Types of Joints, Tendons and reflex arc
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Structural Joint Classification Categories (3)
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, Synovial
Types of fibrous joints (3)
Suture, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis
Types of cartilaginous joints (2)
Symphysis, Synchondrosis
Fibrous joints
Fibrous connective tissue joins 2 bones
Suture
Fibrous joint: found between the bones of the skull
Syndesmosis
Fibrous joint: bones held together by a band of connective tissue e.g. joints between radius-ulna
Gomphosis
Fibrous joint: Periodontal ligament binding teeth into mandible/maxillae; no movement
Cartilaginous joints
Fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage joins 2 bones
Symphysis
Cartilaginous joint: Thin pad of fibrocartilage between 2 bones; eg between pubic bones, between vertebrae
Synchondrosis
Cartilaginous joint: found between ribs and sternum
Synovial joints
Joint capsule between articulate bones (typically long bones), containing synovial fluid; extensive movement
Gliding
Synovial joint: Flattened or slightly curved articulating surfaces; sliding movement; e.g. intercarpal and intertarsal joints
Hinge
Synovial joint: Concave surface of one bone articulates with a depression of another; bending motion in one plane; e.g. elbow, joints of digits
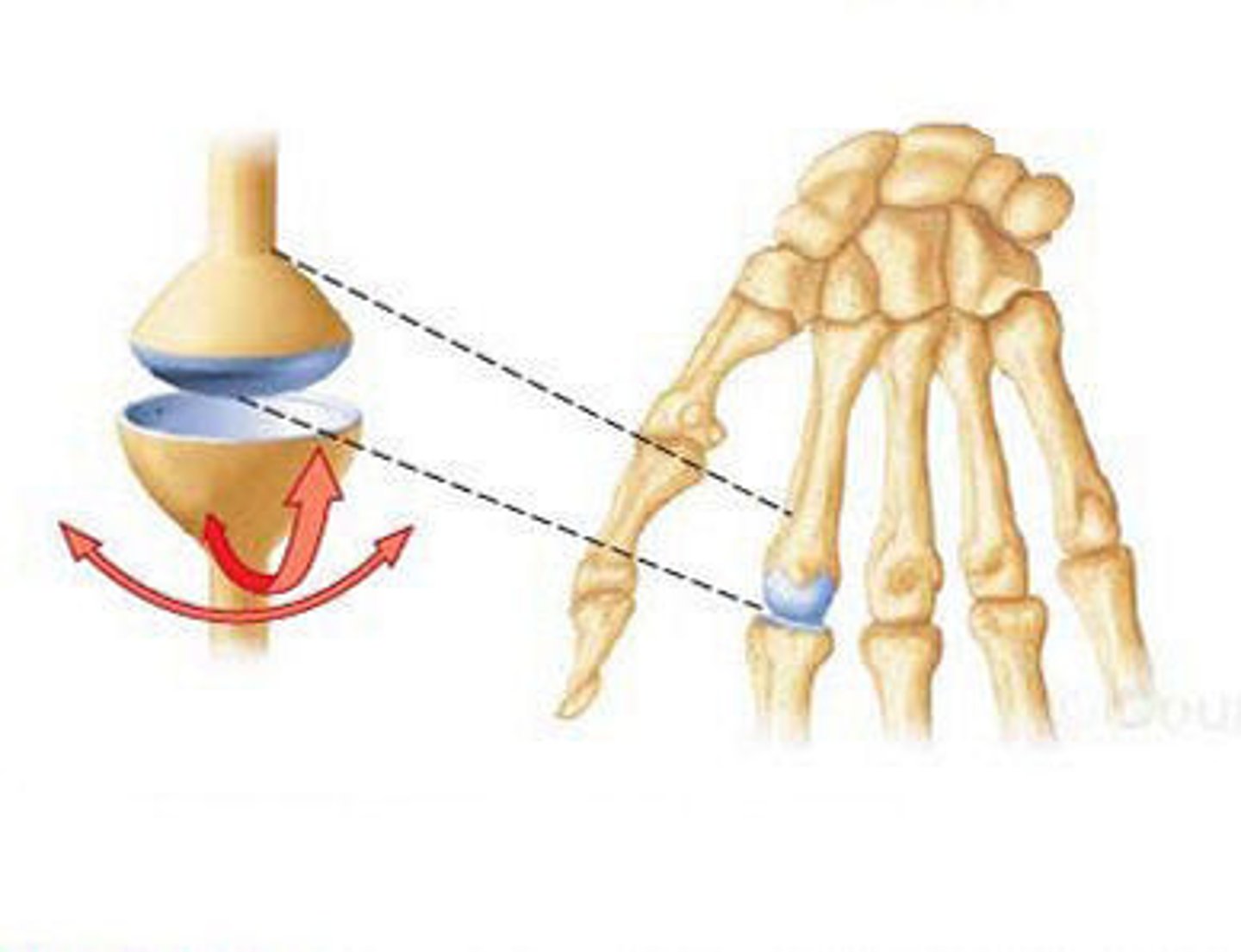
Pivot
Synovial joint: Conical surface of one bone articulates with a depression of another; rotation about a central axis rotational movement; e.g. proximal radioulnar joint, first vertebrae and skull
Condyloid
Synovial joint: Oval condyle of one bone articulates with cavity of another; biaxial movement (moves in 2 directions); e.g. wrist
Saddle
Synovial joint: Concave and convex surface on each articulating bone; wide range of movement; biaxial movement; e.g. carpometacarpal joint at base of thumb.
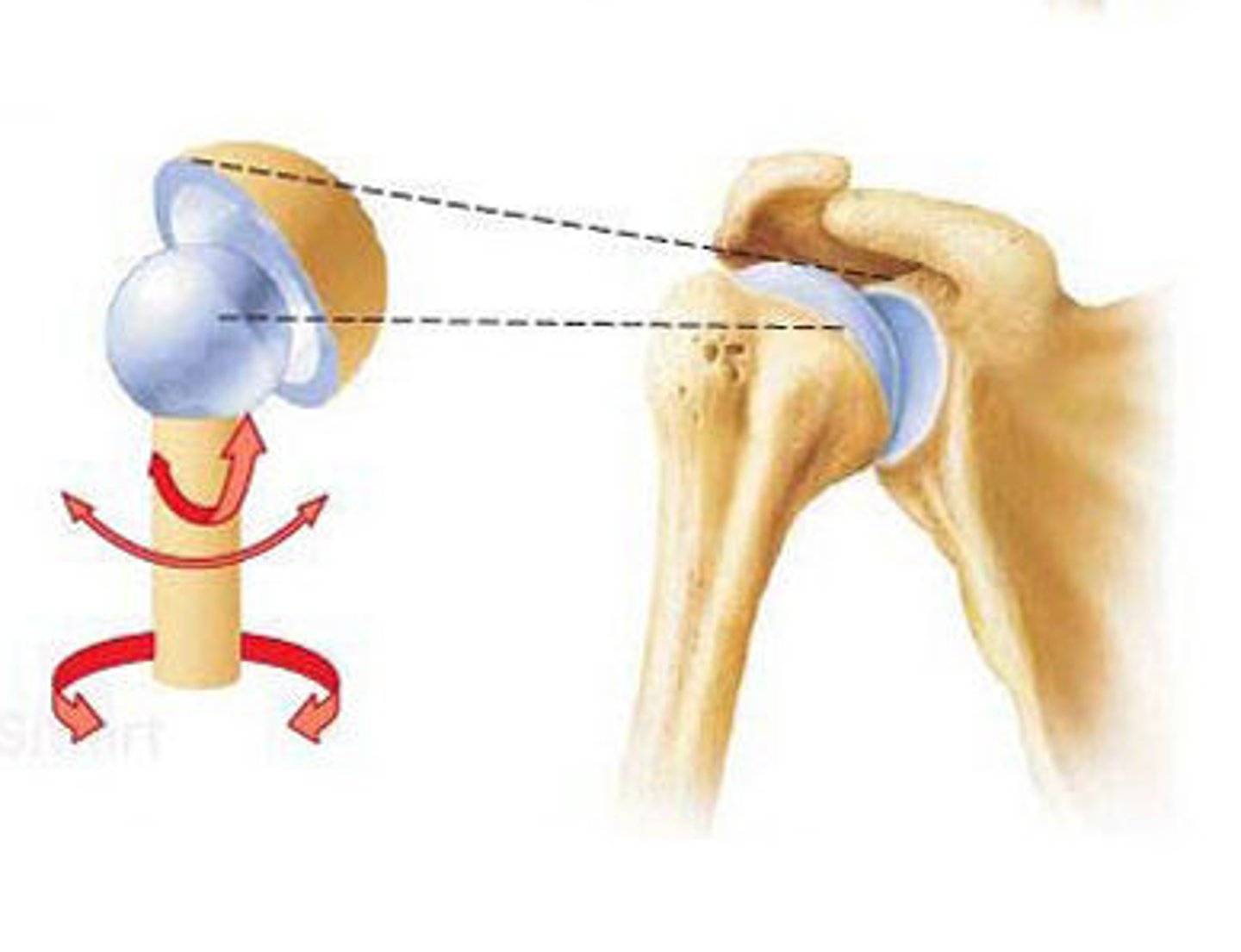
Ball and Socket
Synovial joint: Rounded convex surface of one bone articulates with cuplike socket of another; movement in all planes and rotation; e.g. hip joints and shoulder joints
Types of Synovial Joints (6)
Condyloid, Hinge, Pivot, Saddle, Ball & Socket, Gliding
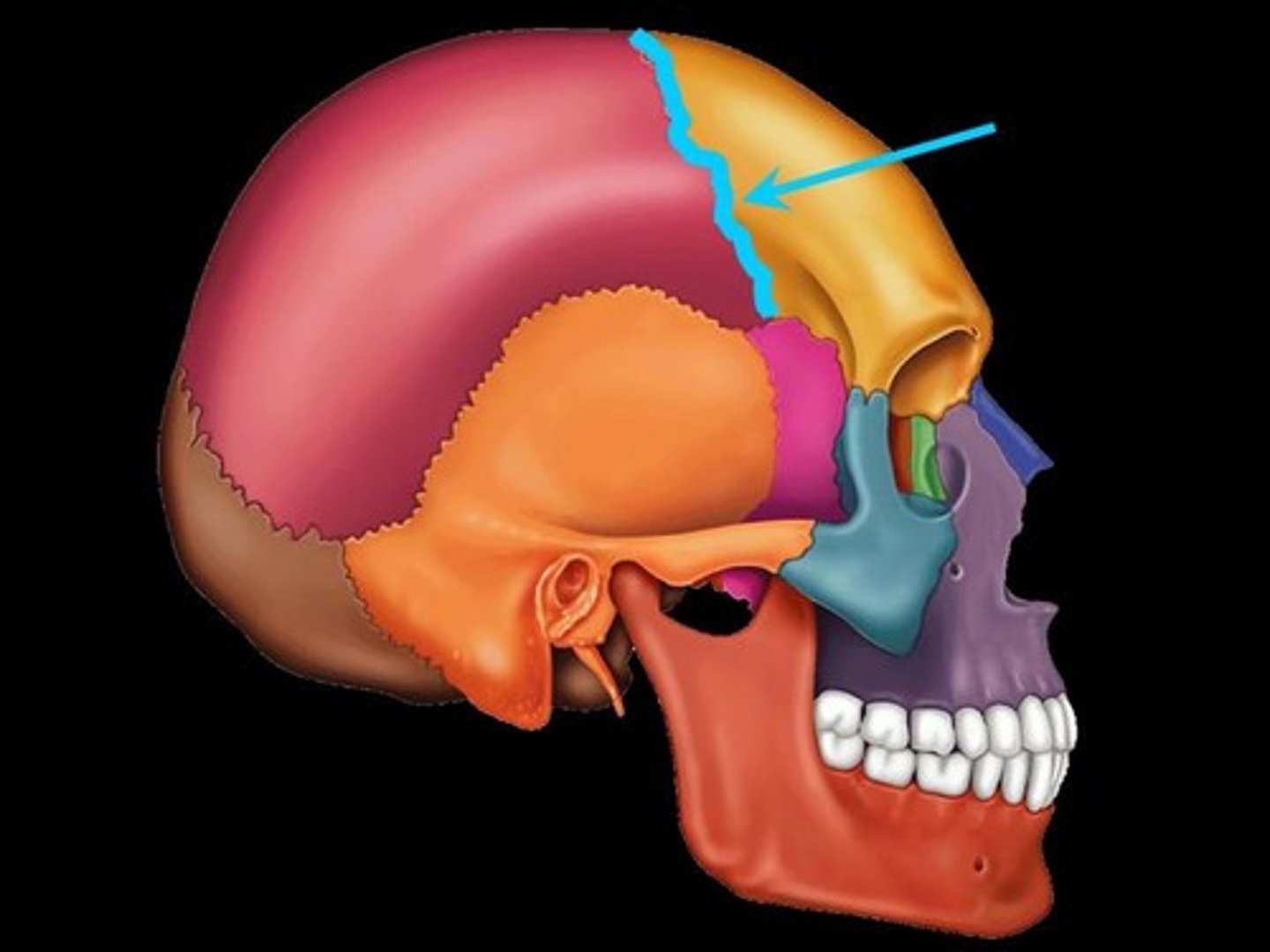
Fibrous Joint (Suture)
type of joint indicated in image
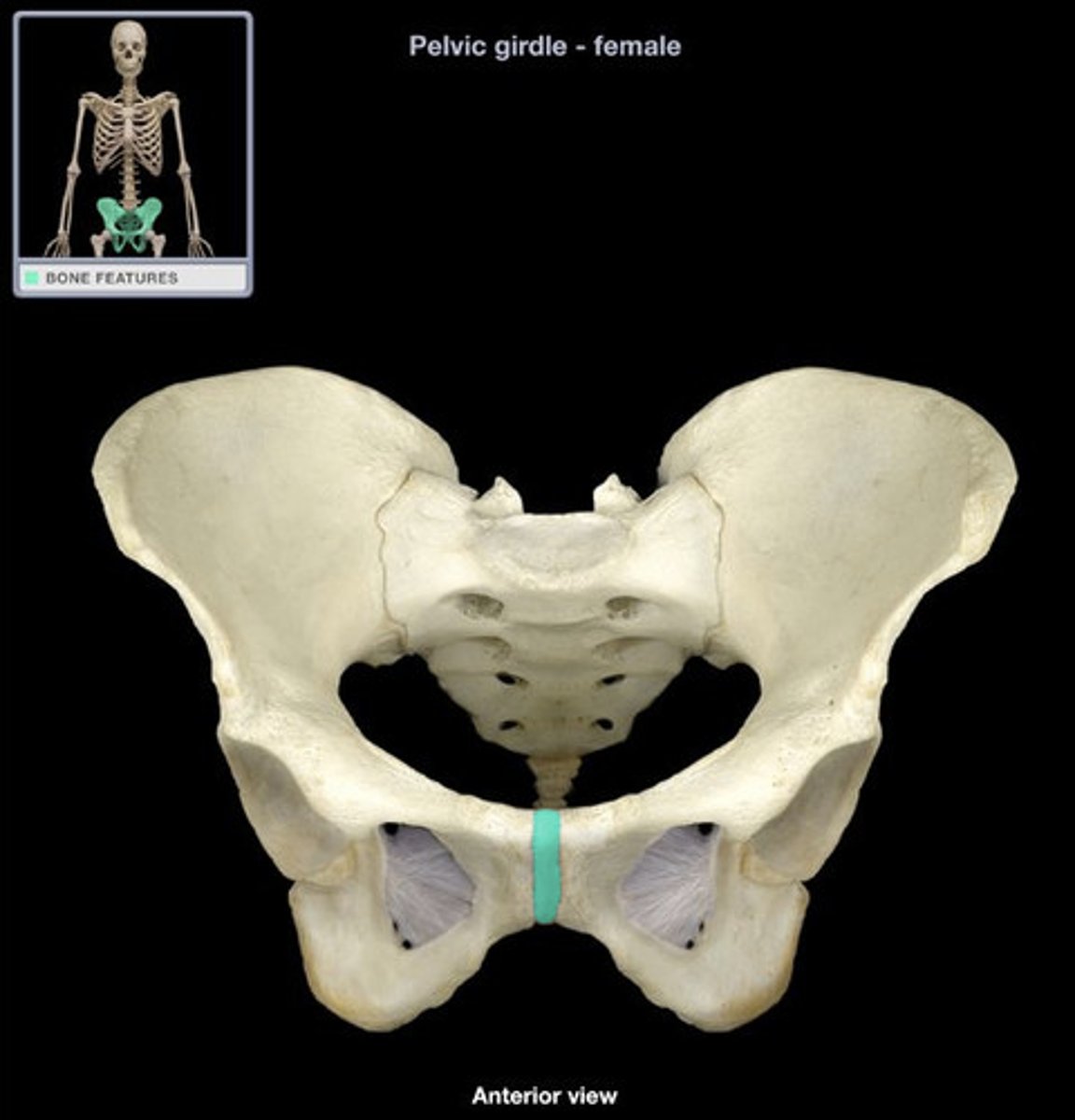
Cartilaginous Joint (Symphysis)
type of joint indicated in image
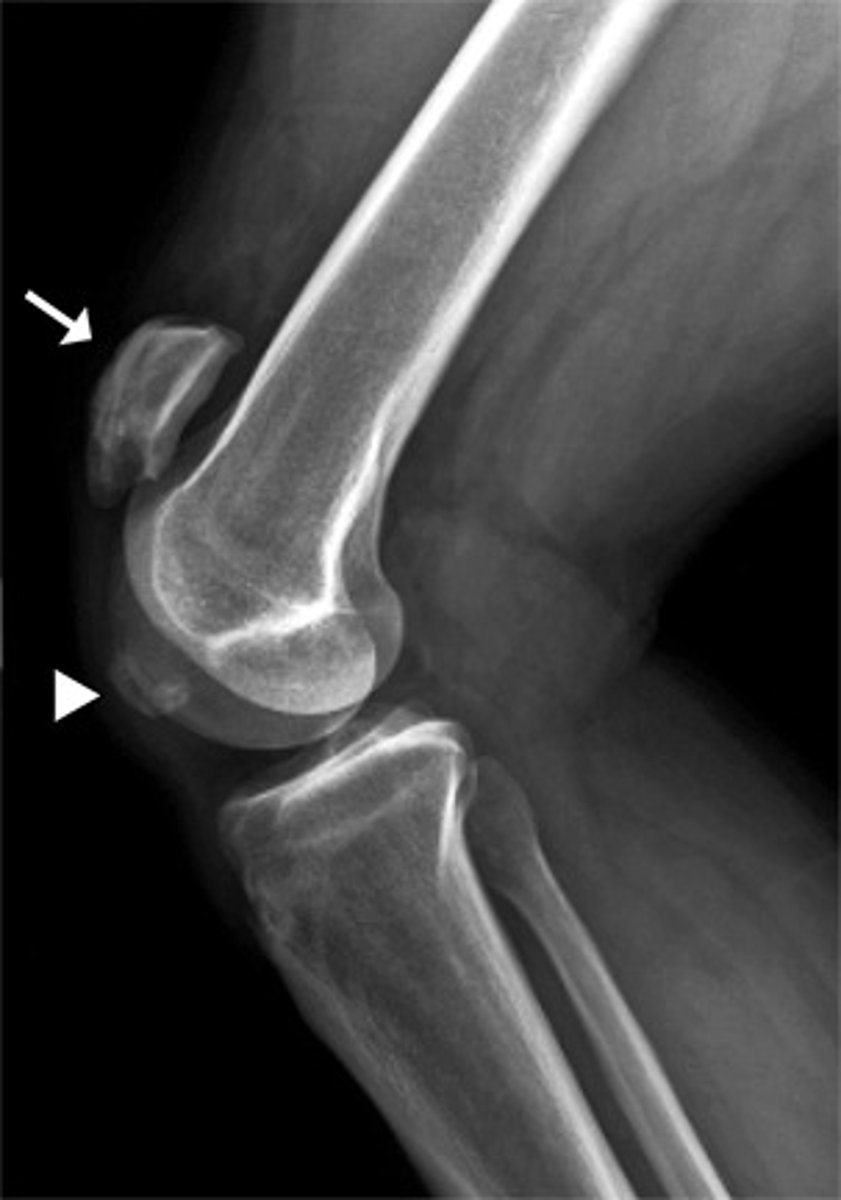
Synovial (Hinge)
type of joint indicated in image
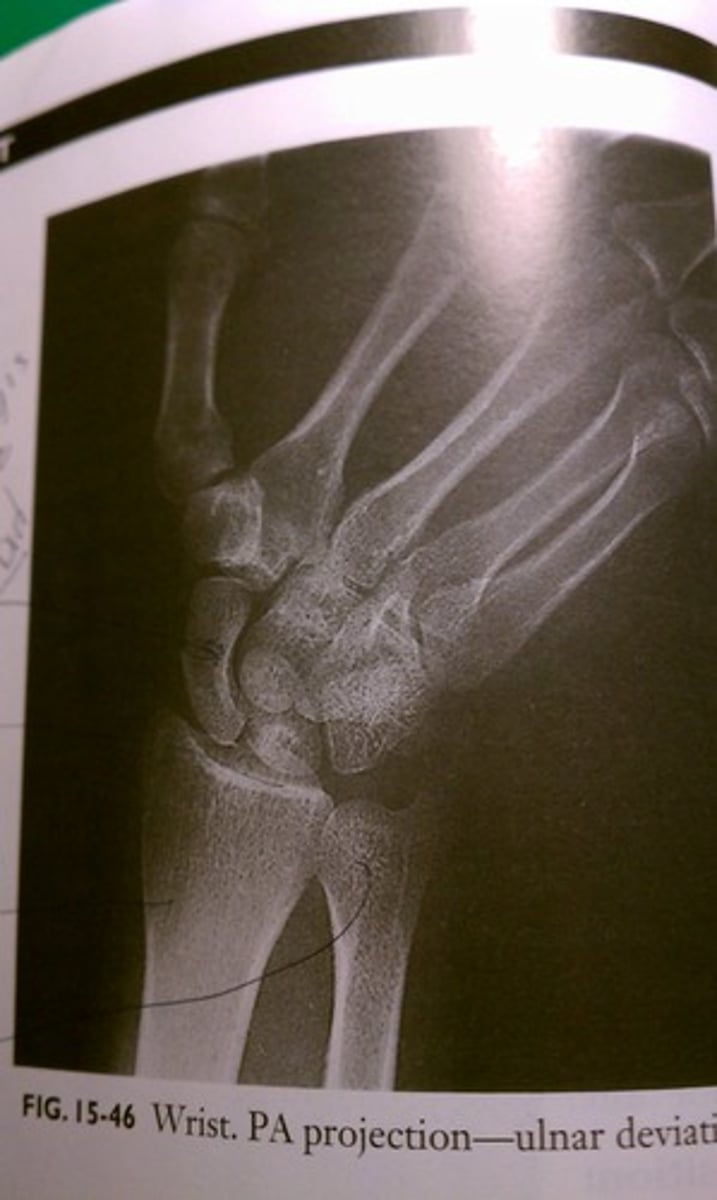
Synovial (Gliding)
type of joint indicated in image
Synovial (Pivot)
type of joint indicated in image

Synovial (Saddle)
type of joint indicated in image
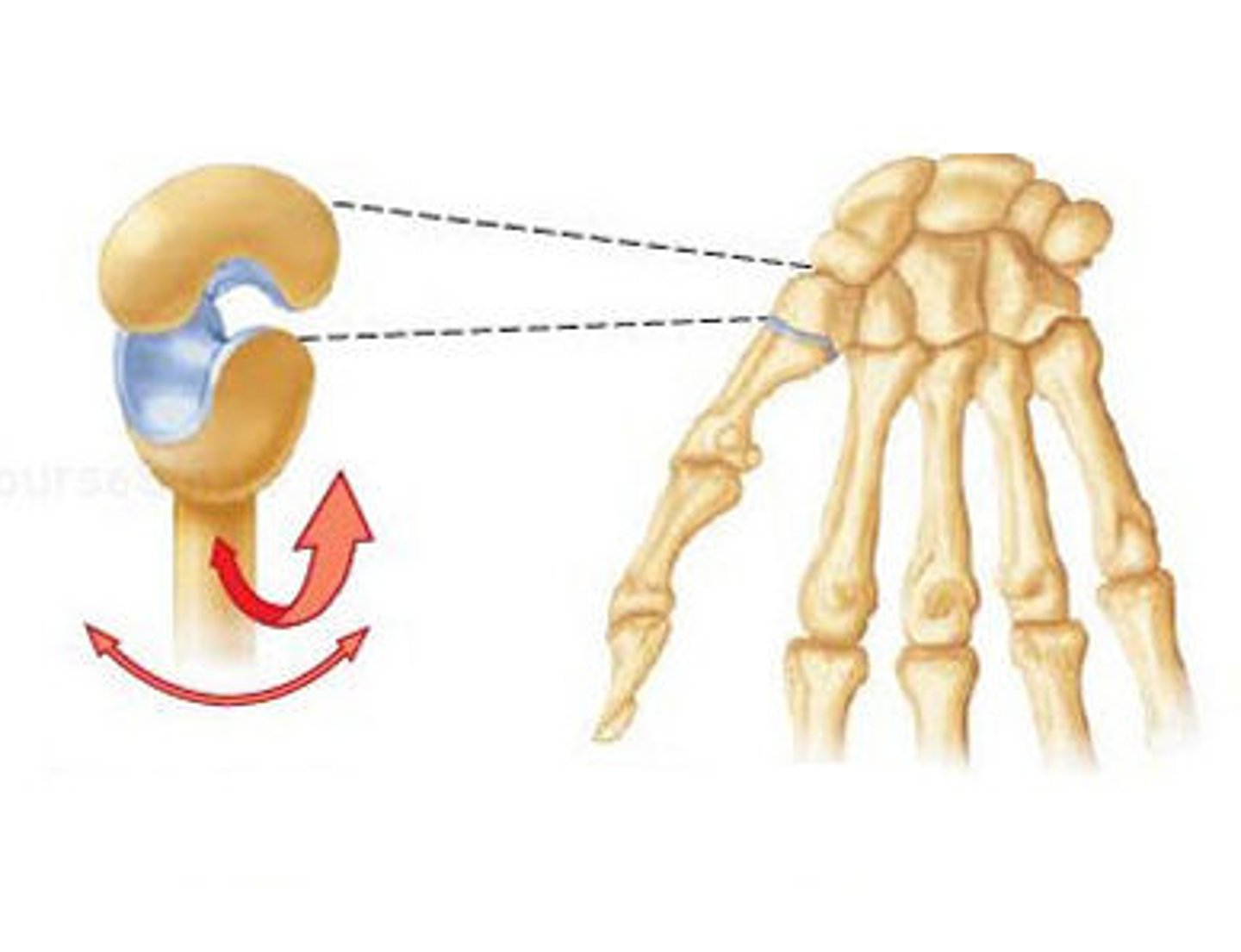
Synovial (Condyloid)
type of joint indicated in image
Synovial (Ball and Socket)
type of joint indicated in image
Subluxation
reduced area of contact between articular surfaces
Tendons
Attach muscle (usually) to bone
Found at either end of the muscle and non-contractile
Aponeurosis
Flattened tendon
Most commonly associated with flat muscle
Attach muscle to soft tissue
Origin:
proximal to muscle attachment
Insertion
distal from muscle attachment
Ligament
attaches bone to bone
What does tendons attach?
It attaches muscle to bone
Aponeurosis
flattened tendon attached to soft tissue rather than bone
reflex arc
Sensory nerve (muscle) detects stretch and tells spinal cord
Motor nerve from spinal cord passes message to contract
Neuromuscular junction - synapse where motor nerve communicates with skeletal muscle
Neuromascular junction
the synapse where the motor nerve communicates with the skeletal muscle
muscle stain
overstretched, torn or twisted muscle
Paralysis
muscle without functioning motor nerve supply so can’t contract
Spasticity
functioning motor nerve but controls from the brain aren’t working
Atrophy
wasting’ of the muscles through inactivity
Hypertrophy
individual myocytes enlarge