Chapter 17: Sampling Distribution Models
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a sampling distribution?
A model of a statistic (like a sample mean or proportion) based on repeated samples from the same population.
What does the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) say?
For large samples, the sampling distribution of the sample mean becomes approximately Normal, regardless of the population’s shape.
When can we use the CLT for sample means?
When the population is Normal
Or when n ≥ 30 (large sample size)
What is the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean (\bar{x})?
\mu_{\bar{x}} = \mu — the population mean
What is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample mean?
\sigma_{\bar{x}} = \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}
Only valid if the sample is random and n \leq 10\% of population.
What is the sampling distribution of a sample proportion (\hat{p}) centered at?
\mu_{\hat{p}} = p — the population proportion
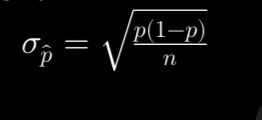
What is the standard deviation of \hat{p}?
What are the conditions for the Normal model for \hat{p}?
Random sample
10\% condition: sample ≤ 10% of population
Success/Failure condition: np \geq 10 and n(1-p) \geq 10
What are the 3 big ideas in sampling distribution models?
Center: Sampling distribution is centered at population value
Spread: Gets smaller as n increases
Shape: Becomes Normal if conditions are met
How does increasing sample size affect standard deviation?
It decreases the standard deviation — more data = less variability
Why is the 10% condition important?
It ensures independence when sampling without replacement
What’s the “Success/Failure” condition used for?
To check if it’s safe to model a sampling distribution of proportions using a Normal model