ddd
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
In vivo
experiments conducted inside living organism
Essential for pre-clinical research before human trials.
These studies are vital in biomedical research because they provide insights into the safety, efficacy, and biological effects of new drugs, chemicals, and therapies before testing them in humans.
White mice
Abino rabbits
What are the most common animal models
Used in pharmacology, toxicology, immunology, genetics, and surgical research.
95-98%
White mice share — genetic similarity with humans
White mice
Short reproductive cycle, easy to breed.
Standardized strains ensure reproductibility
most widely used animal models due to their genetic similarity to humans, ease of breeding, and established role in preclinical studies.
BALB/c
Swiss albino mice
Additionally, many standardized strains exist, such as — and, ensuring reproducibility and reliability in experimental results. Their use has led to countless medical breakthroughs, including treatments for diabetes, cancer, and infectious diseases.
Albino rabbits
Larger body size suitable for surgical and ocular studies.
Have similar eye structure to humans which is a key in opthamology.
Similar with white mice, they are used in antibody production and vaccine testing.
Selection of healthy organisms (6-8 weeks old)
Acclimatization (temperature, humidity, light)
Division to control and experimental group
Drug administration (oral, IV, IP, SC, Topical)
Observation
Data collection and analysis
Methodology of white mice and albino rabbit
20-26C
15-21C
12 hours
Housing and handling
Temperature for mice
Temperature for rabbits
Both are typically housed under — hour light/dark cycle
tunnels or cage ladders
For mice, studies show that non-aversive handling methods such as — or — reduce stress and improve welfare compared to tail handling. Individually ventilated cages provide better air quality and lower stress levels.
Oral gavage
Intraperitoneal
SC
IV
Topical (skin, ocular)
Drug administration techniques for white mice and rabbits
Tail vein injection
IV site for white mice or albino rabbit
Toxicology testing
Pharmacokinetics
APPLICATIONS OF WHITE MICE AND ALBINO RABBITS IN PRE-CLINICAL STUDIES
White mice
In preclinical studies, — are essential for systemic and toxicological research. They help evaluate toxicity, test nanomedicine safety, and model wound healing in diabetic conditions.
Albino rabbits
They are widely used in applied biomedical studies. They serve as reliable models for ocular disease and drug delivery testing, while also remaining the gold standard for dermal irritation and cosmetic safety assessments.
White mices
They are advantageous because of their close genetic similarity to humans, rapid breeding, and cost-effective handling, making them the backbone of systemic preclinical research

Albino rabbits
They are valuable due to their eye and skin physiology that mirrors humans, which makes them ideal for ocular and dermal studies. Their larger size also allows more invasive or repeated procedures that aren’t possible in smaller animals.

White mice
Despite their usefulness, white mice have limitations such as results not always translating clinically, restrictions due to their small size, and ethical concerns.

Albino rabbits
They face similar issues, with species differences in drug metabolism, ethical debates over ocular and dermal testing, and higher costs for housing and care compared to mice.

3Rs principle
This emphasizes replacing animals where possible, reducing their numbers, and refining procedures to minimize suffering.
IACUC Institutional animal care and use committee
All animal studies must be approved by — (oversees the specific use of animals by formally reviewing animal use protocols.)
3Rs principle
IACUC
International guidelines
What are the ethical considerations for white mice and albino rabbits
In vitro cell culture
In silico simulation
Organoids and tissue engineering
Alternative animals to use for white mice or albino rabbits

In vitro cell culture
In silico simulation
Organoids and tissue engineering
ALTERNATIVES
— systems using human cells allow for detailed cellular-level studies
— computer simulations predict drug interactions using algorithms.
— can mimic organ-level responses.
Organoids
— work by mimic the structure and function of real organs from stem cells
True
True or false
Reproducibility is better with albino rabbits so good with seeing long term effects; White mice lifespan is short
ELISA
Specific interactions between antigens and antibodies
Replicating the interaction allows to detect or measure the presence of specific biological molecules.
Pyrogen
___ test in industrial field is often conducted
Copper, blue
Clumps (gel clot formation)
Limulus polyphemus
LAL Test vs. Rabbit Pyrogen test
Blood of crab has — (— in color), so in med supply testing, blood is applied to the med supply and if — appear, its positive inoenditoxin
CI name of the organism
Temperature
— is based in rabbit testing
Pyrogen
Horseshoe crab or LAL test is now the gold standard for - testing
Antigens
Molecular markers, triggers an immune respons
Found on the surfaces of viruses, bacteria, allergens, parasites, and body cells.
Antibodies
Immune system proteins
Recognize and eliminate foreign or harmful substance.
Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
Uses enzymes as labels
Identification and quantification of target molecules.
The catalytic activity of these enzymes produces a detectable signal, enabling the identification and quantification of target molecules
ELISA
One component is immobilized onto a solid phase: (1) microtiter plate (2) magnetic particle (3) plastic bead
Separates bound and unbound reactants
Enhance sensitivity and specificity
ELISA
Gold standard among immunoassays
Safer alternative to Radioimmunoassay
Developed in 1970s replacing radioactive isotopes
Engvall & Perlman
Van Weemen & Schuurs
Who pioneered ELISA
independently developed the method by replacing radioactive labels with enzyme conjugates
Coating, wash
Blocking, wash
Detection, wash
Final read
ELISA Methodology
Immunoassays
— are laboratory techniques that rely on the specific interaction between antigens and antibodies.
RIA (Radioimmunoassay)
— was considered dangerous mainly because it used radioactive isotopes as labels to detect antigen–antibody reactions.
Immunoglobulin G
Human chorionic gonadotropin
ELISA
Its first applications were measuring — in rabbit serum and detecting — in urine using horseradish peroxidase.
ELISA
It is an enzyme immunoassay that uses an enzyme-labeled antibody or antigen to detect and measure a specific target. The target is bound to a solid phase (e.g., 96-well plate), unbound components are washed away, and a substrate produces a measurable signal.
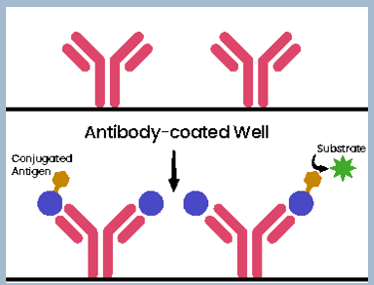
Direct elisa
Binds antigens, including the desired target, in a simple directly to the plate. An enzyme-conjugated antibody in then added as a probe for the desired analyte.
horseradish peroxidase (HRP)
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) with chromogenic substrates.
* Detection systems of ELISA: —
Armoracia rusticana
Horseradishperoxidase is from —
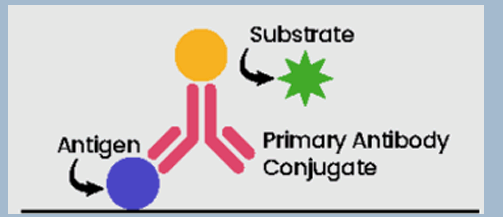
Indirect ELISA
Binds antigens, including the desired target in the sample to the plate. However, it involves two antibodies; a primary and a secondary conjugated antibody.
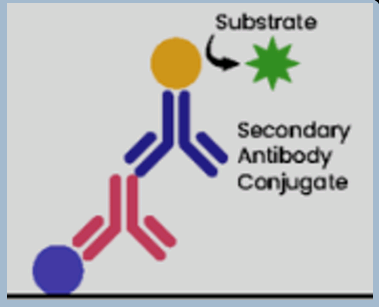
Sandwich ELISA
The target is bound between a captured antibody (for antigen detection) or capture protein (for antibody detection) and the conjugated detecting antibody
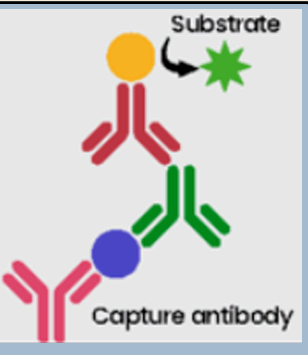
Competitive ELISA
Involves competition between the binding of the sample antigen and conjugated antigen to a specific amount of antibody. The more antigen in the sample, the less conjugated antigen binds and the lower assay signal.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodybamis / biomarker analysis
Immunogenicity
Drug stability and tissue distribution
Toxicology / safety biomarkers
APPLICATIONS OF ELISA IN DRUG DEVELOPMENT/PRE-CLINCIAL STUDIES
Horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus)
Source of Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL):
They have blue blood containing amebocytes.
ELISA
It quantifies therapeutic proteins (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins) in animal serum to calculate PK parameters like half-life, Cmax, AUC.
ELISA
— assays quantify proteins indicative of tissue damage, inflammation, or immune response during preclinical safety studies.
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
Converts mRNA to cDNA using reverse transcriptase + PCR amplification
RNA sequence
Single stranded DNA (cDNA)
RT PCR
It is the template for reverse transcriptase
It is the template for PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
It couples a reverse transcription reaction with PCR-based amplification to generate cDNA from mRNA.
Primers
/— against known coding regions of mRNA will optimize the reaction for a particular transcript of interest, and are also used for cloning.
Specific primer
This RT PCR primer target a transcript of interest and aid in cloning
Poly-dT
This RT PCR bind to most mRNAs via poly-A tail
False
True or false
RT PCR is very sensitive and only needs lrage sample amounts
Two-step reaction
One-step reaction
RT PCR can be done as:
— - RT then PCR separately
— - combined, with specialized enzyme
Heat RNA to unwind secondary structure
Reverse transcribe the RNA ot first strand cDNA
PCR amplify the cDNA
Analyze the PCR products
RT PCR Methodology
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
PCR involves repeating cycles of:

Gel electrophoresis
Sequencing
Quantitative
ANALYZE THE PCR PRODUCTS through what methods
poly-A+
Researchers often enrich for — RNA because messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions for making proteins, making it the most informative RNA type for studying gene activity.
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
assess the effect of a drug candidate on gene expression levels, monitor treatment response or evaluate drug toxicity.