RMIN 5100S - Markets and Career Paths
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Insurance Industry Basics
Insured (Risk Manager) → Intermediary (Agent or Broker) → Insurer (Underwriter)
Insured
The buyer of insurance
Intermediary
Facilitates the purchase of insurance.
Advises Insured
Negotiates with Insurer
Insurer
Provides insurance coverage aka the insurance company
Risk Manager
*NOT Just an Insurance Buyer
Must evaluate risks and determine the best approach to manage risks including Loss Control, Retention and Transfer techniques.
Large companies will have a Risk Manager. Smaller to Mid-sized companies will have someone who serves in this role.
Risk Management Process
Identify
Measure and Analyze
Select a Technique/Combination
Avoid
Retain
Transfer
Insurance
Other Contractual
Control
Implement and Monitor
Agents
An agent is someone who legally represents the principal and has the authority to act on the principal's behalf
The principal is responsible for all acts of an agent when the agent is acting within the scope of authority
Typically has the authority to bind coverage.
Agents - 2 Types
Independent and Exclusive/Captive
Independent Agents
Agent works with a variety of insurance companies
The agent has contracts with several to many insurance companies.
Advantage is that the Agent may find the coverage that is best suited for the client. Not limited to one carrier.
More frequently used in Commercial P&C.
Exclusive/Captive
Agent works with only one insurance company. Cannot sell products from other insurance companies
More frequently used in personal lines and very small businesses.
Insurance companies provide resources and training to agents because Agents only sell products for this Insurance Company/Principal.

Brokers and Independent Agents
Agents are employed at Agencies.
Brokers are employed at Brokerage Firms / Houses
Only one of these intermediaries would be involved in a typical transaction.
Function in a very similar way
Both solicit applications and attempt to place coverage with an appropriate insurer
Both can market to a number of insurance companies.
Both are typically paid on a commission structure (as a % of premium)
Brokers
Legally works on behalf of the insurance buyer
Can work on any size business from personal to Fortune 500.
Typically offers a wider breadth of services including loss control, captive management, loss forecasting, consulting services, etc.
Company is typically paid via commission. However, clients may pay fees and/or commission.
Employees are sometimes compensated via commission and sometimes via salary
Independent Agent
Legally works on behalf of the Insurance company
Can work on any size business from personal to large commercial. Typically does NOTwork on the large international companies.
Typically focus on the insurance transaction and related services.
Producing agents typically paid via commission. Other employees and service team members may be paid via salary.
Underwriters
Underwriting refers to the process of selecting, classifying, and pricing applicants for insurance (sets terms, conditions, pricing)
Job is to accept exposures at appropriate rate
Reject application if underwriting rules do not allow acceptance
Must be a skillful judge of people / industries / product lines (casualty, property, health, etc)
Goal is to produce a group of insureds by categories whose actual experience will approach expected.
A line underwriter makes daily decisions concerning the acceptance or rejection of business
*Breaking a common misconception: Underwriters do NOT reject exposures simply because they expect losses.
Standards to the Underwriting Process
Standards and Guidelines are set by The Chief Underwriting Officer
Underwriting Basics
It’s a balancing act!!
Making Money for the Insurance Company
Keeping Brokers/Agents & Clients Happy…and coming back for more insurance.
Keeping the Balance?
Maintain underwriting standards!
Avoid Pitfalls ….like Adverse Selection!
Why is it difficult to figure out what to charge?
With Insurance, we do not know the cost of the goods until AFTER the product is sold.
Rating and Ratemaking
Ratemaking refers to the pricing of insurance and the calculation of insurance premiums
A rate is the price per unit of insurance
An exposure unit is the unit of measurement used in insurance pricing premium = rate x exposure units
Ex: Office Building – Property Insurance
Exposure Units: Square Footage (10,000)
Rate: Expected Losses + Loading Amount (to account for expenses, overhead, taxes, & profit; $0.20/Square Foot)
Premiums = 10,000 x $0.20 = $2,000
Actuaries…Rating and Ratemaking
Total premiums charged must be adequate for paying all claims and expenses during the policy period
For this, we turn to…the ACTUARIES
Claim Adjuster
Paying Claims is the product. Promise to pay in the event of a loss.
What are the objectives of the Claims Settlement Process?
Verification of a covered loss. Is it covered? Did it happen?
Fair and prompt payment of claims
Personal assistance to the insured
Admitted Markets
Admitted Insurance Companies (aka: Standard): Regulated by the state. They often must subscribe to rating and form regulations of that state.
Advantage: If an admitted company goes bankrupt and cannot pay claims, the state will step in and pay a portion out of the Guarantee Fund.
Disadvantage: Since rate and form regulated by state, insurance companies may not have flexibility to amend rates and/or provide coverages required by the client. Therefore, coverage could be inadequate or the insurer may have to declient to quote
Non-admitted Markets
Non-Admitted Companies (aka: Excess & Surplus (E&S), Surplus Lines, Wholesale) ARE Legal companies, but they are not “admitted” in the state in which they are doing business.
Advantage: Often said to have “freedom of rate & form” which means that they have more flexibility in underwriting unique or complex risks. (aka: Excess & Surplus (E&S), Surplus Lines, Wholesale)
Disadvantages: Clients may have to pay E&S tax on premium to the state. If insurer goes bankrupt, there is no money for client in Guarantee Fund.
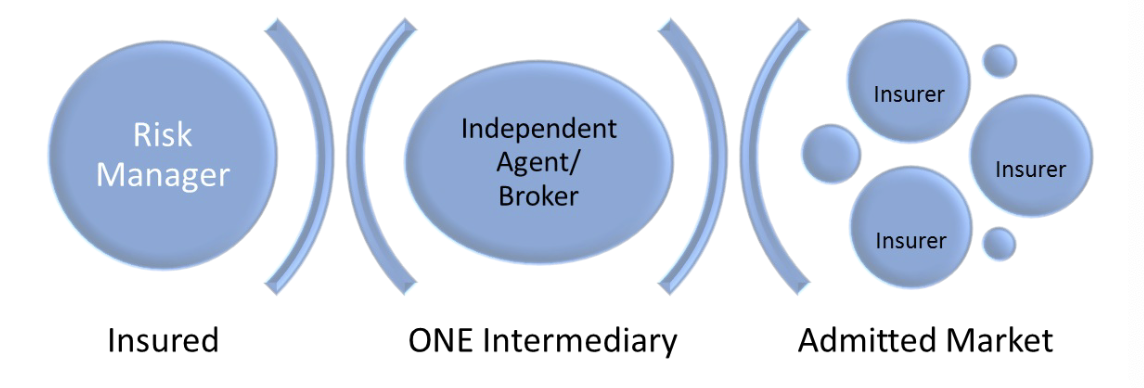
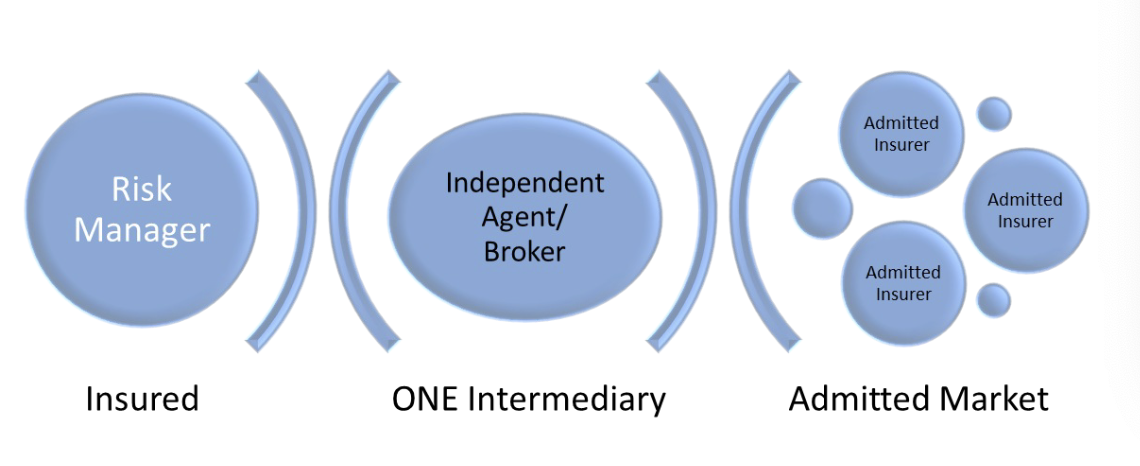
Accessing the Admitted Market
Insured → ONE Intermediary (Agent or Broker) → Admitted Market
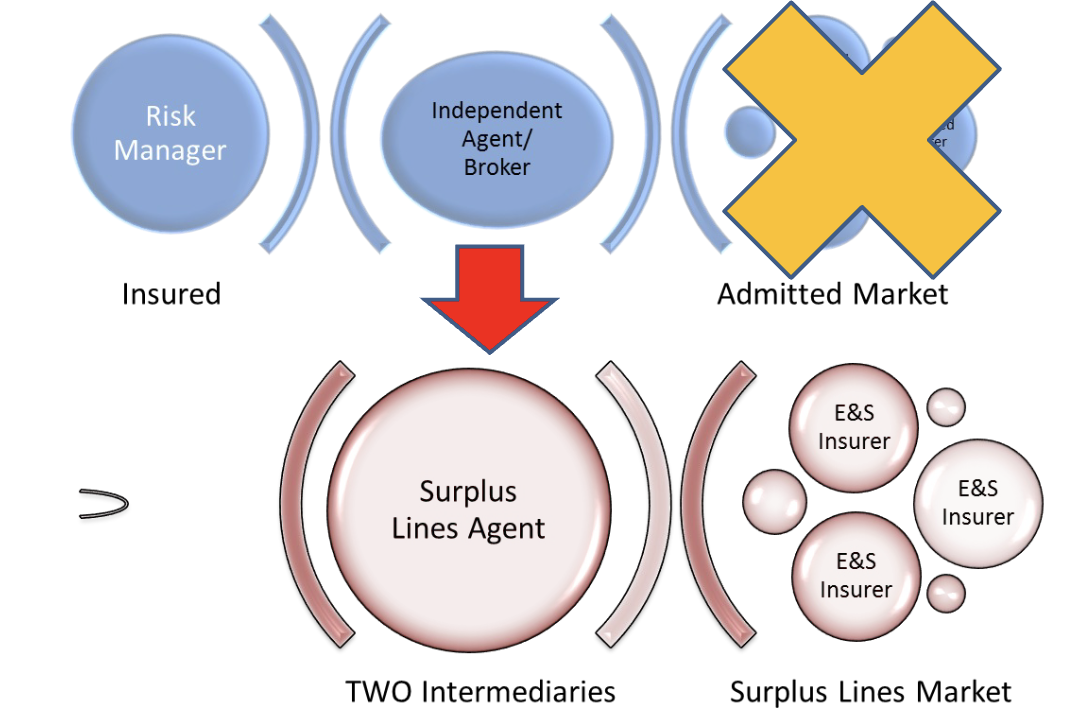
Accessing the E&S Market
Insured → TWO Intermediary: Agent or Broker (1) → Surplus Lines Agent (2) → Surplus Lines Market