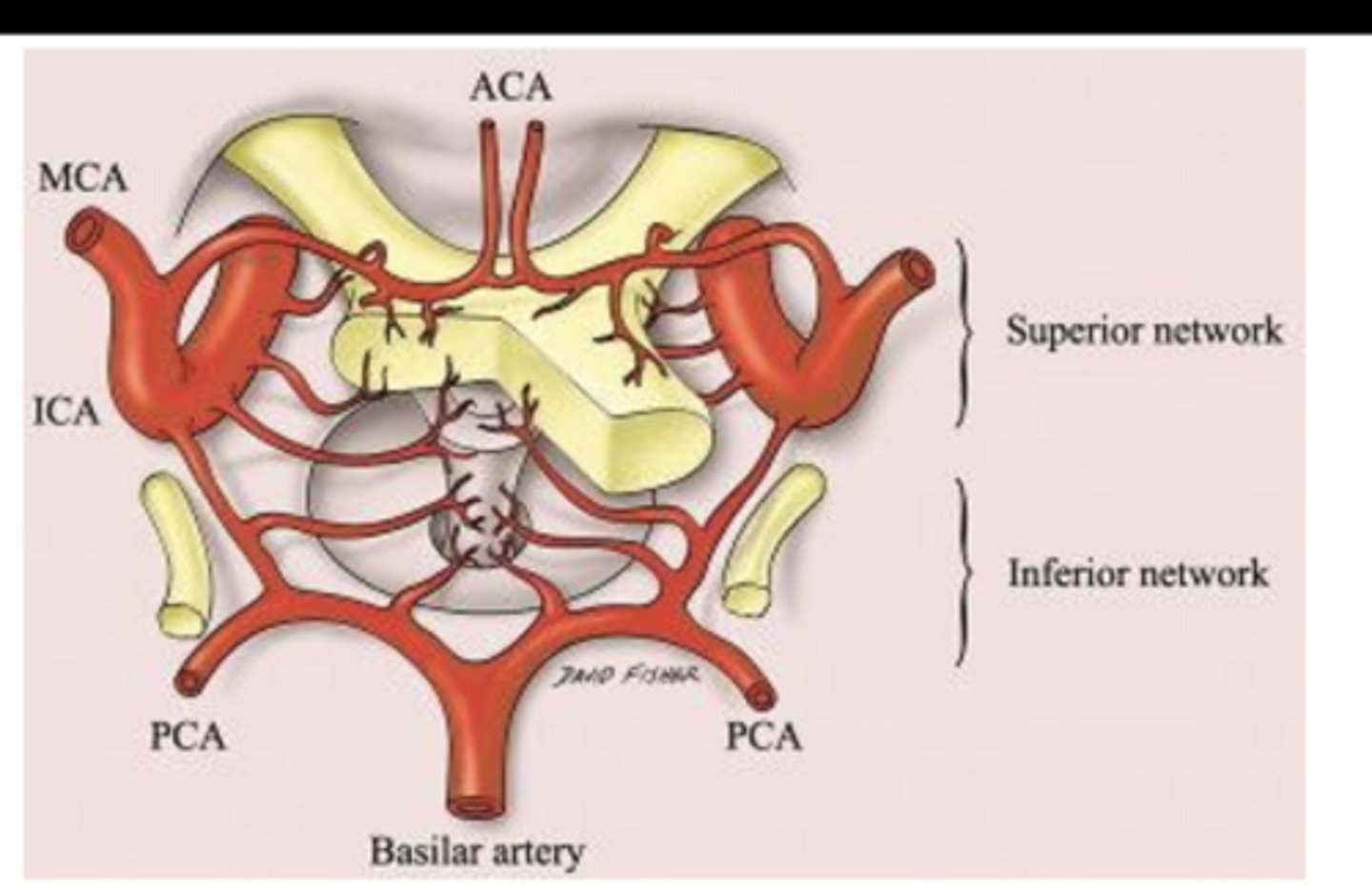
What arteries make up the inferior network supplying the optic chiasm?
-Internal carotid
-Posterior cerebral
-Posterior communicating arteries
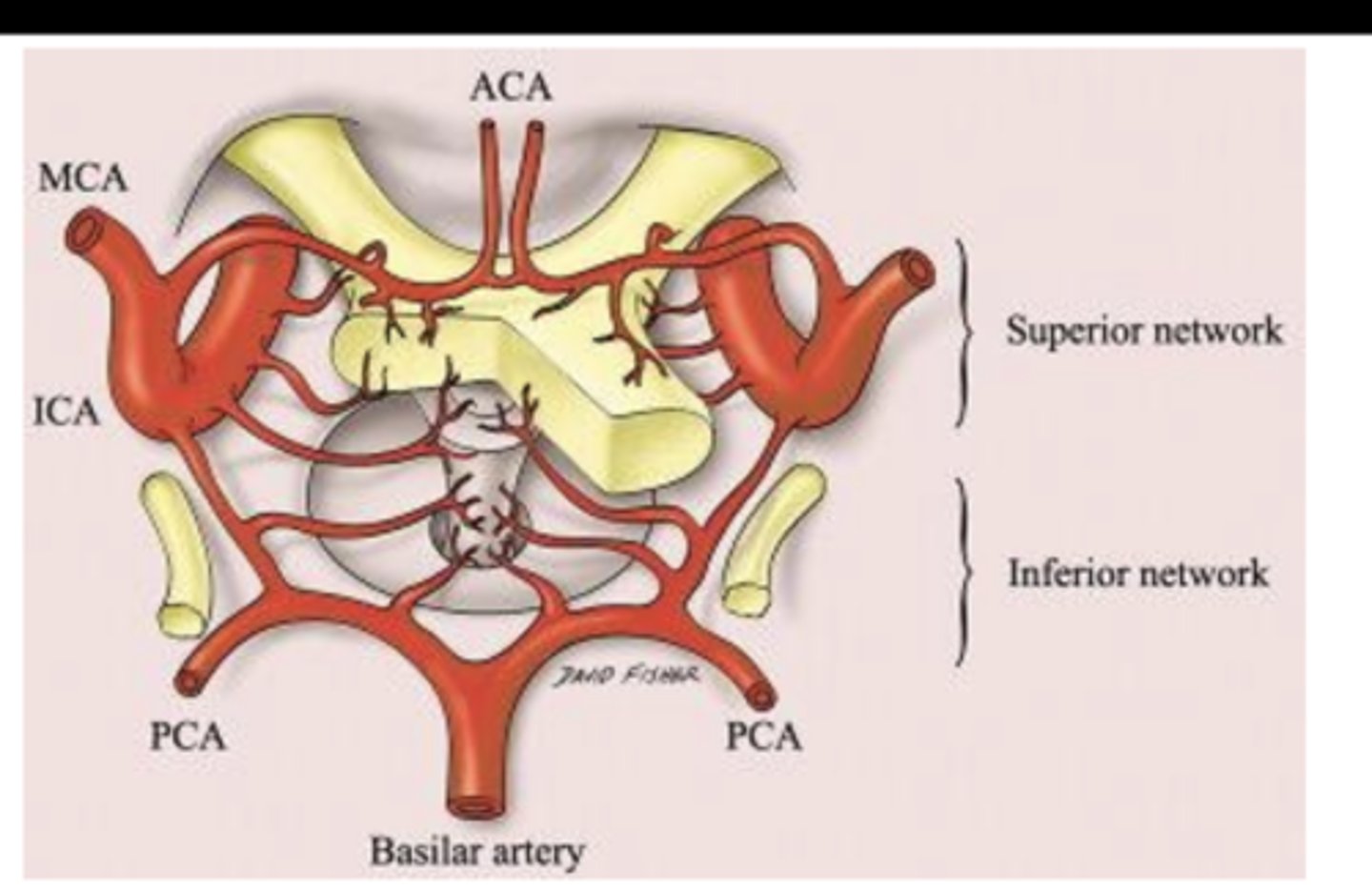
What other structure, besides the optic chiasm, does the inferior network supply?
Portions of the hypophysis (pituitary gland)