The brain and eye: Organism level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
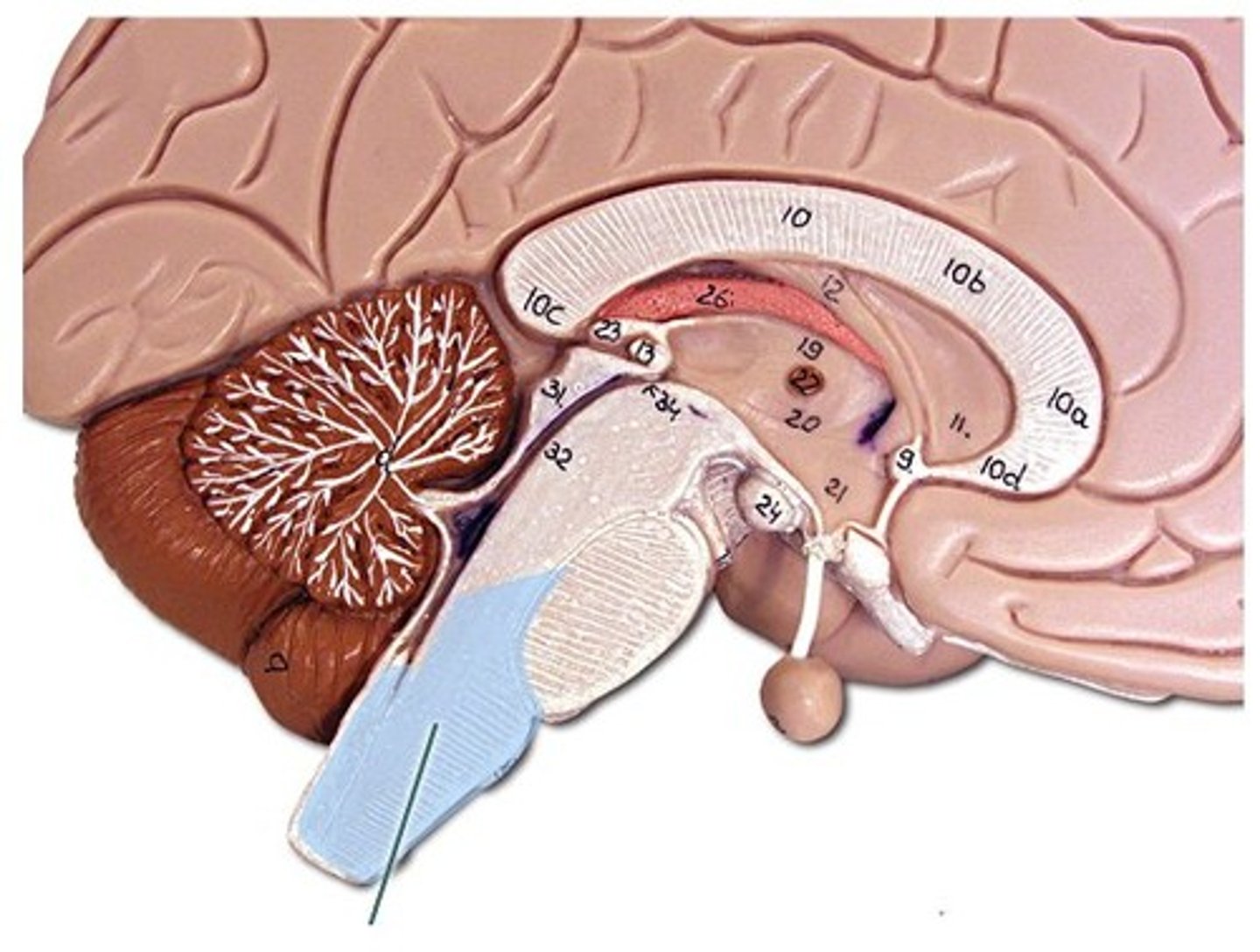
Brain
A mass of nerve tissue consisting of billions of interconnected neurones that acts as the main control centre of the nervous system
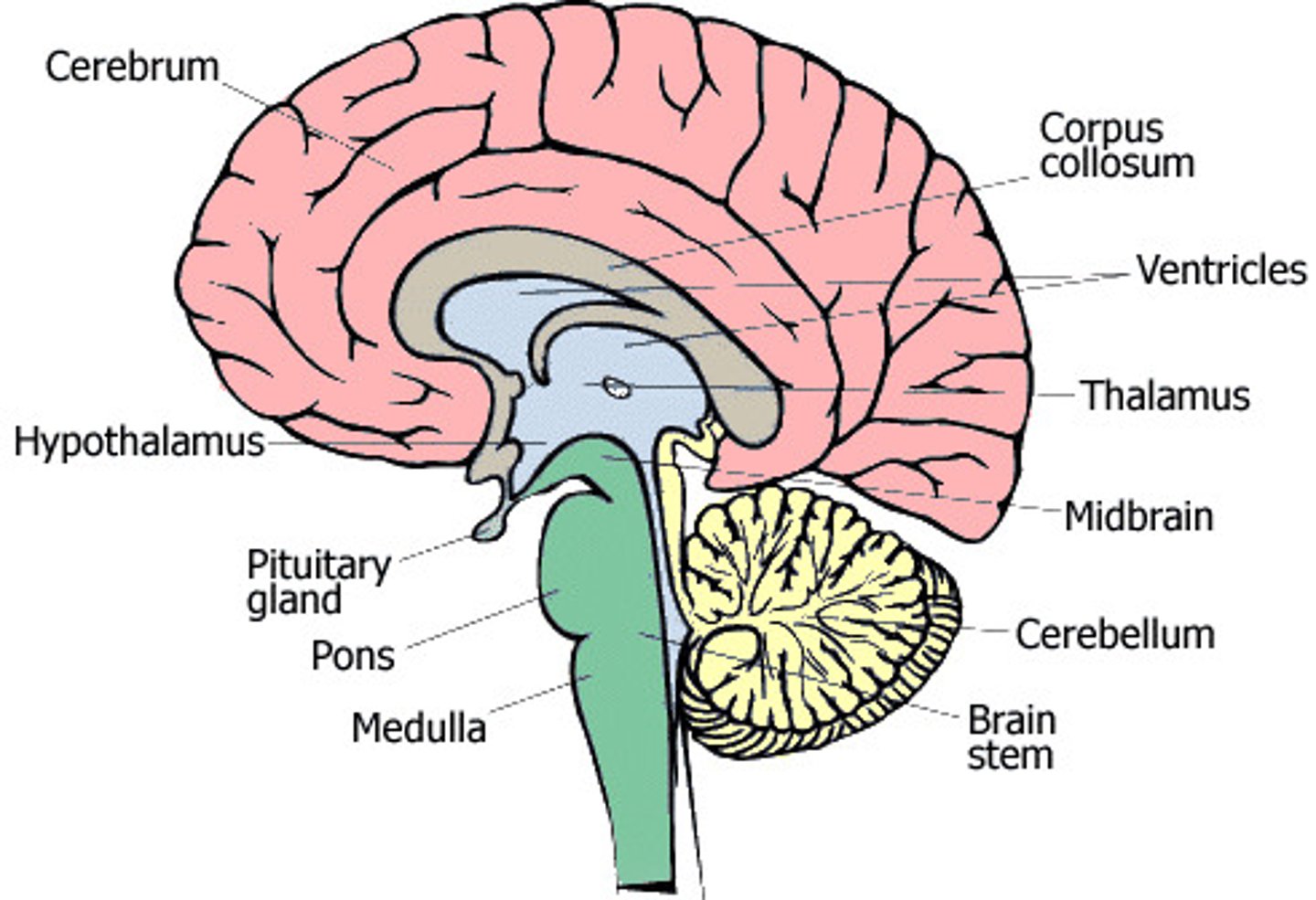
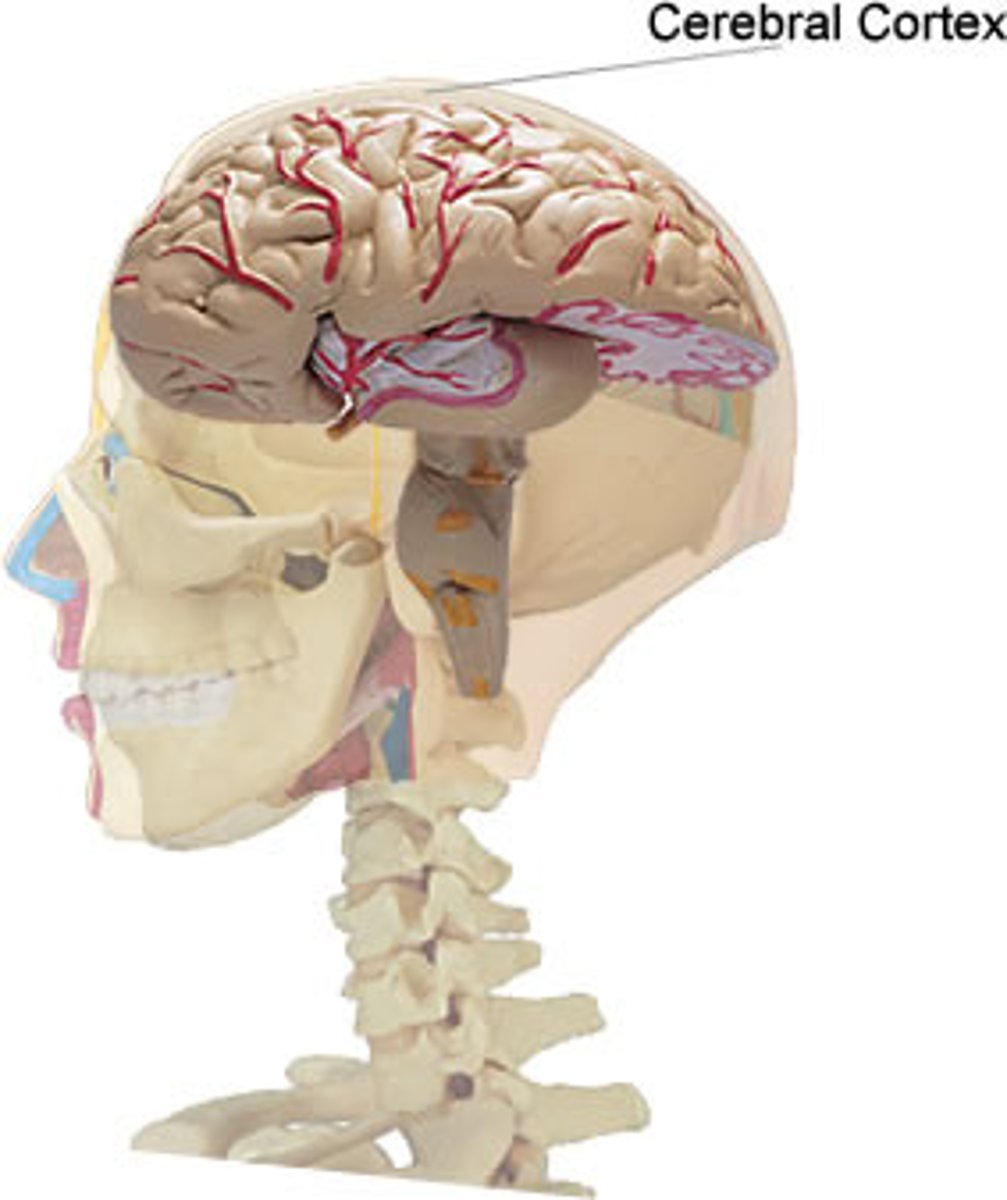
Cerebral cortex
The outer region of the cerebrum that contains sheets of nerve cells controlling memory, consciousness, language and intelligence
Cerebrum
The main part of the brain that is divided into a right hemisphere and a left hemisphere
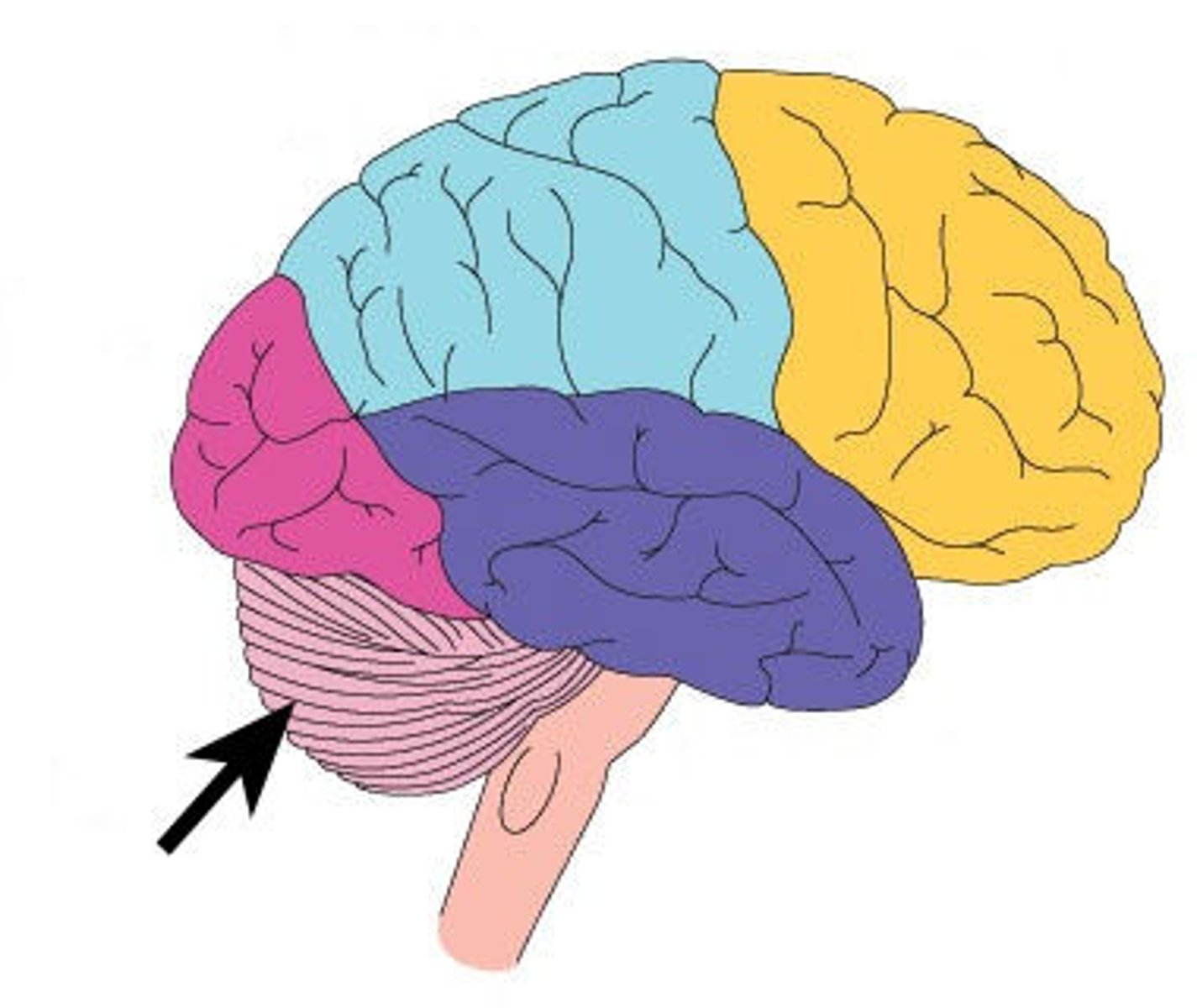
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills including balance and movement
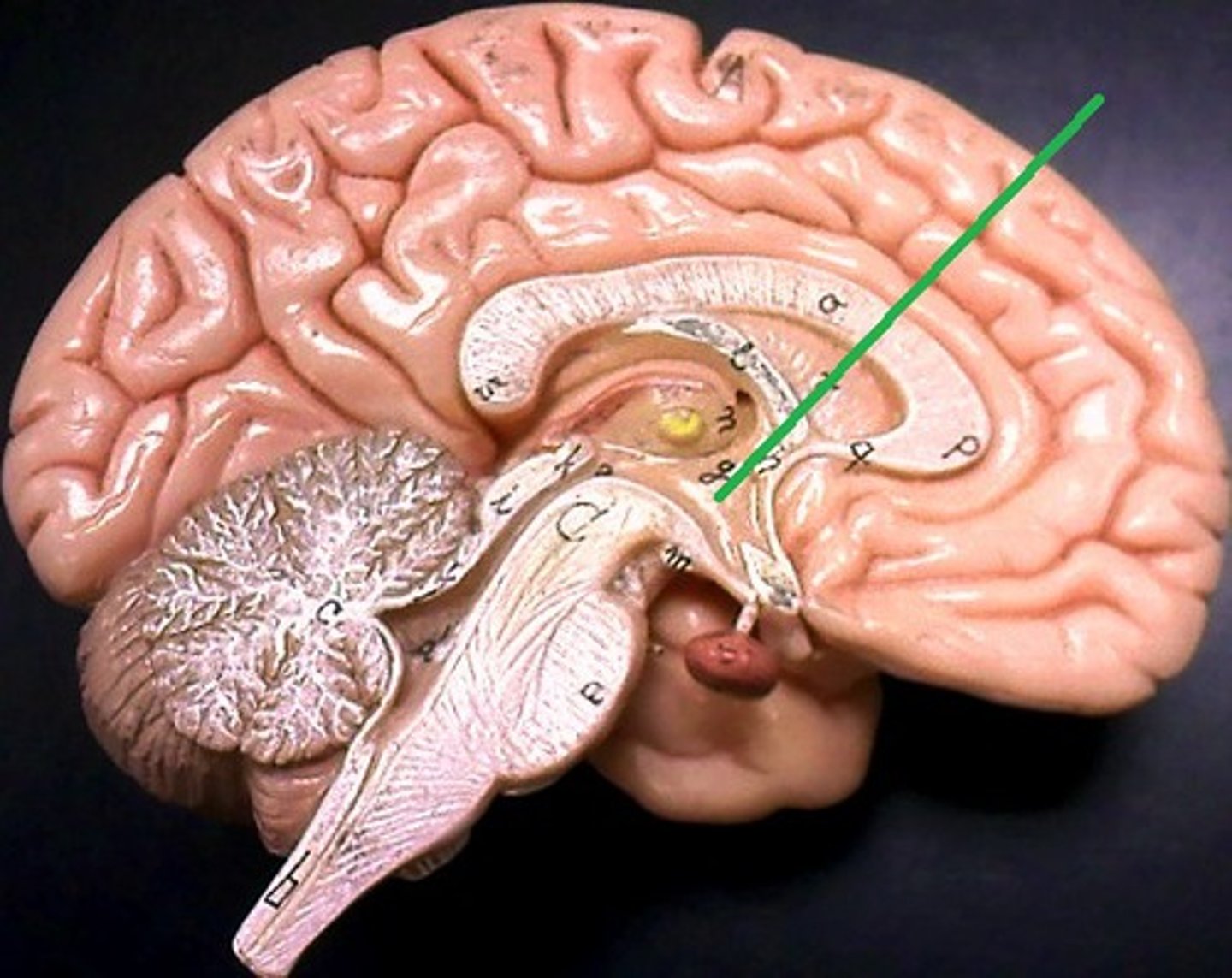
Hypothalamus
A small region at the base of the brain, it directs several maintenance activities such as eating, drinking and controlling body temperature
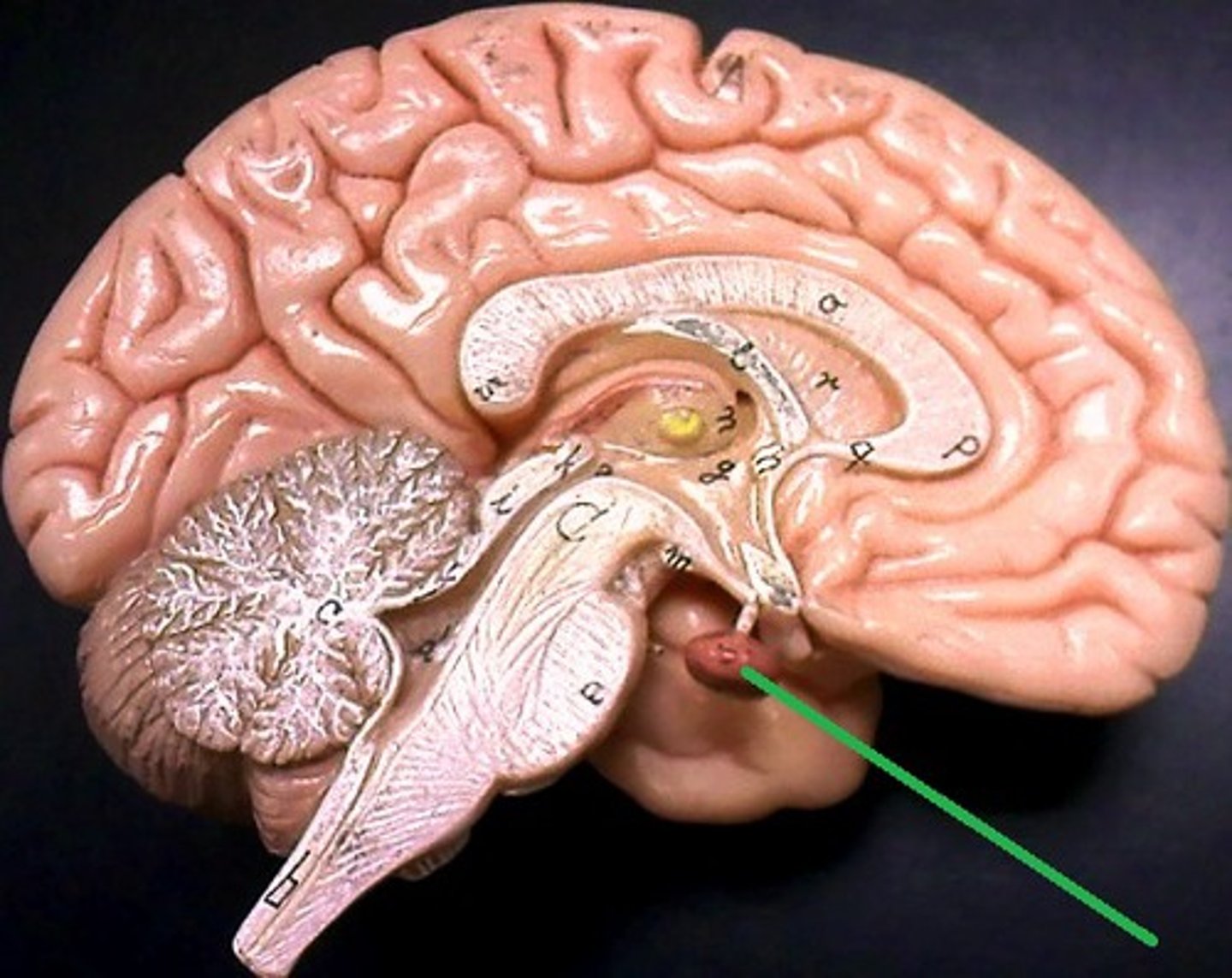
Pituitary gland
A master gland attached to the hypothalamus, responsible for releasing many different hormones that regulate specific processes and functions
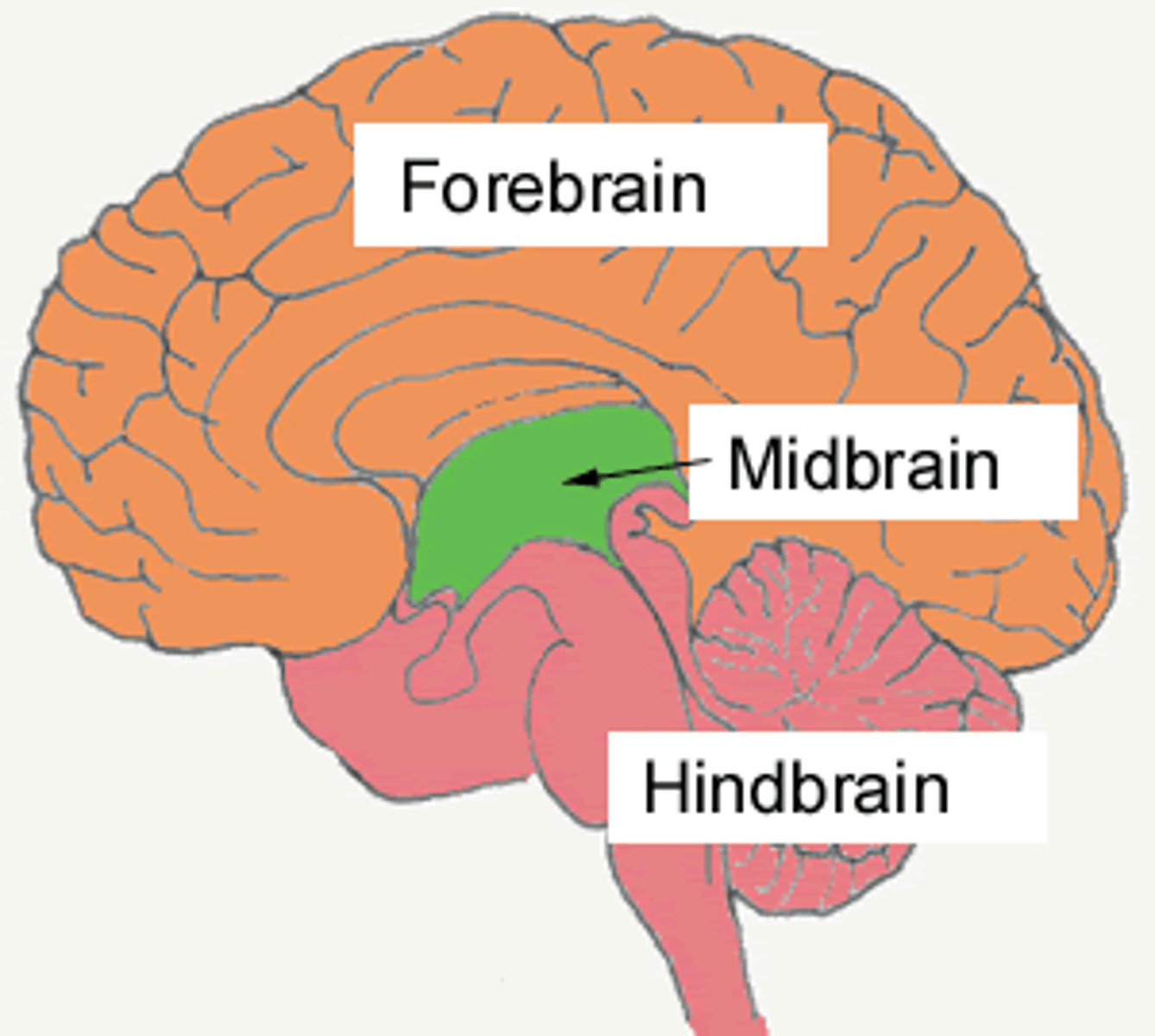
Hindbrain
The lower part of the brainstem that include the cerebellum
Medulla
The base of the brainstem which controls heartbeat and breathing
Eye
A sense organ that detects light and is responsible for vision

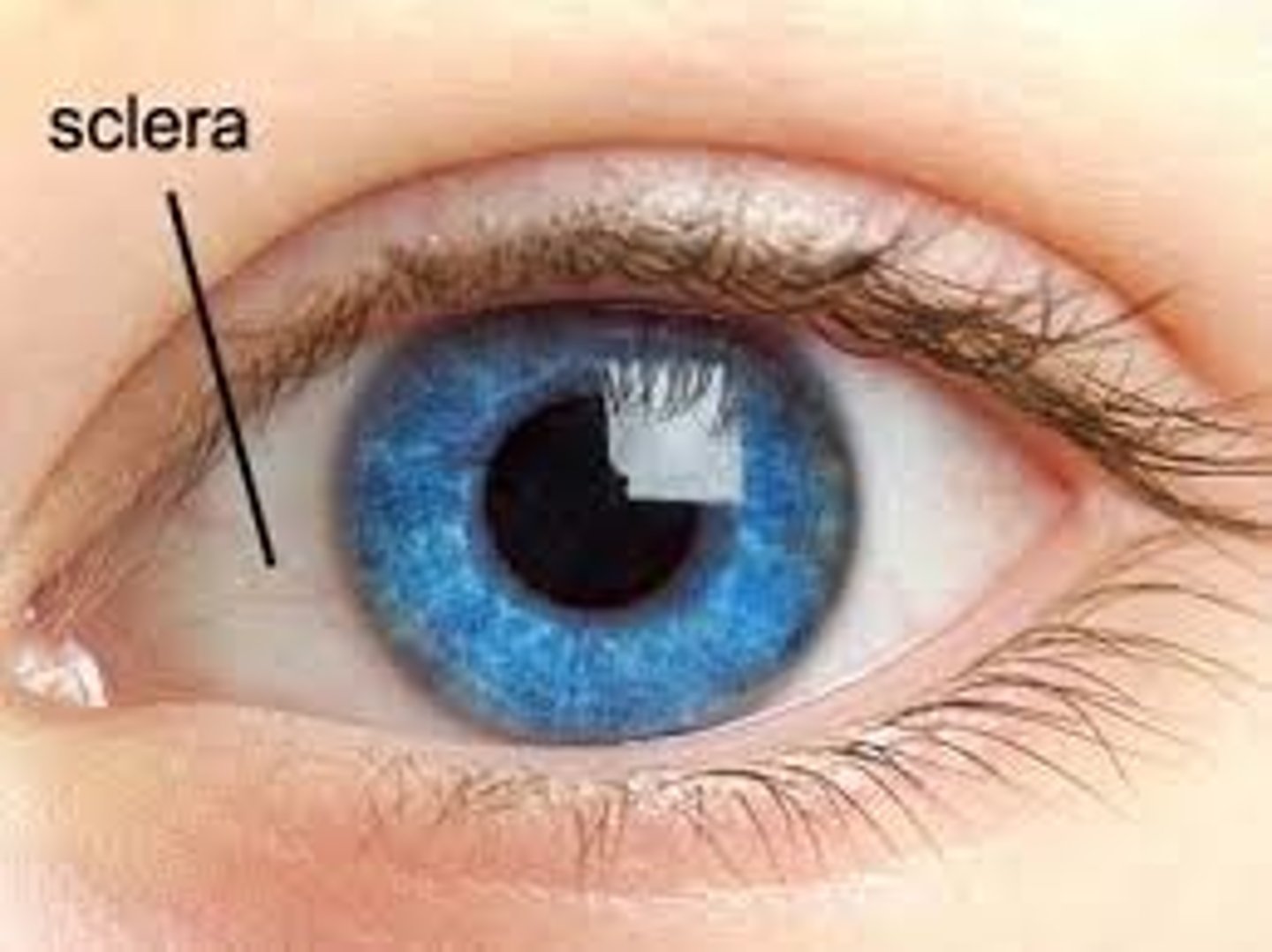
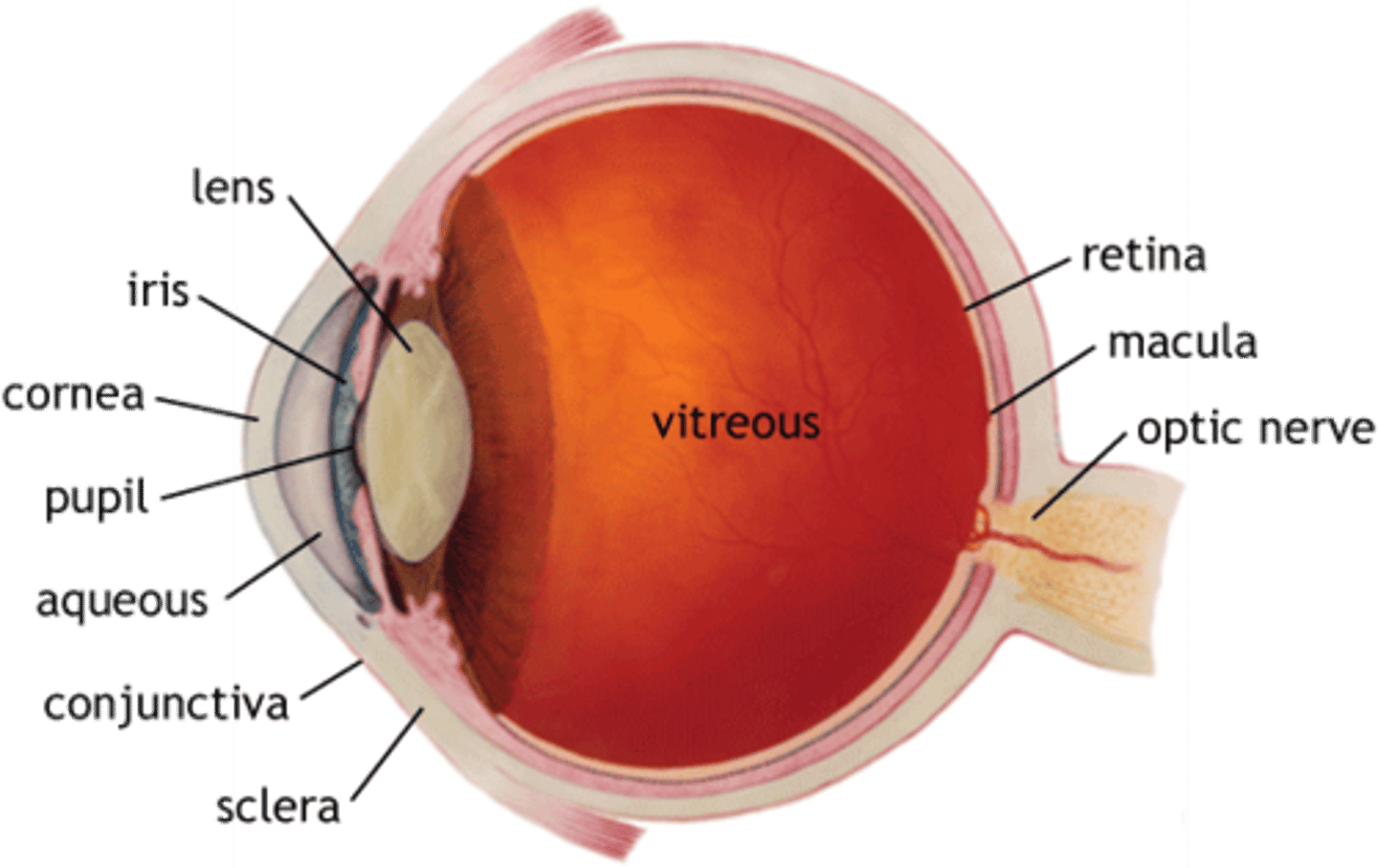
Sclera
The white outer part of the eye that provides protection
Cornea
The transparent tissue that covers the front of the eye, it controls and focuses the entry of light into the eye

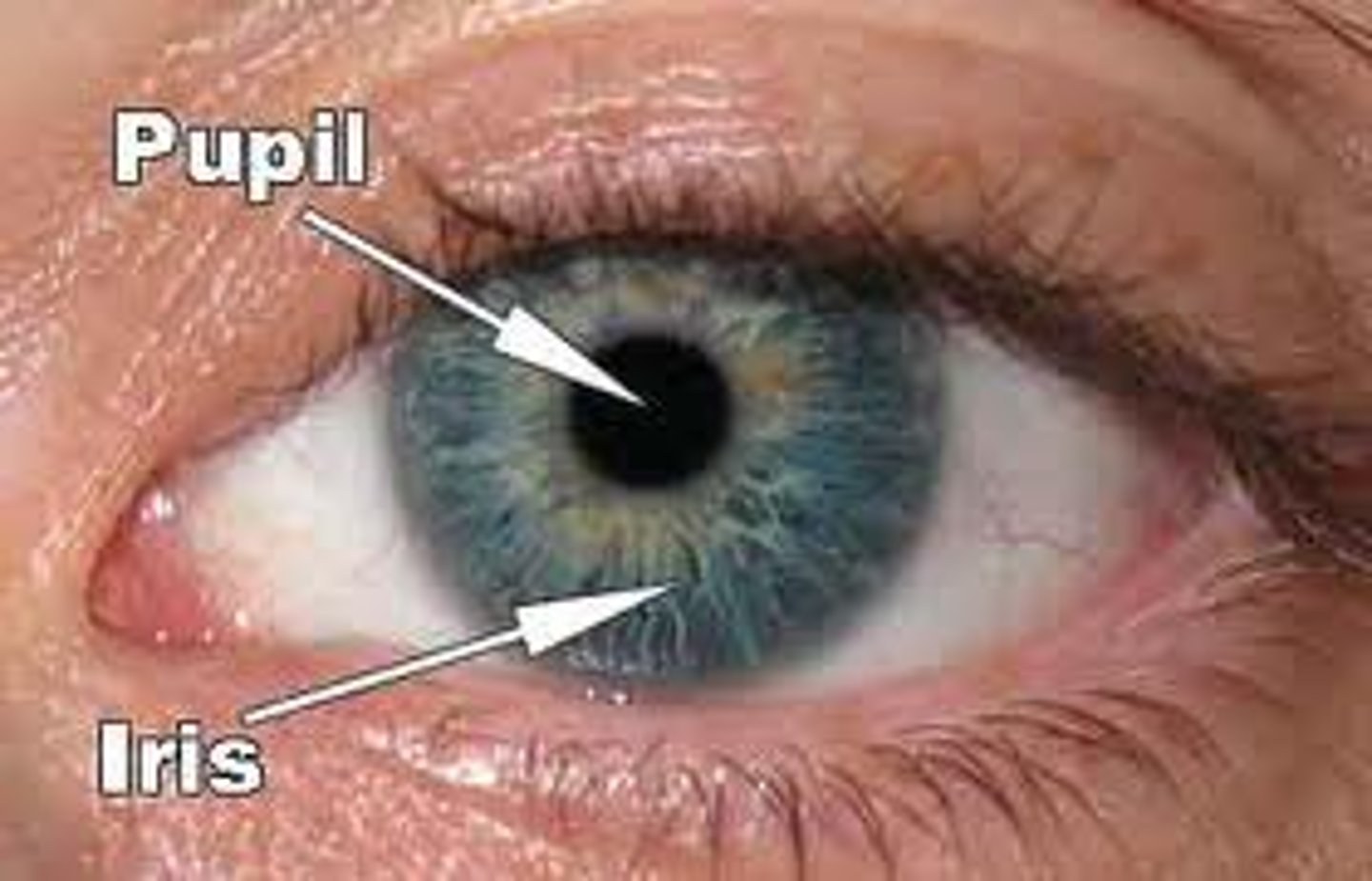
Iris
The coloured part of the eye behind the cornea that regulates the size of the pupil
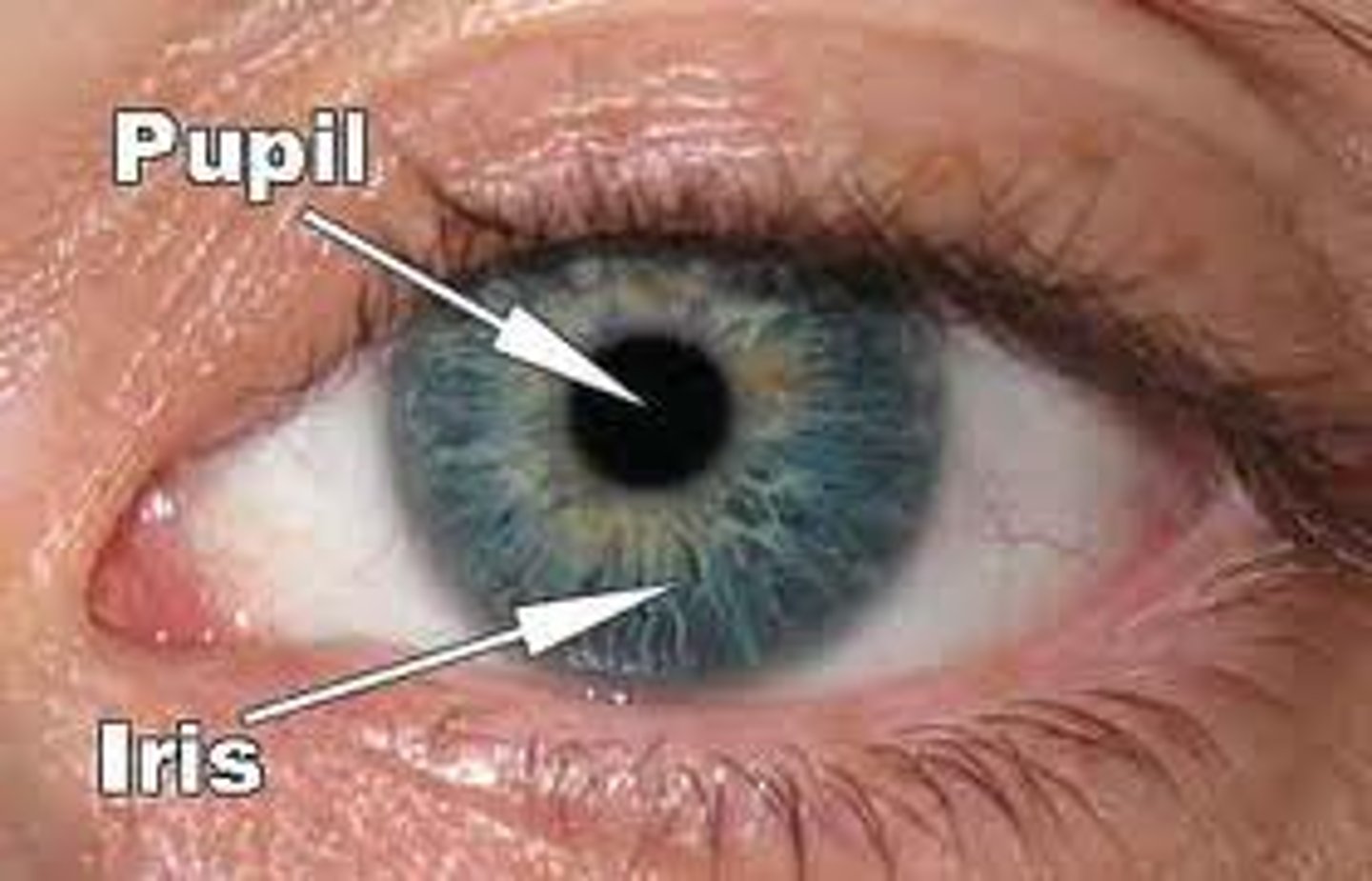
Pupil
The dark opening in the centre of the pupil, it varies in size to regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina
Lens
A transparent structure located behind the iris that focuses light on the retina at the back of the eye
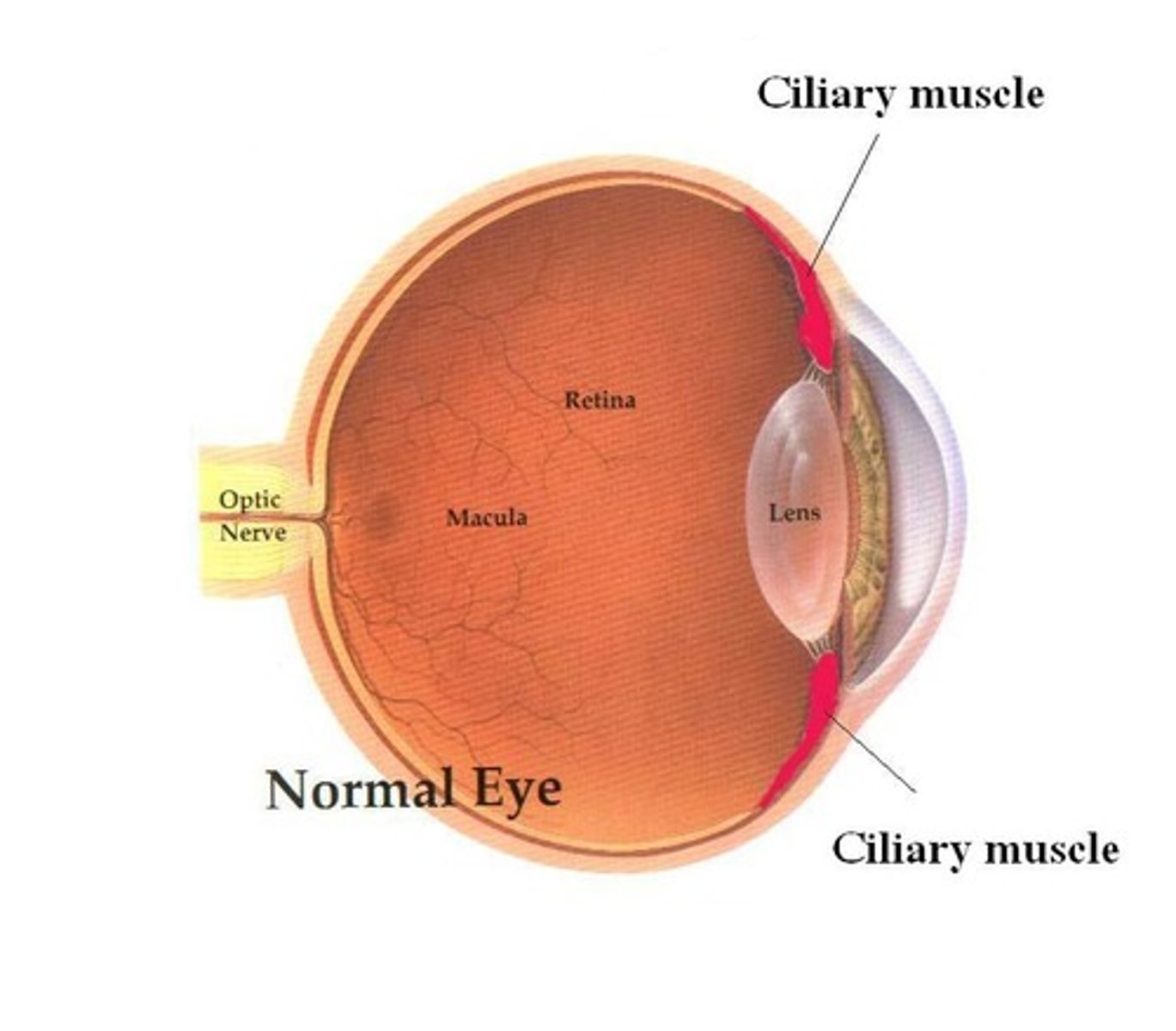
Ciliary muscles
Muscles which work with the suspensory ligaments to adjust the shape of the lens in order to focus on near or far objects
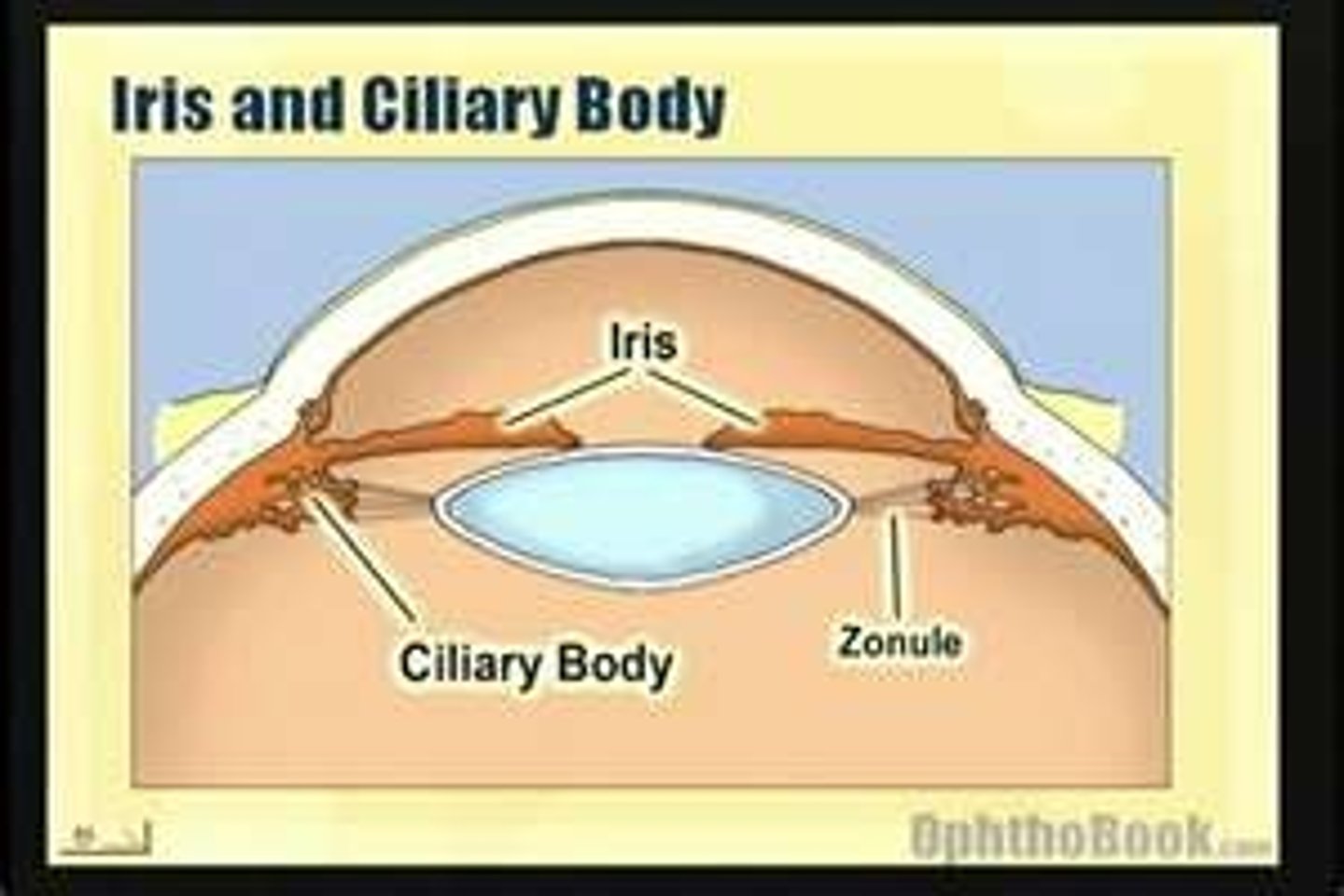
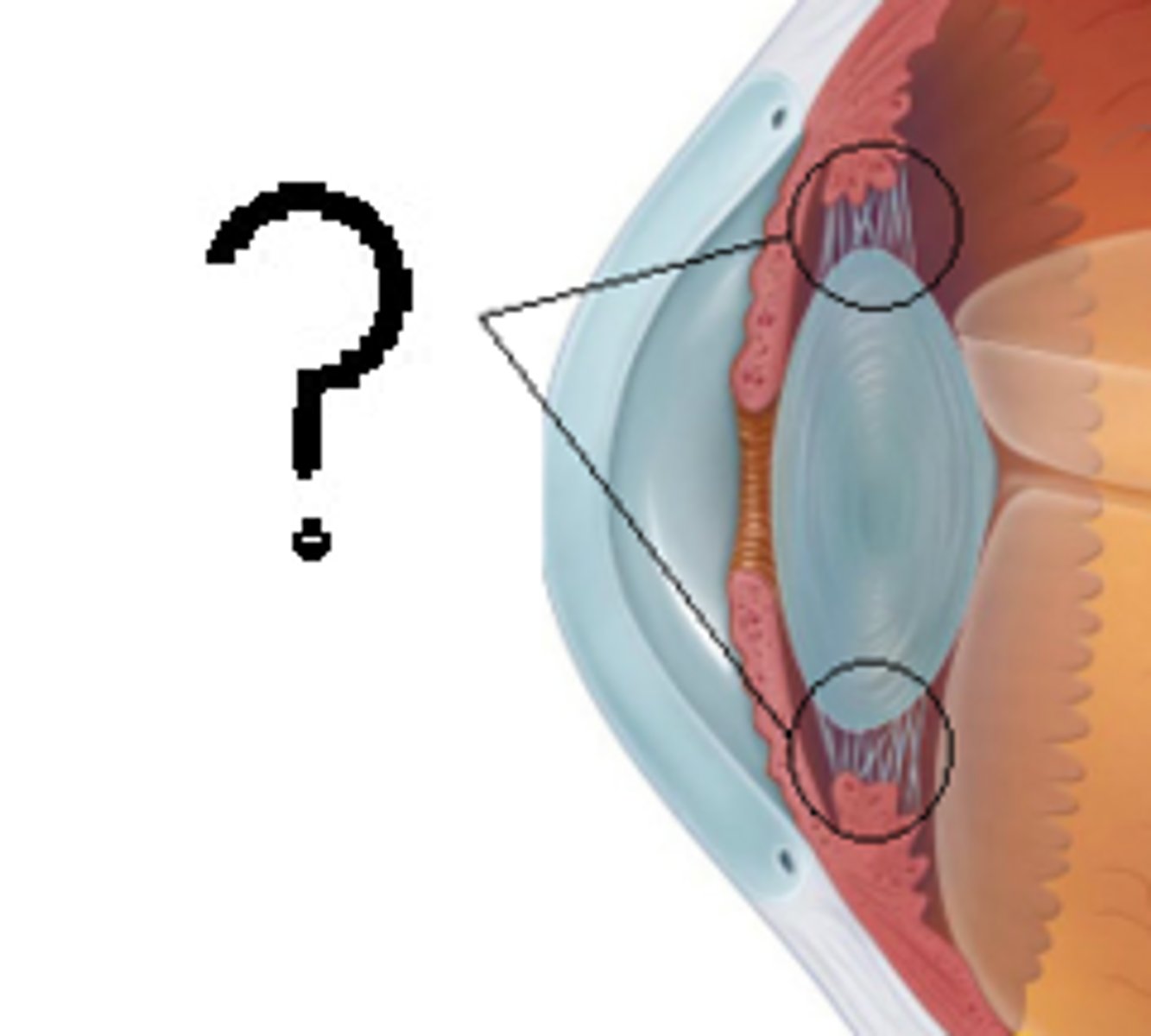
Suspensory ligaments
Ligaments which work with ciliary muscles to adjust the shape of the lens in order to focus on near or far objects
Retina
The light-sensitive surface at the back of the eye containing light and colour receptor cells
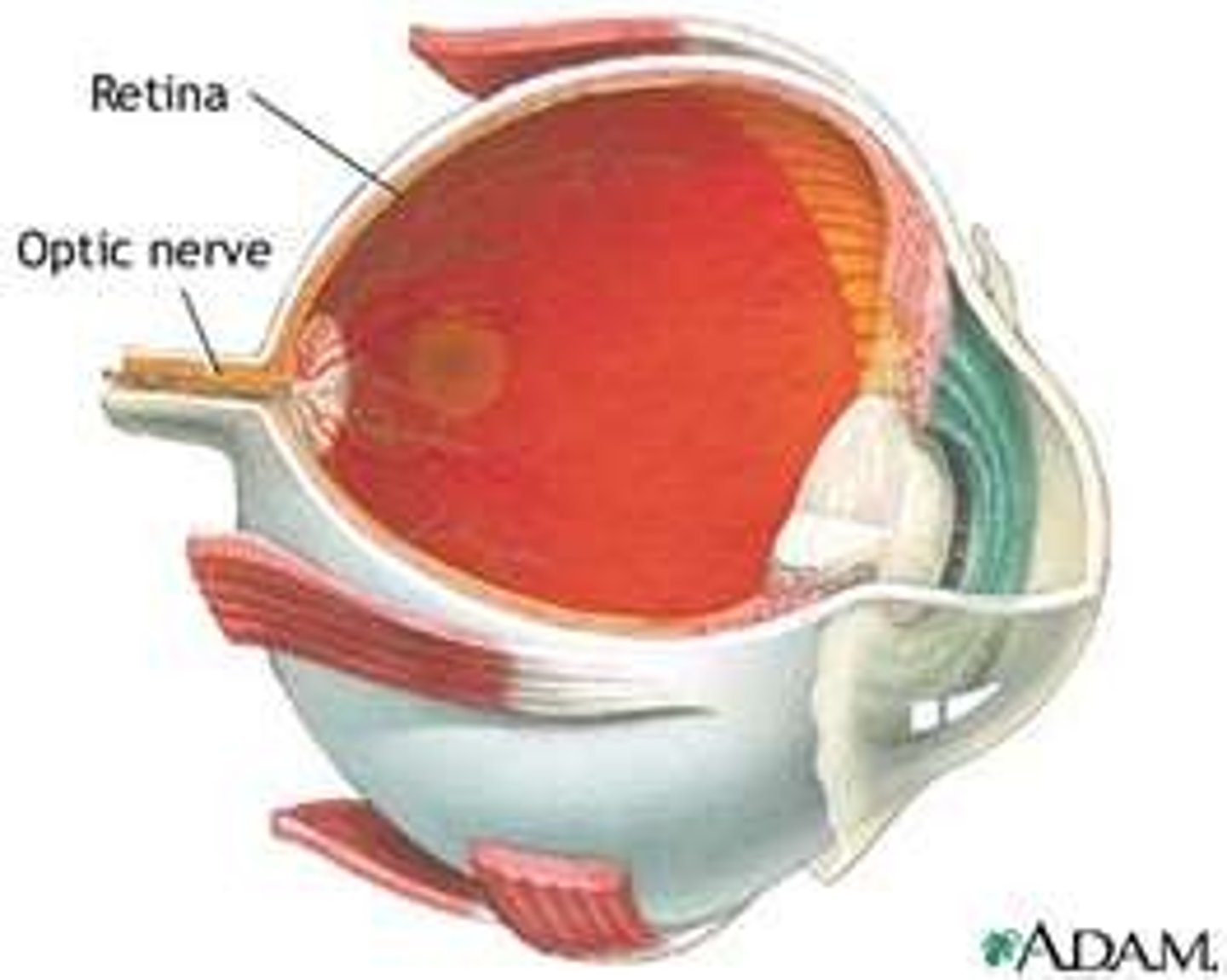
Optic nerve
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the receptor cells of the eye to the brain
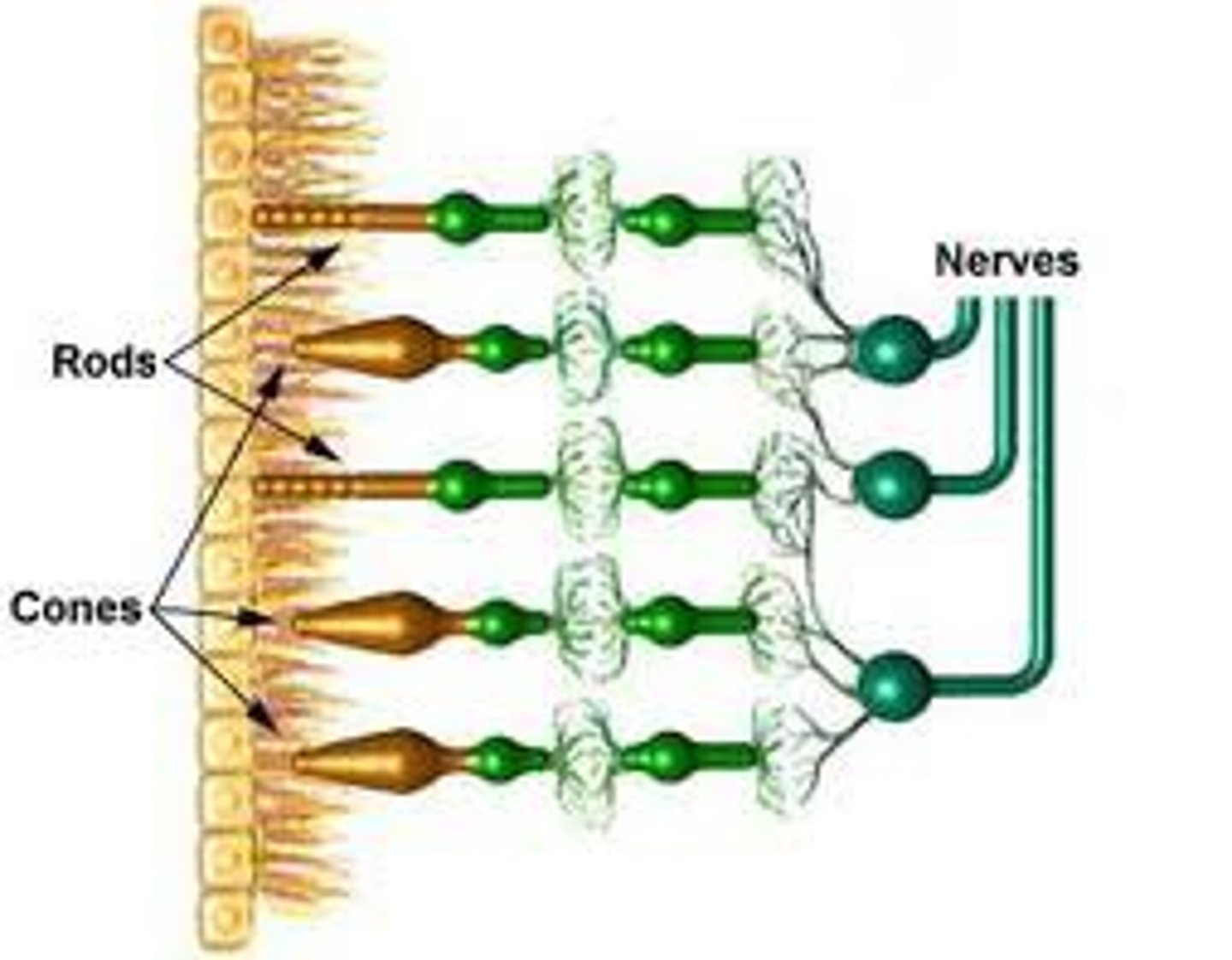
Light receptor cells
Also called rod cells, these are highly light sensitive and are responsible for vision in dimly-lit conditions
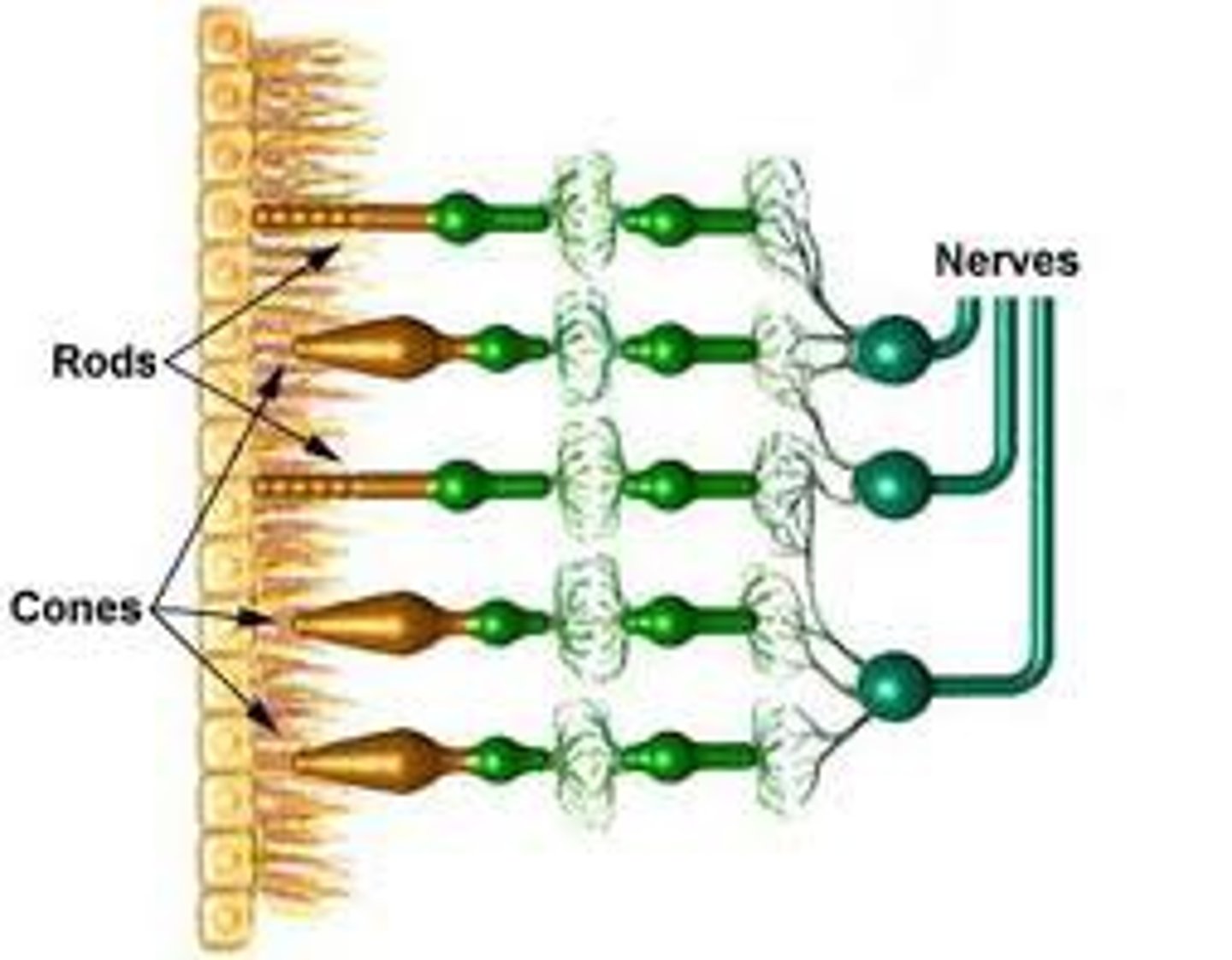
Colour receptor cells
Also called cone cells, these can detect a wide spectrum of light and are responsible for the perception of colour