Exam 2 (Form A) - Intro to Animal Science Lecture
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 8-14 - Arkansas State University, Randy Burnett
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
True or False? Explain if false: An animal that has the same alleles on the chromosome is called heterozygous.
False - Homozygous means same alleles
True or False? Explain if false: The Leydig cells, in male reproduction system, are there to stimulate the production of sperm cells.
False - Leydig cells produce testosterone
True or False? Explain if false: Milk is ultimately synthesized from the alveolus of the mammary gland.
True
True or False? Explain if false: Ethology is the study of animal behavior in their natural surroundings.
True
True or False? Explain if false: Lesions are better known as clinical signs that an animal exhibits that are different from normal.
False - Symptoms are clinical signs that an animal exhibits that are different from normal.
True or False? Explain if false: Crossbreeding is the mating of animals of diverse genetic backgrounds, i.e. Angus Bull to Hereford Cow.
True
True or False? Explain if false: In female reproductive system, FSH is responsible for oocyte cell growth and maintenance on the ovary.
True
True or False? Explain if false: Colostrum is better known as an infection of the mammary gland.
False - Mastitis is known as an infection of the mammary gland.
True or False? Explain if false: As heritability values increase, the less the environmental effect controls that trait.
True
True or False? Explain if false: Zoonotic is the ability of a disease to be passed from animal to animal, but has no effect on humans.
False - Zoonotic diseases have the ability to pass from animals to humans and vice versa.
Which of the following are types of learning that animals utilize in their surroundings:
A. Classical Conditioning
B. Habituation Learning
C. Imprint Learning
D. Instrumental conditioning
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. All of the Above
H. None of the Above
G. All of the Above
What is the term that means for the cycle of one “heat” period to the next “heat” period?
A. Estrus
B. Estrous
C. Postpartum Interval
D. A and B
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. All of the Above
H. None of the Above
B. Estrous
Which of the following are anatomical parts of the female reproductive tract:
A. Epididymis
B. A.I. Junction
C. Vas Deferens
D. Infundibulum
E. B and D
F. A and C
G. A, C, and D
H. A, B, and C
I. All of the above
J. None of the above
E. B and D
Which of the following are means for an animal to give or receive communication:
A. Visual
B. Auditory
C. Olfactory
D. A and B
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. All of the Above
H. None of the Above
G. All of the Above
Mammary gland is considered what type of gland:
A. Paracrine
B. Endocrine
C. Exocrine
D. Mixed
E. All of the Above
F. None of the Above
C. Exocrine
This immunity is received via the dam of the newborn animal:
A. Active
B. Passive
C. Internal
D. External
E. All of the Above
F. None of the Above
B. Passive
This means a disease has a sudden onset of symptoms:
A. Chronic
B. Subclinical
C. Clinical
D. Acute
E. All of the Above
F. None of the Above
D. Acute
When are the optimal times to seeing aggressive behavior in the study of animal behavior:
A. Obtaining food
B. Acquiring mates
C. Securing a place in social hierarchy
D. All of the Above
E. None of the Above
D. All of the Above
Draw a basic sketch of a cow, sheep/goat, horse, and swine mammary gland.
Cow - 4 teats, 4 mammary glands
Sheep/Goat - 2 teats, 2 mammary glands
Horse - 2 teats, 4 mammary glands
Swine - Teat row, each teat has a mammary gland
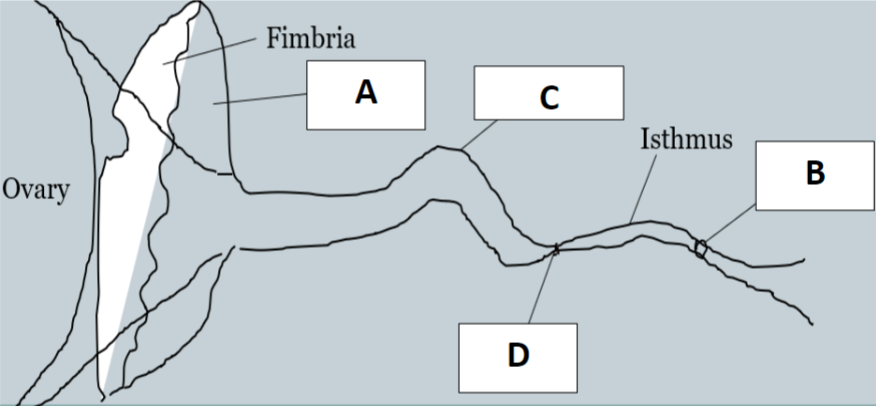
Name the following parts of the male reproductive system:
A - Infundibulum
B - Utero-tubal Junction
C - Ampulla
D - A.I. Junction
Estrogen
Dominant female hormone
Oxytocin
Milk letdown
PGF2A
Regression of CL
FSH
Stimulates growth of oocytes on the ovary
Progesterone
Dominant hormone from CL
Testosterone
Dominant male hormone
LH
Causes the production of Testosterone in males
Prolactin
Constant milk production
Draw/illustrate/or describe the central dogma of life for genetics.
DNA →(Transcription) → RNA → (Translation) → Amino Acid → Protein
What are the two main purposes for milk consumption in any mammal?
Nourishment and immunity
What is the overall genetic formula?
P (Phenotype) = G (Genotype) + E (Environment)
When discussing in class about lactation, we discussed about imitation/substitute dairy products. We described these as “inferior”, what does this mean? Give an example.
Imitation looks like, tastes like, intended to replace “real” but is nutritionally inferior.
Examples - Almond milk, soy milk, etc.
Give me three predisposing causes for a disease and two direct causes of disease related to pathogens.
Predisposing causes - Poor nutrition, genetic make up, injuries
Direct causes - Bacteria, Rickettsia, Protozoa, Mycoplasma, Prions, Fungi, External/Internal Parasites, Viruses
Venesa discussed about reproductive technologies that are currently available for all animal scientist and veterinarians for animal production and management. Please list and describe about two of them.
Artificial insemination - Manually impregnating an animal
Embryo transfers - Transferring an embryo from one female to another
Cloning -
Genetic Modification/Engineering -
Amber discussed about colostrum in depth during her presentation over lactation. Please list three items that colostrum can provide in the first days of a neonatal animal.
Energy, Strengthen the immune system, lipids, carbohydrates, immunoglobins, minerals, vitamins.
BONUS: We discussed about the use of bovine somatotropin (BST) in the dairy industry. Why was this outlawed? Based on what you learned in lactation, does this truly have an effect on human development? Why or Why not?
Human perception of hormones being injected into their food products, which in turn caused the average population to believe that adolescents were reaching puberty sooner.
This does not have an effect on human development. BST is naturally occurring in cattle, particularly in their milk. That protein hormone is denatured during pasteurization and the human body actually digests / breaks it down into typical protein structures that we consume from day-to-day occurrences.
BONUS: In reproduction and lactation, we highlighted the fact that hormones are released and affect another part of the brain before releasing other hormones that affect the body. What are these two islands in the brain called that we discussed about?
Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland