Topic 1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
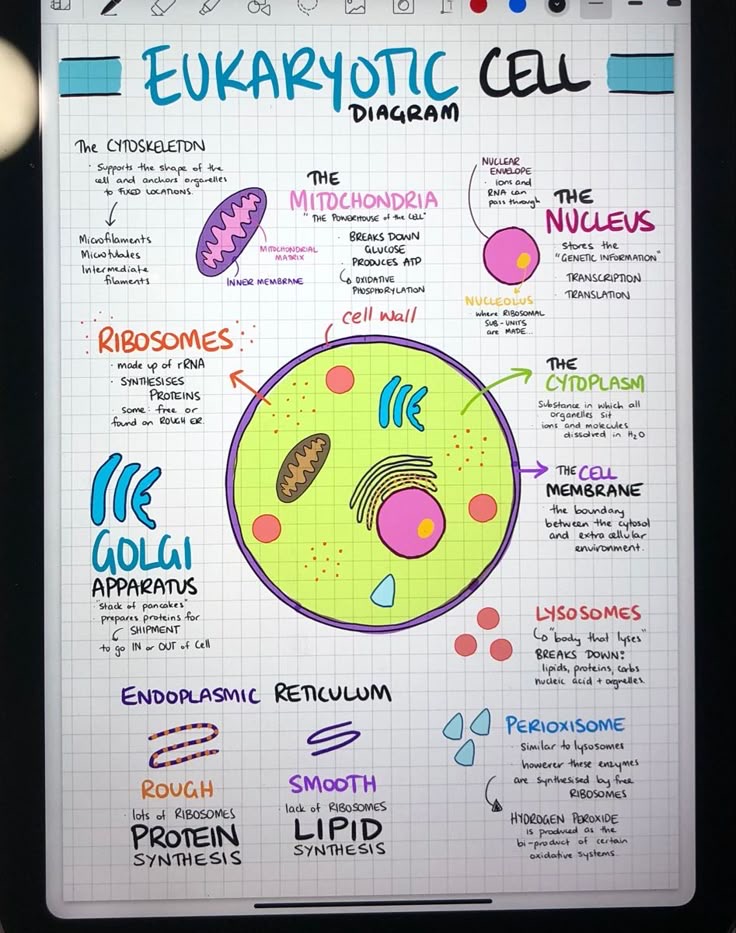
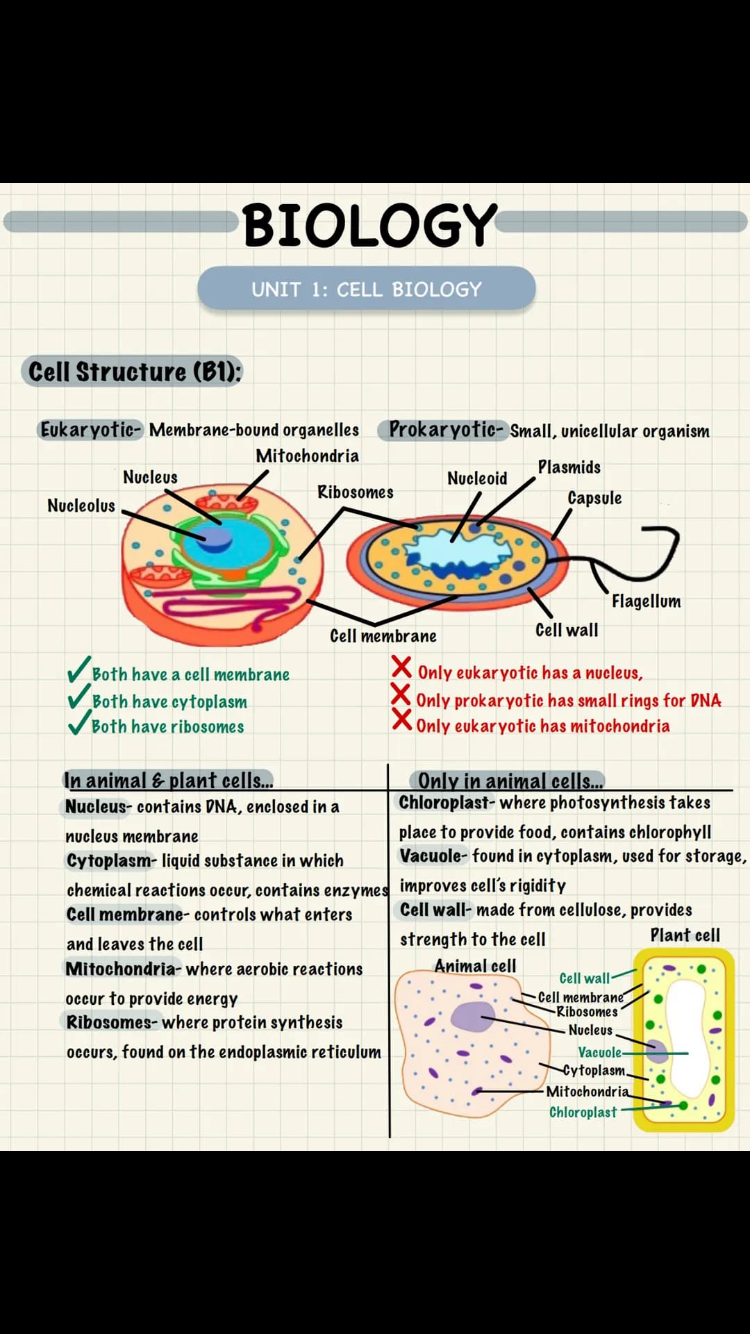
What are eukaryotic cells
Animal or plant cells with genetic material (DNA) is enclosed in a nucleus
What are prokaryotic cells? Include genetic material, nucleus and its size
cells (e.g bacteria) with genetic material or enclosed in a nucleus. Its size is much smaller than eukaryotic
Genetic material in a prokaryotic cell
A single loop of DNA
May also have one or more plasmids
What’s the function of the nucleus
Nucleus: Control cell activity
What’s the function of the cell membrane?
control the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration→ releases energy from glucose
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance where chemical reactions take place
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
What are the additional parts of a plant cell?
Cell wall, chloroplasts and permanent vacuole
What is the cell wall made of and what’s the function of it for a plant?
the cell wall contains cellulose→ it strengthens the cell (algal cells have one too)
What is the function of the chloroplasts in a plant cell?
Contains chlorophyll→ absorbs light for photosynthesis to make glucos
What is the permanent vacuole filled with? And what’s its function?
It is filled with cell sap→ help plant cell turgid/support the plant/ improve rigidity
What do plant cells and bacteria cells have in common
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA ribosomes.
Cell wall and plasmids, it doesn’t have mitochondria or a nucleus or chloroplasts and a vacuole
Compare the structure of a red blood cell (RBC) with the structure of a plant cell (6 marks)
: Both have cytoplasm, cell membrane
RBC has no cell wall, plant cell does
RBC does not contain chloroplasts or chlorophyll, plant cell doesRBC has no (permanent) vacuole, plant cell does
RBC contains haemoglobin, plant cell don't
Specialisation of sperm cells
function of flagellum
Function of the mitochondria
How does it break into the egg?
Sperm cells :
flagellum to swim to the egg
Iots of mitochondria to release energy from swimming.
Digestive enzymes to break into the egg
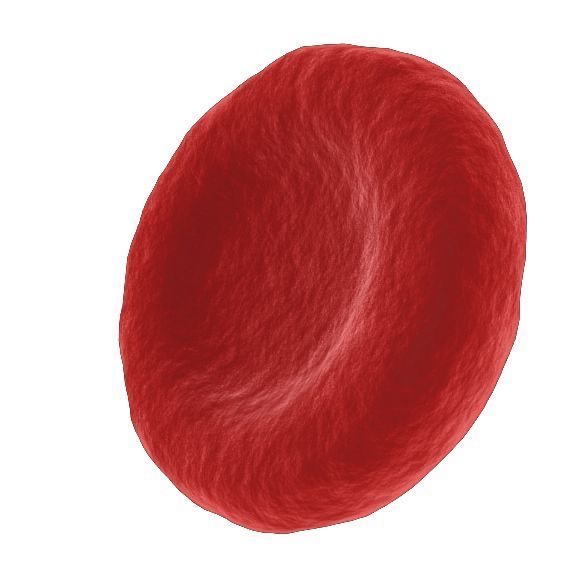
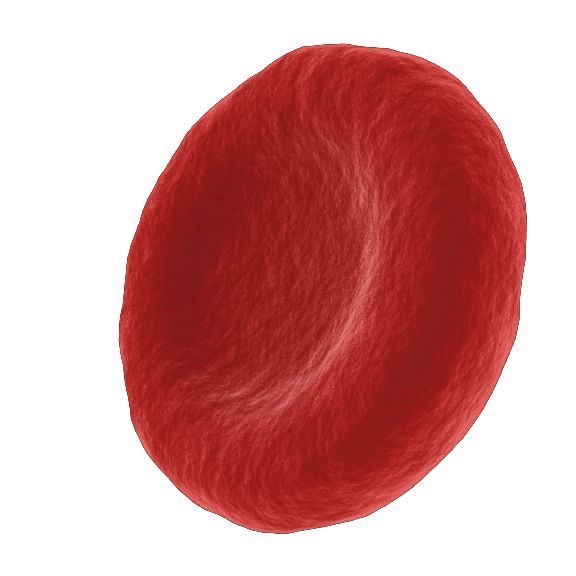
Red Blood cells specialisation
nucleus
Haemoglobin
Shape
Red blood cells :
no nucleus, so more room for oxygen
haemoglobin binds to oxygen molecules.
bi concave shape to increase surface area.