Coastal Environments Exam 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Geomorphology
the study of the characteristics, origin, and development of landforms
LIDAR
Light Detection and Ranging
Explain LIDAR
Remote imaging method that users laser light, often used by airplanes or satellites.
Multibeam Sonar
Employs an array of sound sources and listening devices to obtain a profile of a narrow strip of seafloor
Coastal Zone
Where the land meets the sea
MWL
Mean Water Level
Tidal Range
the difference in water level between a high tide and a low tide
Intertidal Zone
Land that can be submerged or exposed depending on tide level
Closure Depth
Where wave orbitals make contact with the sea floor
Shoaling
When a wave becomes modified due to wave orbitals hitting the sea floor
Breaker Zone
Where waves break
Surf Zone
The region between the breaking waves and the shore.
Swash Zone
Where land is constantly exposed due to wave cycle
Foreshore
That part of a shore that gets wet under normal conditions
Backshore
Area between dunes and the foreshore; doesn't get wet under normal conditions
Shoreface
Coastal area underwater
Offshore
Area outside the coastal area
Littoral Zone
Portion of the coastal profile where sediment can be transported by wave action
The five coastal classification strategies
Visual (What it looks like)
Genetic (How it was formed)
Process (What processes are shaping the coast)
Energy (Based on hydrodynamic energy)
Morphodynamic State (How the morphology of the coast affects wave action)
Morphodynamic State
the interaction and adjustment of the seafloor topography with fluid hydrodynamic processes
Lithosphere
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
Asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere "floats".
3 types of crustal plate boundaries
1. Convergent
2. Divergent
3. Transform
Convergent plate boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other.
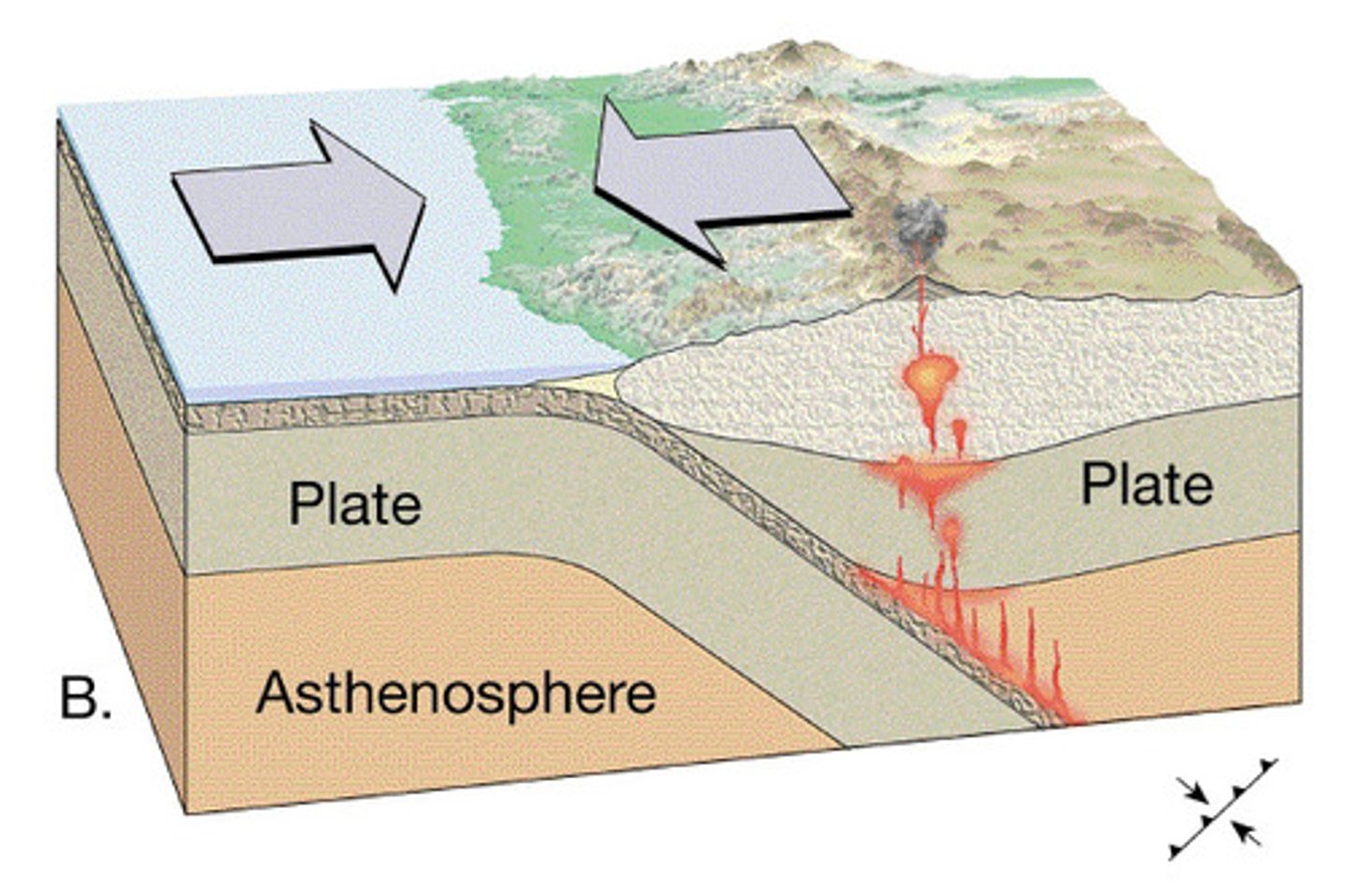
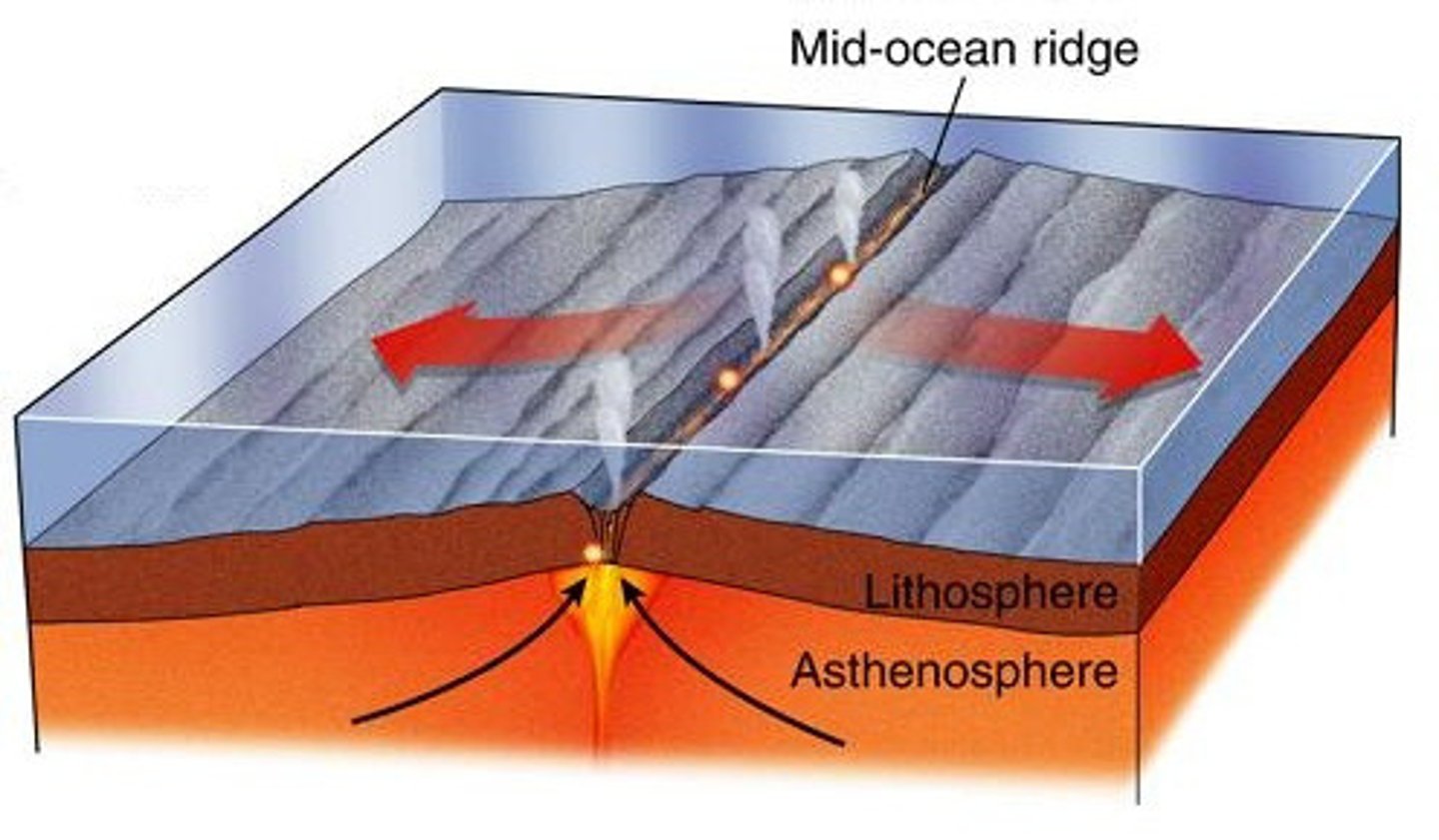
Divergent plate boundary
Boundary between tectonic plates in which the two plates move away from each other, and new crust is created between them
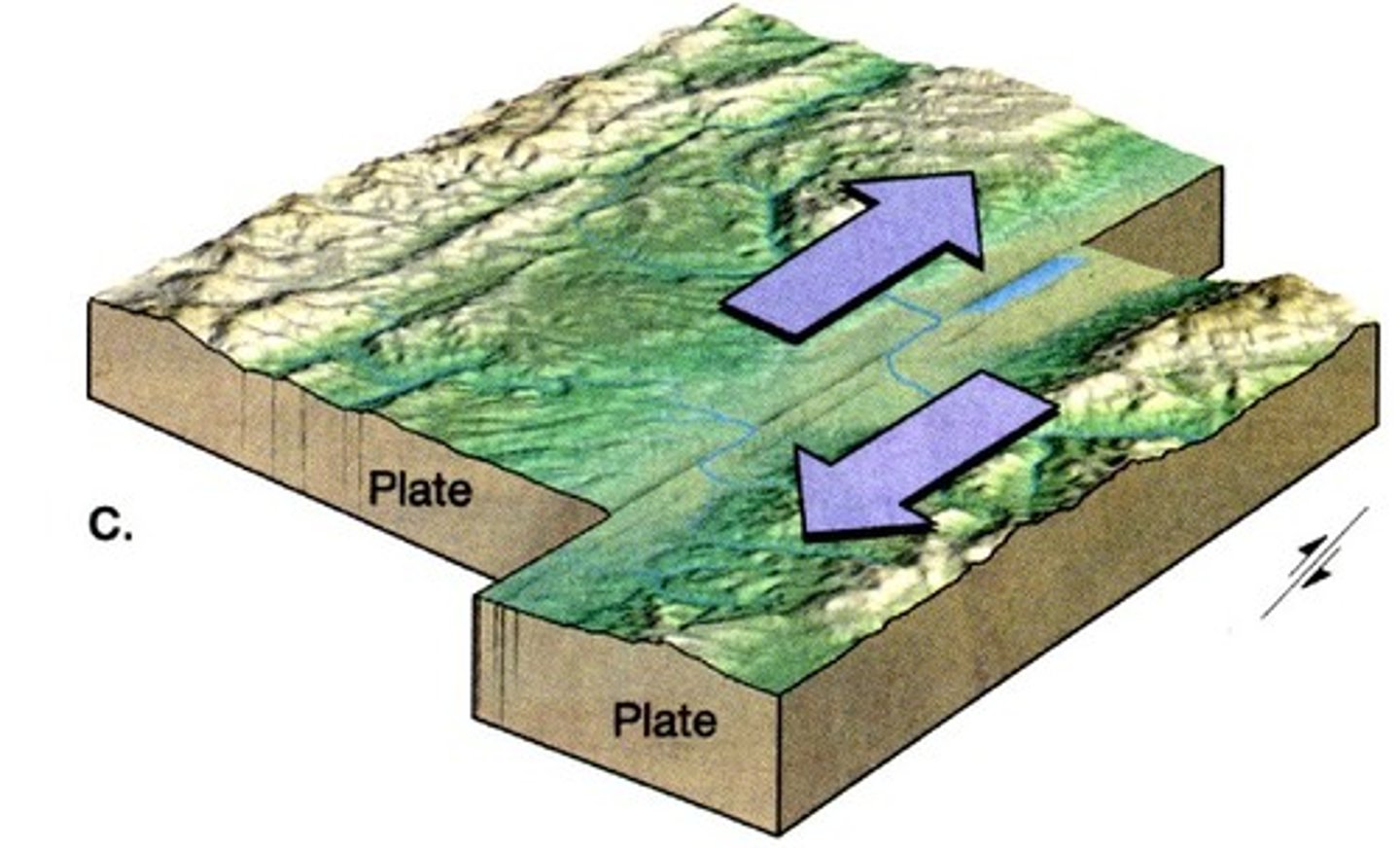
Transform plate boundary
Boundary between two plates that are sliding past each other.
Tidal Gauge
A mechanical instrument consisting of a stilling well and a float used to measure tidal levels
Geoid
the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity and rotation of Earth alone, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent.
Crustal Uplift
surface moves upward from heat beneath
Crustal Subsidence
The sinking of the crust
Erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away; Opposite of deposition
Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations; Opposite of erosion
Equilibrium Theory of Tides
Simplistic tide theory that assumes that solar and lunar gravity are the only tidal influences
24 hours and 50 minutes
Length of time of a full tidal cycle (two high tides and two low tides)
12 hours and 25 mintutes
Time between two high tides or two low tides
6 hours and 12.5 minutes
Time between a high tide and low tide, or vice-versa
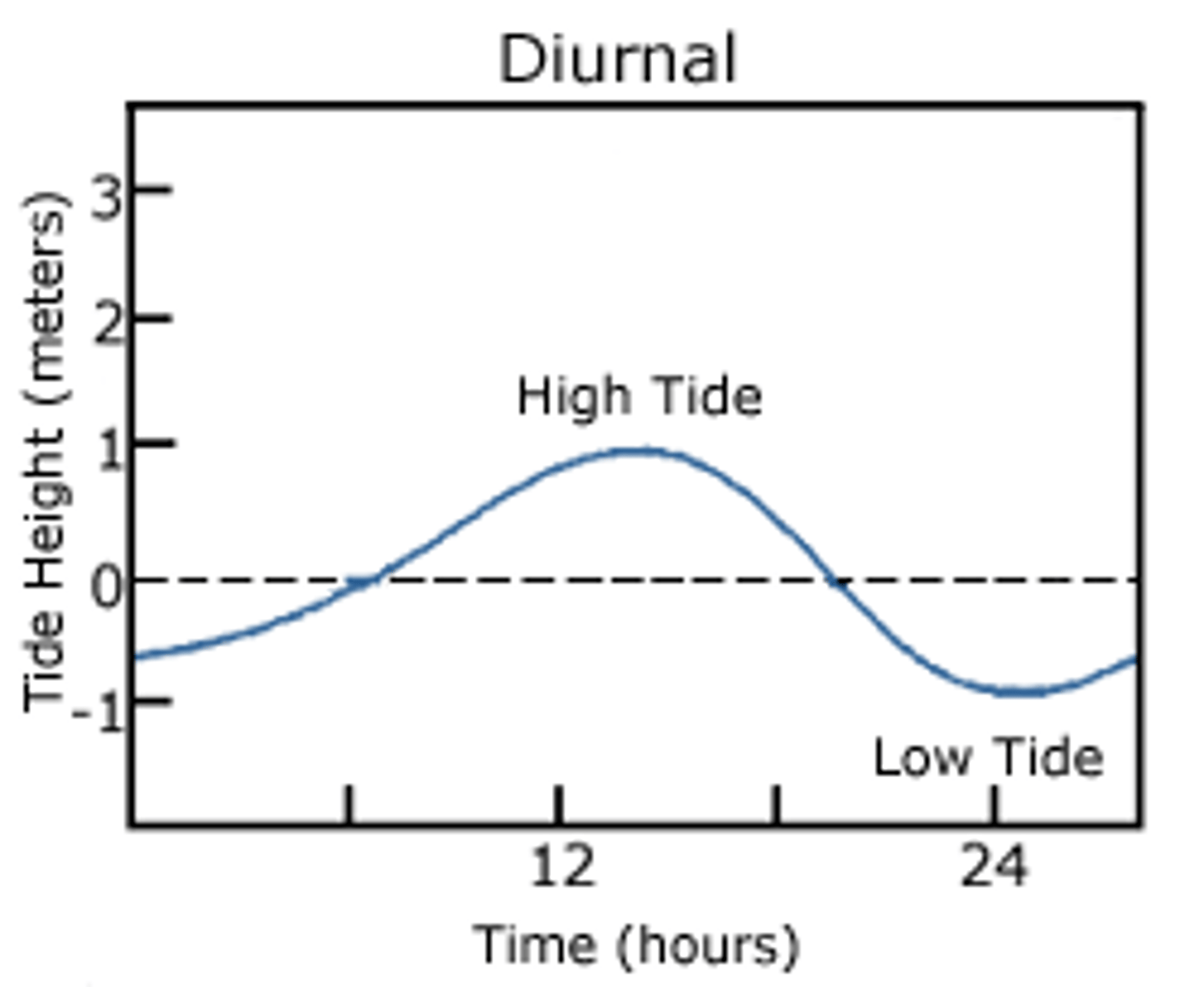
Diurnal Tide
A tidal cycle of a single high tide and a single low tide each lunar day
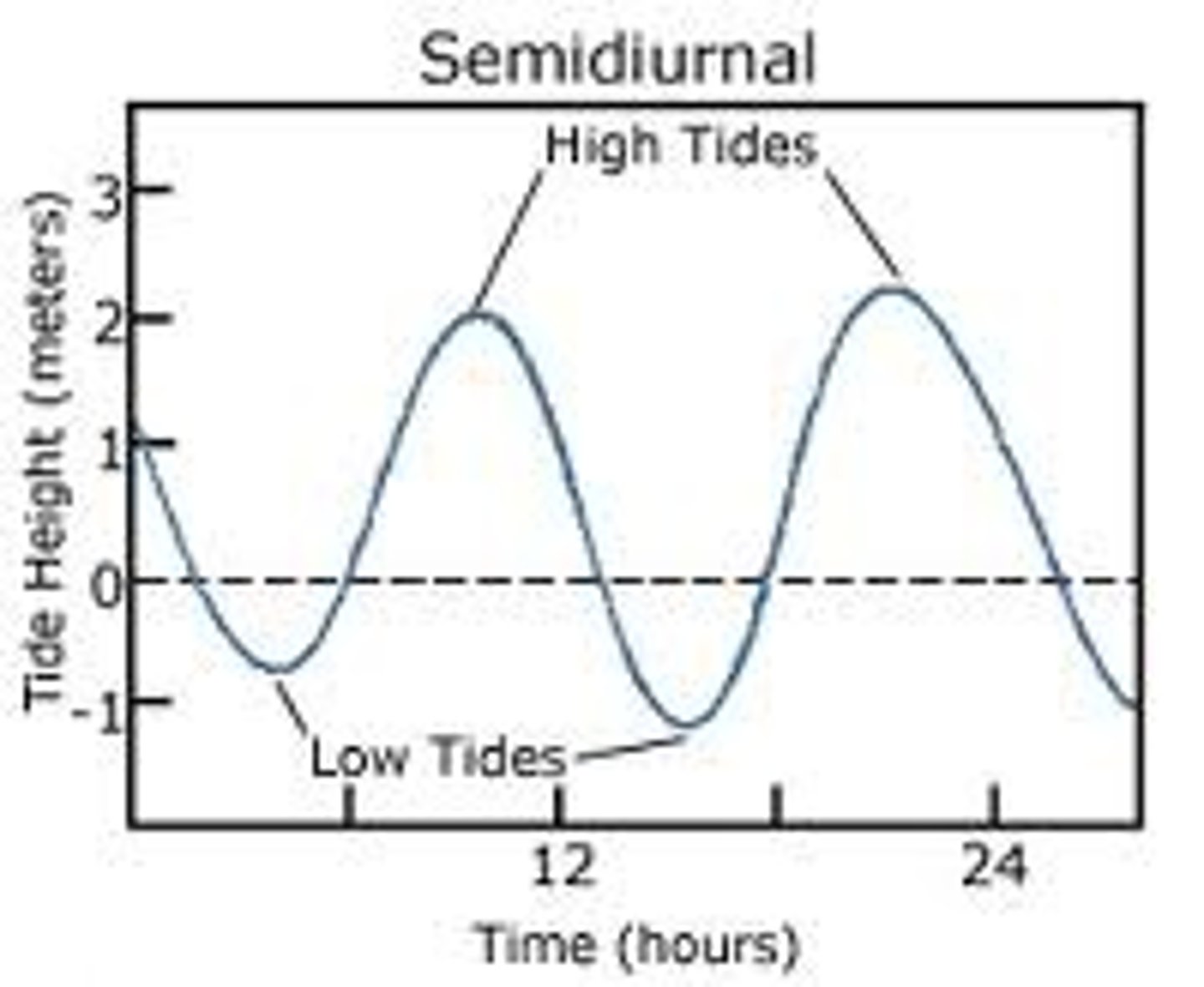
Semidiurnal Tide
A tidal cycle of two high tides and two low tides each lunar day
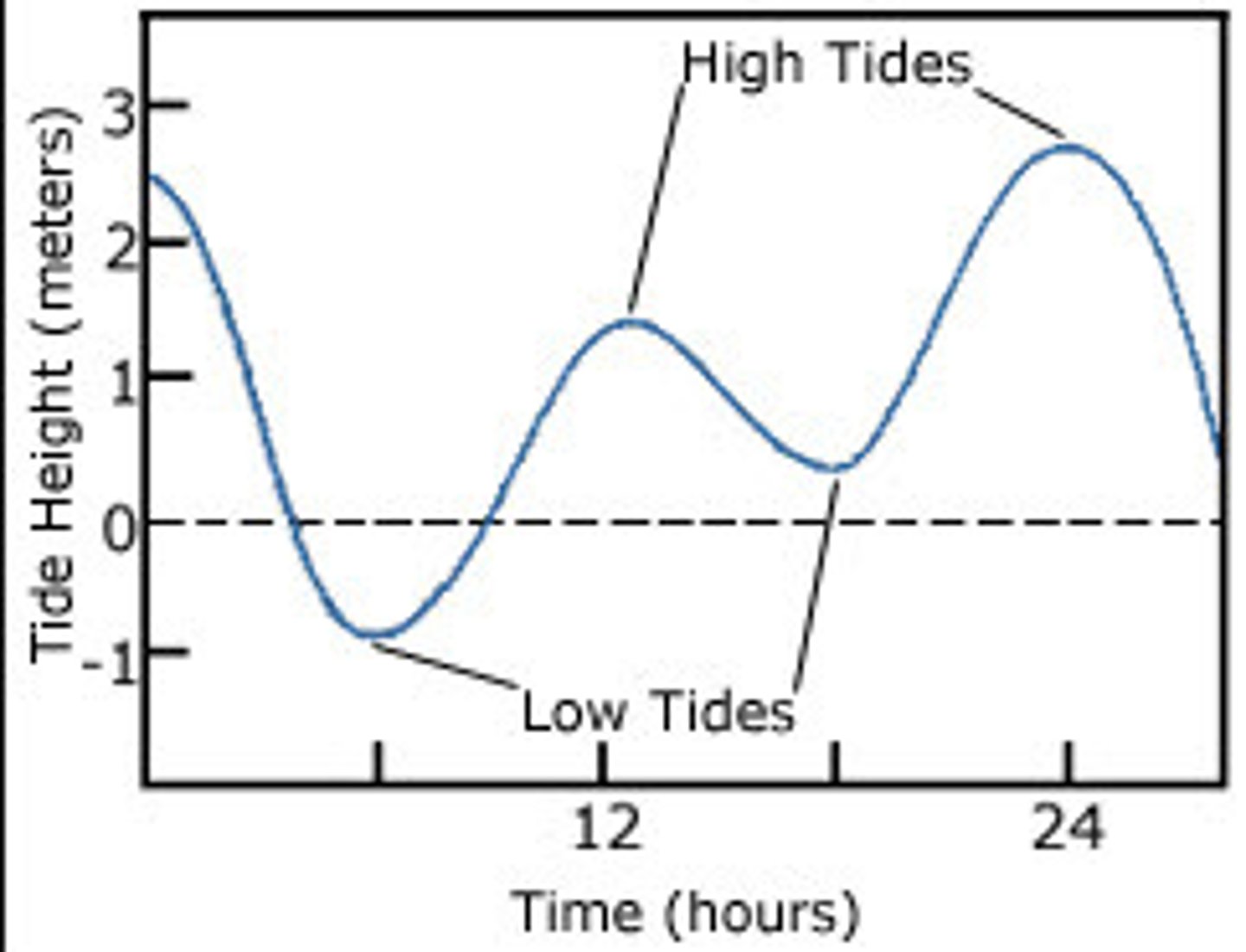
Mixed Tide
The tidal pattern of two unequal high and low tides daily
False
True or False: Tidal ranges decrease with distance from amphidromic points
Amphidromic Point
Tidal Node; A geographical point where tidal height between tidal cycles is at a consistent point.
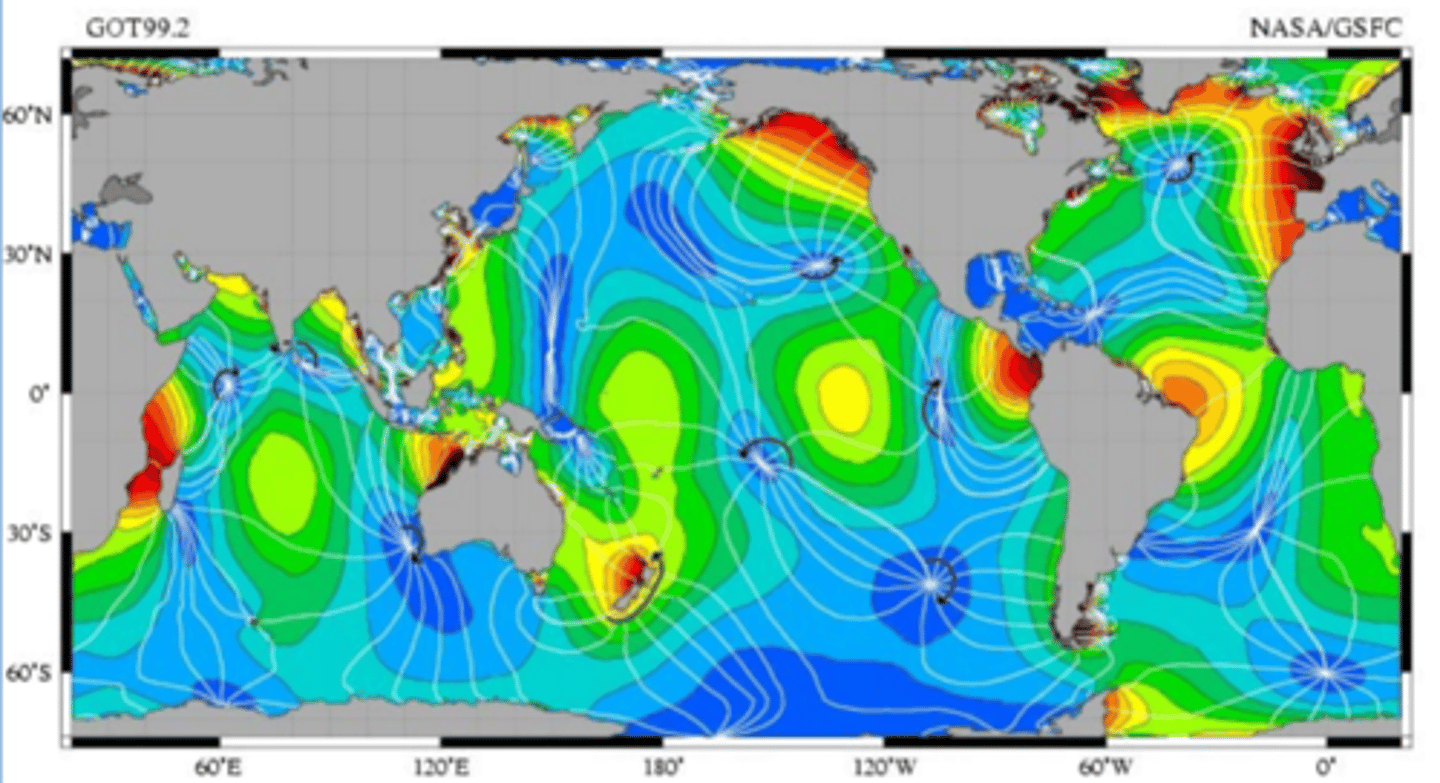
Tidal Node
Amphidromic Point; A geographical point where tidal height between tidal cycles is at a consistent point.
Tidal Datum
The reference level (0.0) from which tidal height is measured.
Tidal Range
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide
Tidal Bore
A steep wave moving upstream at certain inlets
Deviations in tide predictions can be caused by
Storm surges, strong winds, and tsunamis
Sinusoidal Wave
a perfect wave pattern; crests, troughs, and wavelengths are at consistent patterns throughout the wave
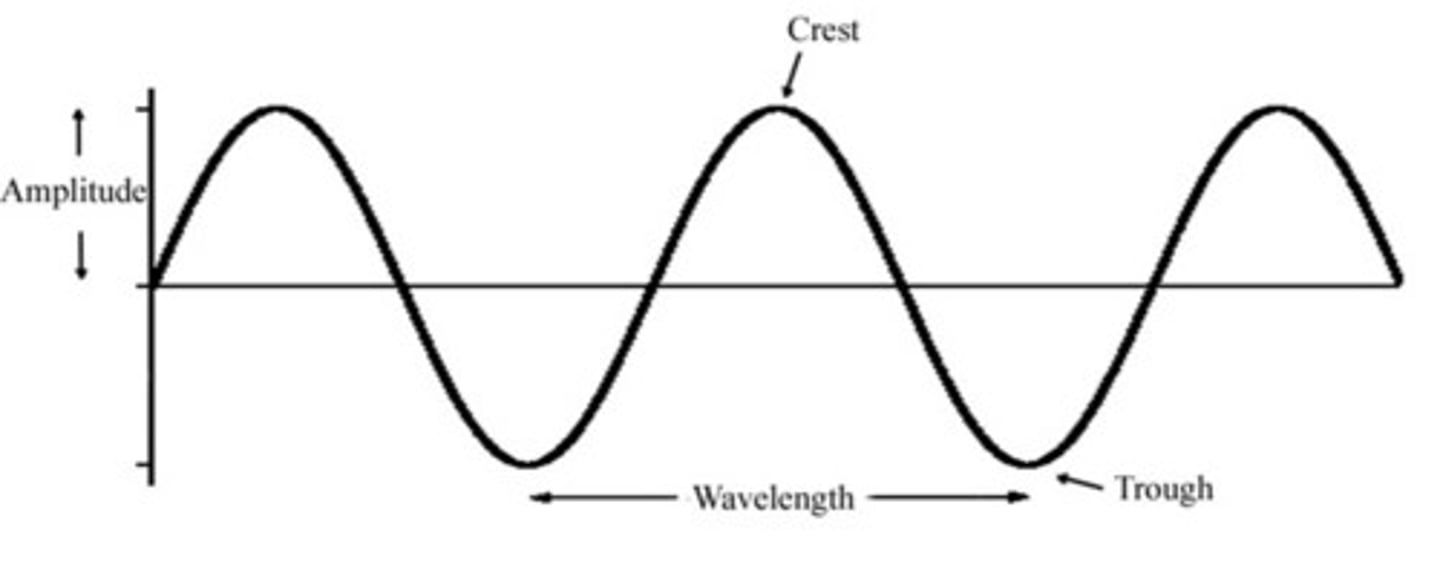
Period
Amount of time it takes one wavelength to pass a point
True
True or False: Waves move energy, not mass
Wave Orbitals
Water within a wave moves in an orbital motion, decreasing in size the deeper below the surface it goes.
Celerity
Wave speed; Wavelength divided by Period (L/T)
Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
Fetch
The distance that the wind has traveled across open water
Disturbing force
The energy that causes a wave to form.
Restoring force
The dominant force trying to return water to flatness after formation of a wave.
Gravity is a
restoring force
Wind is a
disturbing force
Capillary waves
Small ripples, the first waves to form
Chop
Waves taller than a meter caused by wind speeds greater than 10 knots
Swell
long wave of water that moves continuously without breaking
False
True or False: Waves get faster and shorter as they get closer to land
Wave refraction
the bending of waves so that they move nearly parallel to the shoreline