Statistics and Relationships between Variables(All you need for Unit 2 AP Statistics)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to statistical analysis, focusing on variables and their relationships.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Categorical Variable
A variable that can be divided into groups or categories.
Quantitative Variable
A variable that can be measured numerically and can be either continuous or discrete.
Scatterplot
A graphical representation of two quantitative variables to show their relationship.
Correlation
A measure of the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
Causation
The action of causing something; indicating that one event is the result of the occurrence of another event.
Residual
The difference between the observed value and the predicted value in regression analysis.
Regression Line
A line that best fits the data points in a scatterplot, used to predict the value of the dependent variable.
Joint Relative Frequency
The frequency of a specific outcome occurring in relation to the total frequency of the event.
Conditional Relative Frequency
The frequency of an outcome occurring given a certain condition or event.
Intercept
The value of the dependent variable when all independent variables are equal to zero.
Strength of Correlation
A measure that determines the degree to which two variables are related, indicating how closely they move together.
Linear Model
A mathematical model that describes a linear relationship between variables, often represented as a line.
Strength of Direction
Indicates whether the relationship between two variables is positive, negative, or nonexistent.
Two-Way Table
A statistical table that displays the frequency distribution of variables.
Slope
The rate of change of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable in a linear model.
Correlation formula
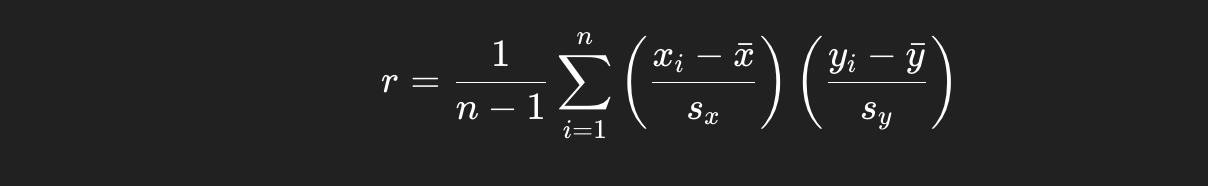
slope for LSRL
r(correlation) * (S.D of y/ S.D of x)