Endocrine Glands + Hormones
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
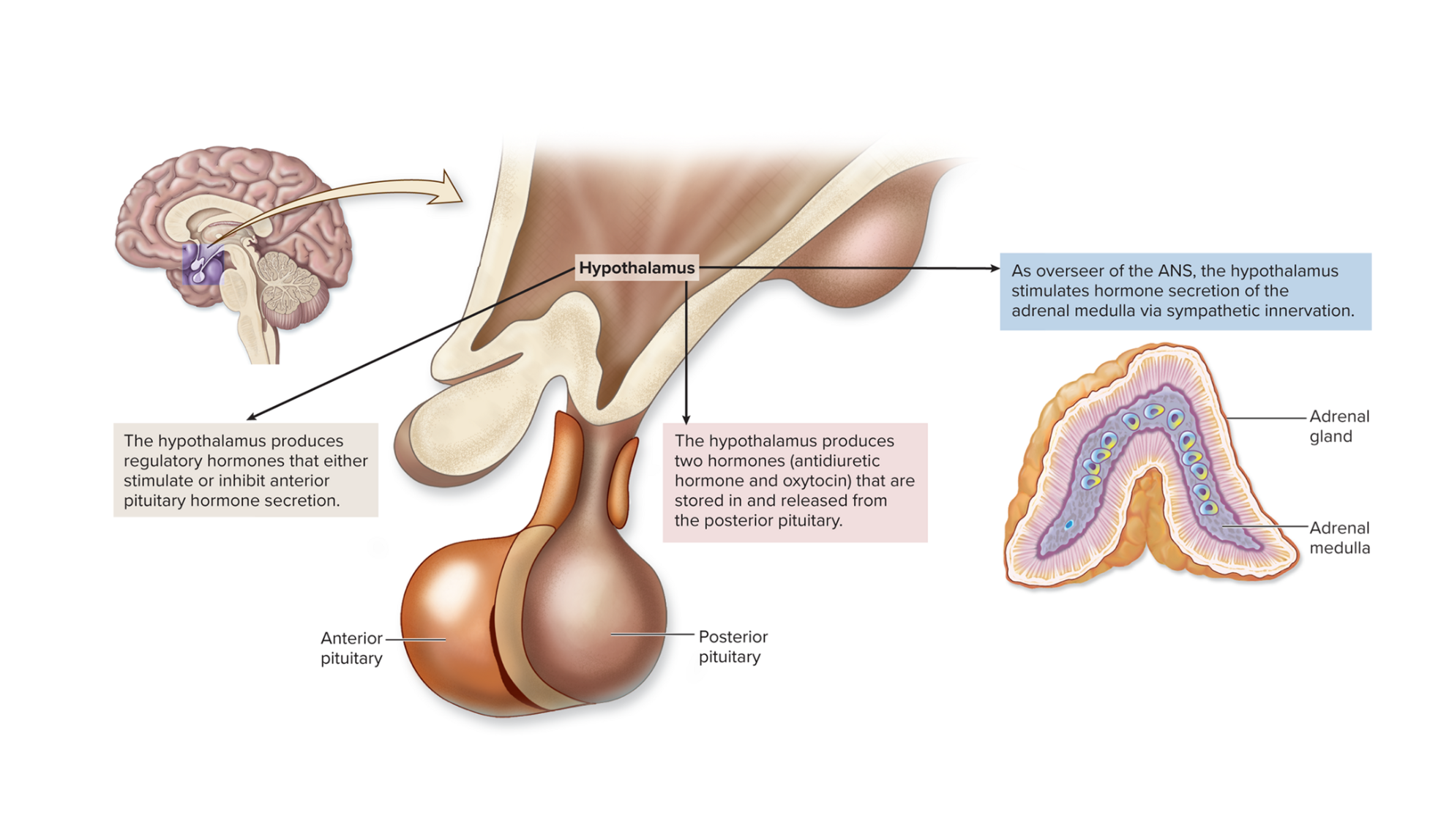
Hypothalamus
“master control center” → assisting the pituitary gland
produces antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
oxytocin (OT)
regulatory hormones
→ Releasing hormones (RH): stimulate the production and secretion of specific anterior pituitary hormones
→ Inhibiting hormones (IH): deter the production and secretion of specific anterior pituitary hormones
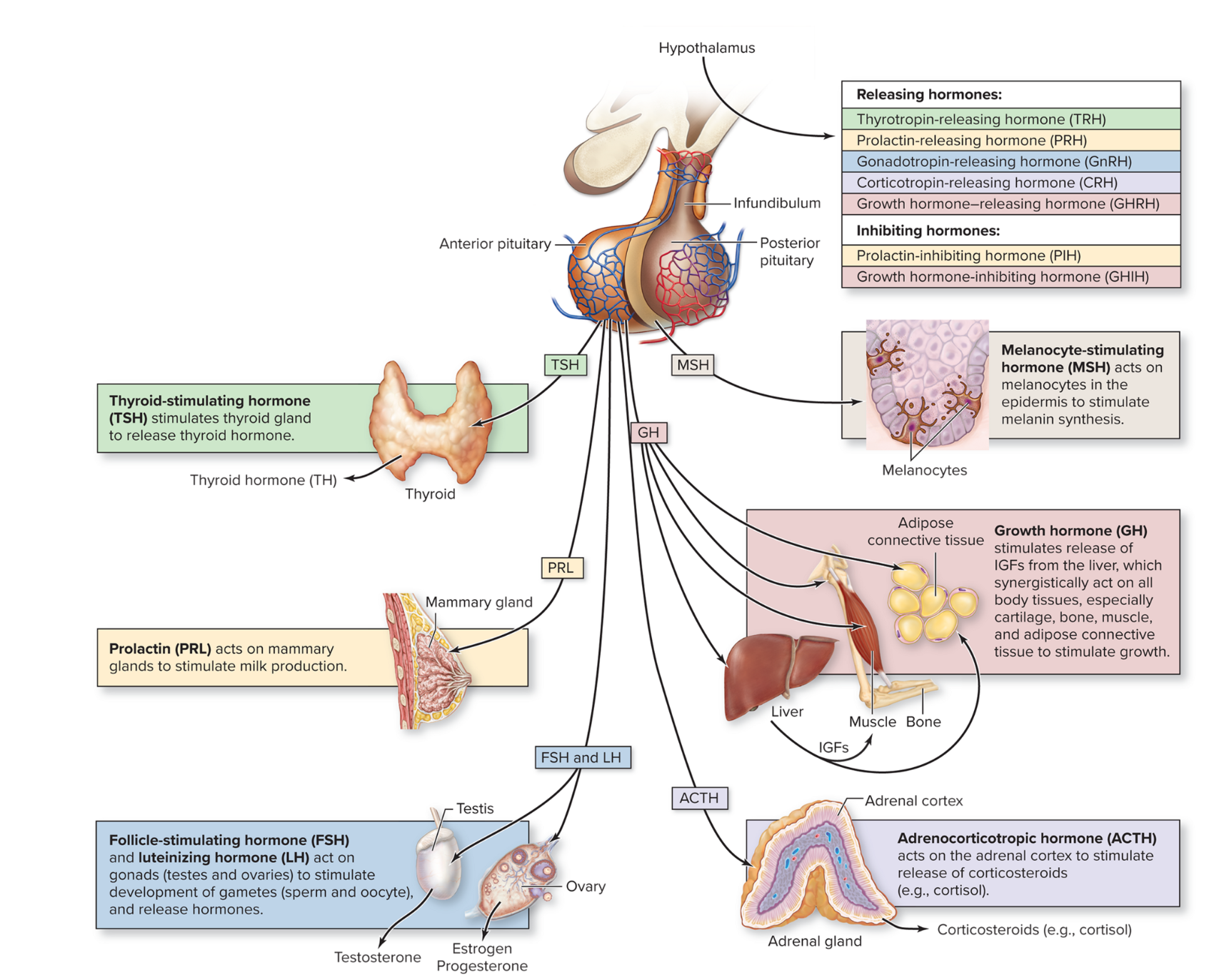
Pituitary: Anterior Pituitary (adenohypohysis)
most of the pituitary gland is composed of the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
→ regulatory hormones reach the anterior pituitary gland by traveling through a blood vessel network called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal
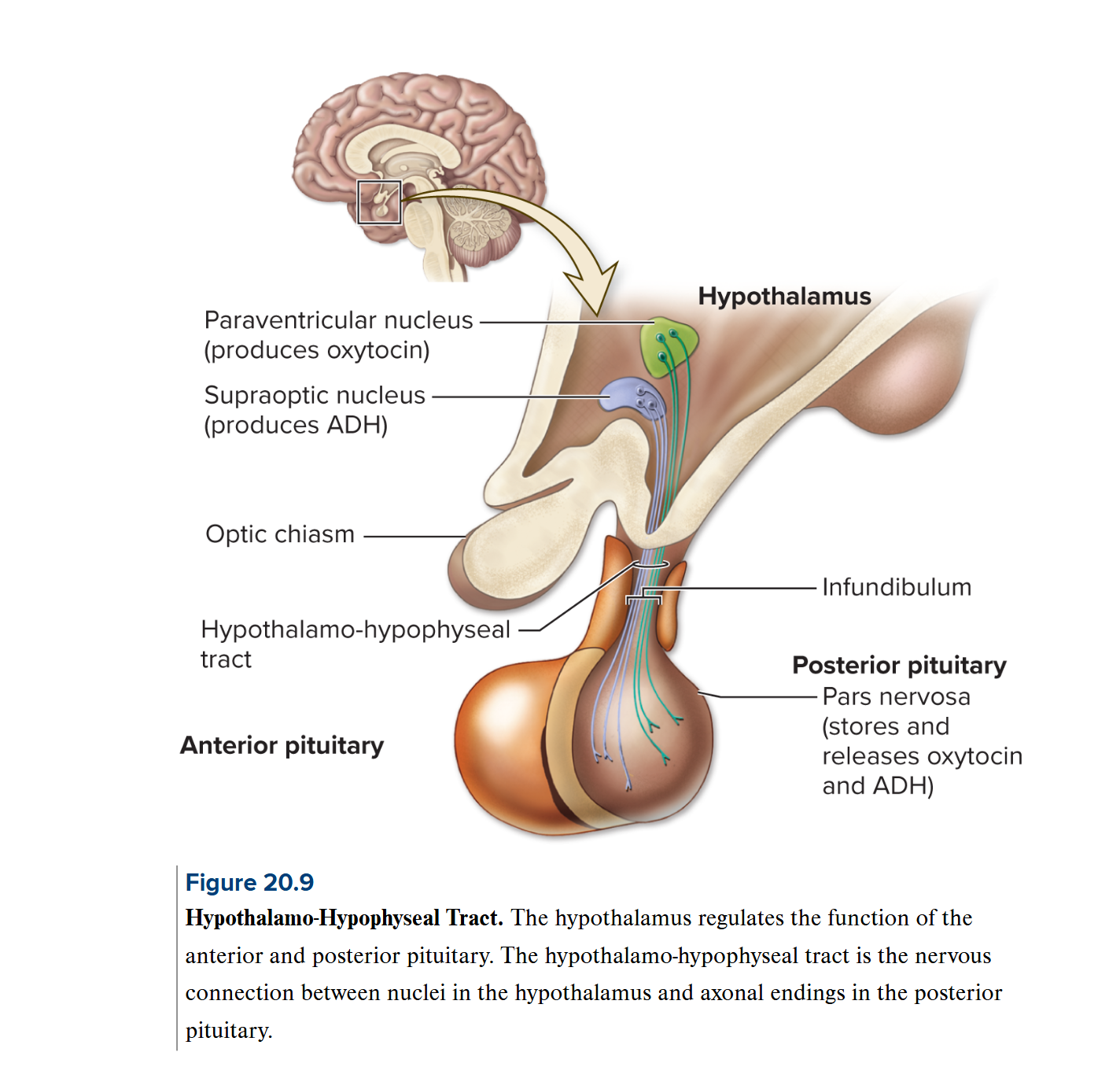
Pituitary gland: Posterior pituitary (neurohypohysis)
→ the neural connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary gland is called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
→ hypothalamic neurons: neurosecretory cells bc they secrete hormones
→ releases Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): water reabsorption, concentrating urine, can increase blood pressures
→ releases Oxytocin: stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth, milk ejection, social bonding + pleasure
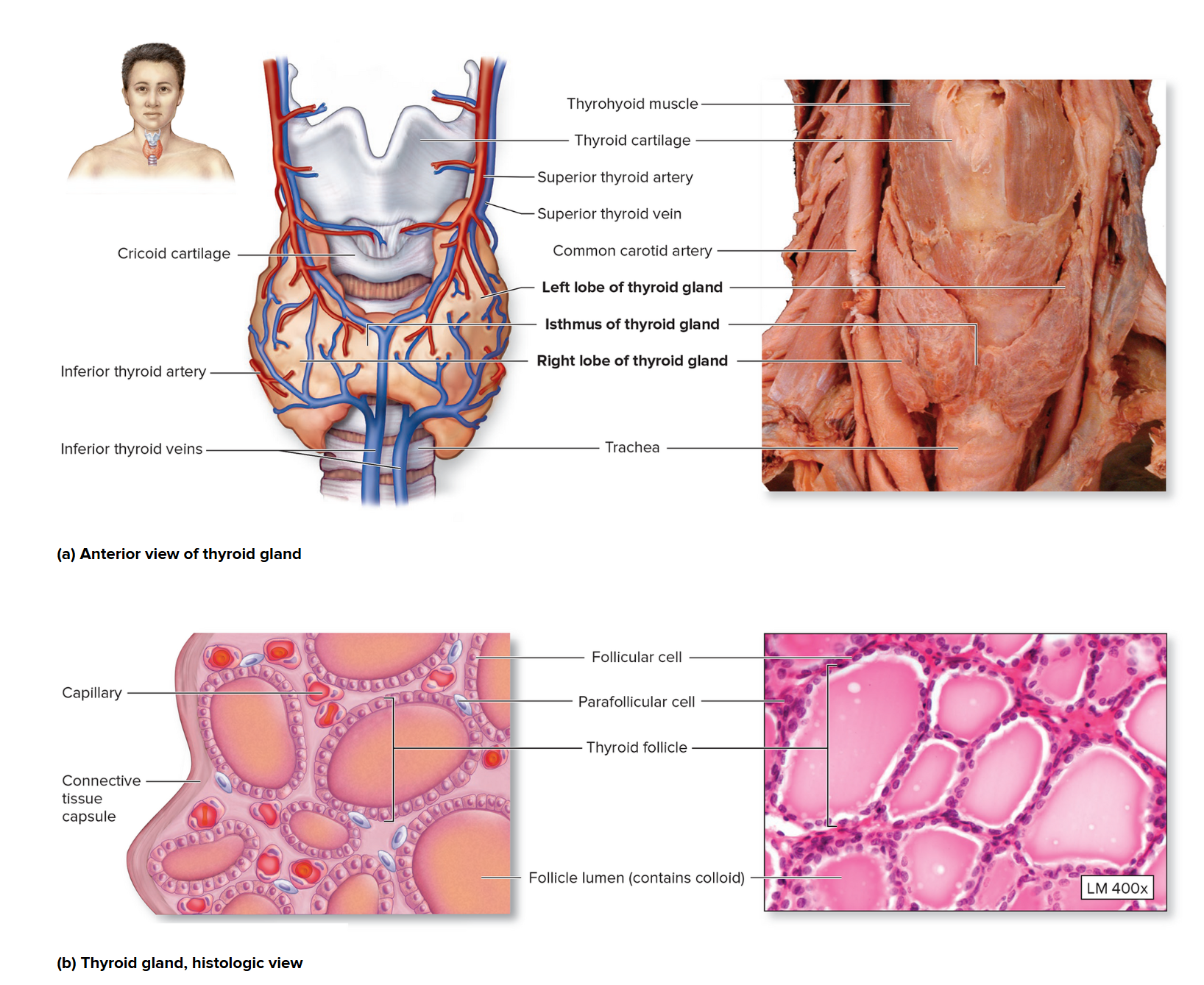
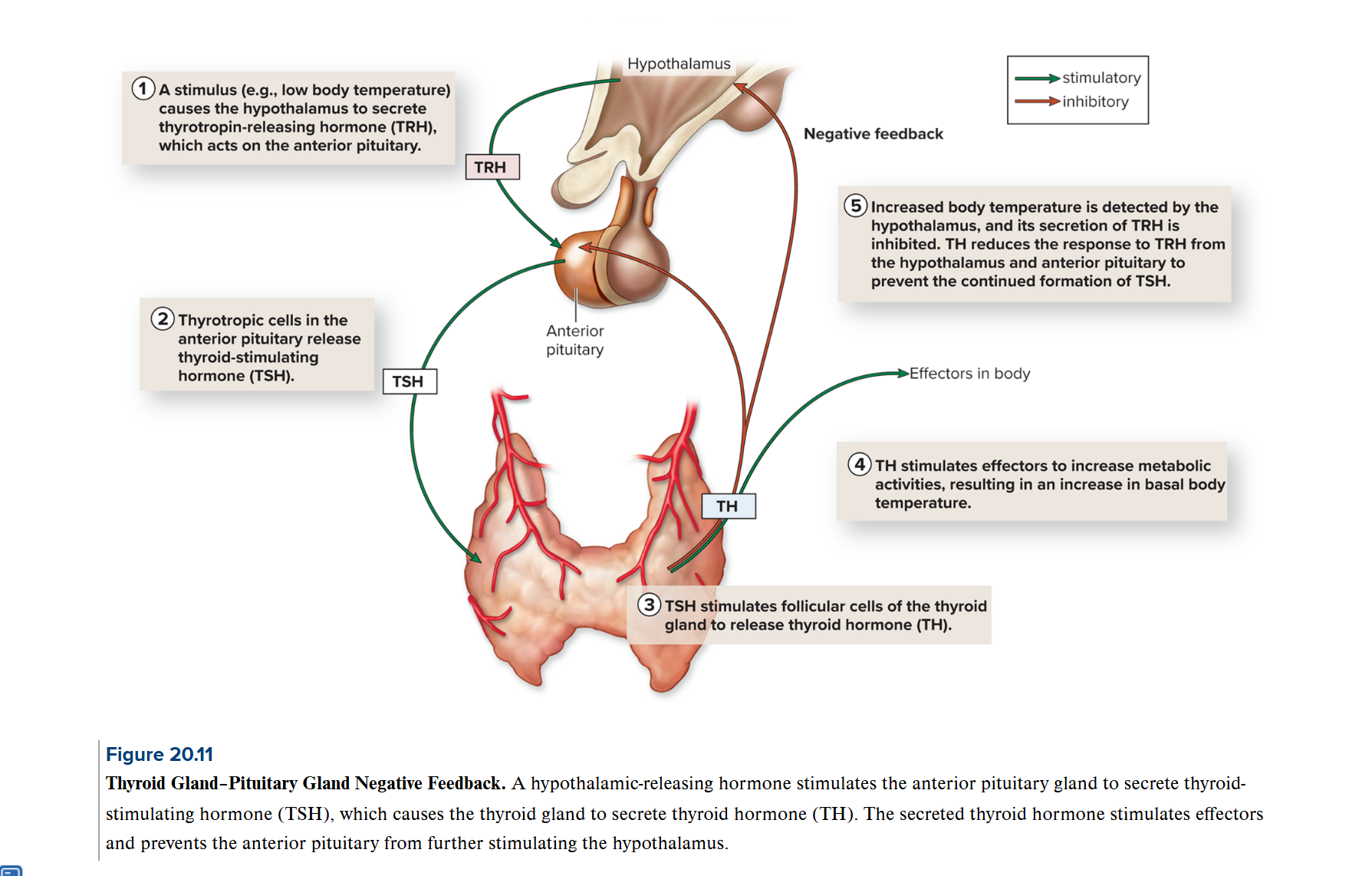
Thyroid gland
the thyroid gland is butterfly shaped, composed of left and right lobes
avg weight in adults: 25-30 grams (largest gland)!
highly vascular = red color
Calcitonin (CT): secreted by parafollicular cells reduces calcium levels in the body fluids, decreases bone reabsorption by osteoclasts and increases calcium loss through kidneys
Thyroid Hormone (TH): increases metabolism, oxygen use, growth, and energy use, supports and increases rate of development
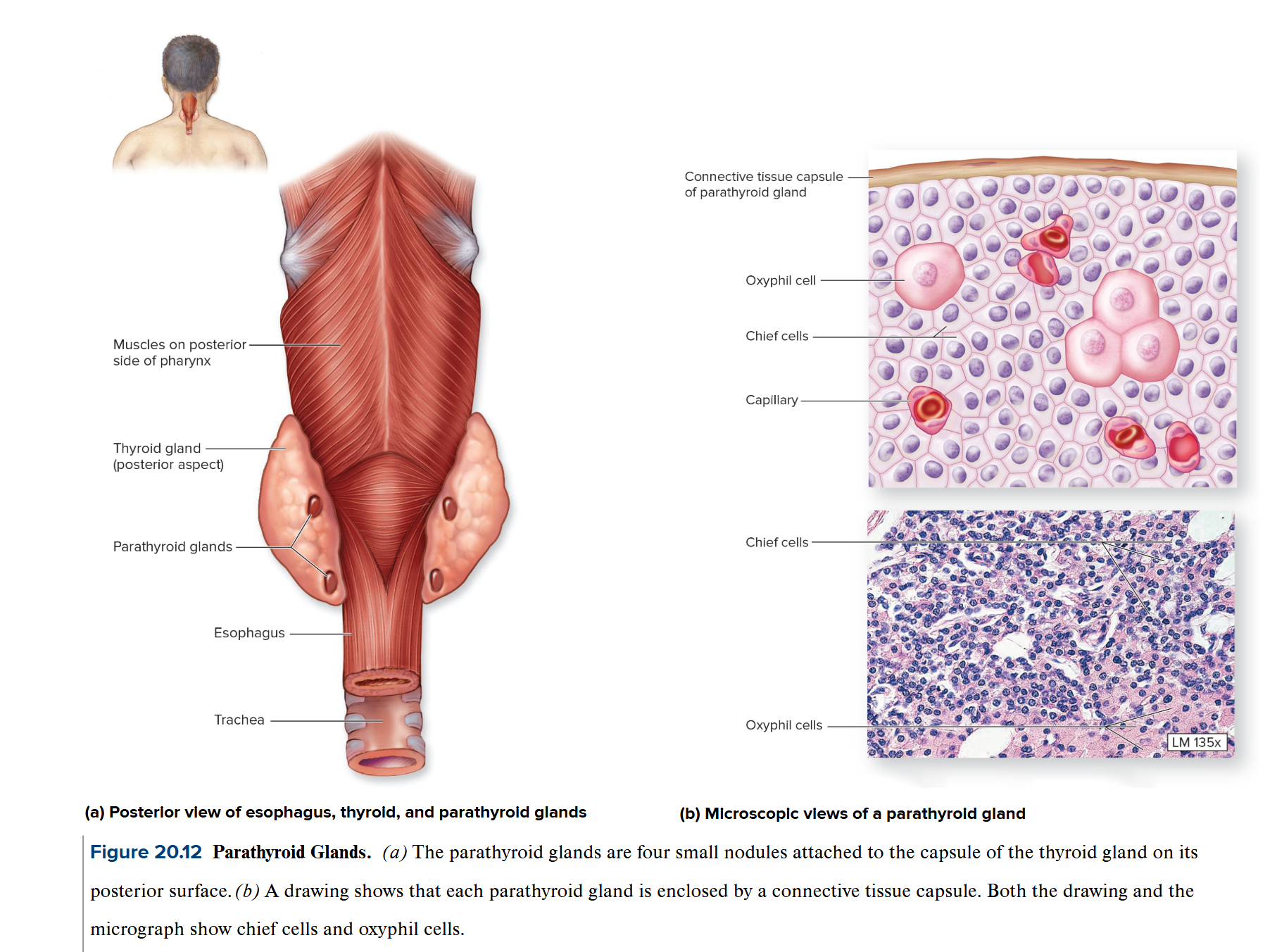
Parathyroid glands
small, brownish-red are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
chief cells are source of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
→ increases calcium lvls in blood through bone reabsorption
→ increases calcium absorption by small intestine by calcitriol
→ decreases calcium loss through the kidneys
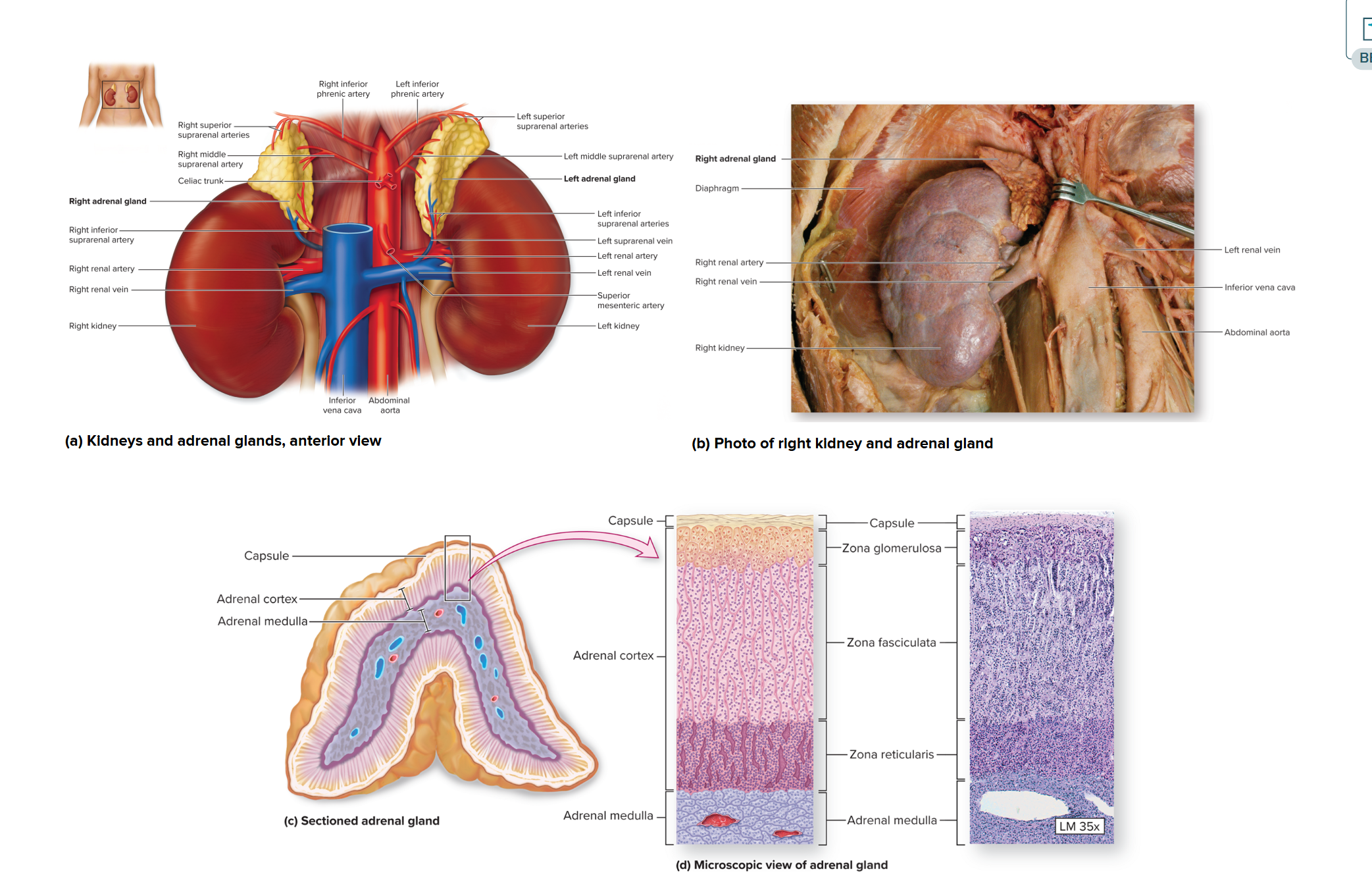
Adrenal Glands (suprarenal): Adrenal Cortex
are paired, pyramid shaped endocrine glands anchored on the superior surface of each kidney
has an outer adrenal cortex and inner adrenal medulla
Adrenal Cortex
synthesize more than 25 diff steroid hormones called corticosteroids
→ vital to our survival; trauma to or removal of the adrenal glands requires corticosteroid supplementation throughout life
Zona glomerulosa (outer cortical layer): synthesize mineralocorticoids
→ grp of hormones that help regulate the composition and concentration of electrolytes(ions) in body fluids; aldosterone (regulating Na+ and K+ ions in blood
Zona fasculata (middle layer): Glucocorticoids elevate blood gluclose lvls and stimulate use of lipids and proteins as energy resources
→ esp when the body attempts to resist stress + repair injured/damaged tissues
→ most common glucocorticoids are cortisol and corticosterone
Zona reticularis: secrete gonadocorticoids
→ androgens, which are sex hormones
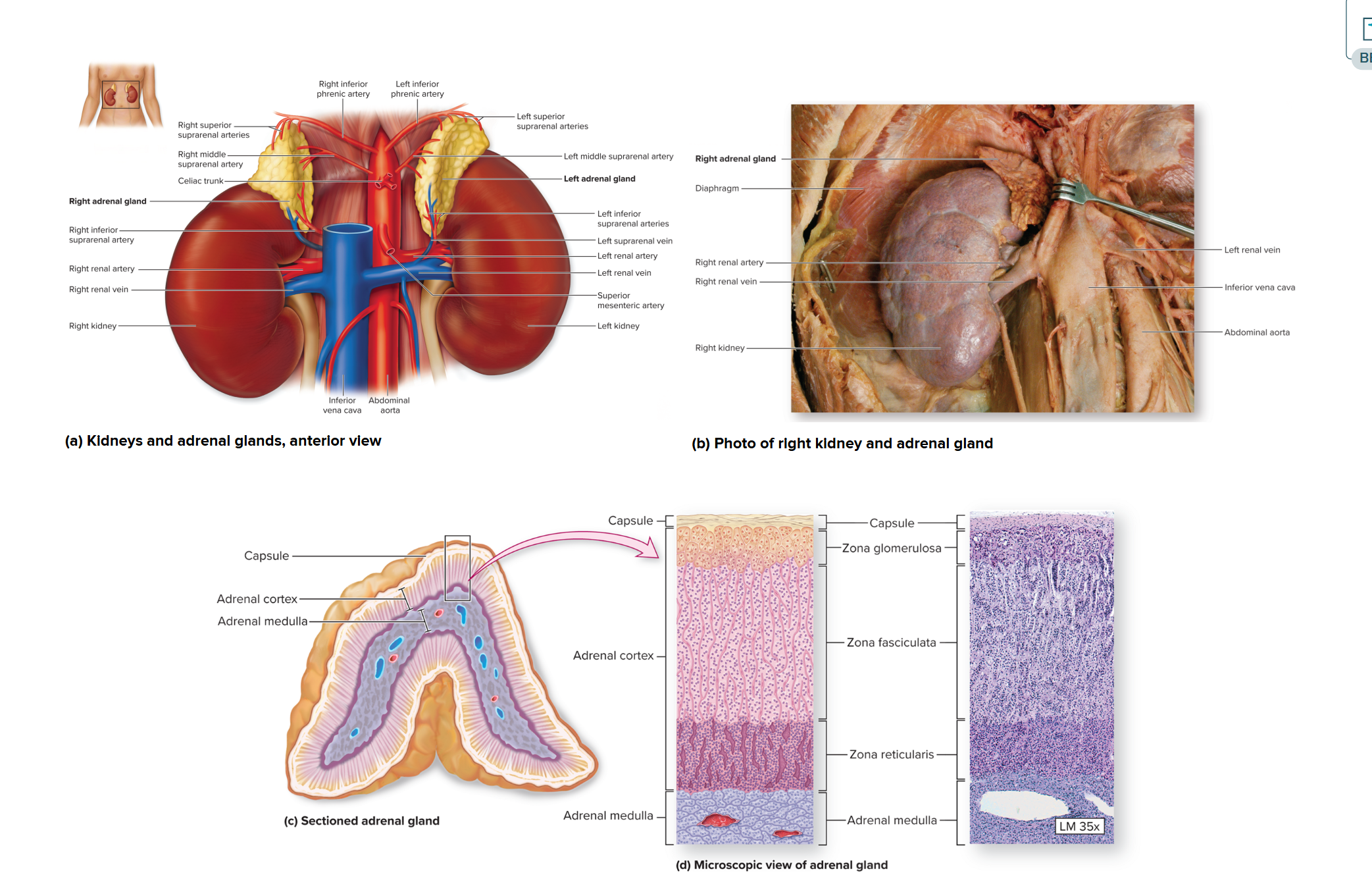
Adrenal Glands (suprarenal): Adrenal Medulla
inner core of each adrenal gland
has a red-brown color bc its highly vascularized
secretes epinephrine (also called adrenaline)
secretes norepinephrine (also called noradrenaline)
→ these hormones work together w/ the sympathetic division of the autonomic nerv sys to prepare body for fight or flight responses
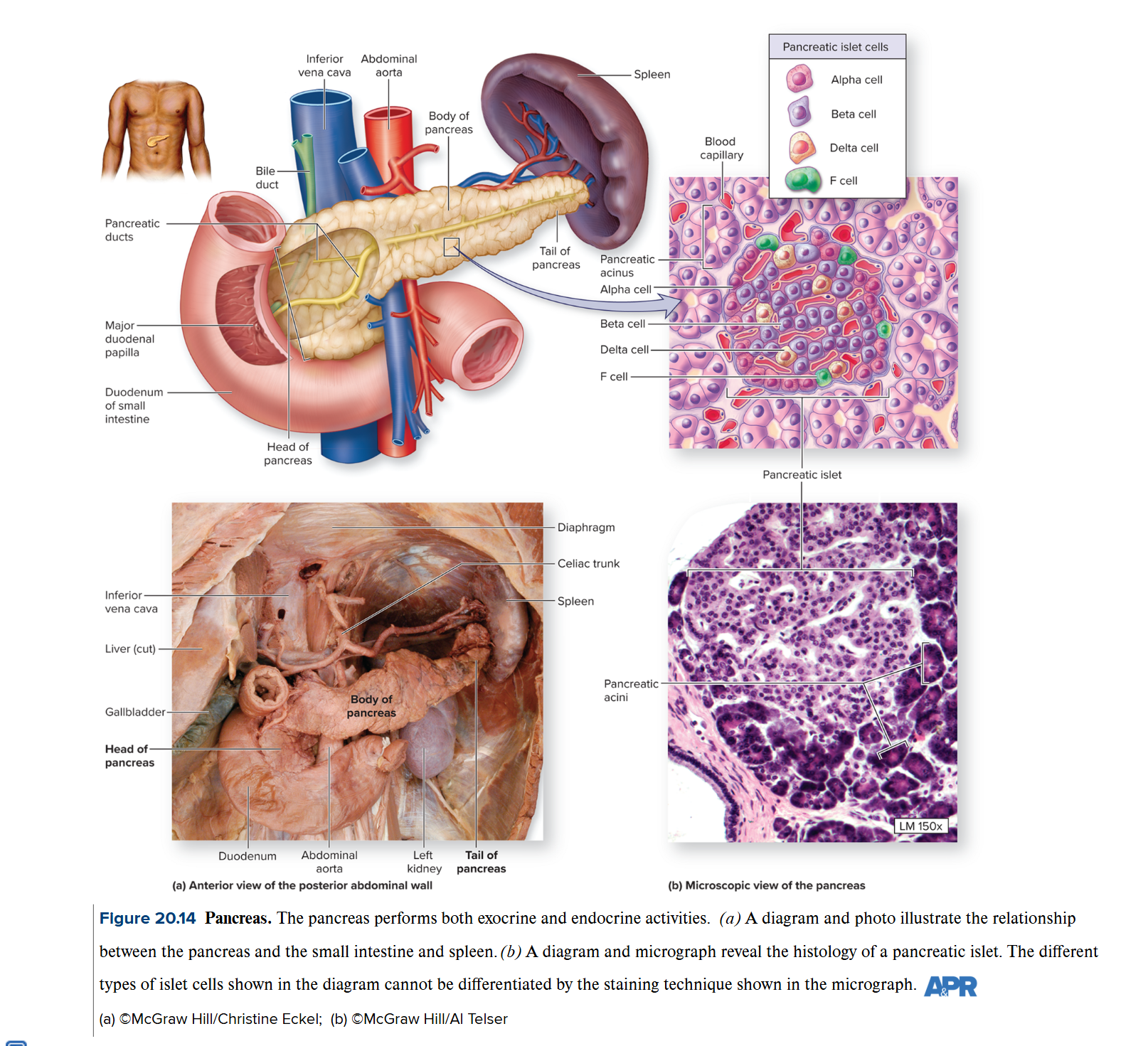
Pancreas
performs both exocrine and endocrine activities → considered a heterocrine or mixed gland
mostly composed of cells called pancreatic acini → producing alkaline pancreatic juice that helps w/ digestion
has endocrine cells called pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) which produce their own hormone
Alpha Cells
secrete glucagon when blood glucose lvls drop
live breaks down glycogen into glucose and release glucose into the blood to increase blood sugar lvls
stimulates adipose cells to break down lipid and secrete it into the blood
Beta Cells
secrete insulin when blood glucose lvls are too high
liver + body cells respond to insulin by taking up the glucose, thus lowering blood sugar lvls
also promotes glycogen synthesis + lipid storage
Delta Cells
stimulated by high lvls of nutrients in the blood
synthesize somatostatin (growth hormone-inhibiting hormone)
slows the release of insulin and glucagon + activity of digestive organs, slowing the rate of nutrient entry into the blood
F cells
stimulated by protein digestion in the digestive tract
secrete pancreatic polypeptide (PP) to suppress and regulate somatostatin secretion from delta cells
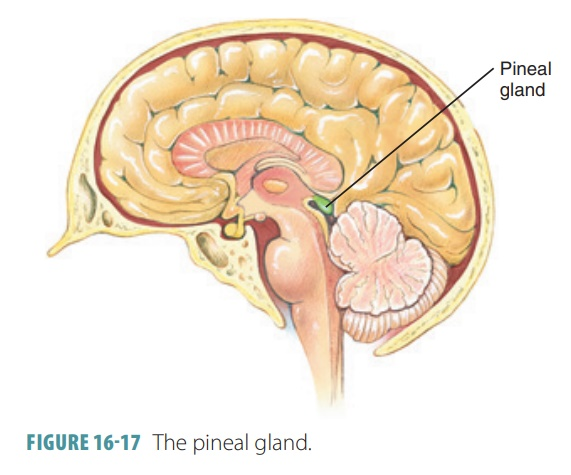
Pineal Gland
composed primarily of pinealocytes which secrete melatonin
→ a hormone that makes us drowsy
→ its production tends to be cyclic; it increases at night and decreases during the day
helps regulate circadian rhythm (24 hr body clock)!
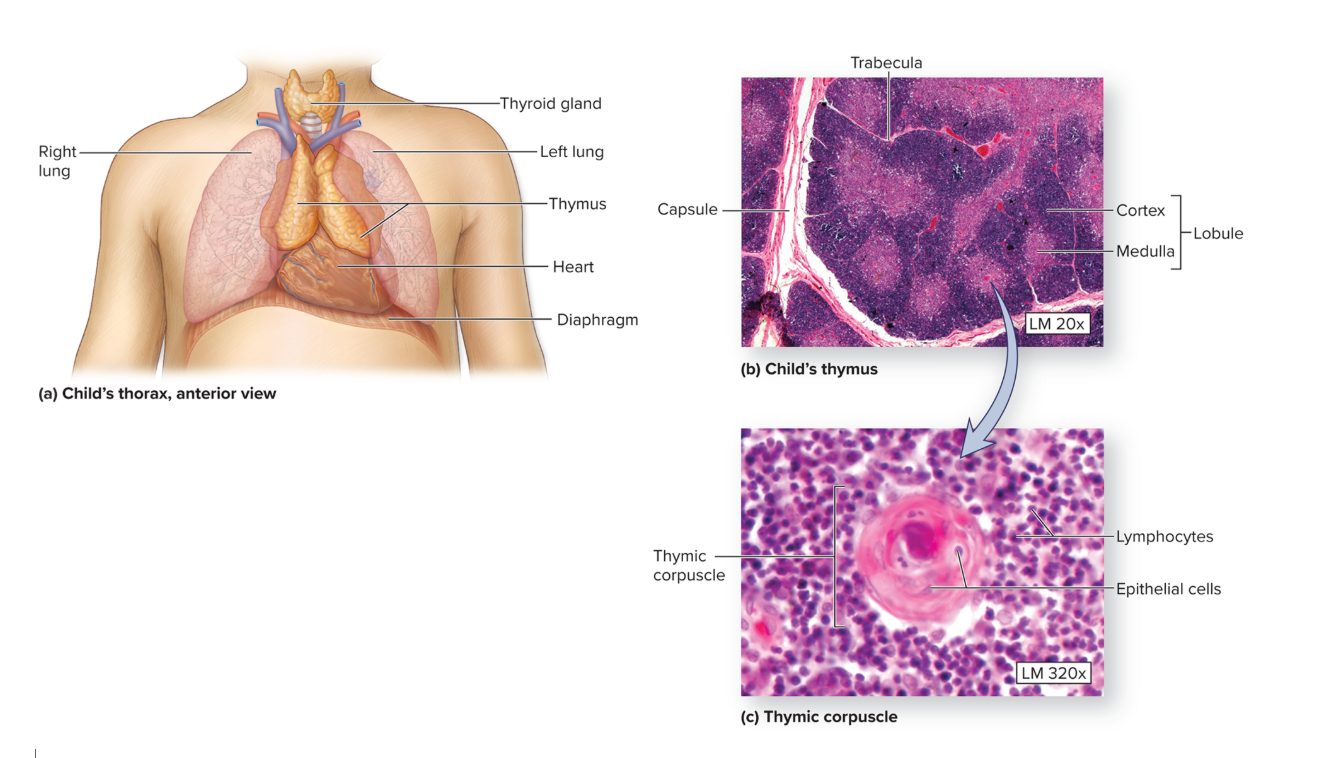
Thymus
the size of thymus varies among individuals; relatively large in infants, continues to grow until puberty then diminishes in size and activity.
functions in association w/ the lymphatic system to regulate and maintain body immunity
→ produces thymopoietin and thymosin (grp of complimentary hormones)
→ hormones act by stimulating and promoting the differentiation, growth, and maturation of T-lymphocytes
Gonads
primary sex organs
Ovaries
Estrogen: stimulates development of reproductive organs, follicle maturation, regulates menstrual cycle, stimulates growth of mammary glands
Progesterone: regulates menstrual cycle, stimulates growth of uterine lining, stimulates growth of mammary glands
Testes
Androgens (primarily testosterone): stimulates reproductive organ development, production of sperm
gonads also produce inhibin
inhibits follicle-stimulating hormone secretion