Chem
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The total energy of the universe is constant.
What describes an exothermic process?
Liquid vanadium solidifies at 1,500°C.
An ideal gas performs 166.7 J of work against a movable piston and an external pressure of 0.577 atm. The final volume of the gas is 57.4 L. What was the initial volume of the gas? Hint: 101.3 J = 1L•atm
54.5L
If the same amount of heat is removed from 50.0 g of different substances initially at 150°C, which will have the lowest temperature after cooling?
steel
A 251 g porcelain plate, initially at 22.2°C, was heated with a candle. If the candle supplies 15.0 kJ of heat, what is the final temperature of the porcelain plate?
77.3 C
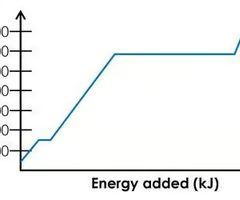
The cooling curve of magnesium at 1 bar of pressure is shown below. Approximate the melting point of Mg and identify the phase/s that exist at this temperature.
650°C; Mg(s) and Mg(l) exist at this temperature.
An unknown metal weighing 108.6 g was heated at 89.7°C and dropped in a coffee cup calorimeter containing 163.2 g mineral oil initially at 15.0°C. After thermal equilibrium is established, the temperature of the mixture is 27.2°C. What is the metal?
vanadium
Consider the dissolution of potassium bromide: KBr(s) → K+(aq.) + Br-(aq.) A 10.5-g sample of KBr(𝓜 = 119.0 g/mol) is dissolved in 125 g water, with both substances at 24.2°C.After the KBr dissolves, the final temperature of the solution is 21.1°C. Assuming that the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/g·°C, what is the enthalpy of dissolution of KBr in kJ/mol?
+19.9 kJ/mol
Consider the following reaction at 600°C: 2Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3H2O(g); ΔH° = +923 kJ How much heat is evolved when 20.2 g Fe is produced?
+167 kJ.
Which of the following hydrocarbons has the greatest ΔH°vap?
CH3CH2CH2CH3(l)
How much heat is released to convert 57.2 g of liquid gallium at 29.8°C to solid Ga at -23.4°C?
-5.72 kJ.
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide and molybdenum(VI) oxide are "layered transition metal compounds" used as catalysts in the hydrodesulfurization of petroleum products. MoS2 is heated at 1,000 K to produce MoO3 as follows: 2MoS2(s) + 7O2(g) → 2MoO3(s) + 4SO2(g); ΔH° = -2,207 kJ What is the ΔH°' of the following reaction: 6MoO3(s) + 12SO2(g) → 6MoS2(s) + 21O2(g); ΔH°' = ?
+6,621 kJ.
Given the standard enthalpies for the following reactions: 2Pb(s) + O2(g) → 2PbO(s); ΔH°rxn1 = -434.6 kJ 2Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2ZnO(s); ΔH°rxn2 = -696.6 kJ What is ΔH°rxn3 for the following reaction: PbO(s) + Zn(s) → Pb(s) + ZnO(s); ΔH°rxn3 = ?
-131.0 kJ
Which of the following equations describes the formation of one mole of HCl(g) from its component standard-state elements?
½H2(g) + ½Cl2(g) → HCl(g)
Consider the combustion of dimethyl ether: 2CH3OCH3(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g) What is the ΔH°rxn of this reaction?
-2,657 kJ
Which of the following is true about a nonspontaneous process?
The Gibbs free energy of a nonspontaneous process is always positive.
Which of the following processes is spontaneous?
Snow in Louisiana melts at 60°F
Predict which element has the greatest absolute entropy at room temperature
ytterbium
Which of the following is true, according to the third law of thermodynamics?
All molecular motion stops at absolute zero
Which of the following solid-state reactions involving gases would you predict has the most positive ΔS°rxn at 250 C
V2O5(s) + C3H6O(l) → 16VO2(s) + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
Sodium azide was previously used in car's airbags. During an automobile crash, the following reaction occurs rapidly: 2NaN3(s)→ 2Na(s)+3N2(g); ΔS° = +332.4 J/mol•K Calculate the S° of NaN3(s).
+173 J/mol•K
Which of the following is true about exothermic reactions?
ΔS°surr > 0 (+)
Calculate the ΔSuniv of the following reaction at 379°C: CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) +O2(g)
-766 J/K
At what temperature is the following reaction spontaneous? H2(s) +I2(g) → 2HI(g)
The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
Zirconium is a transition metal used for space vehicles. What is the normal boiling point of Zr? Use the thermodynamic data below to answer this question:
4,380°C
For which of the following species is ΔG°f = 0?
Br2(l)
Silicon tetrachloride reacts violently with water to produce silicon dioxide: SiCl4(l) + 2H2O(l) → SiO2(s) + 4HCl(aq.) What is the ΔG°rxn for this reaction?
-284 kJ
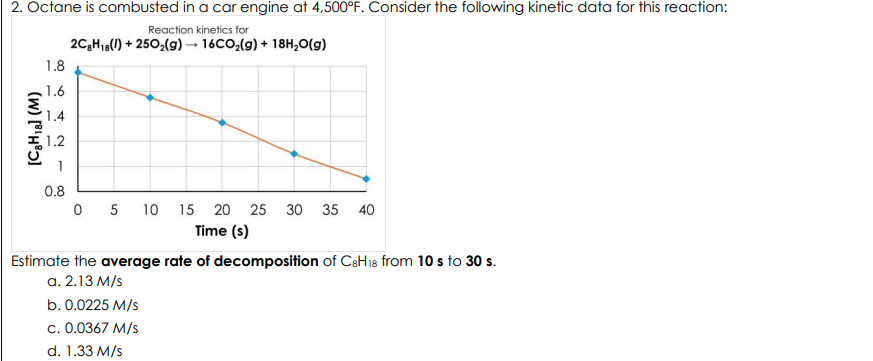
Octane is combusted in a car engine at 4,500°F. Consider the following kinetic data for this reaction: Estimate the average rate of decomposition of C8H18 from 10 s to 30 s.
0.0225 M/s
Consider the gas-phase decomposition of phosphine at 120°C: 4PH3(g) → P4(l) + 6H2(g) The rate of disappearance of PH3 is 1.10 mM/s for the first 40 s of the process. What is the rate of formation of H2?
1.65 mM/s
The reaction of iodine monochloride with hydrogen is first order in ICl and second order in H2 at 555 K: 2ICl(g) + H2(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) In an experiment, the rate constant was determined to be 2.24 M-2•s-1 when the concentration of ICl is 0.0764 M and the concentration of H2 is 0.245 M. Calculate the rate of the reaction.
1.03 × 10-2 M/s
The direct combustion of carbon monoxide in open air occurs at 690°C. In a particular experiment, the following initial rates data were collected: What is the rate law of this reaction?
rate = k[CO]
A hypothetical substance decomposes following third order kinetics. What happens to the rate of consumption of the substance when its concentration is tripled?
The rate increases by a factor of 27
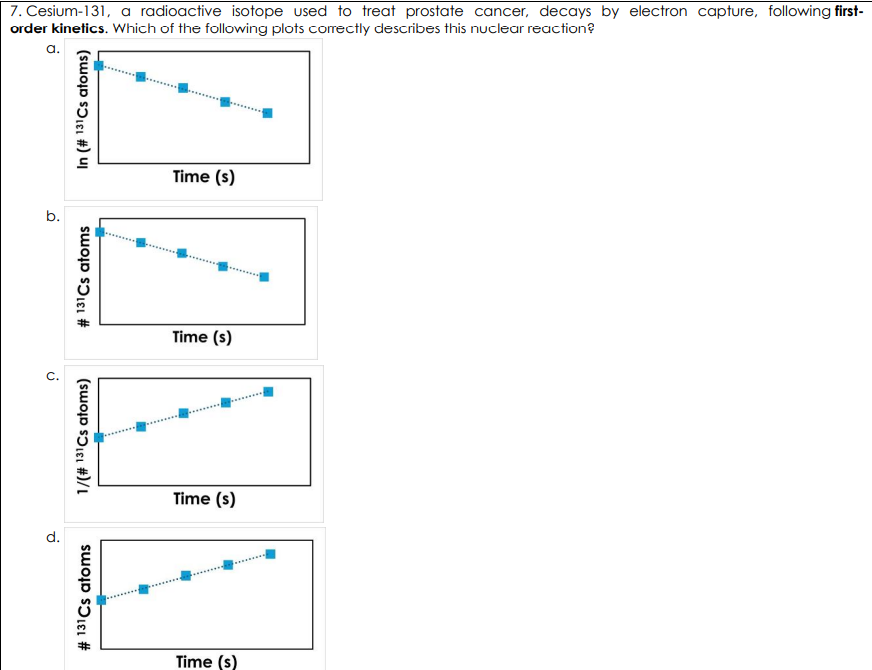
Cesium-131, a radioactive isotope used to treat prostate cancer, decays by electron capture, following first order kinetics. Which of the following plots correctly describes this nuclear reaction?
A
The thermal decomposition of ozone was monitored at 123°C and the following linear plot was generated: Based on the graphical information, the reaction is ____ order with respect to O3. The initial concentration of O3 is ____.
second; 0.07949 M
Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is metabolized in the liver following first-order kinetics, with a rate constant of 0.139 hr-1. If a person initially consumes 10.3 mM C8H10N4O2, how much C8H10N4O2 will remain in their system after 8.21 hr?
3.29 mM
Phosgene is a toxic gas that was historically used as a chemical weapon. At 333°C, it decomposes following second order kinetics, with a rate constant of 0.432 M-1•s-1: COCl2(g) → CO(g) + Cl2(g). If the initial concentration of COCl2 is 0.665 M, how long will it take for the concentration to decrease to 0.123 M?
15.3 s
In the human body, the metabolism of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) follows zero order kinetics, with a half-life of 2.54 hr. Assume an adult starts at the legal blood alcohol concentration of 0.0174 M. Calculate the rate constant for this process.
3.43 × 10-3 M/hr
On Mars, MgCO3 is found in surface rocks, indicating past water activity. The planet's high surface temperature can cause MgCO3 to decompose, as described by following first-order solid state reaction: MgCO3(s) → MgO(s) + CO2(g) At 427°C, the first half-life of MgCO3 is 17.8 days. Estimate the fifth half-life for this reaction.
17.8 days
According to the collision theory, which of the following statements is true?
The number of reactant particles with KE ≥ Ea increases with increasing temperature.
Difluoroperoxide is a highly unstable compound that readily explodes into fluorine and oxygen: FOOF(g) → F2(g) + O2(g) The activation energy of this decomposition reaction is 72.4 kJ/mol. At 234 K, the rate constant is 4.15 × 10-4 s-1. What is the rate constant for this reaction at 349 K?
87.6 s-1
In deep-sea hydrothermal vents, water reacts with olivine (Mg2SiO4) in oceanic crust to form serpentine minerals {Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4}. This process, known as serpentinization, is important in studying the origin of life. Serpentinization can be described by the following reaction profile diagram:
110 kJ/mol
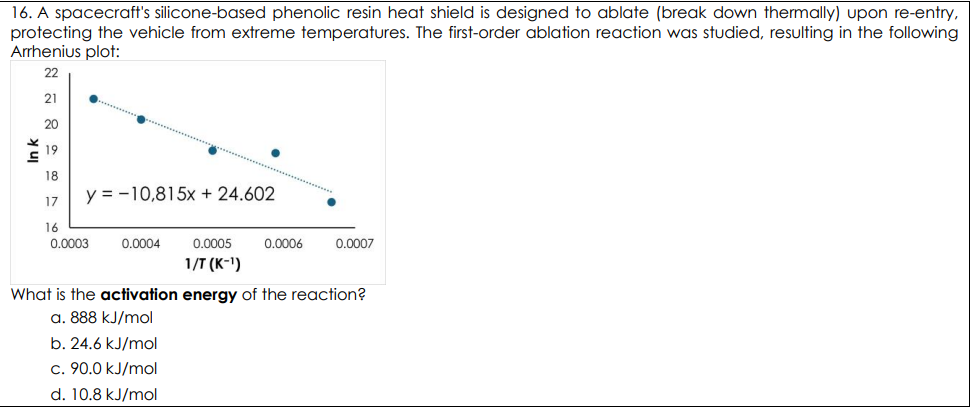
A spacecraft's silicone-based phenolic resin heat shield is designed to ablate (break down thermally) upon re-entry, protecting the vehicle from extreme temperatures. The first-order ablation reaction was studied, resulting in the following Arrhenius plot: What is the activation energy of the reaction?
90.0 kJ/mol
7. Sulfur dioxide, emitted from burning fossil fuels, reacts in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid, a key component of acid rain. The proposed reaction mechanism involves the following elementary steps: What is the rate law for this process?
rate = k[SO2][OH]
How does a catalyst make a reaction proceed faster?
A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
The oxidation of CO in automobile catalytic converters occurs in the presence of NO2. This helps reduce harmful emissions by converting toxic CO into less harmful CO2. The following mechanism is proposed for the oxidation of CO: Identify the intermediate(s) and catalyst(s) of the reaction.
NO and N2O3 are the intermediates; NO2 is the catalyst.
Materials chemistry is both an art and a science: it has a lot of applications in medicine, engineering, etc. However, solid-state reactions are intrinsically slow. Reaction rates can be increased by scaling solid precursors down to nanometer dimensions. Explain why solid-state reactions are faster when nanomaterials are used.
The increased surface area of nanomaterials increases the rate of the reaction.
Which of the following is true about systems in equilibrium?
The concentrations of reactants and products are constant as a function of time.
Consider the following reaction: The diagram below represents the equilibrium mixture of the reaction. Estimate the value of Kc.
0.281
Carbon dioxide dissolves in seawater to form carbonic acid, which plays a crucial role in ocean acidification: CO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq.) At 25°C, the Kc for the reaction is 1.7 × 10-3. What does this value of Kc tell us about the reaction?
The reaction favors reactants, so only a small amount of CO2 dissolves into H2CO3.
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide and molybdenum(VI) oxide are "layered transition metal compounds" used as catalysts in processes such as hydrodesulfurization of petroleum products. MoS2 is heated at 1,000 K to produce MoO3 as follows: 2MoS2(s) + 7O2(g) ⇌ 2MoO3(s) + 4SO2(g) Derive the KP expression for the above reaction.
B

Solar water-splitting is a promising alternative source of renewable energy. This fossil fuel-independent technology involves solar light harvesting and the redox reaction of water to produce energy-dense fuels, H2 and O2.: 2H2O(g) ⇌ 2H2(g) + O2(g) At 1,045 K, the partial pressures of an equilibrium mixture are: 4.00 × 10-2 atm H2O, 4.50 × 10-3 H2, and 3.00 × 10-3 O2. Calculate KP at 1,045 K.
3.80 × 10-5
In which of the following reactions is Kc = KP?
Ru2O3(s) + 3CO(g) ⇌ 2Ru(s) + 3CO2(g)
Ammonium carbamate decomposes into NH3 and CO2 in the production of urea, a key fertilizer: NH4CO2NH2(s) ⇌ 2NH3(s) + CO2(g) At 177°C, KP = 2.85. Calculate the value of Kc for this reaction.
5. 65 × 10-5
Given the following information: Calculate Kc3 for the following reaction at 888 K: AlF3(s) ⇌ Al(s) + 32 ⁄F2(g)
1.778
Ammonium iodide decomposes at 673 K as follows: NH4I(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HI(g); Kc = 7.00 × 10-5 A reaction mixture contains 0.0531 mol NH4I, 0.0115 mol NH3, and 0.00837 mol HI in a 1.00-L container. From this information, the value of Qc is _____. The reaction must run in the _____ direction to achieve equilibrium
9.63 × 10-5; reverse
Calculate ΔG° for the following complexation equilibrium at 25°C: Cu2+(aq.) + 4NH3(aq.) ⇌ [Cu(NH3)4]2+(aq.); Kf = 1.7 × 1013
-75.5 kJ
Lithium carbonate is a inorganic salt used to treat bipolar disorder. It is produced from lithium hydroxide at 150°C: 2LiOH(s) + CO2(g) ⇌ Li2CO3(s) + H2O(g); ΔH°rxn = -89.4 kJ Which of the following can be done to minimize the amount of the greenhouse gas CO2 in the reaction?
Run the reaction at 101°C.
Iron can be produced from iron(III) oxide via hydrothermal reduction at 300°C: Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2Fe(s) + 3H2O(g); ΔH° = -481.2 kJ Predict how the system in equilibrium responds when the amount of H2 is doubled
To restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts to the right to produce more water vapor.
Carbon disulfide is a foul-smelling gas that can be prepared by heating elemental sulfur with methane at 500°C: 4CH4(g) + S8(s) ⇌ 4CS2(g) + 2H2(g); KP = 2.0 × 1012 An experiment was conducted by initially flushing the reaction flask with 0.285 atm CH4. When setting up an "ICE table," which of the following best describes the equilibrium partial pressure of CH4?
0.285 M - 4x
Nitrogen dioxide decomposes into nitrous oxide and oxygen at 25°C as follows: 2NO2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) + O2(g); KC = 2.5 × 10-13 A reaction was conducted at 100°C where 2.28 M of NO2 was initially placed in a flask. What is the equilibrium concentration of NO?
1.37 × 10-4 M
Which of the following equations describes the dissociation of SnS2 in a saturated aqueous solution?
SnS2(s) ⇌ Sn4+(aq.) + 2S2-(aq.)
Which of the following correctly describes the Ksp of V2O5 as a function of its molar solubility in water?
Ksp = 12,500s7
At 25°C, what mass of SrCO3 (𝓜 = 147.6 g/mol) is dissolved in a 275-mL saturated solution?
1.62 mg
A saturated Ag2CrO4 solution contains 2.62 × 10-4 M Ag+ at 25°C. What is the value of Ksp for Ag2CrO4 at this temperature?
8.99 × 10-12
Which of the following halide salts has the highest molar solubility in water at 25°C?
BaF2
Which of the following best describes what happens when you add 1.00 mL of 1.0 M HI to a saturated aqueous AgI solution?
A

What is the molar solubility of Fe(OH)3 in 0.281 M Fe(NO3)3 solution at 25°C?
1.74 × 10-13 M
Which of the following is the correct definition for a Brønsted-Lowry base?
proton acceptor
What is the formula for the conjugate base of H2AsO4-?
HAsO42-
Which of the following is true for an aqueous solution that has a pOH of -0.12 at 25°C?
The solution is characteristic of a strong base.
Citric acid is a weak triprotic acid found in lemons and oranges. Which of the following Ka expressions best describes the stepwise dissociation of the second proton of C6H2O7H3 in aqueous solutions?
D

An aqueous hydrazine (NH2NH2) solution has a pOH of 6.101 at 25°C. How much H3O+ is in this solution?
1.26 × 10-8 M
"HONO(aq.) is a weak acid." What does this mean?
HONO dissociates <100% into ions in water.
Which of the following is the weakest acid?
H2O2
What is the pH of a 0.262 M Ba(OH)2 solution?
13.719
Aniline (C6H5NH2) is a basic aromatic compound that is used in the production of synthetic dyes. What is the pH of an aqueous solution containing 0.420 M C6H5NH2 at 25°C?
9.128
Butyric acid [CH3(CH2)2COOH] is a fatty acid mainly responsible for the unpleasant taste and odor of vomit. An aqueous solution containing 0.531 M CH3(CH2)2COOH has a pH of 2.549 at 25°C. What is the Ka of CH3(CH2)2COOH at 25°C?
1.51 × 10-5
Which of the following aqueous solutions of formic acid (HCOOH) has the highest %dissociation at 25°C?
0.123 M HCOOH
Which of the following acids produces the weakest conjugate base?
H2Te(aq.)
Which of the following is the strongest carboxylic acid?
C

Which of the following is a Lewis base but NOT a Brønsted-Lowry base?
B
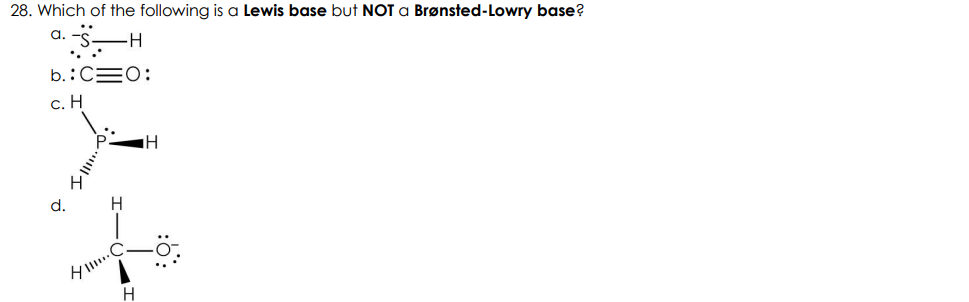
When dissolved in water, which of the following salts creates an aqueous solution that has a pH of c.a. 7.0 at 25 C
Ba(ClO4)2
Sodium benzoate (NaC6H5COO) is a salt that is widely used as a food preservative and a pickling agent. What net ionic reaction occurs when NaC6H5COO is dissolved in aqueous solution
C6H5COO-(aq) + H2O(L) → C6H5COOH (aq.) +OH-(aq.)
Which of the following aqueous solutions is a good buffer
1.0 M HN3 and 1.0M KN3
What is the pH of a buffer solution composed of 0.472 M C5H5NHCl and 0.819 M C5H5N? The Kb of C5H5N is 1.8 × 10–9 at 25°C.
5.495
. Blood is buffered by the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system (H2CO3/HCO3 –). If the pH of the blood starts to rise (for example if your kidneys fail to metabolize urea properly) which component of the buffer system will react to maintain the correct pH?
. H2CO
A 150.-mL buffersolution contains 0.576 M C6H5OH and 0.231 M LiC6H5O. If 12.9 mmol KOH were added to this buffer, what is the pH of the resulting solution? Assume that the volume of the solution does not change upon adding KOH. The Ka of C6H5OH is 1.6 × 10–10 at 25°C
. 9.607
What happens to the pH of a buffer that is composed of 0.778 mol HCOOH and 0.638 mol KHCOO when 0.471 mol Sr(OH)2 is added?
The pH will dramatically increase; the buffer capacity is exceeded.
. All of the following can be added to 0.321 M K2HPO4 to create a buffer except (assume 1 L of solution):
0.111 M H3PO4
In which of the following substances is the oxidation number of Br positive?
HBrO2
Consider the following redox reaction: 2ClO2(aq.) + H3AsO4(aq.) → 2ClO3 –(aq.) + HAsO2(aq.) + 2H+(aq.) In the above redox reaction, the reducing agent is _____. Its oxidation number changes from _____ to _____.
ClO2(aq.); +4; +5

Consider the following galvanic cell
Ir(s); gains
How many electron moles are transferred in the following redox reaction? 3Ti(s) + 18F–(aq.) + N2(g) + 16H+(aq.) → 3TiF6 2–(aq.) + 4NH4 +(aq.)
12
When the following incomplete and unbalanced redox equation is balanced properly under acidic conditions, H2O(l) appears as a _____ with a coefficient of _____? PbO2(s) + Mn2+(aq.) → Pb2+(aq.) + MnO4 –(aq.)
product, 2
Which of the following electrochemical cells is electrolytic? To answer this question, refer to the electrochemical series provided.
Pd(s) | Br2(g) | Br–(aq.) || Al3+(aq.) | Al(s)
Which of the following is the weakest oxidizing agent? To answer this question, refer to the electrochemical series provided
Na+(aq.)
Based on the electrochemical series provided, which of the following species will oxidize Th but not H2?
Ni2+(aq.)
The identity of an unknown metal M was determined by setting up an electrochemical cell. M and 1.0 M of its salt M(NO3)x were placed in the anode whereas Cu and 1.0 M Cu(NO3)2 were placed in the cathode under standard conditions. The standard cell potential is +2.00 V. What is the identity of M (and Mx)? To answer this question, refer to the electrochemical series provided.
Al (and Al3+)
Refined iron-based materials used in infrastructure are highly susceptible to rust (Fe2O3 and Fe(OH)3) formation over time. Rust spontaneously forms when water and O2 come in contact with iron. The reduction half-reaction that is responsible for rust-formation can be described as: O2(g) + H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq.); E°cell = +0.400 V To mitigate rust formation, metallic nanoparticles are embedded in iron alloys as sacrificial anodic coatings. Using the electrochemical series provided, pick and explain the best choice of metallic nanoparticles to use as a sacrificial coating for iron alloys.
Mg nanoparticles; E°red(Mg | Mg2+) << E°red(Fe | Fe2+), so nano-Mg is more susceptible to oxidation than Fe.
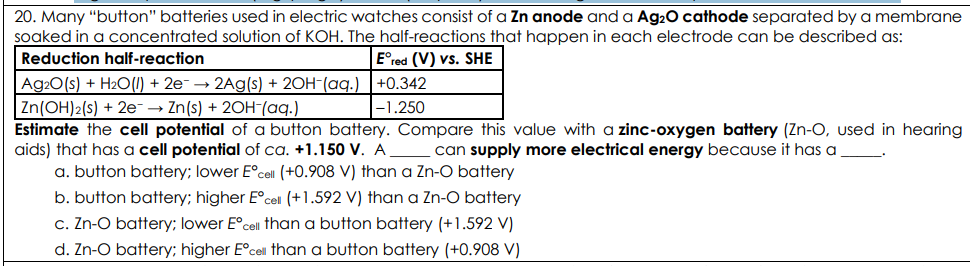
Many “button” batteries used in electric watches consist of a Zn anode and a Ag2O cathode separated by a membrane soaked in a concentrated solution of KOH. The half-reactions that happen in each electrode can be described as: Estimate the cell potential of a button battery. Compare this value with a zinc-oxygen battery (Zn-O, used in hearing aids) that has a cell potential of ca. +1.150 V. A _____ can supply more electrical energy because it has a _____.
button battery; higher E°cell (+1.592 V) than a Zn-O battery