psychopathy exam two
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
agoraphobia
marked fear or anxiety about 2 or more of the following five situations
using public transportation
being in open spaces
being in enclosed spaces
standing in line or being in a crowd
being outside of the home alone
the individual fears or avoids these situations because of thoughts that escape might be difficult or help might not be available in the event of developing panic like symptoms or other incapacitating or embarrassing symptoms
the agoraphobic situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety
the agoraphobic situations are actively avoided, require the presence of a companion, or are endured with intense fear or anxiety
the fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual danger posed by the agoraphobic situations and to the sociocultural context
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
if another medical condition is present, the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is clearly excessive
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
amygdala
emotional memories
fear and aggression
anxiety
response from your thoughts
anxiety disorder
always consider
development
culture
never due to substance use or general medical conditions
anxiety sensitivity
is a psychological trait characterized by an intense fear of anxiety-related sensations and their potential consequences
autonomic nervous sytem
a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal.
behavioral inhibition
a temperamental predisposition characterized by restraint in engaging with the world combined with a tendency to scrutinize the environment for potential threats and to avoid or withdraw from unfamiliar situations or people. It is often related to social anxiety and a predisposition for greater physiological reactivity to novel situations.
depersonalization
a dissociative experience characterized by a feeling of detachment from oneself, one's body, or one's thoughts. It is a common symptom that can occur in various mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and trauma.
derealization
is a dissociative experience characterized by a persistent feeling of detachment from one's surroundings, making the world seem unreal, dreamlike, or distorted
emotional processing (in exposure)
seeing that your fear wasn’t realistic/rational
changing feelings about your fear
exposure hierarchy
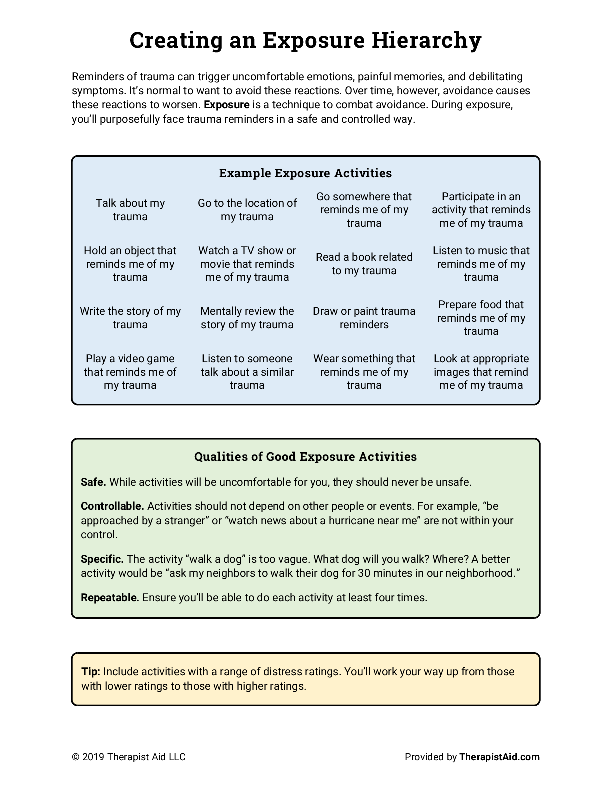
exposure therapy
is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) that involves gradually exposing a person to their feared situations or objects in a safe and controlled environment. The goal is to help them reduce their anxiety and avoidance behaviors.
extinction
the gradual weakening or complete disappearance of a learned behavior. It can occur when a behavior is no longer reinforced
fear
response from immediate danger
fear circuit
the brain pathways and structures involved in processing and responding to perceived threats, primarily focusing on the amygdala and its connections, which lead to physiological and behavioral fear responses.
generalized anxiety disorder
excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation) occurring more days than not for at least 6 months, about a number of events or activities
the individual finds it difficult to control the worry
The anxiety and worry are associated with three (or more) of the following six symptoms (with at least some symptoms having been present for more days than not for the past 6 months)
restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge
being easily fatigued
difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
irritability
muscle tensions
sleep disturbance
the anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g. a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition (e.g. hyperthyroidism)
the disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder
habituation
getting used to a behavior
hippocampus
factual memory
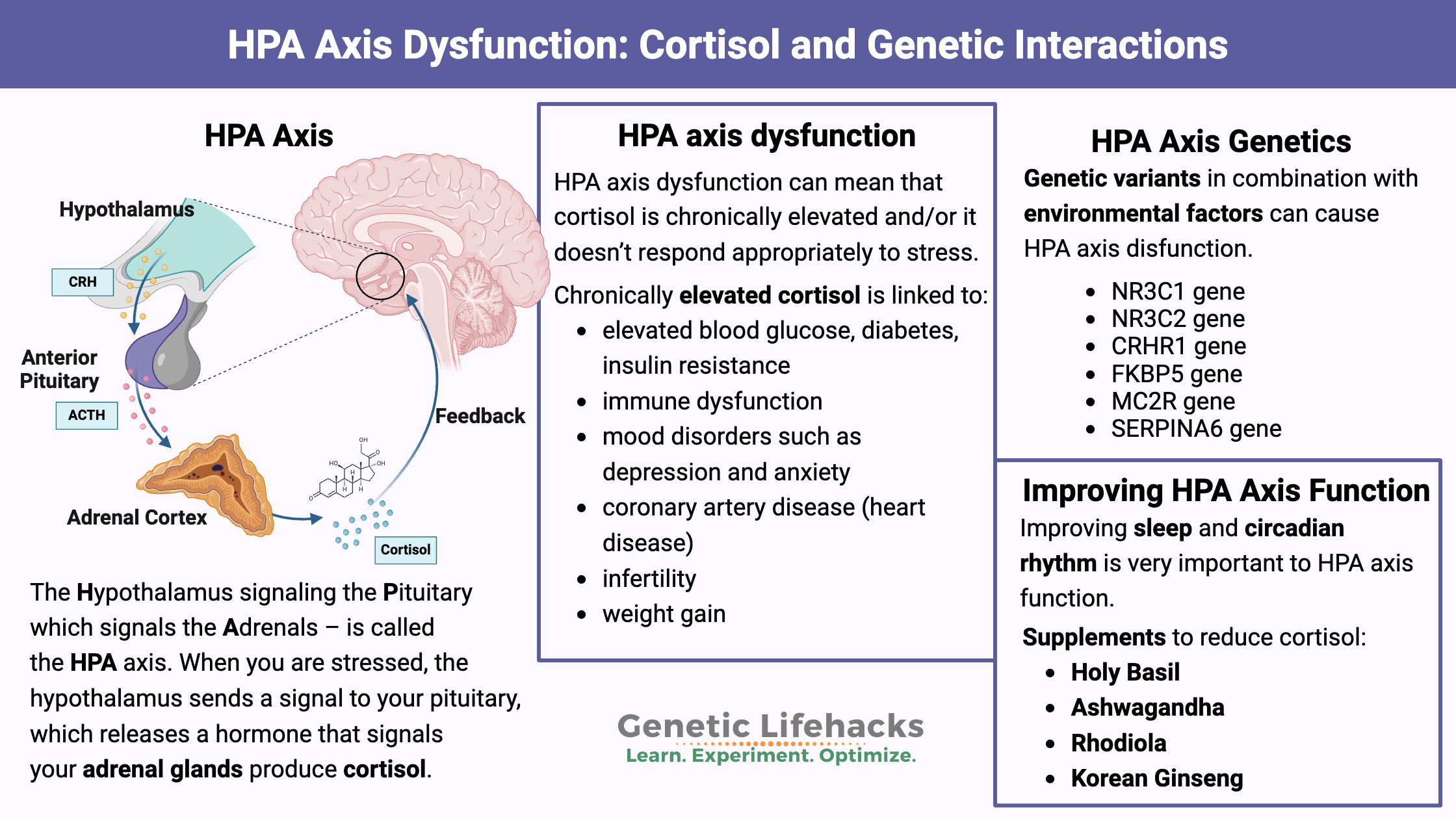
HPA axis
a complex endocrine system that plays a crucial role in regulating the body's response to stress. It involves three main components:
Hypothalamus: A region in the brain that produces corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
Pituitary gland: A small gland located below the hypothalamus that releases adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
Adrenal glands: Two glands located on top of the kidneys that produce cortisol, a stress hormone.
interoceptive sensitivity
the ability to perceive and interpret internal bodily sensations, such as heart rate, breathing, temperature, and hunger.
expected/cued panic attacks
Also known as situational panic attacks
Can be triggered by phobias, stressful situations, or anticipated situations
For example, someone with a fear of public speaking might have a panic attack when giving a speech
unexpected/uncued panic attacks
Also known as spontaneous panic attacks
Can occur without an obvious cause or warning
For example, someone might suddenly feel short of breath and dizzy while shopping for groceries
panic disorder
recurrent unexpected panic attacks
at least one of the attacks has been followed by one month or more of one or both of the following
persistent concern or worry about additional panic attacks or their consequences
a significant maladaptive change in behavior related to the attacks
the disturbance is not attributable to physiological effects of a substance
the disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder
parasthesias
refers to an abnormal sensation of tingling, prickling, burning, or numbness in the skin or extremities. It can be temporary or chronic and may affect any part of the body.
parasympathetic division
(PNS) is a part of the autonomic nervous system that controls the body's "rest and digest" functions. It's responsible for many automatic functions, including digestion, urination, and heart rate.
phobia
a persistent and irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity that causes significant distress and avoidance behaviors
prefrontal cortex
a region of the brain located in the frontal lobe, anterior to the motor cortex. It plays a crucial role in various cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functions.
self efficacy
the belief that you can accomplish a task or goal. It's a confidence that you can control your behavior, motivation, and social environment.
social anxiety disorder
marked fear or anxiety about one or more social situations in which the individual is exposed to possible scrutiny by others
the individual fears that he or she will act in a way or show anxiety symptoms that will be negatively evaluated
the social situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety
the social situations are avoided or endured with intense fear or anxiety
the fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual threat posed by the social situation and to the sociocultural context
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the fear, anxiety or avoidance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
if another medical condition (e.g. parkinson’s disease, obesity, disfigurement from burns or injury) is present, the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is clearly unrelated or is excessive
specific phobia
marked fear or anxiety about a specific object of situation
the phobic object or situation almost always provokes immediate fear or anxiety
the phobic object or situation is actively avoided or endured with intense fear or anxiety
the fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual danger posed by the specific object or situation and to the sociocultural context
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more
the fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the disturbance is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
sympathetic division
responsible for the "fight-or-flight" response, mobilizing the body in stressful or threatening situations, characterized by increased heart rate, blood pressure, and pupil dilation, among other effects.
basal ganglia
are a group of brain structures that affect mood, cognition, and motor control. They're involved in many psychological functions, including:
Emotional processing: The BG help regulate mood and emotional responses to events, such as feeling good or bad about something
Cognitive functions: The BG help with complex thinking, decision-making, and learning
Habit formation: The BG help form habits and strengthen behaviors that lead to desired outcomes
body dysmorphic disorder
preoccupation with one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others
at some point during the course of the disorder, the individual has performed repetitive behaviors or mental acts in response to the appearance concerns
the preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the appearance preoccupation is not better explained by concerns with body fat or weight in an individual whose symptoms meet diagnostic criteria for an eating disorder
caudate nucleus
key part of the basal ganglia, plays a crucial role in various psychological functions, including motor control, learning and memory, reward processing, and cognitive flexibility,
cingulate gyrus
a crucial part of the limbic system, plays a vital role in regulating emotions, behavior, and pain perception, and its dysfunction has been linked to various psychiatric disorders.
compulsion
repetitive behaviors (including mental acts)
clearly excessive, not realistic
driver to perform; overwhelming distress if resisting
not pleasant or enjoyable
in response to an obsession or performed in a highly ritualized way
aimed at preventing/reducing distress or preventing dreaded event/outcome
cortio-striatal-thalamo-cortical circuit
brain pathway that plays a crucial role in motor control, reward processing, and cognitive functions, and its dysfunction is implicated in various psychiatric disorders like OCD and ADHD.
disconfirmatory bias
the phenomenon in which people tend to believe and accept evidence that supports their prior beliefs while dismissing evidence that refutes their beliefs.
excoriation
recurrent skin picking resulting in skin lesions
repeated attempts to decrease or stop skin picking
the skin picking causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning
the skin picking is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the skin picking is not better explained by symptoms of another mental disorder
exposure and response prevention (EXRP)
psychoeducation
development of exposure hierarchy
exposure to stimuli
prevention of compulsive ritual
repeated exposure over time with response prevention
hoarding disorder
persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value
this difficulty is due to a perceived need to save the items and to distress associated with discarding them
The difficulty discarding possessions results in the accumulation of possessions that congest and clutter active living areas and substantially compromises their intended use. If living areas are uncluttered, it is only because of the interventions of third parties
the hoarding causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning (including maintaining a safe environment for self and others)
the hoarding is not attributable to another medical condition
the hoarding is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
intolerance of anxiety
a tendency to react negatively to situations involving uncertainty, potentially leading to anxiety disorders, and is often associated with excessive worry.
negative appraisal
the process of evaluating or understanding a situation or event as having negative or harmful consequences, impacting an individual's well-being. This often involves seeing a situation as a threat, something they are unable to cope with, or something that has a negative impact on their self-esteem.
negative emotionality
refers to a tendency or trait to experience and express negative emotions like anxiety, fear, sadness, anger, and worry
obsession
recurrent and persistent
cognitive experiences
thoughts, urges, images
intrusive and unwanted
unlikely to be related to real problems
obsessive compulsive disorder
presence of obsession, compulsions, or both
obsession defined by:
recurrent and persistent thoughts, urges, or images are experience (at some time) as intrusive and unwanted, and that in most individuals cause marked anxiety or distress
the individual attempts to ignore, suppress, or neutralize them with some other thought or action
compulsions defined by:
repetitive behaviors or mental acts that the individual feels driven to perform in response to an obsession or according to rules that must be applied rigidly
the behaviors or mental acts are aimed at preventing or reducing anxiety or distress, or preventing some dreaded event or situation; however, these behaviors or mental acts are not connected in a realistic way with what they are designed to neutralize or prevent, or are clearly excessive
the obsessions or compulsions are time-consuming or cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the obsessive compulsive symptoms are not attributable to physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the disturbance is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
orbito frontal cortex
part of the brain that plays a key role in decision-making, emotion, and learning
orbito frontal caudate circuit
linked to reward-value processing, decision-making, and goal-directed behavior, with the OFC processing emotional and motivational cues
orbito frontal striatum circuit
reward-based decision-making, evaluating risk, regulating emotions, and learning/forming habits by interacting with areas involved in sensory integration and value representation
pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS)
a condition where children develop or experience worsening OCD or tic disorders after a strep infection, potentially triggered by molecular mimicr
response prevention
psychoeducation
development of exposure hierarchy
exposure to stimuli
prevention of compulsive ritual
repeated exposure over time with response prevention
thought fusion
individuals believe that thoughts, even if intrusive or unwanted, are equivalent to or can cause actions or have the same moral implications as real actions, often associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
thrichotillomania
recurrent pulling out of ones hair, resulting in hair loss
repeated attempts to decrease or stop hair pulling
the hair pulling causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social occupational, or other important areas of functioning
the hair pulling or hair loss is not attributable to another medical condition
the hair pulling is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder
bipolar
a chronic mental health condition characterized by extreme and persistent mood swings between periods of mania (high energy and euphoria) and depression (low mood and loss of interest)
bipolar I disorder
at least one manic episode
hypomanic episodes common (not required)
major depressive episode, depression, and mixed experiences common (not required)
psychotic experiences may occur (not required)
bipolar II disorder
at least one hypomanic episode and at least one major depressive episode
mixed experiences may occur (not required)
no history of mania
no psychotic symptoms
cyclothymia
For at least two years there have been numerous periods with hypomanic symptoms that do not meet criteria for a hypomanic episode and numerous periods with depressive symptoms that do not meet criteria for a major depressive episode
During the above two year period, the hypomanic and depressive periods have been present for at least half the time and the individual has not been without the symptoms for more than 2 months at a time
Criteria for a major depressive, manic, or hypomanic episode have never been met
The symptoms in Criterion A are not better explained by schizoaffective disorder, schizophrenia, schizophrenia spectrum, and other psychotic disorder
the symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functions
depression
a common mental health condition characterized by a persistent low mood, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, and other symptoms that interfere with daily functioning.
distractibility
an individual's tendency to have their attention easily drawn away from a current task or focus by internal or external stimuli, resulting in difficulty concentrating or maintaining focus.
dysthymia/persistent depressive disorder
Depressed mood for most of the day, for more days than not, as indicated by either subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 year
presence, while depressed of two or more of the following
poor appetite or overeating
insomnia or hypersomnia
lower energy or fatigue
low self esteem
poor concentration or difficulty makin decisions
feelings of hopelessness
during the 2 year period of the disturbance, the invidious has never been without the symptoms in Criteria A and B for more than 2 months at a time
Criteria for a major depressive disorder may be continuously present for 2 years
there has never been a manic episode or a hypomanic episode
the disturbance is not better explained by a persistence schizoaffective disorder, schizophrenia, delusional disorder, or other specified or unspecified schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorder
the symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social occupational, or other important areas of functioning
elevated mood
higher than appropriate confidence, exaggerated energy and well-being
happiness and euphoria
higher mood can be infectious and pep up other people as well
euthymia
a stable and balanced emotional state characterized by:
Absence of significant mood disturbances:
state where a person does not experience symptoms of depression, mania, or other mood disorders.
Positive affect:
individuals typically exhibit positive emotions such as contentment, cheerfulness, and optimism.
Emotional stability:
state of emotional equilibrium, where a person is able to cope with everyday stressors and maintain a relatively even mood.
Psychological well-being:
flight of ideas
a rapid, continuous succession of superficially related thoughts or ideas, often manifesting as hurried speech with abrupt topic shifts
grandiosity
an inflated sense of self-importance, superiority, and entitlement.
hypersomnia
chronic sleep disorder characterized by persistent, excessive daytime sleepiness, even after adequate sleep,
hypomania
a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased activity or energy, lasting at least four consecutive days and present most of the day, nearly every day
during the period of mood disturbance and increased energy and activity, three or more of the following have persisted, represent a noticeable change from usual behavior, and have been present to a significant degree
inflated self
the episode is associated with an enquaiovla change in functioning that is uncharacteristic of the individual when not symptomatic
the disturbance in mood and the change in functioning are observable by others
the episode is not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning or the necessitate hospitalization. If there are psychotic features, the episode is, by definition, manic
4+ days
not markedly impaired; unequivical change distinctly noticeable to observer
no psychotic symptoms
no hospitalization due to hypomania
major depressive disorder
1+ major depressive episodes
no history of manic or hypomanic episodes
At least one major depressive episode is not superimposed on a psychotic disorder
we diagnose the disorder; to do that we must identify the episodes
mania
idea of exuberance, too much energy and excitement
a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased activity or energy, lasting at least one week and present most of the day, nearly every day or any duration is hospitalization is necessary
during the period of mood disturbance and increased energy or activity, three or more of the following symptoms are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change from usual behavior
inflated self esteem or grandiosity
comes with feelings of being special, chosen, etc
decreased need for sleep
someone who doesn’t need the sleep
more talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
rapid, frenzy speech, can be loud, difficult to interrupt, uses gestures more exaggerated than socially expected
Some patients report that their thoughts are going fast so they feel they need to get those thoughts out verbally
flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing
distractibility as reported or observed
increase in goal directed activity or psychomotor agitation
excessive involvement in activities that have a high potential for painful consequences
the mood disturbance is sufficiently sever to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning or to necessitate hospitalization to prevent harm to self or others, or there are psychotic features
the episode is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
7+ days or any length if hospitalized
marked impairment
psychotic experiences may occur
hospitalization due to mania may occur
marked impairment
a serious limitation in one or more key areas of mental functioning, such as understanding, remembering, applying information, concentrating, and adapting, interfering with independent, appropriate, and effective functioning
mixed episode/features
a bipolar disorder episode characterized by the simultaneous presence of both manic and depressive symptoms, or rapidly alternating between them, rather than a clear separation of distinct mood states
mood
predominant emotional state and/or conscious frame of mind
mood episode
major depressive, hypomanic, and/or mixed
persistent depressive disorder
Depressed mood for most of the day, for more days than not, as indicated by either subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 year
presence, while depressed of two or more of the following
poor appetite or overeating
insomnia or hypersomnia
lower energy or fatigue
low self esteem
poor concentration or difficulty makin decisions
feelings of hopelessness
during the 2 year period of the disturbance, the invidious has never been without the symptoms in Criteria A and B for more than 2 months at a time
Criteria for a major depressive disorder may be continuously present for 2 years
there has never been a manic episode or a hypomanic episode
the disturbance is not better explained by a persistence schizoaffective disorder, schizophrenia, delusional disorder, or other specified or unspecified schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorder
the symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
the symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social occupational, or other important areas of functioning
premenstrual dysphoric disorder
in the majority of menstrual cycles, at least five symptoms must be present in the final week before the onset of messes, start to improve within a few days after the onset of menses, and become minimal or absent in the week post-meses
one or more of the following symptoms must be present
marked affective albility
marked irritability or anger or increased interpersonal conflicts
marked depressed mood, feelings of hopelessness, or self-deprecating thoughts
marked anxiety, tensions, and/or feelings of being keyed up or on edge
one or more of the following symptoms must additionally be present, to reach a total of five symptoms when combined with symptoms from Criterion B above
decreased interest in usual activities
subjective difficulty in concentration
lethargy, easy fatigability, or marked lack of energy
marked change in appetite, overeating, or specific food cravings
hypersomnia or insomnia
a sense of being overwhelmed or out of control
physical symptoms such as breast tenderness or swelling, join or muscle pain, a sensation of bloating or weight gain
Criteria A-C must have been met for most menstrual cycles that occurred in the preceding year
the disturbance in not merely an exacerbation of the symptoms of another disorder
Criterion A should be confirmed by prospective daily rating during at least two symptomatic cycles
the symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance or another medical condition
pressured speech
a symptom characterized by rapid, intense, and often uncontrollable verbal output, frequently observed during manic episodes or related to thought disorders, and is characterized by an inability to stop talking or difficulty following through with a coherent train of though
psychomotor agitation
a state of intense restlessness and irritability marked by increased and often purposeless motor activity, reflecting underlying mental tension and anxiety
psychomotor r*
a slowing down of both thought processes and physical movements, often seen as a symptom of depression or other conditions. It's characterized by decreased energy, slower speech, and reduced physical activity.
psychosis
a mental health condition characterized by a loss of touch with reality. It involves a significant disturbance in perception, thinking, and behavior, leading to a distorted understanding of the world
sadness
a negative emotional state characterized by feelings of unhappiness, grief, and loss
unequivocal change
a distinct period of elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and increased activity or energy, representing a noticeable and abnormal shift in an individual's functioning, easily observable by others and recognized as a change from their usual state.
unipolar
where the focus is on persistent depressive episodes alone, without the alternating manic or hypomanic episodes characteristic of bipolar disorder; MDE, MDD, PDD, PMDD
acute stress disorder
Similar to PTSD in earlier phases
9+ symptoms across PTSD-like symptom categories
Duration: 3 days to 29 days
adjustment disorder
The development of emotional or behavioral symptoms in response to an identifiable stressor(s) occurring within 3 months of the onset of the stressor(s)
These symptoms or behaviors are clinically significant, as evidenced by one or both of the following
marked stress that is out of probation to the severity or intensity of the stressor taking into account the external context and the cultural factors that might influence symptoms severity and presentation
significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
The stress-related disturbance does not meet the criteria for another mental disorder and is not merely an exacerbation of a preexisting mental disorder
The symptoms do not represent normal bereavement and are not better explained by the prolonged grief disorder
once the stressor or its consequences have terminated, the symptoms do not persist for more than an additional 6 months
avoidance
the act of steering clear of situations, people, or thoughts that cause negative feeling
equifinality
different pathways and risk factors may have the same outcome
exaggerated startle reponse
a neurological disorder characterized by an excessive and often uncontrollable reaction to sudden, unexpected stimuli, such as noises or touch, leading to exaggerated muscle spasms and reaction
eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
combines therapy and eye movements or other types of stimuli (sounds, taps)
helps access and and process unresolved traumatic memories
treats PTSD, anxiety, mood, and substance use disorders
hypervigliance
a psychological state characterized by an excessive and heightened awareness of potential threats or dangers in the environment. It involves a constant scanning and monitoring of surroundings, leading to an increased state of alertness and anxiety.
intrusion symptoms
the persistent, unwanted, and distressing experiences associated with a traumatic event, including intrusive thoughts, memories, dreams, and flashbacks that feel so real, the person feels like they are reliving the event
multifinality
similar pathways and risk factors may have different outcomes
overgeneralization of fear
the tendency for a fear response, learned to a specific threat or stimulus, to spread or generalize to other, similar but unrelated, stimuli, contributing to anxiety and related disorders
prazosin
cardiovascular medication called an “alpha-blocker”
Relaxes blood vessels to ease blood flow
blocks the alpha1 receptor for norepinephrine
another commonly used medication is propranolol (beta blocker)
propranolol
a beta-blocker, is sometimes used "off-label" in psychiatry for anxiety and related conditions like performance anxiety, PTSD, and social anxiety, primarily to manage the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as a rapid heart rate and shaking.
PTSD
Exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence in one or more of the following ways
directly experiencing the traumatic event(s)
witnessing, in person, the event(s) as it occurred to others
learning that the traumatic event(s) Occurred to a close family member or close friend. In cases of actual or threatened death of a family member of friend, the event(s) must have been violent or accidental
doesn’t meet criteria if you learn family member died of cancer, heart disease, etc
experiencing repeated or extreme exposure to averse details of the traumatic event(s)
Presence of one or more of the following intrusion symptoms associated with the traumatic event(s), beginning after the traumatic event(s) occurred
recurrent, involuntary, and intrusive distressing memories of the traumatic event(s)
recurrent distressing dreams in which the content and/or affect of the dream are related to the traumatic event(s)
dissociative reactions in which the individual feels or acts as if the traumatic event(s) were recurring
intense or prolonged psychological distress at exposure to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event(s)
Marked physiological reactions to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event
Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the traumatic event(s), beginning after the traumatic event(s) occurred, as evidenced by one or both of the following
avoidance of or efforts to avoid distressing memories, thoughts, or feelings about or closely associated with the traumatic event(s)
avoidance of or efforts to avoid distressing memories, thoughts or feeling about closely associated with the traumatic event(s)
Negative alterations in cognitions and mood associated with the traumatic event(s), beginning or worsening after the traumatic event(s) occurred, as evidenced by two or more of the following
inability to remember an important aspect of the traumatic event(s)
persistence and exaggerated negative, beliefs or expectation about oneself, others, or the world
persistent, distorted conditions about the cause of consequences of the traumatic event(s) that lead the individual to blame himself/herself or others
persistent negative emotional state
markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities
feelings of detachment or estrangement from others
persistent inability to experience positive emotions
Marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with the traumatic event(s) beginning or worsening after the traumatic event(s) occurred, as evidenced by two or more of the following
irritable behavior and angry outbursts typically expressed as verbal or physical aggression toward people or objects
reckless or self-destructive behavior
hypervigilance
exaggerated startle response
problems with concentration
sleep disturbance
Duration of the disturbance (Criteria B, C, D, and E) is more than one month
the disturbance causes clinically significant distress or important in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (I.e. medication, alcohol) or another medical condition
resilience
the ability to adapt well to difficult life experiences, or "bounce back" from adversity. It's a process that involves mental, emotional, and behavioral flexibility
sensitized ANS and HPA
an increased or heightened responsiveness of both the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to stress, often following exposure to severe or repeated stressors
stress
internal psychological and physiological response to a stressor
stressor
difficult life circumstance or event that places physical/psychological demand on a person
trauma
psychological and physiological response to a traumatic event
traumatic event
Experience that is deeply distressing or disturbing