Ch. 11 lecture PP nerve physiology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
neural tissue
A. cells
A-1 neurons (information transfer)
*extreme longevity
*amitotic (lose ability to divide)
*very high metabolic rate (high O2 and glucose requirements)
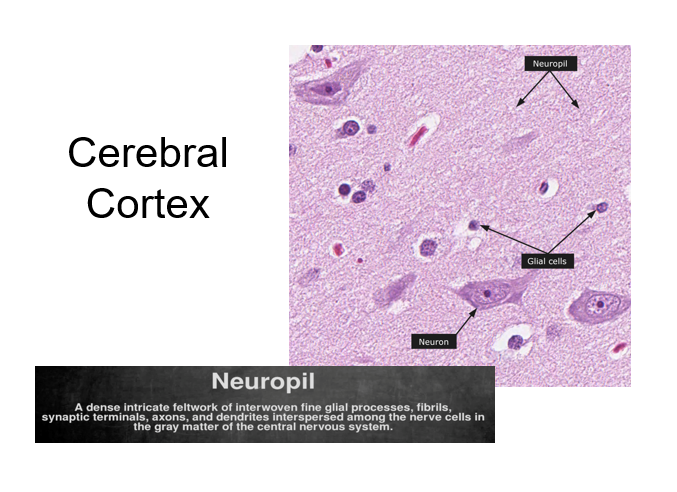
Neural tissue
A. Cells
A-2 neuroglia (supporting cells)
*outnumber neurons
*retain ability to divide (mitotic)
wrap around or located near neurons
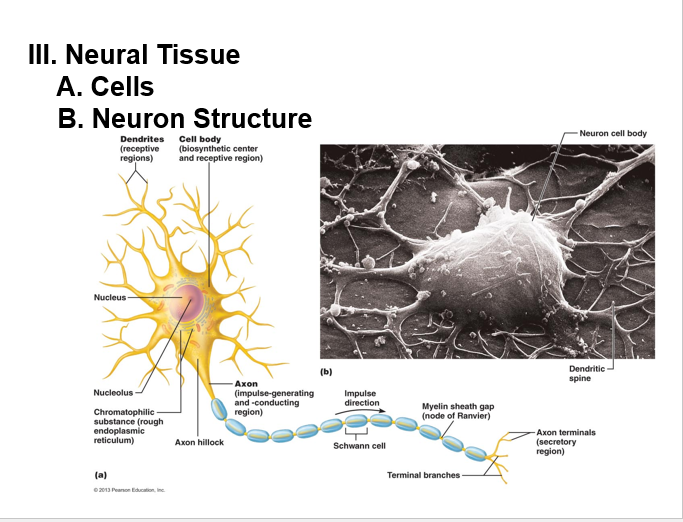
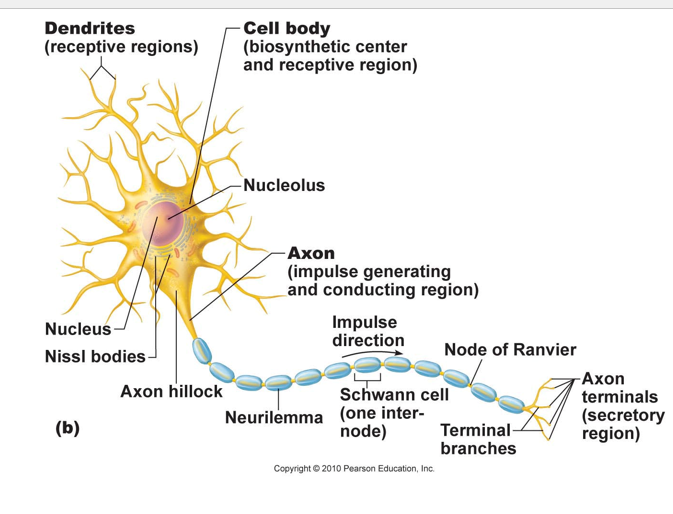
Neuron structure
Perikaryon
cell body (soma)
contains neurofilaments
contains microtubules
neuron structure
organelles
a. typical (mitochondria, lysosomes, etc.)
b. specialized:
-Nissl bodies= aggregations of free and fixed ribosomes
-that will contribute to gray matter of N.S. (not in axons)
Note: following differentiation, most neurons become incapable of undergoing mitosis (cannot replace themselves after cell death)
neuron structure
dendrites:
• Highly branched processes
• Provide large surface area for receiving input
• Transmit electrical changes toward body (soma)
neuron structure
Axon with axon hillock (area of the axon closest to the soma)
•a long axon also called a nerve fiber.
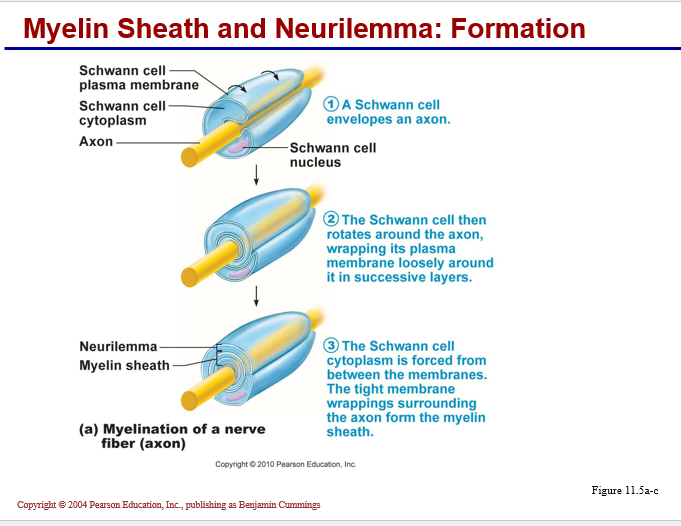
• Myelin Sheath: Whitish, fatty (protein-lipid), segmented sheath around most long axons
o It functions to:
- Protect the axon
- Electrically insulate fibers from one another
- Increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission
neuron structure
collaterals
axonal branches
neuron structure
telodendria
fine extensions of a collateral (terminal branches)
neuron structure
synaptic knobs (aka terminals):
expanded ends of the axon
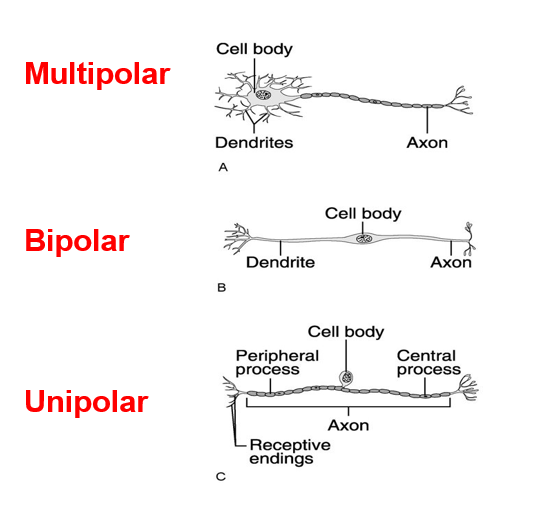
neuron classification
C-1. “structural”
multipolar
large, several dendrites, single axon
common in CNS, eg). motor neurons
neuron classification
C-1. “structural”
unipolar:
•soma off to one side
• dendritic and axonal processes are continuous
ex). sensory neurons (general)
neuron classification
c-1. “structural”
bipolar:
•one dendrite, one axon
• soma between
ex). sense organs, (eye, ear)
neuron classification
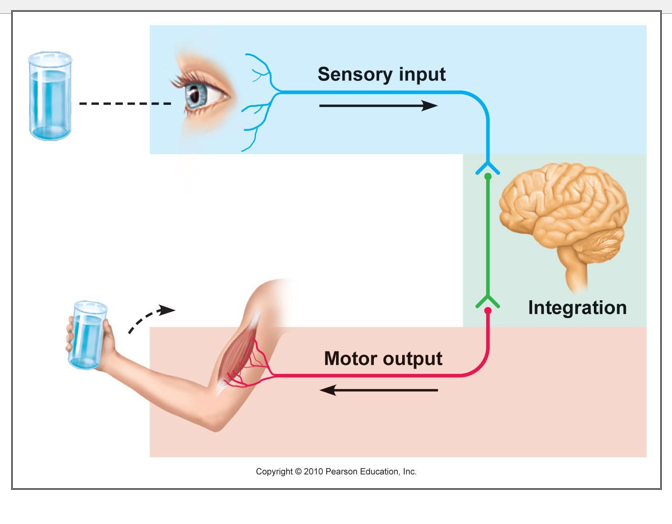
C-2 “functional”
afferent (sensory)-
carry impulses toward CNS
neuron classification
C-2. “functional”
efferent (motor)-
carry impulses away from CNS
neuron classification
C-2 “functional”
interneurons (association)
•Located between sensory and motor n. in CNS only (brain & sp. chord)
• Will “shuttle” impulses
• 99% of neurons in the body of this type
nueroglia classifications
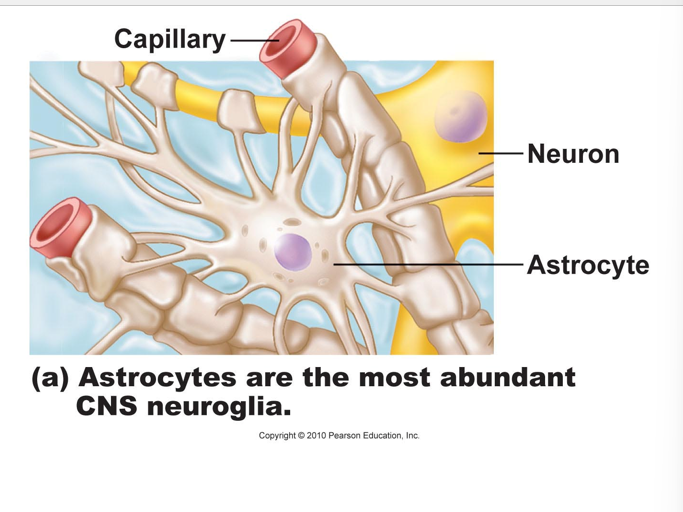
CNS neuroglia
astrocytes
•largest, most numerous
• functions include:
a. maintenance of BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER (isolates brain
from general circulation, will discuss in later chapter)
b. create 3-D framework (via microfilaments)
c. regulate interstitial fluid composition
neuroglia classifications
CNS neuroglia
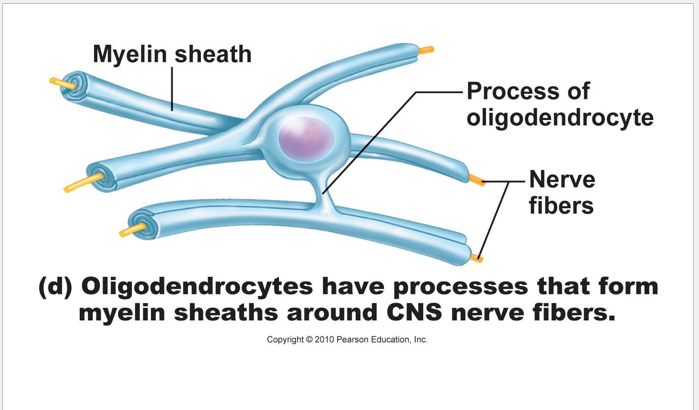
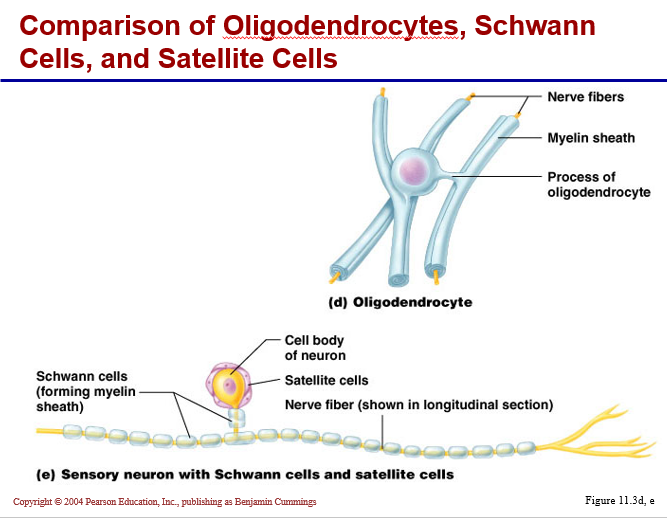
oligodendrocytes:
•large, few slender extensions
• many layers of membranous wrapping creates MYELIN in CNS
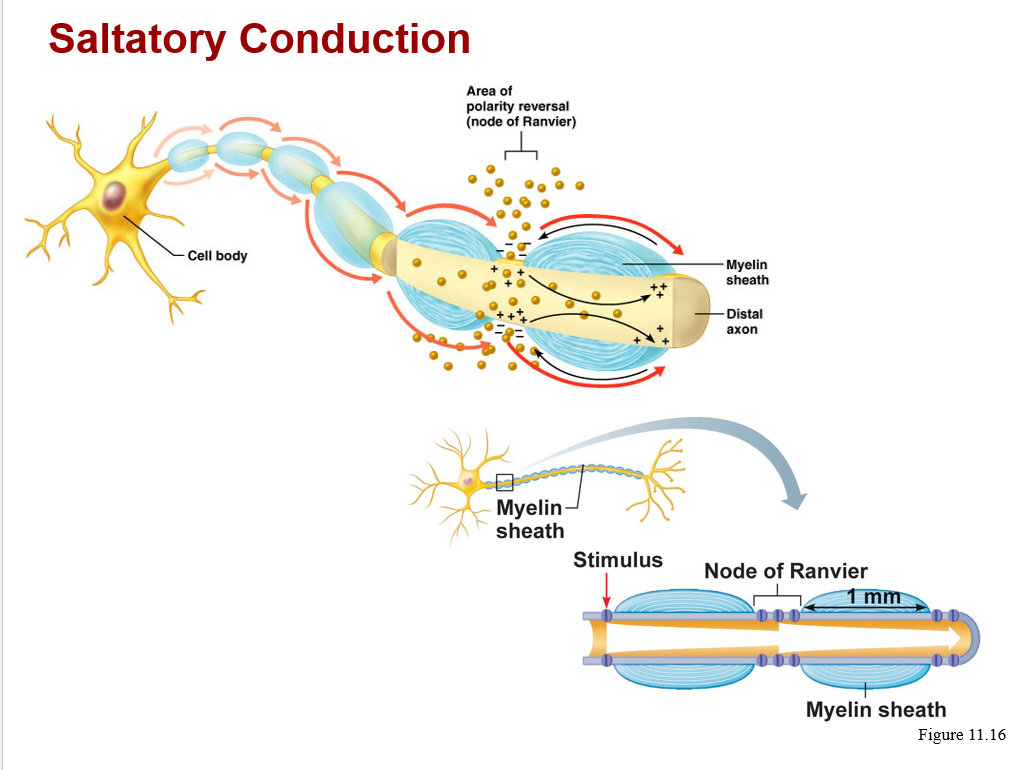
• gaps between the myelinated segments of the axon are called nodes of Ranvier
Note: myelinated segments are glossy white
* will appear white and thus make up the "white matter" of the CNS
* whereas, "gray matter" constitutes the area where cell bodies predominate
* axons without myelin = unmyelinated axons
CNS neuroglia
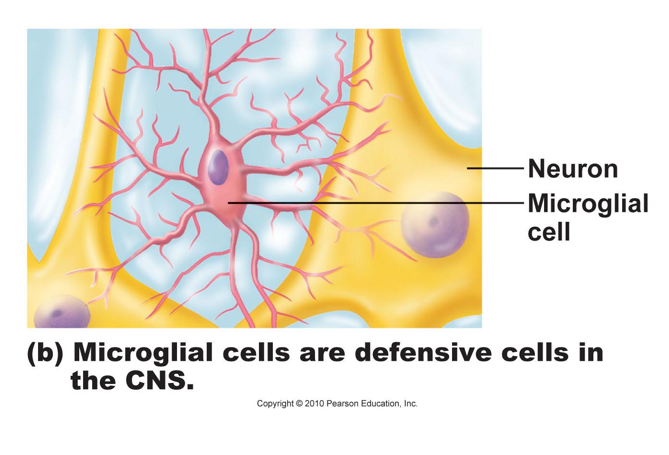
Microglia
•small mobile cells (macrophages), move toward debris
• phagocytotic WBC that have migrated into the CNS….migrate,
• enlarge, then engulf
CNS neuroglia
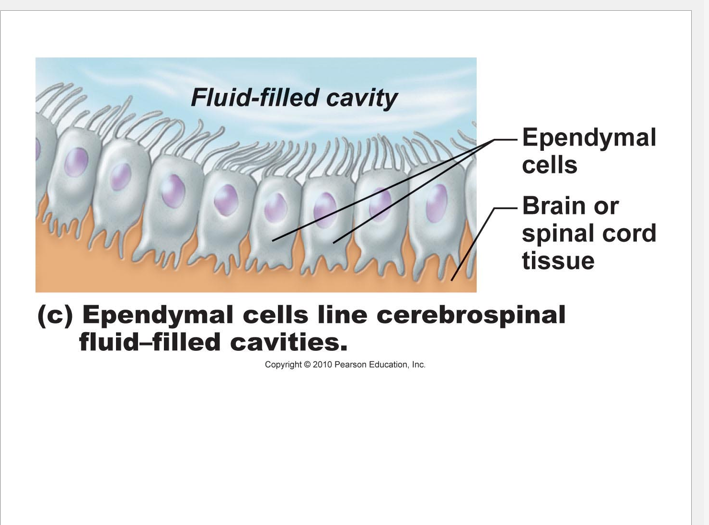
Ependymal cells
•will line the central canal and ventricles which are filled with CSF = cerbrospinal fluid
• will aid in CSF circulation
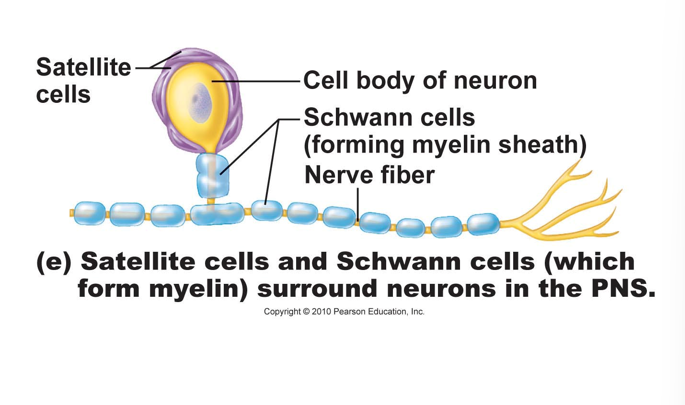
PNS Neuroglia
satellite cells:
surround cell bodies of ganglia cells (sensory cells)
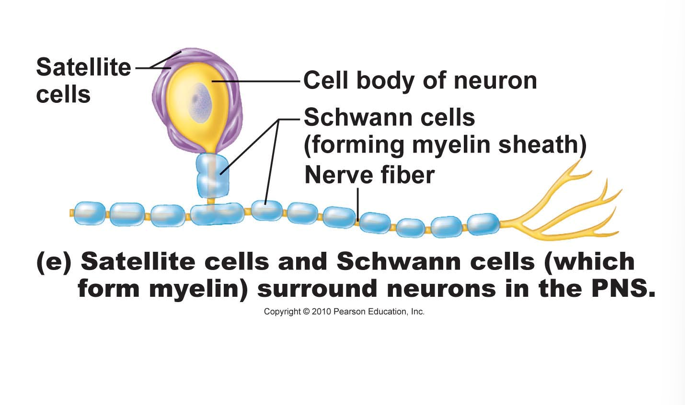
PNS Neuroglia
Schwann cells:
•create neurolemma around every peripheral axon
• will myelinate a single axon (as shown with oligodendrocytes)
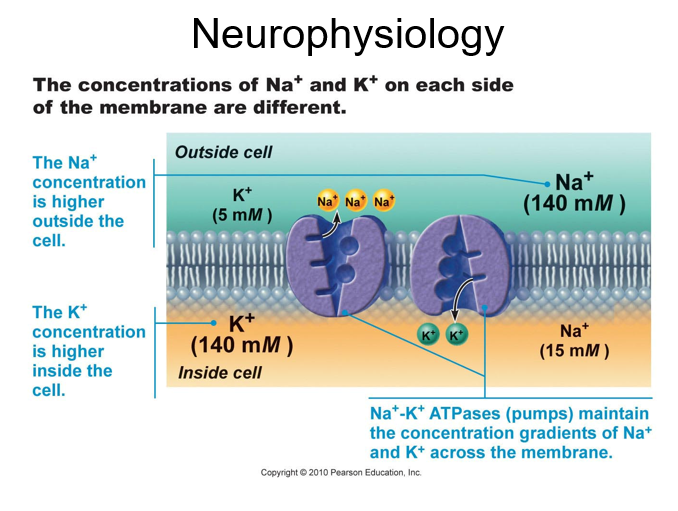
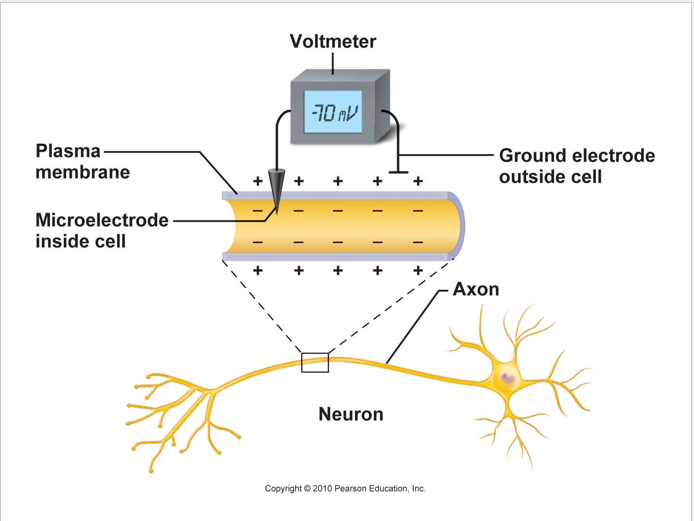
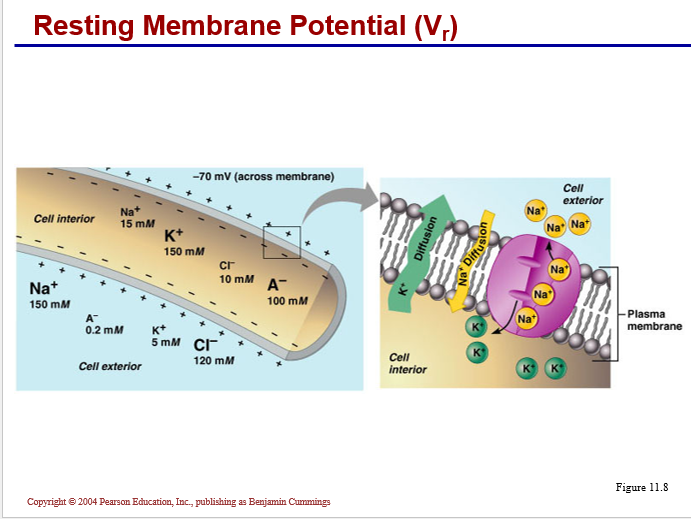
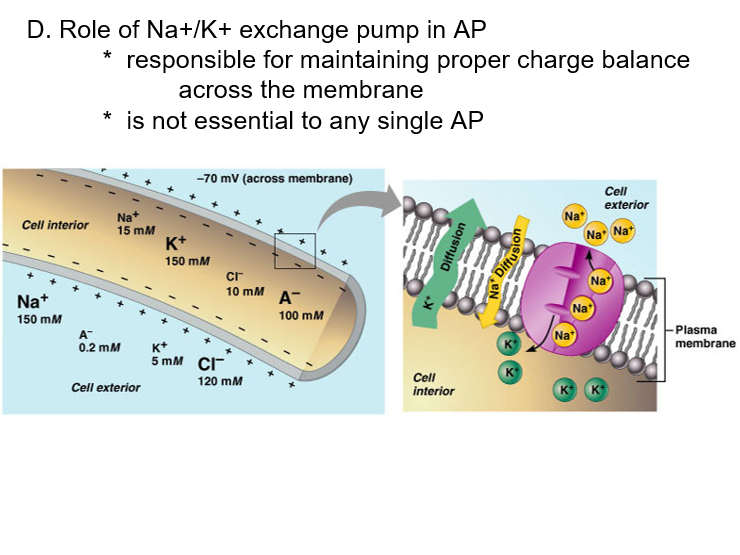
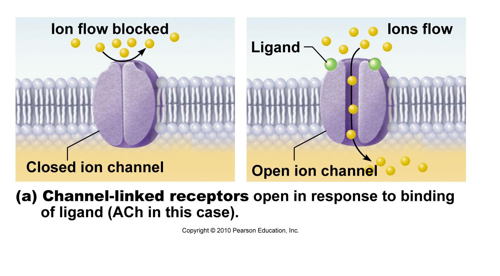
Membrane channels: (proteins within the cell membrane)
chemically (ligand) regulated
a. will open or close when specific chemicals bind the channel
eg.) ACh receptor of the skeletal muscle cell
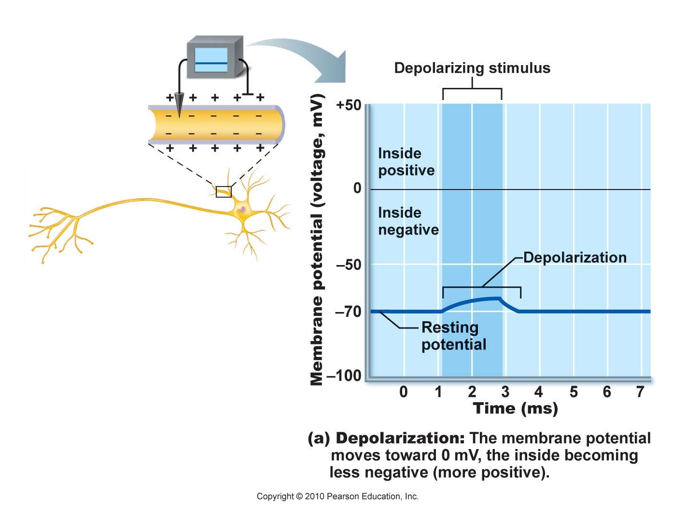
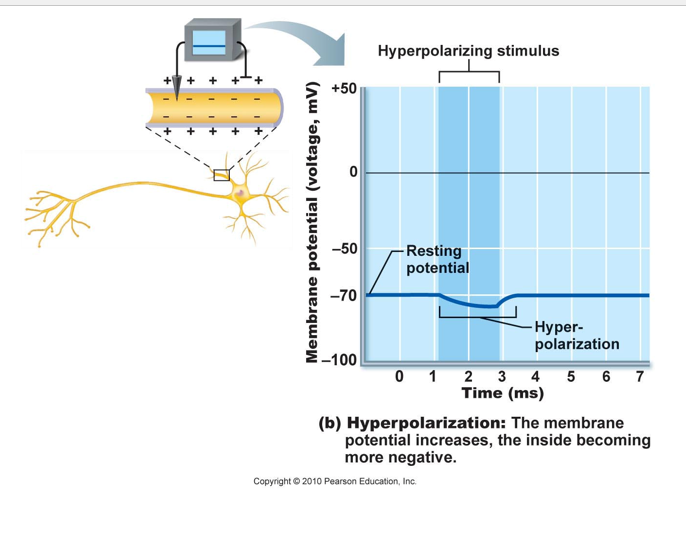
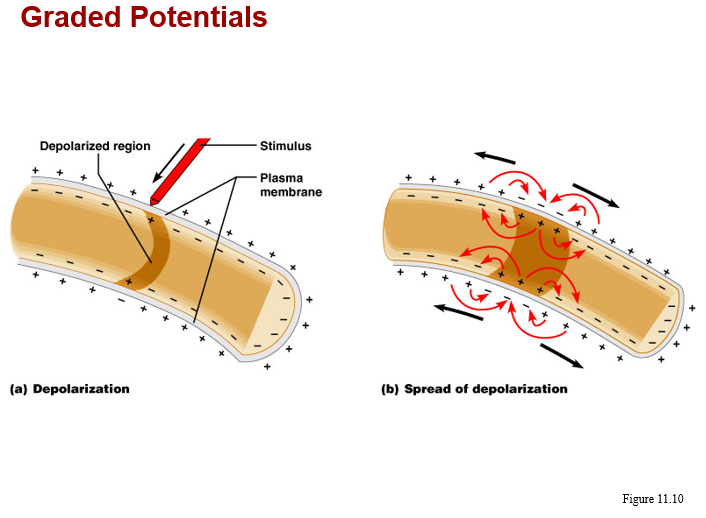
b. produce graded potentials
-which may be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing
c. found at dendrites, soma, presynaptic surfaces of axon, the motor end plate
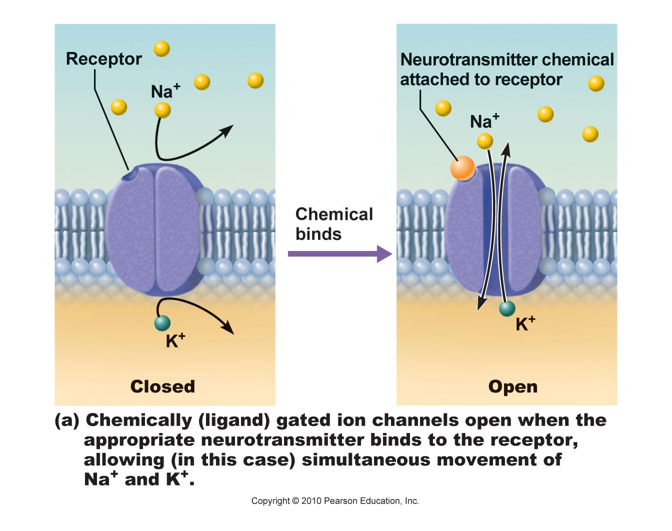

Membrane channels: (proteins within the cell membrane)
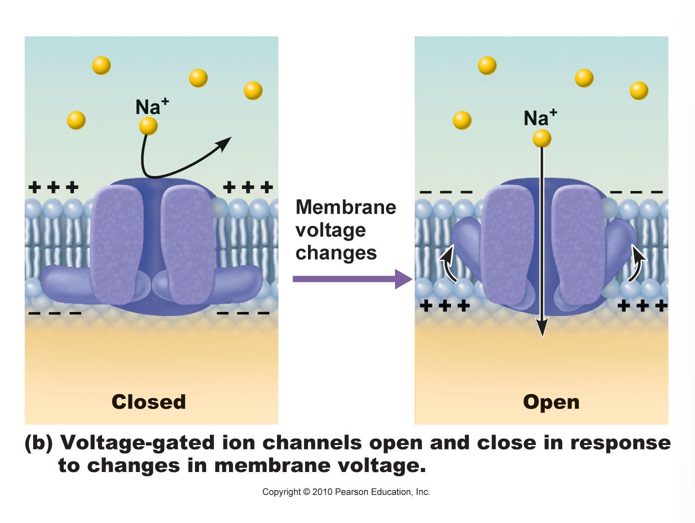
voltage regulated
a. will open or close in response to changes in the transmembrane potential.
Eg. 1) sarcolemma channels in response to depolarization
Eg. 2) axonal channels
b. produce action potentials
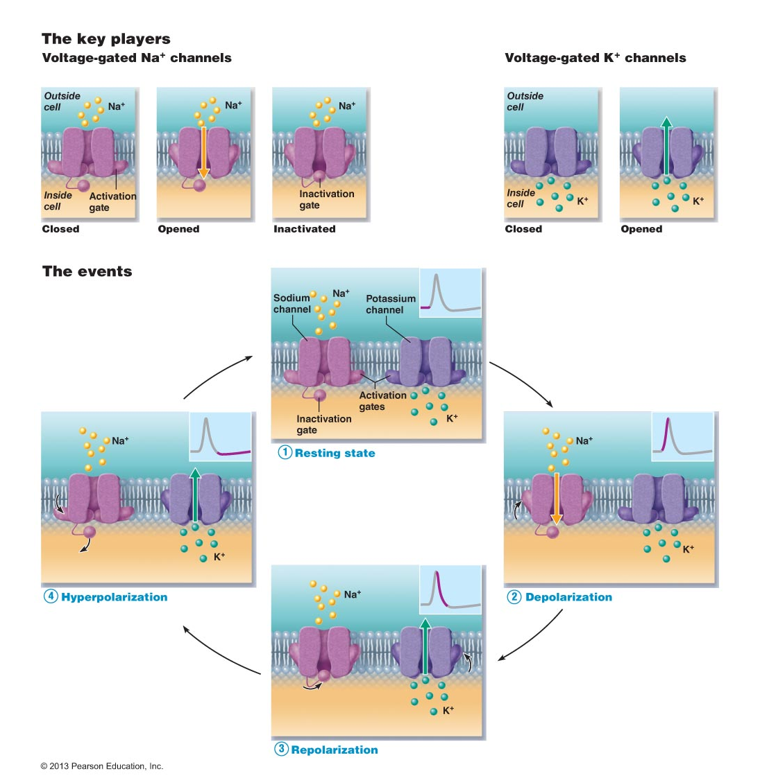
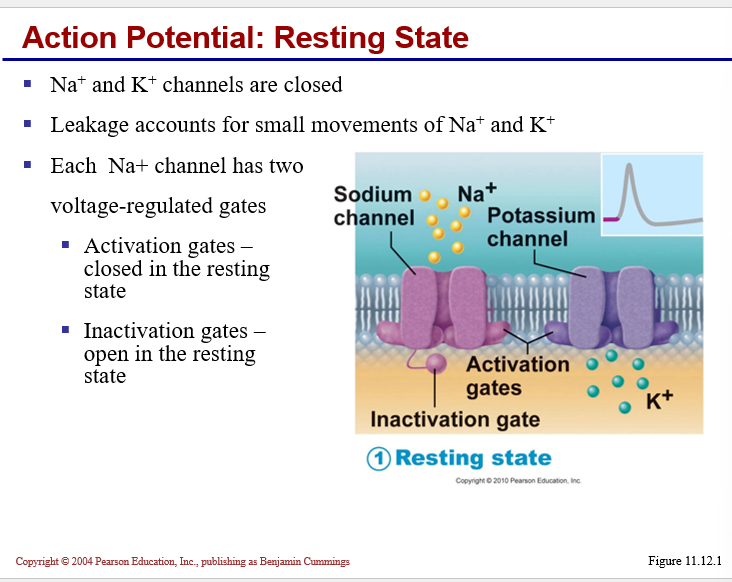
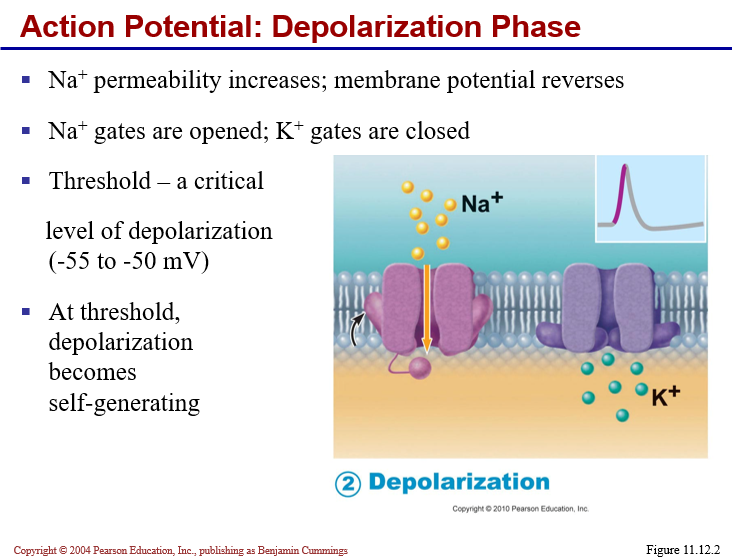
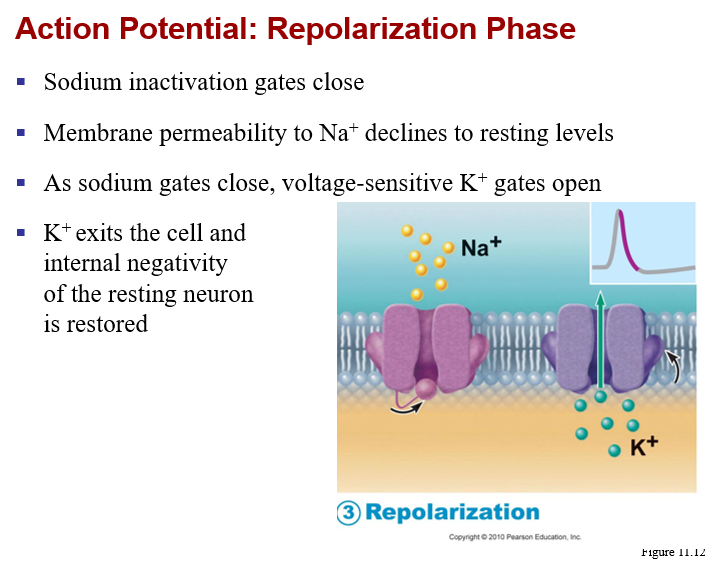
Generation of an ACTION POTENTIAL
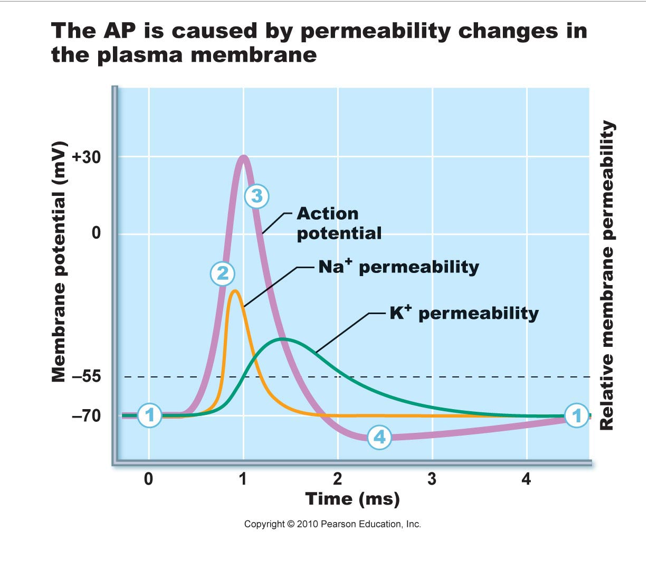
Graded potential brings membrane to threshold (approx. -55 mV)
results in activation (opening) of voltage-regulated
Na+ channels
Na+rushes IN!
results in rapid depolarization of membrane
(up to +30mV)
“All or None” phenomenon means if threshold is reached, an AP is always generated, if threshold not reached, NO AP generated.
Na+ channels are closed (inactivated), due to new (+30)
transmembrane potential
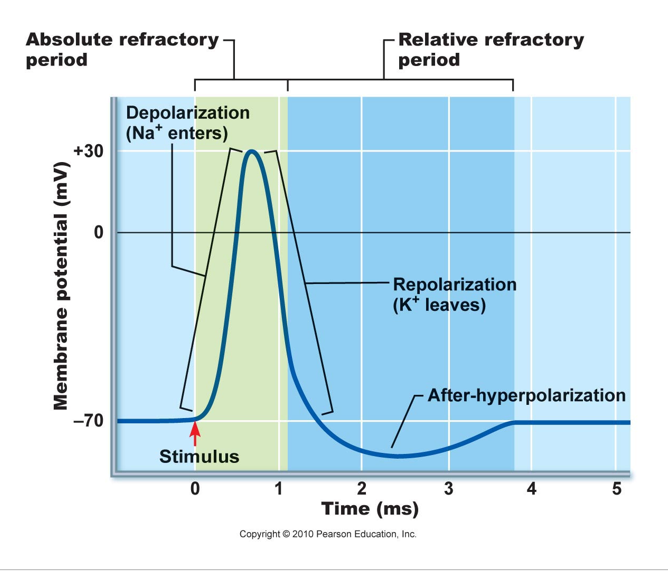
Generation of an ACTION POTENTIAL
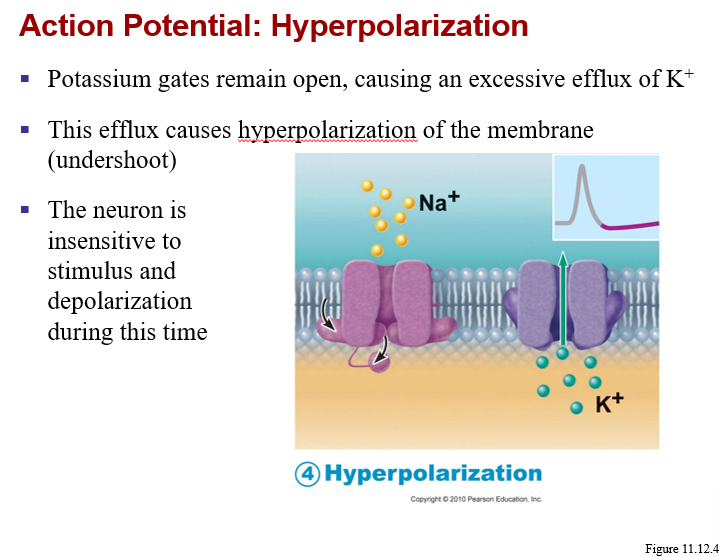
Voltage regulated K+ channel activation (opening)
K+ rushes OUT!
results in repolarization of the membrane (back toward -70mV)
Normal permeability is established:
Na+ channels closed but capable of opening
K+ channels begin closing, will allow for a hyperpolarization before permeability returns to normal
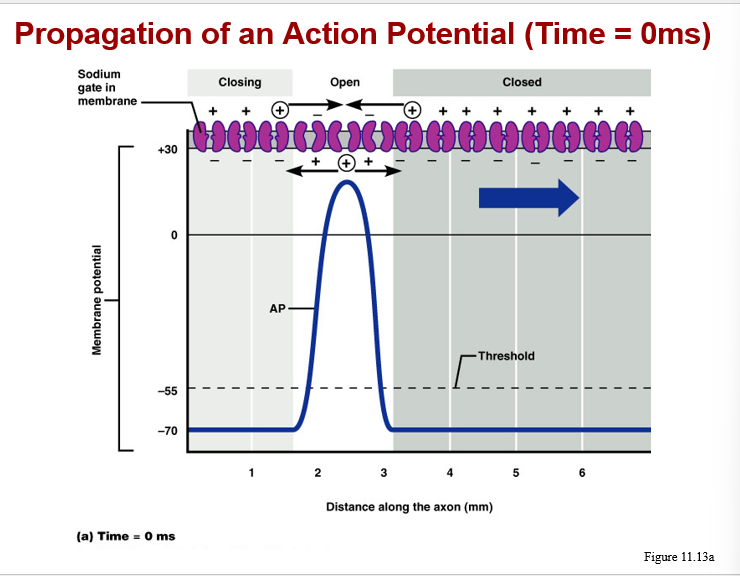
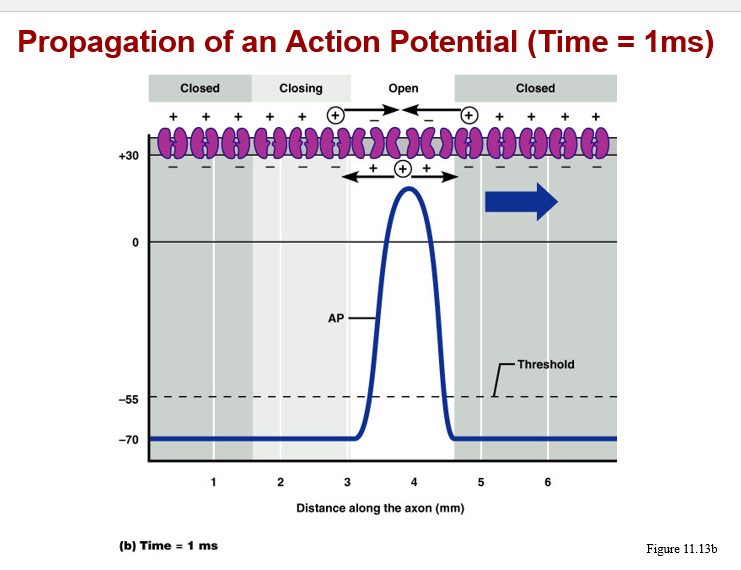
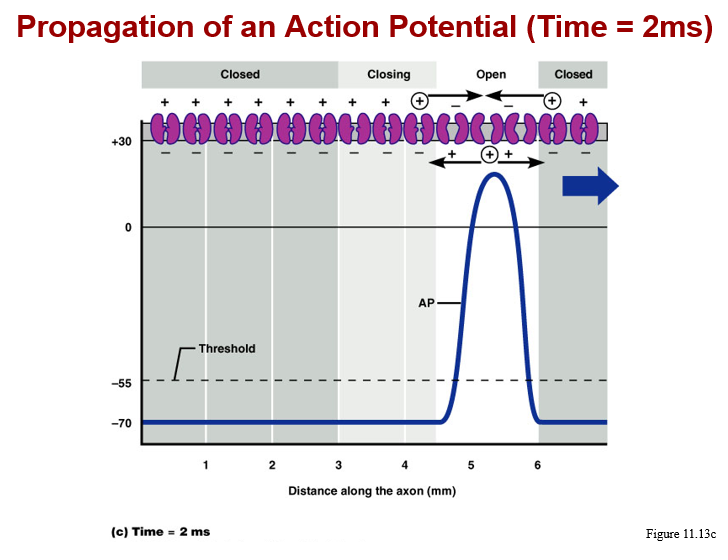
Action potential conduction:
proceeds away from the point of initial stimulation
affects the entire membrane surface via a “chain reaction”
velocity of AP depends upon:
a. presence or absence of myelin sheath
b. diameter of the axon (larger axon is faster)
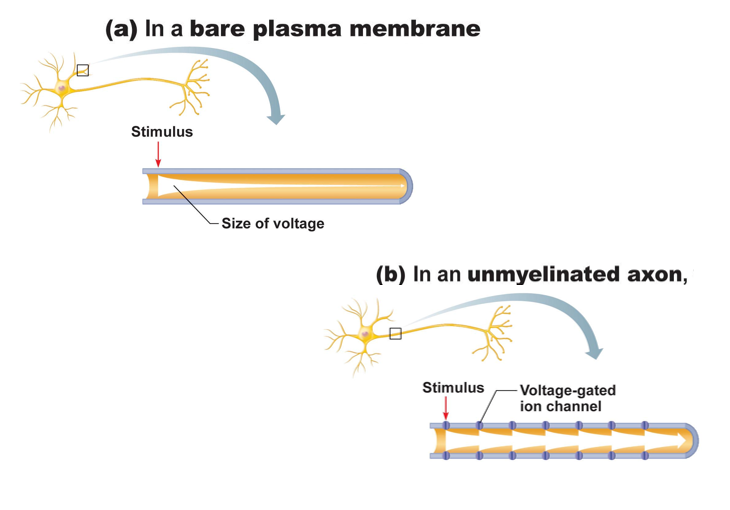
types of conduction:
a. continuous, along unmyelinated axons
b. saltatory, on myelinated axons, is 7X faster
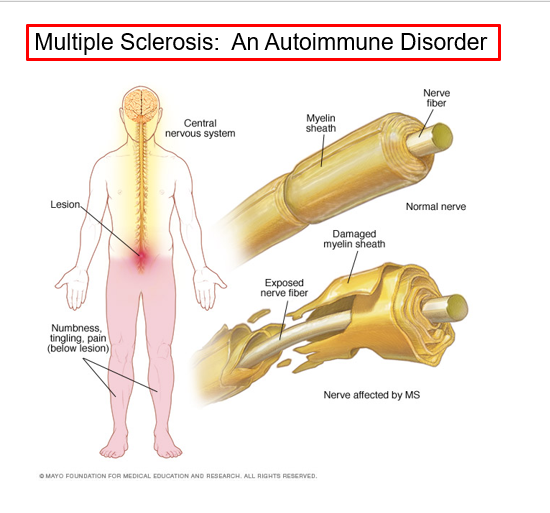
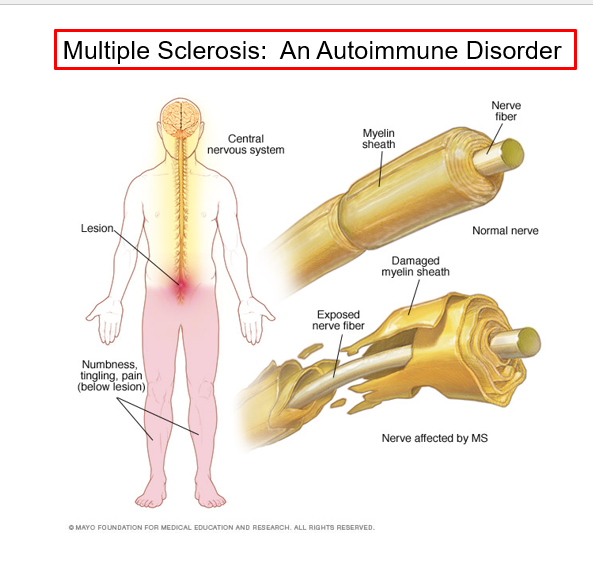
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disease that mainly affects young adults
symptoms include visual disturbances, weakness, loss of muscular control, and urinary incontinence
nerve fibers are severed and myelin sheaths in the CNS become nonfunctional scleroses
shunting and short circuiting of nerve impulses occurs
Multiple sclerosis: Treatment
The advent of disease modifying drugs including interferon beta-1a and -1b, Avonex, Betaseran, and Copazone
Hold symptoms at bay
Reduce complications
reduce disability
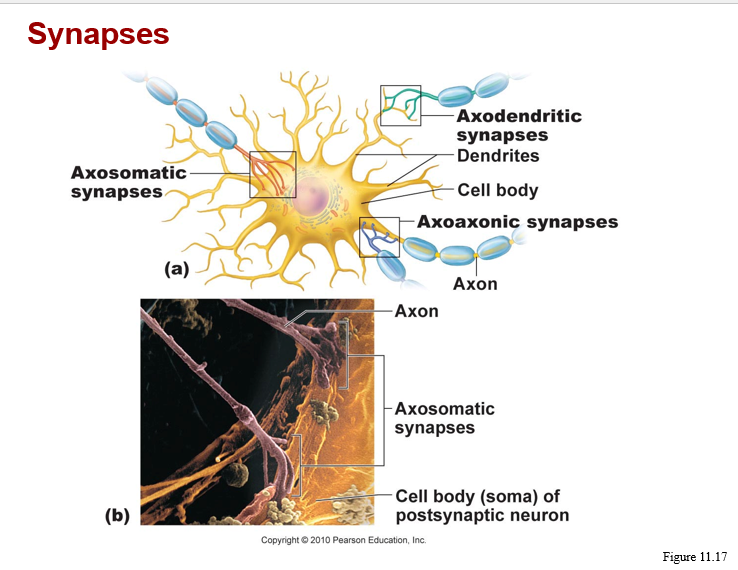
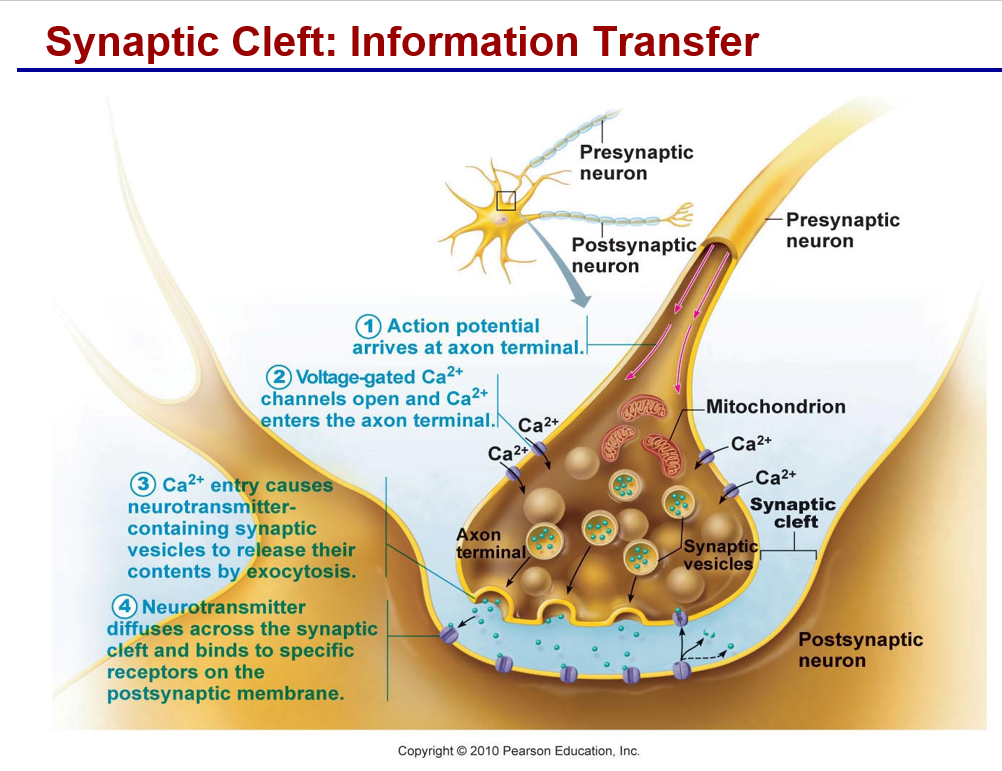
synaptic communcation-
characteristics of a synapse
junction of information transfer from neuron to another cell
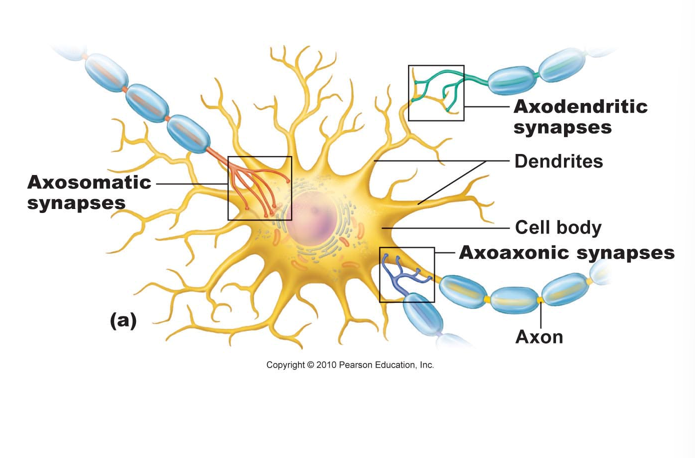
synaptic communication-
characteristics of a synapse
types- (note: presynaptic vs postsynaptic cells)
based on location: axondendritic, axosomatic, axoaxonic
based on mechanism of information transfer: electrical or chemical
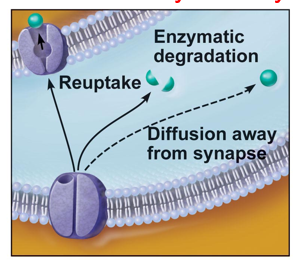
Synaptic communication-
Termination of neurotransmitter (NZ) effects:
a. Degradation of NZ by enzymes (in cleft)
b. Removal from the synapse (reuptake)
c. Diffusion of NZ away from synapse
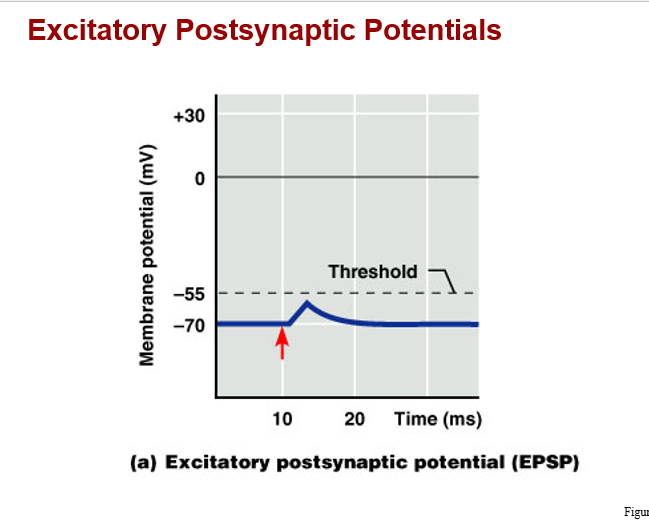
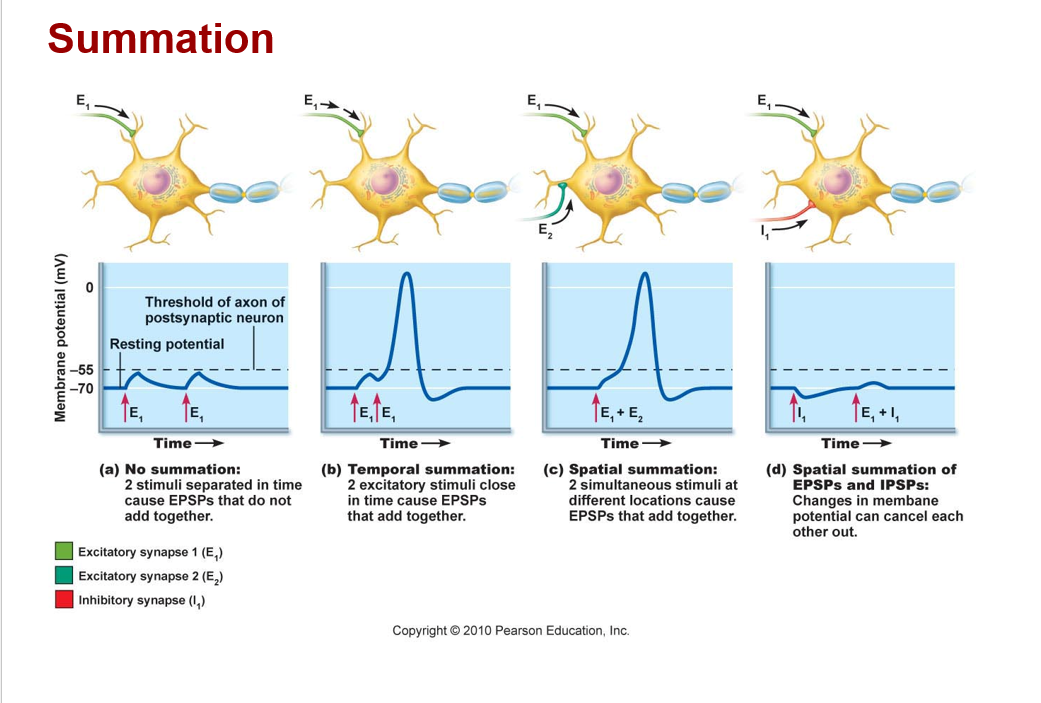
Postsynaptic potential and integration
a. EPSP: excitatory postsynaptic potential
*a graded potential that moves the transmembrane potential closer to threshold (a depolarization)
Ex) chemical binds and opens sodium channels, causes depolarization
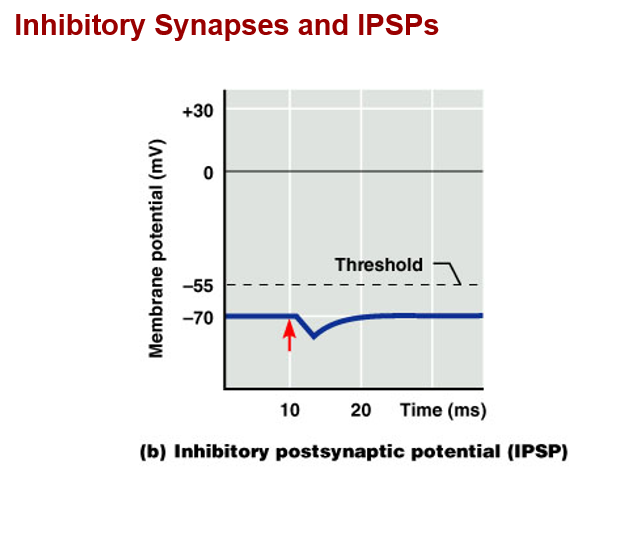
Postsynaptic potential and integration
b. IPSP: inhibitory postsynaptic potential
*a graded potential that moves the transmembrane potential further from threshold (hyperpolarization)
Ex) chemical binds and opens potassium or chloride channels, causes hyperpolarization
Classification of neurotransmitters-
a. Acetylcholine, Ach (cholinergic synapses)
*produces graded potential via ion movements, usually depolarizing (excitatory)
*located at neuromuscular junctions, brain, and peripheral autonomic neurons
*acetylcholinesterase present to degrade Ach
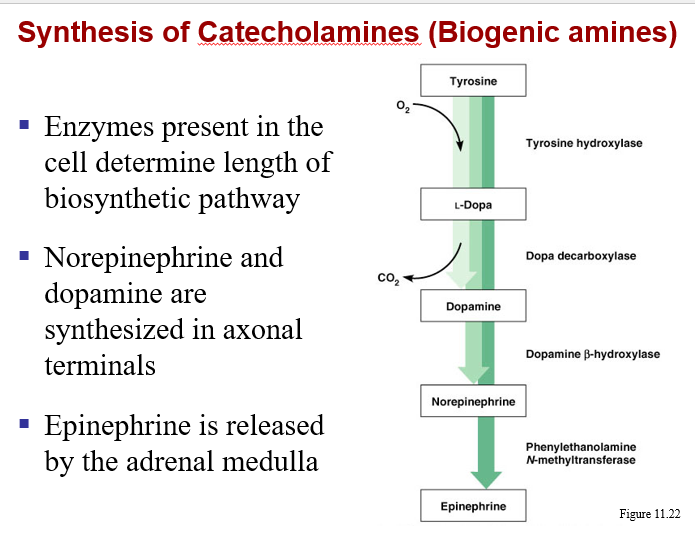
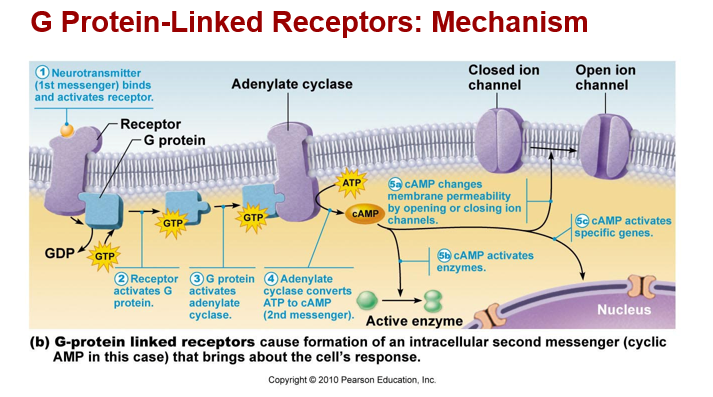
Classification of neurotransmitters-
b. biogenic amines (adrenergic synapses)
*includes norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, histamine
*effects alter metabolism through second messenger molecules
*can be excitatory (depolarizing) or inhibitory (hyperpolarizing)
Classification of neurotransmitters-
c. amino acids- *includes GABA, Glycine, glutamate
d. peptides - *includes endorphins, substance P
e. others- *purines (ATP and adenosine)
*Dissolved gases: Nitric oxide, carbon dioxide (“signaling gases”)