Science 8 Atomic Chemistry Quiz
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Are there more atoms in 1 grain of sand, than there are grains of sand on Earth?
Yes, there is more atoms in 1 grain of sand, than grains of sand on Earth.
Elements
AKA atoms
The “smallest” unit of matter that ALL KNOWN objects are made up of
How many atoms are found in 12.00 grams of carbon?
602 septillion atoms!
Also known as a mole or Avogadro’s number
What are atoms mostly made up of?
Mostly empty space ( proved by gold foil experiment)
Subatomic particles - protons, electrons, neutrons
Protons
a positive subatomic particle of an atom
positively charged
found near in the nucleus ( center )
mass is 1835/1836 AMU or ~1 AMU
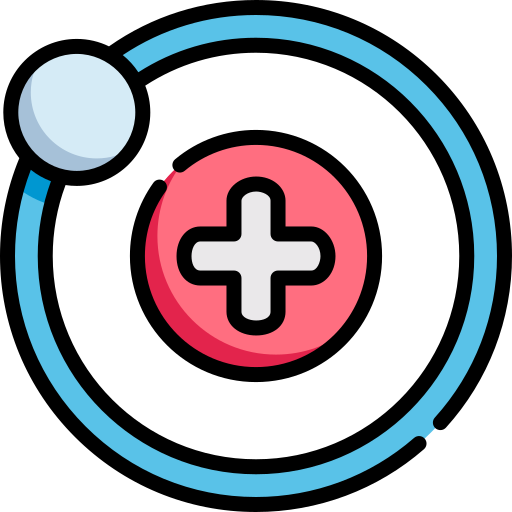

Electrons
negatively charged subatomic particle in atom
it is on the outside of the atom, (shell, orbitals, lobes)
1/1836 AMU, or ~ 0 AMU
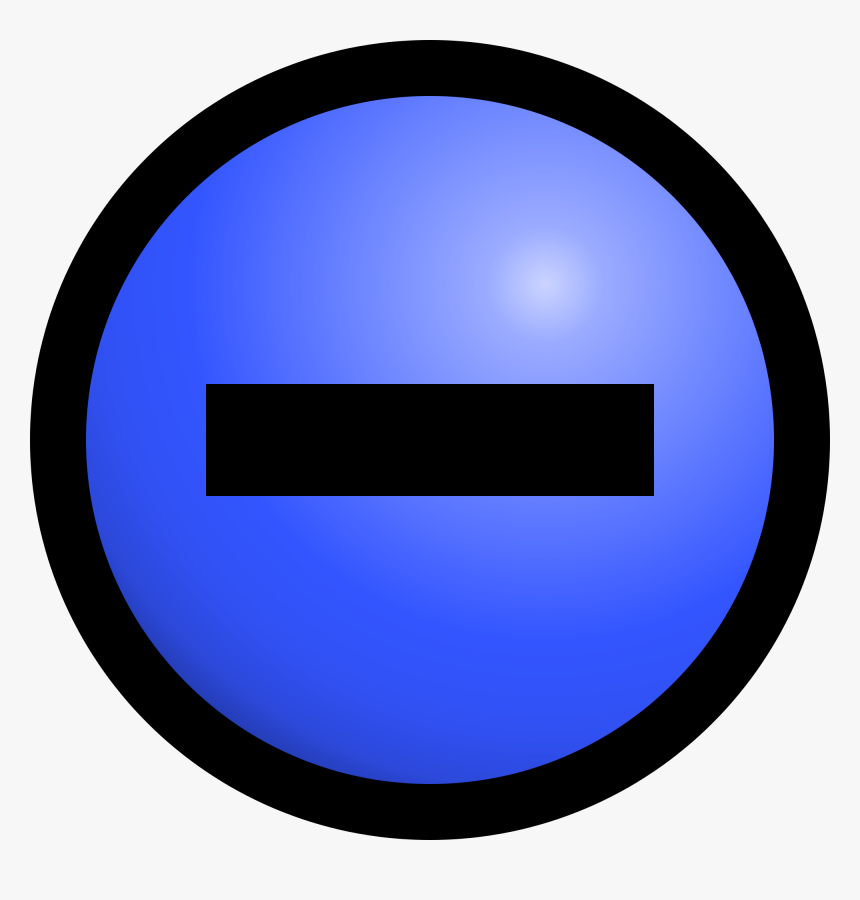

Neutrons
neutrally, no charged subatomic particle in atom
in the nucleus (center)
1 AMU

AMU
=atomic mass unit
How do we determine the Atomic Mass?
Add the # of protons to the # of neutrons!
Ignore the electrons!
In the periodic table, the atomic mass is an average
***ROUND THAT NUMBER ***
ATOMIC NUMBER
=the NUMBER of PROTOMS
How do we determine the number of neutrons?
Atomic Mass - Atomic Number
Number of Electrons
= the ATOMIC NUMBER or # of Protons
Where are Electrons located?
rings, shells, lobes, orbitals of an atom
Electron Orbitals
location of electrons
we need to know the first 3 orbitals K, L, M
1st orbital(closest)=K orbital
2nd orbital=L orbital
3rd orbital=M orbital
4th orbital= N orbital
K-Orbital Max
max of 2 electrons
L-Orbital Max
8 electrons
M-Orbital Max
8 electrons(for our class) or 18
Bohr Model
A model of an element that shows the # of electrons in each orbital of an element.
Valence Electrons
Electrons that are located on the last orbital. Does not mean N ORBITAL. Ex. Oxygen has 8 electrons, and so therefore it would have 6 valence electrons.
THE MAXIMUM # OF VALENCE ELECTRONS IS…
8 electrons. An exception of this is helium and hydrogen, they can only have a max of 2 (only have a K orbital)
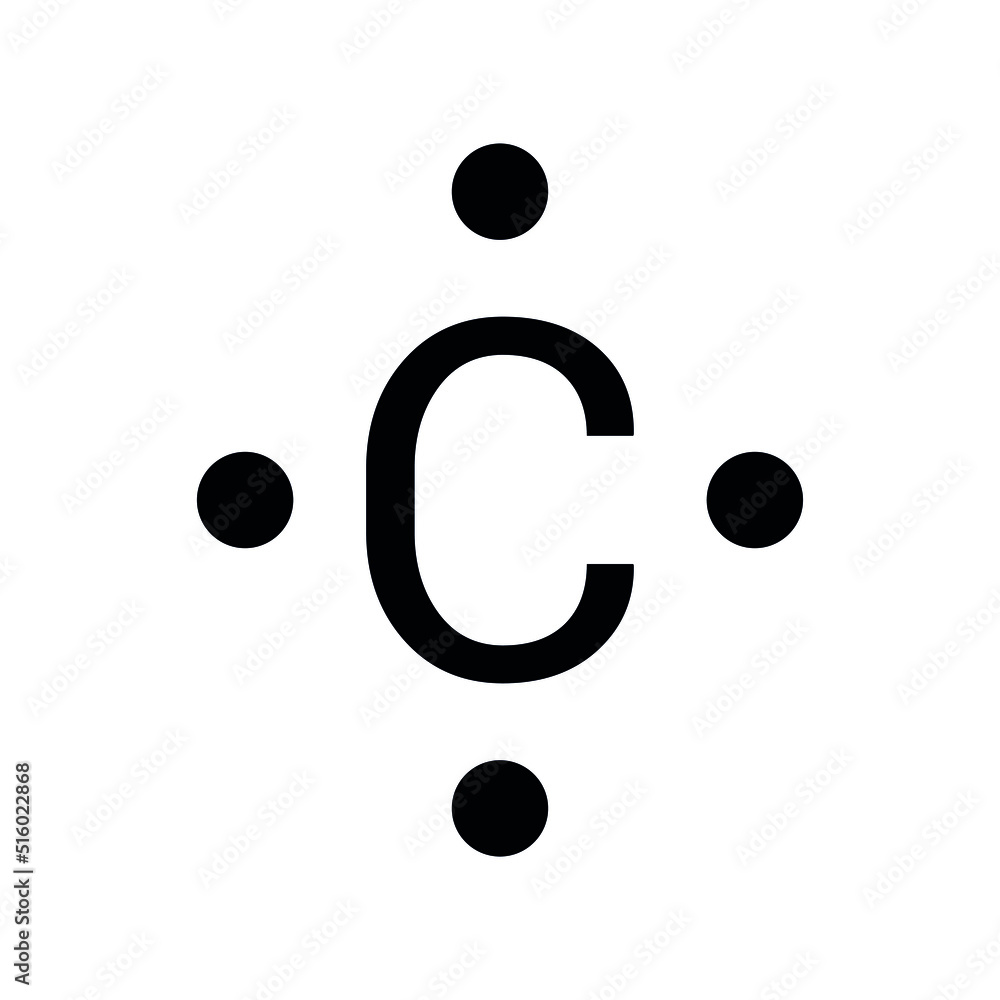
Lewis Dot Structure
shows only the valence electrons of the element
want electrons to be close together in pairs
Periodic Table Patterns Families
Families have the same # of valence electrons, vertical
Ex. Family 3 has 3 valence electrons
Periodic Table Patterns Periods
Periods have the same amount of orbitals, horizontal
Ex. Period 3 has 3 orbitals
As you down a family….
the amount of orbitals increase
As you go across the a period
the valence electrons increase
What’s a nonmetal on the metal side of the periodic table?
Hydrogen only
How many families are there?
8 families
What is 1A family?
Starts with hydrogen, alkali metals, 1 valence electron
What is 2A family?
Alkaline earth metals, starts with beryllium, 2 valence electrons
What is 3A family?
3 valence electrons, starts with boron
What is 4A family?
Starts with carbon, 4 valence electrons
What is 5A family?
5 valence electrons, starts with nitrogen
What is 6A family?
6 valence electrons, starts with oxygen
What is 7A family?
They are halogens, starts with fluorine, 7 valence electrons
What is 8A family?
Noble Gasses, starts with helium, 8 valence electrons
Exception: helium only has a k orbital, 2 valence electrons
It’s a family bc of full valence, and it’s chemical stability
Non-Metals Cut
From boron, staircase to including Uus
Period 1
only hydrogen and helium
1 orbital
Period 2
From lithium, 2 orbitals
Period 3
From sodium, 3 orbitals
Period 4
From potassium, 4 orbitals
Period 5, 6,7
5 orbitals, 6 orbitals, 7 orbitals