calorimetry and cooling curves
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is calorimetry
Using a calorimetry to measure change of state and chemical reactions in terms of associated heat transferred
What are the types of thermometers
liquid-fluid
Electronic
What does a liquid fluids thermometer have to operate
Either alcohol or mercury , as it will expand and rise to temperature change
What is the liquid filled thermometers main applications
Use in hospitals and general industries for liquid temp measurements
What does the electric thermistor have to operate
A thermistor
Resistance
Thermocouple
Infra red waves
What is the main application for a electric thermometer
can be used in industry for high temperatures
Used in hospitals
Conduction
The transfer of heat energy in a solid where there exist a difference in temperature
Convection
The transfer of heat by currents in high density regions to low density , resulting in drop in temp
Thermal equilibrium
Point which there is no temp change due to heat energy being used to break molecular forces at phase change
Latent heat
The heat energy taken in or given out when a substance changes state
The greater the molecular forces mean what in terms of temperature
That higher temperature is needed to reduce force of attraction binding the molecule
Chromatography
Method used Ito separate chemical mixtures for analysis
What is the mobile phase
Liquid that transports the substance along the stationary phase
What is the stationary phase
The solid material that absorbs the mixture , (the chromatography paper)
How to calculate the Rf value
Distance travelled by solute / distance travelled by solvent
you do the dye components divided by the solvent front
TLC compared to paper chromatography
the stationary phase is a thin layer of unrest I’ve substance like silica on a flat surface like glass
TLC advantages
mobile phase moves quickly through stationary phase
They show a greater range of separation of components that paper chromatography
How dependant or results are and how replicable they are is linked to keeping what in constant :
the solvent
The amount of stationary phase used
Teh temperature controls
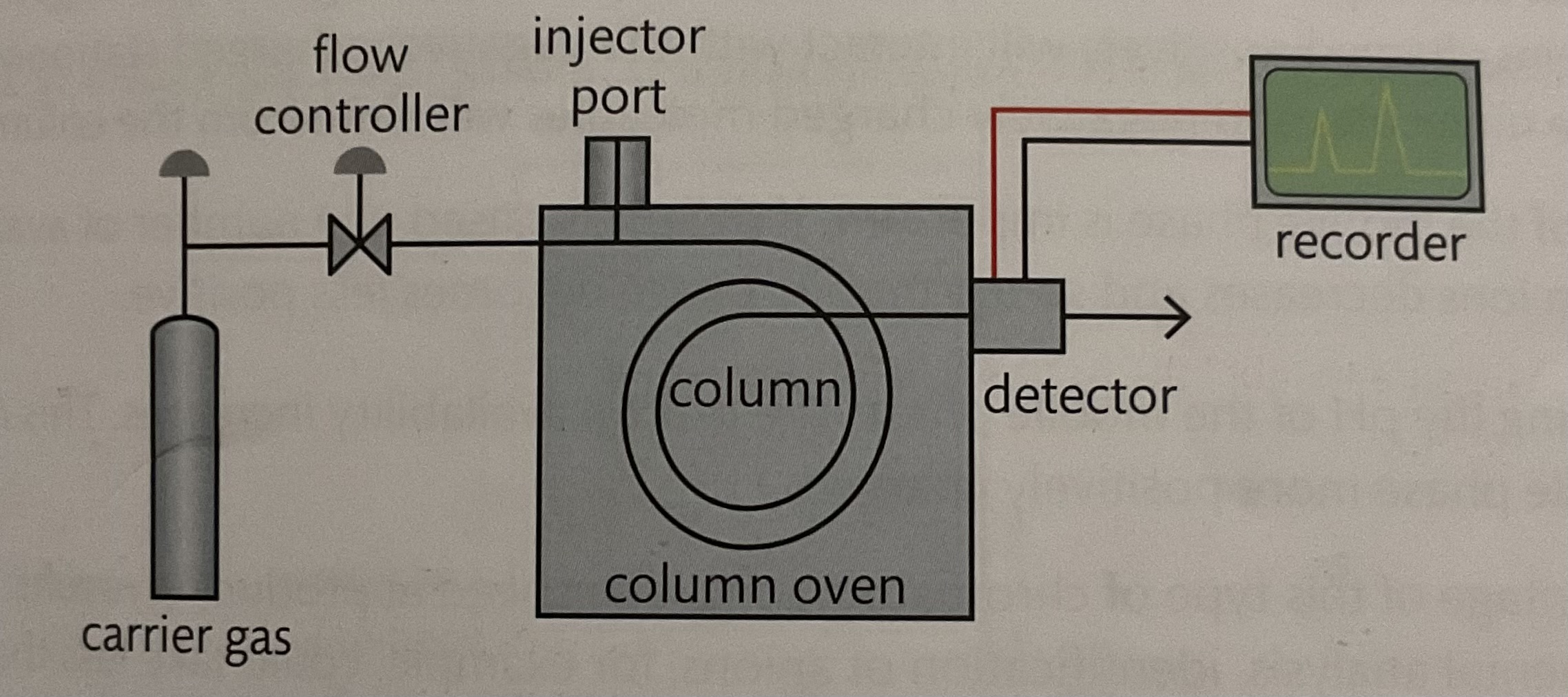
Gas liquid chromatography steps to working
liquid sample is injected into the oven
The oven boils the sample into vapour
Vapour is carried by inert gas ( helium) through column
Molecule move through into contact with liquid solvent (helium gas) absorbed onto the solid material
The tiem taken for sample to pass through machine to detector is the retention time
The retention time depends on solubility of the sample in the solvents
The applications of gas chromatography
Used t analyse concentration of alcohol in the blood
This is gas chromatography
What is ion exchange chromatography
method For purification of particles and other charged molecules including amino acids
The method of ion exchange
relies on oppositely charged ions between the mobile phase and stationary phase , typically a low concentration mobile phase interacting with stationary ions weakly thereby ELUTING
What does eluting mean
Extracting one substance from another using a solvent
Cation exchange
the stationary phase in this type of chromatography is positively charged
The ionic interaction between positive and negative ions in stationary phase is strong
Anion exchange
stationary phase is negatively charged
Positive charged proteins will interact with negative stationary phase molecules and negatively charges molecules will ELUTE from the columns
By lowering the pH in ion exchange chromatography what happens to proton availability and mobile phase
The proton availability increases which makes the mobile phase more positive
What are polar molecules
Molecules without equal distribution of electrons causing opposite electric poles
What’s re non polar molecules
Molecules with equal distribution of electrons resulting to no obsevable poles