Biochemistry Fundamentals: DNA Structure, Interactions, and Thermodynamics
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is biochemistry?
The study of the chemistry of life processes involving macromolecules and low-molecular-weight metabolites.
What are the two main types of organisms in biochemistry?
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes.
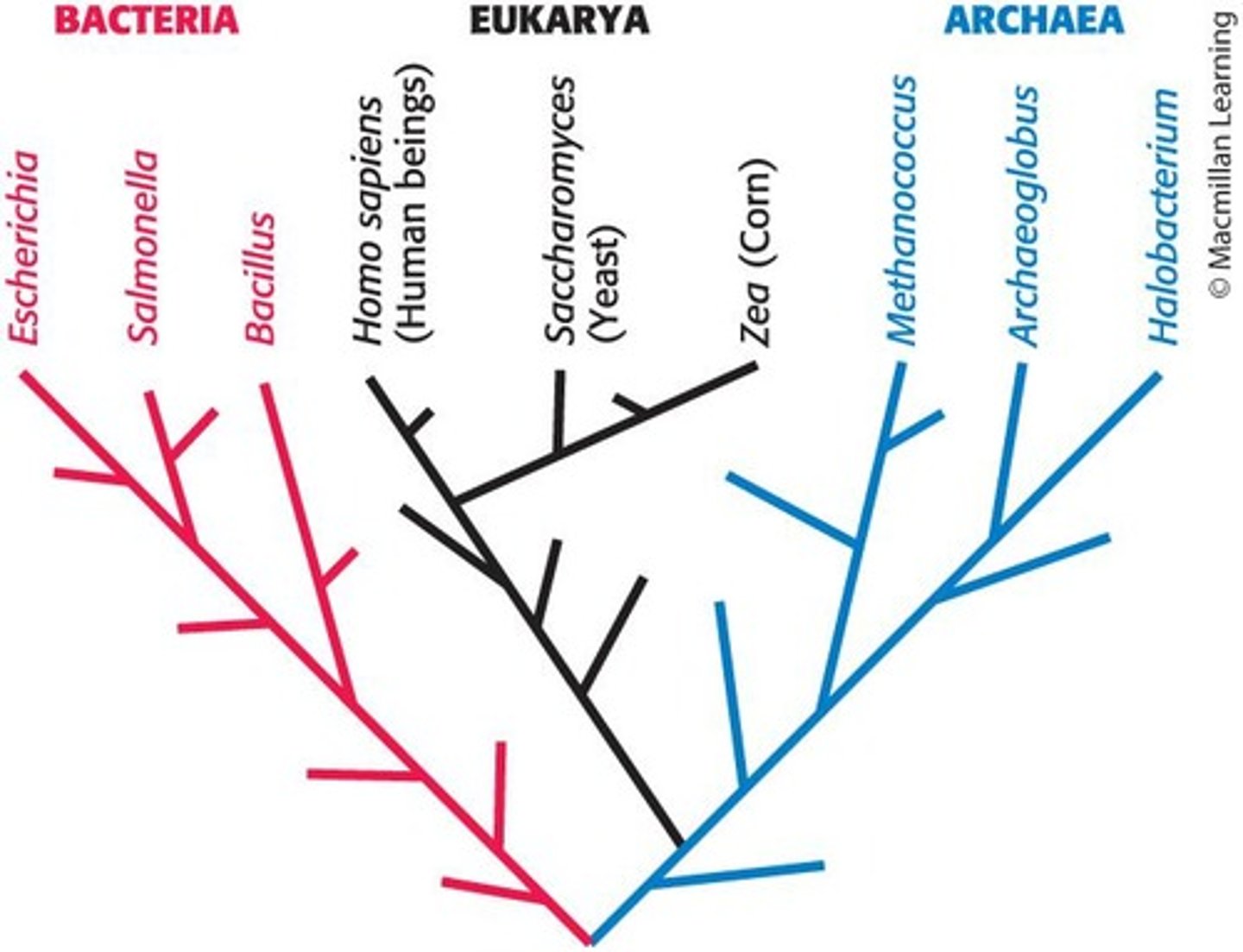
What does the phylogenetic tree of life classify organisms into?
Three domains: Eukarya, Bacteria, or Archaea based on biochemical characteristics.
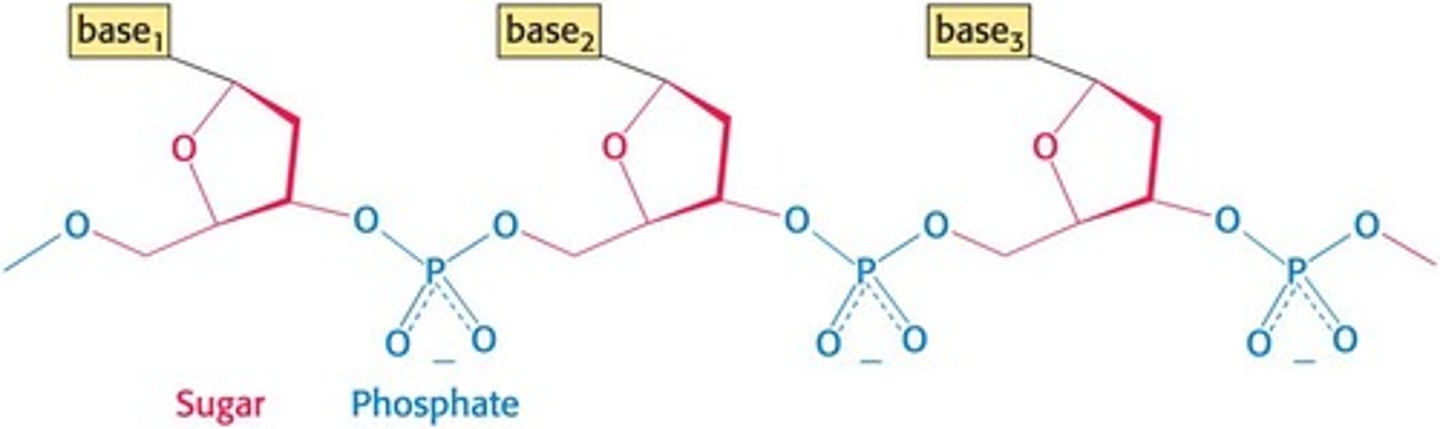
What is the structure of DNA?
A linear polymer composed of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous bases.
What is the significance of DNA's polarity?
It indicates the directionality of the DNA strands.
What forms the backbone of DNA?
Linked sugars and phosphates.
What is the structure of base-paired DNA?
It forms a double helix structure with specific base pairs held together by hydrogen bonds.
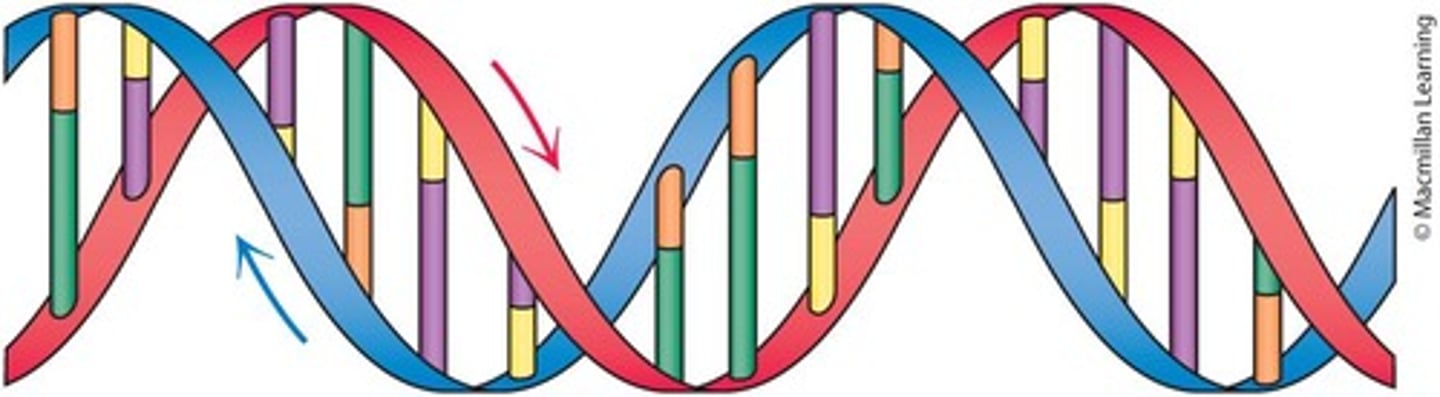
What is the orientation of the two strands in a DNA double helix?
The strands are antiparallel.
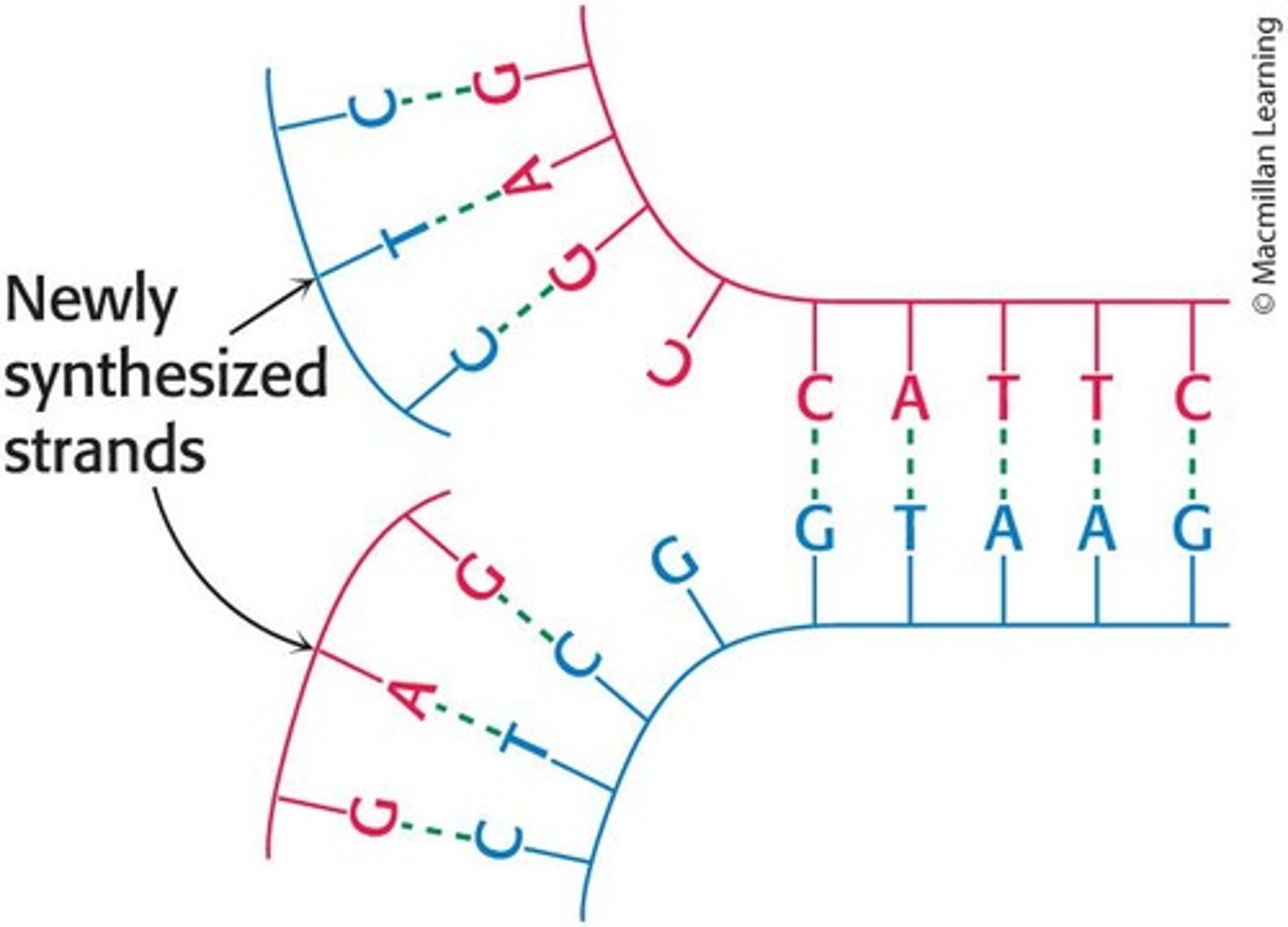
How does DNA explain heredity?
Each strand serves as a template for a new partner due to specific base pairing, allowing for the generation of identical daughter helices.
What is the timescale for biochemical interactions?
On the order of picoseconds to microseconds (10−12 to 10−6 seconds).
What are covalent bonds?
Bonds formed by electron sharing between adjacent atoms, and they are the strongest type of bonds.
What is resonance in molecules?
The phenomenon where some molecules exhibit multiple covalent structures.
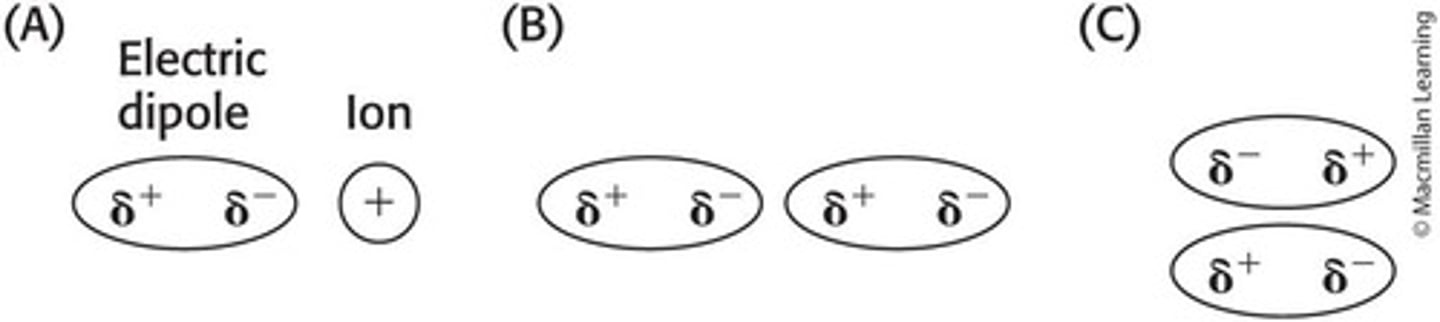
What are ionic interactions?
Noncovalent interactions that occur between fully charged atoms or molecules.
What is Coulomb's law in the context of ionic interactions?
E = kq1q2/Dr, where E is energy, k is a constant, q1 and q2 are charges, D is the dielectric constant, and r is the distance between atoms.
How do electrostatic interactions differ in water versus hexane?
In water, the bond energy is lower due to a higher dielectric constant compared to hexane.
What are electric dipoles?
Regions in molecules with uneven electron distribution that can interact with ions or other dipoles.
What defines a hydrogen bond?
A specific dipole-dipole interaction between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to another electronegative atom.
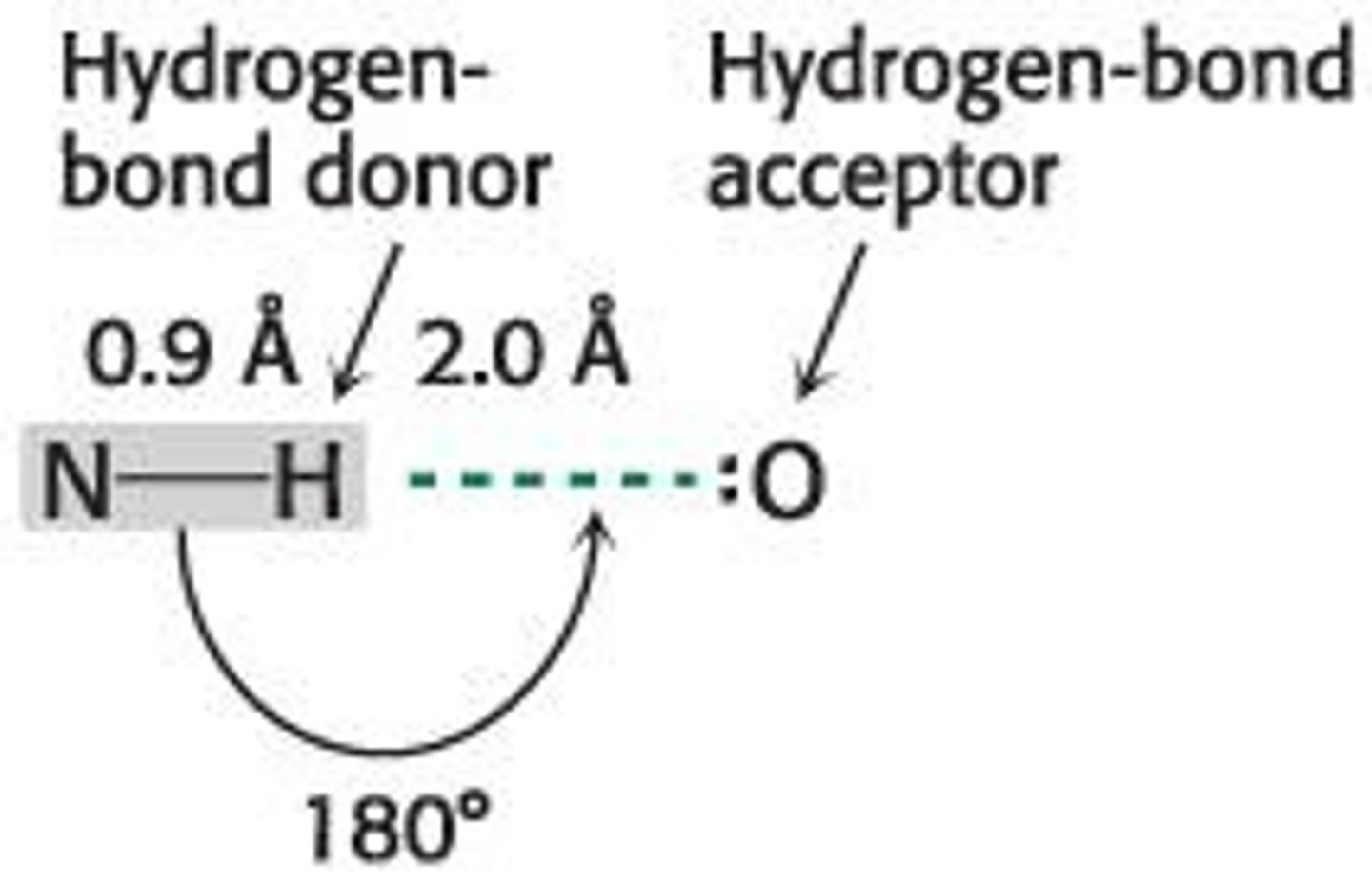
What is the bond distance range for hydrogen bonds?
From 1.5 Å to 2.6 Å.
What is the bond energy range for hydrogen bonds?
From 4 to 20 kJ mol−1 (1-5 kcal mol−1).
What is the importance of studying learning objectives in biochemistry?
They guide the focus of study and help understand key concepts for each chapter.
What should students do to prepare for quizzes or exams in biochemistry?
Ask TAs questions and practice explaining mechanisms to themselves or study partners.
Why is memorization important in biochemistry?
Certain concepts, like structures and names of amino acids, require straight memorization.
What is the role of macromolecules in biochemistry?
They are involved in key biochemical processes and structures in all organisms.
How does biochemical evolution suggest common ancestry?
Key metabolic processes and similar macromolecules across different organisms imply they evolved from a common ancestor.
What defines a hydrogen-bond donor?
A hydrogen-bond donor includes both the atom to which the hydrogen atom is covalently bonded and the hydrogen atom itself.
What is a hydrogen-bond acceptor?
A hydrogen-bond acceptor is the lone pair of electrons on the atom that is less tightly linked to the hydrogen atom.
What are van der Waals interactions?
Van der Waals interactions occur when two atoms are sufficiently close, involving transient asymmetry in electron distribution that induces complementary asymmetry in a neighboring atom.
What is the bond energy range for van der Waals interactions?
The bond energies for van der Waals interactions range from 2 to 4 kJ mol−1 (0.5-1.0 kcal mol−1).
What happens to attraction between atoms as they approach each other?
Attraction increases until they reach the van der Waals contact distance, beyond which strong repulsive forces become dominant.
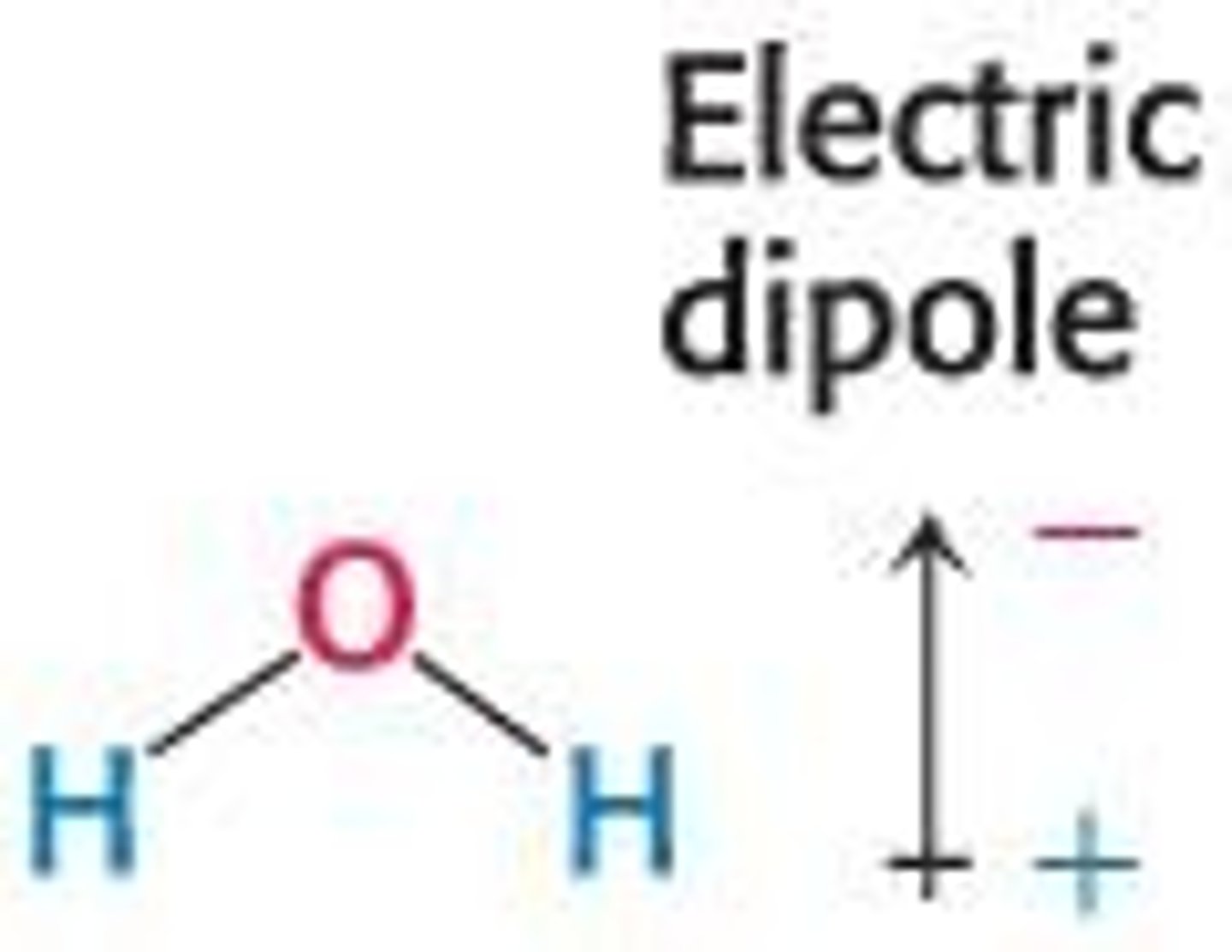
What is a key property of water as a molecule?
Water is a polar molecule with a partial positive and partial negative end.
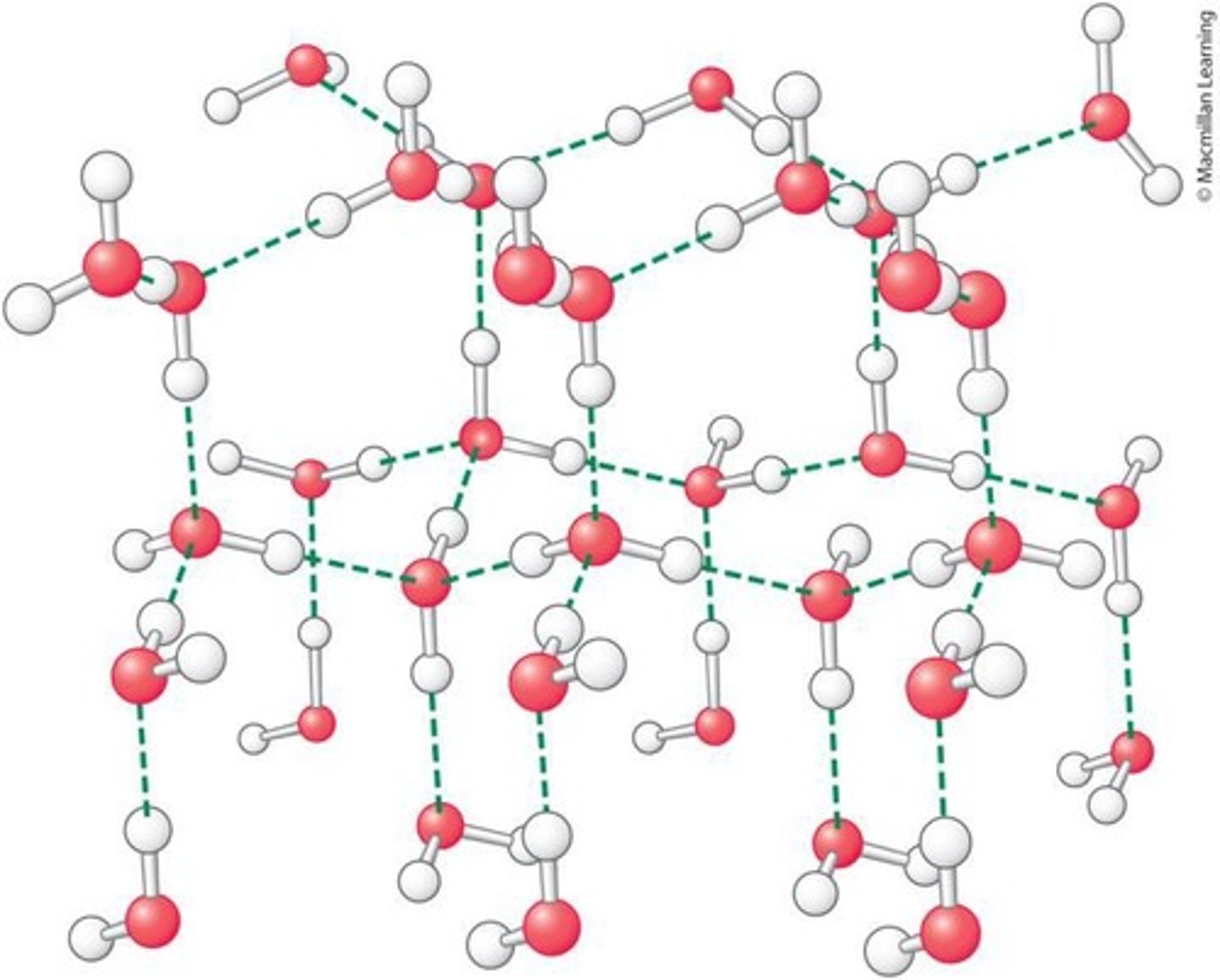
How does water exhibit cohesion?
Water is highly cohesive due to the large number of hydrogen bonds formed in liquid water.
What drives nonpolar molecules together in water?
The hydrophobic effect, which is powered by the increase in entropy of water.
What are hydrophobic interactions?
Hydrophobic interactions occur when nonpolar molecules are not soluble in water, as water interacts with itself and excludes these nonpolar molecules.
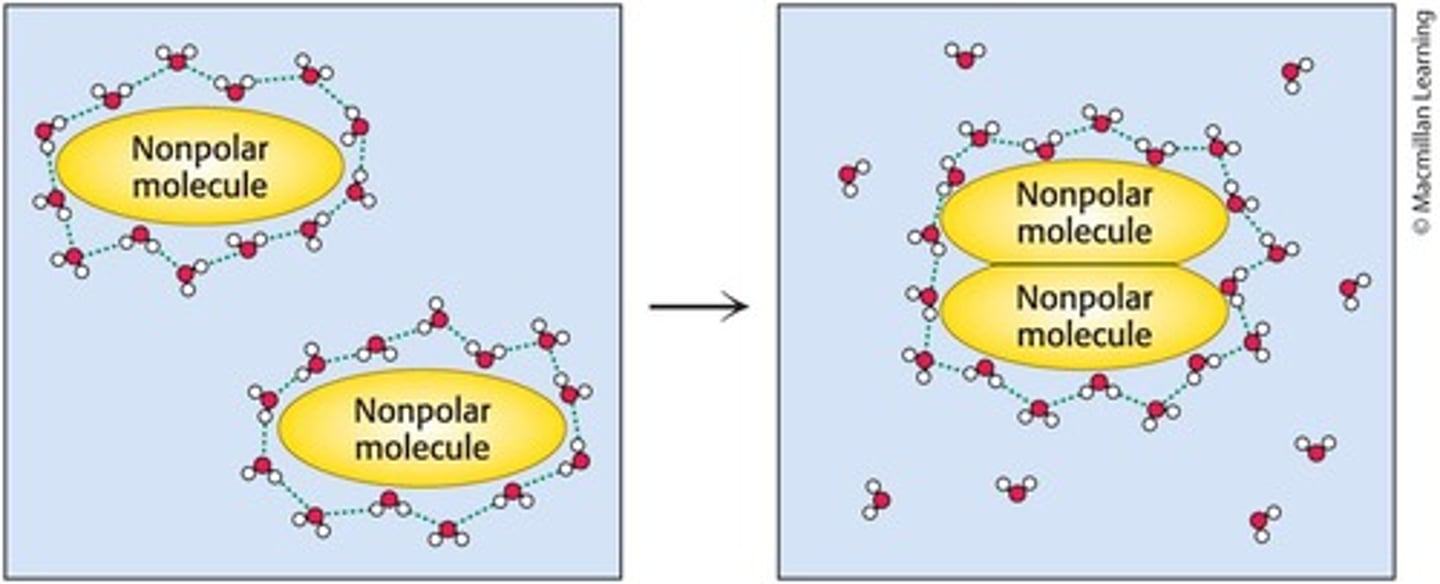
Why do phospholipids form biological membranes in water?
Phospholipids form membranes due to the hydrophobicity of their fatty acids.
What occurs during the formation of a double helix?
Charge repulsion occurs between the negatively charged phosphates of the backbone, reduced by the high dielectric constant of water and interaction with positively charged ions.
How do hydrogen bonds between complementary bases contribute to DNA?
Hydrogen bonds explain the specificity of sequence pairing in DNA.
What is the optimal distance for DNA base pairs?
DNA base pairs are optimally spaced apart by van der Waals distance in the interior of the helix.
What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
The total energy of a system and its surroundings is constant.
What does the Second Law of Thermodynamics state?
The total entropy of a system plus that of its surroundings always increases.
How can entropy decrease locally in a system?
Entropy can decrease locally if there is a corresponding increase in entropy in the surroundings.
What is the relationship between heat transfer and entropy change?
The change in entropy of the surroundings is proportional to the heat transferred from the system and inversely proportional to the temperature.
What is the equation for total entropy change?
Total entropy change is given by ΔStotal = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings.
What is Gibbs Free Energy?
Gibbs Free Energy is defined as −TΔStotal and is used to describe the energetics of biochemical reactions.
When will biochemical reactions occur spontaneously?
Biochemical reactions will occur spontaneously only if ΔG is negative.
What happens to the entropy of surroundings during double helix formation?
The heat released by helix formation increases the entropy of the surroundings, satisfying the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
What do acid-base reactions involve?
Acid-base reactions involve the addition or removal of a hydrogen ion (H+).
What does pH measure?
pH measures the H+ concentration and is defined by the equation pH = −log [H+].
What ions are formed upon the dissociation of water?
H+ and OH− ions.
What is the equilibrium constant (K) for the dissociation of water?
K = [H+][OH−]/[H2O].
What is the ion constant of water (KW)?
KW = [H+][OH−] = 10−14.
How can proton or hydroxide ion concentration be calculated?
If one concentration is known, the other can be calculated using [H+] = 10−14/[OH−] or [OH−] = 10−14/[H+].
What happens to DNA when base is added to the solution?
The double helical structure of DNA is disrupted or denatured.
What is the chemical basis for the denaturation of DNA?
The disruption of base-pairing, such as the loss of a proton by guanine preventing base-pairing with cytosine.
What does the pKa value indicate?
The susceptibility of a proton to removal by reaction with a base.
What is the relationship between pH and pKa?
When pH equals pKa, the concentration of the protonated form (HA) is equal to the deprotonated form (A−).
What is the pKa of the N-1 proton of guanine?
The pKa is 9.7.
What occurs when pH is near or exceeds the pKa of guanine?
The proton is increasingly likely to be lost, disrupting base-pairing and denaturing the helix.
What is the function of buffers in a solution?
Buffers resist changes in the pH of a solution.
When are buffers most effective?
Buffers are most effective at a pH near their pKa.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log ([A−]/[HA]).
What is the significance of phosphoric acid in biological systems?
It acts as an important buffer, with physiological pH typically near 7.4.
What is the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH−] in an aqueous solution with pH 9?
10−5 M.
Order the types of interactions by bond strength from strongest to weakest.
Covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions.
Which characteristic is NOT found in eukaryotic cells?
Circular chromosome.
What is a hydrogen bond acceptor?
A molecule that can accept a hydrogen bond, typically possessing a lone pair of electrons.
What is a hydrogen bond donor?
A molecule that can donate a hydrogen bond, typically having a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom.
What is the hydrophobic effect?
The tendency of nonpolar molecules to self-associate in the presence of an aqueous solution.
What is the relationship between pH and pOH?
pH + pOH = 14.
How does pH affect the double helix structure of DNA?
Changes in pH can disrupt hydrogen bonding and base-pairing, leading to denaturation.