The nervous system
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the function of the nervous system?
It carries messages to/from the spinal cord and brain (CNS) to different parts of the body.
So it effectively helps all parts of the body communicate with each other.
What is the nervous system made up of?
It is a complex network of nerve cells.
What controls the nervous system?
The brain - it has many billions of neural cross-connections.
The brain is the “powerhouse of the body”.
How does the brain control the human body?
The brain oversees the workings of the body, while its higher functions provide us with consciousness and make us who we are.
What is the nervous system divided into?
The central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system.
True or false, these are further divided into different components?
True.
What is the CNS divided into?
Spinal cord, brain
What is the peripheral nervous system divided into?
The somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system.
(The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system)
The CNS: what are the two main functions of the CNS?
The control of behaviour
The regulation of the body’s physiological processes
What does the brain have to do in order to perform these functions?
Receive information from sensory receptors (eyes, ears, etc) and be able to send messages to muscles and glands of the body.
This involves the spinal cord.
What is the spinal cord?
A collection of nerve cells that are attached to the brain and run the length of the spinal column.
What is the spinal cord’s main function?
To relay information between the brain and the rest of the body.
What does this allow the brain to do?
Monitor and regulate bodily processes (eg digestion and breathing) and to coordinate voluntary movements.
How is the spinal cord connected to different parts of the body?
Through spinal nerves - which connect with specific muscles and glands.
(Eg spinal nerves that branch off from the thoracic region of the spinal cord carry messages to and from the chest and abdomen)
What does the spinal cord also contain?
Circuits of nerve cells that enable us to perform some simple reflexes without the direct involvement of the brain.
Eg pulling your hand away from something that’s hot.
What happens if the spinal cord is damaged?
Areas supplied by spinal nerves below the damaged site will be cut off from the brain and will stop functioning.
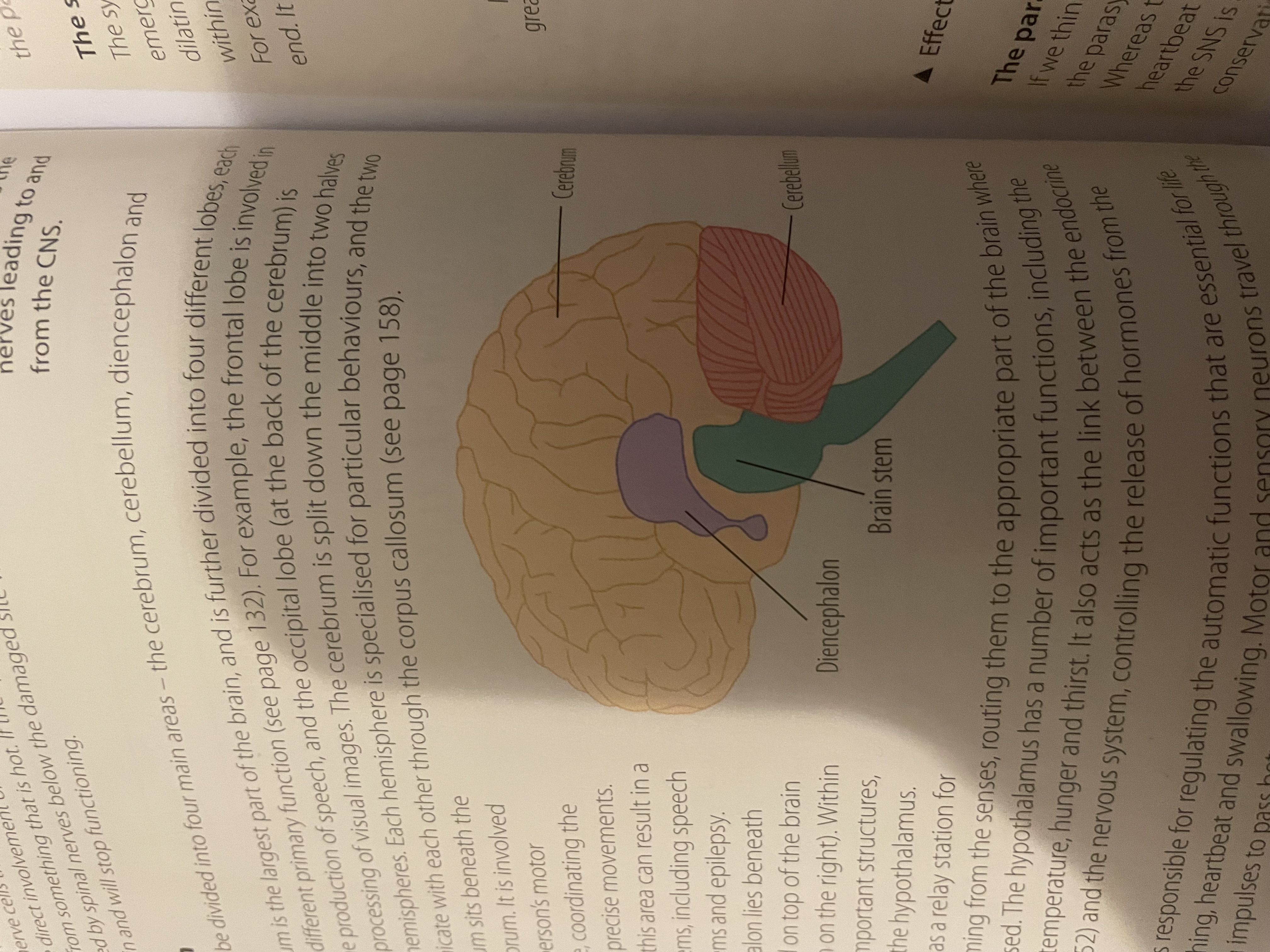
What are the four areas the brain can be divided into?
The cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon and brain stem.
Which of the four parts is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum.
Describe the structure of the cerebrum.
It is further divided into four different lobes (frontal, occipital etc).
It is also spilt down the middle into two halves called cerebral hemispheres.
How are the two hemispheres different?
They’re are specialised for different particular behaviours.
How do the two hemispheres communicate with eachother?
Through the corpus callosum.
Where is the cerebellum located?
Beneath the back of the cerebrum.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
It’s involved in controlling a person’s motor skills and balance, coordinating the muscles to allow precise movements.
What can abnormalities in the cerebellum result in?
Problems such as speech/motor problems and epilepsy.
Where is the diencephalon located?
Above the brain stem.
What are the two important structures in the diencephalon?
The thalamus and hypothalamus.
What is the function of the thalamus?
It acts as a relay station for nerve impulses coming from the senses - routing them to the appropriate part of the brain where they can be processed.
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
Regulating body temperature, hunger and thirst.
It also acts as the link between the endocrine system and the nervous system, controlling the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
Where is the brain stem located?
At the bottom of the brain.
What’s the function of the brain stem?
Regulating automatic functions essential to life (eg breathing, heartbeat).
Motor and sensory neurons also travel through the brain stem, allowing impulses to pass between the brain and spinal cord.
Labelled brain diagram