GCSE Chemistry: Organic Chemistry (T7)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is crude oil?
Crude oil is a finite (non-renewable) resource found in rocks.
its remains of ancient biomass → mainly plankton that was buried in mud.
Mixture of hydrocarbons → mainly alkenes
What is crude oil used for?
Plastics (polymers)
Fuels :
petrol → cars
Diesel → buses , Lorrie’s
Kerosene → aircraft
Heavy fuel oil→ships , power stations
Liquified petroleum gas (LPG) →heating & cooking gas
Cosmetics
Pharmaceuticals
How is crude oil formed?
Crude oil is formed over millions of years from the remains of tiny sea creatures called plankton which were buried in mud and sediment
These organisms die,sink to the ocean floor and are gradually covered by layers of sediment
over millions of years→ due to high pressure and temperature of overlying layers causes organic biomass to transform into crude oil.
Why’s it important?
Society relies heavily on it for both energy and materials→ scientists researching alternative fuels and recycling plastics
What is a hydrocarbon?
Molecules made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
What is an alkane ?
Saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they contain only single bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
What is the general formula for alkanes?
CnH2n+2
if know num. of carbon atoms in the alkane (n) →can calculate the number of hydrogen atoms
To do that → multiply num of carbon atoms by 2 & then +2
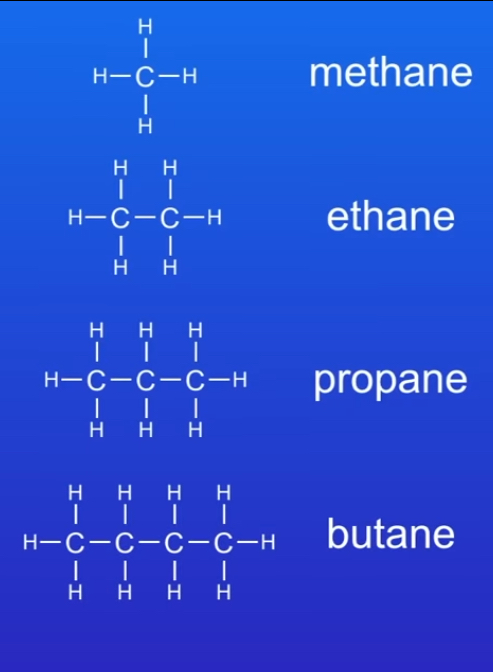
What are the first 4 alkanes ?
methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
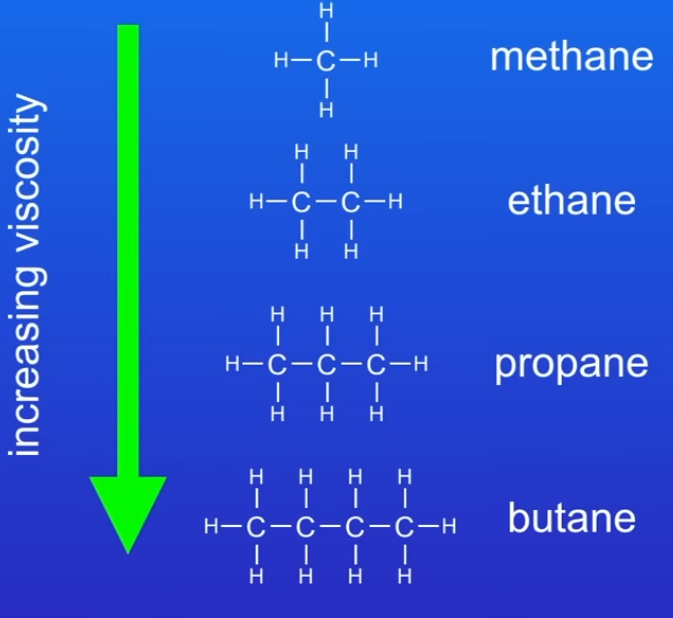
What are the 3 properties of a hydrocarbon?
Viscosity → tells us the thickness of a fluid→As size of hydrocarbon molecules increase → molecules get more vicious
Flammability → how easily a hydrocarbon combusts (burns)→as size of hydrocarbon increases →molecules get less flammable
Boiling point →the temp. At which a liquid turns to a gas →size of hydrocarbons molecules increases the boiling point increases
Describe the properties of long chained hydrocarbons.
have a high viscosity → flow slowly
aren’t very flammable-.hard to burn
have high boiling points and melting points.
Not volatile
Describe the properties of short chained hydrocarbons.
They have low viscosity
They are highly flammable
They have low boiling points
They are volatile
Describe complete combustion of hydrocarbons
Combustion = chemical reaction where a substance burns in oxygen to release enegy
Complete combustion = Hydrocarbons (e.g alkenes) burns fully in plenty of oxygen producing carbon dioxide and water only & release energy
During combustion the hydrogen and carbon atoms in the fuel react with oxygen ( the carbon and hydrogen are oxidised).
If the oxygen is unlimited, this reaction produces carbon dioxide and water. (This is called complete combustion).
If limited oxygen →promises carbon monoxide or carbon (soot) →less energy is released and dangerous gases are made
How can hydrocarbons be used as fuels?
-release energy when they burn during combustion (chemical reaction)
+;
burn easily in air
Release large amounts of energy per gram
Readily available from crude oil & natural gas
Transported & stored easily
Eg:
natural gas →methane (CH4)→ home heating ,cooking gas
Petrol → mixture of alkanes → car engines
Diesel → longer chain alkanes → Lorrie’s & trains
Kerosene→ medium -chain alkanes → jet engines
Why do we separate hydrocarbons?
Different hydrocarbons have different uses and in order for them to be useful they need to be separated.
(we separate them via fractional distillation)
Writing balanced equations for complete combustion of hydrocarbons?
General formula:
Hydrogen + O2 → CO2 + H2O
EG: methane:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide & water
Balanced ;
1 carbon atoms
4 hydrogen
4 oxygen atoms on both sides
Describe fractional distillation
- used to make hydrocarbons in crude oil useful
Crude oil is separated into fractions →fractions contain hydrocarbons with a similar number of atoms
Firstly crude oil is heated to a very high temperature →boils →so all of the hydrocarbons evaporate and turn into gas
The crude oil vapour is now fed into the fractional distillation column. The column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top.
The hydrocarbon vapours now rise up the column. Hydrocarbons condense (turn back into liquid)when they reach their boiling point and the liquid hydrocarbons then collect in trays and drain out.
Remaining hydrocarbons continue moving up the column & condense when reach their boiling points
As very long chained hydrocarbons have high boiling points →they’re removed at the bottom of the column
very short chained hydrocarbons have low boiling points →don’t condense → they’re removed at the top of the column as gases
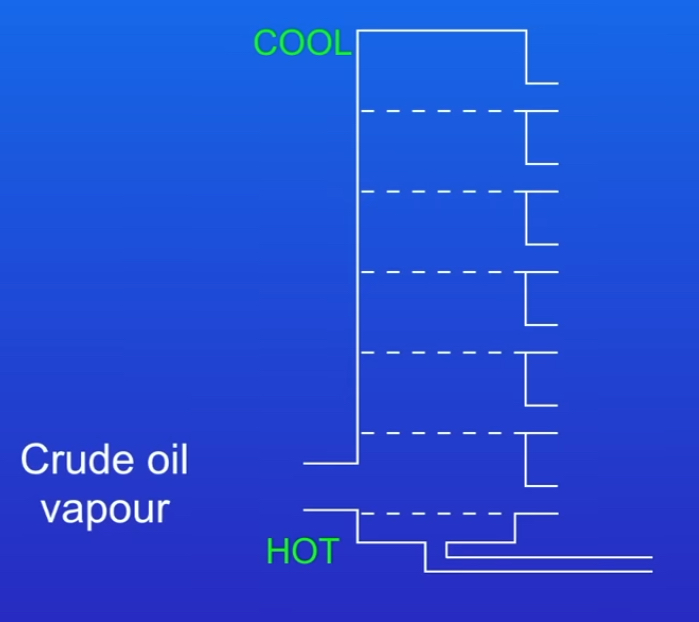
What are fractions ?
Groups of hydrocarbons with similar Boiling points that are separated from crude oil during fractional distillation
Some fractions used as fuels
Some used as feedstock for petrochemical industry
Feedstock = a chemical used to make other chemicals
EG:
solvents
Lubricants
Detergents
Polymers(
Why don’t long chained hydrocarbons make very good fuels?
Because they aren’t very flammable
What is cracking?
A chemical process that breaks down long chained hydrocarbons into shorter , more useful hydrocarbons.
What are the products of cracking?
A long chained alkane is converted into a shorter chain alkane and an alkene.
What is catalytic cracking?
Cracking is a type of thermal decomposition which requires high temperature (550 degrees C) and the use of a a catalyst → e.g zeolite
Heat long chained hydrocarbons to vaporise them
Then the vapour can be passed over a hot powdered aluminium oxide catalyst
Converts alkanes → shorter alkanes + alkenes
Helps meet demeans for petrol & plastics
Happens faster & at lower temp due to catalyst
What is steam cracking?
Cracking is a type of thermal decomposition which requires high temperature (over 850 degrees C) and steam.
Heat long chained hydrocarbons→alkane → to vaporise them
Mix this vapour with steam and the heat them to a very high temperature
Long chains break apart into :
short chain alkanes (used as fuels)
Alkenes (to make plastic)
What is an Alkene and its formula ?
Unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one double bond between carbon atom (C=C)
Made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms
Type of hydrocarbon
General formula :
CnH2n
have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes
Are unsaturated hydrocarbons due to → double bonds
Examples of alkenes
ethene → C2H4
Propene → C3H6
Butene →C4H8
Pentene→ C5H10
Test for alkenes
add bromine water to the solutions
Alkene present:
Bromine water turns colourless
Alkene not present:
Bromine water stays orange
Balance an equation for cracking
1)choose shorter alkane
2)work out what’s missing to make the atoms balanced
3)remainder is usually an Alkene (with a C=C double bond and fewer Hs)
EG:
C25H52 → C20H42 + C5H10