cosmetic dentistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is the goal of cosmetic dentistry
improve the look and appearance of teeth, oral structures and correct/restore function.
Esthetic Dentistry
focuses on enhancing the smile's aesthetics through direct and indirect restorative materials, or by using whitening techniques.
Types of cosmetic procedures
placement of bridges, crowns, veneers, tooth whitening, straightening of teeth, lengthening of teeth, recontouring of gingival tissues, correcting bites, closing gaps, repairing chips/fractures and replacing missing teeth.
Psychological factors
personality, desires and expectations that can influence a person's perception of their smile and decision to undergo cosmetic procedures.
Sociological influences
Media, television, and advertising that set the standards for what is deemed acceptable and attractive in society
Occlusion
Occlusion refers to the alignment of teeth when the jaws are closed, and restoring proper occlusion can enhance both the aesthetics of a smile and the overall functionality of the mouth.
What type of dental specialist can make changes to a person’s bite/smile/function of the mouth.
An Orthodontist
Choosing a cosmetic dentist
referrals, credentials, availability
First steps
diagnosis, treatment planning, legal forms (consent)
Oral Photography
case presentation, patient records, lab communication, insurance, marketing and education
Extraoral
full face and profile
intraoral
various views, uses mirrors and retractors
Fundamentals of cosmetic dentistry
light, colour, illusion, shape and form
Hue
Name of colour
Chroma
Intensity or quality of the hue
Value
Brightness of the shade of the tooth
Vitapan classic shade guide
16 shades, white with varying degrees of grays, yellow or orange, use natural light when choosing shade
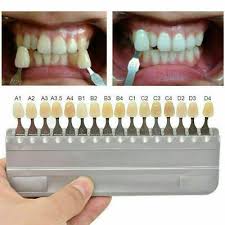
blurry but what is this
Vitapan Shade guide
Specific conditions
discolouration due to extrinsic or intrinsic staining
anomalies caused by developmental disturbances
abnormal spacing between teeth
trauma
Bonded restorations
Bonded restorations use a process of adhesion creating a contact
of one material to another.
Non-Bonded restoration
Restorations are retained by mechanical retention between
restorative materials and tooth structure.
Direct restoration
applied to the tooth while the material is pliable/flexible. Some examples are amalgams, composites, glass ionomer, etc
indirect restoration
created in the lab, also known as castings. Can be gold or ceramic, final cast is either bonded or cemented into place.
Restoration completed in 1 visit
direct
restoration completed in 2 visits
indirect
CAD/CAM
Indirect restoration without the wait, computer-aided design and manufacturing, can make crowns, bridges, veneers, inlays, onlays, and surgical guides
what type of restoration is this
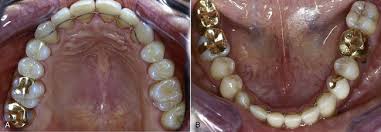
indirect
Inlay
covers portion of occlusal and proximal surfaces (INNNNNlay)
Onlay
Covers proximal and most or all occlusal surfaces (ONNNlay)
This restoration would be?
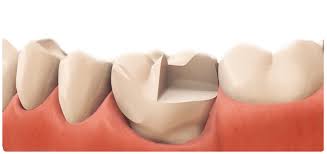
Onlay

this restoration would be?
inlay
Veneers
Thin, tooth coloured material, applied to facial surface of tooth.
Direct technique uses ____ material to create a veneer
composite resin
indirect technique uses ___ material and is ___ to the tooth
porcelain, cemented
tissue contouring
electrosurgery or laser to enhance the appearance of gingival tissues due to excessive or inflamed gums
Bleaching
Free radicals, breakdown of pigment during tooth bleaching procedures
tooth whitening
abrasive agents contained in a dentifrice to remove extrinsic stain
Chemicals involved in tooth whitening
Hydrogen peroxide, carbamide peroxide, sodium perborate
Carbamide peroxide or Hydrogen peroxide
Various concentrations: 10%, 16%, and 22% for patient applied techniques
sodium perborate
weak oxidizing agent, once used with water to whiten non-vital teeth
hydrogen peroxide
high concentrations are added for non-vital teeth
whitening techniques
non-vital bleaching, vital bleaching in office, home whitening.
vital whitening
one full arch at a time
non-vital whitening
one tooth at a time
Adverse effects of tooth whitening
thermal hypersensitivity (vital teeth)
tissue irritation
root resorption due to heat used during application (non-vital tooth)