12 - Introduction to Mechanical Ventilation (2/2)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
normal pleural pressure
-5 cmH2O
What can disruption of pressure cause?
pneumothorax or effusion
lung compliance (CL)
ability of the lungs to stretch and accept air
static lung compliance (Cstat)
lung compliance without airflow
dynamic lung compliance (Cdyn)
lung compliance with airflow (Raw)
airway resistance (Raw)
pressure needed to move gas through airways
how to prevent barotrauma
keep plateau pressure (Pplat) ≤ 30 cmH2O
Cdyn formula
C__ = VT ÷ (PIP − PEEP)
PIP = peak inspiratory pressure; aka: peak pressure (Ppeak)
Cstat formula
C__ = VT ÷ (Pplat − PEEP)
Pplat = plateau pressure
Raw formula
__ = (PIP − Pplat) ÷ flow
negative pressure ventilation
ventilation that mimics natural breathing
ex: iron lung
positive pressure ventilation
ventilation that forces air into lungs; standard method of mechanical ventilation
dead space ventilation
ventilation without perfusion
ex: pulmonary embolism
shunt
perfusion without ventilation
ex: atelectasis, ARDS
volume control (VCV)
MV mode that has a preset volume; pressure will vary
pressure control (PCV)
MV mode that has a preset pressure; volume will vary
pressure support (PS) and synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
MV modes that assist spontaneous breathing
parameters for breathing in MV
trigger
time, patient effort
limit
maximum volume allowed (like pressure)
cycle
what ends breath (time, flow, volume)
volume control
pressure graph

volume control
volume graph
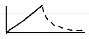
volume control
flow graph

pressure control
pressure graph
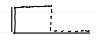
pressure control
volume graph

pressure control
flow graph
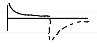
triggering for VCV
time-triggered (mandatory) or patient-triggered
pressure or flow trigger starts breath if patient effort detected
trigger sensitivity must balance between responsiveness and auto-trigger
triggering for PCV
time-triggered for mandatory breaths
patient-triggering breaths use flow/pressure sensors
preset pressure delivered for fixed time
cycling for PCV
time cycle: inspiration ends after preset i-time
constant pressure given until time ends
VT varies based on CL/Raw
cycling for VCV
volume cycle: inspiration ends after set VT delivered
flow constant, pressure will vary
may cause high pressure with poor CL
cycling for PS
flow cycle: breath ends when inspiratory flow drops to set percentage of peak flow (usually 25%)
patient-triggered and patient-cycled
emulates natural breathing
MV settings and interpretation
PEEP
__ improves oxygenation by preventing alveolar collapse
MV settings and interpretation
FiO2
__ is titrated to maintain SpO2 ≥ 90%
MV settings and interpretation
critical waveform indications
air trapping (auto-PEEP)
secretions
patient-ventilator dyssynchrony