10.0 How the Macroeconomy Works (All in 1)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
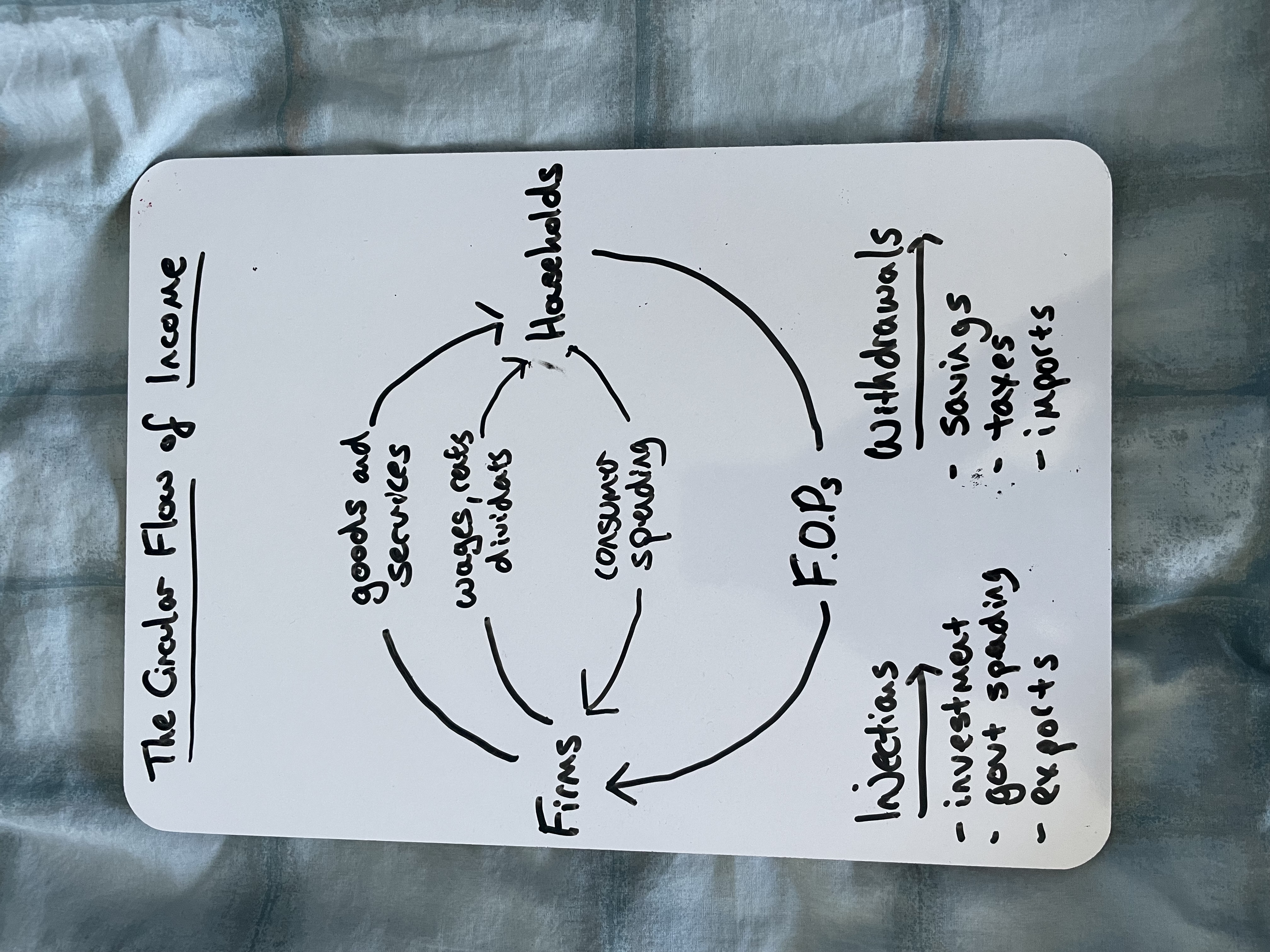
What do households supply to firms in the circular flow of income
Households supply factors of production such as labour and capital
What do firms provide to households in exchange for factors of production
Wages, dividends, and goods and services
What are injections in the circular flow of income
Injections are additions to the economy, including government spending, investment, and exports
What are withdrawals in the circular flow of income
Withdrawals are leakages from the economy, such as taxes, savings, and imports
Draw the Circular Flow of Income
What is the accelerator effect
The idea that changes in national income can cause proportionally larger changes in investment by firms
Why do firms invest more when the economy grows quickly
Firms expect higher future demand and invest in capital goods to expand productivity capacity when national income rises rapidly
What happens to investment when economic growth slows, even if GDP is still rising?
Firms may reduce investment due to expectations of lower future demand
What is the key differences between the accelerator and the mulitplier
The accelerator deals with how investment changes based on growth
The multiplier explains how initial spending leads to an increase in national income
What are the components of AD
C + I + G + (X - M)
C (consumer spending) is the largest, making up just over 60% of GDP
What factors influence consumer spending in an economy
Interest Rates
Consumer Confidence
Disposable Income
MPC and MPS
What is the marginal propensity to consume
MPC is the proportion of additional income that a consumer spends on goods and services
What influences investment by firms
Economic growth
Business confidence
Interest rates
Govt Regulation
What is the accelerator effect in investment
It suggests that investment levels are linked to the rate of change in GDP
What influences government spending in the economy
Trade cycle (recession increases, boom decreases)
Fiscal Policy
What affects the (X - M) or net exports components of AD
Real income
Exchange rates
State of World Economy
Protectionism
Competitiveness
What are the main factors that influence the level of economic activity
Employment
Confidence
Events (e.g. natural disasters, Christmas)
Taxes + Interest rates
How does employment affect economic activity
It influences production and consumption
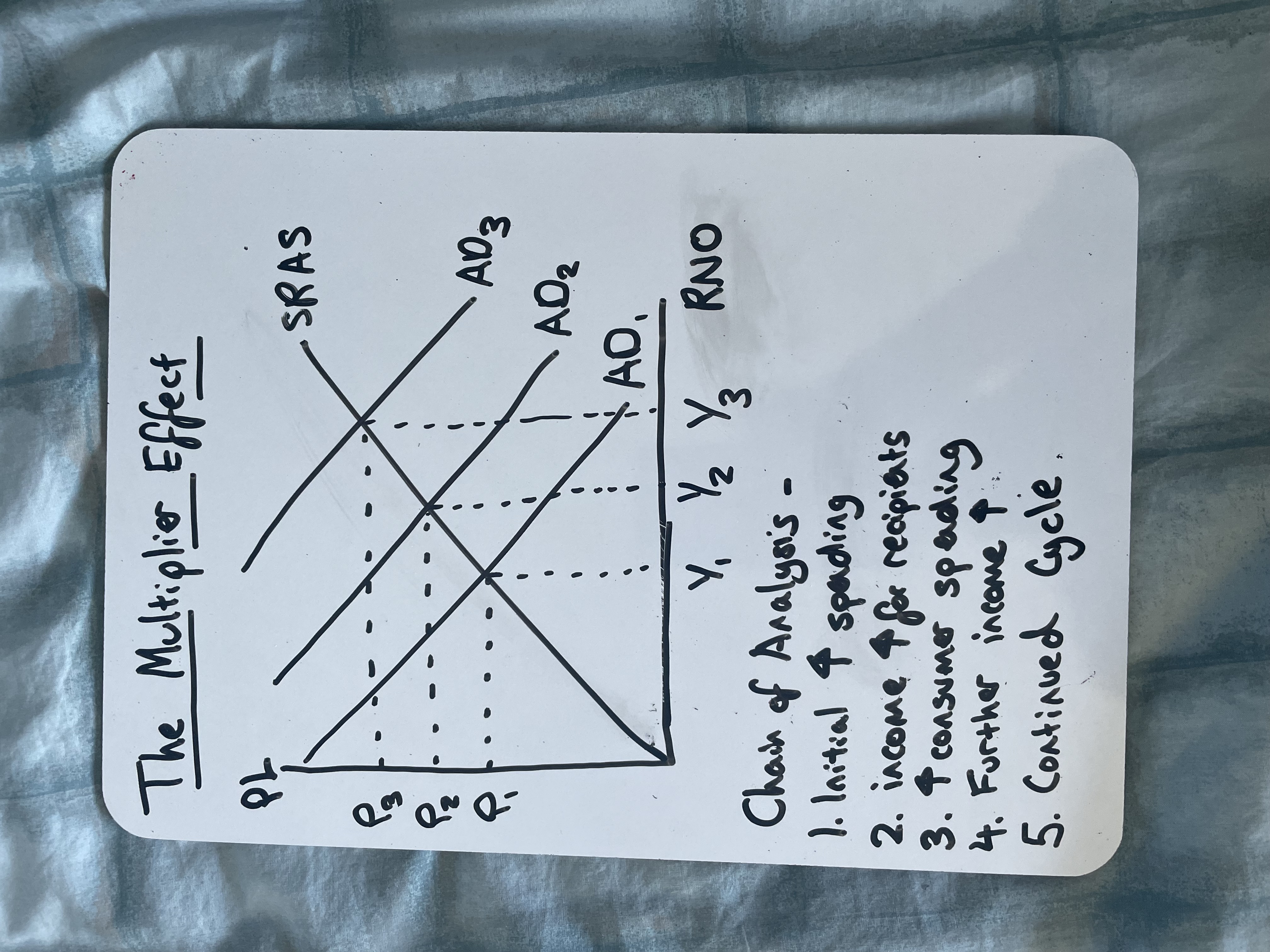
What is the multiplier effect
It is the process where an initial increase in aggregate demand leads to a greater final increase in national income
Why does the multiplier effect occurs
Because one person’s spending is another person’s income, creating a chain reaction
Draw the Multiplier Effect
How is the multiplier calculated using the marginal propensity to consume
Multiplier = 1 / (1 - MPC)
How does spare capacity in an economy affect the multiplier
If spare capacity is high (elastic SRAS), the multiplier effect is larger because more output can be produced without causing inflation
What is reverse multiplier effect
A withdrawal of income from the circular flow can lead to a larger decrease in national income, reducing growth
What factors cause the SRAS curve to shift
Changes in the conditions of supply, such as:
Employment costs
Input costs
Exchange rates
Regulations
Capital Investment
How do rising employment costs (e.g. wages, taxes) affect SRAS curve
They increase production costs and shift the SRAS curve inwards
What impact does a stronger currency have on SRAS
It lowers the price of imports, reducing input costs and shifting SRAS outwards
How can govt regulation affect SRAS
Excessive regulation can reduce business efficiency, causing SRAS curve to shift inwards
What is the long-run assumption about the LRAS curve in classical economics
LRAS curve is vertical, meaning output is fixed at full employment and not affected by price level
What can shift LRAS to the right
Increase in the quanitity or quality of factors of production
In the Keynesian AS curve, what does the horizontal section represent
It shows spare capacity - output can increase without increasing the price level
According to Keynesian theory, what happens when resources are fully employed and AD increases
Output causes inflation, moving the price level up from P2 to P3