Population Cycles - Predation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
do predators reduce prey populations below K?
yes, prey N is lower than K in the presence vs in the absence of predators
do predator prey interactions cause populations to oscilate?
ex. hudson bay company
yearly data on number of lynx and hare furs exploited by trappers
showed large, regular cycles every 10 yrs
N of predator and prey species are highly synchronized - predator N trail prey N
lotka volterra models
foundation for understanding predator prey population oscillations
P
predator population size
H
prey population size
underlying principle of lotka volterra model
population sizes of predators and prey are linked through density dependent influences each species has on the other’s birth and death rates
prey - ____ rates influenced by size of predator pop
predator - ____ rates influenced by size of prey pop
death, birth
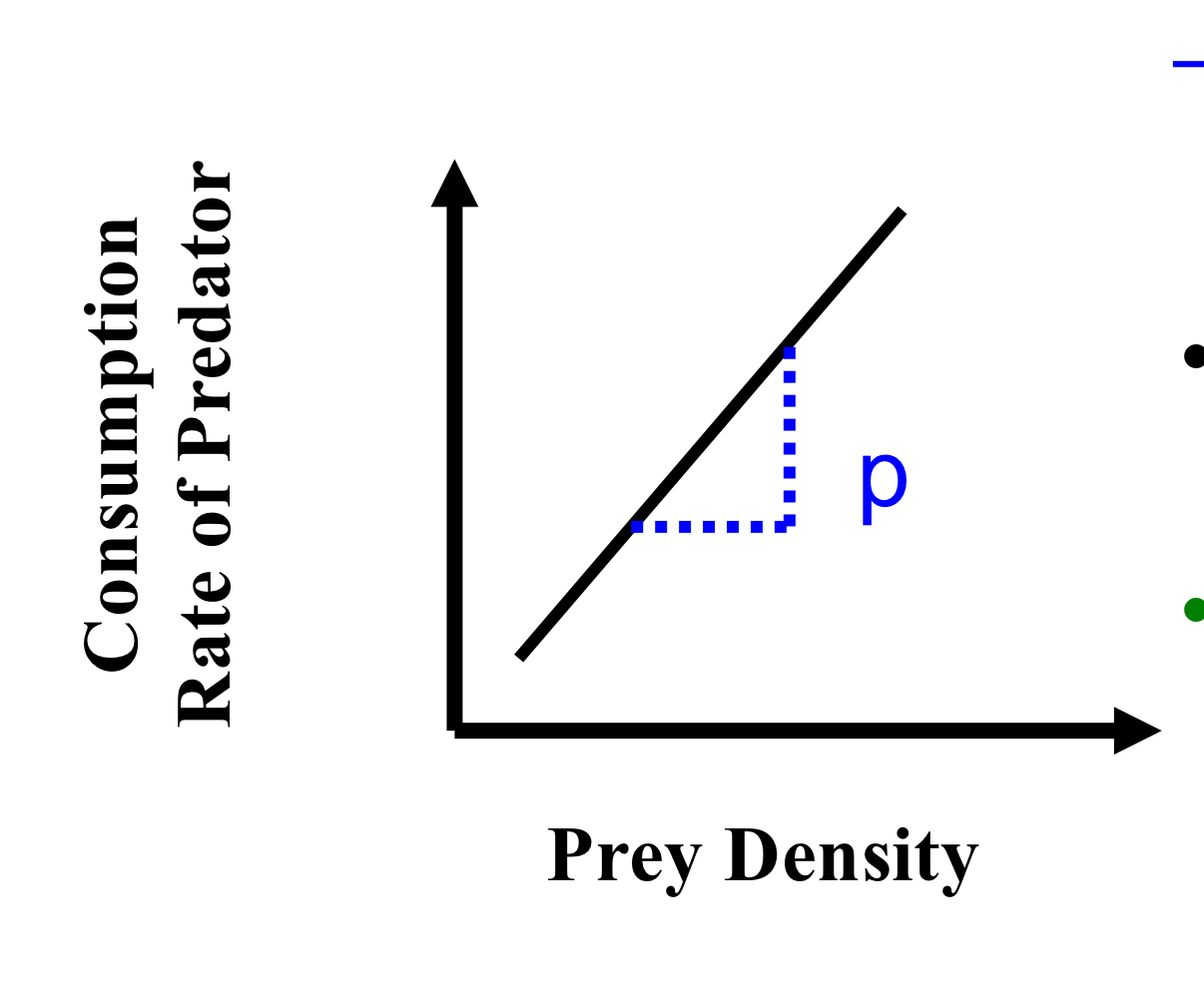
what is it
effects of prey density on predator consumption rate
functional response= relationship between prey density and predator consumption rate
predator consumption rate increases with prey density
p
p
efficiency of predator to capture prey (predator efficiency)
(effects of prey density on predator consumption rates)
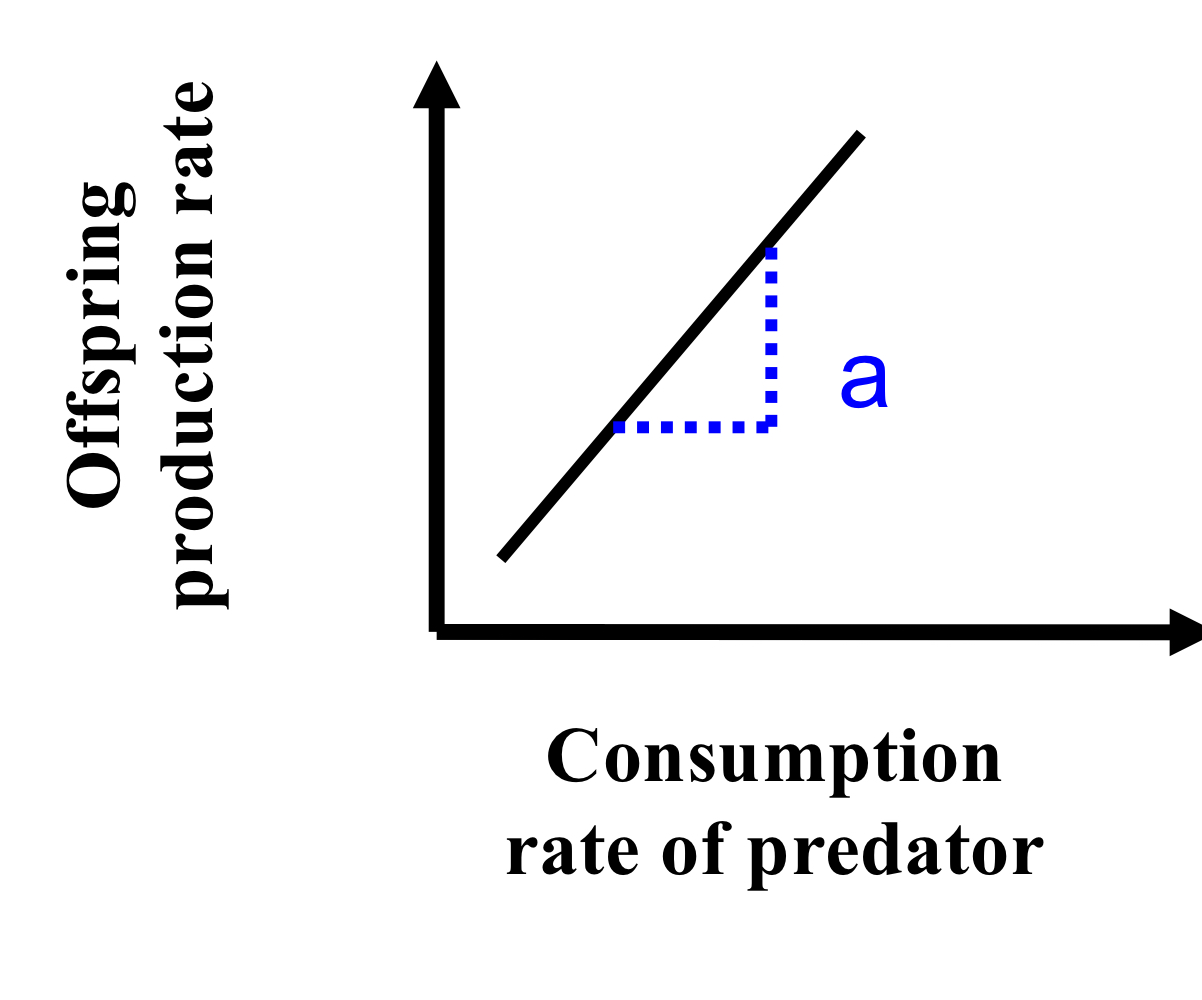
what is it
effects of prey density on predator population size
numerical response
predators produce offspring at a higher rate as their consumption rate of prey increases
a
efficiency of the predator to convert the prey consumed into offspring
(effects of prey density on predator population size)
numerical response
relationship between predator consumption rate and predator offspring production rate
LV model prey population equation has 2 components
exponential growth model (unlimited growth)
mortality of prey pop inflicted by predator only
growth of prey population will _______ as p, H, and P increase
grow faster
LV model assumes
predation varies in direct proportion to H and P
as H and P increase, encounter rates of predators and prey increase (s decreases)
LV predator population equation has 2 components
birth rate of predator
assume b of predators is +vely related to # of prey captured
# of prey captured =pHP
predators do not use 100% of energy consumed to produce offspring
predator pop will increase by apHP
mortality rate of predator
predators die at a constant rate = dP
independent of prey pop size
dependent on prey pop (intraspecific comp)
dH/dt=rH-pHP
prey pop
dP/dt=apHP-dP
predator pop
how do predator and prey pops oscillate
predator-prey interactions result in a stabilization of population growth for both pops
what is happening at dN/dt=0
r=0, b=d, stable equilibrium around which a population size is regulated
here instead of K, we assume that
the prey population size (H) will be regulated around an equilibrium predator pop size (where dH/dt=0)
the predator population size (P) will be regulated around an equilibrium prey pop size (where dP/dt=0)
explain this equation dH/dt=rH-pHp
prey population, rH=how prey pop increases, pHP=mortality rate
explain the equation dP/dt=apHP-dP
a=energy consumed that’s converted to predator offspring, p=efficiency of prey capture, dP=death rate of predators
what do predators acts as on prey species and vice versa
selective pressures
prey traits that reduce chances of being detected and captured by predators will increase what. and what are some examples
fitness. cryptic colouration, chemical defenses, protective armour, behavioural strategies (schooling, flocking)
natural selection will result in what for prey
smarter, more evasive prey
failure to capture prey results in what
reduced fitness of predators
natural selection will result in what for predators
smarter, more skilled predators
explain how predator and prey populations are in arms race
predators and prey coevolve, with the prey one step ahead of the predators to avoid going extinct
predators (can or cannot) reduce prey populations and predator prey interactions cause both populations to oscillate
can
______ models are an extension of the _____ equation and are the basis for understanding predator prey population oscillations
lotka volterra, logistic
population sizes of predators and prey are linked through the _____ influences each species has on the other’s birth and death rates
density dependent
predator prey interactions act as selective pressures, resulting in the ________ of predator and prey species through natural selection
co evolution