FINAL EXAM Review
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are cells and what do they represent?
Cells are the basic unit of life and represent the successful design of life on this planet.
What is the basis for evolution?
Random mutations that occur during the replication of a genome, combines with natural selection are the basis of evolution
What are some key factors of evolution?
Evolution always builds on existing structures and changes them or combines them into new functions
Evolution cannot go back and start from scratch
Evolution is like a junkyard builder, designing new cars from pieces of old ones
What is the approximate size of Human Hair?
100μm
What is the approximate size of a red blood cell
10μm
What is the approximate size of a bacterium?
1μm
What is the approximate size of a Virus particle?
100nm to 10nm
What is the approximate size of a DNA molecule?
10nm to 1nm
What is the approximate size of a Glucose molecule?
1nm to 0.1nm
What is the approximate size of an atom?
0.1nm
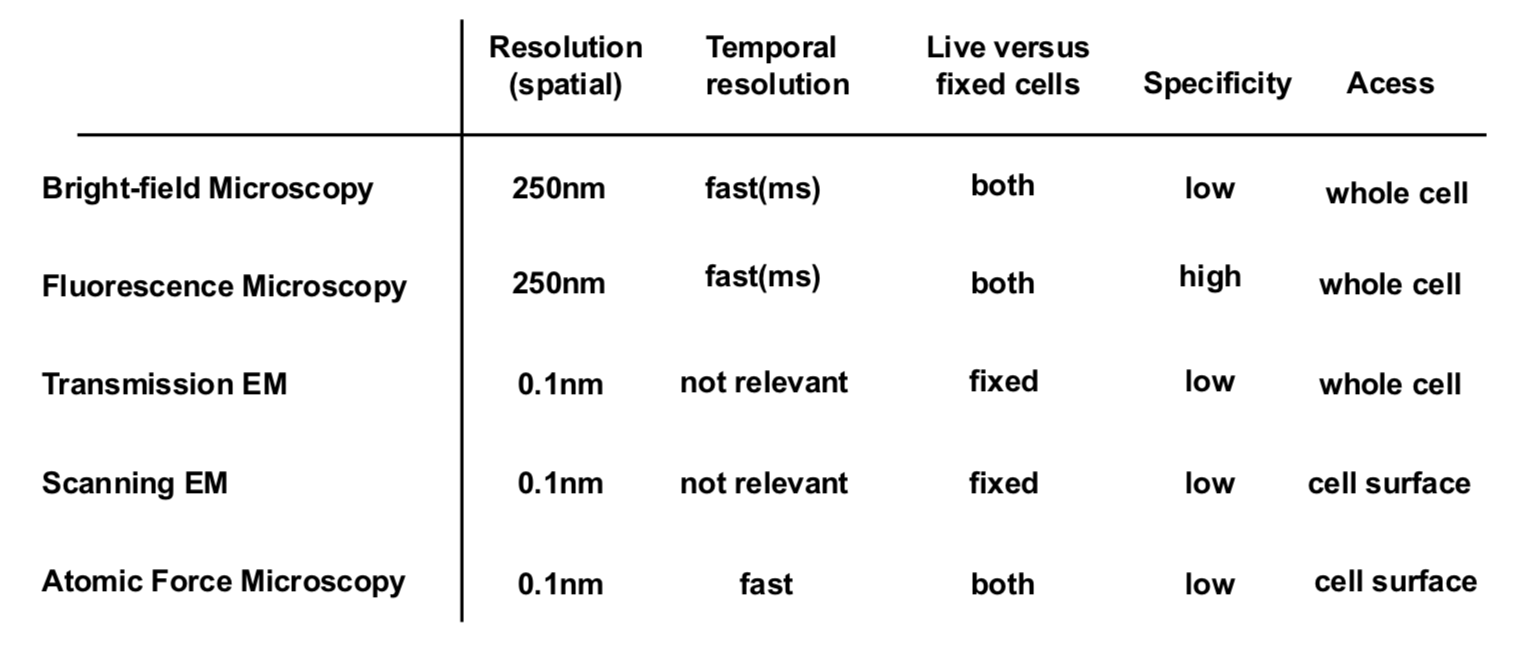
What is Spatial Resolution?
The minimal distance of between two object that can be visually separated.
What is Temporal Resolution?
How fast can the specimen be visualized
What is Speceficity?
How well can you visualize a specific object within a cell, for example only visualize the plasma membrane or any or organelle.
What is Live versus Fixed cell when it comes to microscopy?
Should the cell be alive or chemically fixed(dead)
What is access when it comes to microscopy?
Which part of the cell can be visualized (surface vs intracellular)
What are the all the factors of all the types of microscopy?
What are the Three Domains of Life and what type of cell do they fall into?
Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotes: Eukarya
What is the are all the organelles and what do they do?
Nucleus: The 'command center' of the cell; a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls its growth and reproduction.
Mitochondria: The 'powerhouses' of the cell; organelles that generate most of the cell's supply of ATP (energy) through cellular respiration.
Chloroplasts: Found in plant and algal cells; the site of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy (glucose).
Lysosomes: The cell's 'recycling center'; organelles containing digestive enzymes that break down waste materials, foreign invaders, and old cell parts.
Vacuoles: Storage sacs found in cells; they store water, nutrients, and waste. Plant cells typically have one large central vacuole that maintains turgor pressure.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes (protein synthesis), while Smooth ER synthesizes lipids and detoxifies substances.
Golgi (Apparatus/Complex): The cell's 'post office'; it modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Peroxisomes: Small organelles that contain oxidative enzymes, primarily involved in breaking down fatty acids and detoxifying harmful substances.
Endosomes: Membrane-bound compartments that sort material entering the cell through endocytosis before it travels to the lysosome for digestion.
Plasma Membrane: The semipermeable barrier that surrounds the cell, separating its interior from the outside environment and controlling which substances enter and leave.
Transport Vesicles: Small, membrane-enclosed sacs that transport molecules (like proteins) from one part of the cell to another, such as from the ER to the Golgi.
Cytoskeleton: A network of protein filaments (microtubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments) that provides the cell with shape, support, and a framework for movement.
Cytoplasm (or cytosol): The entire content within a cell, excluding the nucleus, all suspended in the jelly-like substance called cytosol. It is where many metabolic reactions occur.
Where do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts come from?
They are ancient endosymbionts
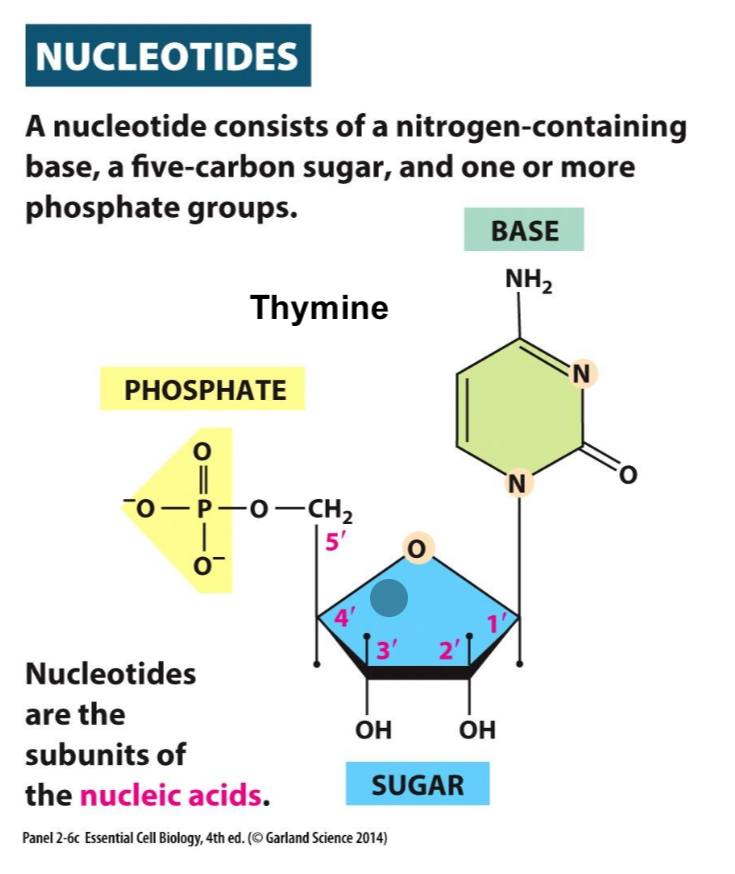
What is a Nucleotide?
A chemical component of a cell that contains nitrogen base, five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups.
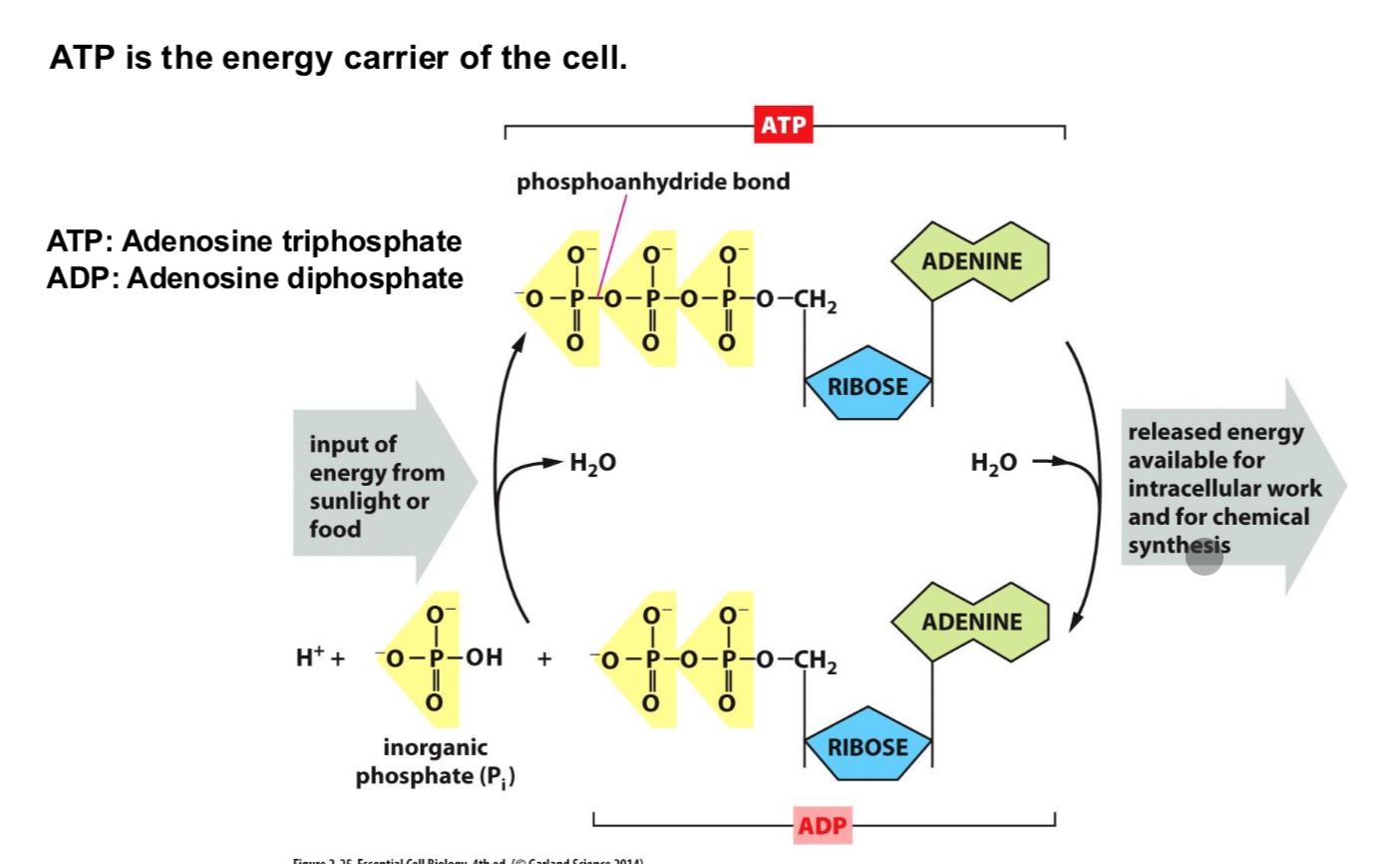
What is ATP?
The energy carrier of the cell.
What is NADH/NADPH?
They are activated carriers of electrons (high energy electrons)
What are sugars?
Monomer: glucose or any other single sugar.
Disaccharides: Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose), Lactose (Galactose + Glucose)
What is the difference between condensation and hydrolysis?
In condensation you release a water molecule to join two monomers, in Hydrolysis you add a water molecule to break down a polymer into two monomers.
What is the difference between glycogen and starch?
Glycogen is the storage of glucose in the liver while starch is the storage of glucose in plants.
What are the different types of lipids?
Phospholipid: most common type of lipid, contain fatty acid, glycerol phosphate and polar head group.
Fatty acid: vary in length and in number of double bonds.
Saturated if it doesn’t have a double bond
Unsaturated if has a double bond
What are amino acids?
The building blocks of proteins.
What is the difference between Ionic Interaction and Van deer Waals interactions?
Ionic: A very strong bond within a compound, formed by transferring electrons.
Van der Waals: A very weak force between molecules, caused by temporary shifts in electron clouds.
How do proteins obtain their structure?
Their amino acid sequence causes unique folding.
What causes protein denaturing and can it be reversed?
High temperatures or by adding detergents. Anything that weakens interactions within a protein can denature.
They can be refold if they haven’t aggregated.
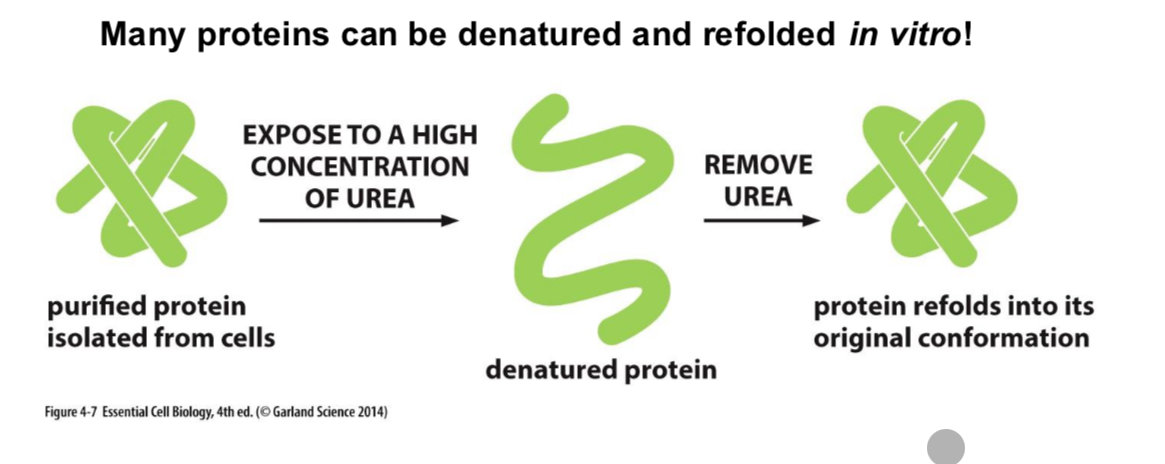
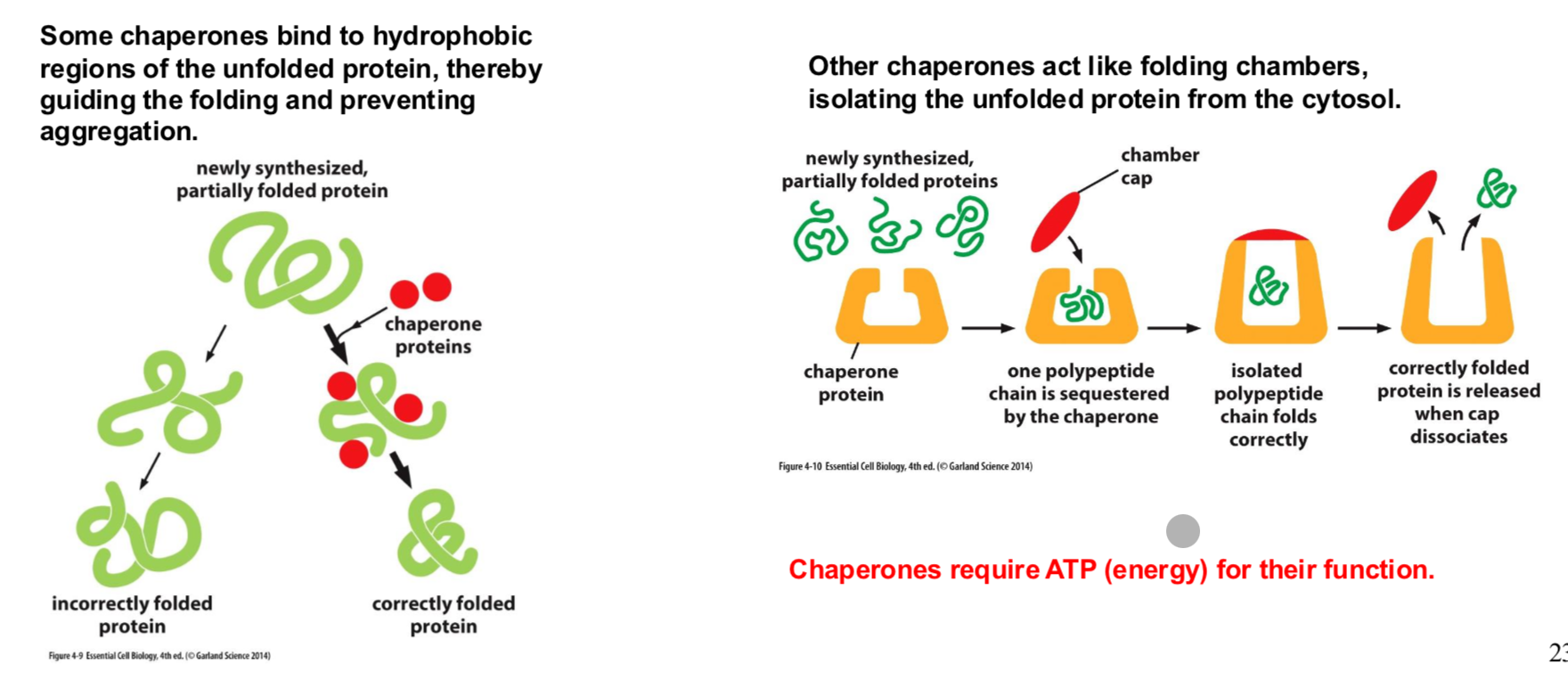
What are molecular chaperones and what do they do?
Help prevent protein aggregation and help the protein properly fold.
Describe the four level of protein structure?
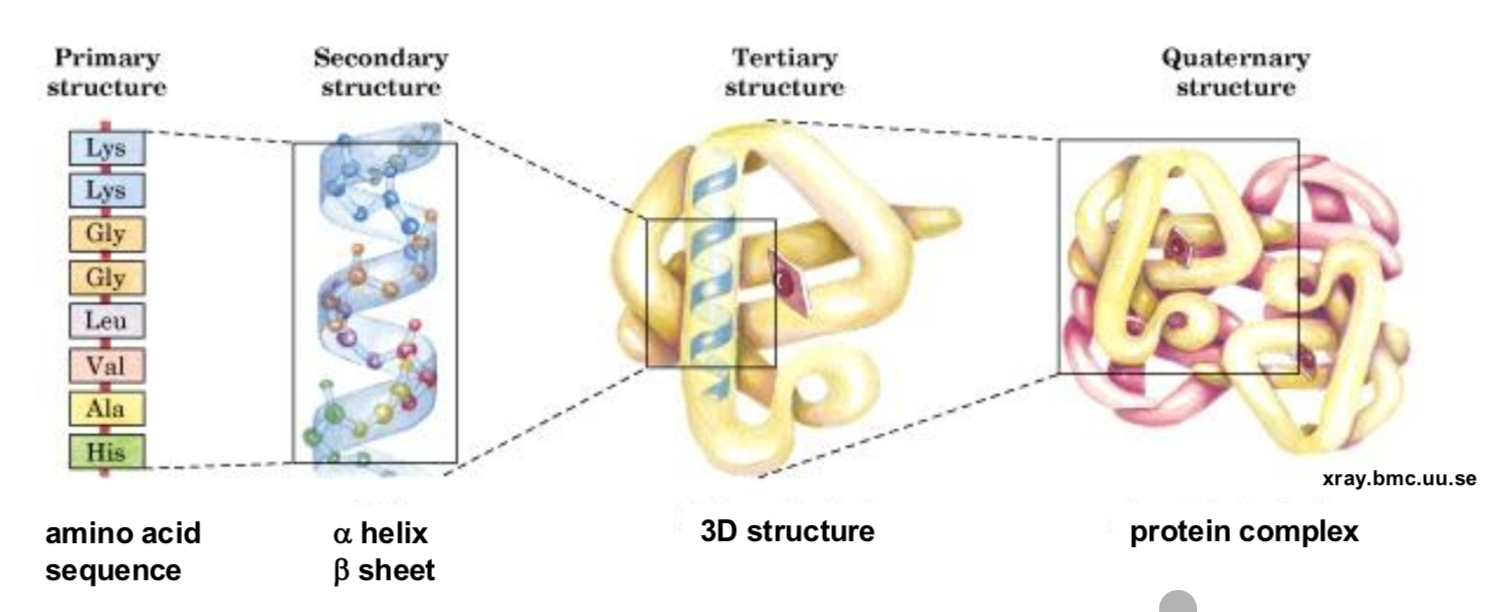
What is the secondary strucutre of Proteins?
The local, repeating folding patterns that form within a polypeptide chain. This structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbone's amide (N-H) and carbonyl (C=O) groups, not involving the side chains (R-groups).
Alpha-Helix (α-helix): A right-handed, coiled or spiral staircase shape (like a spring).
Beta-Pleated Sheet (β-sheet): Formed when two or more segments of the polypeptide chain line up side-by-side, creating a flat, folded, sheet-like structure.
How are protein’s stabalized
Covalent bonding of 2 cysteines in the same protein or ebtween 2 proteins
What are Protein Domains?
Large proteins often contian several protein domains
A domain is a strucutral unit that folds independently
Domains are linked together by felxible regions
Evolution combines domains into new proteins
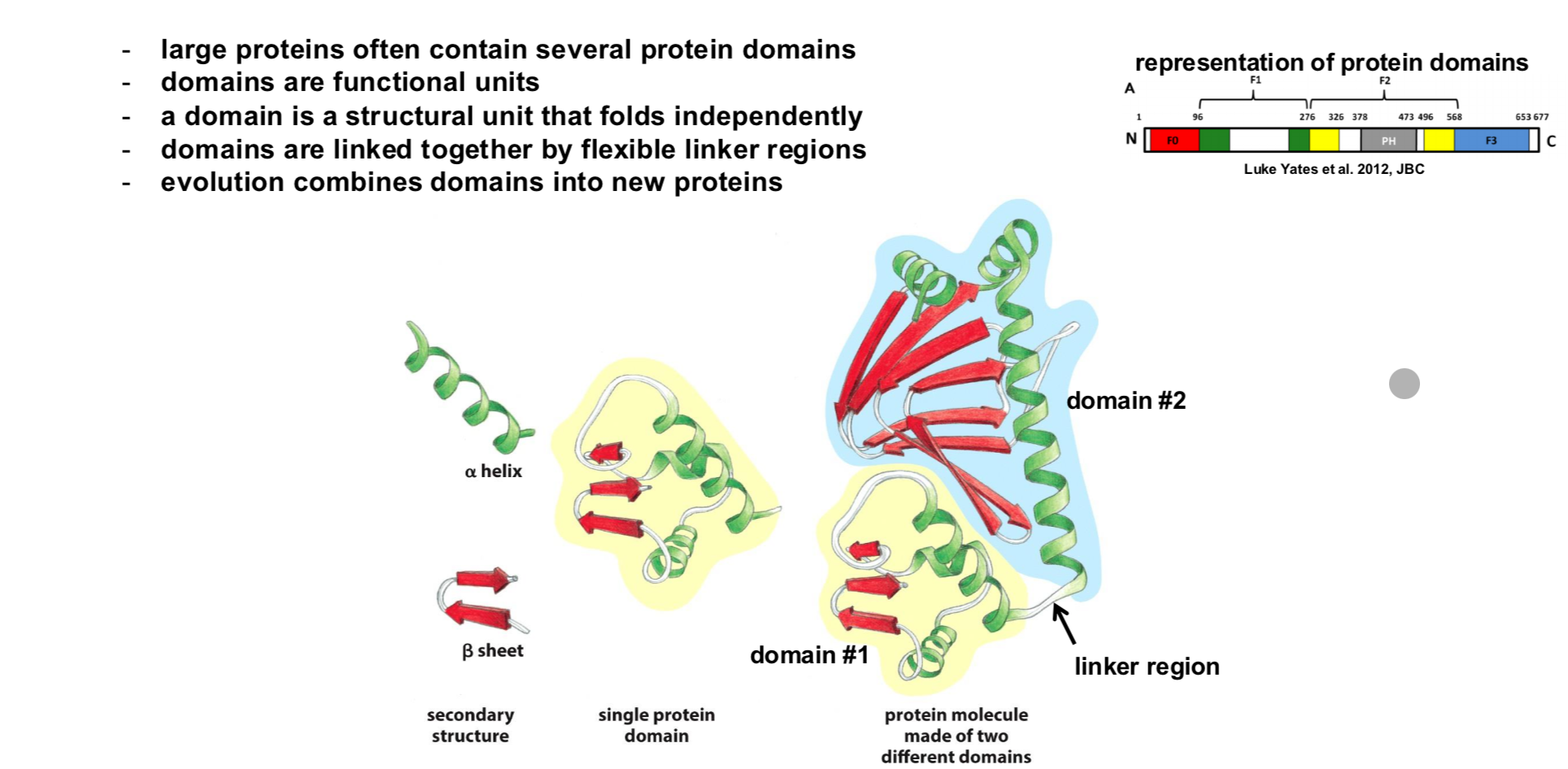
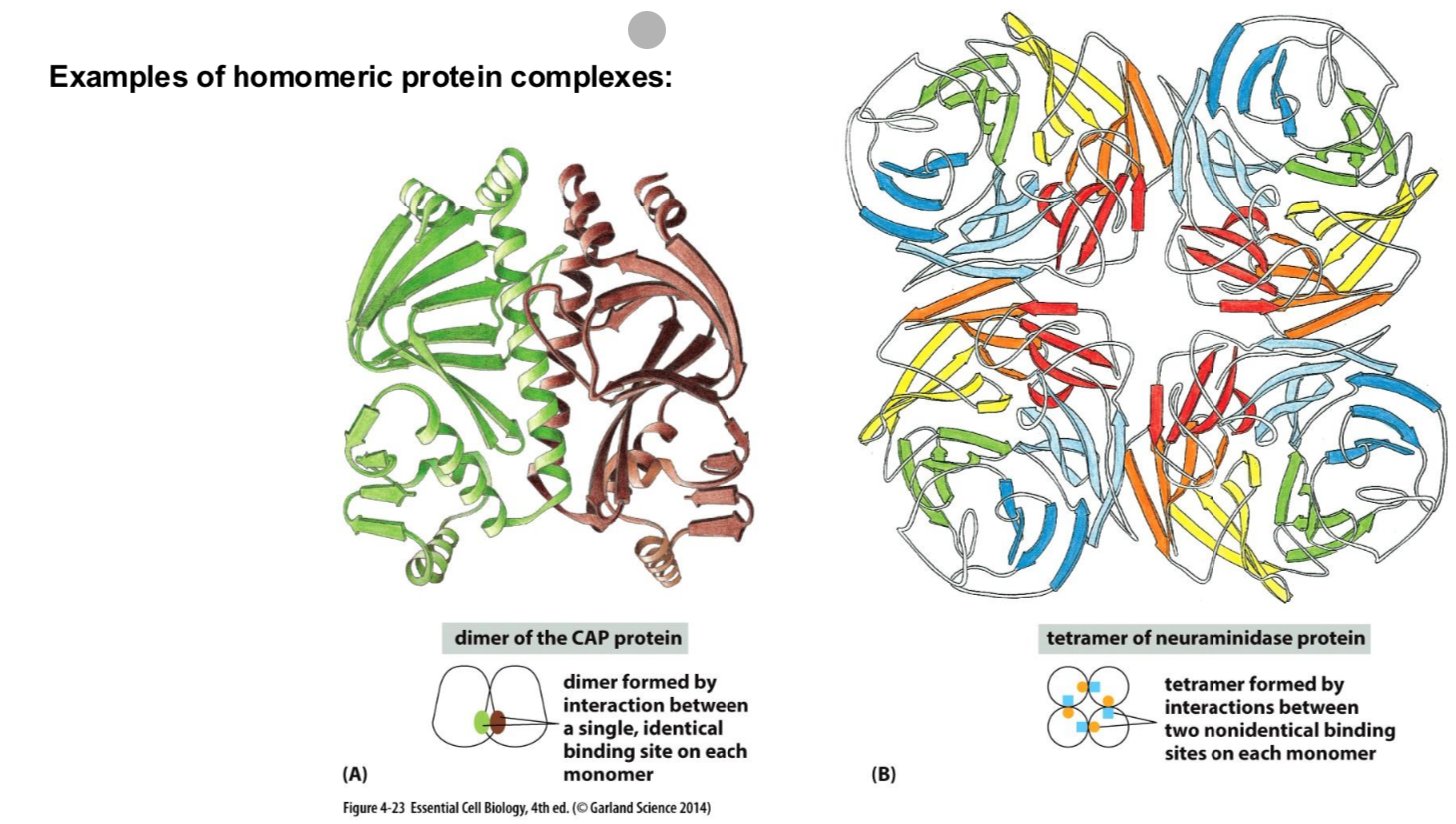
What is a protein complex?
Several proteins can assemble into stable, larger strucures, called “protein complexes”
The single proteins in a complex are called a “subunit”
Homomeri complexes contain all the same subuntis
heteromeric complexes are composed of different subuntis
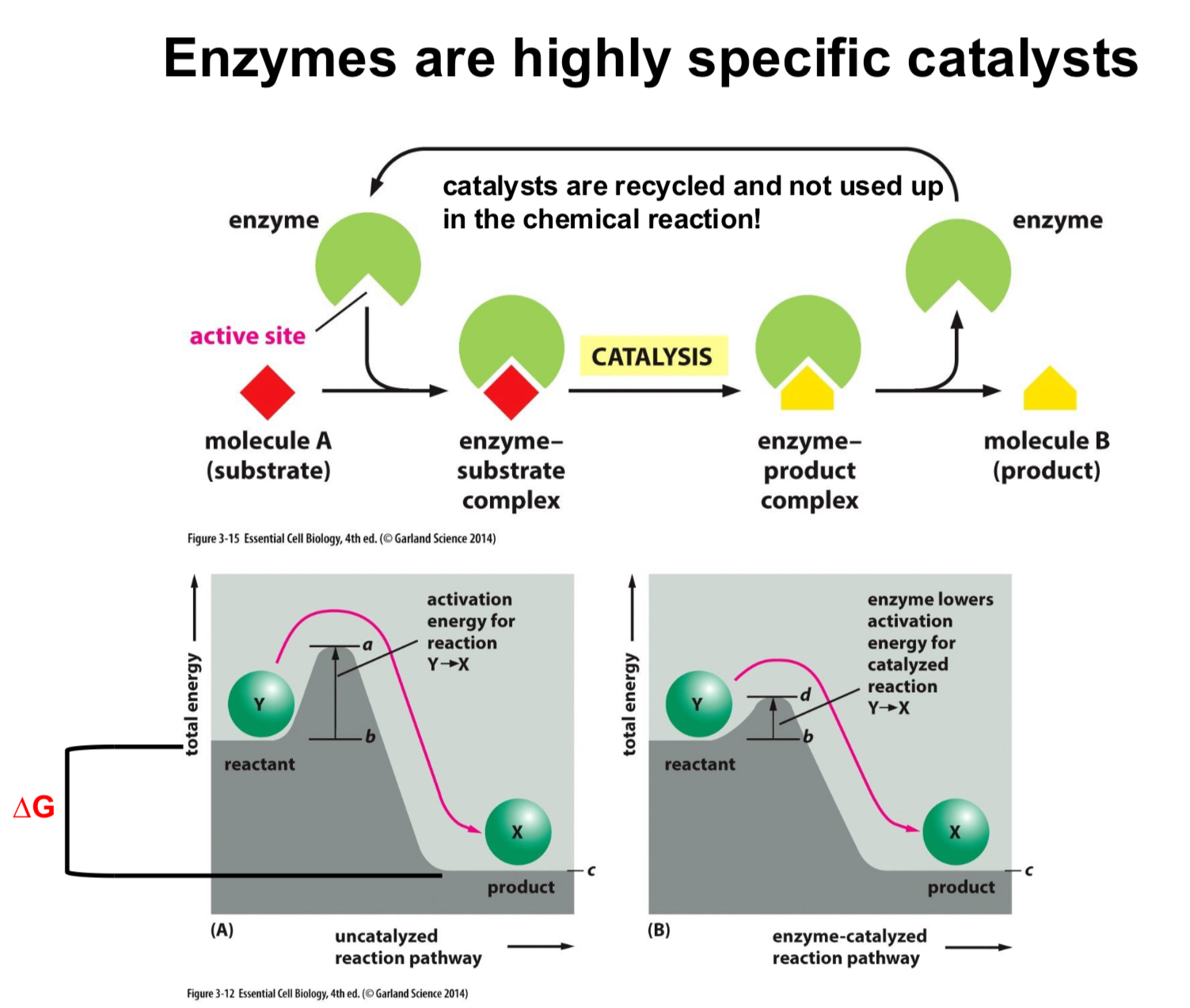
What are enzymes and how do they work?
Ezymes are highly specific catalysts
Catalysts are not used up in the chemical reaction, so enymzes are not used up
They decrease activation energy
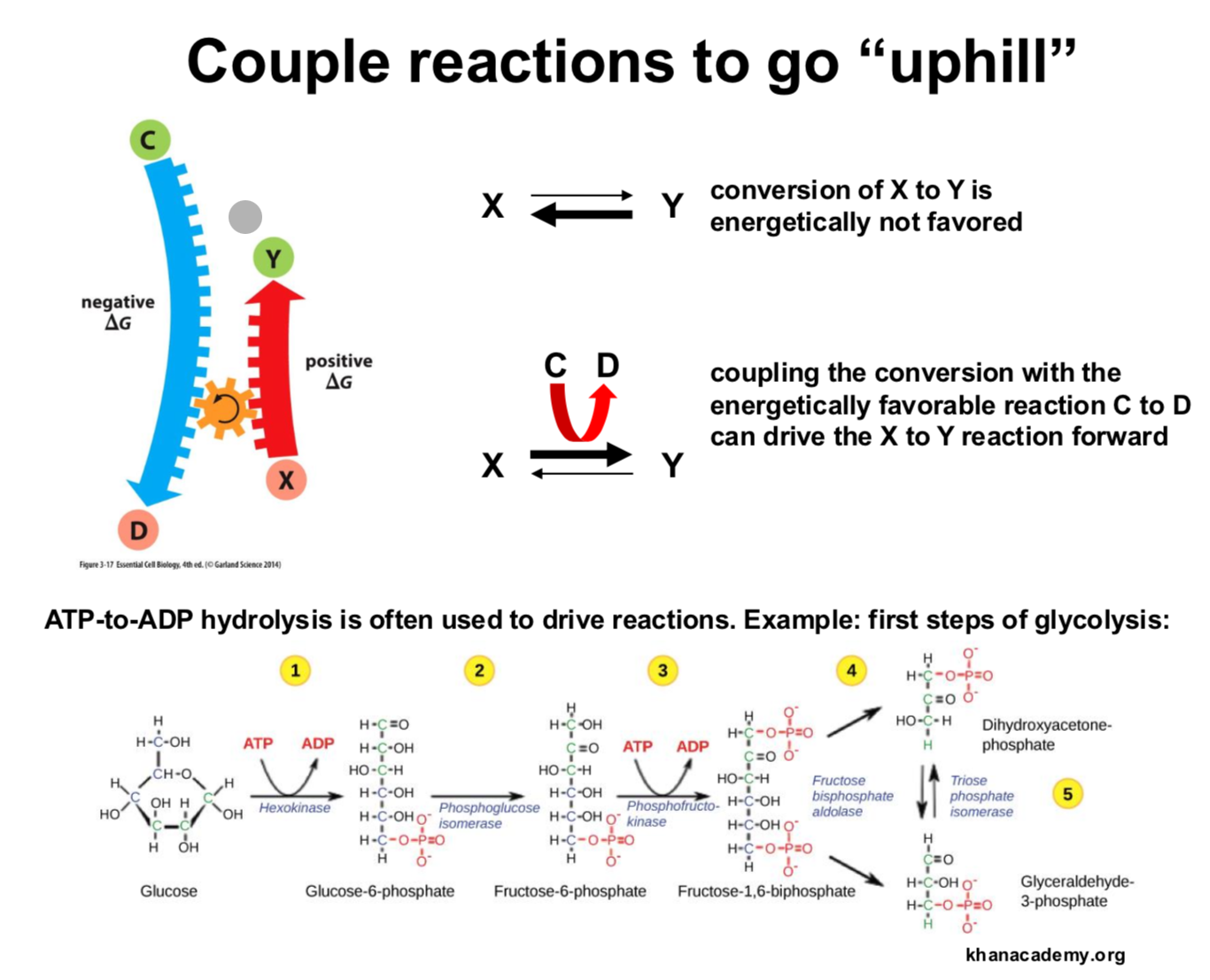
What is standard free energy and what do positive and negative values represent?
The measure of a reactions spotaneous nature.
Negative means that it is spontaneous
Positive means additional energy is required
How does coupling reaciton allow energyetically unfavorable reactions to happen?
A genetically unfavorable reaction can be couples with a genetically favoirable reaction to allow both of them to happen at the same time.
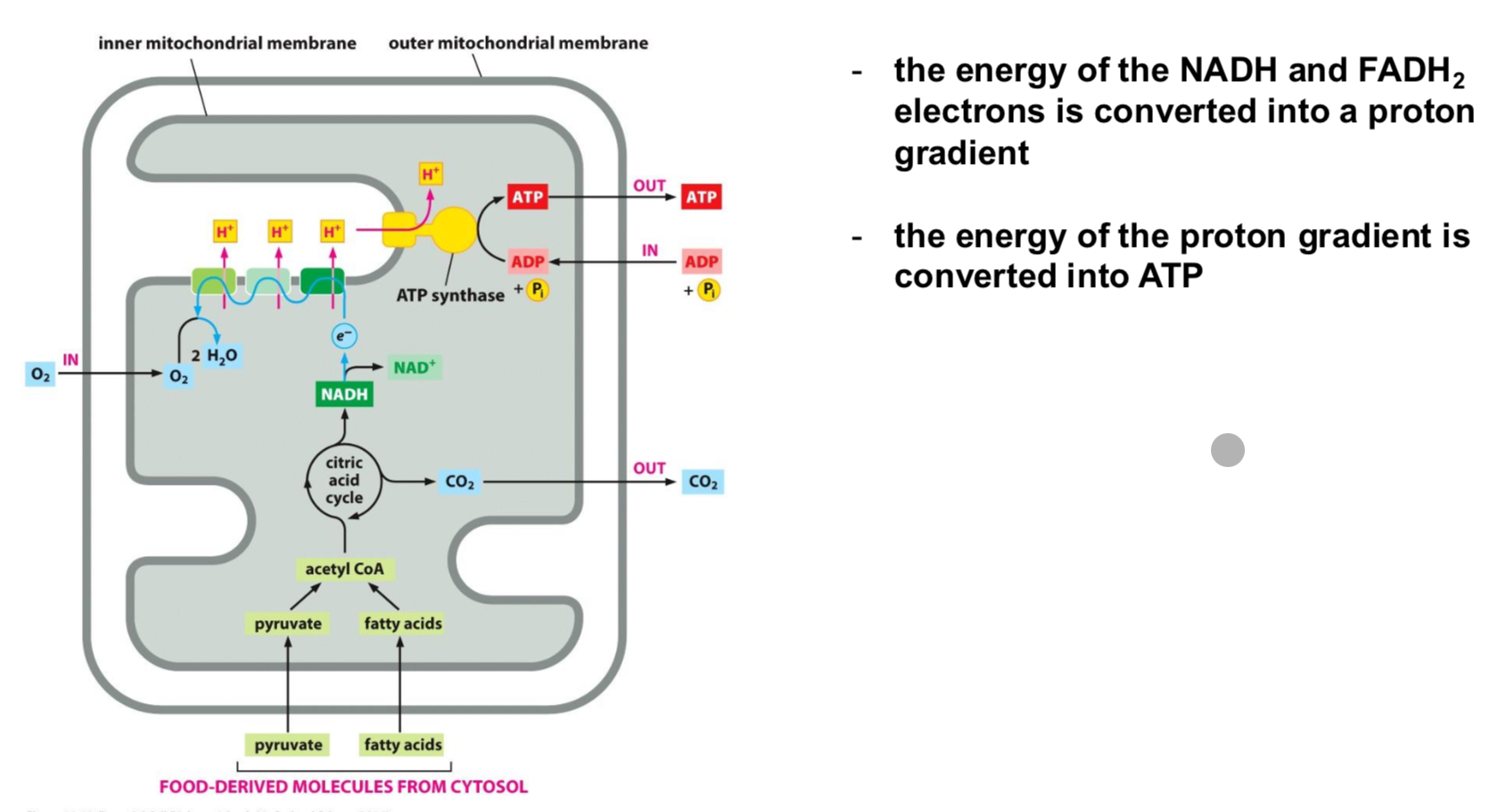
What is catabolism?
Energy production from food
Key steps are glycolosis and citric acid cycle
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
The matrix of the mitochondria
Describe the citric acid cycle?
What is anabolism?
The creation of organic molecules
Glycolosis and the citric acid cycle provide the precursors needed for cells to synthesize the important organic molecules
Catabolic and anabolic pathways are linked
Most comple organic compounds rae not directly taken from food, but instead are synthesized
What does a chloroplast look like?
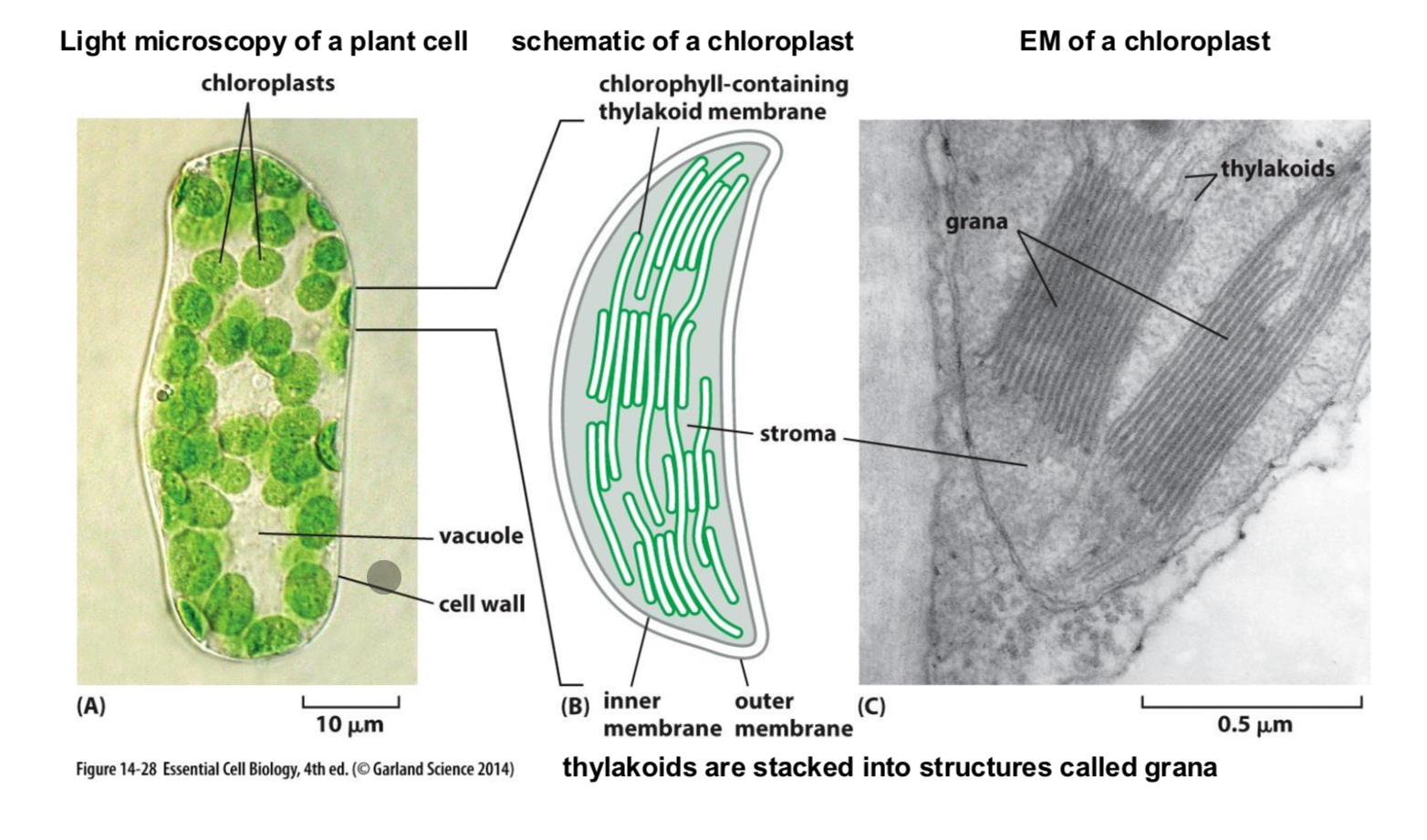
Describe the steps on photosynthesis in the ER?

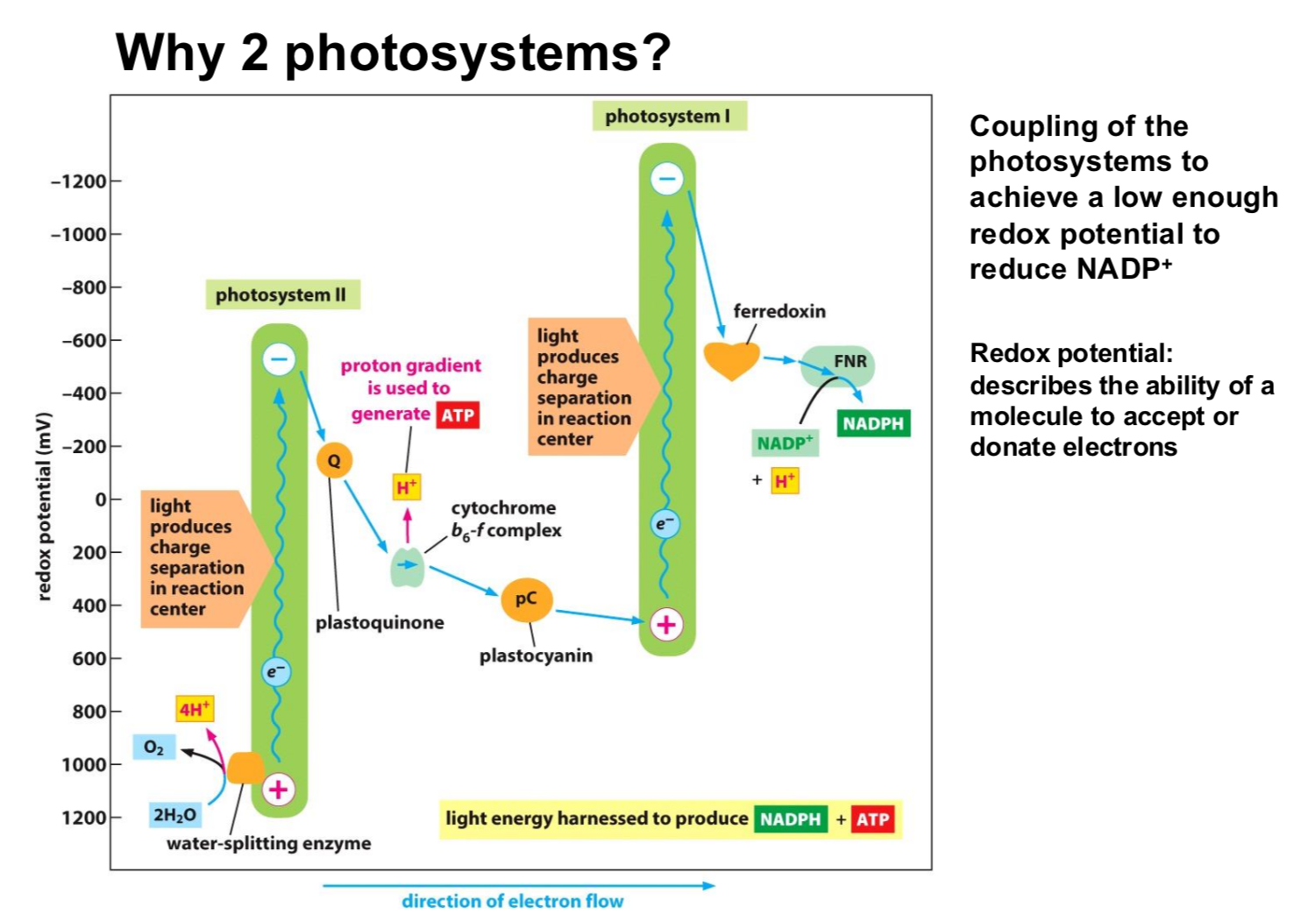
How do the two photosystems work together?
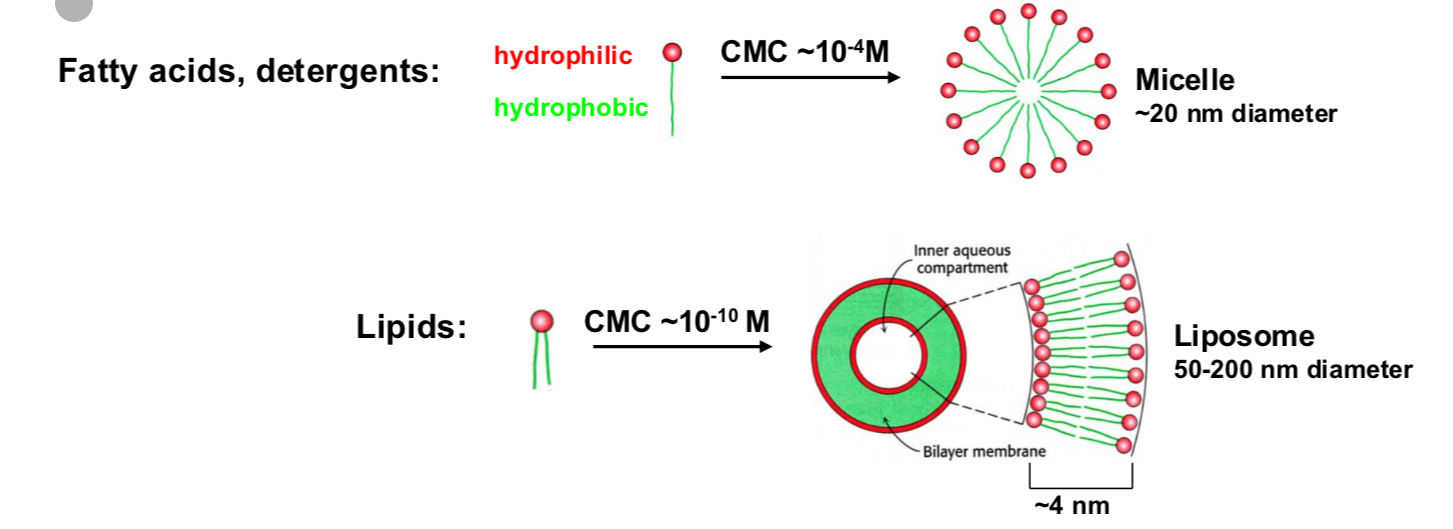
Describe the strucutre of Membranes.
Stable lipid bilayer which form spontaneously in water
Stabalized by hydrophobic interactions
Low permeability for charged molecules (polar or hydrophillic moleucles)
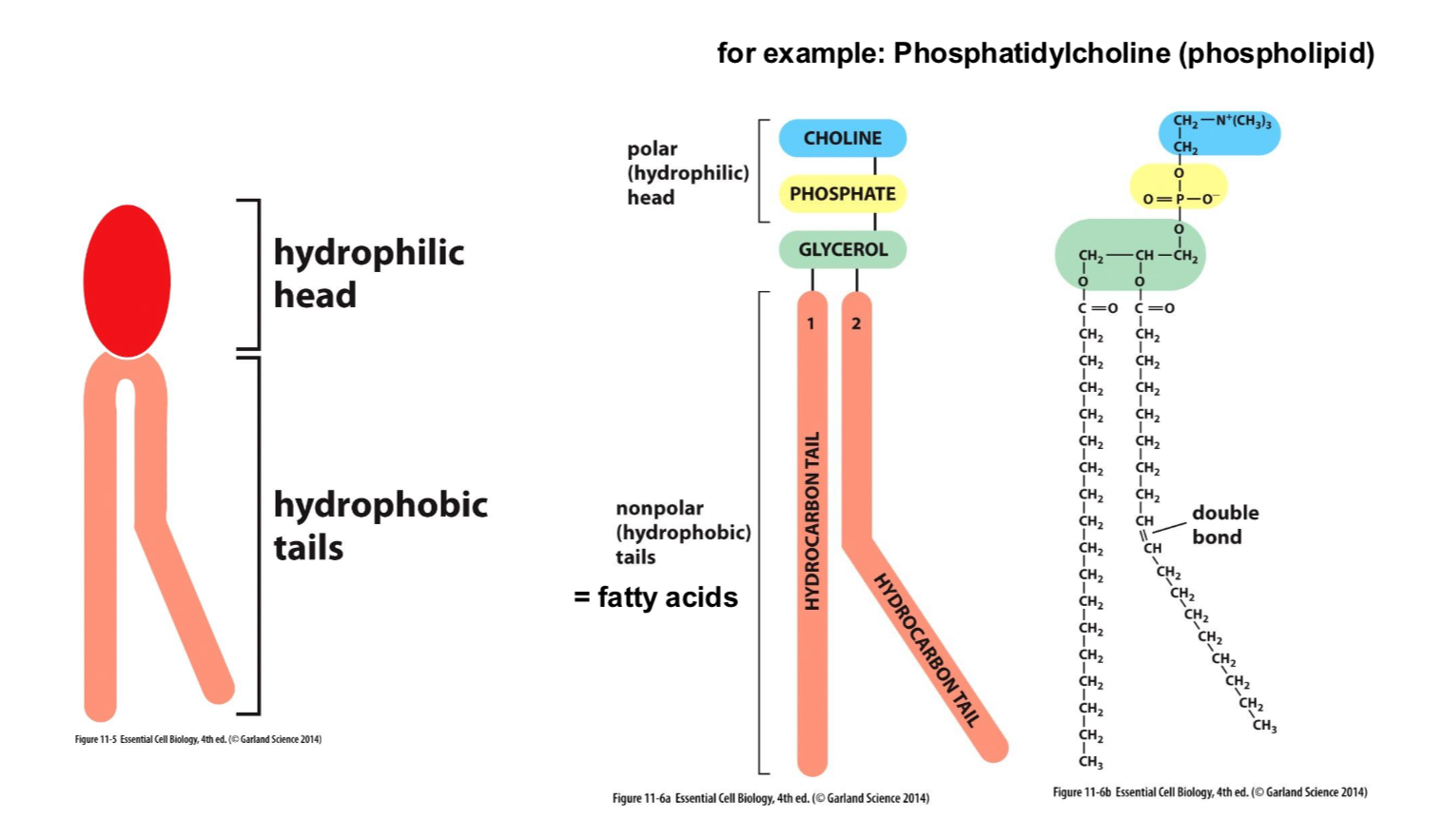
What is the strucutre of lipids?
Hyrdrophilic head with a Hydrophobic tail
What does the asymetry of lipid composition mean?
Lipid composition of the two bilayers are different
What are factors that adujsut lipid composition?
Dependent on the orgenlle
Temperature
Funciton (inner mitochondiral membrane has a special lipid composition to minimize leaking)
What is Osmolarity/Turgor preasure?
The total concentration of all solute particles (water interacting moleucres)
Cytoplams has a higher osmolarity than extracellular space
Causes water to push into the cell, causing turgor preasure
What allows the transport of water through membranes?
Aquaporins, they only allow water to pass and not ions
What is the Electrochemical gradient
Electrochemical gradient = Membrane potential + concentration gradient
Determines the direction in which charge solutes (ions) move
What is membrane potential?
Unequal charge distrubution across the membrane
How do transport moleucles and ions across membranes
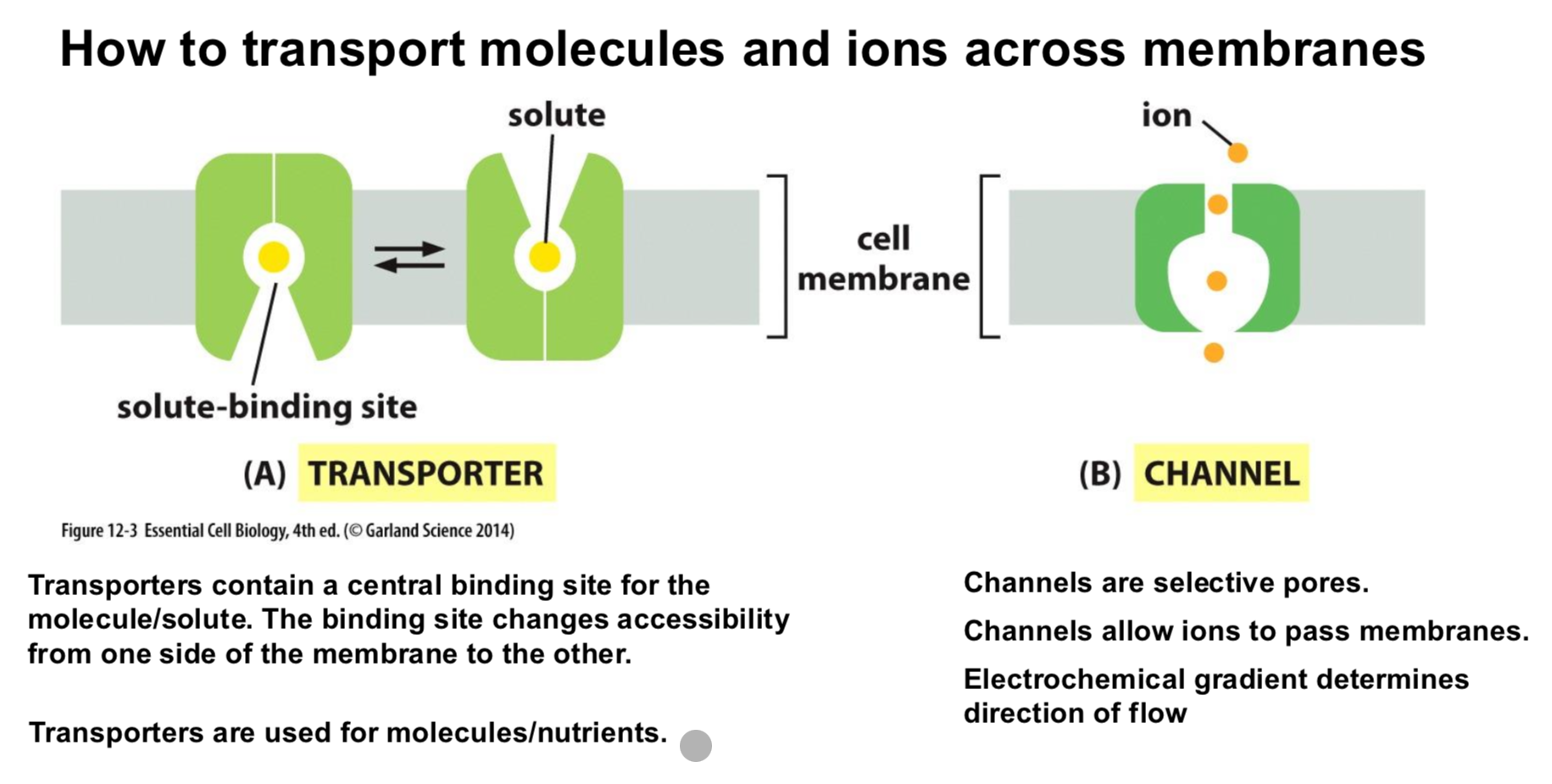
What is symport and how is it used for nutrient transport.
When the unfavorbale transport reaction is coupled with a favorable one

What is a selectivity filter in an ion channel?
Only allows specific ions to pass, and no water
What does it mean for an ion channel to be gated?
Signal can turn the channel on and off
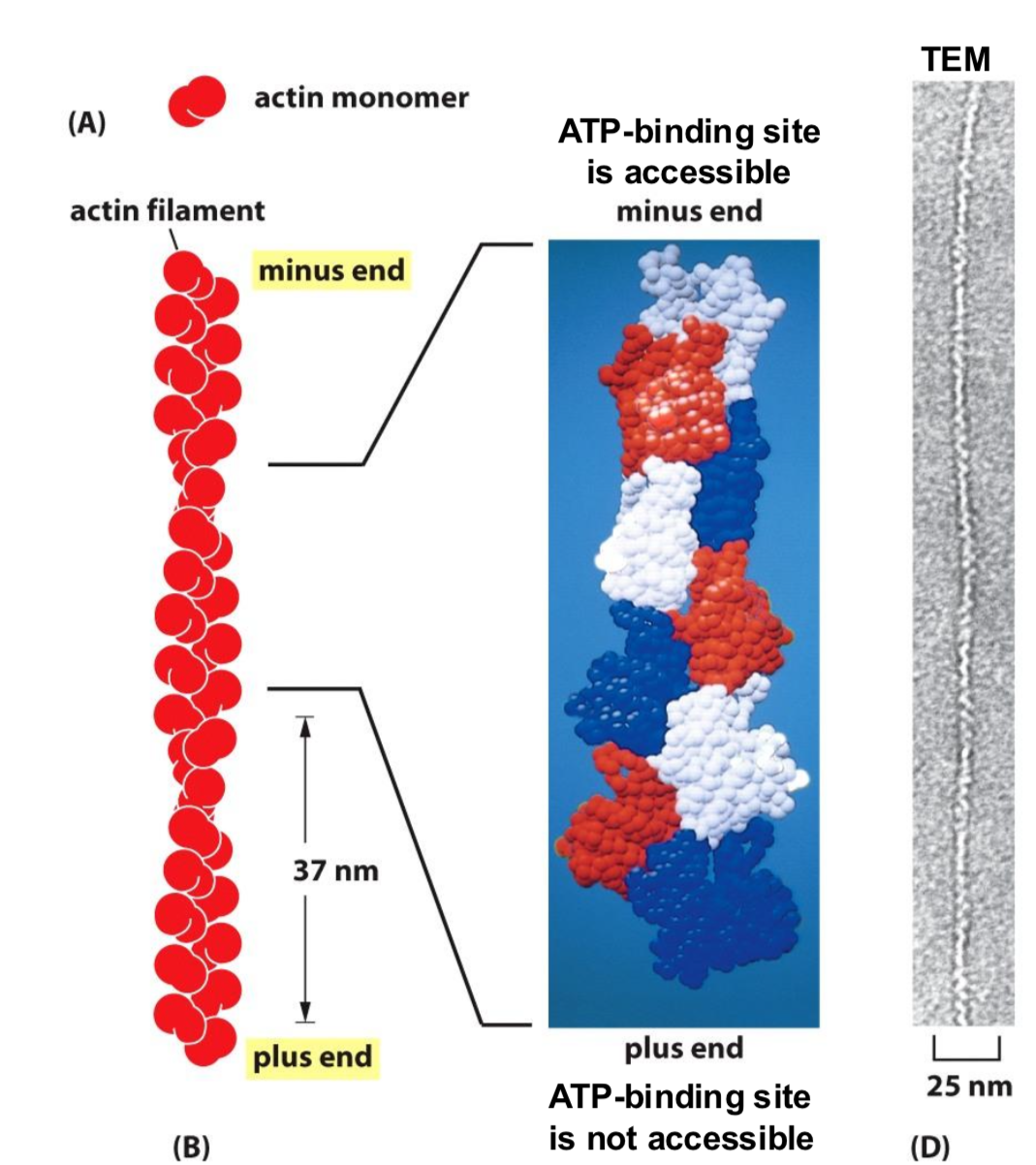
Describe the strucutre of Actin?
Twisted two strand strucutre, 8 -9 nm diameter
Made of
G actin: globular, monomeric actin
F actin: filamentous actin polymer
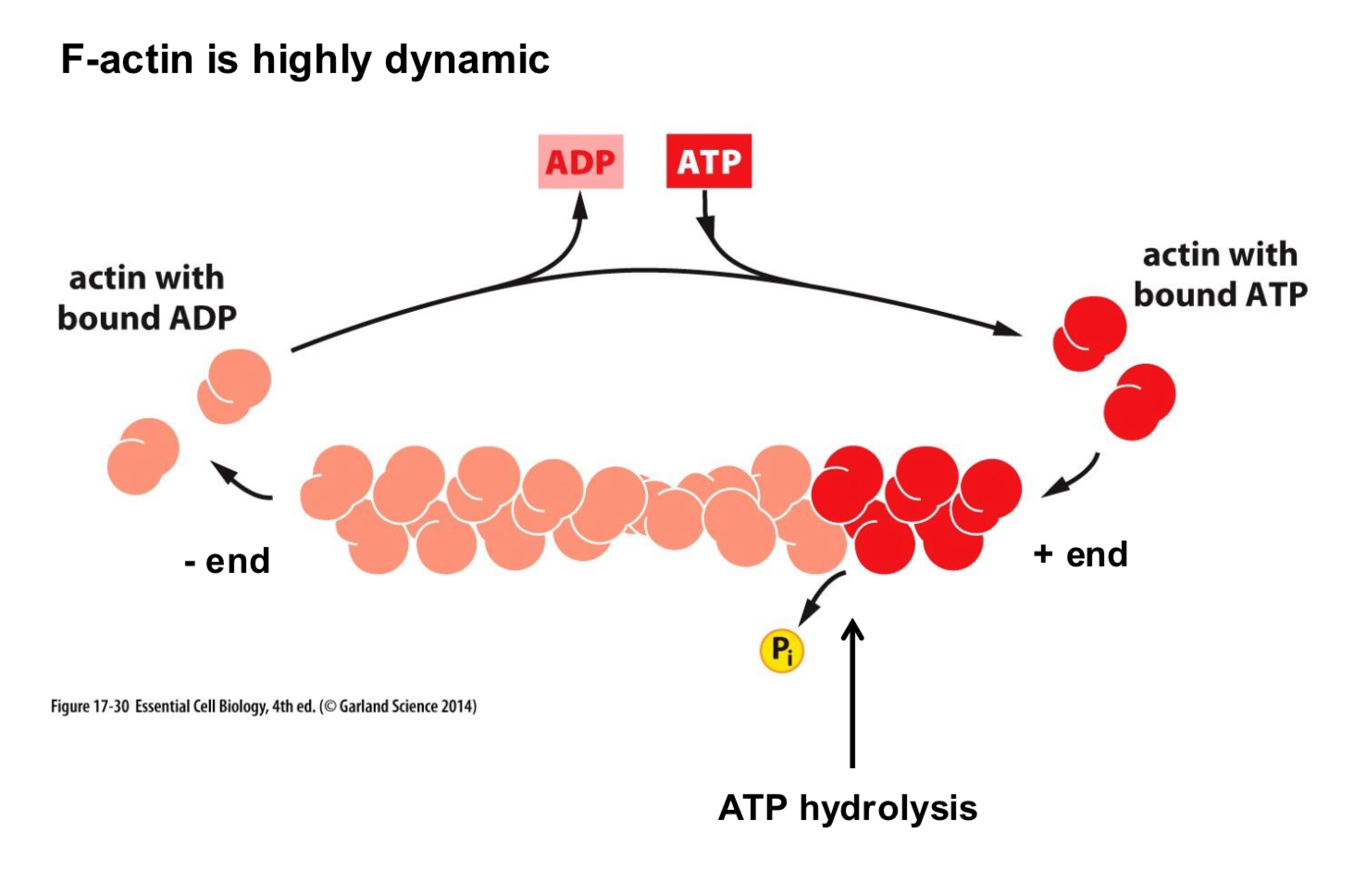
What does it mean for actin to be highy dynamic?
The treadmilling of actin molecules
How do Actin binding proteins orgnaize and regulate actin filaments in vivo
Proteisn can block actin from polymerizing. They also do a lot more
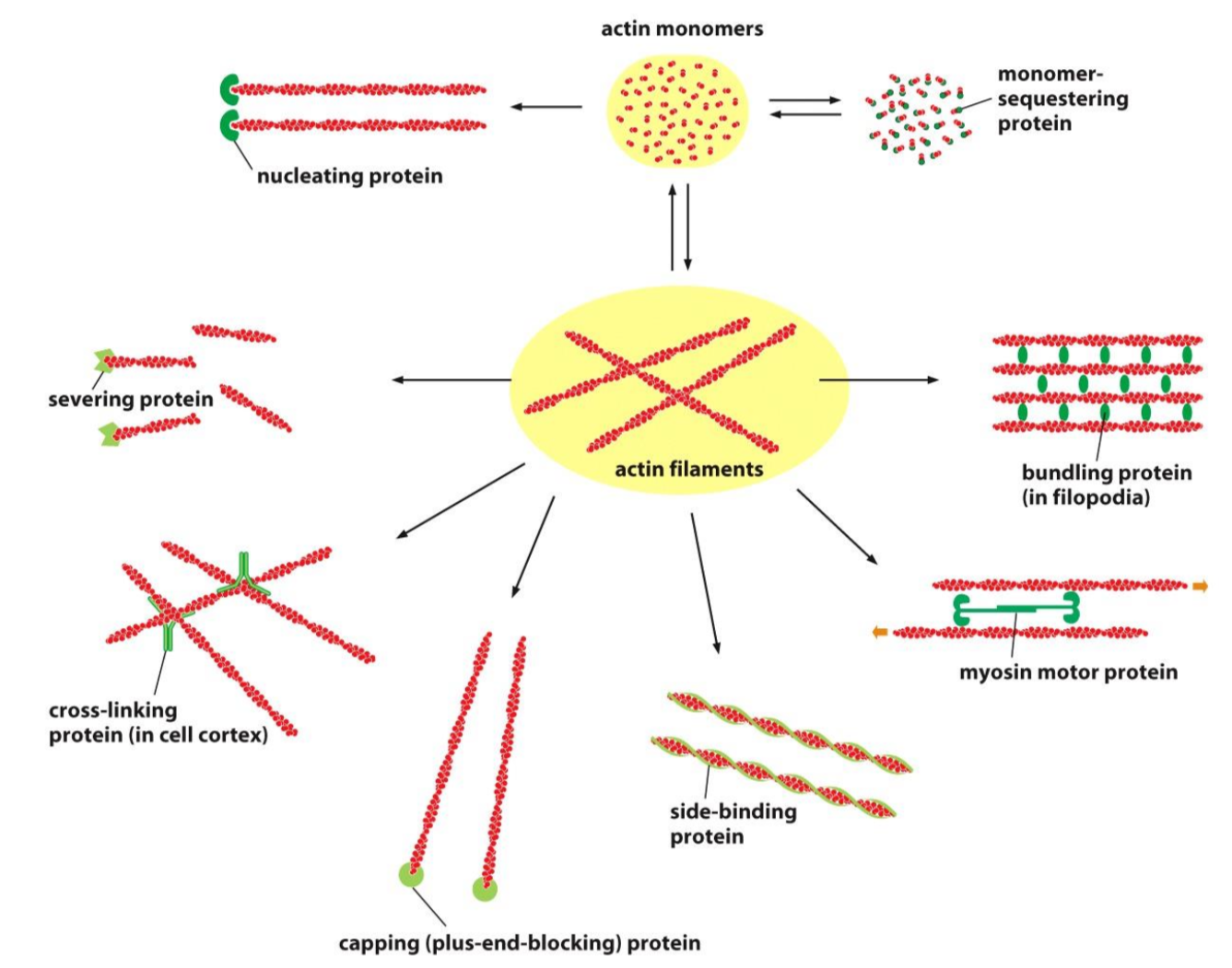
What are the main function of actin?
Shape, move, and divide cells
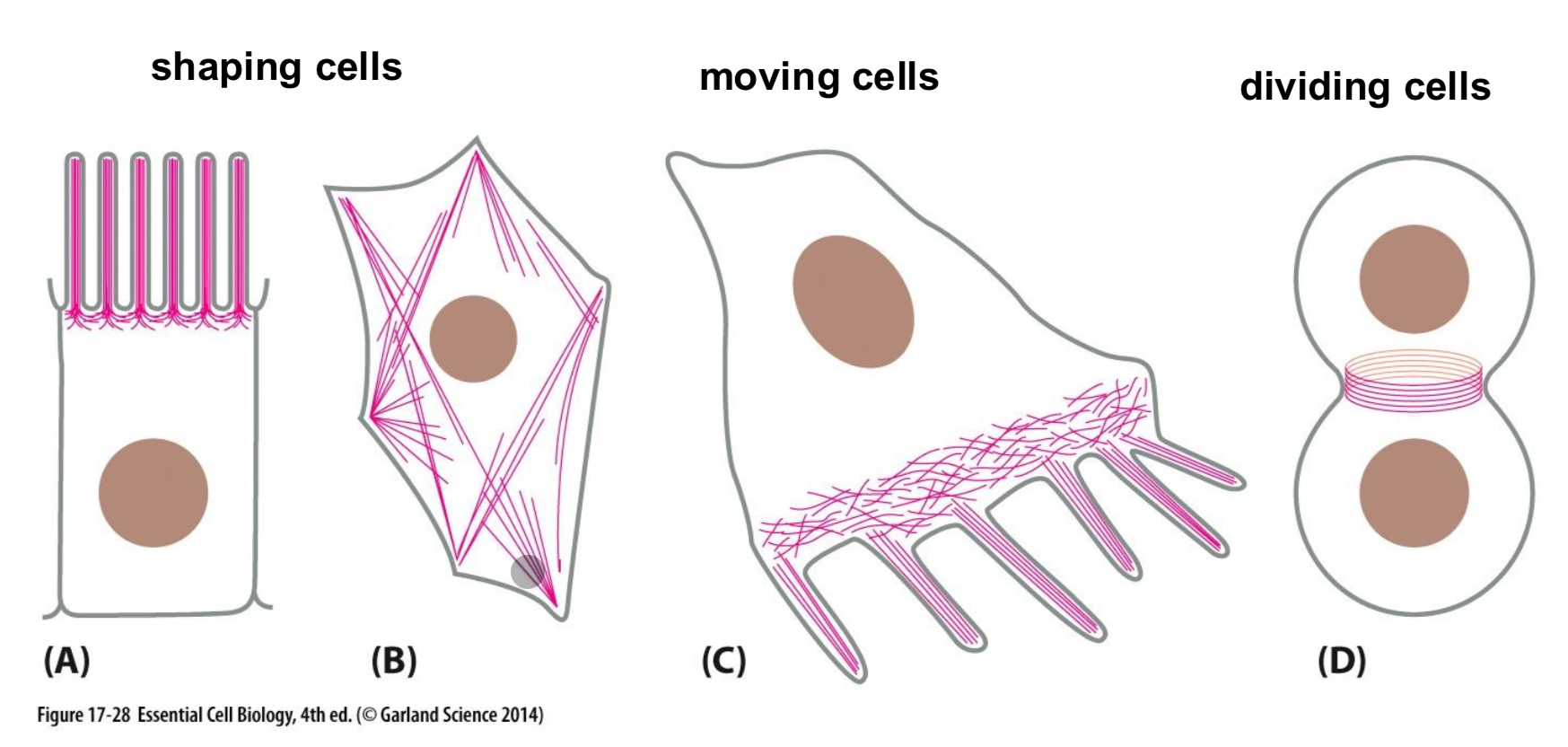
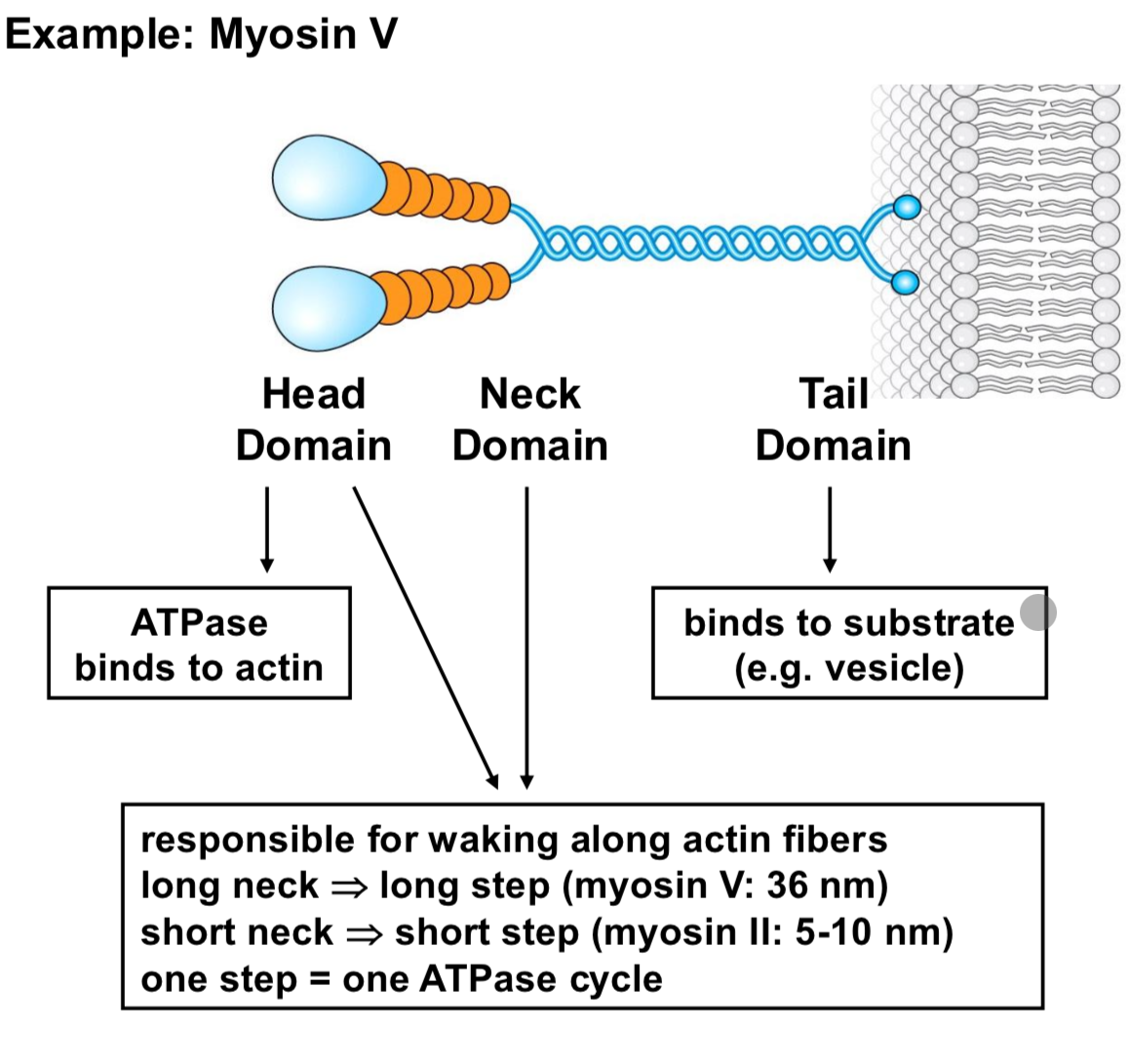
What are myosin motos and what do they do
Forve generating ATPases that walk along actin cables
What is the strucutre of Microtubules?
Hollor tubles made out of Alpha nad Beta subunits that form tubulin subunits. These form protofilaments that make up the tube
24nm diameter
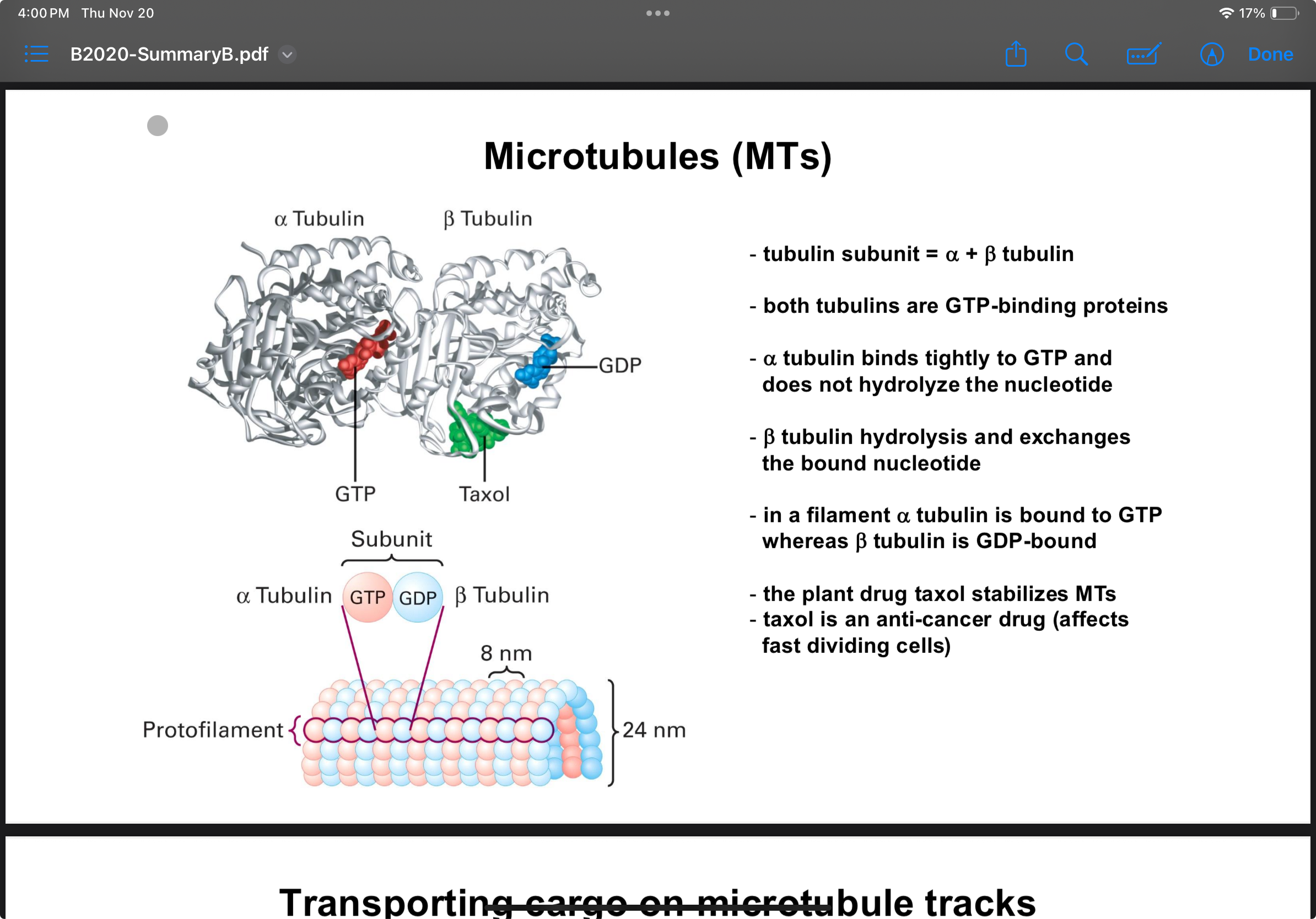
What side of microtublues face outwards from the centriols
The positive end
What direction do dynein and kinesin go
Kinesin goes to the positive end, outward
Dynein goes to the negative end, inward
What is the Central Dogma of molecular biology?
The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Proteins
What is Gene expression?
How the information stored in DNA is used to produce proteins
Describe the strucutre of DNA.
Bases form hydrogen bonds, A to T and G to C
Opposite orientation of the two DNA strands
5’ to 3’
Double Helix

What is a codon?
3 bases that code for one amino acid
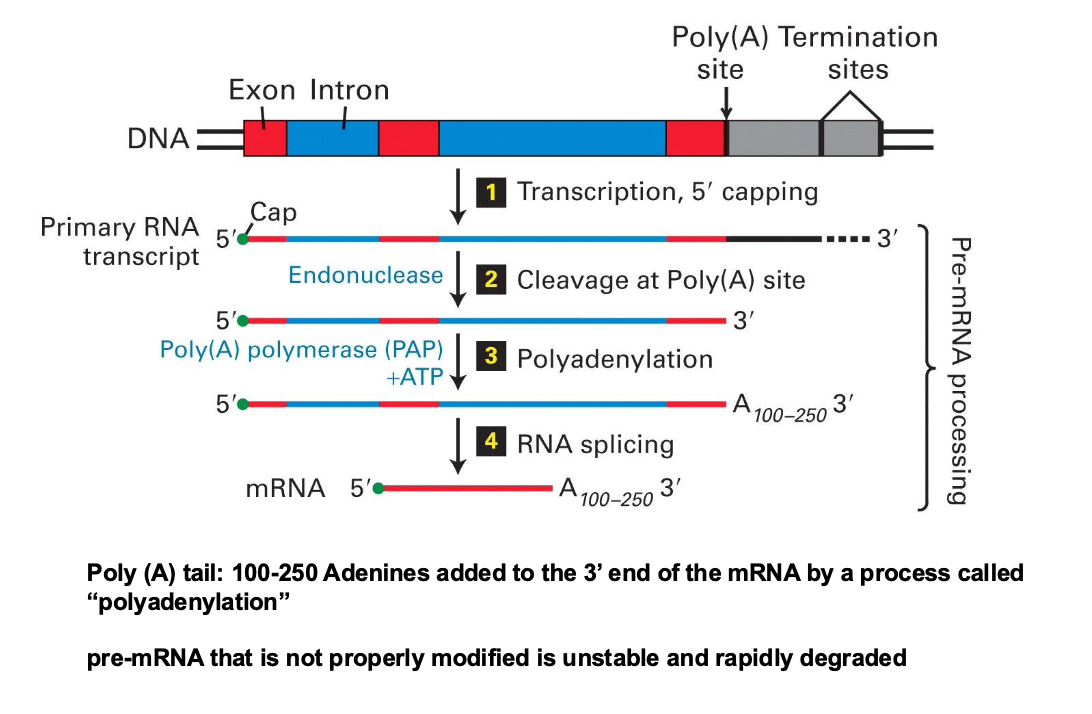
Describe all the steps of transcription.

Describe the steps of pre mRNA processing
Describe the strucutre of the nucleus?

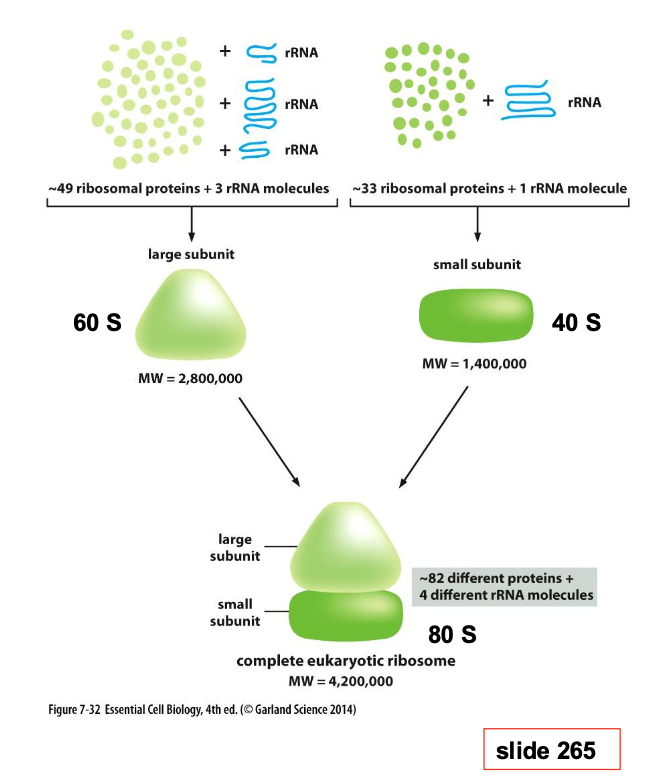
What is a ribosome and what does it do? Descirbe the strucutre of ribosomes
Make proteins by reading mRNA
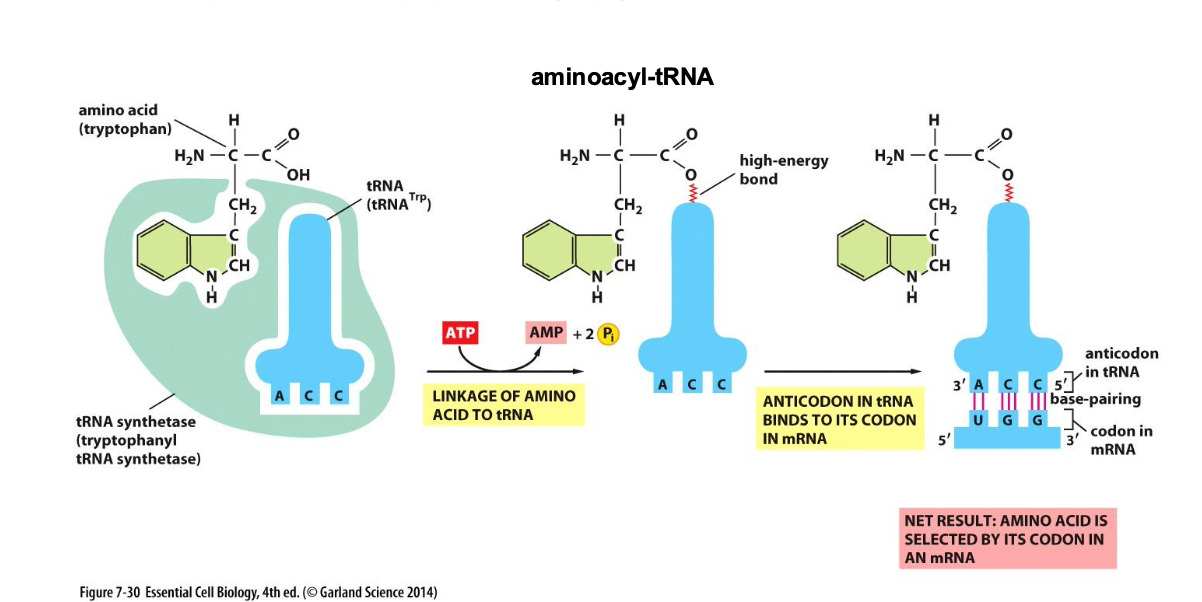
What is tRNA synthetase and why does it have to be highly specific?
Links an amino acid to tRNA and it has to be highly specific as this isn’t double checked at the ribosome
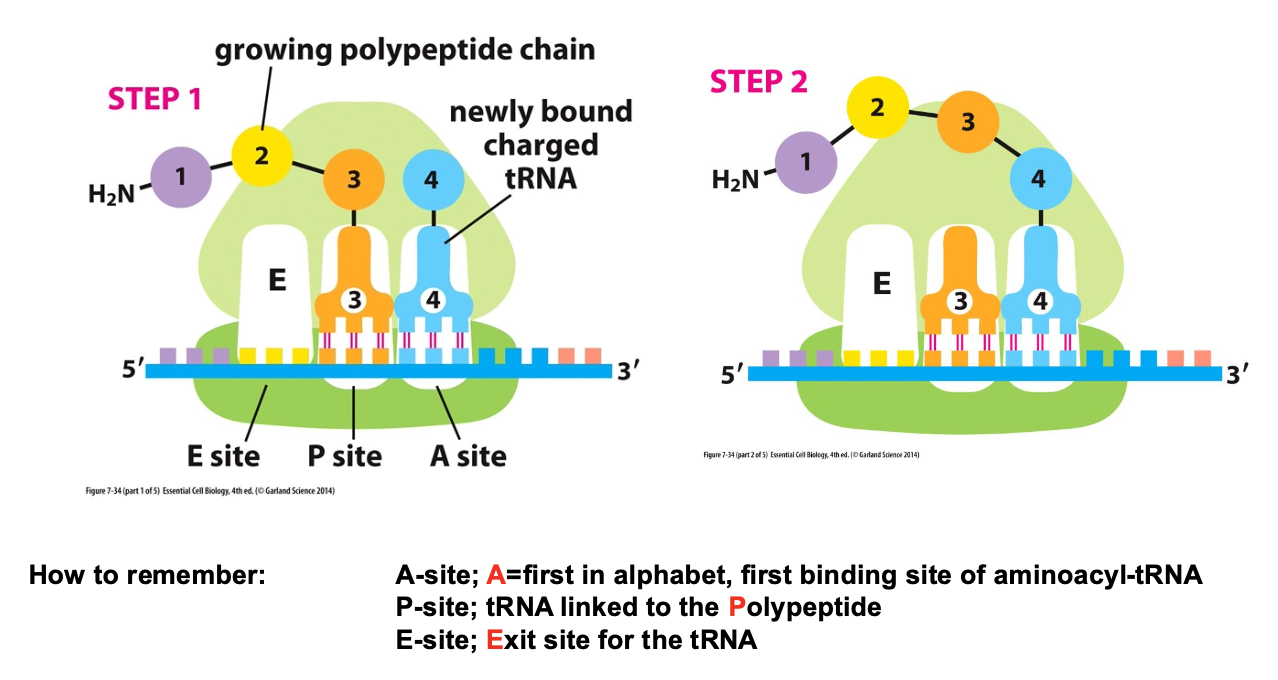
Describe the steps of translation within a ribosome.
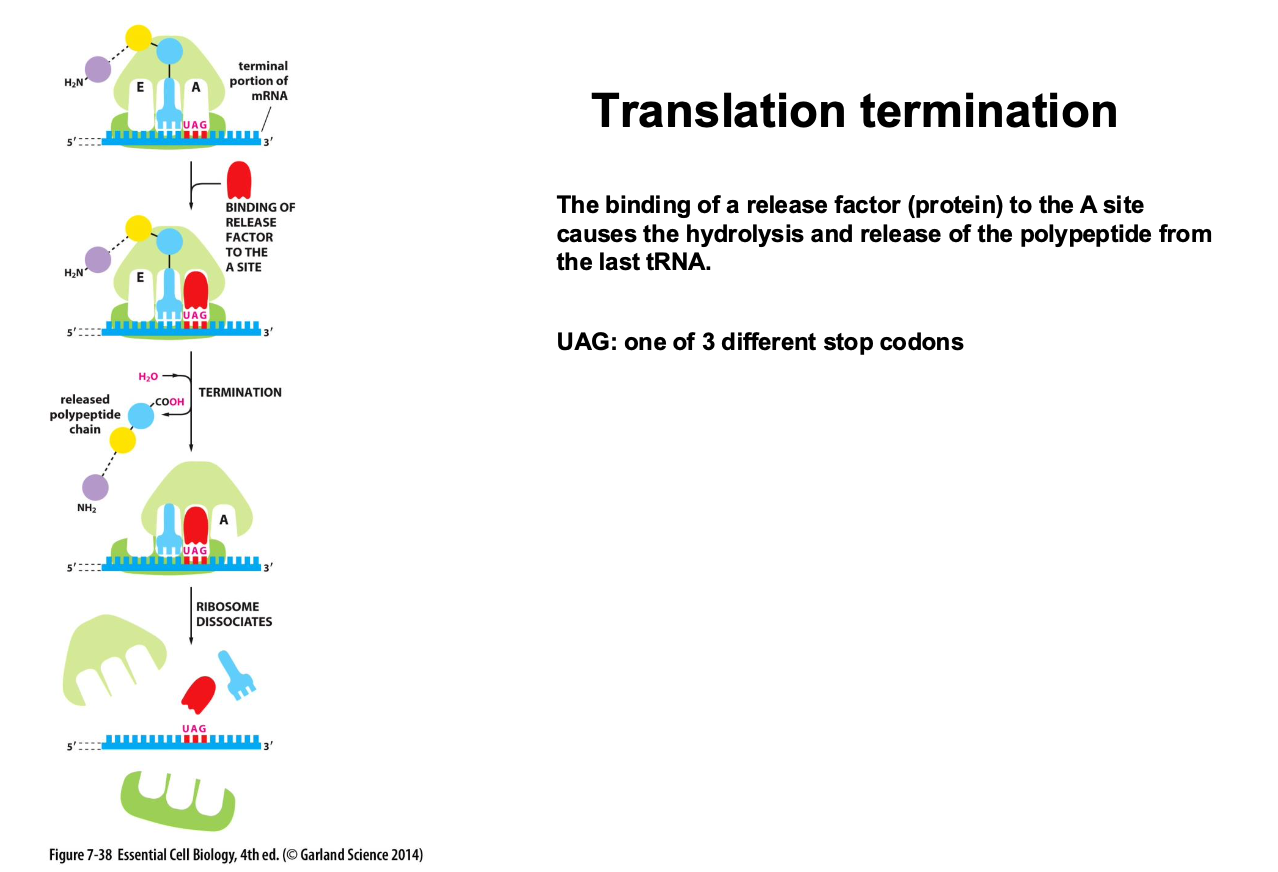
How is translation terminated?
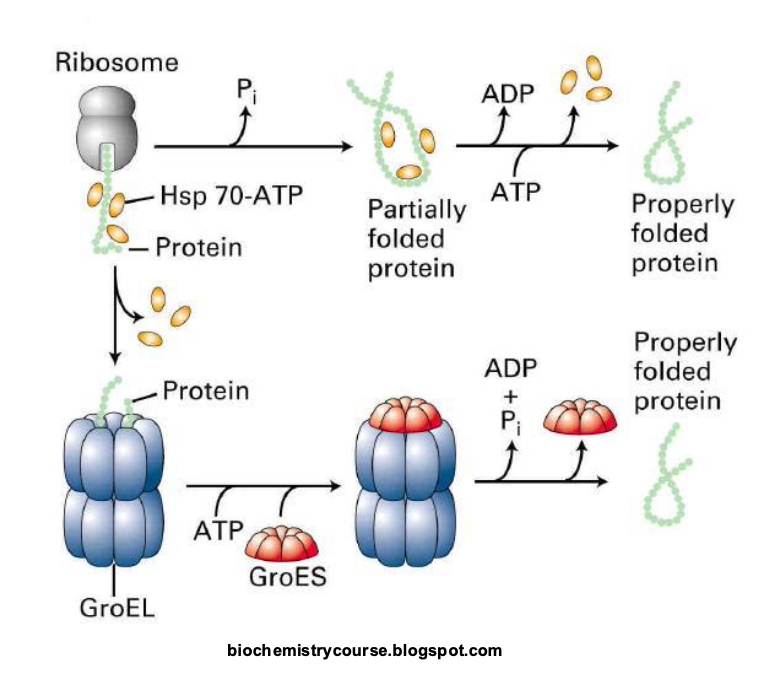
What are molecular chaperones and how do they work?
Help protiens fold properly
Hsp70 binds to hyrophobic regions and prevents aggregation giving the protein time to fold
Hsp60 (GroEL) forms a large cavity that seperates the unfolded protein from the cytosol and thus prevents aggregation.
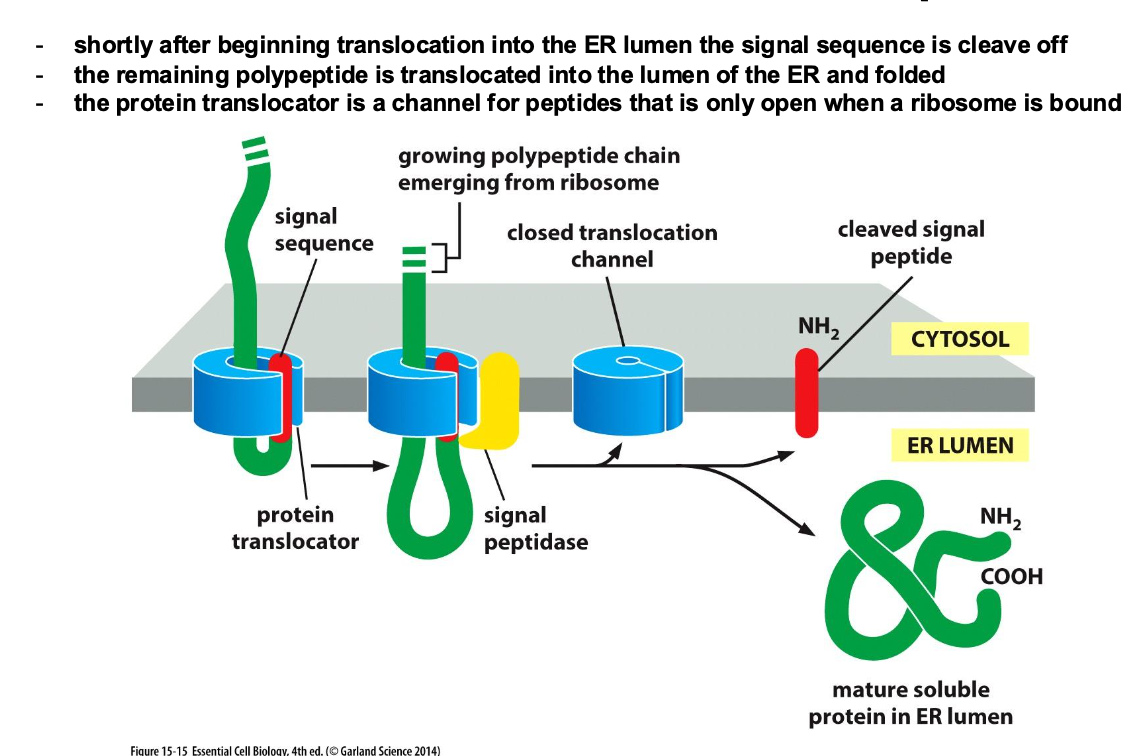
How does a ribosome know that a protein belongs to the ER?
Signal sequences in the protein

How are protein transolcated at the ER membrane for a lumenal protein?
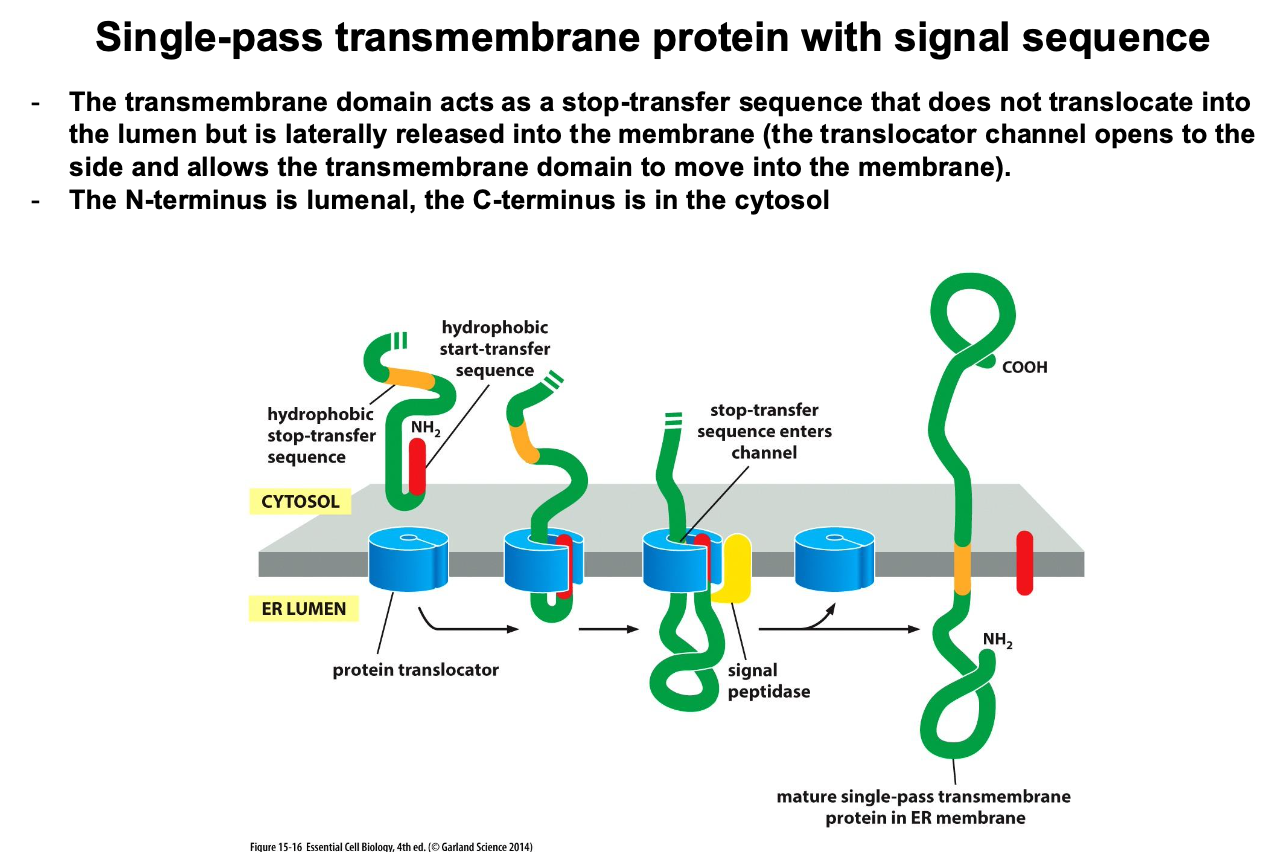
How are proteins transolcated at the ER membrane for a transmembrane protein?
What is protein glycosylation and what is its purpose?
N linked glycosylation: modifcation of an asparagine (amino group)
O linked glycosylation: modifcation of a serine or theorine (OH group)
Most proteins that are translated and translocation at the ER become glycosylated
Increases stabailtiy of secreted proteins
Glycosylation of surface proteins is iportant for recognition of self versus foregin (immune system)
Describe the process of vesicle formation
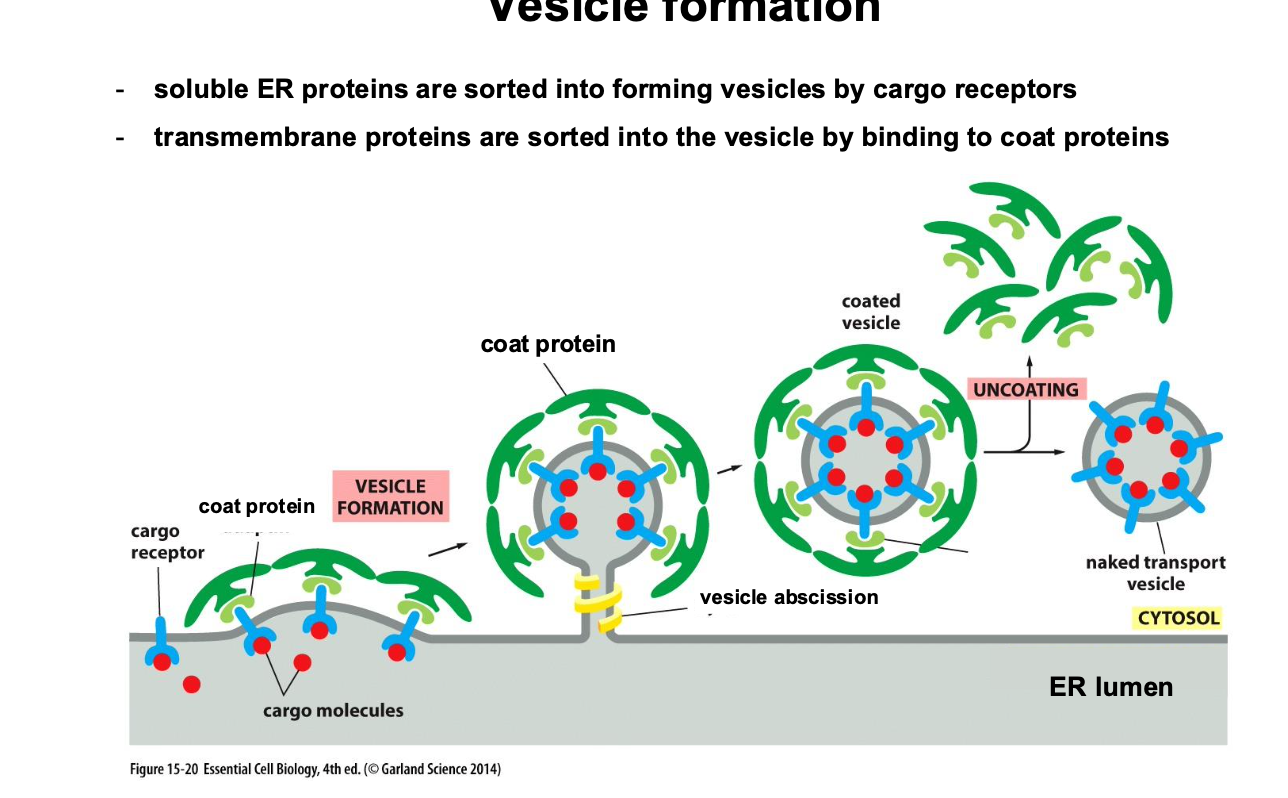
Describe the process of Vesicle fusion
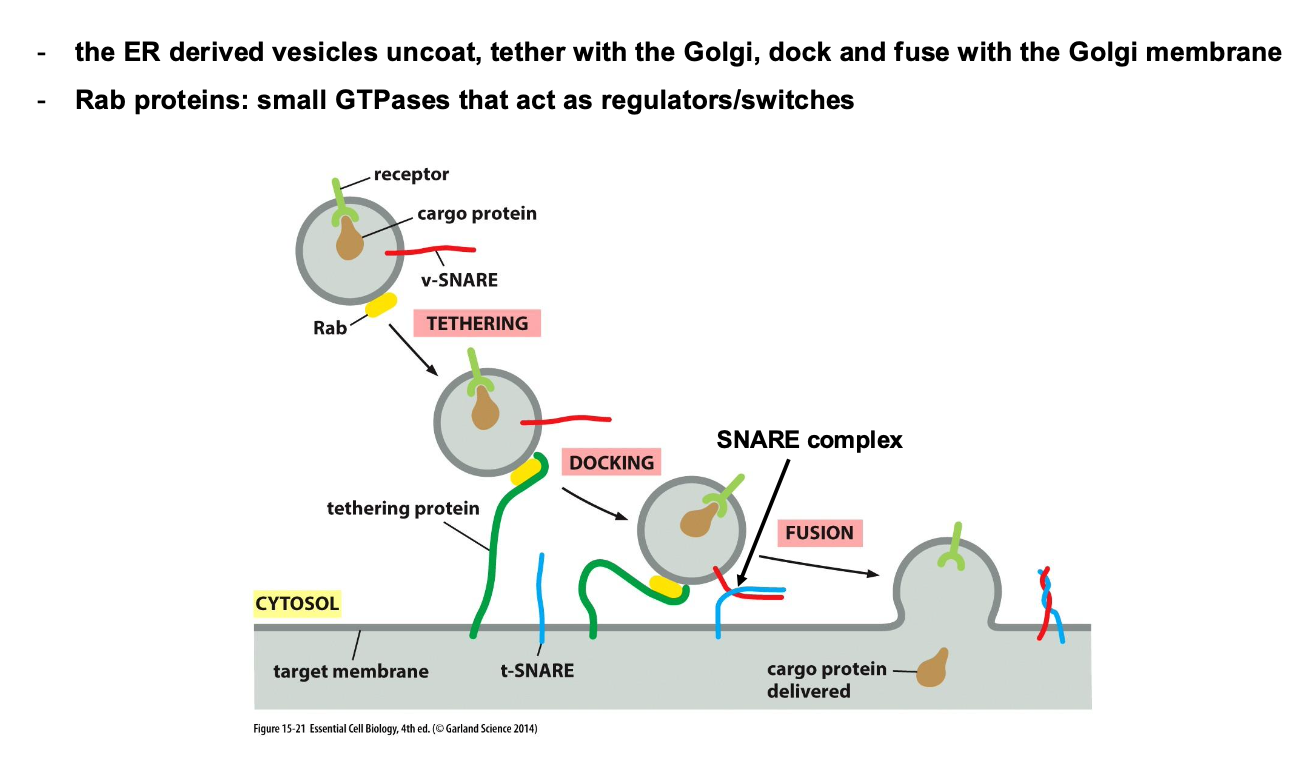
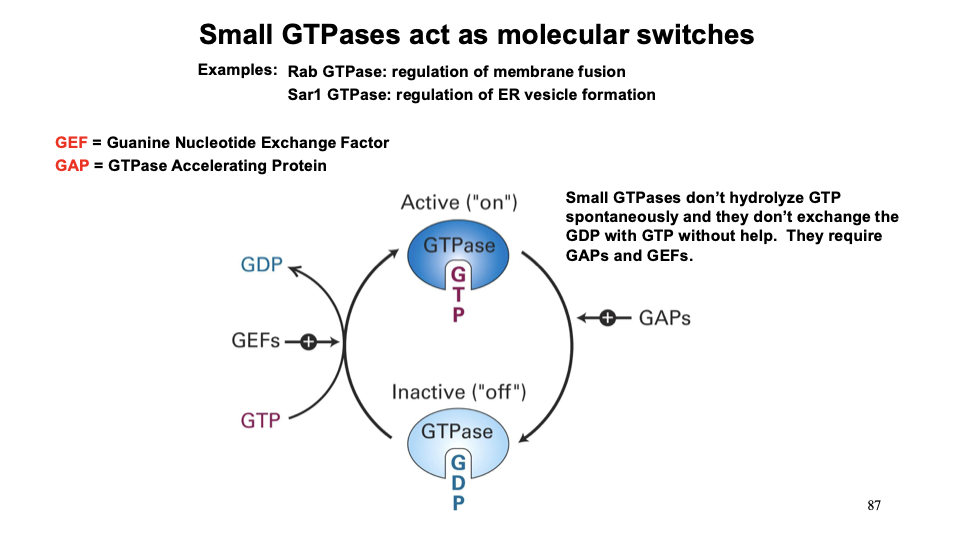
What are GTPases and what tursn them on and off?
Molecular switches that control processes
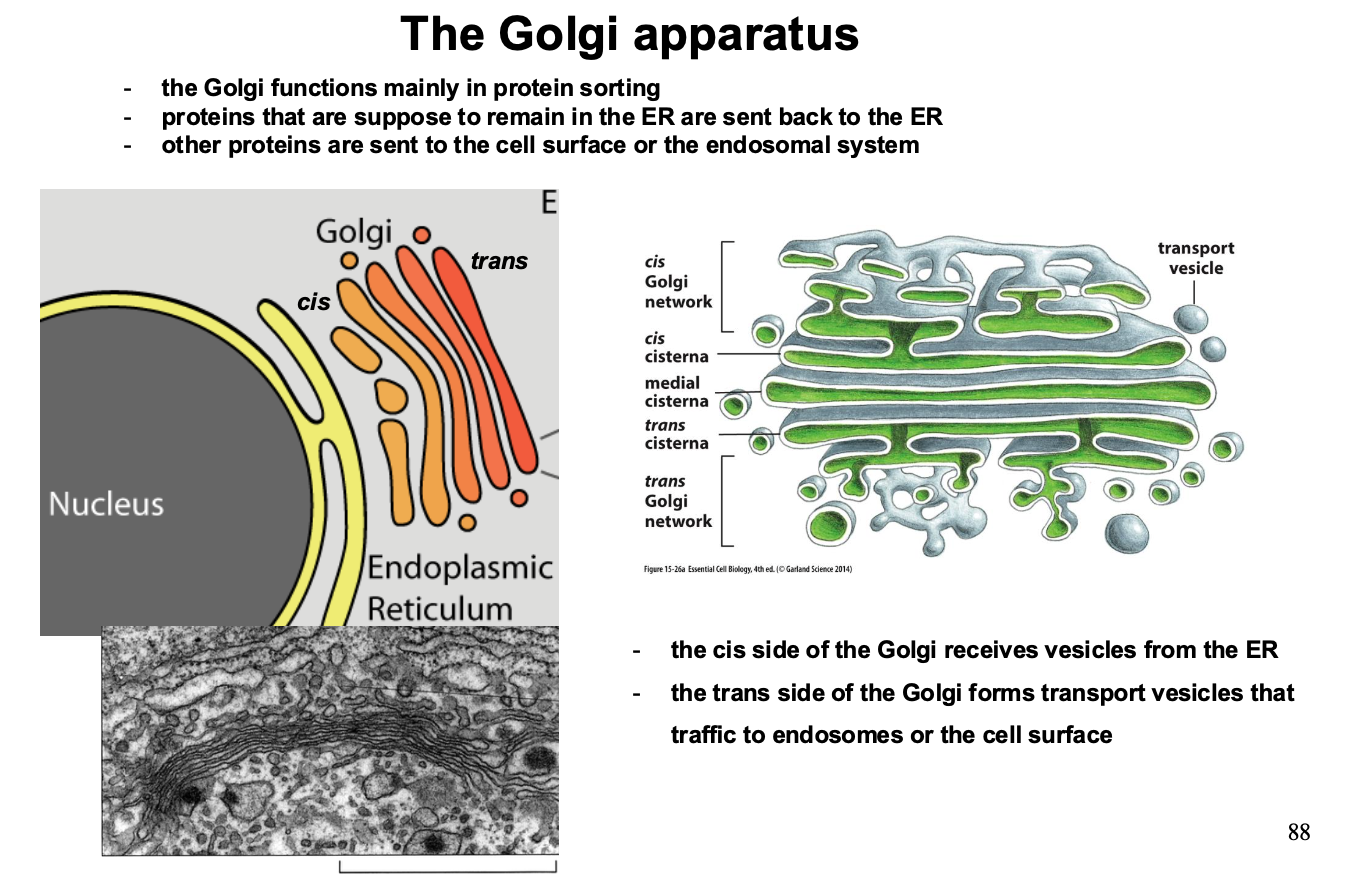
What is the main funciton of the Golgi and descirbe its strucutre?
Its main function is protein sorting
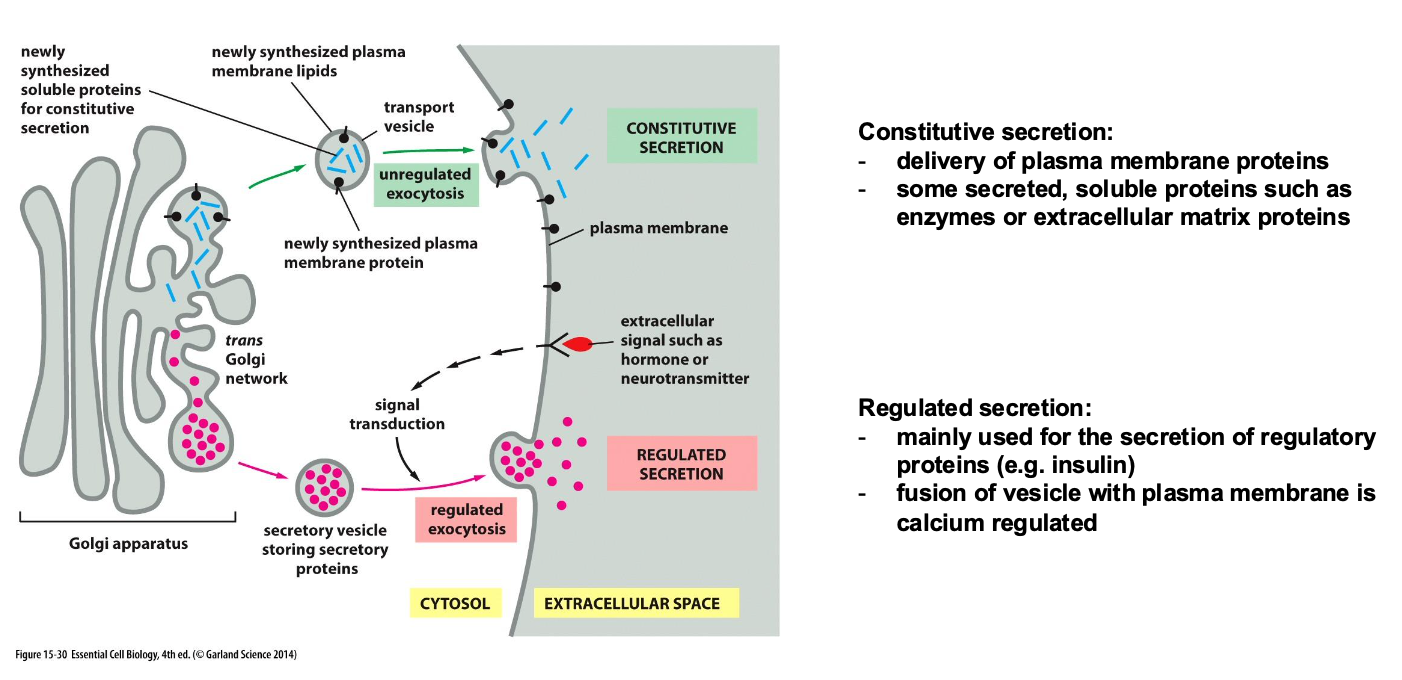
What is the difference between Constitutive secretion and Regulated secretion?
Constitutive is unregulated while reguated is regulated