Dental management of the medically complex patient 1+2
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Aim and objectives

common/important conditions for dentistry:
cardiac (3)
respiratory (3)
Renal (4)
Hepatic (4)
Haematological (4)
Endocrine (3)
Neurological (4)
Psychiatric (5)
Immune system (4)
Genetic (2)
Oncology (4)

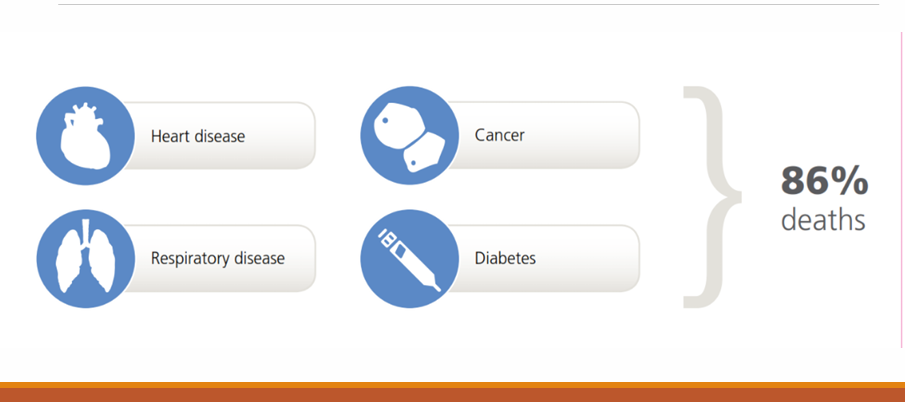
4 conditions accounting for 86% of deaths
heart disease
cancer
respiratory disease
diabetes
smoking/diet
What should you do when you first see your patient when they walk in through the door? (4 main things)
Look at their:
Skin
Height/weight/frailty
Gait/wheelchair/walking frame
IV or central access, tracheostomy, PEG tubes, indwelling catheter, stoma bag (additional medical devices)

What is the first history you should go through?
MH
Sometimes if its really complex they don’t know everything - might need to work with GP/consultant - to get all necessary information to provide safe dental care
MC, medications, allergies, under consultant or gp care?, how frequently they visit hospital, care support?
Along with MH what factors as you also assessing for?
Patient factors
Well controlled Diabetes or uncontrolled?
what might you do to make sure you got all the details regarding medical history?
liaise with the medical specialists
e.g if on dialysis ask the nephrologist - which date is best for extraction due to AC and dialysis days
Now that you have all the information, what do you do with it?
Address/minimise risks e.g Arrange cover (AB for IE)if necessary, optimise condition before treatment (talk to diabetic consultant or consultant to help get diabetes under control if currently not controlled)
Take precautions (medical emergencies) e.g if the pt is epileptic make sure they have taken their medications before hand, asthmatic - have inhaler, angina - have GTN spray on the go and with the patient
Good infection control - infectious diseases e.g HIV,HBV/HCV
Minimise intra-operative and post-operative complications e.g haemophilia - give cover - local haemostatic measures to reduce risk of post operative bleeding
Review the patient - check on them a few days after in case of complications so if you need to treat again - helps us learnt what to avoid next time
Overall

For each condition what are the medical (5) and dental (4) considerations ?
Diagnosis
Characteristics
Medical management
Prognosis
likely for there to be a ME?
oral manifestation of condition
oral affects of management
direct dental treatment implications
indirect dental treatment implications

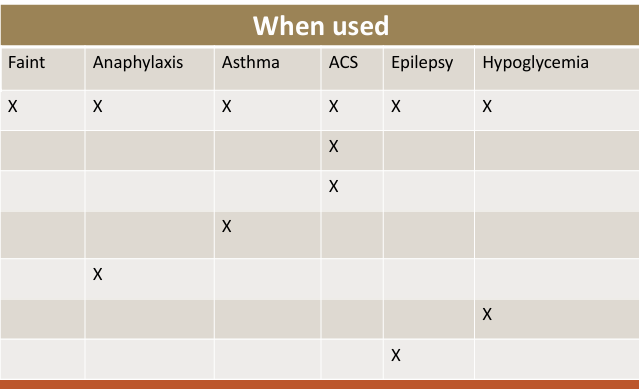
Drugs for each medical emergency
Acute coronary syndrome
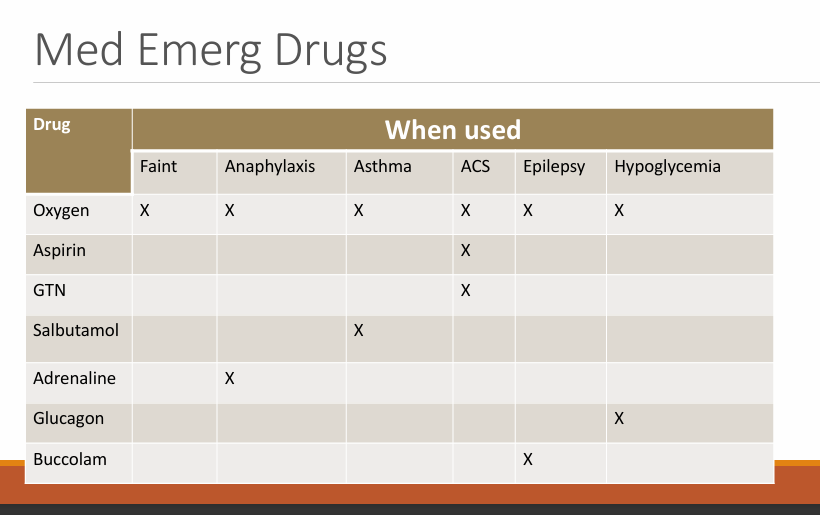
What is the ASA classification?
Classify how generally healthy/medically complex a patient is
healthy. mild, severe, constant threat to life, needs operation, brain-dead - donor
1-3 relevant to dentistry, referral criteria ASA 1-2 are safe in general practice, 3+ need to be seen in hospital
controlled diabetes - ASA class 2
uncontrolled - having severe impact on life - ASA class 3
set up for drawing blood

What is the first thing you do when collecting blood and then what is the order of colours?
[mnemonic]
culture, blue, red, yellow, purple, green
Specific colours and order of taking blood

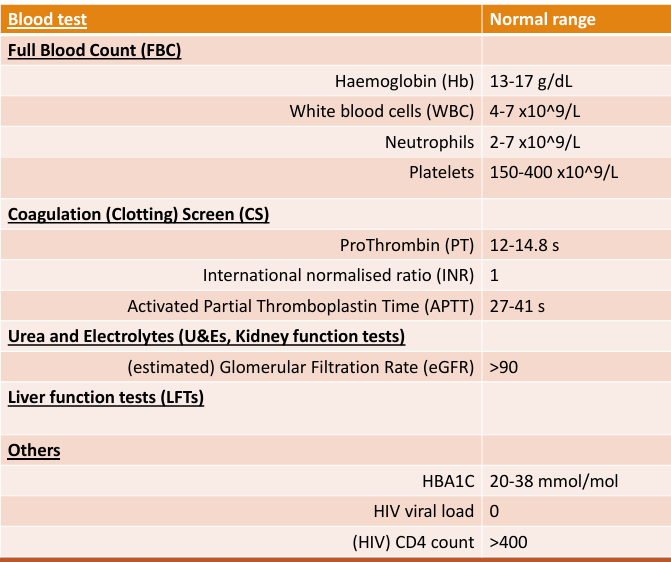
5 main types of blood tests?
FBC - platelet, neutrophil, Hb, WBC
Coagulation screening times - Pt, INR, APTT
urea and electrolyte - eGFR
Liver function test -
others: HIV/Diabetes
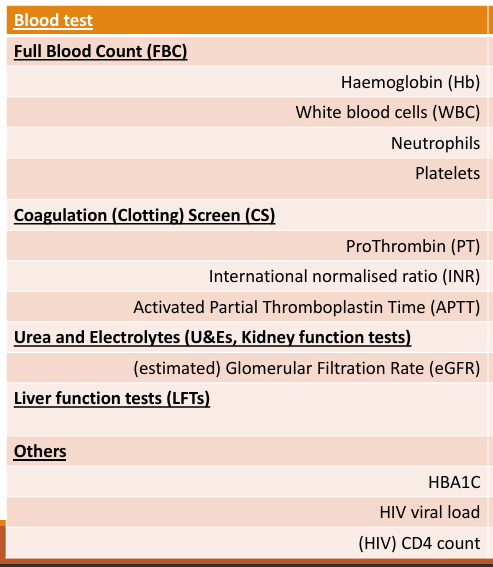
What are the normal ranges for each?
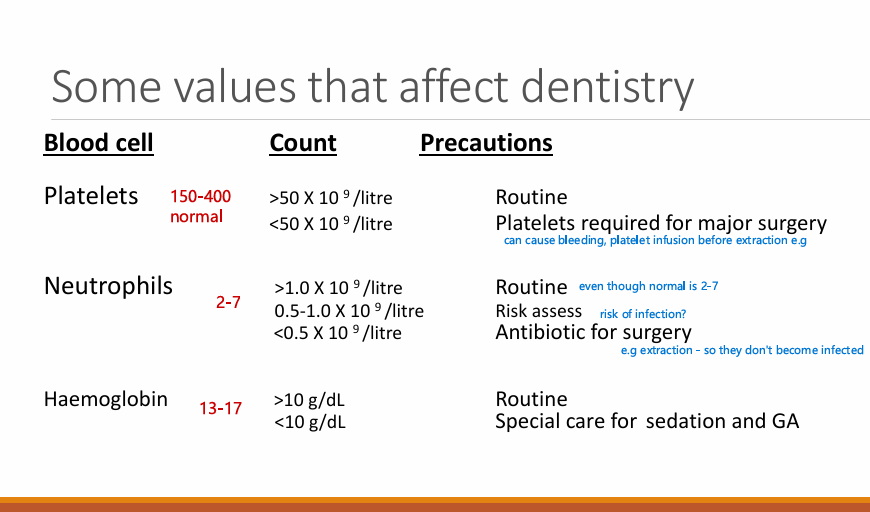
Significance of polypharmacy? (5)
Dry mouth
Caries risk - some drugs directly increase risk through sugar in the formulation/dry mouth
Drug interactions - analgesics/AB prescribed don’t interact
Signs of increased medical complexity - comorbidities - they have risks for dentistry
Direct oral affects of medications - OAC - bleeding in mouth, gingival hypertrophy - Epilepsy medications

3 main cardiac conditoins?
Ischaemic heart disease: Angina, MI
Hypertension
IE and associated conditions
What is angina (types) and what is MI? (simple)
controlled - when sitting on a dental chair, ASA 2
Uncontrolled - become anxious or climbed up a flight of stairs - ADA 3
MI - irreversible

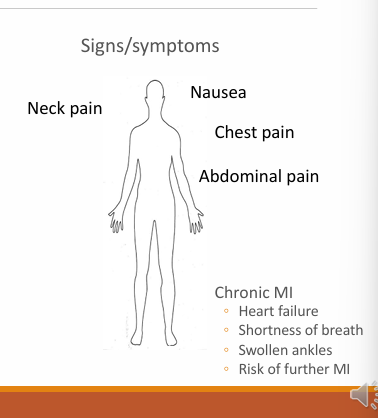
symptoms of Ischaemic heart disease? (4
neck pain
nausea
chest pain
abdominal pain
What are some medical managements for Angina/MI?
Manage risk factors: smoking, HTN, stress
GTN spray or other meds - AC, BB, diuretics
Surgery - stents, bypass graft

Prognosis of ischaemic heart diseas?
uncontrolled - worse
Heart failure or repeated or recent MI = worse
Medical emergencies with ischaemic heart disease?
Acute coronary syndrome - severe unremitting chest pain - could be uncontrolled angina (reversible) or MI (if irreversible)
Chronic MI may cause what in the patient? (4)
Heart Failure
Shortness of breath
Swollen ankles
Risk of further MI
Oral affects of management? (2)
Can have dry mouth and caries risk - due to polypharmacy
Anti-coagulated
Direct dental treatment implications? (1)
Bleeding from anticoagulation (mainly during extractions)
Indirect dental implications?
stress/anxiety (worsens) and pain management crucial (inadequate pain control - release of adrenaline - increases load on the heart)
Higher risk of IV sedation
IHS with NO2 very useful (can dilate arteries to the heart so not only reduces anxiety but also helps with angina pain)
hospital setting for sedation if previous MI
Higher risk of another MI within 6 months (careful when supplying any kind of dentistry within this time frame, delay all elective treatment, precaution with emergency tx)
sedation/GA risk, access, timing of appointment etc
LA with adrenaline, generally if it is controlled you can still use them, if uncontrolled you might need to use plain solutions or restrict the use of LA as the adrenaline increases the load on the heart
What medications are used a lot with ischaemic heart diseases?
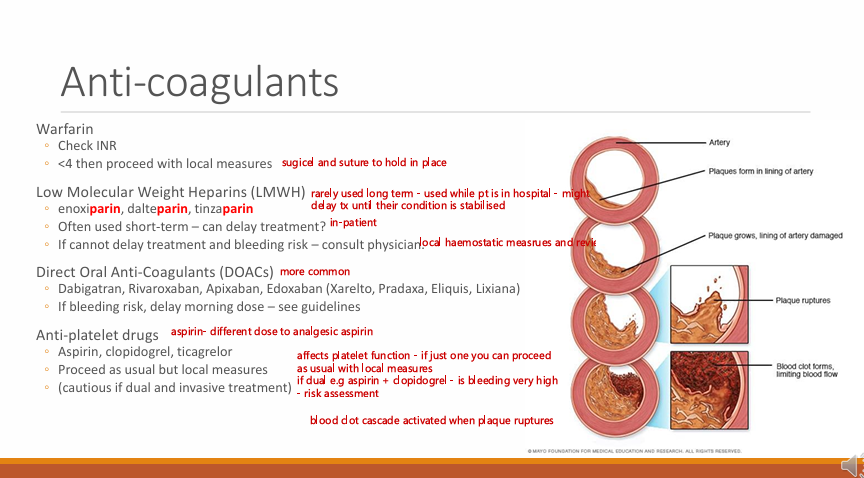
Anti-coagulants
What are 4 main types of anti-coagulants?
Warfarin
Low molecular weight heparin
Direct oral anti-coagulants DOACs
Anti-platelet drugs
What must you check with Warfarin? what is the implication?
INR, it is less than 4 then you can proceed with local measures (local haemostatic measures such as surgicel and sutures)
LMWH, when are they used? give 3 examples and what do they always end in? what is this implication?
-parin
Enoxiparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin
often used short-term (rarely used long-term, used while patient is in a hospital - might delay treatment until their condition is stabilised)
If you cannot delay tx and bleeding risk - consult physician
DOACs, give some examples (4)? implicaiton?
Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban Apixaban
If bleeding risk, delay/skip the the dose
Anti-platelet drugs, name some (3) implications (2)?
Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor
Proceed as usual if just one but local measures
cautious if dual and invasive treatment
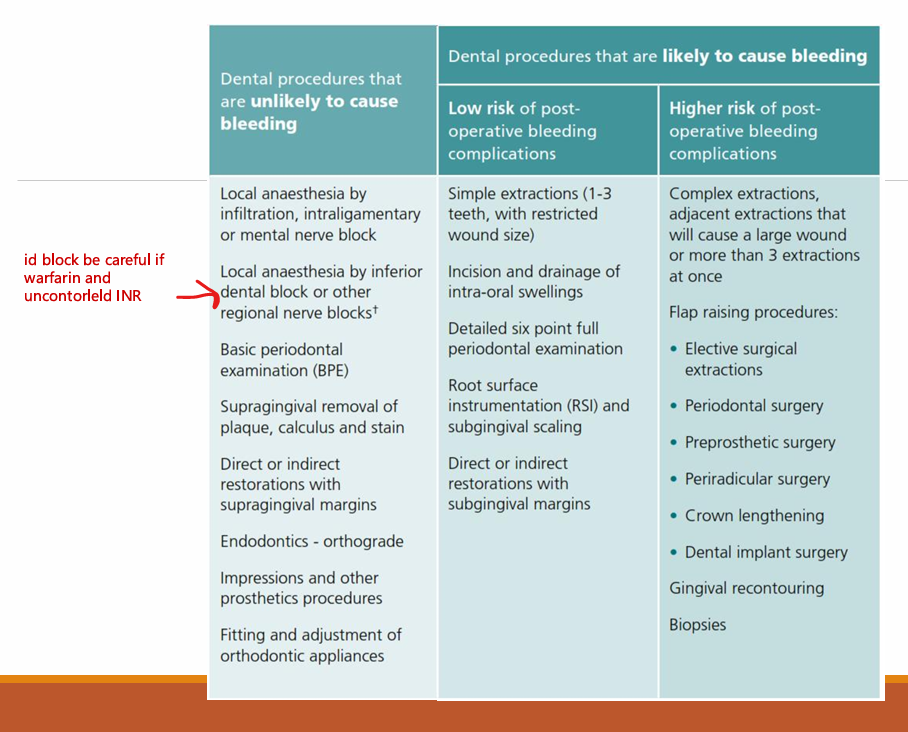
Name dental procedures that are unlikely to cause bleeding according to SDCEP
Dental procedures likely to cause bleeding: low and high risk of post op bleeding
LA, BPE, supraPMPR, supra restos, endo, impressions, fitting/adjustment of ortho appliances
low risk: Simple extraction (1-3 teeth - if next to each other - then a bigger wound so is it restricted?), 6PPC, RSD, sub restos
high risk: complex extraction, flap raising procedures
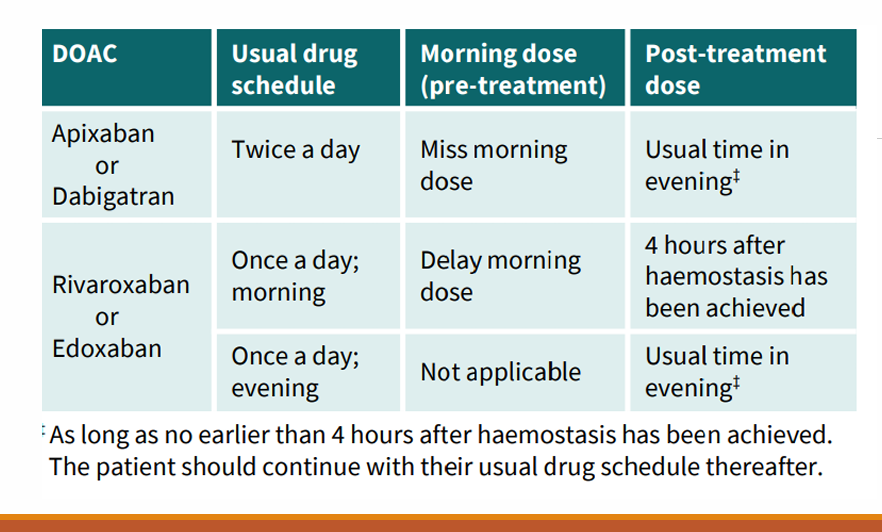
What are the usual schedule, morning does (pre-treatment) or not applicable, and post-treatment changes to the DOACS: Apixaban, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Edoxaban
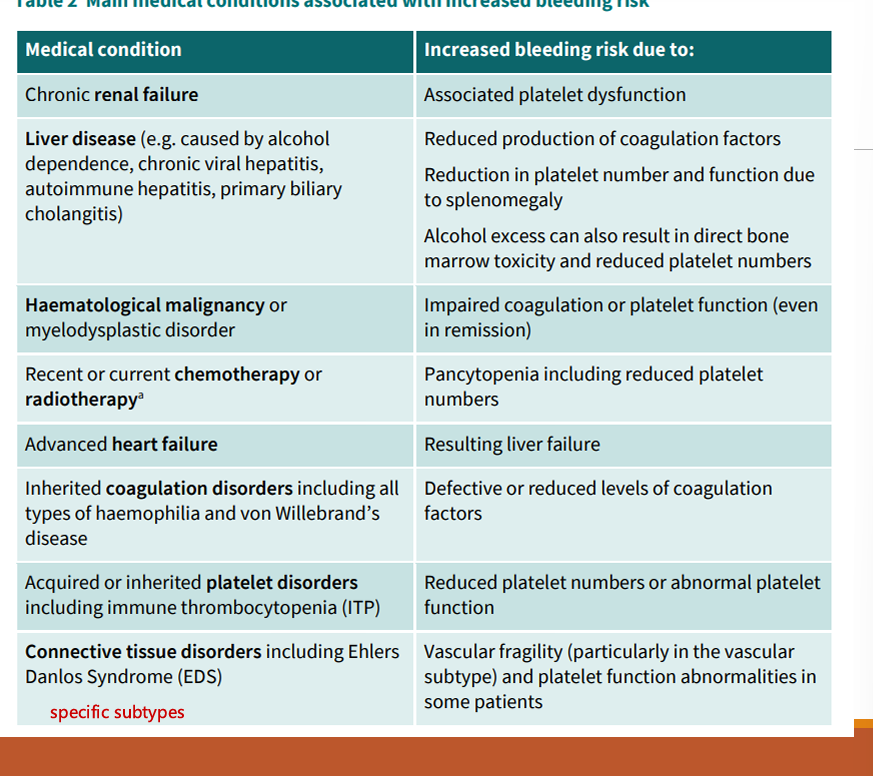
What are some medical conditions that are associated with an increased bleeding risk?
Chronic renal failure (platelet)
Liver disease (coagulation factors)
haematological malignancy
coagulation disorder
CT disorders
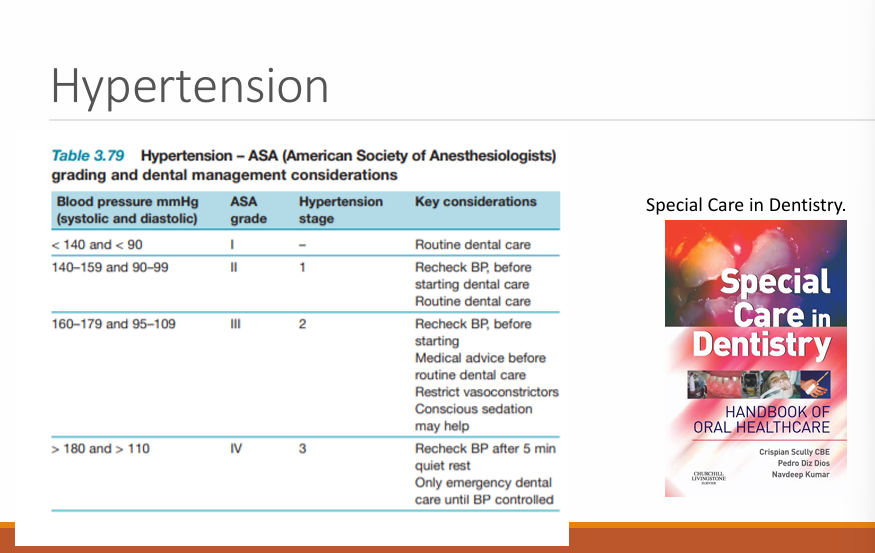
Hypertension:
what is it and symtpoms?
High blood pressure
Generally no symptoms, blurred vision, tingling extremities headache
Medical management of hypertension? (2 main) (3 drugs)
risk factors: weight, exercise, diet, smoking
Diuretics, BB , statins
ADA grades 1- 4 for blood pressure?
high - increased risk of a heart attack
might write to GP - to try and bring it under control
conscious sed - lowers BP, but slightly more risk as well for having conscious sedation
NO2 - reduce anxiety and help reduce bp
sometimes gives time to rest before taking BP
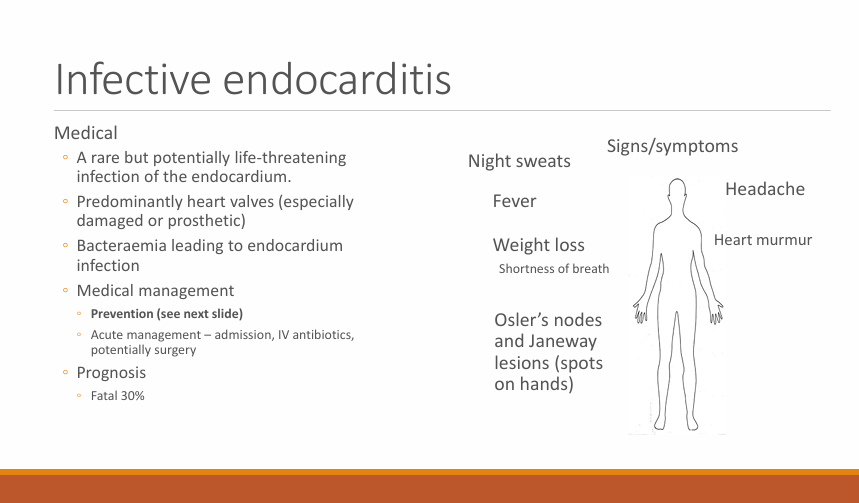
What is infective endocarditis?
A rare but potentially life threatening infection of the endocardium
Predominantly heart valves - especially damaged or prosthetic
Bacteraemia leading to endocardium infection (gingivitis/extraction/surgery bacteria enter mouth and attach to valves and form biofilm)
Symptoms/signs of IE? (7)
night sweats
fever
Weight loss
head aches
heart murmur
Osler’s nodes
Janeway lesions (spots on hand)
Medical management?
Prevention
cute management - admission, IV AB, potentially surgery
Prognosis?
30% fatal
Infective endocarditis linked to dentistry how? (3)
Any oral bleeding likely to cause transient bacteraemia, including tooth brushing with gingivitis
Reports of IE after invasive dental tx
Oral bacteria frequently cultured from IE patients endocardium
Again what was the main management of IE?
prevention
What is included in prevention? (3)
ID patients at risk
oral hygiene (Need to give good OHI, take out tooth risk of bacteraemia is 2 weeks, brushing everyday - with gingivitis - longer risk- PD disease is more important in preventing IE so we need to focus more on OH than AB prophylaxis)
follow national guidance
What does the NICE, EU and American guidelines say about cover and if there is cover what type of cover is it?
Amox and clindamycin
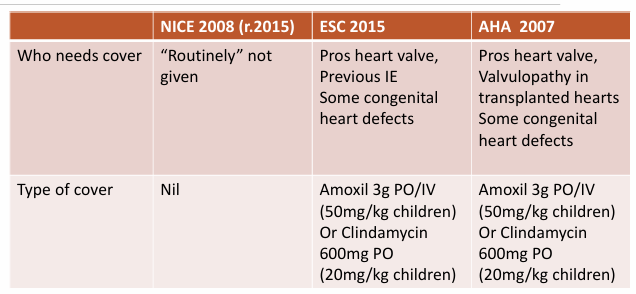
What does SDCEP say?
Advise of risk no AB cover
Patients at risk and sub-groups requiring special considerations
bold - consult with cardiologist in the increased risk
most cardiologists - say yes
remember to educate on symptoms and OHI

3 conditions in Respiratory conditons
Asthma
COPD
OSA - obstructive sleep apnoea
What is Asthma?
reversible airway obstruction, inflammation, bronchial hypersensitivity
Signs/symptoms of Asthma? 3 severe symptoms?
wheeze
cough
dyspnoea
use of accessory muscles for respiration
cyanotic
unconscious
apnoea (stop breathing?)
Medical management of Asthma?
Beta agonist - salbutamol
Steroids
Other meds - Theophylline
who treating - consultant - if under consultant - this means that their asthma isn’t well controlled so more likely to have asthma attack during tx
Prognosis?
Good but risks with severe asthma attack
some grow out of it
ME?
Acute asthma
Oral manifestation of condition?
incorrect use of inhalers - trauma/ candida
Indirect dental implications? (3)
careful if severe and conscious sedation
prepared or ME, contact consultant if needed
review status on the day
What is COPD?
primarily caused by what
Chronic, progressive, irreversible airway obstruction
smoking
What are some signs or symptoms? Advanced severe (3)
wheeze, Chronic cough, dyspnoea and sputum
Dependent on oxygen, respiratory failure, cor pulmonale (heart failure caused by respiratory failure)
Medical management of COPD? (drugs (3))
Risk factor
Bronchodilators, steroids, AB for chest infections
Oxygen in severe cases
Prognosis of COPD? (3 categories )
Low risk - Normal blood gases
Moderate - on steroids and multi-pharmacy
High - symptomatic or untreated - (affects their day to day life)
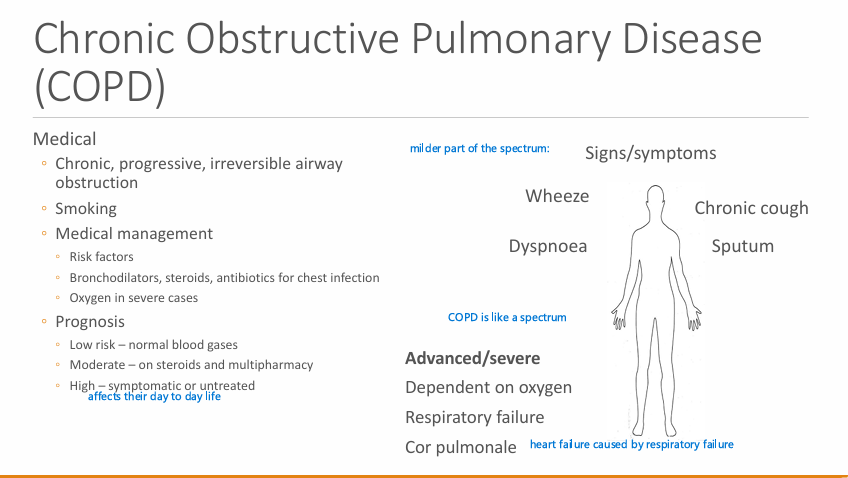
Indirect dental implications of COPD? (5)
IV sedation high risk (avoid in severe COPD, hospital setting for mild/mod)
High risk GA
Transport, access and O2 practicalities
In very severe cases avoid giving oxygen
treat upright position

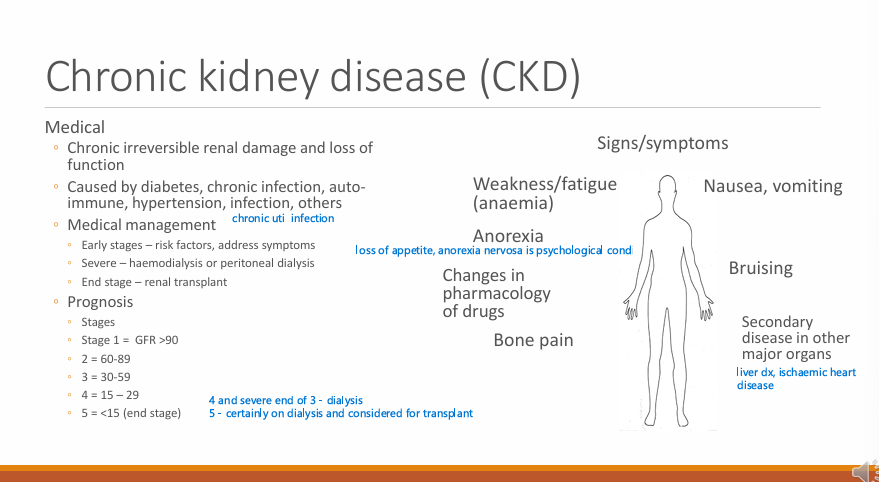
What is Chronic Kidney Disease CKD?
What can it be caused by? (4)
Chronic irreversible renal damage and loss of function
Diabetes, chronic infection, autoimmune, hypertension, infections others
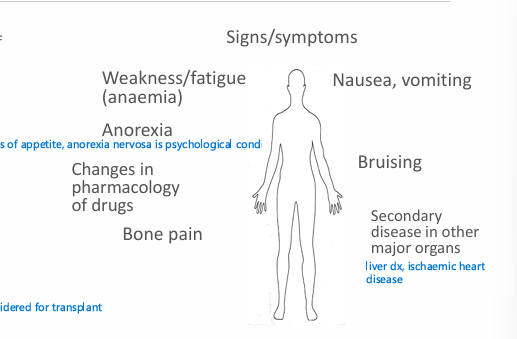
What are signs/symptoms of CKD?
weakness/fatigue (anaemia)
Anorexia (loss of appetite)
nausea/vomiting
Bruising
Bone pain
Secondary disease in other major organs - liver and IHD
What are the managements of Chronic Kidney Disease CKD at the early, severe and end stage?
Early - Risk factors and address symptoms
Severe - haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
End-stage - Renal transplant
Prognosis in terms of stages and GFR ?
1 - >90
2 - 60-89
3- 30-59
4 - 15-29
5 - < 15
What are oral manifestations of the condition? (4)
Bone issues, dry mouth, swollen salivary glands
Discolouration of soft tissues - Pale buccal mucosa
(remember kidney control water and electrolytes)
Direct dental treatment implications of CKD? (3)
Bleeding risk (platelet function, anticoagulated during haemodialysis) - local haemostatic agents, consult nephrologist, DDAVP (desmopressin)
Infection risk (WBC function) - aggressive tx of infections, antibiotics but take care of doses
Anaemia (EPO)
oral affects of management are due to dialysis
Indirect dental implications (3)
High risk IV sedation/GA
Change prescription dose/drug
Timings of appointment on day after haemodialysis and associated anticoagulant - consult nephrologist (drug may still be in their system and have effect the next day - usually use LMWH)
Medical management of renal transplant/transplant in general?
life long immunosuppressed to avoid rejection
often with steroids
Prognosis of organ transplant?
70% at 5 years
sign/symptoms of renal; transplant? (3)
Immunosuppression
Oral infections : candida, herpes simplex
Symptoms associated with failure of transplant organ
Steroid effects - coming up
Oral manifestations of condition/management of transplant? (2)
immunosuppression and viral oral cancers
oral infections
Direct dental treatment implications of organ transplants? (4)
Bleeding risk if function of organ low and involved in clotting (live renal)
High infection risk (immunosuppression)
anaemia
if chronic steroid use might need steroid cover
Indirect dental implications?
Usually high sedation risk (depending on organ)
Contact medical team (if doing complex work/ga/sedation)
Complete dental work before transplant
Defer elective treatment until after 6 months post transplant
What are steroids?
general functions? (4)
what are the synthetic steroids used for?
Naturally occurring hormones secreted by adrenal glands. Glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Generally referrers to glucocorticoids like cortisol
Multiple functions: immune system, metabolism, infection response, stress
mainly used for immunosuppression but also replace natural corticosteroids if low such as in Addison’s disease - autoimmune disease
Signs and symptoms of chronic steroid use? (8)
weight gain in face and back
HTN
diabetes
immunosuppressed
muscle weakness
mood changes
hirsutism
osteoporosis - put on bisphosphonates
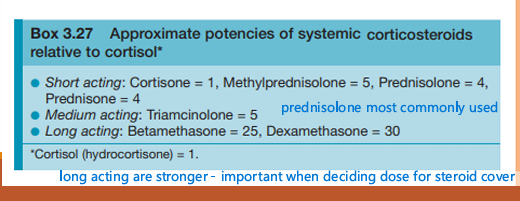
Are all steroids equal, what are the approximate potencies of systemic corticosteroids relative to cortisol?
Prednisolone the most widely used
Those on steroids are at increased risk of? (2)
oral infections and viral cancers
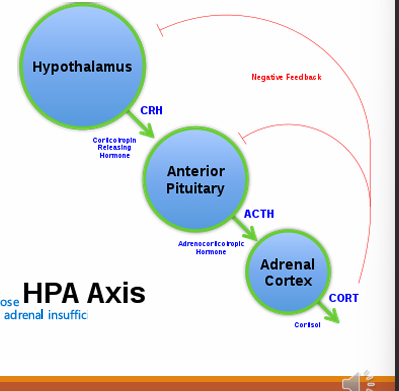
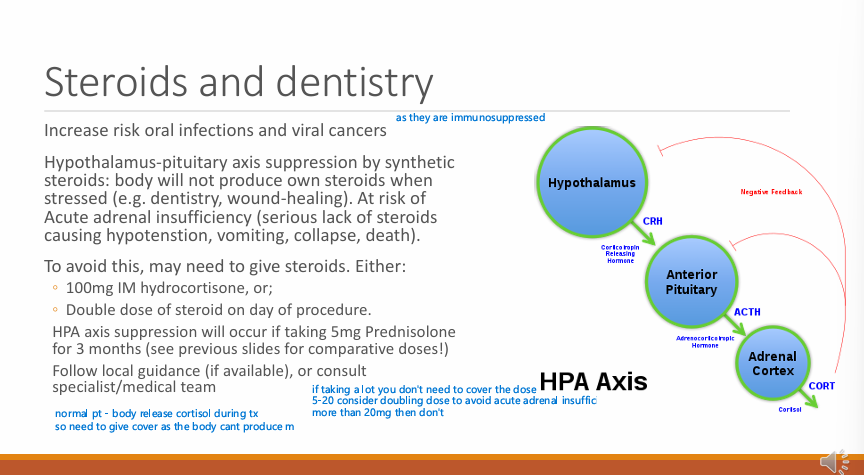
Synthetic steroids do what to the hypothalamus-pituitary axis?
so the body cannot what?
Therefore at risk of?
what are some signs/symptoms of this? (4)
Supress it
HPA supressed by synthetic steroids
So the body will not produce own steroids when stressed e.g during dentistry or wound healing
At risk of acute adrenal insufficiency - serious lack of steroids causing hypotension, vomiting, collapse and death
How could you give steroid cover? (2)
100 mg IM hydrocortisone
Double dose of steroid on day of procedure
HPA axis suppression will occur if taking what dose of prednisolone for how long?
5 mg Prednisolone for 3 months - (if taking other consider the comparative dose)
Follow local guidance if available or consult specialist/medical team
(5-20 mg then consider doubling the dose, anything more than 20mg doesn’t need cover)

What is the guidance for Addison’s disease?
Addison’s is more severe and not quite applicable for those with chronic steroid use

Chronic liver disease, could have C and later on this can become what?
Cirrhosis - irreversible damage to liver structure with loss of function - liver failure
can be caused by? (3) (rarer (3))
Caused by alcohol, viral hep B/C
rarer- toxins, heart failure, biliary obstruction
Signs/symptoms of chronic liver disease?
Bleeding/bruising
Regurgitation
Jaundice
Finger clubbing
Encephalopathy
Oesophageal varices
Hepato-renal syndrome (renal function is reduced with absence of kidney dx)
Ascites
Spider naevi
Medical management of chronic liver disease patients? (3)
Address cause
Risk factors
Liver transplant
Prognosis of Chronic liver disease? (if severe)
if severe, life expectancy - 5-10 years
ME for chronic liver disease?
bleeding/drug metabolism
Oral affects of management of chronic liver disease? (3)
Dry mouth, caries risk
immunosuppressed if transplant
Direct dental treatment implications? (4)
High bleeding risk (clotting factors)
Increased infection risk
anaemia (sedation)
Adjust dose/drug of choice of prescriptions (drug metabolism)
Indirect dental implications of chronic liver disease?
High risk sedation (Benzodiazepines m[higher toxicity risk] metabolism, anaemia)
Chronic alcohol abuse can cause?
anxiety/depression
Liver disease/cirrhosis
Pancreatitis
GI ulcers
Wernicke/Korsakoff syndrome (cognitive impairment - build up of toxins in the brain (may impact capacity)
Ischaemic heart disease
Anaemia
Immune system dysfunction
gout
Haematological?
Bleeding disorders (haemophilia/VWD)
anticoagulated/deficiencies
Sickle cell aneamia
What is haemophilia and VWD?
haemophilia is a x-linked congenital deficiency of clotting factors A=8 B=9
VWD - deficiency in VW factor which is involved in platelet function and stability
Signs/symptoms of H and VWD
Bleeding:
immediate = platelet dysfunction (VWD, thrombocytopenia)
Delayed = clotting factor dysfunction (H/liver disease)
Joint damage/deformity
Bruising/petechiae
heavy menstrual cycle
Medical management of these bleeding disorders? (4)
Close relationship with haemophilia centres
Replace missing factors/platelets
Desmopressin DDAVP/tranexamic acid (stabilise the clot when it is alr there)
Prevention (e.g OHI to prevent gingivitis which would cause even mroe bleeding)
Prognosis of these bleeding diorders?
managed quite well nowadays so good
ME?
Bleeding can be fatal