APHUG - Unit 1 Key Terms
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Absolute Distance
Distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length
Ex. mile or kilometre
Absolute Location
The exact position of an object of place
Longitude and latitude
Accessibility
The relative ease with which a destination may be reached from some other place
Aggregation
To come together into a mass, sum, or whole
Azimuthal Projection
Map projection
Where the plane is the most developable surface

Breaking Point
The outer edge of a city’s sphere of influence
Used in the law of retail gravitation to describe the area of a city’s hinterlands that depend on that city for its retail supplies
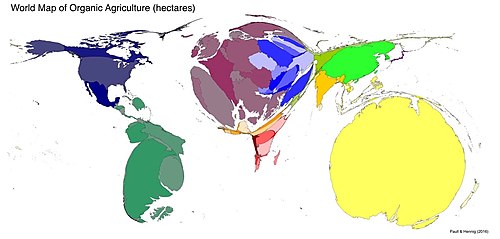
Cartograms
Thematic map
Transforms space so the political unit with the greatest value for some type of data is represented by the largest relative area
Cartography
The theory and practice of making visual representations of Earth’s surface in the form of maps
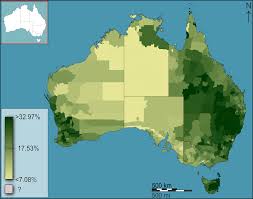
Choropleth Map
Thematic map
Uses tones or colours to represent spatial data as average values per unit area
Cognitive Map
An image of Earth’s surface in an individual’s mind.
Can include knowledge of actual locations and relationships among locations
Personal perceptions and perspectives of particular places
Complementarity
The actual or potential relationship between two places
Usually economic
Connectivity
The degree of economic, social, cultural, or political connection between two places
Contagious Diffusion
The spread of a disease, an innovation, or cultural traits through direct contact with another person or place
Transmitted over a distance because people are close to each other
Coordinate System
Grid of latitude and longitude to determine the absolute location of any object/place/feature
Cultural Ecology
Nature-society geography
Study of the interactions between societies and natural environments
Cultural Landscape
Human-modified environment
Contains imprint of a particular culture of society
Distance Decay Effect
Decrease in interaction between two phenomena, places, or people as the distance between them increases
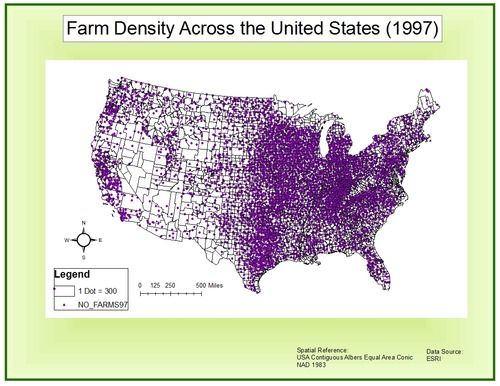
Dot Maps
Thematic map
Use points to show the precise locations of specific observations/occurrences (ex. crimes, car accidents, births)
Environmental Geography
Intersection between human and physical geography
Spatial impacts humans have on the physical environment and vice versa
Expansion Diffusion
Spread of ideas, innovations, fashion, or other phenomena
Through contact and exchange
Remains in its area of origin and spreads to surrounding areas
—> Contagious diffusion and hierarchical diffusion
Formal (Uniform) Region
Regions that have specific characteristics that are relatively consistent within the designated region
Ex. physical features (rolling hills, landscape) or cultural features (language, religion)
Friction of Distance
Measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places
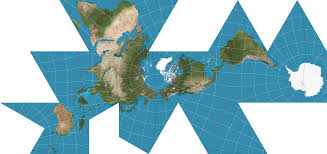
Fuller Projection
Map Projection
Maintains shape and size
Distorts direction completely
N/S/E/W have no meaning
Functional (Nodal) Region
Defined by the connections and interactions that occur between them
Organized around a node or a focal point
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Set of computer tools to capture, store, transform, analyze, display geographic data
Uses thematic layers
Allows for examination of multiple variables and their roles
Geographic Scale
Conceptual hierarchy of spaces, from small to large
Ex.
The neighbourhood, the urban area, the metropolitan area, the region
The watershed, ecosystem, landscape, biome
The finer the scale of analysis, the richer the level of detail
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Integrated network of satellites that orbit Earth
Broadcast location information to a handheld receiver on Earth
Gravity Model
Formula which describes the level of interaction between two places
Interaction Strength = (Population 1*Population 2)/Distance Apart
Hierarchical Diffusion
When something is transmitted over a distance because the level of interaction between places overcomes the actual distance between them
Because of a physical or cultural community between those places
Ex. NYC and LA, Paris and Milan
Human Geography
Study of spatial variation in patterns and processes related to human activity
International Date Line
Line of longitude
Marks where each new day begins
Centered on 180th meridian
Intervening Opportunity
Potential alternatives that may arise which may block individual from original goal/destination/product
Ex. supplier closer to the buyer
Frequently used because transportation costs decrease w/ proximity
Isoline
Map line that connects points of equal/very similar values
Elevation, temperature, precipitation…
Large Scale
Small ratio between map units and ground units
Higher resolution
Cover smaller regions
Ex. neighbourhood, mall, city
Latitude
Horizontal
North or south of equator
Lines of latitude/parallels
Originate at equator and terminate at the poles
Law of Retail Gravitation
People will be drawn to larger cities to conduct their business since larger cities have a wider influence
Longitude
Vertical
East or west of the prime meridian
Lines of longitude/meridians
Originate at the prime meridians (oº) and terminate at the International Date Line (180º)
Map Projection
Transferring Earth’s sphere onto a flat surface
All map projections have some sort of distortion (area, direction, distance, shape)
Mercator Projection
Map Projection
Preserves direction
Distorts areas of landmasses relative to each other
Landmasses become amplified in size at poles
Useful for navigation
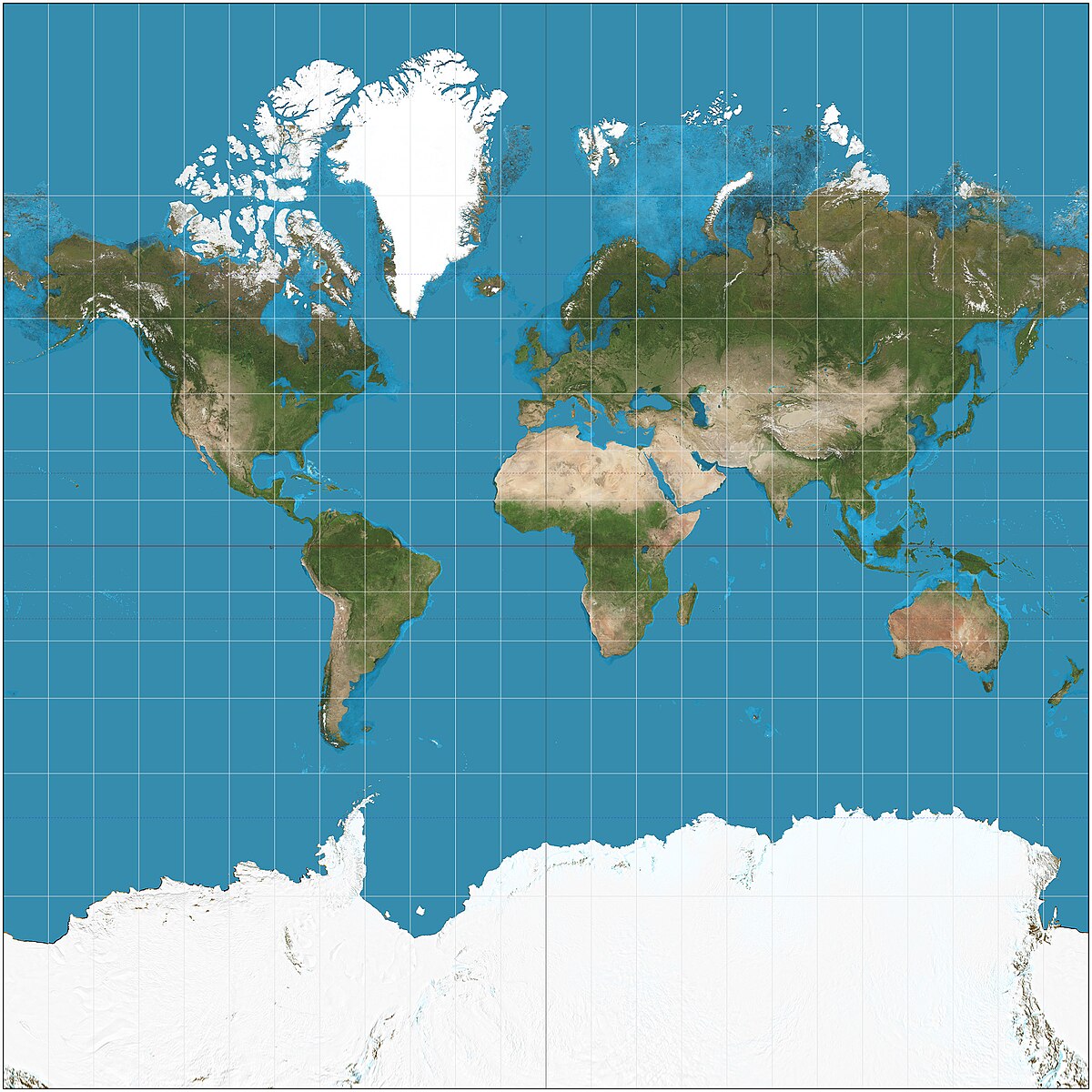
Meridian
Line of longitude
Runs north-south
All lines of longitude are equal in length and intersect at the poles
Natural Landscape
The physical landscape/environment that has not been affected by human activities
Nature-society
Study of the interactions between societies and the natural societies in which they live
Parallel
East-west lines of latitude
Runs parallel to the equator
Marks distance north or south of the equator
W.D. Pattison
Four distinct traditions of geography:
Earth-science tradition (physical geography)
Culture-environment tradition (environmental geography)
Locational tradition (analysis of spatial data through cartography)
Area-analysis tradition (regional geography)
Perceptual (Vernacular) Region
Individualized definition of regions
Exist in the minds of people
Defined by feelings and prejudices
Ex. the American Deep South, Silicon Valley
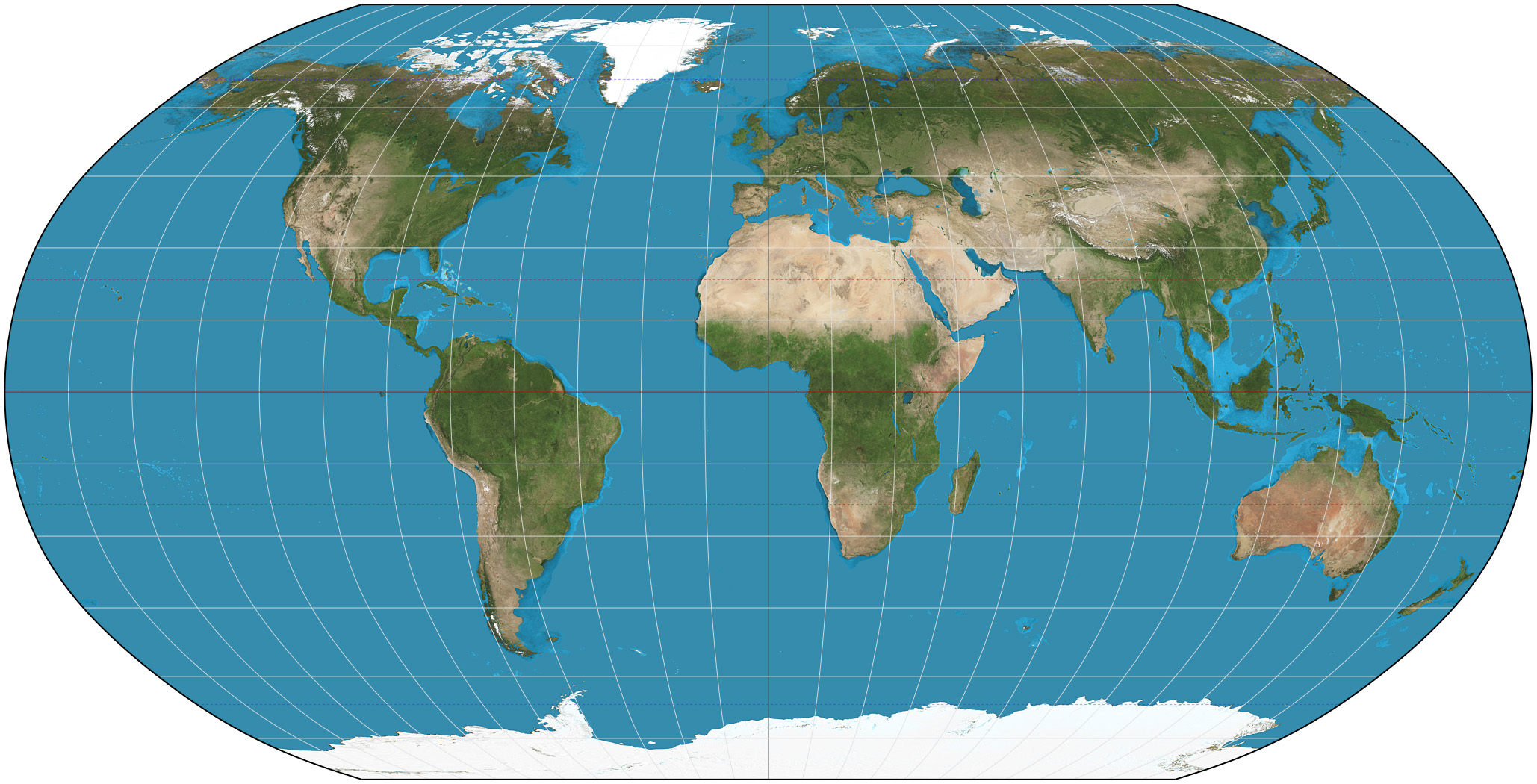
Gall-Peters Projection
Map Projection
Centres on Africa
Preserves area
Distorts shape
Physical Geography
Studies natural structures, processes, distributions, changes of natural phenomena of Earth’s surface
Landforms, climate, vegetation, ecosystems
Preference Map
Displays individual preferences for certain places
Prime Meridian
Imaginary line
Marks the 0º line of longitude
Divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres
Projection
System used to transfer locations from Earth’s surface to a flat map
Proportional Symbols Map
Thematic map
The size of a symbol indicates the relative magnitude of something (quantitative)
Ptolemy
Roman geographer-astronomy
Author of Guide to Geography
Included maps w/ longitude and latitude
Reference Map
Shows geographical information for a place
Landmarks, navigation
Region
Area of land that contains some unifying social and/or physical characteristics
Formal (Uniform)
Functional (Nodal)
Perceptual (Vernacular)
Relative Distance
Measurement of distance that incorporates social, economic, or cultural factors
Time, cost, effort
Ex. “I’m a 15-minute drive away”
Relative (Situation) Location
Position of a place relative to the places around it
Ex. “The store is across the street from the library”
Relocation Diffusion
When people migrate from one place to another and bring their ideas, innovations, behaviours, and cultures
Ex. Little Italy, Chinatown, Buddhism, food traditions
Disappears in its place of origin
Remote Sensing
Capturing images of Earth’s surface from airborne platforms (aircraft, satellites)
Photographic images, thermal images, multispectral scanners, radar images, etc.
Resolution
A map’s smallest discernible unit
If an object has to be 1 km long to show up on a map, that map’s resolution is 1 km
Robinson Projection
Map projection
Does not maintain area, shape, distance, or direction
Minimizes errors in each
Aesthetically pleasing balance
Carl Sauer
UC Berkeley
Defined cultural landscapes as the focus of geographical analysis
Virtually no landscape has escaped alteration by human activities
Scale of Analysis
Geographic unit at which one investigates various patterns/processes
Local, regional, national, global
Sense of Place
Feelings evoked as a result of experiences/memories associated with a place
Site
Specific physical characteristics and absolute location of a place
New York: Deep natural harbour, Hudson River, originally abundant freshwater, coastal location.
Situation
Relative location of a place in relation to the physical and cultural characteristics of the surrounding area, connectivity
New York: Gateway between the U.S. and Europe; located at the mouth of the Hudson, giving access to inland markets.
Small Scale
Large ratio between map units and ground units
Lower resolution
Cover larger regions
Ex. continents, world, atlases
Spatial Diffusion
The ways in which phenomena travel over space
Ex. technological innovations, cultural trends, outbreaks of disease...
Spatial Perspective
Examines arrangements of various phenomena across space, why they’re there, and the relationships between them and other phenomena in other places
Sustainability
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Thematic Layers
Different datasets on a map that are layered to visually represent a specific spatial theme or topic
In a GIS
Understand and analyze a spatial relationship
Thematic Map
Specialized maps that focus on specific themes or topics
Provides representation of data related to those themes
Time-Space Convergence
The decrease in travel time or distance between places as a result of technological advancements
More rapid communication and increased interaction
Topographic Maps
Reference map
Uses isolines to represent constant elevations
Useful for hiking, navigation, etc.
Transferability
Ease and cost of moving goods and services across space