Immunology exam 3: HIV pathogenesis
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all done (mostly with speech to text so if issues beware)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What type of virus is HIV?
Lentivirus
components of HIV
integrase, protease, reverse transcriptase & RNA genome surrounded by nucleocapsid, all surrounded by envelope with gp120 spikes connected to gp41
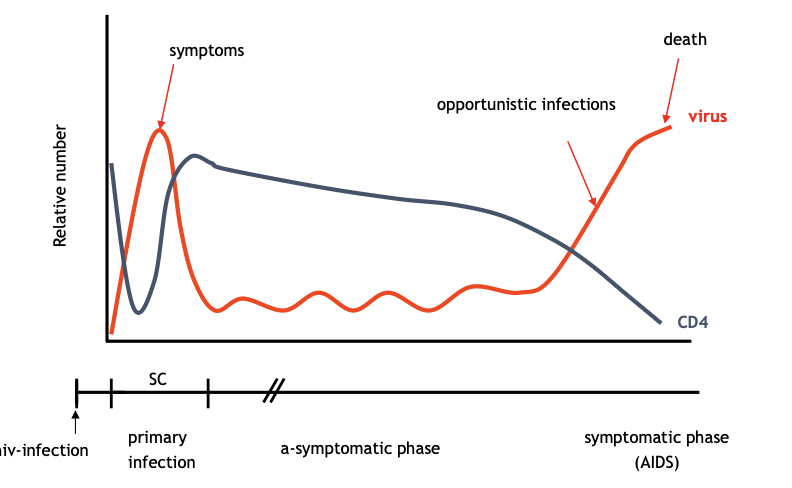
What does this image show?
natural course of HIV infection
What is the hallmark of HIV infection?
Gradual depletion of CD4 T cells
when does HIV become AIDS?
CD4 < 200 cells/ul
what are some characteristics of AIDS (3)
Opportunistic infections (candida, cytomegalovirus, etc), cancers (lymphoma, etc), AIDS dementia
phases of HIV infection
HIV infection, primary infection (flu like symptoms, detectable Ab against it), asymptomatic phase (viral load comes down, CD4 T cell slowly depleating), symptomatic phase (AIDS)
three different clinical courses of HIV infection
Rapid (AIDS 2 yrs post infection), typical (8-9 years for AIDS to develop), slow (10+ yrs for AIDS to develop)
factors that influence the clinical course of HIV infection (3)
The specific virus you have, immune response (adaptive T cell response), genetic background (protective genotypes)
There can theoretically be 10^10 variants produced per day within any single infected person. Explain why there are only millions of viral variants within a person usually
Many mutations caused defects and make the virion be less feasible
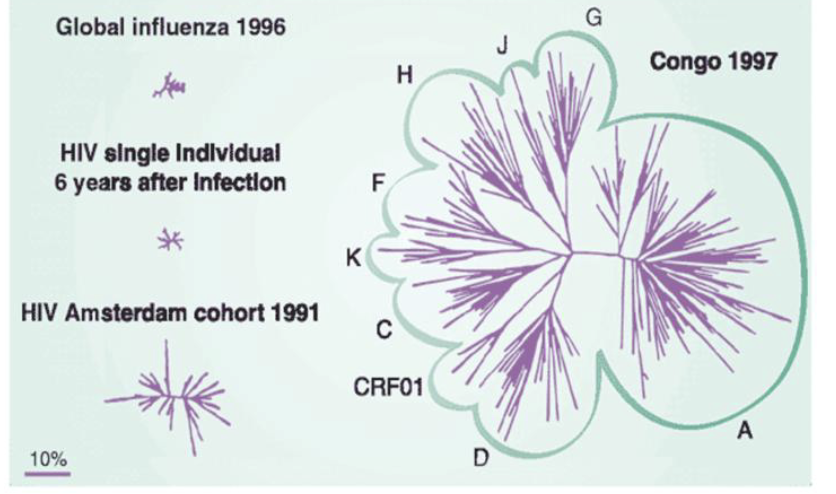
What does this image show?
Just how diverse HIV is: HIV in one person is comparable to the global influenza pandemic in 1996 (influenza already needs a new vaccine every year) and the HIV present in Congo is so variable
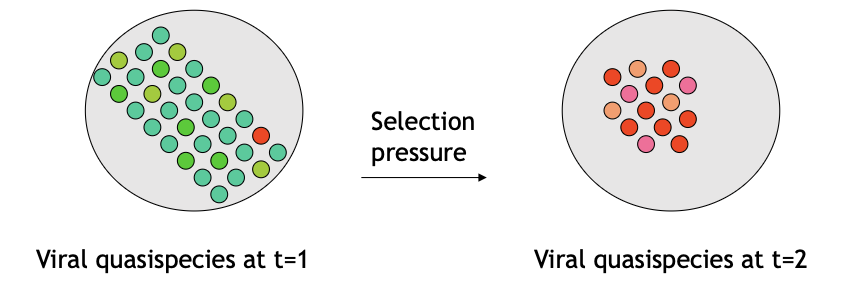
Explain this image
Due to a selection pressure, you can go from only one variant having a specific mutation to all viruses sharing the escape mutation
what are selection pressures for HIV (3)
Escape of CTL, neutralizing antibodies, antiviral drugs, etc
adaptive immune response against HIV (2)
CD8 T cells, antibodies
what do CD8 T cells do with HIV infected cells?
They kill them
what do CD8 T cells need to kill?
detection on HLA-I
What is special about each HLA
Each HLA-allele presents distinct peptides (9 to 11 amino acids long)
CTL long
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte
What is special about positions two and the last position in an amino acid sequence to be presented on MHC
They are the ones that attach to MHC (anchor residues), if altered, the peptide will not bind to that MHC
what happens if there's a mutation in the second position of an amino acid sequence
There will be no presentation on MHC
what happens if there's a mutation outside of the second or last position in an amino acid sequence
It will be presented on MHC, but there will be no recognition by the TCR
what happens as a result of viral escape mutations
Loss of immune control
what was the international controller study?
Genome wide association study for control of HIV infection, analysis of genetic variation in a multinational consortium
what is TL9
Amino acid sequence with nine amino acids: it starts with a T and ends with an L
what does TL9 bind to?
HLA-B7
SNP long
Single nucleotide polymorphism- what most genetic variation in humans is, called that when variation is present in >1% of the population
How much of the variation in the human genome is due to SNPs
90%
Where can SNPs occur?
in both coding and noncoding regions of the human genome
Which SNP was found relevant with HIV infection
Chromosome 6: genetic variation found in HLA-B peptide binding pocket (determining peptide binding) (specifically HLA- B57/B27 associated with slow disease course and B35 associated with rapid disease course)
What is special about HLA-B57? (4)
It was able to control HIV infection for over 10 years, it presents viral epitopes from conserved regions of the virus (gag, nef), viral escape from these regions associated with attenuation of fitness, it has a very high affinity for TCR (strong CD8 T cell response)
What is the HIV spike made of?
gp41 (connect viral envelope) and gp120 (actual spike)
was the antibody response associated with disease progression
no, need to HIV is relatively immunogenic, and majority of people were found capable of eliciting neutralizing antibodies against assumed conserved and vulnerable epitopes
What was HIV sensitivity to autologous antibodies?
HIV escapes from autologous neutralizing antibody responses- they happen too slowly to be able to fight off the virus
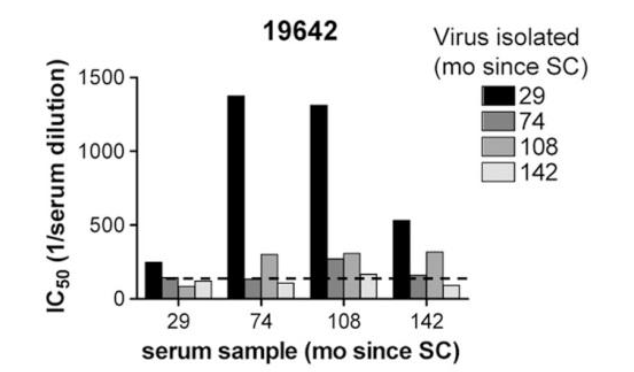
What is this image show?
Sensitivity of viral isolate to autologous antibodies
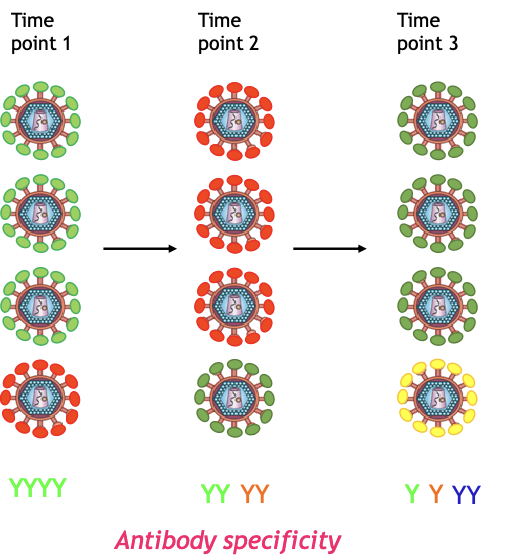
What does the image show?
How HIV escapes the autologous antibody response
Summary of cellular immune response to HIV
Efficient T cell response, viral escape: evasion of CTLs and drives viral evolution, which sometimes leads to viral attenuation
Summary of humoral immune response to HIV
Broadly neutralizing antibodies found in 30% of the patients, viral escape: neutralizing antibodies are ineffective but drive viral evolution
most common ART regimen
Reverse transcript inhibitor and integrase inhibitor
drawbacks of ART (2)
HIV persists and viral reservoir during ART, no immune control after interruption ART
time to eradication with ART
Over 73 years
three current research focuses with HIV
Reduction/ elimination of viral reservoir, boosting of immune response, vaccine development