Chapter 12 Microeconomics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
The objective of imposing a higher pollution tax is to
provide adequate incentive for firms to reduce their emissions by more.
A pollution charge gives the trucking industry an incentive to reduce its emissions, as long as the of reducing the emissions is .
marginal cost; less than the tax
If a government wants to establish a marketable permit program, it must begin by determining
the overall quantity of a certain pollutant that will be allowed.
The flexibility of marketable permits program developed for the oil refining industry is credited with achieving the reduction in lead pollution for____less cost than command and control regulation would have required.
at least 20%
include both the private costs incurred by firms and also costs incurred by third parties outside the production process.
Social costs
Using the term "spillover" is a less formal means of describing
an externality.
Traditionally, policies for environmental protection in the U.S. have focused on pollutant could be emitted.
setting limits for how much of each
Which of the following have historically been more willing to sacrifice their environmental quality for some additional economic output?
low incomes and command economies
describes a situation where a third party, outside the transaction, suffers from a market transaction by others.
Negative externality
If an externality of pollution exists for all manufacturers in a given industry, then all related social costs
are not represented in their supply curves.
While the traditional approach of U.S. government policies for environmental protection has had some level of success, some economists are proposing a change to
a range of more flexible, market-oriented pollution control policies.
Property rights are the legal rights of ownership on which others are
not allowed to infringe without paying compensation.
The equilibrium price and quantity when social costs are taken into account when
Quantity Demanded=Quantity Supplied after Paying Social Costs
Which of the following is an example of economic output that can injure the environment?
gold mine discharging arsenic into a natural lake it's using for a tailings pond
paper mill discharging raw chemical waste into a river
excessive clear cutting of wood resources by logging companies
radio-active waste leaking into a river, and all of the above
radio-active waste leaking into a river, and all of the above
When the quantity of environmental protection is low so that pollution is extensive, then there are usually ____to reduce pollution and the __.
a lot of cheap and easy ways; marginal benefits of doing so are quite high
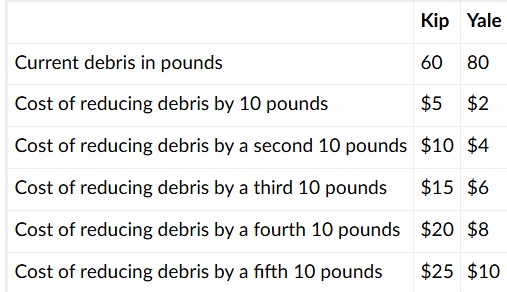
If each mining company is forced to cut its debris in half, the respective cost to Kip and Yale will be
$30, $20
The main categories of market-oriented approaches to pollution control are
marketable permits; better-defined property rights; pollution charges.
A positive externality arises in a situation where a third party, outside the transaction,
benefits from a market transaction by others.
The refundable charge of 5 or 10 cents for returning recyclable cans and bottles works like
a subsidy to avoid littering.
Market failure describes a situation in which the market itself in a way that balances social costs and benefits.
fails to allocate resources efficiently
The main categories of market-oriented approaches to pollution control are
marketable permits; better-defined property rights; pollution charges.
A beekeeper decides to locate her business on a plot of land that is between an apple orchard and an elementary school. A positive externality that can result is
the bees helping to pollinate the orchard, leading to more fruit.
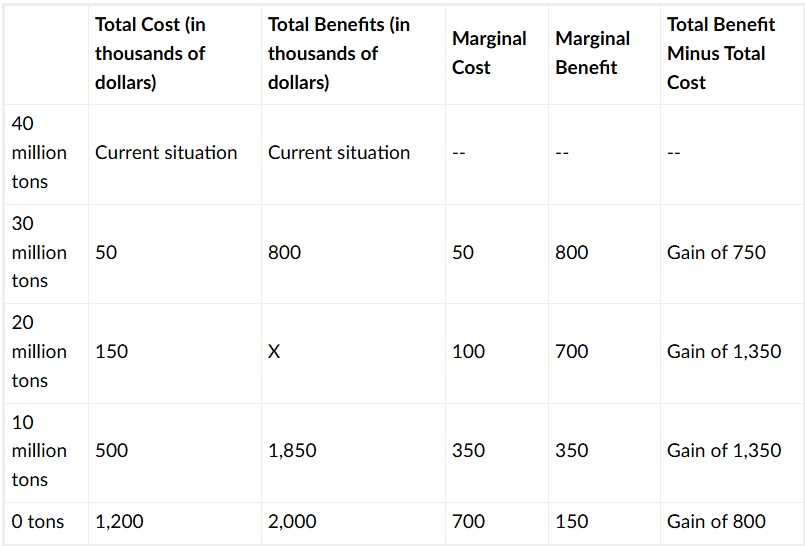
A country is currently creating 40 million tons of toxic waste per year. The table below shows the marginal costs and benefits of reducing the amount of toxic waste to various amounts. What number belongs in place of X?
x=1500
A pollution charge is a form of tax imposed on
the quantity of pollution that a firm emits.
Why do U.S. economists commonly refer to externalities as an example of market failure?
externalities present a case where markets only consider some social costs
If a steel manufacturer considers the costs of labor and materials, as well as the broader costs of environmental injuries resulting from its manufacturing processes,
it is factoring in the social costs of the pollution it generates.
The term refers to a market exchange that affects a third party who is outside or external to the exchange.
spillover
If no externalities of pollution exist in a particular industry, the interaction of demand and supply .
will coordinate social costs and benefits
When a government establishes a marketable permit program to address environmental pollution, it is actually issuing a form of
permit to pollute.
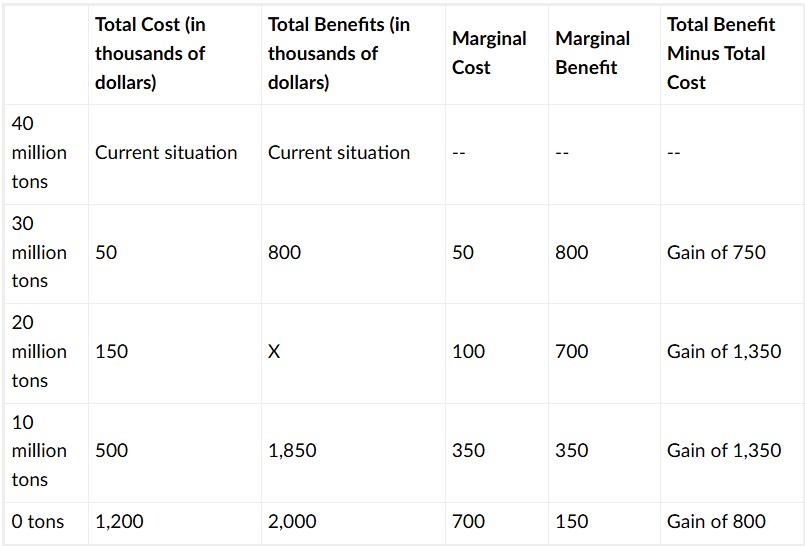
A country is currently creating 40 million tons of toxic waste per year. The table below shows the marginal costs and benefits of reducing the amount of toxic waste to various amounts. What level of toxic waste should the country reduce to?
10 million tons
In circumstances involving millions of emitters of small amounts of pollution who have no strong interest in trading, ____will typically offer a better choice for achieving desired reductions of environmental pollution levels.
pollution charges
Some economists argue that if privately owned firms were required to pay the social costs of their pollution, the result would be:
each would create less pollution
each would lower production to decrease pollution levels
the price of goods will rise
In the U.S., the command-and-control environmental laws of the early 1970s, together with the ensuing amendments and updates that have been made to them over time,
are given considerable credit for cleaner air and water in recent decades.
Command-and-control regulation is a body of law that
specifies allowable quantities of pollution.
details which pollution-control technologies must be used.
Four companies, Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta, are burning coal to produce electricity. As a result, they also produce emissions. The first row of the table below shows the total pounds of emissions currently produced by each firm. The other rows of the table show the cost for each firm of reducing emissions by the first 50 tons, the second 50 tons, and so on. The government wants to reduce emissions by one third, and does so by issuing marketable permits based on the current level of emissions where the permits will shrink the allowable amount of pollution by one third.
How to solve?
Find out how much is a 1/3 for each company. Add it up. Get rid of the cheapest 50 tons at a time. Note from what company they are from to know how much emissions each company reduced by.
What type of environmental tool was adopted by the U.S. government in 1990, in order to reduce emissions of coal burning electricity-generating plants?
shrinkable marketable permits
free marketable permits
Since 1969, when the Cuyahoga River in Ohio was so polluted that it spontaneously burst into flame, the overall quality of water in the U.S. has
steadily improved.
If you are highly asthmatic, then having high levels of industrial air pollutants waft over your house every day
would be a negative externality.
As environmental protection increases,
the biggest marginal benefits are achieved first, smaller marginal benefits follow.
inexpensive and easy methods of reducing pollution begin to dwindle.
the quality of environmental protection increases.
An economist is more likely to identifyas a more efficient and flexible way for society to.
marketable permits; allow a limited, declining amount of pollution to occur
While the U.S. command-and-control environmental regulations initiated in the 1970s have been very effective at reducing pollution, some economists have difficulty with the legislation because
it is full of fine print and exceptions, and costly for some firms to comply with.
If pollutants are emitted into the air and water, what costs might be incurred as a result?
compromised recreation possibilities
decreased property values
loss from destruction of wildlife habitat
health injuries
The arguments presented by economists regarding U.S. environmental command-and-control regulations generally
accept the goal of reducing pollution.
question the regulations as being the best policy tools for meeting reduction goals.
lack flexibility