Bandaging
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
In general, bandages are used to:
Support or stabilize a segment
Restrict motion of a joint
Control edema, swelling or joint effusion
Most common injury that requires bandage
sprain or strain
Types of Bandage Materials
Muslin (unbleached cotton; most common)
Others:
Woven, elastic, porous cotton
Rolled gauze (no elastisticity)
Stockinet, loosely knit cotton formed into a tube
Adhesive tape
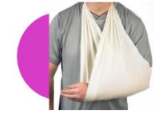
Triangular Bandage
Large piece or cloth cut or formed into a triangle
Used as a temporary sling to support the weight of a patient’s UE
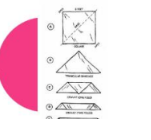
Cravat Bandage
can also be used as a sling
will not support the pt’s UE
Roller Bandage
Most commonly seen in the market
Made of an elastic or non-elastic material formed in a cylindric roll
Used to maintain and protect a dressing, to provide pressure, maintain a splint, support a joint, restrict motion, or control edema
Easiest form of bandaging technique
Circular bandage
(Pattern) Applied in a series of overlapping circular turns around a body part to anchor the bandage initially or terminally
Circular Bandage
Circular Bandage - Proper Applications / Considerations
Bandage should overlap 50% of its width
No wrinkles and creases to avoid skin irritation
Check for the nail beds; blue/whitish nails means that the bandage may be too tight
(Pattern) The bandage is applied in a series of overlapping diagonal turns around a body part
Spiral Bandage
True/False: Spiral Bandage covers a larger area and less likely to cause occlusion
True
Spiral Bandage is beneficial to ___________
reduce edema and swelling of an injured part
(Pattern) series of diagonal turns that do not overlap and have an open space in between each turn; has an open space in between each turn
Open Spiral or Oblique Bandage
Open Spiral bandage is used for?
Used to hold a gauze / dressing; or in acute cases (providing a temporary splint)
(Pattern) series of spiral turns, each of which is folded or reversed on itself midway through its turn
spiral reverse bandage
(Spiral Reverse Bandage) The reverse component allows non elastic bandage to _____________
conform to change in circumference
Reverse Spiral Bandage Procedure
Start with 2 circulars
Go up as a spiral
Reverse the spiral at every turn
Finish with 2 circulars and secure the bandage
(Pattern) series of lengthwise layers applied to the anterior-posterior or dorsal-volar surfaces of a body part
Recurrent Bandage
(Pattern) Series of Spiral turns applied in an alternate directions
Figure of Eight
Primary Aim of Figure of Eight Pattern
position the joint into neutral position
Bandaging size for foot and ankle
4 inch bandage
bandage size for hand and wrist
1-2 inch bandage
bandage size for knee
4 inch; 3 inch for children
Bandage size for elbow
3-4 inch for adults
2-3 for children
Bandage size for Hip
6 inch for adults
4 inches for children
A figure of eight wrapping technique used to support the shoulder joint, secure dressings, or provide mild immobilization
Shoulder Spica
Shoulder Spica is commonly used for?
sprains
dislocations
post-surgical care
Velpeau bandage is used for?
fractures of the clavicle
Shoulder dislocations
Post-surgical support
True/False: The Velpeau bandage fully restricts arm motion by securing the arm to the chest
True
Specialized wrapping technique used to immobilize the hip joint, pelvis, and upper thigh
Hip SPICA
Hip SPICA is commonly used for?
hip injuries
fractures
post-surgical care
stabilize the hip in pediatric conditions like Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Taping or bandaging technique used to support the ankle and assist with dorsiflexion
Dorsiflex Assist
Dorsiflex assist is commonly used for?
foot drop
peroneal nerve palsy
post-stroke rehabilitation
Post-Amputation Bandaging is crucial for?
edema control, shaping the residual limb, and preparing for prosthetic fitting
Most common deformity in stumps
Dog ears
True/False: the stump is a pain-insensitive structure
False
Indications for Bandaging
Wound protection & healing
Hemostasis
Edema control & compression
Immobilization & Support
Joint & Soft tissue support
Post-Amputation Limb Shaping
Orthopedic & post surgical Application
Burns & Skin grafts protection
Contraindications of Bandaging - Impaired Circulation
Peripheral Arterial Disease: bandage → can reduce blood supply, worsening ischemia
Contraindications of Bandaging - Severe Infection or Open Wounds
Uncontrolled infections: covering an infected wound without proper drainage can trap bacteria and worsen the infection
Necrotic Tissue without Debridement: Bandaging over dead tissue without treatment can promote further decay
Contraindications of Bandaging - Allergy or Sensitivity to Bandage Materials
Latex allergy: Some patients may have severe reactions
Adhesive Sensitivity: Skin irritation or rashes can occur with certain medical tapes or adhesives
Contraindications of Bandaging - Fragile or Compromised Skin
Elderly patients with thin skin - can cause tears or pressure ulcers
Burns or Radiation -damaged skin: can lead to further damage and delayed healing
Contraindications of Bandaging - DVT Risk
Improper Compression Techniques - can dislodge clots, leading to pulmonary embolism
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Precaution: Avoid Restrictive Bandage in high-risk individuals without medical supervision
Contraindications of Bandaging - Improperly Applied Bandages
Tourniquet Effect
Bandage Slippage
Tourniquet Effect
Overly tight bandaging can cut off circulation and cause limb ischemia
Contraindications of Bandaging - Unstable Fractures without proper immobilization
Bandaging alone is not enough for fractures needing splinting or casting
Contraindications to Bandaging - Complete list
Impaired Circulation
Severe Infection or Open Wounds
Allergy or sensitivity to bandage materials
Fragile or Compromised Skin
DVT Risk
Improperly Applied Bandages
Unstable Fractures without Proper Immobilization
Precautions to Bandaging - Full List
Ensure Proper Circulation
Use the Right Bandage for the Condition
Apply even pressure
Secure the bandage properly
Check for Signs of complications
Consider Skin Sensitivity
Change Bandages Regularly
Properly Position the Limb
Overlap for the Patterns
¾ Circular
½ Spiral
¼ oblique
pls correct me if i am wrong
(Precautions to Bandaging) avoid wrapping too tightly to prevent _____
ischemia
(Precautions of Bandaging) - Signs of Poor Circulation
Coldness
numbness
bluish discoloration
increased pain
_____ bandages for sprains and swelling control
Elastic bandages
_____ bandages for wound protection
Gauze
_____ Bandages for venous insufficiency
Compression
Compression bandages are for venous insufficiency, but should be avoided in ________
arterial diseases
(Precautions of Bandaging) Apply Even Pressure
more pressure distally, less pressure proximally to prevent fluid buildup
Avoid Tourniquet effect
(Precautions of Bandaging) Ensure the bandage is ___ but not restrictive
firm but not restrictive
(Precautions of Bandaging) Pain, swelling, tingling, or color change →
Loosen the bandage immediately
(Precautions of Bandaging) excessive moisture or foul odor →
may indicate infection, requiring a bandage change
Wound dressings should be changes as per ______
medical guidance
Prolonged bandaging without reapplication can ___________
trap bacteria and cause infections
(Precautions of Bandaging) For limb bandaging, maintain ___________ to avoid ________
functional positioning to avoid stiffness or contractures
Desired shape of stump for BKA
Cylindrical
Desired shape of stump for AKA
Conical