Orbits of Planets and Satellites
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:56 PM on 6/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
Derive Kepler’s Third Law
1. Equate the equations for centripetal force and gravitational force
2. Simplify for v squared
3. Substitute v for 2πr/T
4. Then rearrange for r cubed over T squared
2
New cards
Derive the straight line equation for T and r
How do you get to it?
How do you get to it?
1. Start from Kepler’s third law
2. Take logs of both sides
3. Split the logs on the LHS
4. Rearrange for T as the subject
5. Divide both sides by 2
log(T) = 1.5log(r) - 0.5log(GM/4π^2)
3
New cards
What information can we get from the gradient and from the y-intercept of the logarithmic graph?
gradient - proves Kepler’s law
y-intercept - can be used to calculate the mass of source mass
y-intercept - can be used to calculate the mass of source mass
4
New cards
Define escape velocity
The minimum speed an object must travel at to escape the gravitational field at the surface of a mass
5
New cards
What are the features of a satellite in a geostationary orbit?
* orbits directly above the equator
* has an orbital period of 24 hours
* has an orbital period of 24 hours
6
New cards
What is common to all satellites in geostationary orbits and why?
They all have the same orbital radius because orbital radius depends on mass of the earth and the time period not mass of the satellite
7
New cards
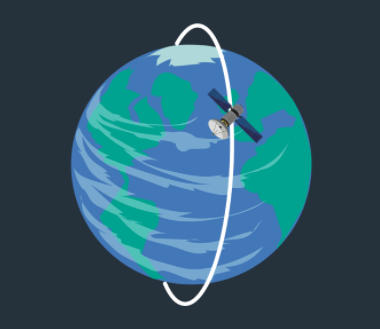
What is a polar orbit?
a (low earth) orbit that always passes over the North and South poles
8
New cards
What is a synchronous orbit?
When the orbital period of the satellite is equal to the rotational period of the object that it is orbiting
9
New cards
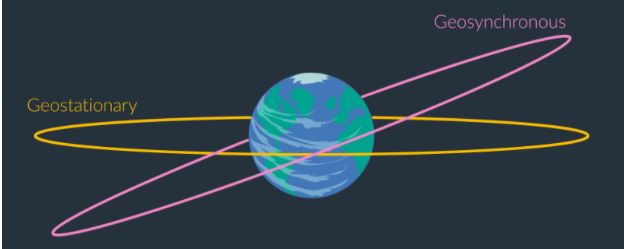
What is a geosynchronous orbit?
an 24 hour orbit that is similar to geostationary but is tilted away from the equator
it appears to move across the sky
it appears to move across the sky
10
New cards
How do you calculate the velocity of a satellite in orbit?
From equating centripetal force to gravitational force and rearranging for v
11
New cards
How do you calculate the total energy of a satellite in orbit? What is it?
Add the satellite’s kinetic energy and potential energy
\-(GMm)/2r
\-(GMm)/2r
12
New cards
How do you calculate the escape velocity of a satellite in orbit?
equate kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy then rearrange for v
where r is the radius of the satellite’s orbit (distance from centre of source mass to satellite)
where r is the radius of the satellite’s orbit (distance from centre of source mass to satellite)
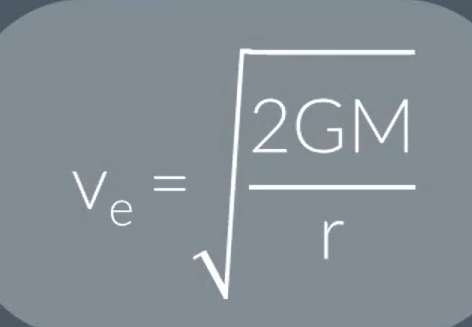
13
New cards
What are geostationary satellites useful for and why?
sending TV and telephone signals because they are always above the same point on the Earth, plane of aerials or transmitters don’t need to be alterred
14
New cards
What is a low earth orbit?
a satellite that orbits the Earth at a low altitude (up to 2000km) so it appears to move aorund the sky
15
New cards
What are low-orbit satellites useful for and why?
* monitoring the weather, making observations about unreachable places
* because they are closer and so require less powerful transmitters
* because they are closer and so require less powerful transmitters