(AnaPhy) Lesson 3: Tissues
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Tissue
a group of cells with similar structure and function, plus the extracellular substance surrounding them.
Histology
the study of tissues.
Epithelial Tissues
covers and protects surfaces, both outside and inside the body
exocrine and endocrine glands
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
Mostly composed of cells
Covers body surfaces
Has an exposed surface
Attaches at the basal surface
Specialized cell connections and matrix attachments
Avascular
Capable of regeneration
Simple epithelium
consists of a single layer of cells, with each cell extending from the basement membrane to the free surface.
Stratified epithelium
consists of more than one layer of cells, but only the basal layer attaches the deepest layer to the basement membrane.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
s a special type of simple epithelium, that appears to be falsely stratified.
It consists of one layer of cells, with all the cells attached to the basement membrane.
Squamous cells
flat or scalelike
Cuboidal cells
cube-shaped—about as wide as they are tall.
Columnar cells
tend to be taller than they are wide.
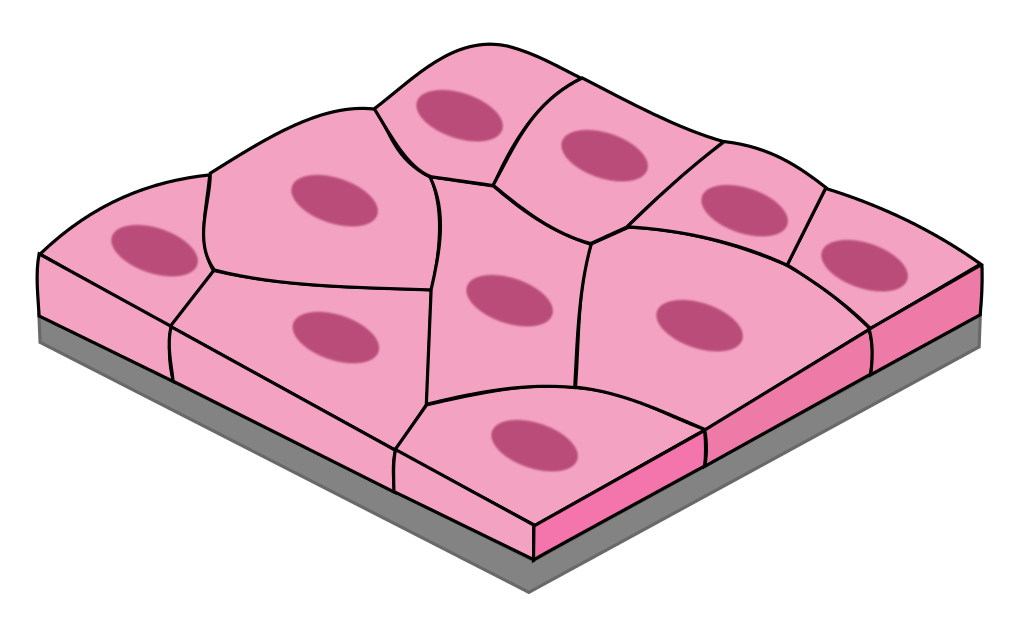
Simple Cuboidal
1 layer of square-shaped cells
Secretion
glands, ovaries, kidneys
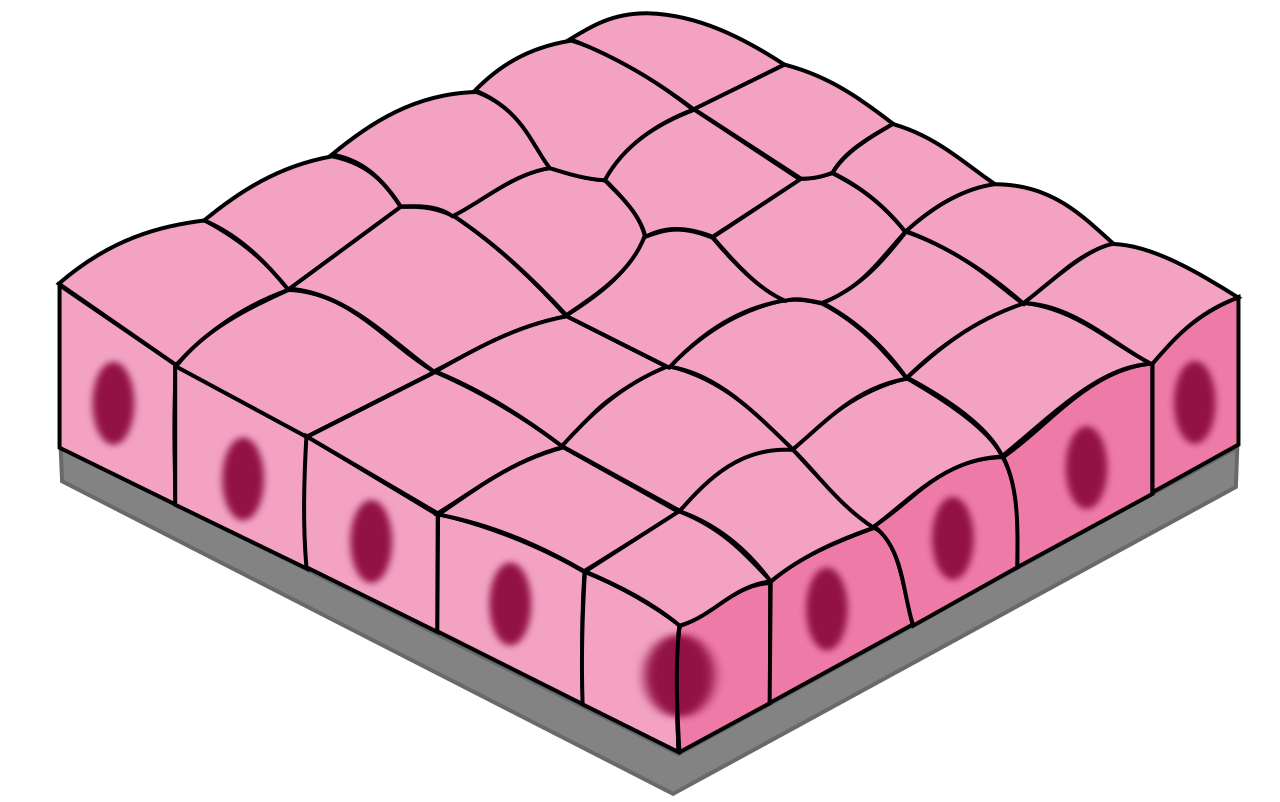
Simple Squamous
1 layer of flat, tile-like cells
good for diffusion & filtration
blood vessels, lungs, heart, kidneys
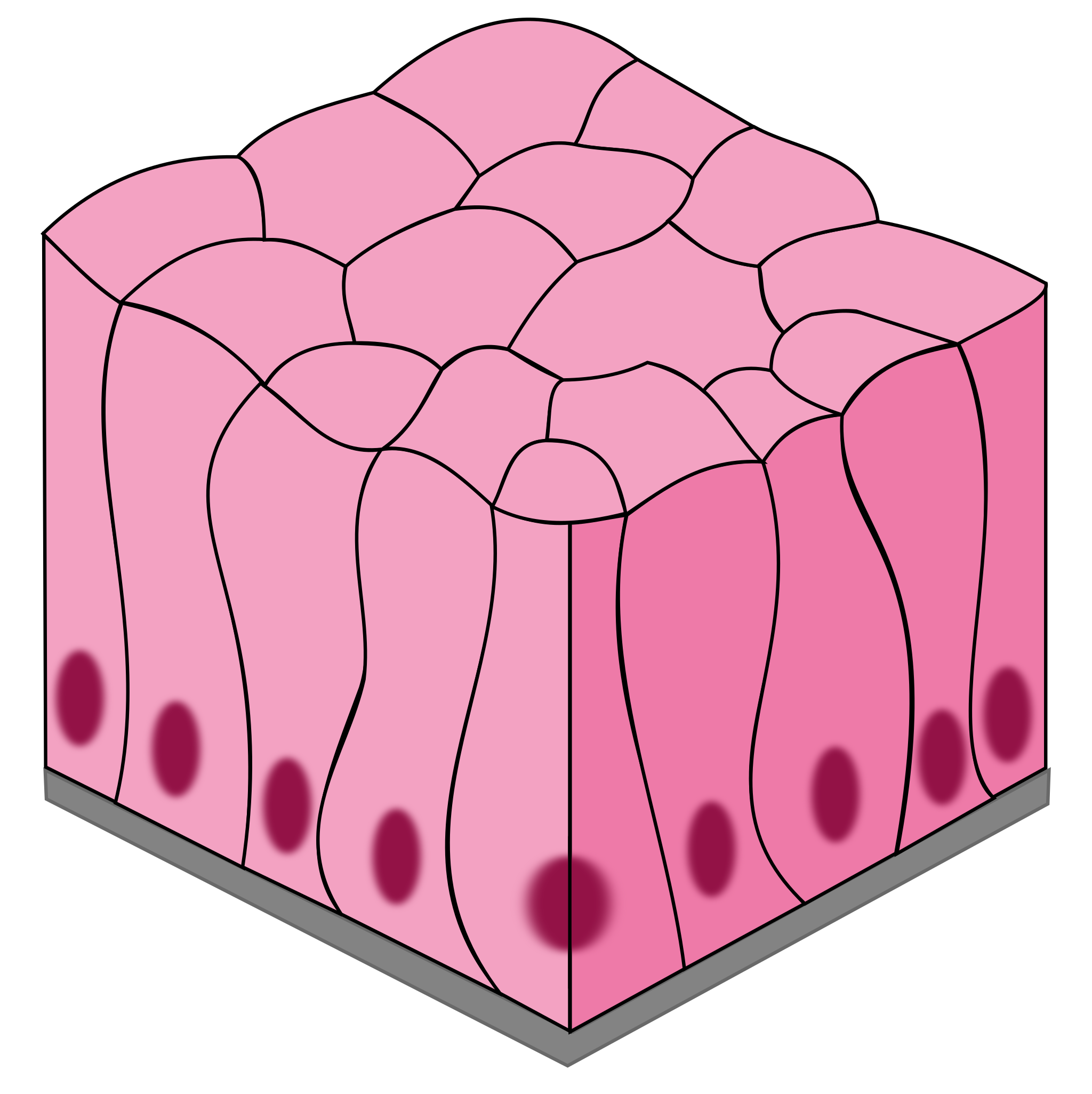
Pseudostratified Columnar
1 layer of tall, narrow cells appears stratified but isn’t
secretes mucus and propel debris out of respiratory tract (cilia)
nasal cavity and trachea
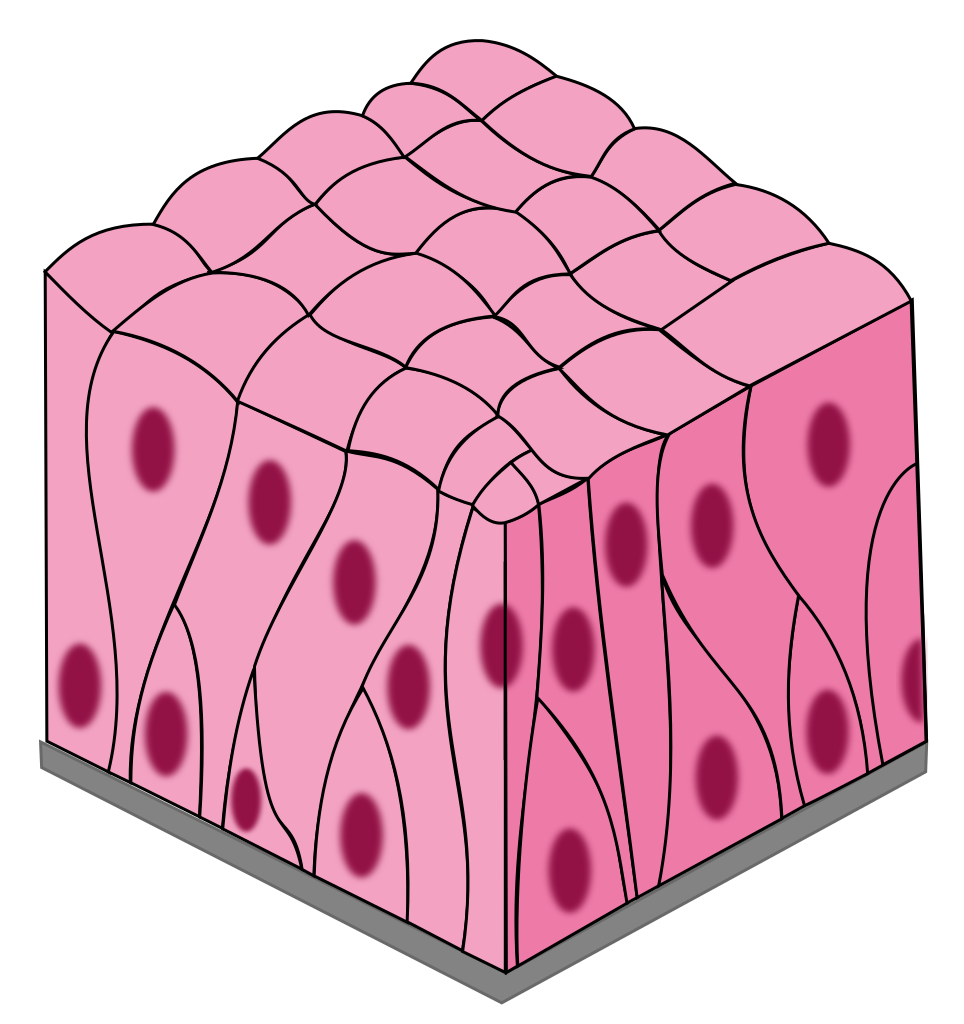
Simple Columnar
layer of tall, narrow cells
secrete mucus and absorption
stomach, intestines, resp. tract
Stratified Squamous
many layers of flat, tile-like cells
protect and acts as a barrier
skin, mouth, throat, esophagus
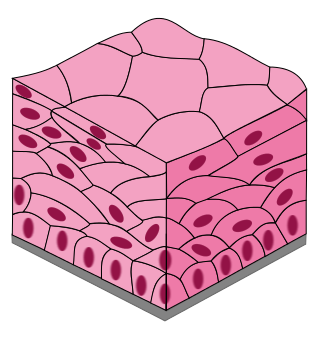
Transitional
special type of stratified epithelium; changes shape -stretched squamous.
hold fluids
urinary bladder
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
The outer layer of the skin
The keratin reduces the loss of water from the body.
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Of the mouth is a moist nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Provides protection against abrasion and acts as a mechanical barrier.
Gastrulation
a critical stage in early animal development when a blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, a multi-layered embryo.
Ectoderm
The outermost layer.
Gives rise to:
Outer epithelium
Neural tube (spinal cord)
Neural crest (nervous system)
Mesoderm
The middle layer.
Gives rise to:
Notochord (bone of spine)
Digestive & urogenital system
Endoderm
The innermost layer.
Gives rise to:
Digestive system: Lining of the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas.
Respiratory system: Lungs.
Endocrine glands: Thyroid, pancreas.
Tight junctions
cell connection structures that form barriers and anchor cells to each other.
Adhesion belts
Are found just below the tight junctions, and help tight junctions anchor epithelial cells to each other.
They prevent the passage of materials between epithelial cells because they completely surround each cell.
Endocrine glands
are ductless glands; they secrete their products (termed hormones) into the bloodstream.
Exocrine glands
glands with ducts; type of gland that release substances through ducts onto the body's surfaces.
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Characterized by tightly packed, parallel collagen fibers, providing high tensile strength in a single direction. (limited space / orderly)
Found in:
Tendons: Connect muscles to bones.
Ligaments: Connect bones to bones at joints.
Aponeuroses: Sheet-like tendons that connect muscles to other muscles or bones.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Collagen fibers are interwoven in a random arrangement, providing strength and resistance to stress in multiple directions. (Scattered & random)
Found in:
Dermis of the skin: Provides strength and resilience.
Joint capsules: Surround and support joints.
Organ capsules: Enclose organs such as the liver and kidneys.
Elastic connective tissues
are a type of dense connective tissue that are characterized by a high proportion of elastic fibers.
The presence of abundant elastin fibers within the extracellular matrix. Elastin is a protein that allows the tissue to stretch and recoil, returning to its original shape.
Areolar Connective Tissue
This is the most common type.
It has a loose arrangement of collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. (connective tissue glue)
Contains various cell types like fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells.
Found beneath epithelia, surrounding organs, and in the dermis of the skin.
Adipose Connective Tissue
Primarily composed of adipocytes (fat cells).
Stores energy in the form of triglycerides.
Provides insulation and cushioning.
Found beneath the skin, around organs, and within bone marrow
Reticular Connective Tissue
Contains a network of reticular fibers that form a supportive framework for cells.
Found in lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow.
Provides a supportive framework for immune cells.
Forms the internal framework of stroma
Cartilage
Firm but flexible.
Provides support, cushioning, and smooth surfaces for joints.
Avascular (lacks blood vessels), so nutrients diffuse through the matrix.
Bone
Hard and mineralized (calcium and phosphorus).
Provides support, protection, and movement.
Stores minerals (calcium) and produces blood cells (in bone marrow).
Blood
Fluid connective tissue.
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Hyaline Cartilage
Most common type.
Found in:
Ends of bones in joints (articular cartilage)
Nose
Trachea
Ribs
Provides smooth surfaces for joint movement, flexibility, and support.
Elastic Cartilage
More flexible than hyaline cartilage due to the presence of elastic fibers.
Found in:
External ear
Epiglottis (flap of tissue that covers the windpipe)
Parts of the larynx (voice box)
Provides support and maintains the shape of structures that need to bend and flex.
Fibrocartilage
Contains a high density of collagen fibers.
Found in:
Intervertebral discs (between vertebrae)
Menisci (cartilage pads in the knee)
Pubic symphysis (joint where the two pubic bones meet)
Provides support and shock absorption in areas that experience high stress.
Osteoprogenitor
Stem cells: These are the precursor cells for all other bone cells, and can differentiate into osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts
Bone-building cells: They are responsible for synthesizing and secreting the organic matrix of bone (collagen) and initiating the process of mineralization (hardening of the bone)
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells: These are the most abundant type of bone cell.
Function: They maintain the bone matrix and regulate bone turnover.
They also play a role in sensing mechanical stress on the bone.
Osteoclasts
Bone-resorbing cells: They are large, multinucleated cells that break down bone tissue.
Function: This process is crucial for bone remodeling, repair, and calcium homeostasis/
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Primarily responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in the body and carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs to be exhaled.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
Key components of the immune system, fighting infections.
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Function: Essential for blood clotting.
Role: When a blood vessel is injured, platelets clump together to form a plug, helping to stop bleeding.
Skeletal Muscle
Appearance: Striated (has visible stripes)
Control: Voluntary
# of Nuclei: Multinucleated
Location of Nuclei: Peripheral
Cardiac Muscle
Appearance: Striated
Control: Involuntary (you don't consciously control it)
# of Nuclei: Mononucleated
Location of Nuclei: Central
Smooth Muscle
Appearance: Non-striated (no visible stripes)
Control: Involuntary
# of Nuclei: Mononucleated
Location of Nuclei: Central
Neurons
These are the functional units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical signals (nerve impulses).
They have specialized structures like dendrites (receive signals), axons (transmit signals), and synapses (junctions where signals are passed between neurons).
Neuroglia
These are supporting cells that provide various functions for neurons, such as:
Protection and defense
Maintenance of the extracellular environment
Support and insulation
Astrocytes
Regulate the chemical environment: Control the levels of neurotransmitters and ions around neurons.
Support and brace neurons: Provide a structural framework.
Oligodendrocytes
Produce myelin, a fatty substance that insulates axons and speeds up nerve impulse transmission in the central nervous system
Microglia
Act as the immune cells of the brain.
Phagocytize (engulf and destroy) debris, pathogens, and damaged cells.
Ependymal Cells
Line the cavities (ventricles) of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
Help circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Schwann Cells
Produce myelin, a fatty substance that insulates axons and speeds up nerve impulse transmission in the peripheral nervous system
Merocrine
secretion involves the release of secretory products by exocytosis.
Apocrine
secretion involves the release of secretory products as pinched-off fragments of the gland cells.
Holocrine
secretion involves the shedding of entire cells
Macrophages
are large cells that are capable of moving about and ingesting foreign substances, including microorganisms in the connective tissue.
Mast cells
are nonmotile cells that release chemicals, such as histamine, that promote inflammation.