BIOL 111 Algae and Seedless Plants
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Shared charactersitics of green algae and land plants
cell wall made of cellulose, store sugars as starch, same pigments for photosynthesis (chlorophyll a and b)
Charophytes
Green algae, chlorophyll a and b, cellulose cell wall, starch, closest relative to land plants
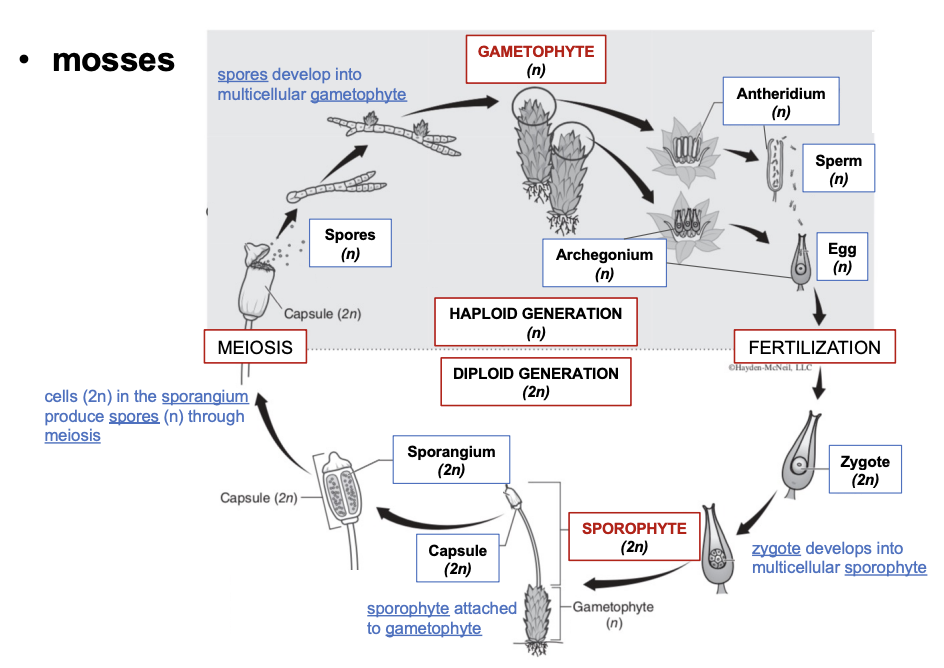
Sporophyte
multicellular diploid individual (2n)
sporangium
location of spore formation and meiosis
gametophyte
multicellular haploid individual (n)
antheridida
location of sperm production
archegonia
location of egg production
Spirogyro
filamentous, colonial green algae, chloroplast in long ribbon shape
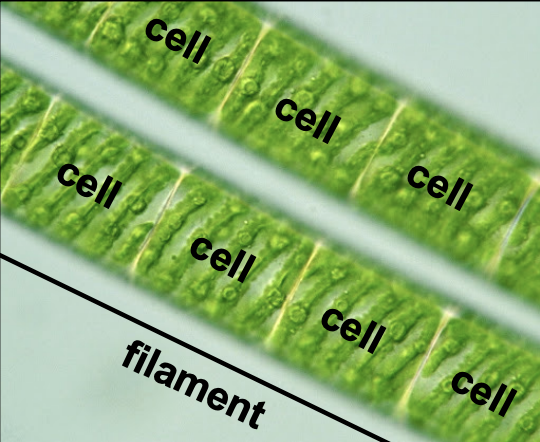
Charophytes — spirogyra
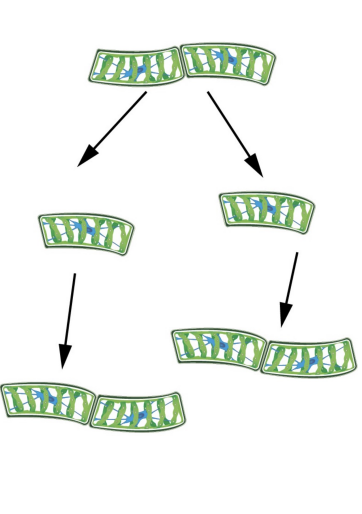
Asexual reproduction of spirogyro
when conditinos are good: cell are haploid (n), they fragment and divide by mitosis so filaments can elongate
Sexual reproduction of spirogyro
when conditions are bad: conjugation, cell (haploid n) from different mating strains (m/f) come together to form diploid 2n zygotes, called zygospores
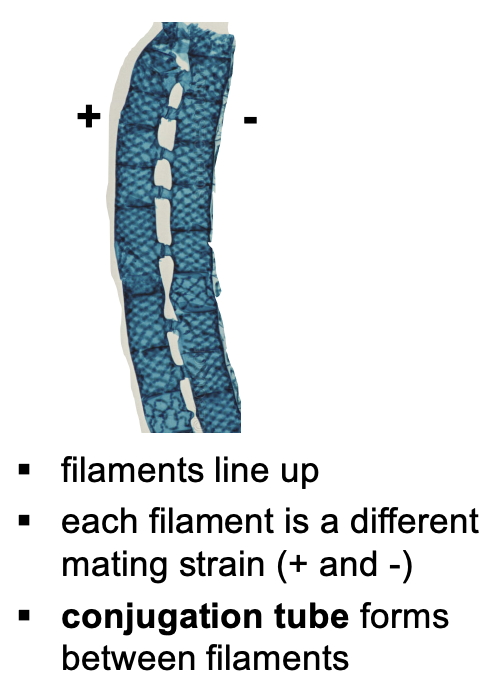
What happens after conjugation tubes form in sexual reproduction of spirogyra?
the cell contents condense (each cell is haploid n) and a cell from one filament moves through tube and fuses with the other cell through the conjugation tube
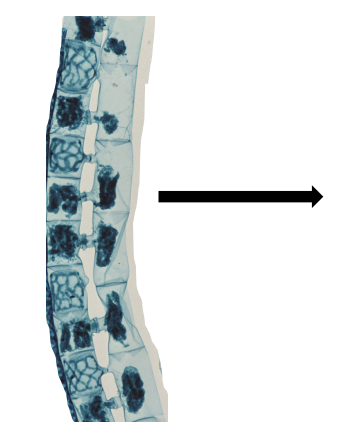
What happens after the contents condense in sexual reproduction of spirogyra cells?
Zygospore is formed (zygote, 2n), has a thick outer coat to survive poor conditions, zygospore will undergo meiosis to form haploid n cells
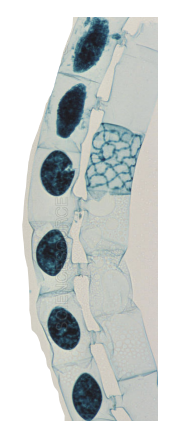
Chara
charophyte, multicellular algae, have gametangia (multicellular structures that produce gametes), have sterile jacket around gametangia that protects gametes from drying out (helped plants transition from water to land)

Chara
What structure is labeled A?
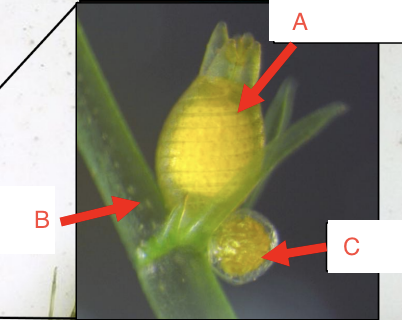
Archegonium, produces eggs
What structure is labeled B?
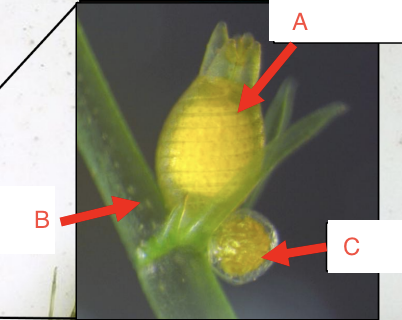
Branch
What structure is labeled C?
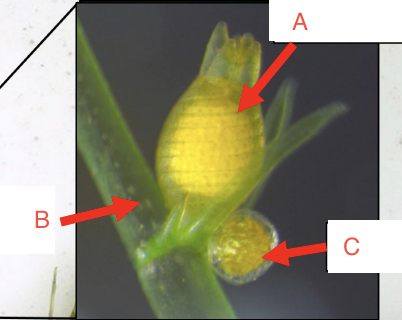
Antheridium, produces sperm
Gametophyte dominant
their main form is haploid, the dominate generation is n
Chara life cycle
f/m gametes n —fertilization—> zygote 2n —meiosis—> spore n —mitosis—> adult n —mitosis—> f/m gametes n
land plants
all multicellular, terrestrial (live on land), the zygote and embryo are protect inside parent tissue, primary producers in m ost terrestrial ecosystems
Land plant challenge: preventing desiccation (drying out)
adaption: wavy, waterproof covering
Land plant challenge: support for body
adaption: fibrous cells for support
Land plant challenge: getting resources for growth
adaption: division of plant into roots, shoots, and vascular tissue
Land plant challenge: gas exchange (O2 and CO2)
adaption: pores in leaves
Land plant challenge: fertilization and protection
adaption: gametangia and pollen
Alteration of generations
Have a multicellular diploid part of life cycle AND a multicellular haploid part of life cycle
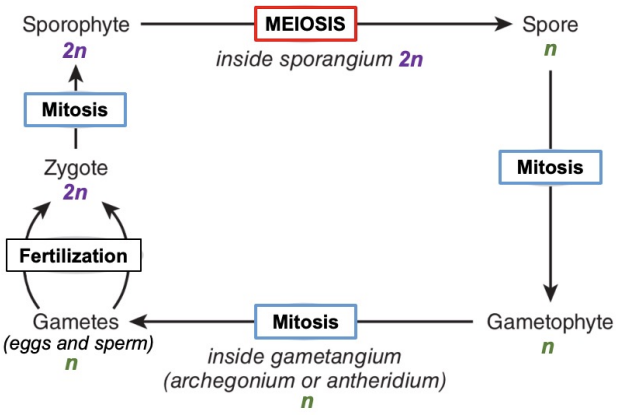
Sporophyte
multicellular diploid 2n phase
Gametophyte
multicellular haploid n phase
Gametophytes produce ___
gametangia
Sporophytes produce ___
sporangia
Sporangia produces ____
spores by meiosis
Alternation of genrations life cycle
fertilization (gametes, egg/sperm, n) —> zygote 2n —mitosis—> sporophyte 2n —meiosis—> spore n —mitosis—> gametophyte n —mitosis—> gametes
Non-vascular land planrs
lack vascular tissue, no internal tissue to transport water and nutrients, places a constraint on how tall they can grow, mosses (part of larger group called bryophytes)
Dominant stage of moss
gametophyte (n)
Moss archegonium (egg)

Moss antheridium (sperm)
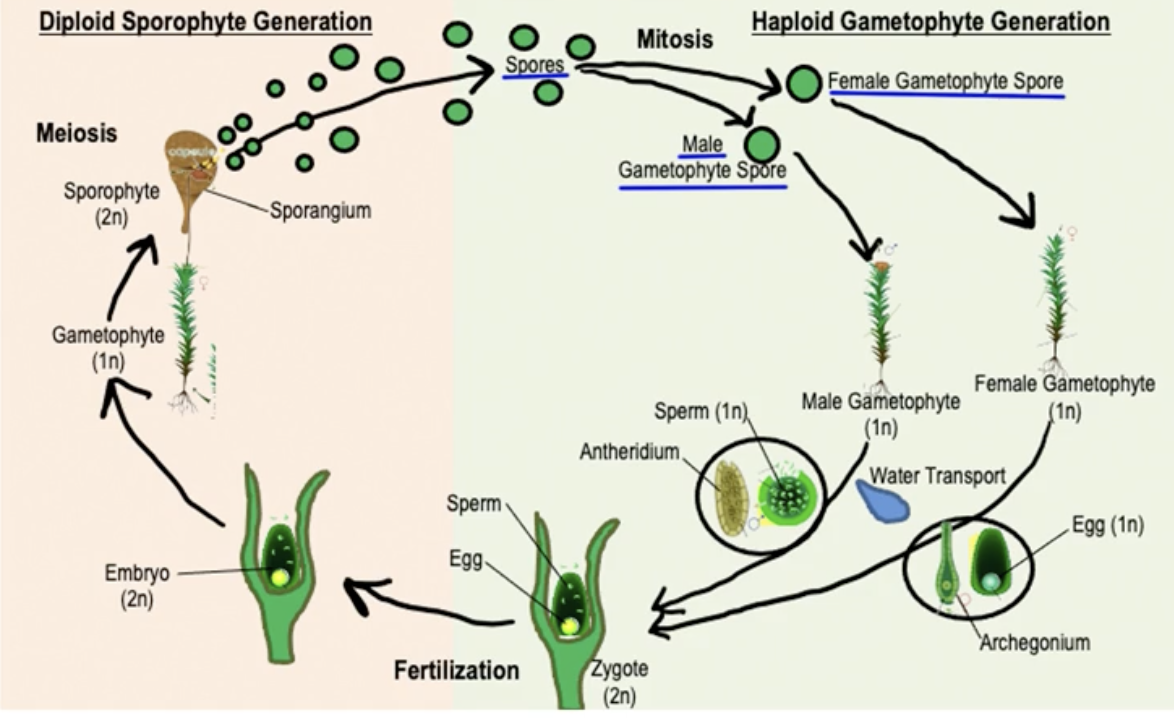
Moss reproduction
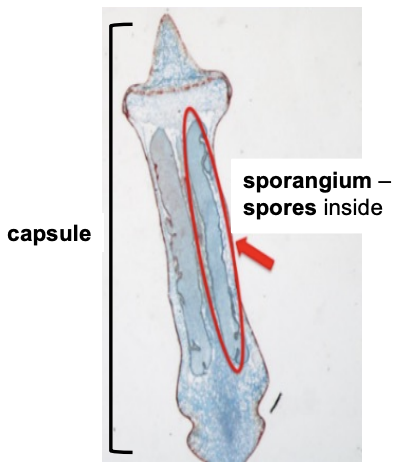
Capsule
holds the sporangium and the sporangium holds the spores
Seedless nonvascular plant cycle
sperm/egg —fertilization—> zygote 2n —> sporophyte 2n —> sporophyte attached to gametophyte 2n —meiosis —> sporangium produces spores n —> spores develop into multicellular gametophyte n —> archegonium/antheridium
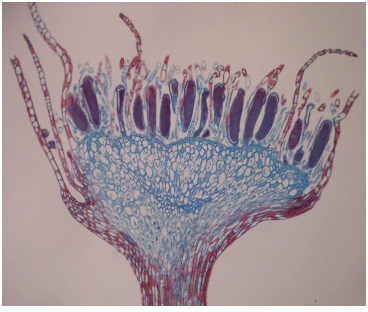
moss antheridium, male reproductive organ, produces sperm, haploid
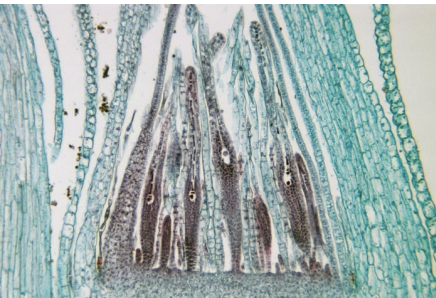
moss archegonium, female reproductive organ, produces eggs, haploid
Sporangium vs sporophyte
sporangium is the sac that contain/produces spores, the sporophyte is the diploid generation of a plant
Vascular land plants
sporophyte 2n stage is dominant, vascular tissue (tissue to transport water and nutrients, allows plants to grow tall)
Fern dominant phase
Sporophyte 2n


fern gametophyte n, sporophyte grows off gametophyte

sorus (cluster of sporangia)
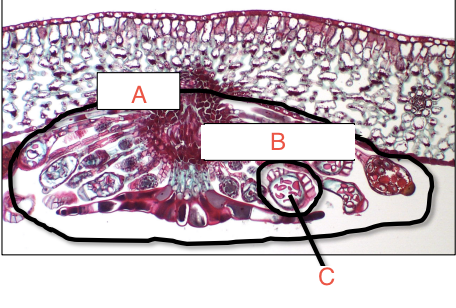
Name structures A-C
Sorus, sporangium, spores