Bio 214 Ch 16 Senses
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Hearing
-A response to vibrating air molecules
Equilibrium
-Coordination, balance, and orientation in a 3D space
Hearing and equilibrium
-Both senses reside in the inner ear, a maze of fluid-filled passages and sensory cells
-Fluid is set in motion and the sensory cells convert this motion into an informative pattern of AP
Sound
-Any audible vibration of molecules
-Vibrating object pushes on air molecules
-In turn, push on other air molecules
-Air molecules hitting ear drum cause it to vibrate
Pitch
-Our sense of whether a sound is High or Low
-determined by vibration frequency: hertz (Hz) or cycles/sec
Human hearing range
-20-20000 Hz
-Infrasonic frequencies below 20 Hz
-Ultrasonic frequencies above 20000 Hz
Most hearing loss
-With age is in range of 250 - 2050 Hz
Speech
-1500 - 5000 Hz
-Where hearing is most sensitive
Loudness
-The perception of sound energy, intensity, or amplitude of the vibration
-Expressed in decibels (dB)
-Prolonged exposure to sounds > 90 dB can cause damage
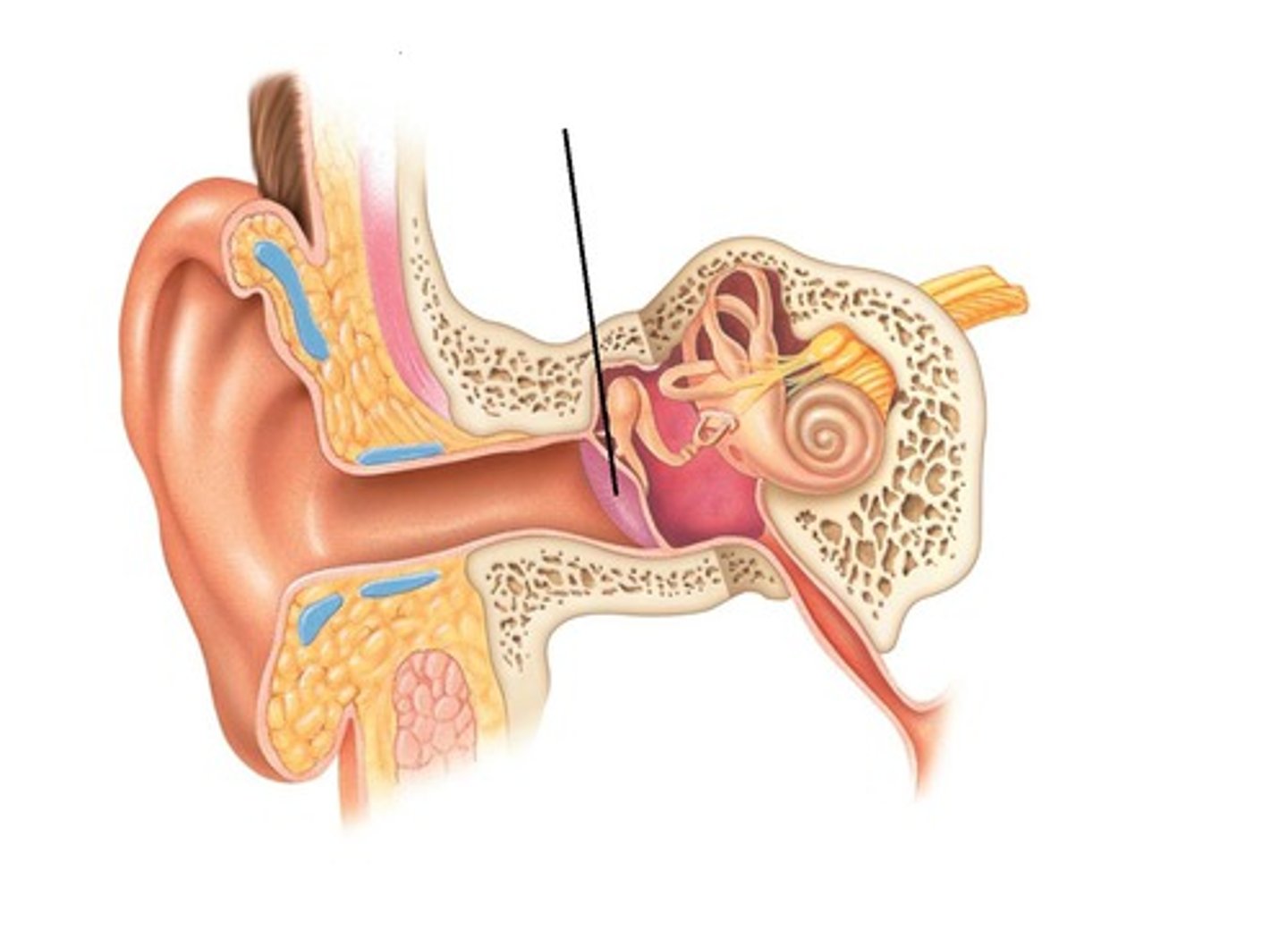
Ear sections
-Outer, middle, inner ear
-First two are concerned only with the transmission of sound to the inner ear
-Inner ear: vibrations converted to nerve signals
Outer ear
-A funnel for conducting vibrations to the tympanic membrane
Auricle
-Pinna
-Directs sound down the auditory canal
-Shaped and supported by elastic cartilage
Auditory canal
-External acoustic meatus
-Passage leading through temporal bone to tympanic membrane
-Guard hairs protect outer end of canal
Cerumen
-Ear wax
-Mixture of secretions of ceruminous and sebaceous glands and dead skin cells
Middle ear
-Located in the air-filled tympanic cavity in temporal bone
Tympanic membrane
-Eardrum
-Closes the inner end of the auditory canal
-About 1cm in diameter
-Vibrates freely in response to sound
Tympanic cavity
-Middle ear
-Continuous with mastoid air cells
-Space only 2-3 mm wide between outer and inner ear
-Contains auditory ossicles
Auditory tube
-Eustachian
-Connects middle-ear to nasopharynx
-Equalizes air pressure on both sides of tympanic membrane
-Normally closed, but swallowing or yawning open it
-Allows throat infections to travel to middle ear
Auditory ossicles
-Malleus
-Incus
-Stapes
-Stapedius and tensor tympani muscles attach to stapes and malleus
Malleus
-First ossicle
-Has long handle attached to inner surface of tympanic membrane
Incus
-Middle ossicle
-Articulates with malleus and stapes
Stapes
-Last ossicle
-Shaped like a stirrup; footplate rests on oval window-where inner ear begins
Otitis media
-Middle ear infection
-Common in children
-Auditory tube is short and horizontal
-Infections easily spread from throat to tympanic cavity and mastoid air cells
Otitis media symptoms
-Fluid accumulation in tympanic cavity producing pressure, pain, and impaired hearing
-Can spread, leading to meningitis
-Can cause fusion of ear inner ossicles and hearing loss
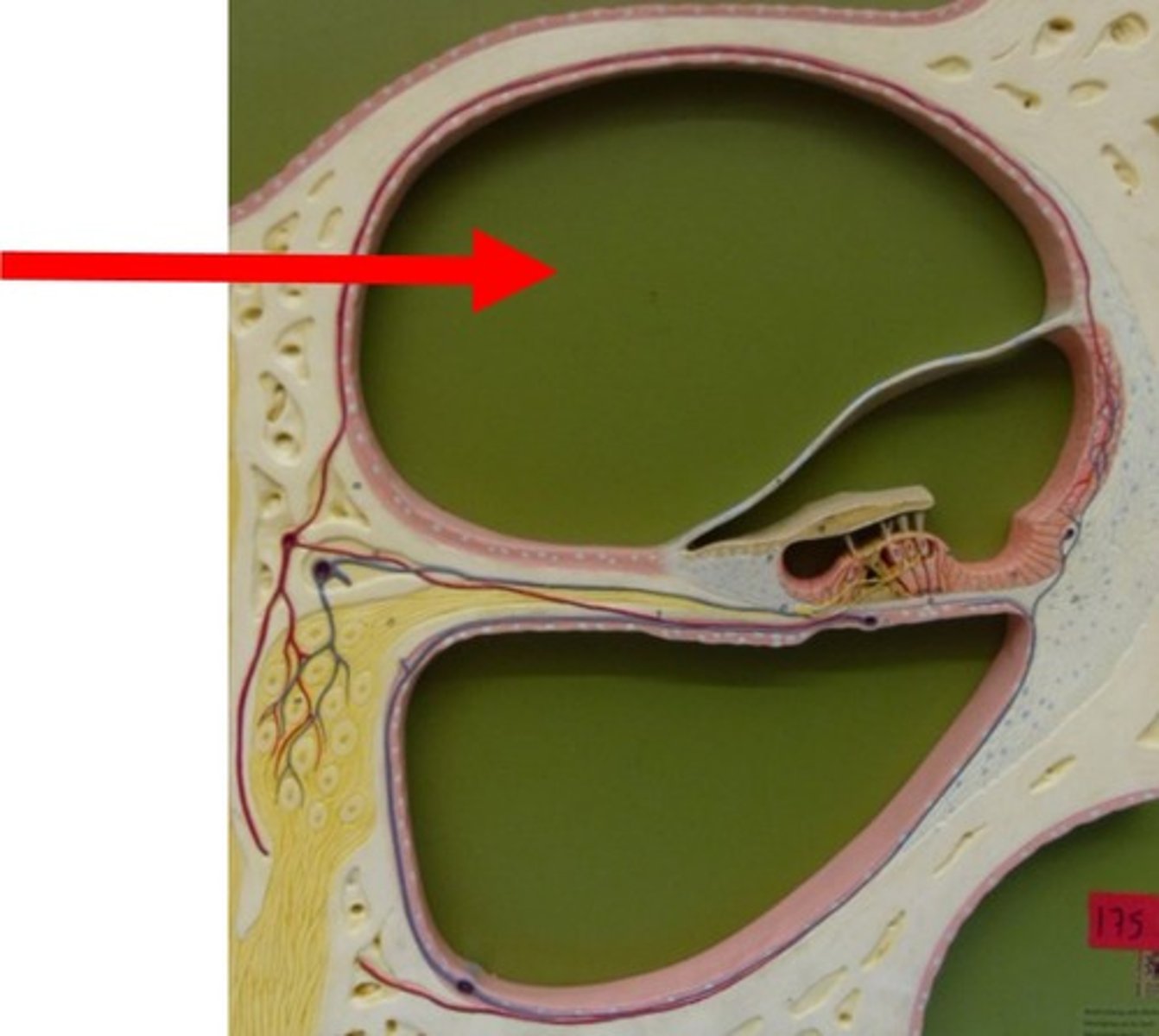
Bony labyrinth
-Passageway in temporal bone
membranous labyrinth
-Fleshy tubes lining bony labyrinth
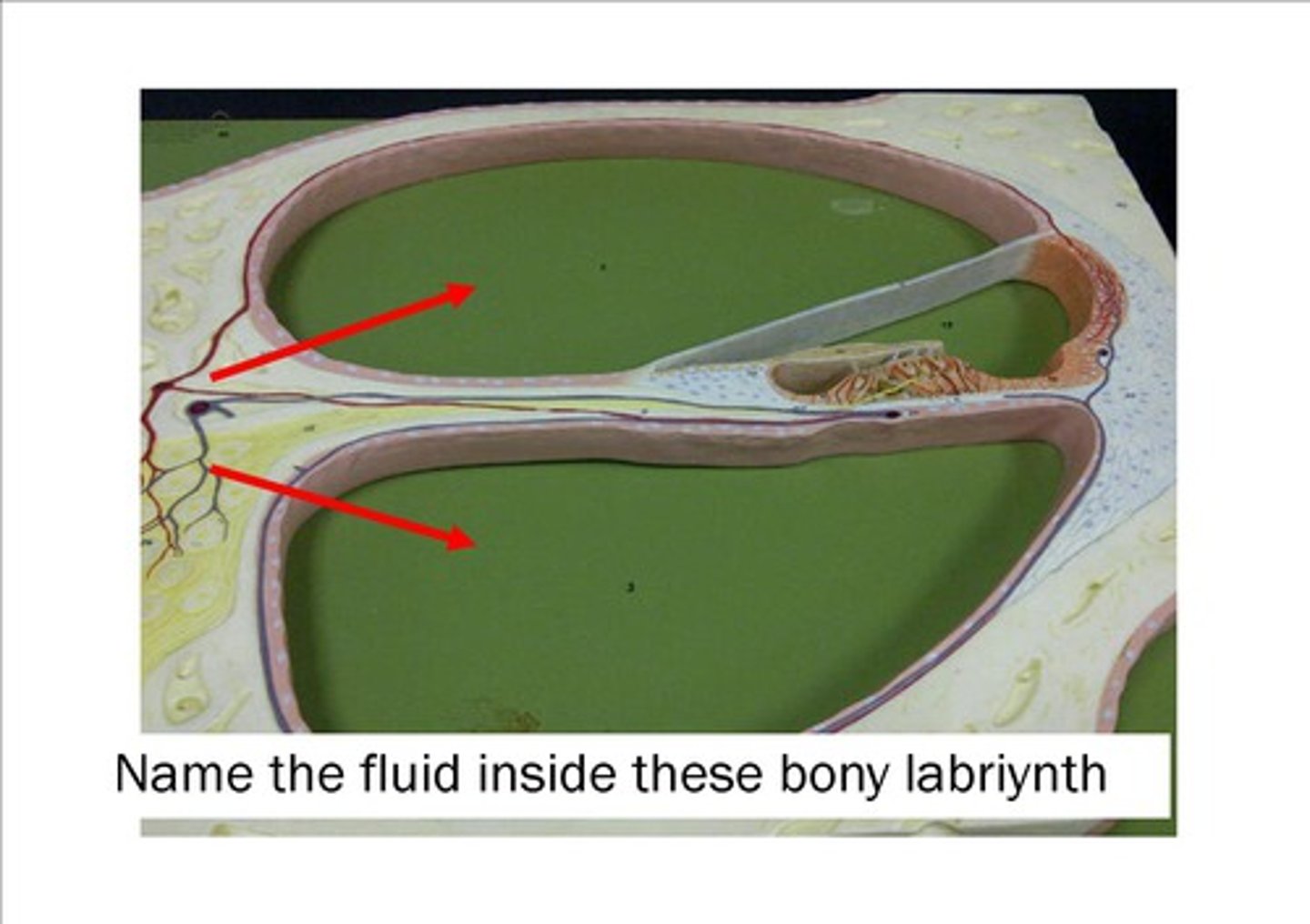
-Filled with endolymph
-Floating in perilymph

Endolymph
-Similar to intracellular fluid
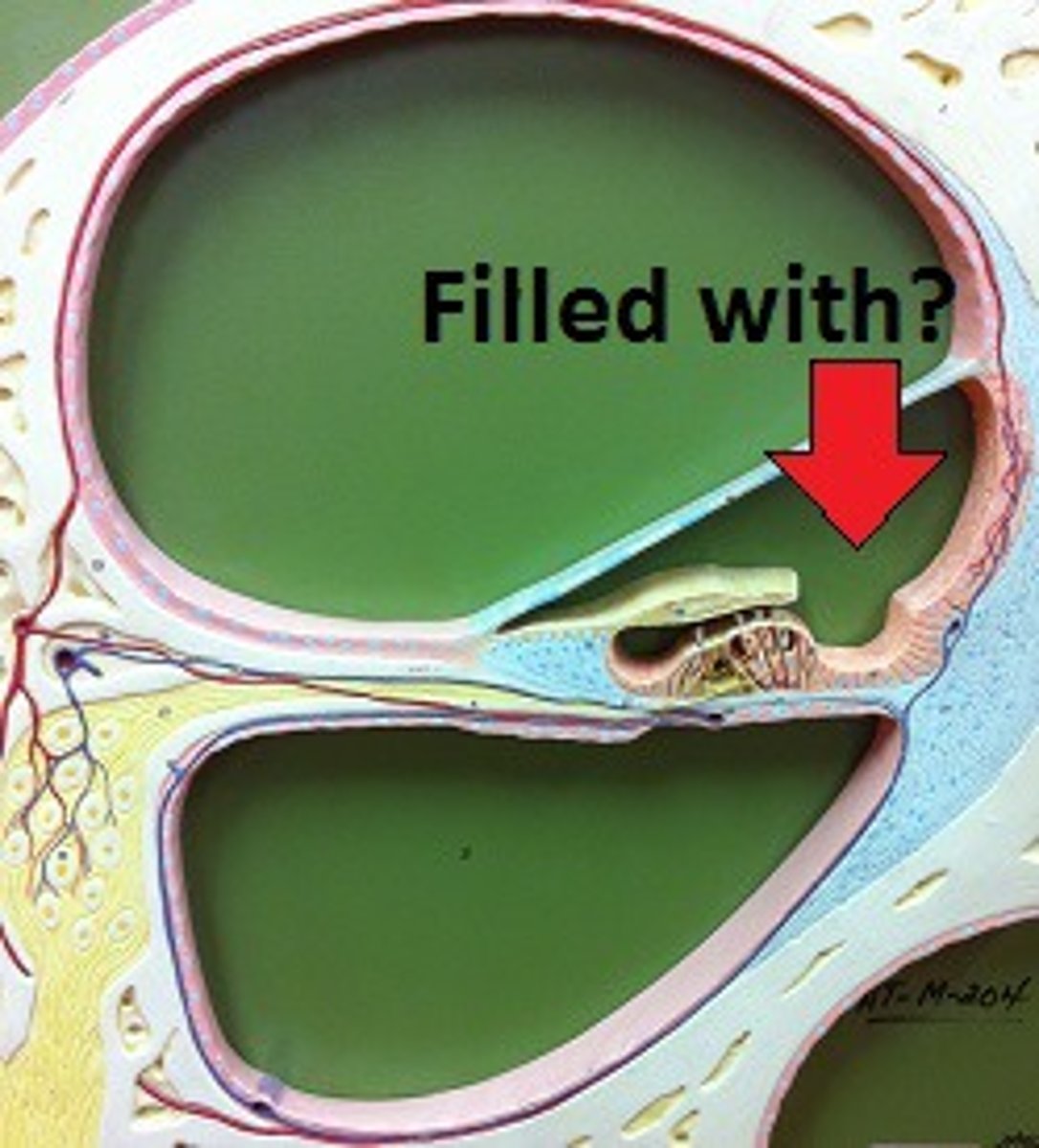
Perilymph
-Similar to cerebrospinal fluid,
Labrynth
-Vestibule and three semicircular ducts
Cochlea
-Organ of hearing
-Winds 2.5 coils around screw-like axis of spongy bone, the modiolus
-Threads of the screw form a spiral platform that supports the fleshy tube of the cochlea
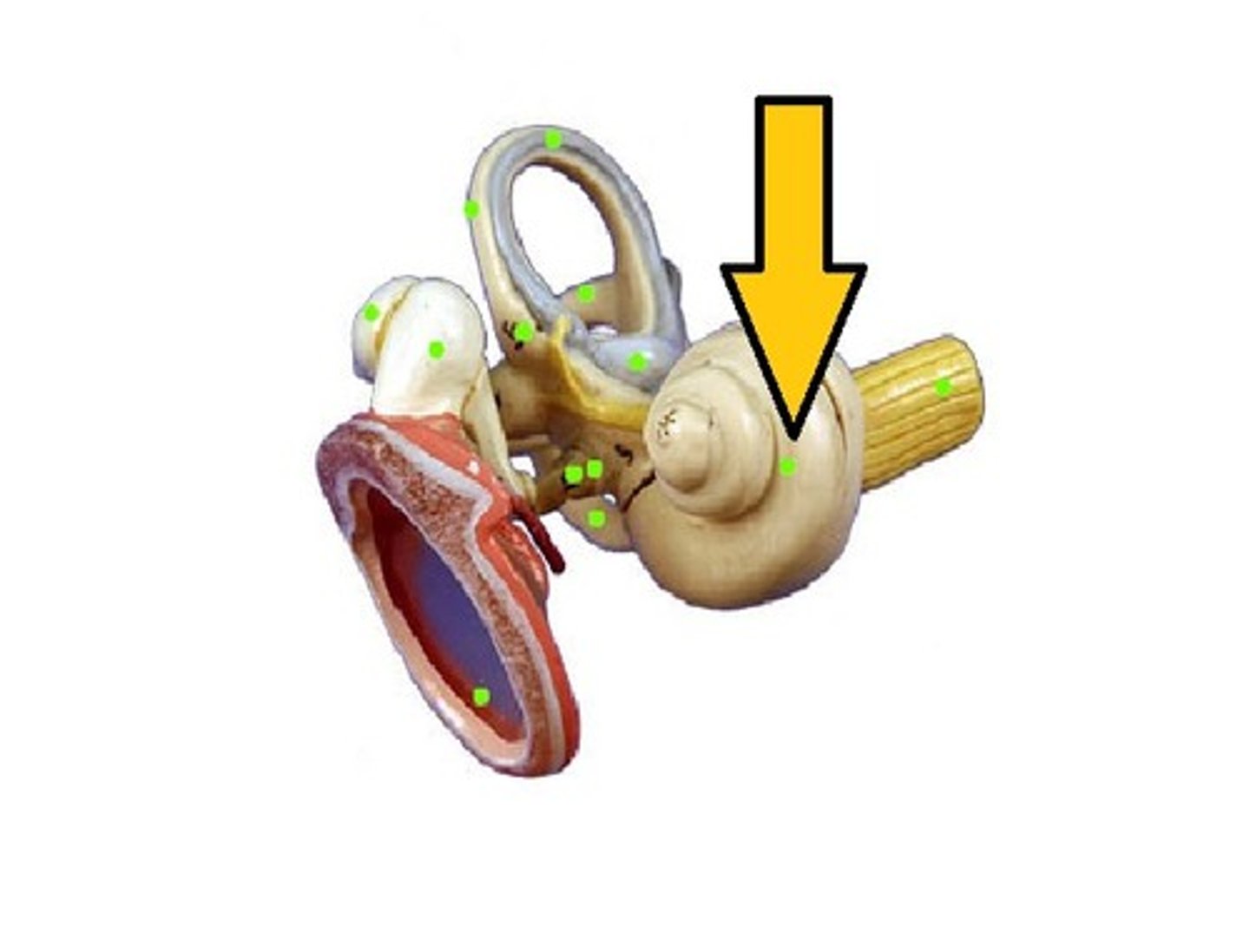
Cochlear chambers
-Scala vestibuli
-Scala tympani
-Scala media
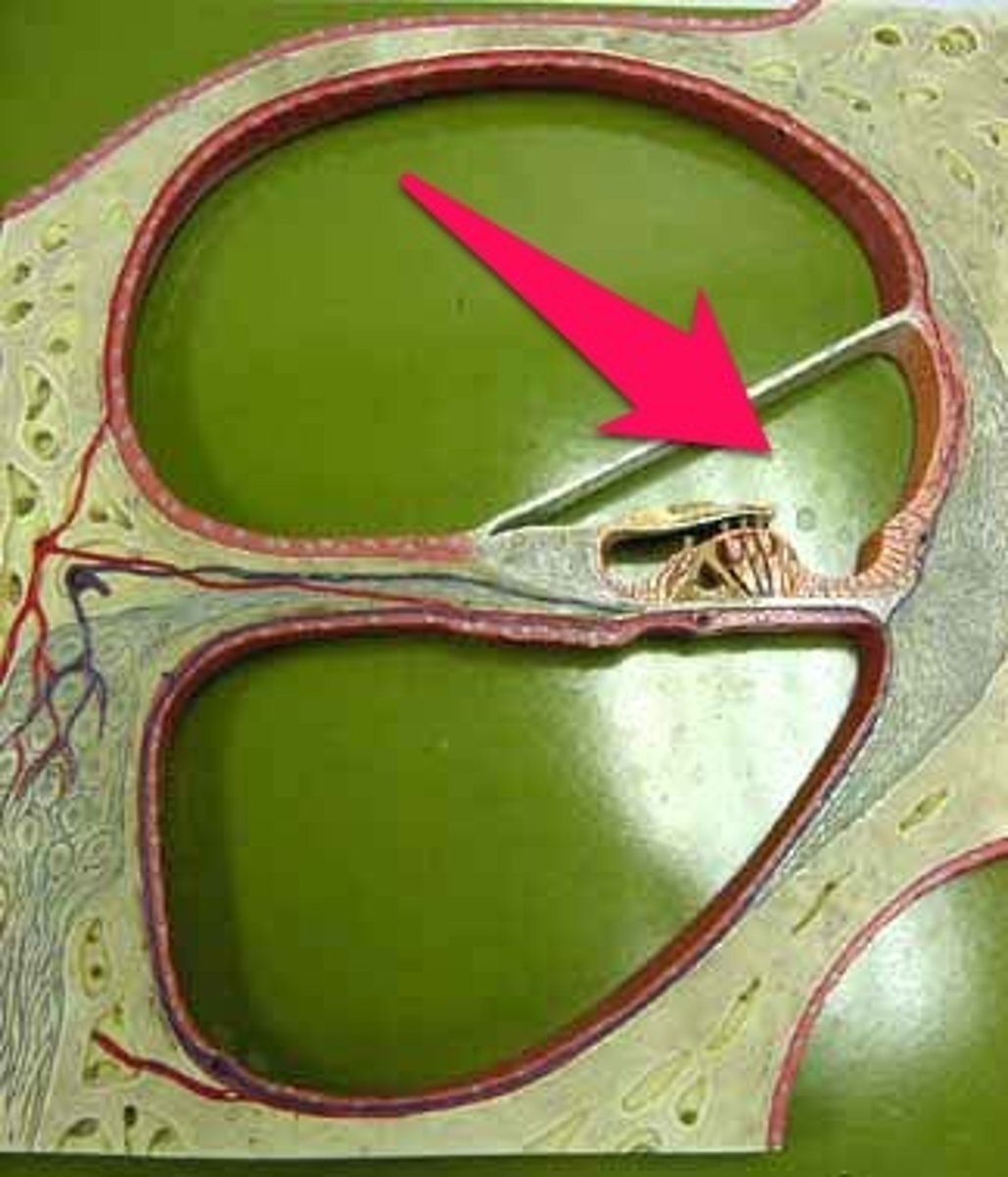
Scala vestibuli
-Superior chamber
-Filled with perilymph
-begins at oval window and spirals to apex
Scala tympani
-Inferior chamber
-Filled with perilymph
-Begins at apex and ends at round window
-Secondary tympanic membrane: covers round window
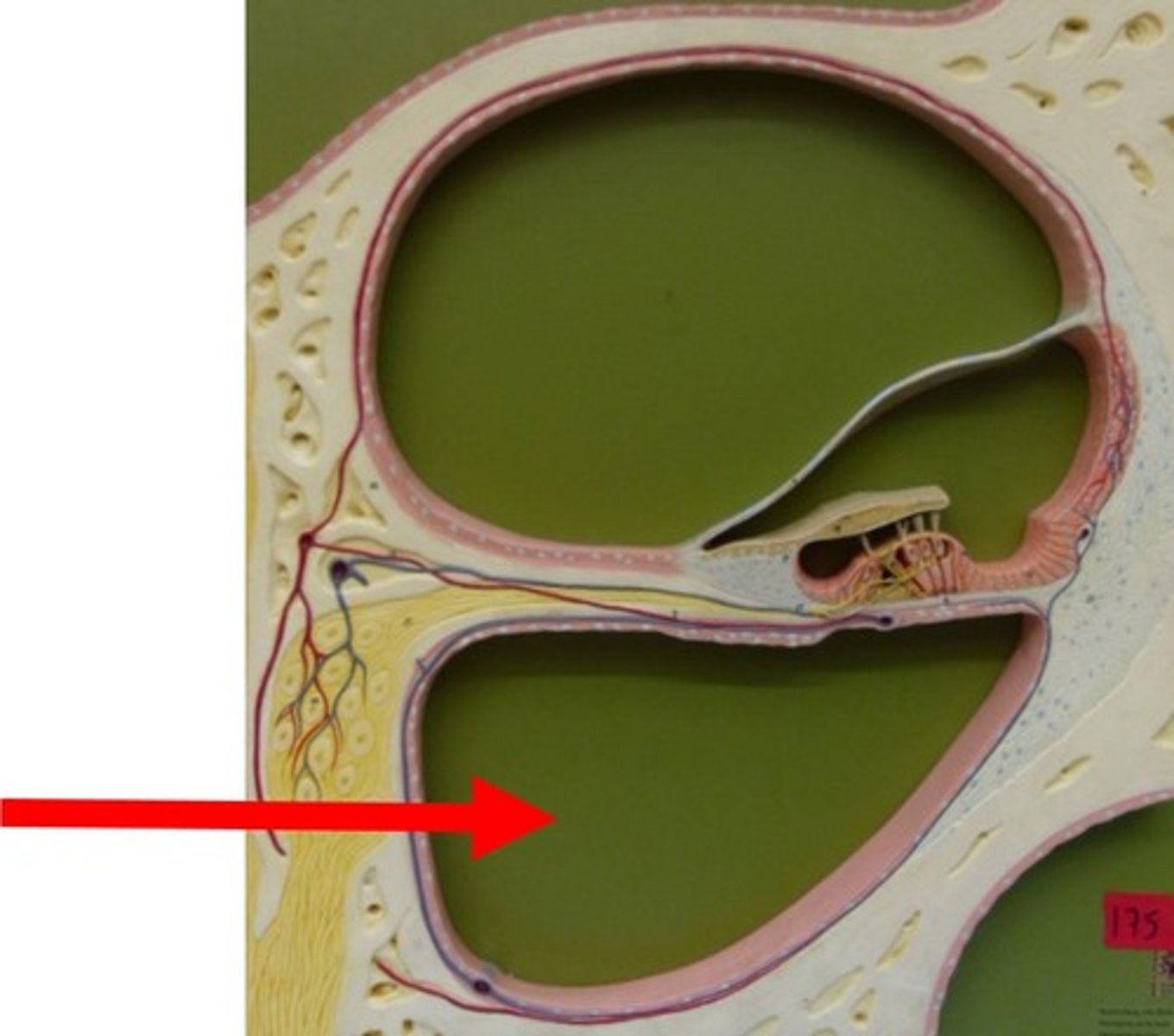
Scala media
-Cochlear duct
-Middle chamber
-Filled with endolymph
-Contains spiral organ
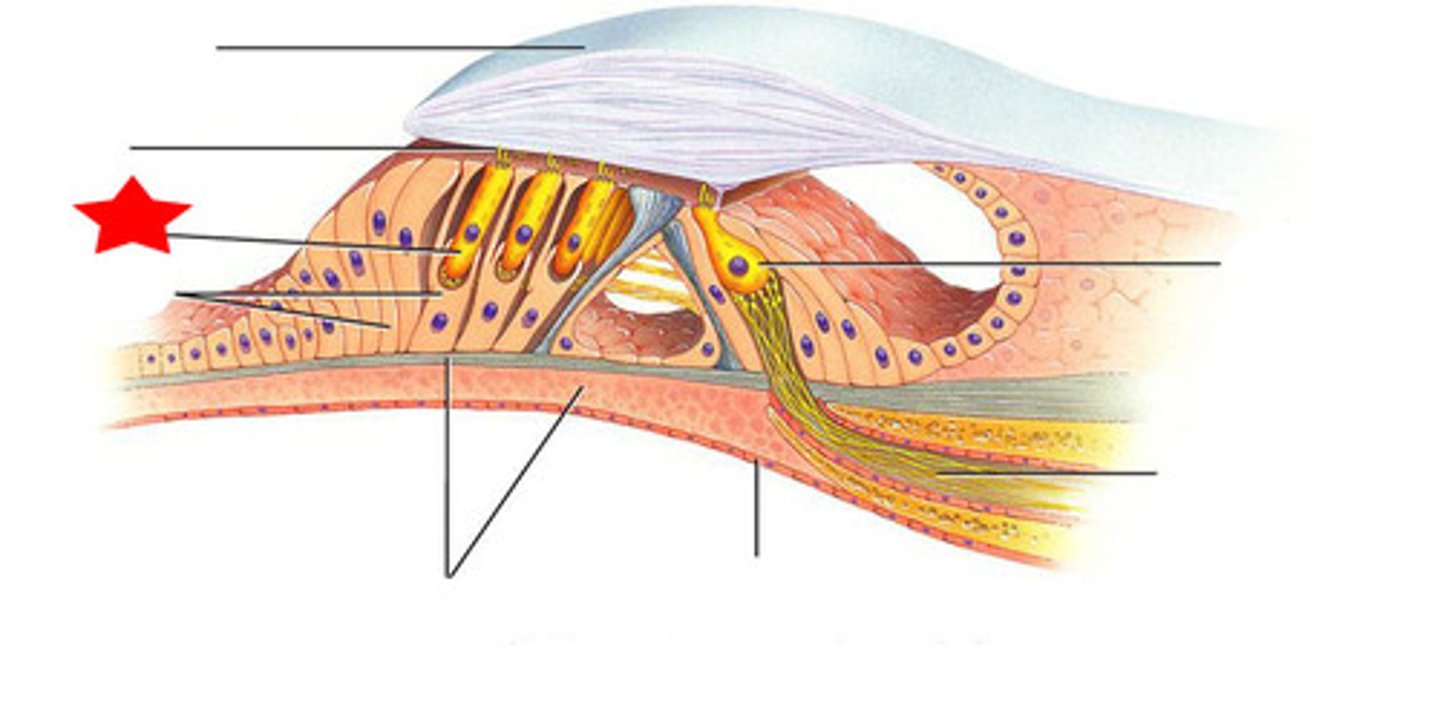
Spiral organ
-Organ of Corti
-Acoustic organ that converts vibrations into nerve impulses
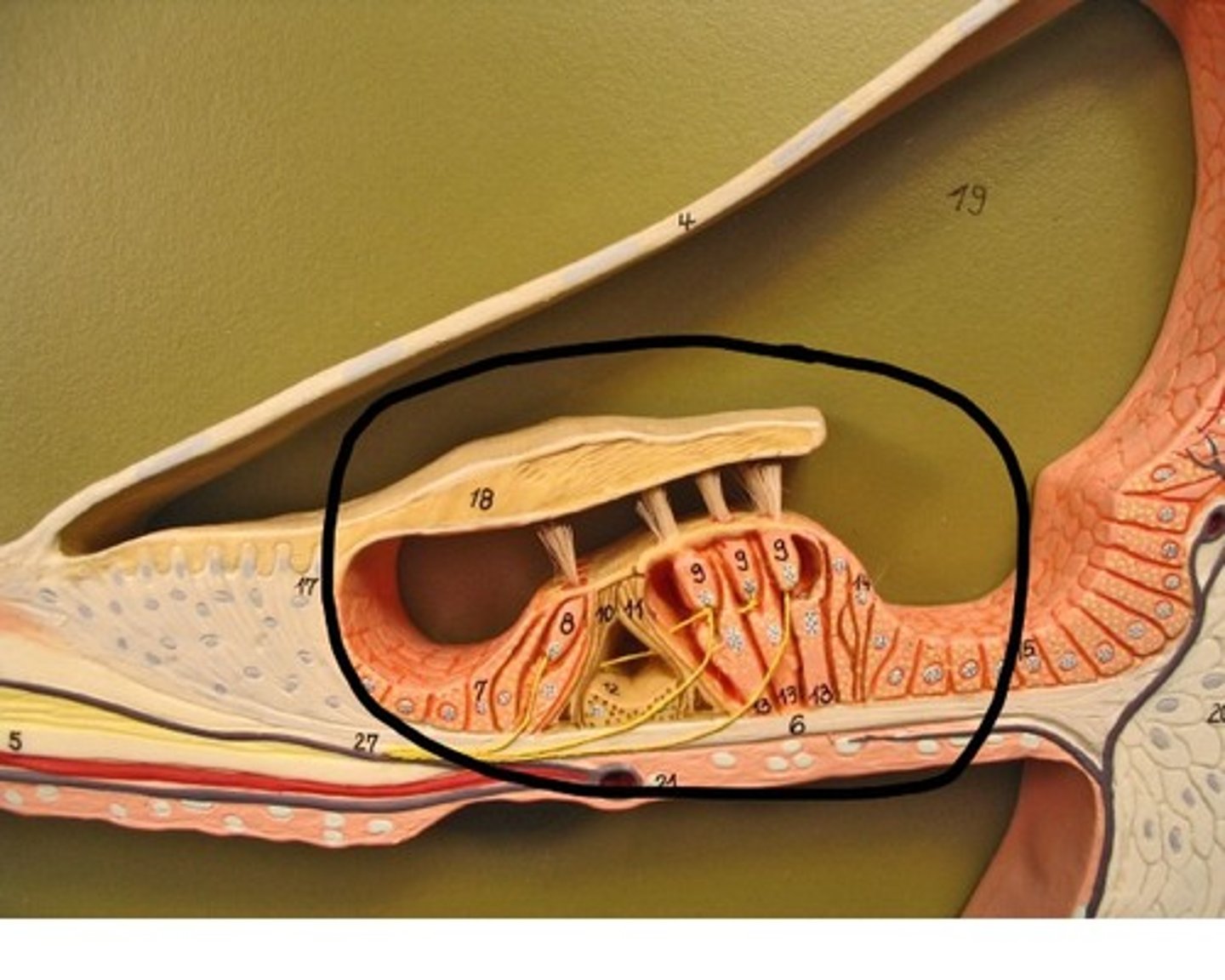
Spiral organ components
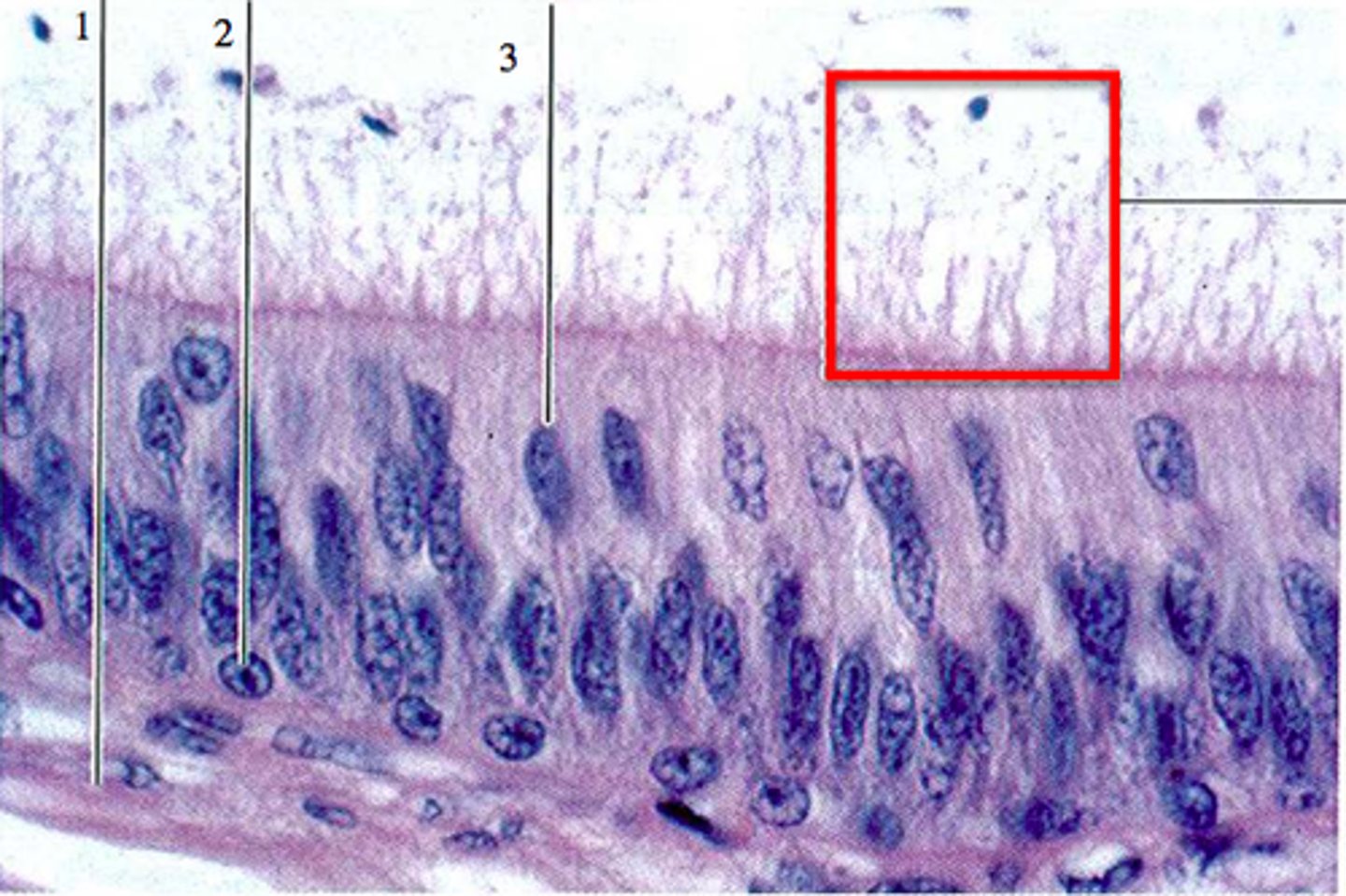
-Has epithelium composed of hair cells and supporting cells
-Hair cells have long, stiff microvilli called stereocilia on apical surface
four rows of hair cells spiraling along its length
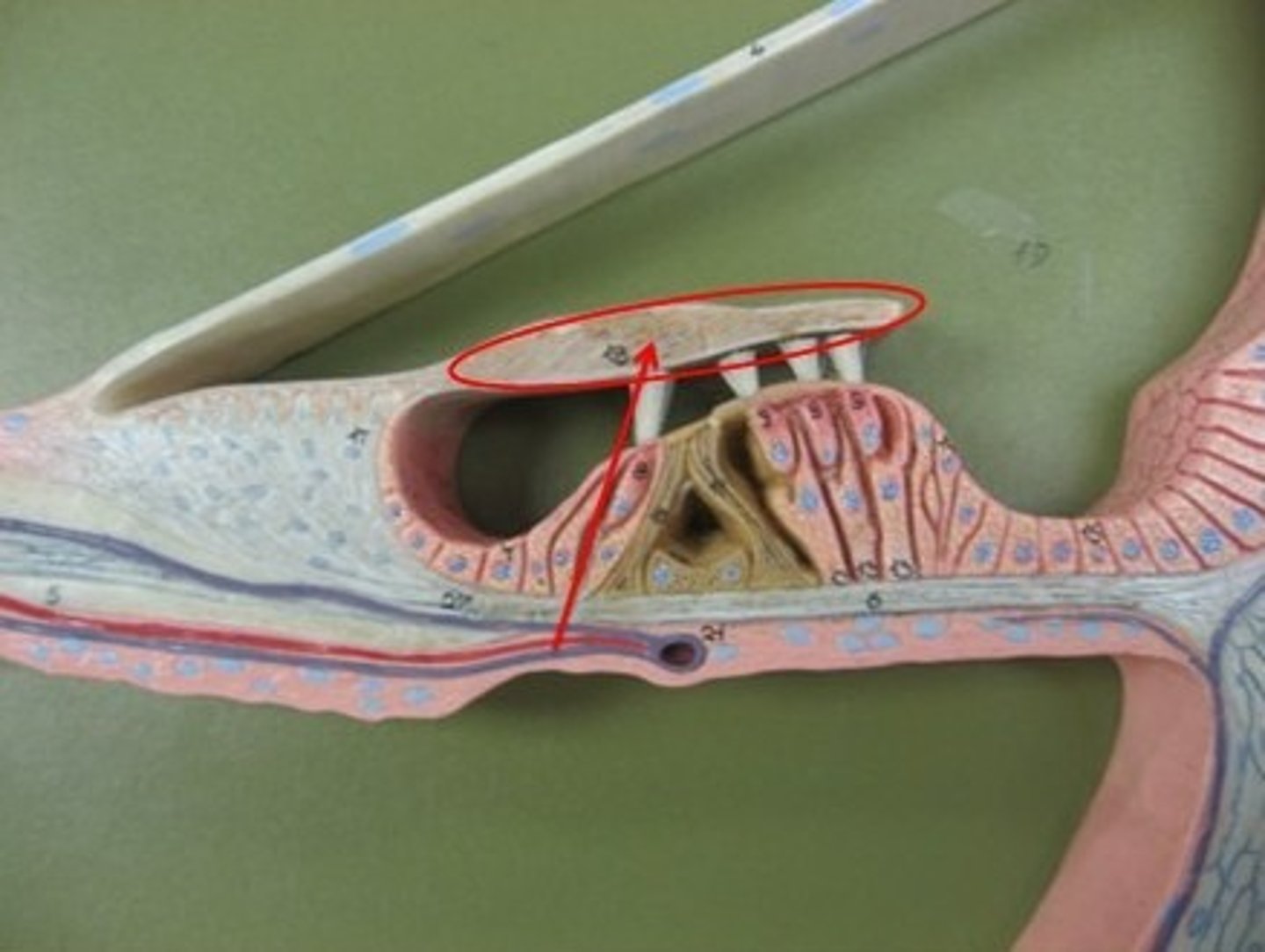
Tectorial membrane
-Gelatinous membrane that rests on top of stereocilia
Inner hair cells
-Single row of about 3500 cells
-Provides hearing protection
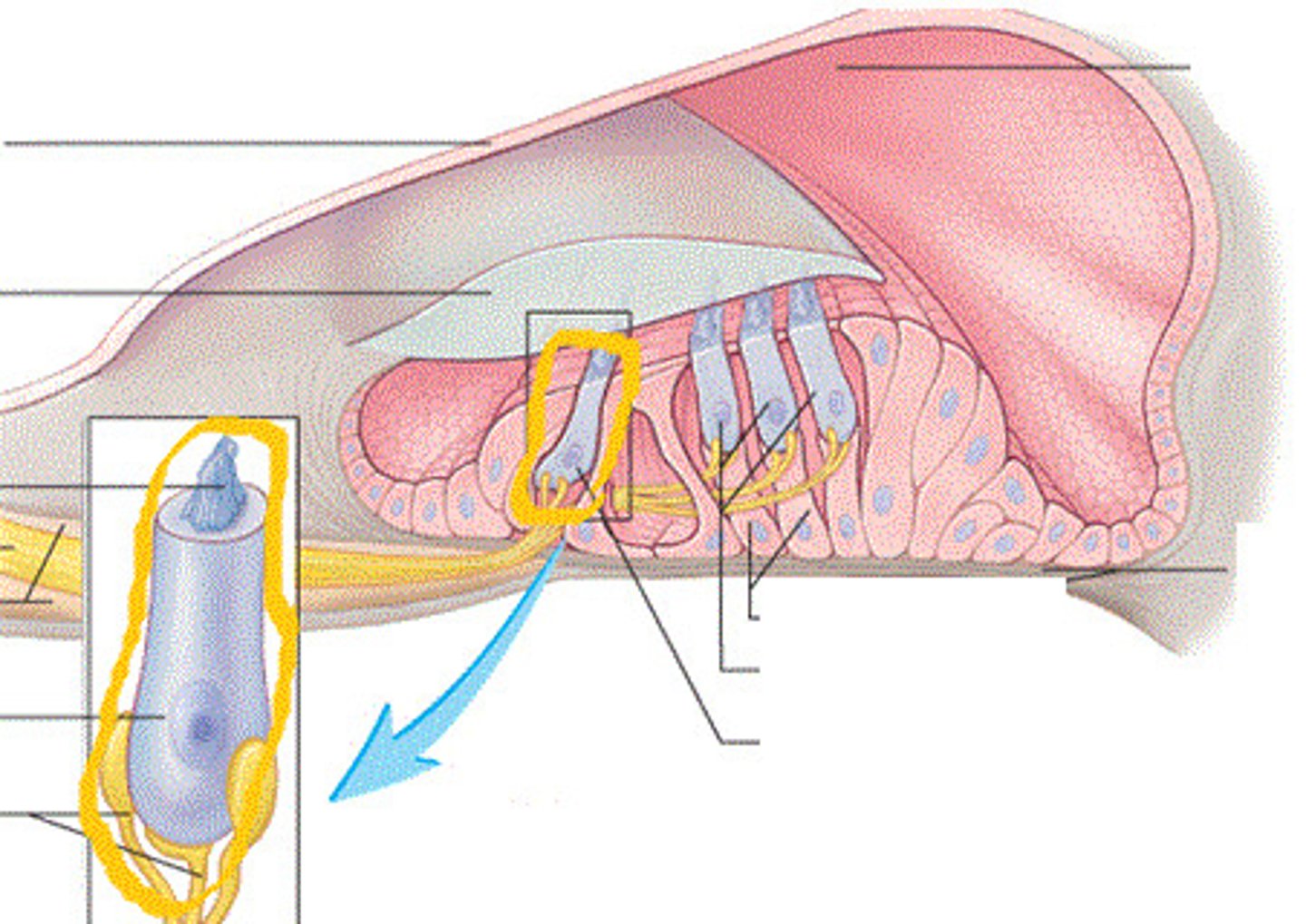
Outer hair cells
-Three rows of about 20000 cells
-Adjusts response of cochlea to different frequencies
-Increases precision
Tympanic membrane
-Has 18 times area of oval window
-Ossicles concentrate the energy of the vibrating tympanic membrane on an area 1/18th that size
-Ossicles create a greater force per unit area at the oval window and overcome the inertia of the perilymph
Protective function
-Ossicles and their muscles
-Lessen the transfer of energy to the inner ear
cochlear hair stimulation
-Vibration of ossicles causes vibration of basilar membrane under hair cells
Basilar membrane vibration
-as often as 20000/sec
-hair cells move with membrane
Sterocilia
- of outer hair cells
-Bathed in high K+ fluid - endolymph
-Creating electrochemical gradient
-Tip embedded in tectorial membrane
Stereocilia gradient
-Outside of cell is +80mV and inside of cell is near -40mV
Stereocilium
-Inner hair cells
-Single transmembrane protein at tip function as mechanically gated ion channel
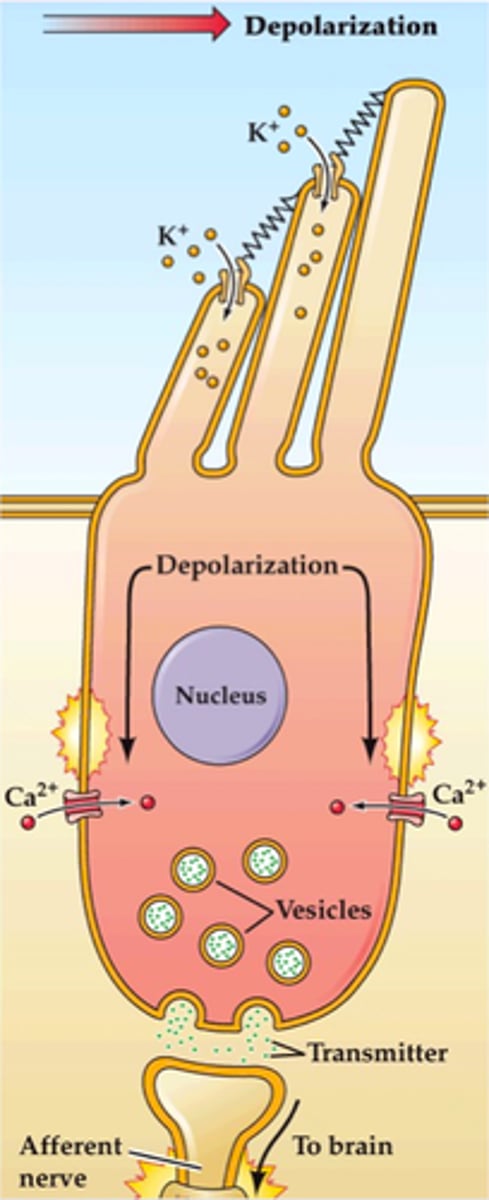
Inner stereocilium function
1. Stretchy protein filament (tip link) connects ion channel of one stereocilium to the sidewall of the next
2. Talles stereocilium is bent when basilar membrane rises up toward tectorial membrane
3. Pulls on tip links and open ion channels
4. K+ flows in depolarization causes release of neurotransmitter
5. Stimulates sensory dendrites and generates AP in the cochlear nerve
Sensory coding
-Variations in loudness (amplitude) cause variations in the intensity of cochlear vibrations
Soft sound
-Produces relatively slight up-and-down motion of the basilar membrane
Louder sounds
-Make the basilar membrane vibrate more vigorously
-Triggers higher frequency of AP
-Brain interprets this as louder sound
Pitch variation
-depends on basilar membrane vibrations
Pitch - basal end
-Membrane attached, narrow and stiff
-Brain interprets signals as high-pitched
Pitch - distal end
-5 times wider and more flexible
-Brain interprets signals as low-pitched
Deafness
-Hearing loss
Conductive deafness
-Conditions interfere with transmission of vibrations to inner ear
-Damage to tympanic membrane, oritis media, blockage of auditory canal, and otosclerosis
Otosclerosis
-Fussion of auditory ossicles that prevents their free vibration
Sensorineural deafness
-Nerve
-Death of hair cells or any nervous system elements concerned with hearing
-Factory workers, musicians, construction workers
Vestibular apperatus
-Constitutes receptors for equilibrium
-three semicircular ducts
-two chambers
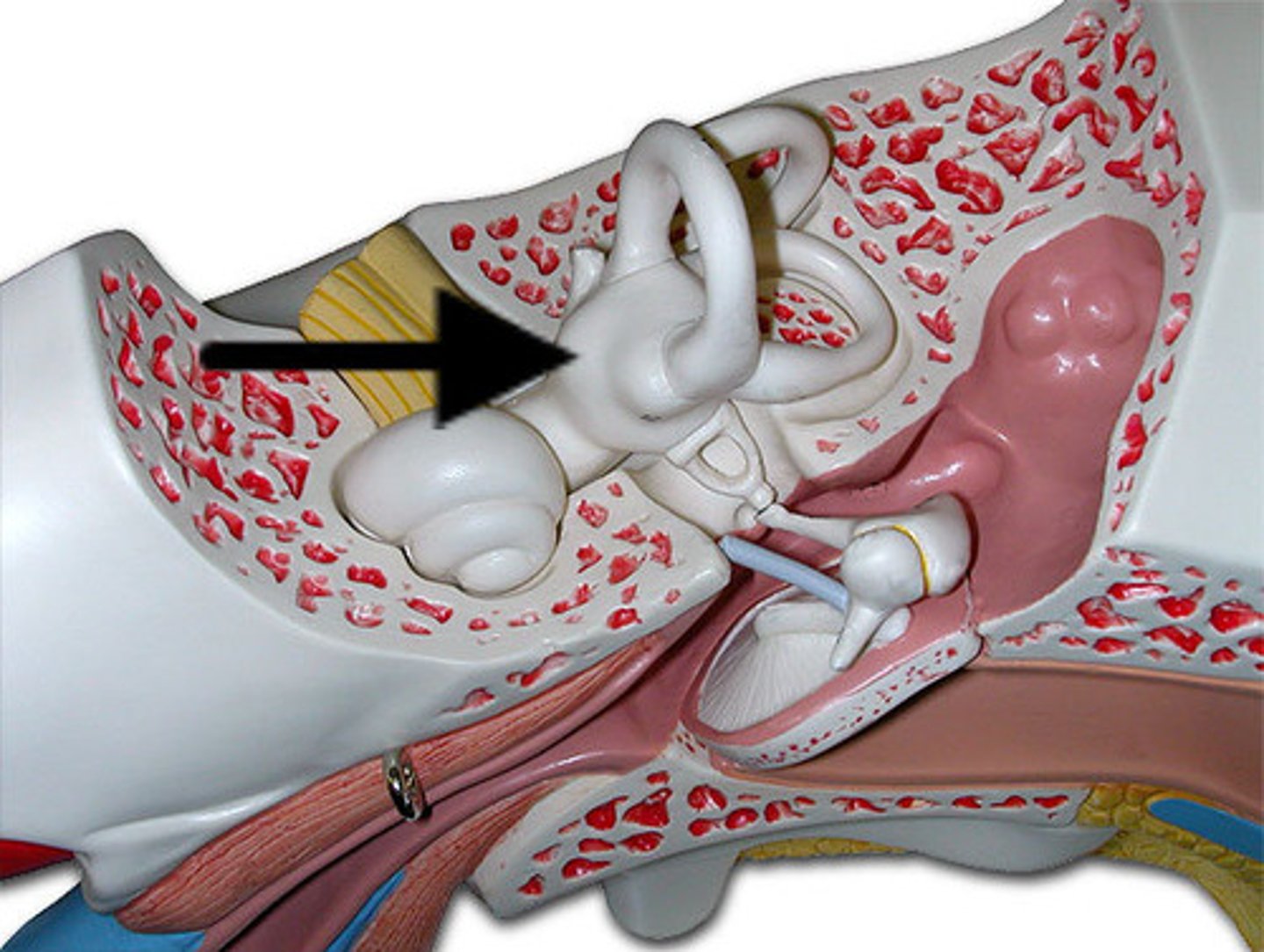
Three semicircular ducts
-Detect only angular acceleration/ rotary movements (dynamic equilibrium)
-Each duct filled with endolymph and opens up as a dilated sac (ampulla) next to the utricle
semicircular canals
-Body canals of temporal bone hold membranous semicircular ducts
Two chambers
-Anterior saccule and posterior utricle
-Responsible for static equilibrium and linear acceleration
Static equilibrium
-The perception of the orientation of the head when body is stationary
-When head is tilted, heavy otolithic membrane sags, bending stereocilia and stimulating hair cells
Dynamic equilibrium
-Perception of motion or acceleration
-Linear/angular acceleration
-Linear acceleration detected as otoliths lag behind, bending the stereocilia and stimulating the hair cells
Linear acceleration
-Change in velocity in a straight line (elevator)
Angular acceleration
-Change in rate of rotation (car turns a corner)
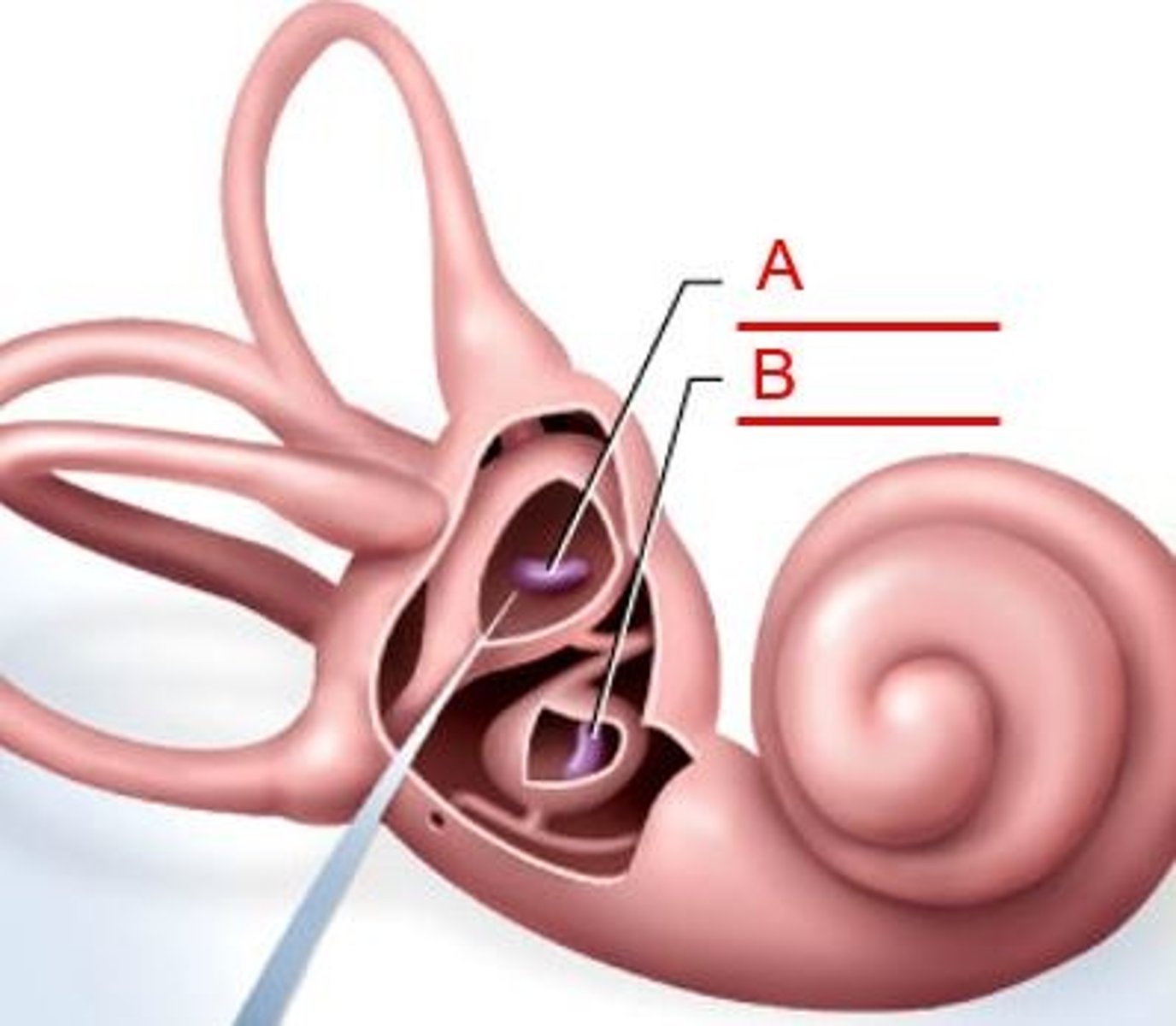
Macula
-a 2-3 mm patch of hair cells and supporting cells in the saccule and utricle
-Macula sacculi
-Macula utriculi
Macula sacculi
-Lies vertically on wall of sacculi
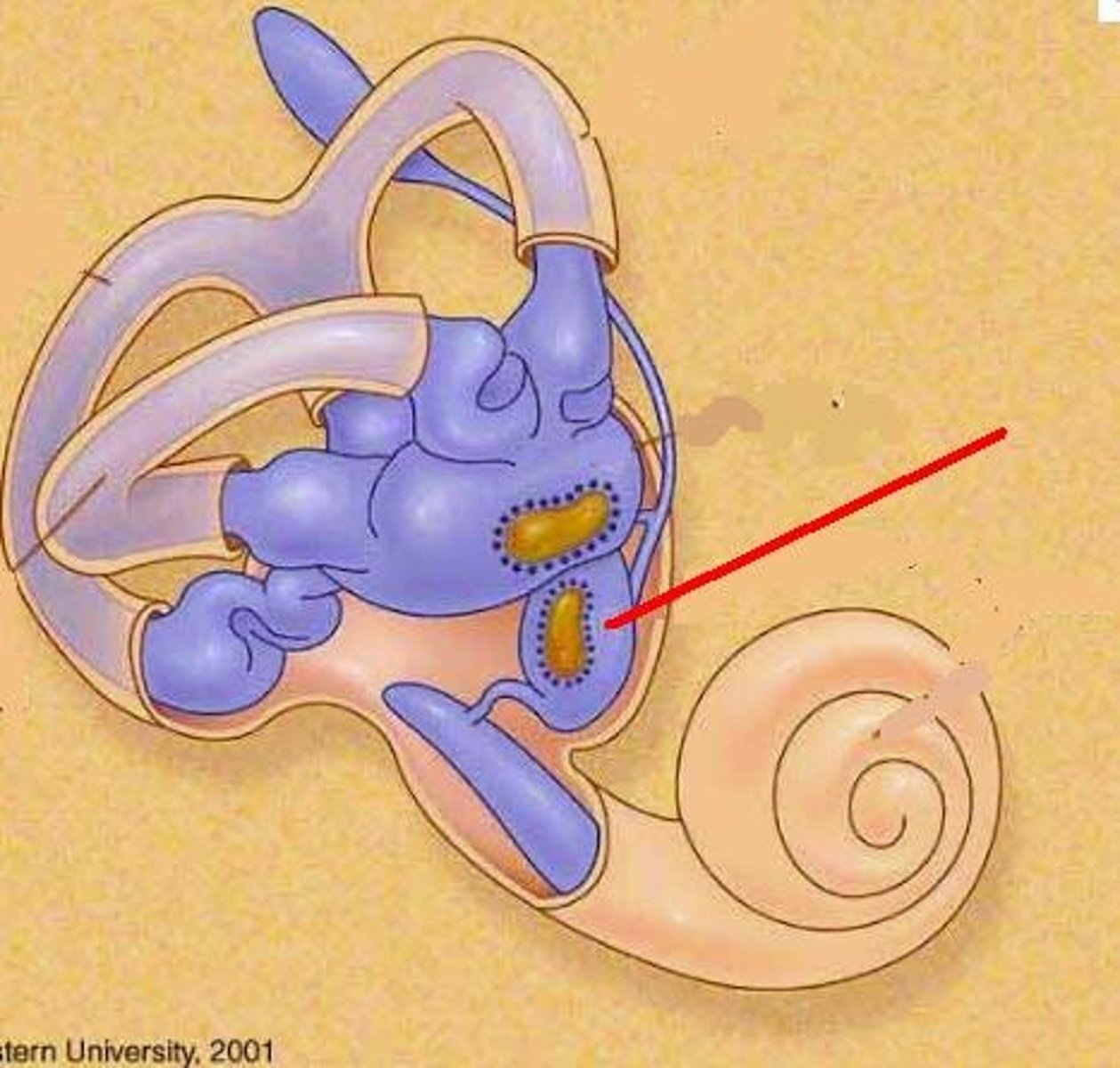
Macula utriculi
-Lies horizontally on floor of utricle
Macula hair cells
-Each hair cell has 40-70 stereocilia and one true cilium
-Kinocilium embedded in a gelatinous otolithic membrane
Kinocilium
-Filamentous structure that's found on hair cells in the inner ear
Otoliths
-Calcium carbonate-protein granules that add to the weight and inertia and enhance the sense of gravity and motion
Ampulla
-endolymph filled sac on each duct next to utricle
-Each sac contains crista ampullaris
Crista ampullaris
-Consists of hair cells with stereocilia and kinocilium buried in a mound of gelatinous membrane called cupula
-special orientation of canals cause ducts to be stimulated by rotation in different planes (XYZ)
Vision
-sight
-Perception of objects in the environment by means of light they emit or reflect
Light
-Visible electromagnetic radiation
Human vision
-limited to wavelengths of light from 400-700 nm (visible light)
_light must cause a photochemical reaction to produce a nerve signal
Ultraviolet radiation
-<400; has too much energy and destroys macromolecules
Infrared radiation
->700 nm; too little energy to cause photochemical reaction, but does warm the tissue
Optical components
-Transparent elements that admit light, refract light rays, and focus images on retina: Cornea, aqueous Humer, lens, vitreous body
Cornea
-Transparent anterior cover
Aqueous humer
-Serous fluid secreted by ciliary body into posterior chamber - posterior to cornea, anterior to lens
-Reabsorbed by sclera venous sinus at same rate it is secreted
Lens
-Lens fibers
-changes shape to help focus light
=rounded with no tension or flattened with pull of suspensory ligaments
Lens fibers
-Flattened, tightly compressed, transparent cells that form lens
Suspensory ligaments
-suspend lens
-from ciliary body
Vitreous body
-humer
-Fills vitreous chamber (posterior segment)
posterior segment
-Jelly filled space between lens and retina
Retina
-Attached to eye only at optic disc and ora serrate
-Pressed against rear of eyeball by vitreous Humer
-contains Blood vessels
-Converts light energy into AP
Detached retina
-Causes blurry areas of vision and can lead to blindness
Macula lutea
-Patch of cells on visual axis of eye
Fovea centralis
-Pit in center of macula lutea
-Contains only 4000 tiny cone cells
-No neuronal convergence (1 cone -> 1 ganglion)
Optic disc
-Blind spot
-Optic nerve exits retina and there are no receptors there
Blind spot
-Close right eye, stare at x and red dot disappears
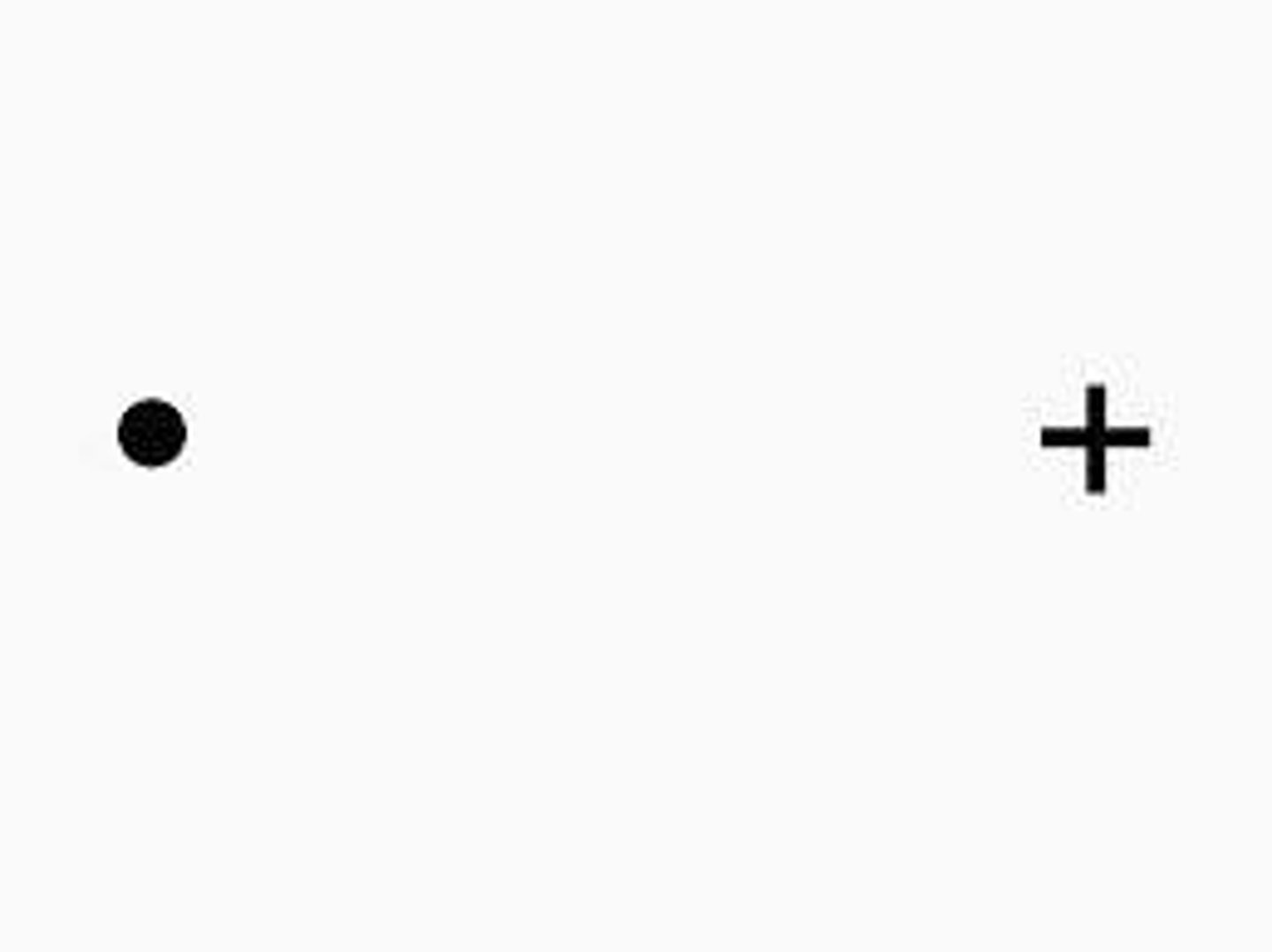
Vision filling
-Brain fills in bar across blind spot area
-Brain ignores unavailable information until saccades (fast eye movement) redirect gaze
Formation of image
-Light passes through lens to form tiny, inverted image on retina
-Iris diameter controlled by two sets of contractile elements
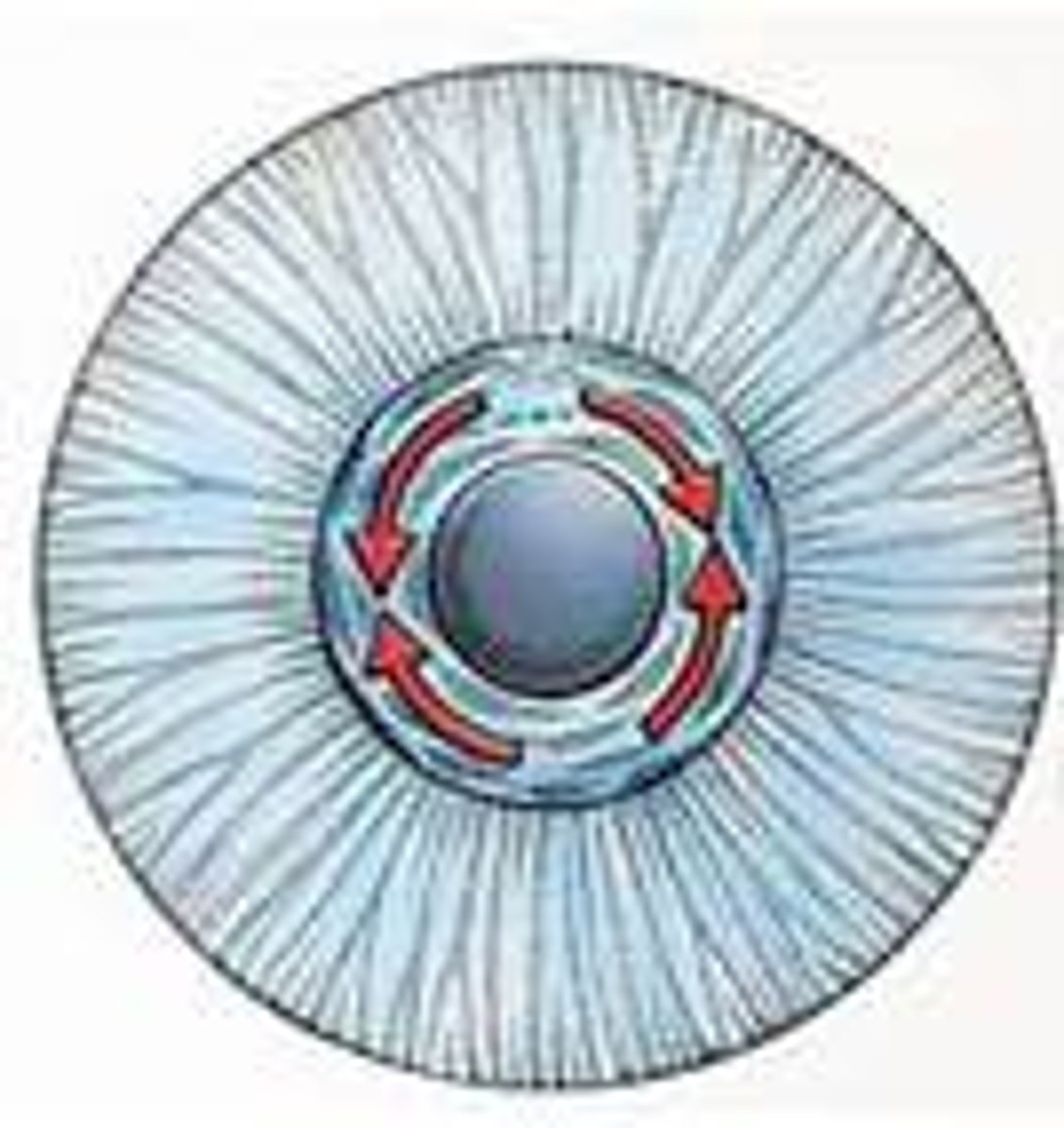
Pupillary constrictor
-Smooth muscle encircling pupil
-Parasympathetic stimulation narrow pupil
-When light levels are high/ when switching between far and near focus
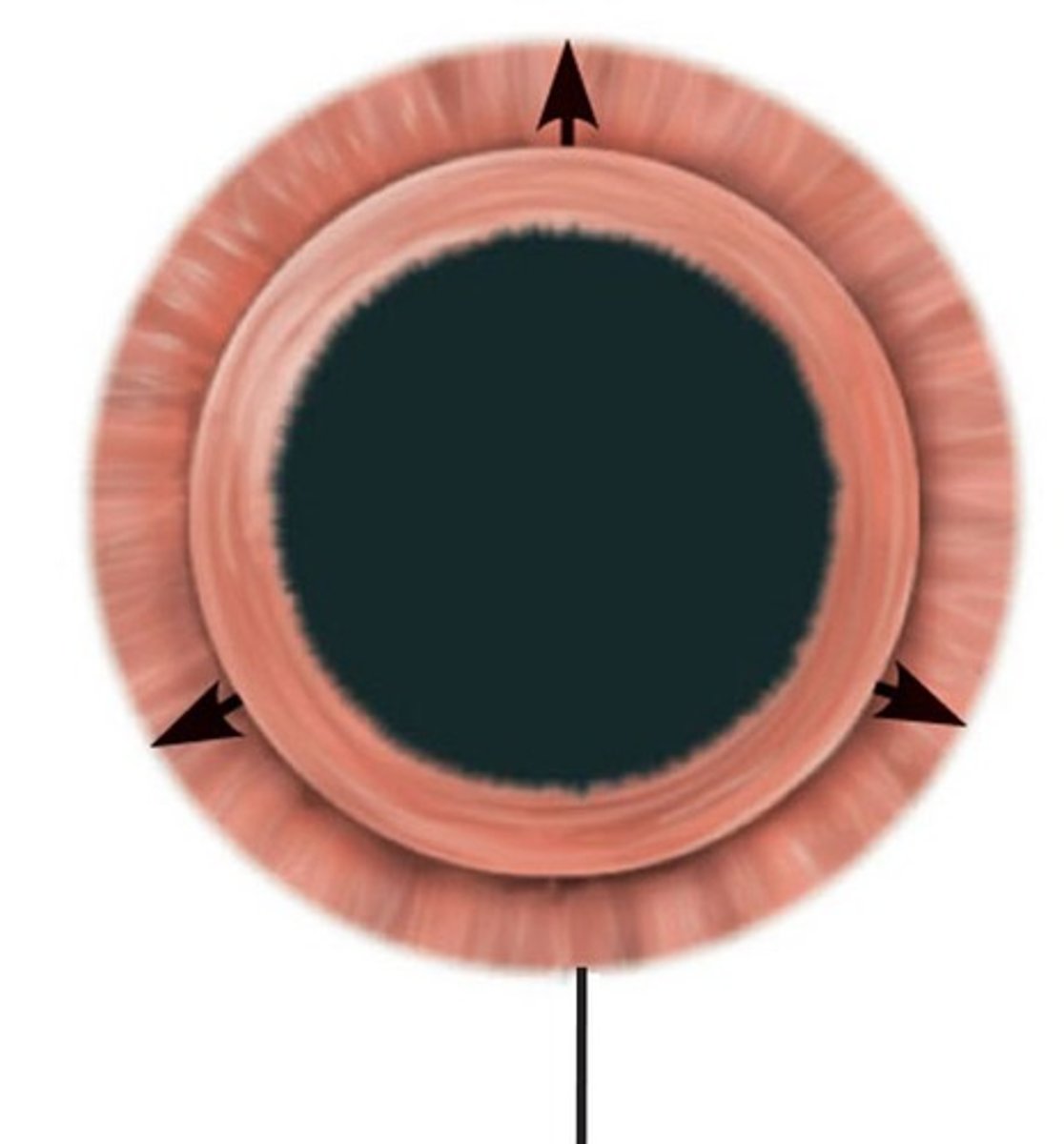
Pupillary dilator
-Spoke-like myoepithelial cells
-Sympathetic stimulation widens pupil
-Occurs in dark light conditions/ when shifts between distant and nearby objects
Photopupillary reflex
-Pupillary constriction in response to light
-Autonomic reflex arc
=light signaled to pretectal region of midbrain
=Excites parasympathetic fibers in oculomotor nerve that travels to ciliary ganglion in orbit
=Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers stimulate pupillary constrictor
Refraction
-The bending of light rays
Speed of light
-300000 km/s in vacuum
-Slower in air, water, glass, or other media
Refractive index
-a measure of how much it retards light rays relative to air