Neurobiology- Auditory System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the important features of sound?
frequency/pitch, duration, intensity, localization
What is sound?
pressure waves, alternating compression and rarefaction of air or water
How fast does sound travel in air?
350 m/sec
What are the three questions regarding how the nervous system detects sound?
How do neural systems detect sound? What are the reception and transduction mechanisms? What is the pathway of transmission to the CNS?
VIIIv
vestibular nerve
VIIIa
cochlear and auditory nerve
Duration
length of time
Intensity
magnitude of sound
frequency/pitch
number of signals per unit of time
Localization
where sound is coming from
List the components of the auditory pathway (nerves)
spiral ganglion > auditory nerve (primary afferent) > ventral or dorsal cochlear nucleus > superior olive > lateral leminiscus > inferior colliculus > MGN > Auditory cortex
Where does the auditory pathway split to go both contralaterally and ipsilaterally
the ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei
Reception
capturing pressure changes
pathway of sound to ear
pinna > ear canal > ear drum (tympanic membrane) > ossicles > semicircular canals > cochlea
Function of the stapes
pushes against the oval window, transferring pressure waves from air to fluid in the scala vestibuli
What does the Organ of Corti have?
hair cells (auditory receptor cells)
pressure waves ascend to the apex of the cochlea in the scala vestibuli
then, pressure waves descend to the base within the scala tympani and transfer force to the round window
Information from one hair cell is encoded in ____________________
many neurons OR one neuron that branches
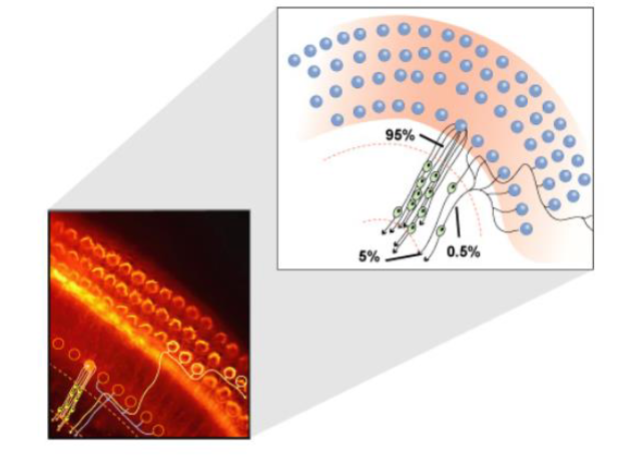
What to remember about innervation of hair cells?
they have different patterns of innervation
What to remember regarding hair cell orientation?
they have the same orientation
What is sensory signal transmission?
turning a physical stimulus into neural activity
what does transduction look like for the auditory system?
turning pressure waves into changes in membrane potential
What are auditory receptor cells also called?
hair cells
What is the function of tip links between stereocilia?
they detect a change in mechanical force
What is the driving force of K+ for a hair cell Apical surface?
inward, K+ depolarizes the hair cell
What is the driving force for K+ on the basal surface of a hair cell?
outwardWh
What is the resting membrane potential for a hair cell?
-45mV
What does the efferent synapse do?
Inhibits/gains control to reduce firing rate in the afferent nerve
efferent synapse mechanism/gain control mechanism
releases ACh, ACh receptors are Ca2+ permeable, causes influx of Ca2+ though sK channels
efferent synapse mechanism (after Ca2+ influx)/ gain control
efflux of K+ through sK channels causes hyperpolarization, reduces rate of ACh release to afferent nerve endingWht
What does the reduction of ACh release cause in the efferent synapse mechanism/ gain control
the reduced rate of ACh neurotransmitter reduces firing rate and probability of AP firing
Where are high frequency signals encoded?
near the base of the cochlea
where are low frequency signals encoded?
near the apex of the cochlea
what is tonotopy
the spatial arrangement of where auditory cells are transmitted, received, and perceived
In which areas is there tonotopy?
in the cochlea and auditory cortex
what is the cochlea?
the inner ear structure that sends information about sound to the brainwhat
what is the auditory cortex?
the part of the brain that receives and interprets sound information
What does the cochlear nucleus encode?
intensity and frequency
what does the pattern of action potential spikes encode in the cochlea?
tonotopic frequency
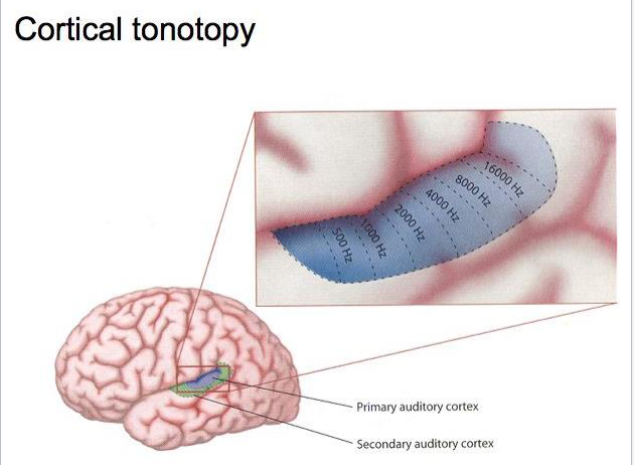
How do the layers of the auditory cortex effect tonotopy?
different frequency signals project to different sections of the cortex, spatial organization of information encoded in the cochlea and where its going to in the brain