MicroBiology Ch 3 Flashcards
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
All bacterial cells possess
- A cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Ribosomes
- A cytoskeleton
- One (or a few) chromosome(s)
Most bacterial cells possess:
- A cell wall
- A surface coating called a glycocalyx
Some but not all bacterial cells possess
- Flagella, pili, and fimbriae
- An outer membrane
- Plasmids
- Inclusions
- Endospores
- Intracellular membranes
Pleomorphism
variations in size and shape among cells of a single species
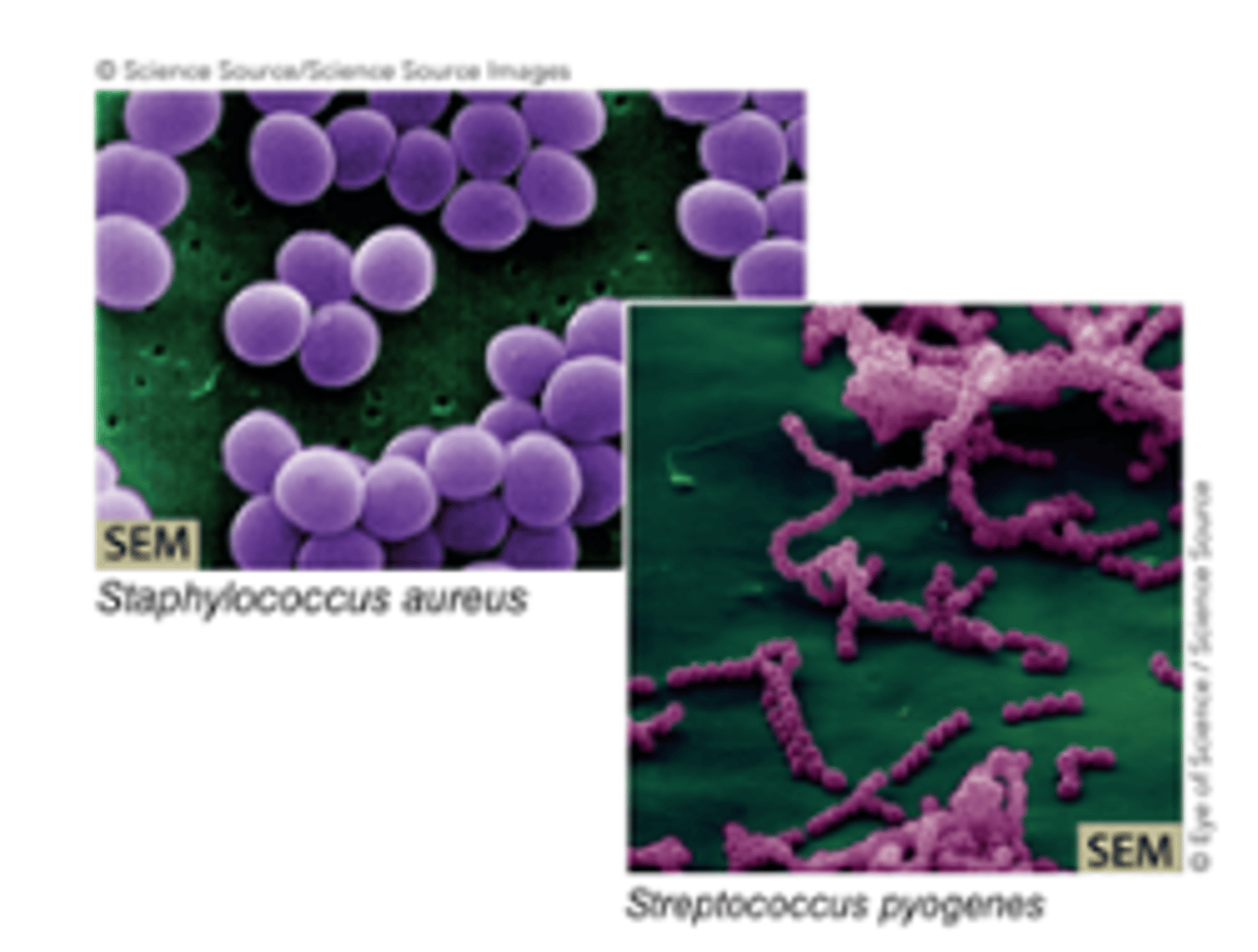
Spherical (s. coccus, pl. cocci)
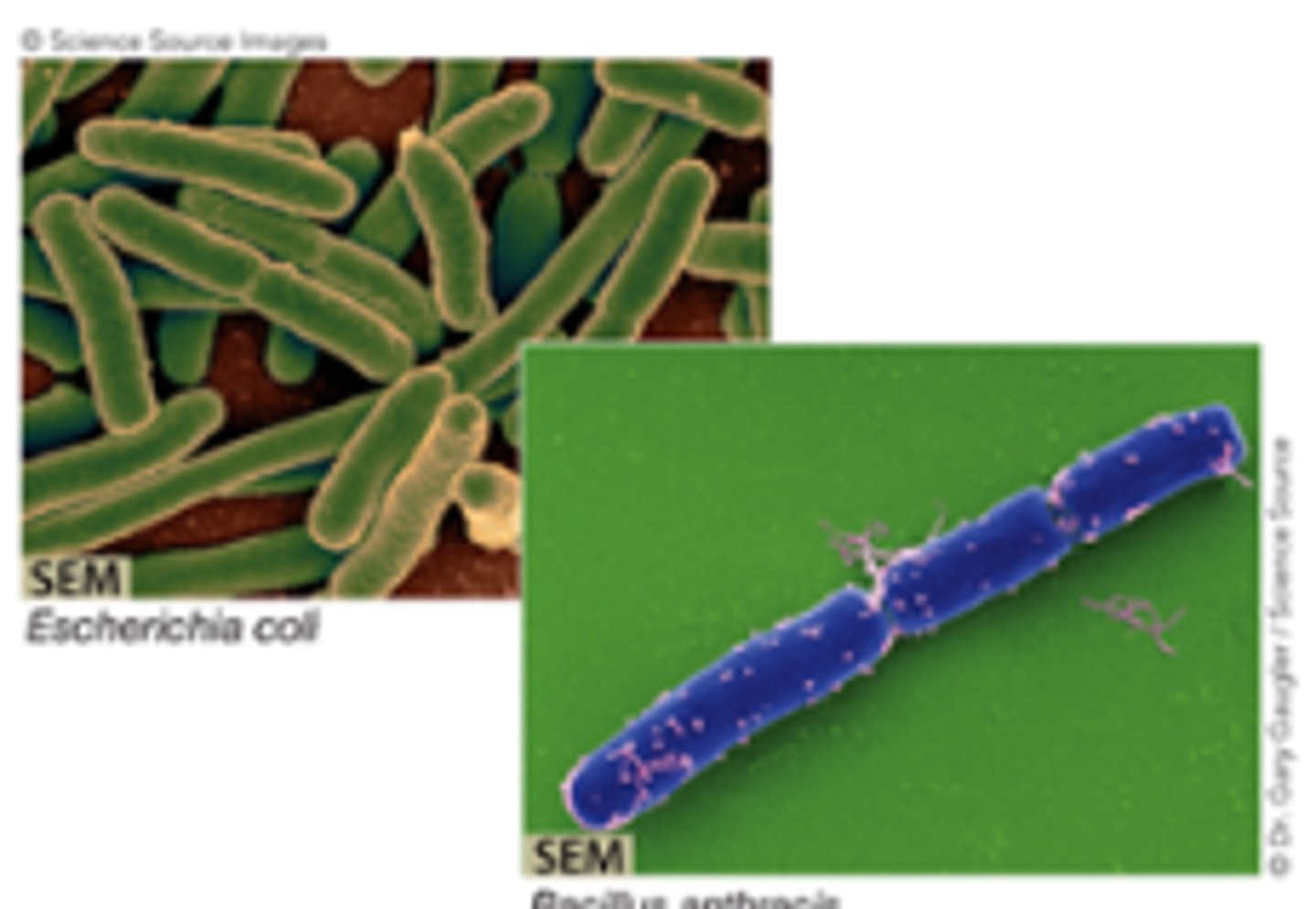
Rod-shaped (s. bacillus, pl. bacilli)
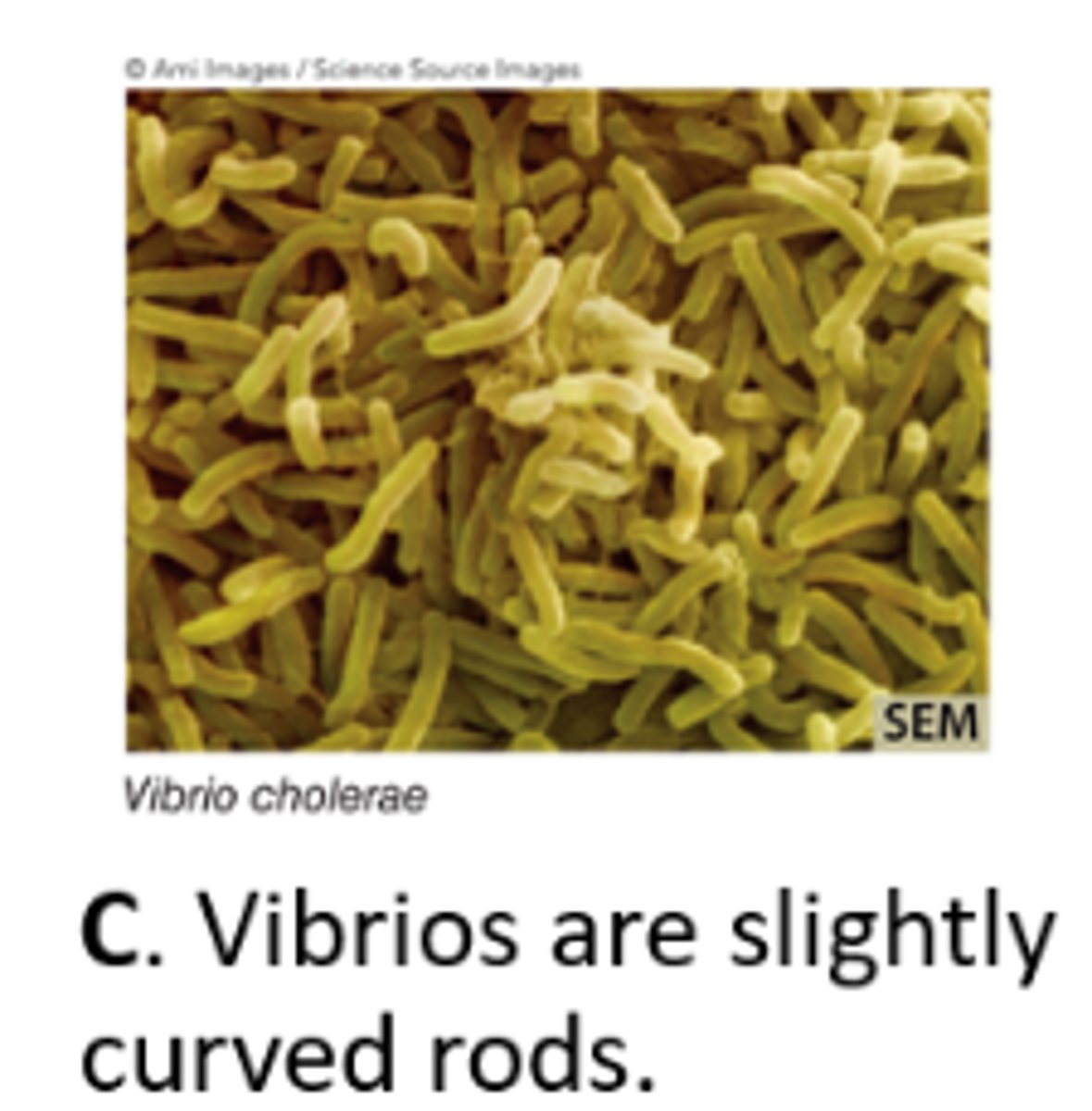
Comma-shaped (s. vibrio, pl. vibrios)
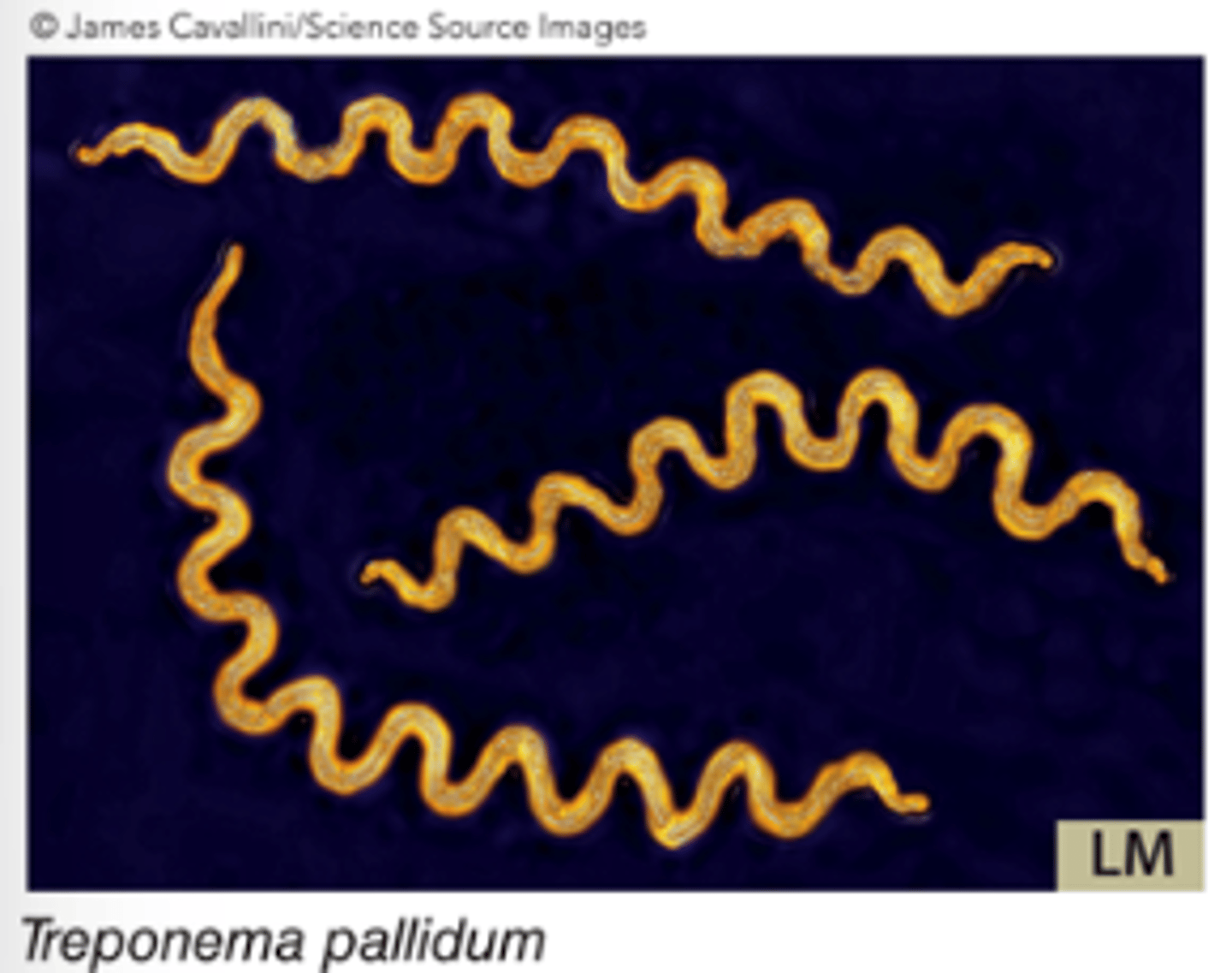
Spiral (s. spirillum, pl. spirilla)
Pleiomorphic (varied shapes)
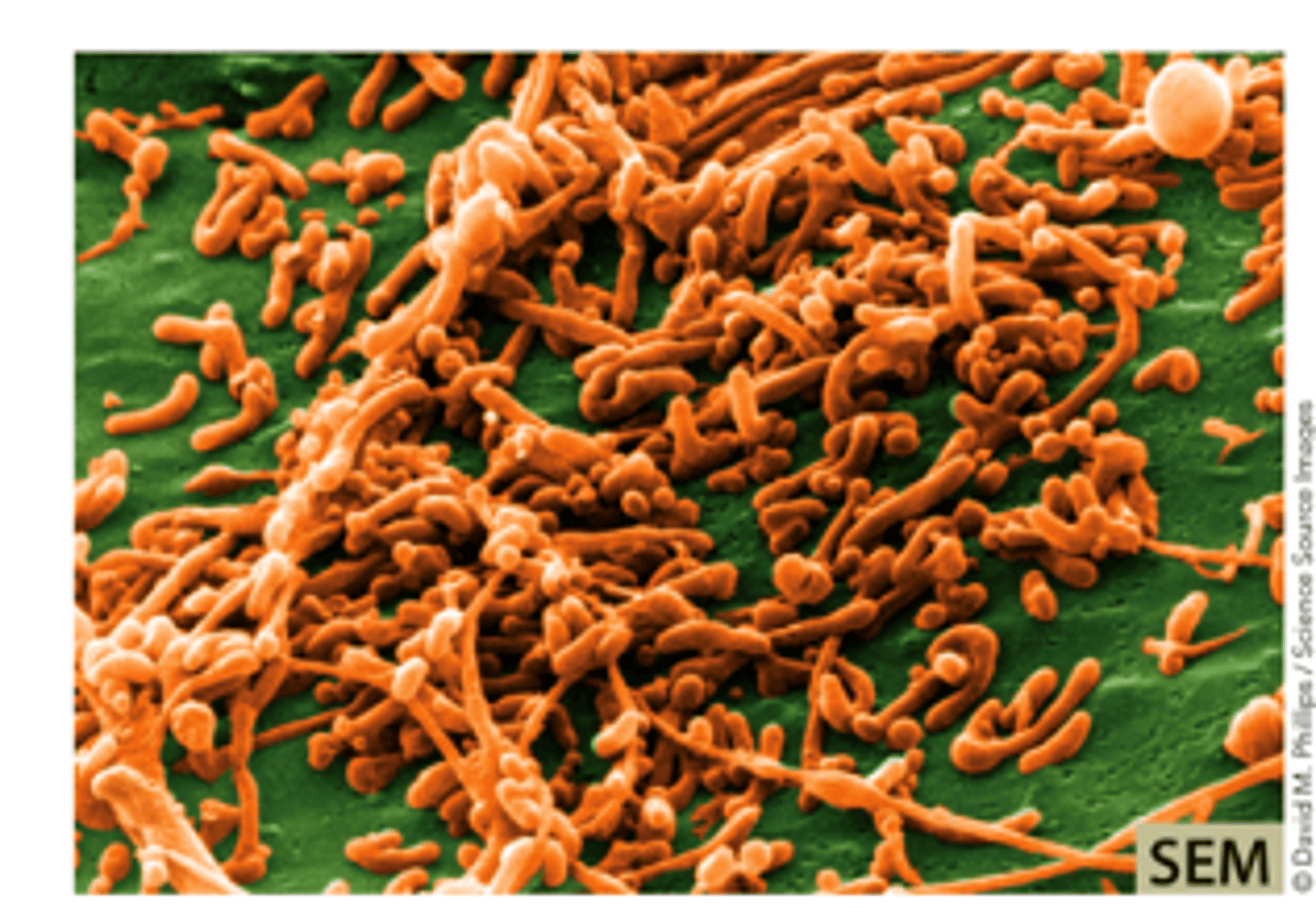
Hyphae (branching filaments of cells)
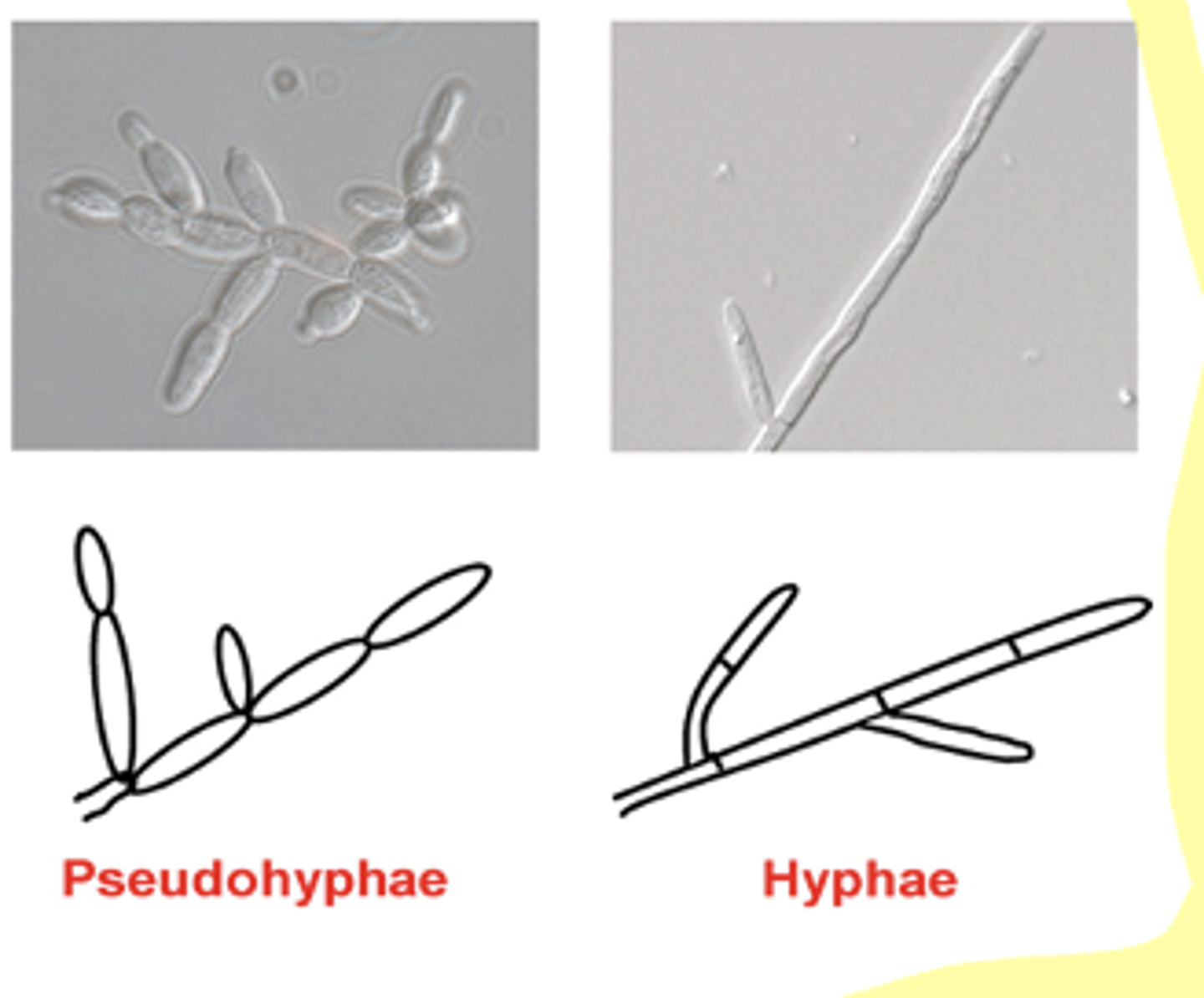
Mycelia (tufts of hyphae)
a network of branching, thread-like structures called "hyphae" that make up the vegetative body of a fungus
Thiomargarita namibiensis
up to 700 μm in diameter
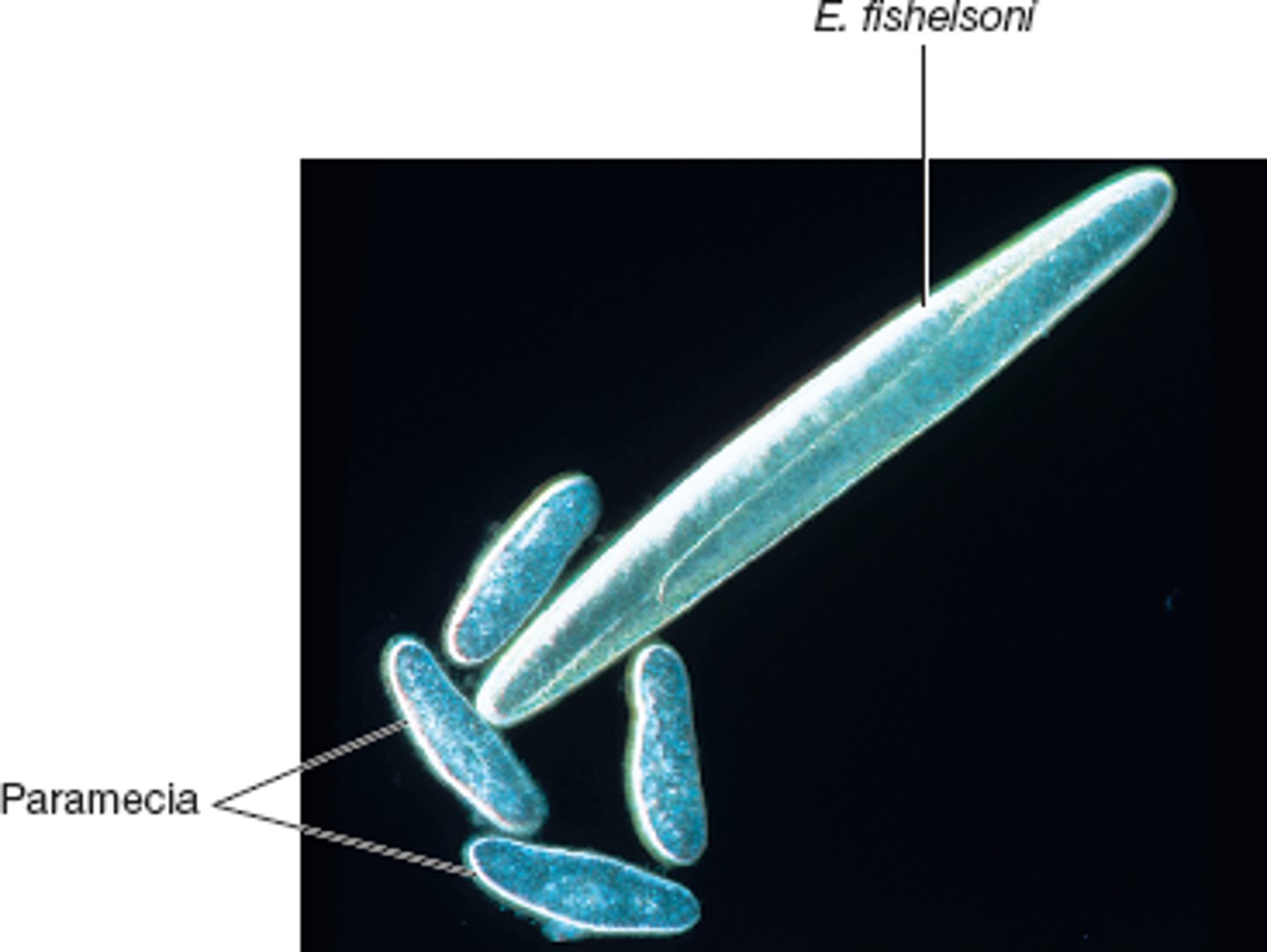
Epulopiscium fishelsoni
200‒700 μm x 80 μm
mycoplasma
some cells are only 0.2 μm in diameter
Appendages
Structures such as legs and antennae that extend from the body wall.
flagella, pili and fimbriae
Cell envelope
• The plasma membrane and all surrounding layers external to it
• Capsules or sheaths, cell wall, plasma membrane
• Composed of two or three basic layers:
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Outer membrane in some bacteria
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
inclusion bodies, nucleoid, ribosomes
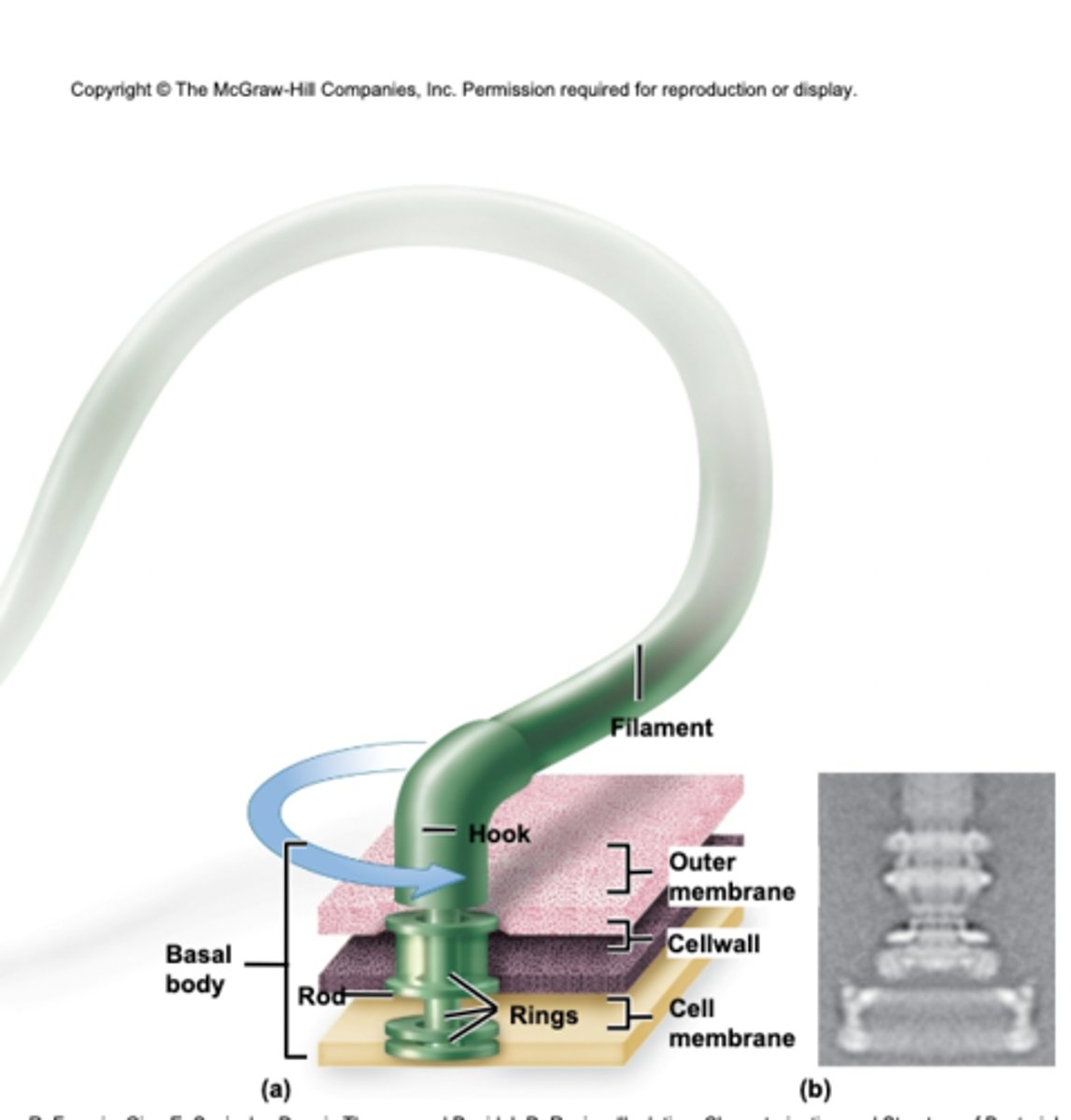
Flagella - Prokaryotic Propellers
• Bacterial locomotion
• Three distinct parts
• Comprised of many proteins
• 360 degree rotation
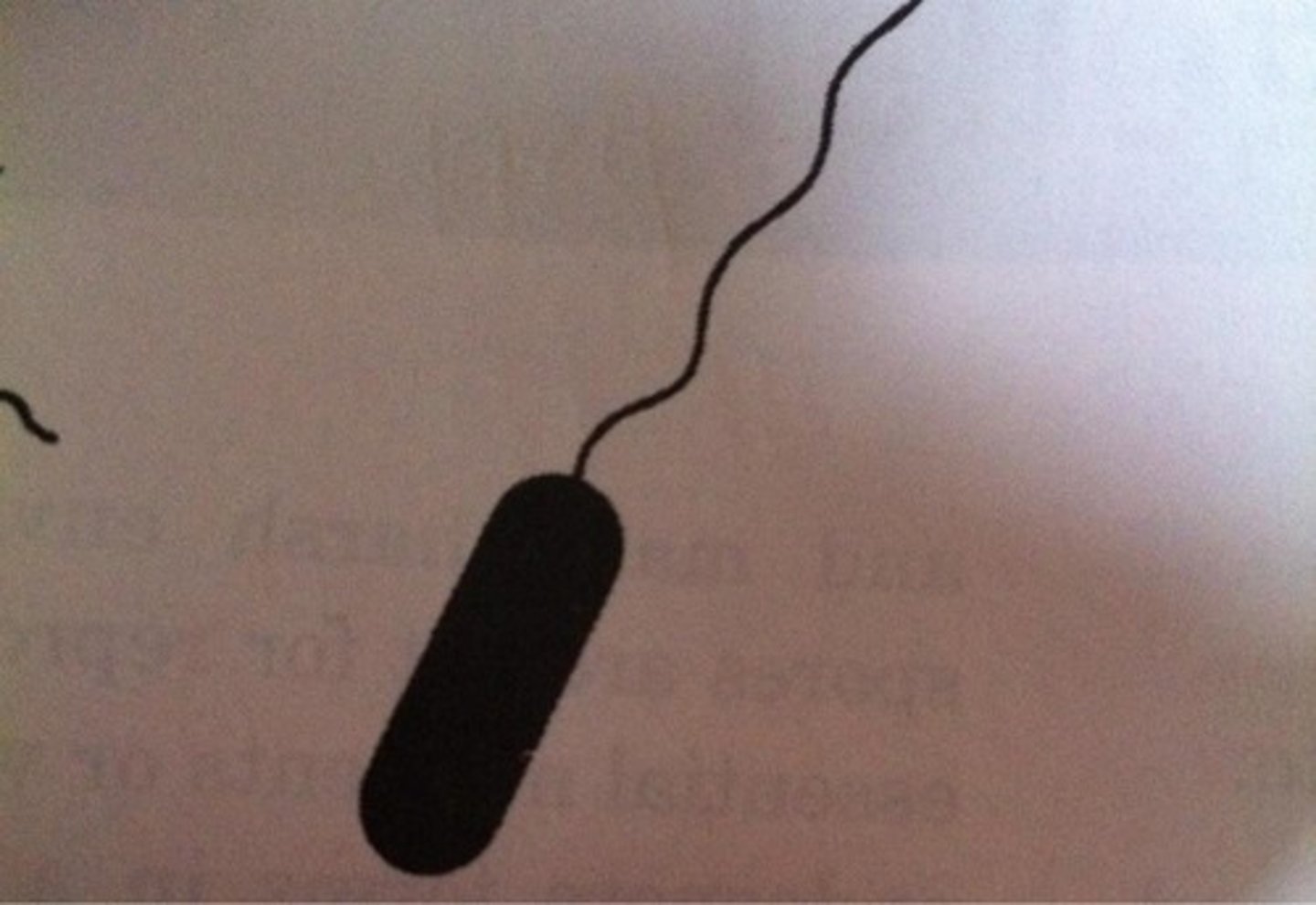
Monotrichous
Single flagellum

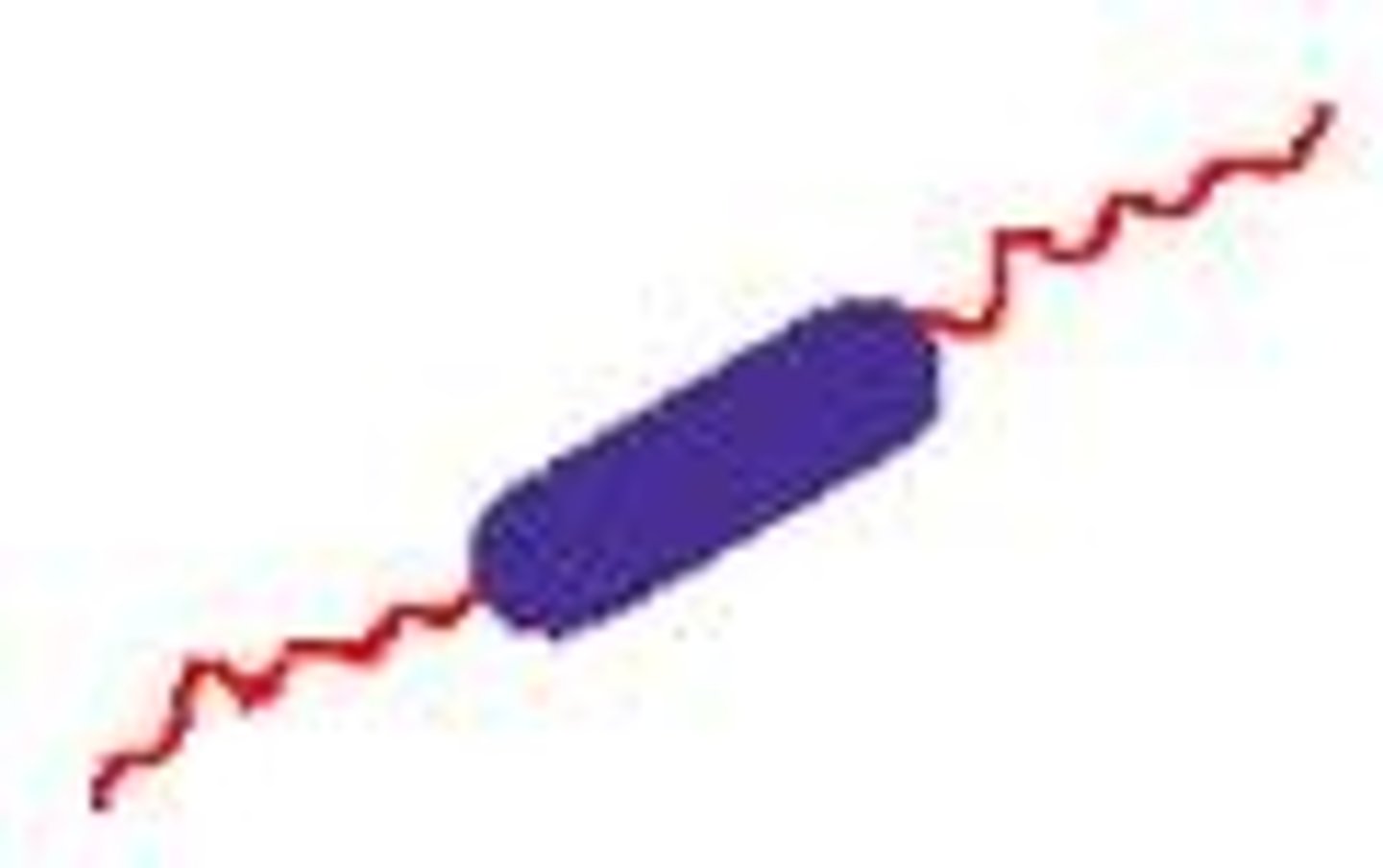
Lophotrichous
Small bunches or tufts of flagella

Amphitrichous
Flagella at both poles of the cell

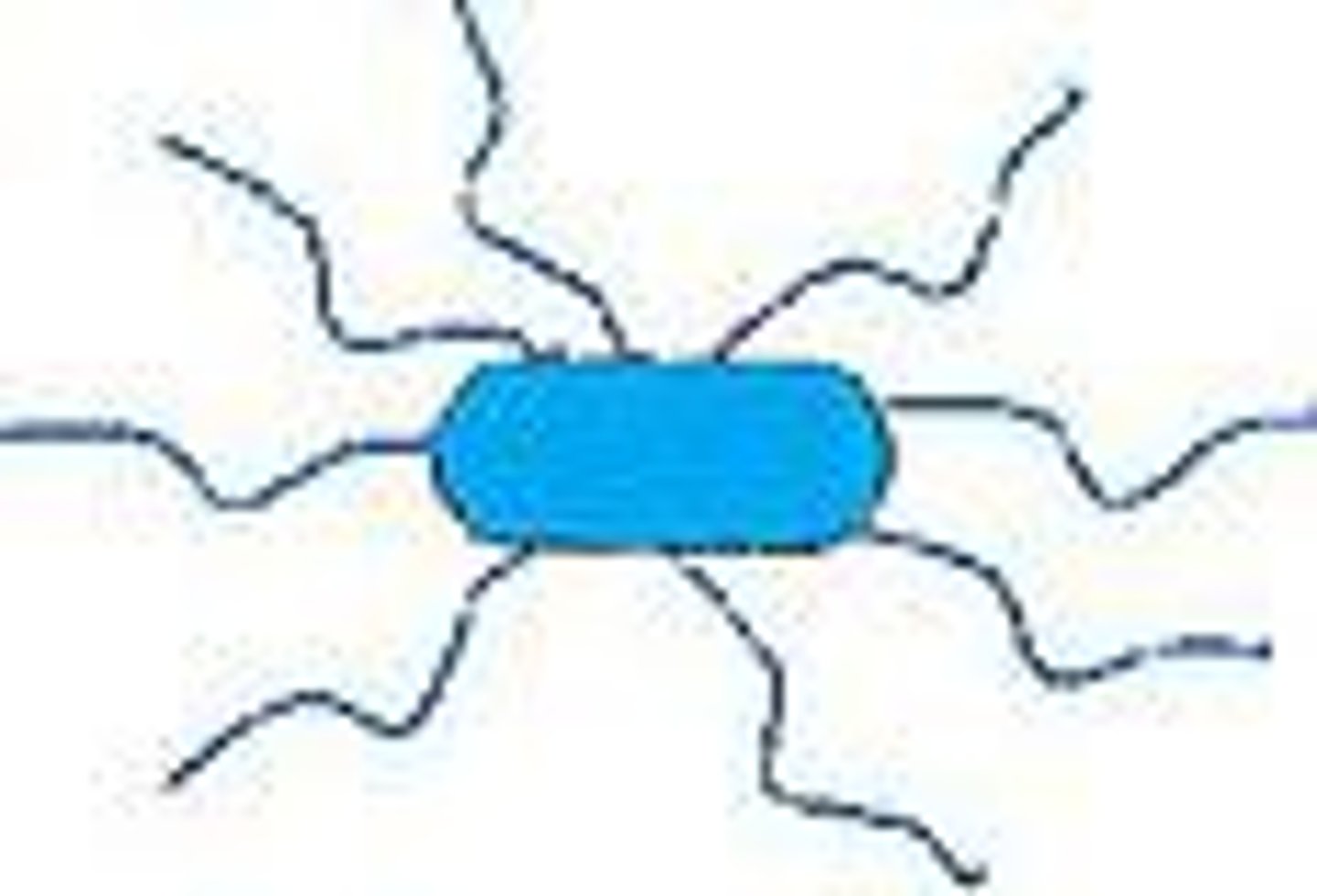
Peritrichous
Flagella dispersed randomly over the surface of the cell
Chemotaxis (Bacterial Movement)
• Bacteria move in response to chemical signals
• Receptors bind extracellular molecules, which triggers flagellum to rotate
Runs (Bacterial Movement)
smooth linear movement toward a stimulus
Tumbles (Bacterial Movement)
flagellar rotation reverses, causing the cell to stop and change its course
Fimbriae
used for attachment
Pili
used for attachment and genetic exchange during conjugation
Glycocalyx
• Composed of polysaccharides, proteins or both
• Varies in thickness
• Used to avoid phagocytosis and for adhesion (biofilms)
Capsule
• Bound more tightly to the cell, denser and thicker than a slime layer
• Visible by negative staining
• Produces a sticky(mucoid) character to colonies
• Encapsulated bacterial cells generally have greater pathogenicity
Peptidoglycan Cell Wall
• Repeating framework of long glycan (sugar) chains cross-linked by short peptide (protein) fragments
• Present in most bacteria
• Provides strength to resist rupturing due to osmotic pressure
Gram Positive Cell
• Thick peptidoglycan
• Teichoic acid, lipoteichoic acid
• One membrane
Gram Negative Cell
• Thin peptidoglycan
• Lipopolysaccharide
• Two membranes
• Porins
Acid-Fast Bacteria
• Mycobacterium sp. and Nocardia sp.
• Contain mycolic acid (a wax)
• Modified Gram-positive structure
• Must use the acid-fast stain to ID important pathogens causing:
- Tuberculosis
- Leprosy
Cell-Wall Deficient Bacteria
• Cell membrane stabilized by sterols, is resistant to lysis(i.e. Mycoplasma pneumoniae)
• Other cell-wall deficient types called L forms are linked to infections
Lipopolysaccharide
• Located in the outermost layer of the outer membrane (OM) in gram-negative bacteria
• Lipid A (endotoxin) stimulates fever and shock
Cytoplasmic Membrane
• A lipid bilayer with proteins embedded
• Provides a site for reactions
• A major action of the cell membrane is to regulate the passage of nutrients into and out of the cell
The Cytoplasm
• 70-80% water
• Soluble proteins, salts, carbohydrates
• Site of nearly all chemical reactions
• Contains the DNA in the nucleoid
Bacterial DNA
• DNA of most bacteria exists in the form of a single circular bacterial chromosome
• DNA is aggregated in a dense area of the cell called the nucleoid
Prokaryotic Ribosome
•Two subunits(30S and 50S)
•Total size is 70S (versus 80S in eukaryotes)
•60% rRNA and 40%protein
•Translates mRNA into proteins
Inclusions or Granules: Storage Bodies
• Non-membrane bound granules
• Usually for storage of nutrients
The Cytoskeleton
• Peptidoglycan layer determines shape of many bacteria
• Others use protein fibers composed of actin and tubulin to alter cell shape
Bacterial Endospores
• Dormant bodies
• Heat resistance due to calcium and dipicolinic acid content
• Cortex, spore coats protect against radiation and chemicals
• Metabolically active vegetative cells can undergo sporulation
• Sporulation is not a reproductive function for most bacteria
• When spores of Clostridium sp. are embedded in a wound with dead tissue, they can germinate, grow, and release toxins
Archaea
• Prokaryotic microorganisms
• Many are found in extreme environments (i.e. psychrophiles)
• Different from members of the domains Bacteria and Eukarya in terms of: cell structure, metabolism, genetics
Bergey’s Manual of Systemic Bacteriology
For studying prokaryotic relationships and origins
Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology
Identify/differentiate unknown microbial species
Organizes the prokaryotes into four major divisions based on cell wall structure:
- Gracilicutes
- Firmicutes
- Tenericutes
- Mendosicutes
Gram-negative cell walls and thus are thin-skinned
Gracilicutes
Gram-positive cell walls that are thick and strong
Firmicutes
Lack a cell wall and thus are soft
Tenericutes
Archaea with unusual cell walls
Mendosicutes
Subspecies, strain, or type
Terms used to designate bacteria of the same species that have differing characteristics
Serotype
Refers to representatives of a species that stimulate a distinct pattern of antibody (serum) responses in their hosts
Plasmid
Can replicate independently
Extrachromosomal DNA
Physically separated from chromosomal DNA