Chemistry of the Atmosphere and Climate Change
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Atmosphere Composition
99% nitrogen and oxygen near Earth's surface.
Non-Uniform Gas Distribution
Gas composition varies with altitude and location.
Troposphere
Lowest atmospheric layer; where weather occurs.
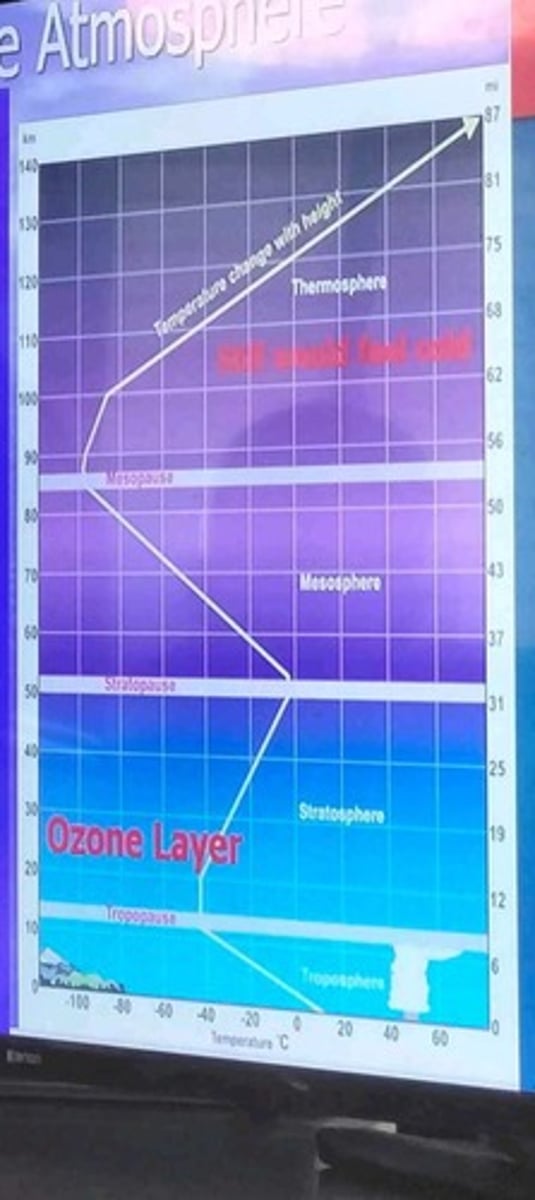
Stratosphere
Second layer; contains ozone layer absorbing UV-B.
Mesosphere
Middle layer; meteors burn up here.
Thermosphere
Upper atmosphere; very few molecules present.
Solar Wind
Charged particles emitted from the Sun.
Auroras
Light displays formed in the thermosphere.
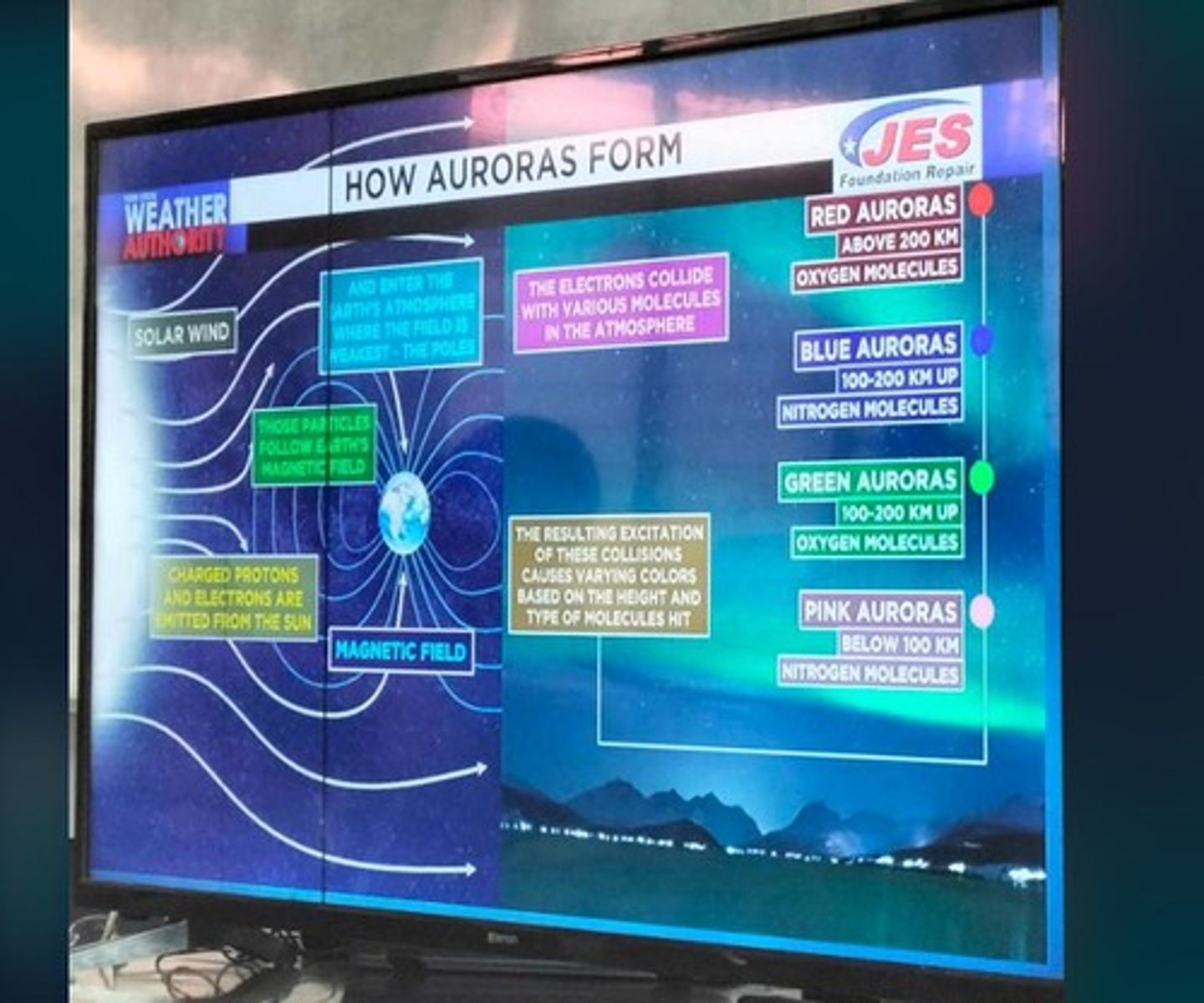
Particle Collisions
Electrons excite atmospheric molecules, emitting light.
Red Auroras
Above 200 km; caused by oxygen molecules.
Blue Auroras
100-200 km; caused by nitrogen molecules.
Green Auroras
100-200 km; caused by oxygen molecules.
Pink Auroras
Below 100 km; caused by nitrogen molecules.
Photodissociation
Chemical bond rupture from photon absorption.
Photoionization
Molecule absorbs radiation, ejects electron, becomes ion.
Ionization Energy
Energy needed to remove an electron from an atom.
Wavelength (λ_max)
Maximum wavelength for ionization of specific molecules.
O2 Dissociation Energy
498 kJ/mol required to break O2 bond.
Planck's Equation
E=hν relates energy to photon frequency.
Speed of Light Equation
c=λν relates speed, wavelength, and frequency.
Avogadro's Number
6.022 x 10^23; used for mole calculations.
Ultraviolet Radiation
Short wavelength radiation; can cause ionization.
Ozone Layer
Protective layer absorbing harmful UV radiation.
Meteors
Burn up in the mesosphere due to friction.
Excited Atoms
Atoms with electrons in higher energy states.
Aurora Formation Process
Involves solar wind, collisions, and light emission.
Reactive Oxygen
Oxygen's lower bond enthalpy makes it more reactive.
Ion Presence
Enables long-range radio communication in the atmosphere.
Ozone Layer
Protective gas ring absorbing harmful UV rays.
Stratosphere
Layer of atmosphere where ozone layer is located.
Ozone Thickness
2 to 8 mm under normal conditions.
UVA Rays
Most common UV rays causing skin aging.
UVB Rays
Causes sunburns, cataracts; 95% absorbed by ozone.
UVC Rays
Most dangerous UV rays; 100% absorbed by ozone.
Photokeratitis
Eye injury caused by UV radiation exposure.
Ozone Absorption Range
Ozone absorbs radiation between 240 and 310 nm.
Ozone Formation
Occurs through O₂ and free oxygen atom reaction.
Photodissociation
Process where UV radiation splits oxygen molecules.
Chemical Reaction for Ozone
O + O₂ → O₃ forms ozone.
Ozone Depletion Discovery
1974 discovery of CFCs harming ozone by Rowland and Molina.
CFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons used in aerosols and refrigerants.
HCFCs
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons; less harmful than CFCs.
Halon
Used in fire extinguishers; ozone-depleting chemical.
Methyl Bromide
Pesticide contributing to ozone depletion.
Ozone Depletion Process
CFCs release chlorine, which reacts with ozone.
Chlorine Monoxide
Product of ozone breakdown by chlorine.
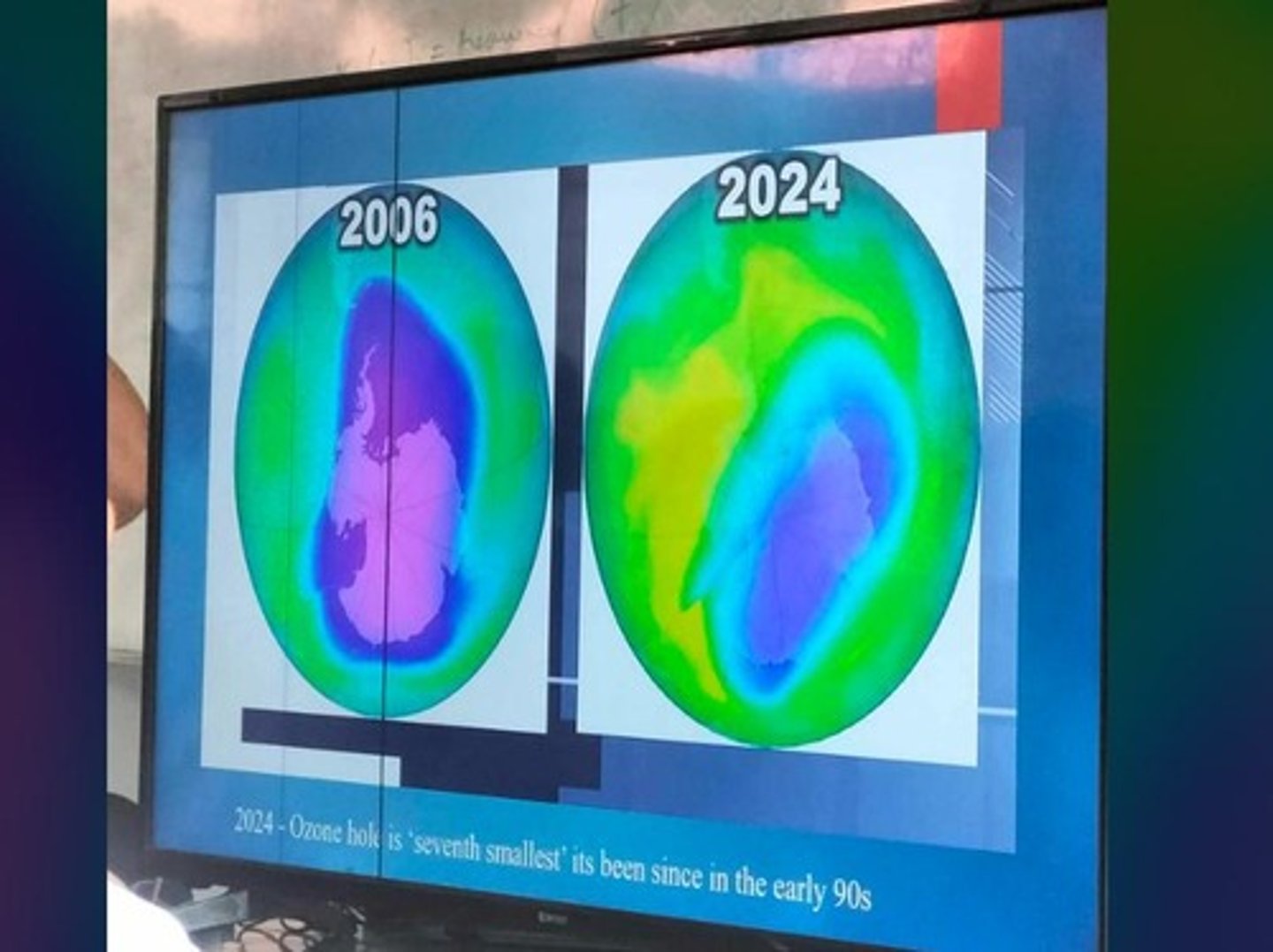
Ozone Hole
Area of severe ozone depletion, notably over Antarctica.
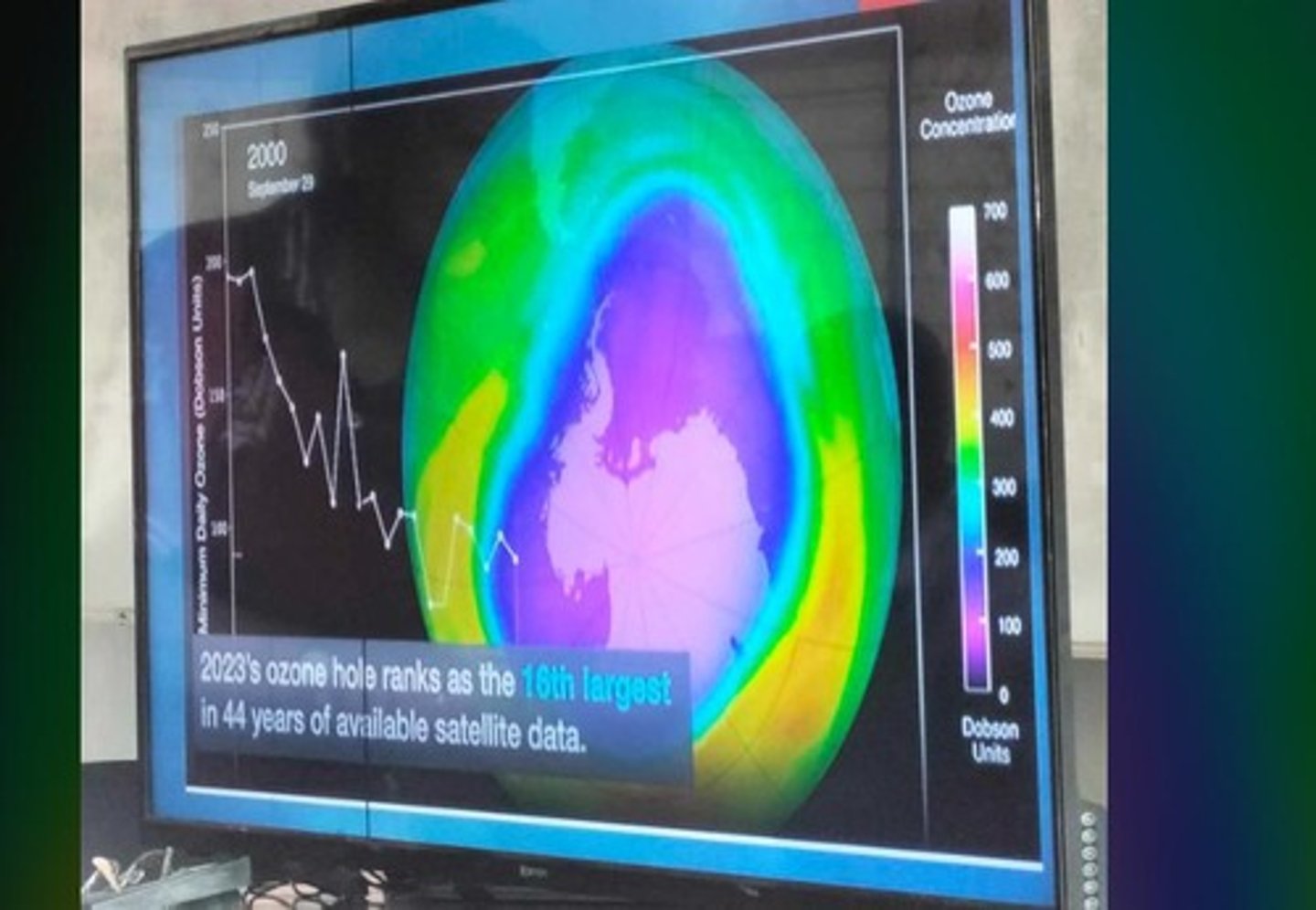
Dobson Unit (DU)
Standard measurement for ozone concentration; 1 DU = 0.01 mm.
Ozone Hole Monitoring
NASA tracks ozone hole size and extent.
UV Radiation Effects
Increased exposure leads to skin cancer and eye damage.
Ozone Layer Importance
Shields life from harmful UV radiation.
Ozone Depletion Impact
Affects ecosystems, increases health risks.
Ozone Layer Shielding
Critical for protecting life from UV radiation.
UV Radiation Types
Includes UVA, UVB, and UVC with varying effects.
Ozone Layer Environmental Concern
Depletion allows more harmful UV radiation to reach Earth.
Ozone Formation Process Steps
UV radiation splits O₂, forming ozone through collisions.
CFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons that deplete ozone layer.
UV radiation
Ultraviolet light causing CFC bond breakage.
Chlorine atoms
Released from CFCs, react with ozone.
Ozone (O₃)
Ozone layer protects Earth from UV radiation.
Chlorine monoxide (ClO)
Intermediate product in ozone depletion cycle.
Montreal Protocol
1987 agreement to phase out CFCs.
Troposphere
Lowest atmospheric layer, contains weather.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Greenhouse gas from organic matter decomposition.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Toxic gas from incomplete combustion.
Methane (CH₄)
Greenhouse gas from organic matter decomposition.
Nitric oxide (NO)
Pollutant from combustion engines and discharges.
Ozone (O₃) in troposphere
Harmful pollutant, differs from stratospheric ozone.
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
Gas from burning fossil fuels, contributes to acid rain.

Acid rain
Precipitation containing sulfuric or nitric acids.
Sulfur trioxide (SO₃)
Forms from oxidation of sulfur dioxide.
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
Result of SO₃ reacting with water.
Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃)
Limestone used in reducing SO₂ emissions.
Calcium oxide (CaO)
Product of heating limestone, reacts with SO₂.
Calcium sulfite (CaSO₃)
Formed from CaO and SO₂ reaction.
Scrubber system
Aqueous suspension removing CaSO₃ from emissions.
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ)
Pollutants contributing to photochemical smog.
Photochemical smog
Smog formed from sunlight-driven reactions.
Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂)
Main component of urban smog haze.
Smog
Mix of smoke and fog, worsened by weather.
Greenhouse effect
Trapping of heat by greenhouse gases.
Respiratory issues
Health problems linked to air pollution.
Pollutants
Substances causing environmental harm.
Decomposition
Breakdown of organic matter releasing gases.
NO₂
Nitrogen dioxide, key in ozone formation.
O₃
Ozone, a pollutant formed from NO₂.
Respiratory Issues
Health problems like asthma and lung damage.
Visibility Reduction
Decreased sight due to air pollution.
Ecosystem Damage
Harm to plants and natural habitats.
Catalytic Converters
Devices reducing NOₓ emissions in vehicles.
Public Transport
Shared transport options to lower fossil fuel use.
Electric Vehicles
Cars powered by electricity, reducing emissions.
Industrial Smog
Grayish pollution from burning coal or oil.
Photochemical Smog
Brownish pollution from vehicle emissions and sunlight.
London Smog
Historical industrial smog associated with London.
L.A. Smog
Smog formed in Los Angeles from vehicles.
Sulfur Oxides (SO₂)
Main pollutants in industrial smog.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ)
Key pollutants in photochemical smog.
Greenhouse Effect
Atmospheric phenomenon retaining Earth's heat.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Major greenhouse gas from fossil fuel combustion.