People and the biosphere
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ts so kevin 😂😂😂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
All of the living things in a given area, interacting with eachother + with their non-living environment
What is a biome?
A very large ecosystem, e.g: deserts or rainforests
What is a biosphere?
The zone where life is found
What are biotic factors?
Living things that are part of and influence an ecosystem, e.g: trees, plants, decomposers, animals
What are abiotic factors?
Non-living things that are part of and influence an ecosystem, e.g: sunlight, rocks, water, wind, temperature
Where is the tundra located?
Far north, 70-80
e.g: Canada, Russia, coastal Greenland
What is the climate of the tundra?
Very temperatures of around 5-10 C in summer and < -30C in winter
High latitudes mean near continuous daylight in summer and little/none in winter
No cloud cover + very little precipitation (10-25cm/yr)
What flora is in the tundra?
Cold climate and lack of light means there’s hardly an biodiversity
Mosses, grasses, lichens, dwarf shrubs
What fauna is in the tundra?
Cold climate and lack of vegetation means few live here
Artic foxes + hares, mosquitoes, birds
Lots of animals migrate south for the winter
Where are tropical rainforests located?
Straddles the equator between 10°N&S
Amazon, Brazil, Indonesia
What is the climate of tropical rainforests?
No definite seasons
High temperatures above 26°C due to sun being concentrated at small area (due to curvature of the earth)
High rainfall around 200mm per year
What type of flora are in tropical rainforests?
Evergreen trees grow all year long
Plants grow quickly + adapted to take in max light
What type of fauna are in tropical rainforests?
Dense vegetation gives food and habitats so there are lots of species
Jaguars, sloths, tree frogs
What is the location of taiga?
60°N
Russia, Canada, Scandanavia
What climate is taiga?
Short summers + long winters
Winter’s average temps are below -20°C
Summer’s average temps are around 10°C and can drop much lower
Low precipitation, less than 500mm a year, mostly snow
Lots of sunlight
What flora is there in taiga?
Most trees are evergreen
Pine, fir, growing moss + lichen
What fauna is there in taiga?
Fewer animal species compared to tropical rainforests as there’s less food and they have to adapt to a cold climate
Black bears, wolves, elk + eagles
Where are deserts located?
30 N&S
North Africa, Australia
What is the climate in deserts?
Very low rainfall of less than 250mm yearly
Hot temperatures, very hot in the day (e.g 45 C) - cold at night (0 C)
More daylight during summer than winter - v little cloud cover means lots of hours of sunshine every day
What flora is there in deserts?
Plant growth is sparse due to lack of rainfall
Cacti, thornbushes
What fauna is in deserts?
Relatively low amount of animals - those that do are adapted to cope with v hot, harsh cliimate
Lizards, snakes, insects, scorpions
Where are temperate forests located?
50-56 N
Eastern North America, northeastern Asia, and central and western Europe
What is the climate in temperate forests?
Average daily temperatures range between -30°C and 30°C
Rainfall is high, up to 1500mm per year, all year round
Hot summers and cold winters are typical in this biome.
What flora is there in temperate forests?
Mix of deciduous and evergreen trees
oaks, maples, beeches, birches, and ash. Evergreens like pines, spruces, and hemlocks are also found.
various shrubs, herbaceous plants
ground cover like mosses and lichens
What fauna is there in temperate forests?
Insects, spiders, slugs, frogs, turtles and salamander
white-tailed deer, raccoons, opossums, porcupines and red foxes
Bears
What is latitude and how does it influence biomes?
How far N or S of the equator the area is
Influences temperature due to curvature of the earth - more sun at equator than poles so less vegetation at higher latitudes than tropics
Influences precipitation, which is generally highest in coastal and highland regions. Precipitation happens where there’s belts of low pressure - main areas of year round rainfall is the equator + mid latitude areas, often forests frow here
What is altitude and how does it influence biomes?
The height above sea level in a particular location.
Influences temperature, as air temperature generally decreases with increasing altitude, affecting vegetation types and climate in mountainous regions, e.g: Mt Kiliminjaro is covered in snow even though its near the equator
Often coniferous forest + tundra with increasing height + tough grasses
What is drainage and how does it influence biomes?
The process by which water is removed from an area, often through rivers, streams, or wetlands.
Affects local conditions + vegetation, e.g: in the UK often entirely deciduous forest, but in parts of Scotland peat bogs replace forest due to the especially wet soil
What is geology and how does it influence biomes?
The rocks and soils
Affects local conditions + vegetation
e.g: limestone bedrock causeses dry soil becoause percolating rainwater passes through it easily - in the UK trees rarely found here
In tropical rainforests, deciduous trees may replace evergreens where limestone is found
How to answer climate graph questions, e.g: DESCRIBE THE PATTERN OF PRECIPITATION IN MANAUS
THROUGHOUT THE YEAR (4)
Start of the graph (including data)
Trend of the data (does it increase or decrease? Is it steady? Does it increase slowly or rapidly? Does the data trend change?)
Anomalies (does any data not fit the general pattern?)
End of the graph (including data)
Who are the Efe people?
Indigenous people of the Congo rainforest in Africa who rely on the forest for their livelihood
How do the Efe people uses their biome? (6)
Small circular houses built from wood + leaves (temporary as they move around the rainforest hunting and gathering)
Wood for cooking fires comes from the forest
Hunt monkeys and antelopes for bush meat, as well as fish from the rivers
Gather wild yams, berries, nuts and mushrooms
Hunt giant forest hog and sell meat to other people around the region or trade it for items like pans + rice
Use plants + wild honey for traditional medicines
What does Malthus believe about population growth and its effects?
Pessimist - “We are all doomed”
Believed only bad could come from population growth
Pop grows faster than resource supply
Believes famines will be common in LICs
Global warming, oil spillage, ozone depletion + desertification can lead to less food grown
What does Boserup believe about population growth and its effects?
Optimist - “necessity is the mother of invention”
Said food supply would increase to accomodate pop growth
New tech, farming methods - higher yields, or renewable energy supplies will be developed
There’s enough food to feed us, not always where it’s needed
Famine more likely to happen cos of natural disasters or war
Green revolution produced seeds that could grow quicker + bigger
What goods does the biosphere provide? (6)
Drinking irrigation water
Fruit, nuts, other products like rubber
Genetic resources
Medicines
Food + fibre crops
Meat, fish, hides, timber, fuelwood
What services does the biosphere provide? (9)
Maintaining biodiversity
Regulate our atmosphere (Amazon “lungs” of earth)
Nutrient cycling
Human or wildlife homes
Employment
Water regulation + purification of supply
Humus for soil formation
Pollination of food web/chai
Gene pool
What is a carbon sink?
natural store for carbon containing compounds like co2 or methane
How do biomes work as carbon sinks ?
Carbon sequestration - removing co2 through photosynthesis + locking it into biotic material
In biomass (leaves, branches, trunks, roots + animal tissues)
When animals + plants die the dead biomass ends up in the soil - important carbon sink
What 2 ways can humans destroy biomes and affect carbon stores?
Deforestation so biomes absorb less co2
Burning biomass such as trees, and soil destroyed, releasing stored carbon
What is the nutrient cycle?
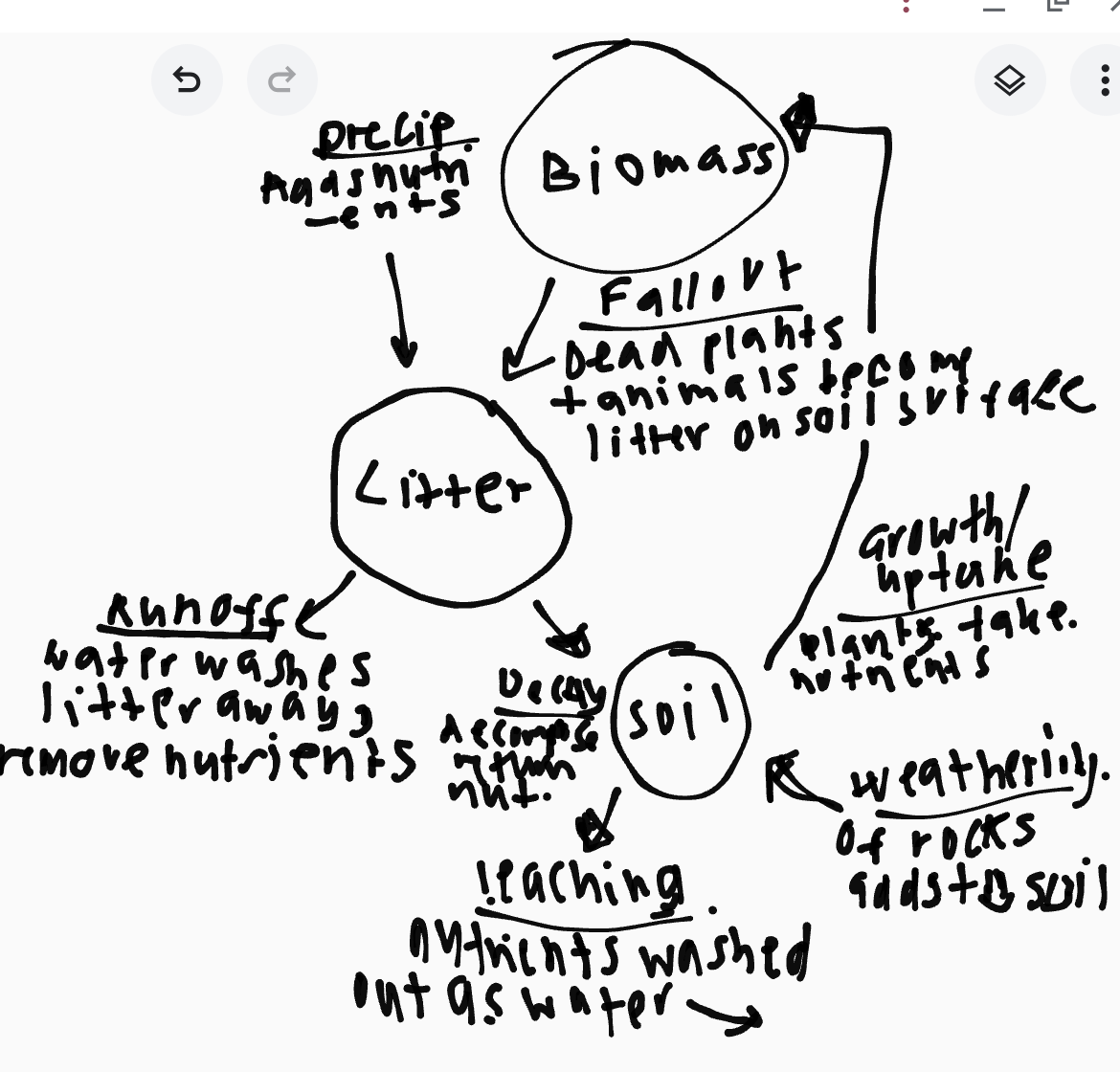
What ways can humans effect the nutrient supply?
Humans can remove biomass through logging timber, taking away a large nutrient source
Deforested areas are at a risk of soil erosion - removing another source
Explain the importance of the biosphere to the water cycle
With no trees, interception is reduced and rainfall hits the soil surface directly causing soil erosion
Without trees there is much less infiltration of water into the soil, this means groundwater supplies are lower
Surface runoff increases which increases soil erosion and means water enters rivers much faster
Flooding becomes more frequent and river water is made dirty of the soil washed in the river
With no forest the soil dries are very quickly, so overall evaporation is reduced, which can mean fewer clouds, less rain and dry climate