KNPE 400
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Kinesiologist Core Competencies
Foundational Knowledge
Professional Practice: Assessment
Professional Practice: Intervention
Professionalism and Ethical Conduct
Communication and Collaboration
Ongoing Professional Development
What does professionalism encompass?
Respect the rights and dignity of all individuals who seek my services or with whom I work.
Act in a compassionate and trustworthy manner in all aspects of my services.
Exercise sound professional judgment while abiding by legal and ethical requirements.
Demonstrate integrity during interactions with colleagues, other health care providers, students, faculty, researchers, the public, and payers for the enhancement of patient care and the advancement of the profession.
Enhance my practice through lifelong acquisition and application of knowledge, skills, and professional behaviour.
Participate in efforts to meet needs of local, national, and global communities.
Therapeutic Alliance
The working relationship between the patient and therapist
Established by collaboration, communication, therapist empathy and mutual respect
A strong therapeutic alliance positively influences treatment outcomes such as improvement in symptoms, health status, and patient satisfaction with care
Effective clinician-patient communications can:
Support better history-taking, diagnoses and clinical decisions
Increase a patient's adherence to recommendations and follow-ups
Help patients to self-manage a chronic condition
Influence patients to adopt preventive health behaviours
Improve patient satisfaction and experience of care
What is regulation?
Professional regulation is the framework under which health professions are regulated.
Supported by the laws that give or limit rights and assign responsibilities to the people that are subject to.
Defines the philosophical framework for professional regulation in a jurisdiction
Sets out the roles, rights and responsibilities of the government, regulatory agencies (colleges), registrants of the agencies and the public.
What makes a profession unregulated?
The profession is not listed in the RHPA.
Does not have a college that protects the public from the members of that profession.
An individual does not have to be a member of a regulatory college to call themselves a member of that profession.
Examples include:
Personal support workers
Physician assistants
Physiotherapy assistants
Athletic therapists
Regulated Health Professions Act (RHPA), 1991
Legislative framework for regulating the scope of practice of health care professions in Ontario.
The RHPA framework is intended to:
Better protect and serve the public interest
Be an accountable system of self-governance
Provide modern framework for the work of health professionals
Provide consumers with freedom of choice
Provide mechanisms to improve quality of care
Practical rules for colleges set out by the Health Professions Procedural Code (HPPC)
registering members
handling complaints
conducting investigations
carrying out discipline hearings
handling fitness to practise hearings
quality assurance program
patient relations program
mandatory reporting
funding for victims of sexual abuse by members
appeal processes regarding registration and complaint decisions
Profession-specific acts
Establish each health profession’s college and its governing council.
Defines the scope of practice of the profession they govern.
Lists the controlled acts that professions are authorized to perform (if it can perform controlled acts).
Has the Health Professions Procedural Code deemed to be part of them.
Kinesiology Act, 2007
Under the RHPA each professions has its own act
Scope of practice
The practice of kinesiology is the assessment of human movement and performance and its rehabilitation and management to maintain, rehabilitate or enhance movement and performance
Define the restricted titles
No person other than a member shall use the title "kinesiologist", a variation or abbreviation or an equivalent in another language"
Controlled Acts
A kinesiologist can perform zero controlled acts
Representations of qualification
No person other than a member shall hold himself or herself out as a person who is qualified to practise in Ontario as a kinesiologist or in a specialty of kinesiology.
Health Professions Regulatory Advisory Council
An independent body to the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care with a mandate to advise the Minister of a number of items related to the regulation of health professions
Health Professions Appeal and Review Board
Independent third party with a mandate to review registration and complaints decisions of the health regulatory College
Concept of scope of practice
What members of a profession are competent at doing, and legally permitted to do, in a given jurisdiction
A member of the profession may have a personal scope of practice that is of large breadth with respect to the whole profession's scope.
May be relatively narrow with respect to the whole profession's scope.
May include acts outside of usual legal scope for the profession.
Kin scope of practice
The assessment of human movement and performance and its rehabilitation and management to maintain, rehabilitate or enhance movement and performance
Why do we need scopes of pratice?
Each regulated health profession has a statement that describes in a general way what the profession does and the methods that it uses.
Protects the public to ensure that care provided by a practitioner is not beyond the practitioner's skills and knowledge.
Does not prevent others from performing the same activities.
R.Kin modalities and services

Scope of Practice - Physiotherapy
The practice of physiotherapy is the assessment of neuromuscular, musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems, the diagnosis of diseases or disorders associated with physical dysfunction, injury or pain and the treatment, rehabilitation and prevention or relief of physical dysfunction, injury or pain to develop, maintain, rehabilitate or augment function and promote mobility
Overlapping scopes of practice
Physiotherapists, chiropractors and physicians have overlapping scopes of practice for diagnosing low back pain.
Physiotherapists and occupational therapists have overlapping scopes of practice with respect to selecting an appropriate wheelchair for a patient and contributing to a team process for designing custom seating systems.
Physiotherapists and speech-language pathologists have overlapping scopes of practice for assessing and treating patients with swallowing disorders
Physiotherapists, nurses and respiratory therapists have overlapping scopes of practice for managing patients in an intensive care unit who need ventilator support.
Physiotherapists, kinesiologists, chiropractors, massage therapists, physicians, nurses and occupational therapists have overlapping scopes of practice to prevent disorders which affect function.
Almost all healthcare professions have overlapping scopes of practice with regard to communicating with patients in distress, respecting their autonomy and gaining their consent for any assessment or treatment process.
Controlled Acts
Procedures or activities which may pose a risk to the public if not performed by a qualified practitioner.
Considered higher risk and could pose the potential for serious harm
RHPA dictates what regulated professions can do.
14 controlled acts
The 14 Controlled Acts
Communicating to the individual or his or her personal representative a diagnosis identifying a disease or disorder as the cause of symptoms of the individual in circumstances in which it is reasonably foreseeable that the individual or his or her personal representative will rely on the diagnosis.
Performing a procedure on tissue below the dermis, below the surface of a mucous membrane, in or below the surface of the cornea, or in or below the surfaces of the teeth, including the scaling of teeth.
Setting or casting a fracture of a bone or a dislocation of a joint.
Moving the joints of the spine beyond the individual’s usual physiological range of motion using a fast, low amplitude thrust.
Administering a substance by injection or inhalation.
Putting an instrument, hand or finger,
beyond the external ear canal,
beyond the point in the nasal passages where they normally narrow,
beyond the larynx,
beyond the opening of the urethra,
beyond the labia majora,
beyond the anal verge, or
into an artificial opening into the body.
Applying or ordering the application of a form of energy prescribed by the regulations under this Act.
Prescribing, dispensing, selling or compounding a drug as defined in the Drug and Pharmacies Regulation Act, or supervising the part of a pharmacy where such drugs are kept.
Prescribing or dispensing for vision or eye problems, subnormal vision devices, contact lenses or eyeglasses other than simple magnifiers.
Prescribing a hearing aid for a hearing-impaired person.
Fitting or dispensing a dental prosthesis, orthodontic or periodontal appliance or a device used inside the mouth to protect teeth from abnormal functioning.
Managing labour or conducting the delivery of a baby.
Allergy challenge testing of a kind in which a positive result of the test is a significant allergic response
Treating, by means of psychotherapy technique, delivered through a therapeutic relationship, an individual’s serious disorder of thought, cognition, mood, emotional regulation, perception or memory that may seriously impair the individual’s judgement, insight, behaviour, communication or social functioning.
Delegation of Controlled Acts
The act of transferring authority from one practitioner to another to perform a controlled act.
Permitted in order to make delivery of health care more efficient and effective for patients/clients
Must be in the best interests of the patient
Must be safe and effective as if being performed by the person delegating.
Responsibility always remains with the person delegating the act - however you should alway familiarize yourself with the delegation standards of the practitioners you work with.
CKO’s standard for delegation
Controlled acts which under most circumstances would be considered unsuitable for delegation to an R.Kin:
#2, #4, #6, #8, #9, #10, #11, #12, #13
Where is acupuncture in the Controlled Acts?
Controlled Act #2
Healthcare professionals who are authorized to perform acupuncture in Ontario:
Chiropractors
Dentists
Medical doctors
Naturopathic doctors
Nurses
Optometrists
Physiotherapists
Traditional Chinese medicine practitioners
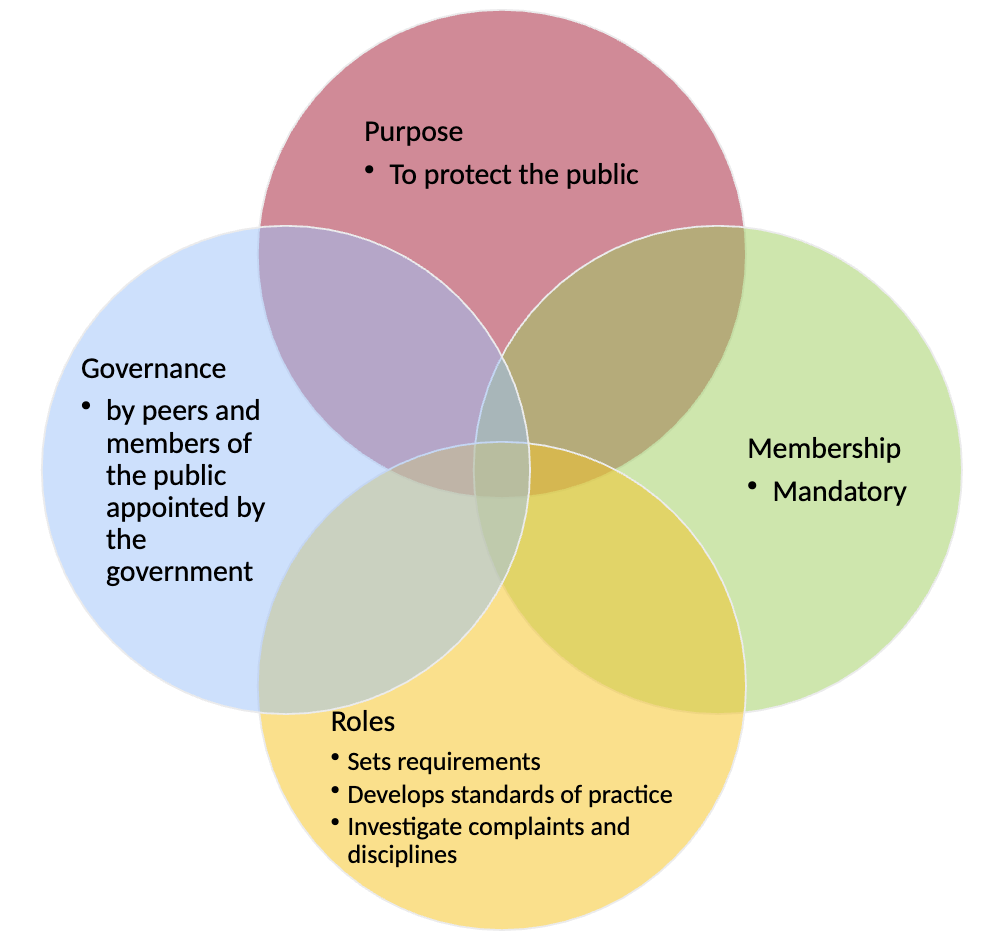
Regulatory Body
Purpose
Protects interest and safety of the public
Created by legislation to regulate the profession of kinesiology in the public interest
Governance
Governed by a council elected by peers and members of the public appointed by the government
Accountable to the public, the Ontario government and members of the College
Membership
Mandatory
Membership requires passing exam
Requires proof of continuing competency Regulatory Body
Roles
Sets requirements for entry to the profession
Develops standards of practice
Receives and investigates complaints about practitioner’s practice and administers appropriate disciplinary action when necessary
Maintains a register of individuals eligible to practice
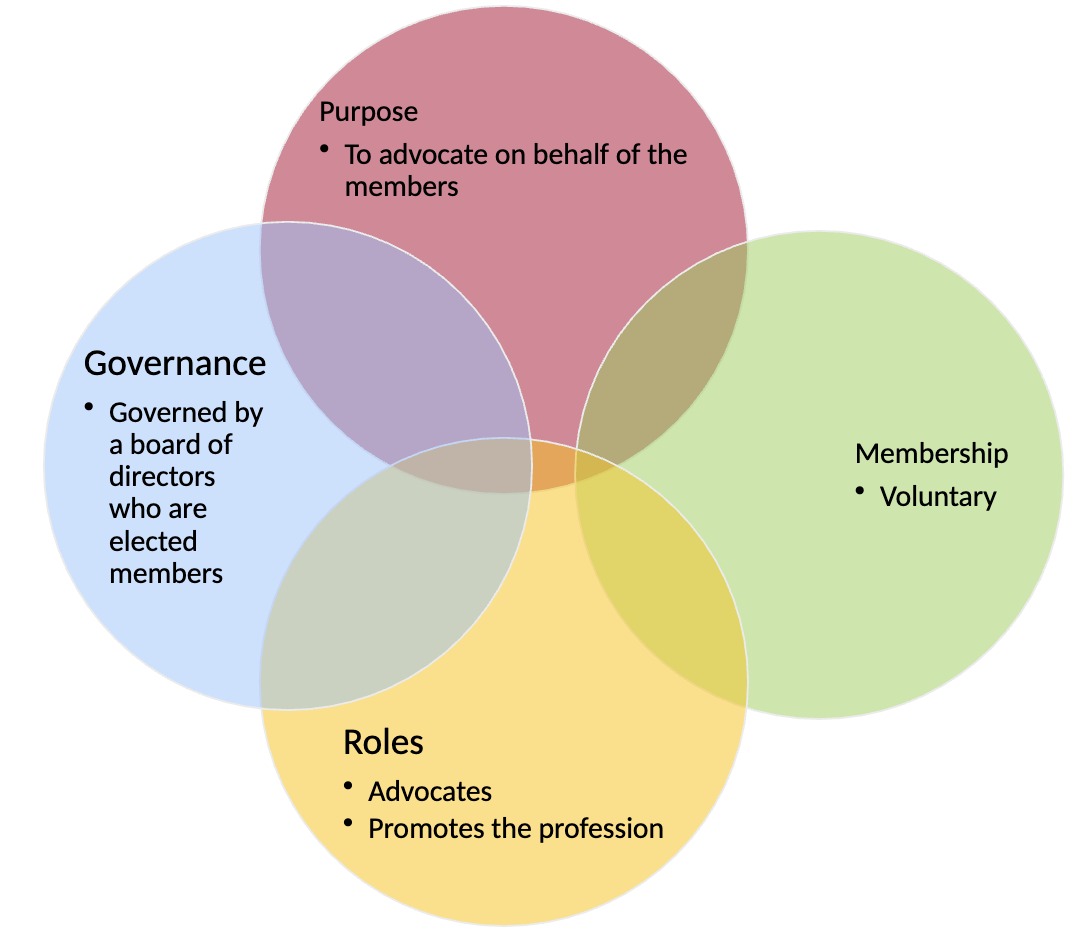
Association
Purpose
To advocate on behalf of the members
Mandate is to advance awareness of the profession and market the profession to:
the public
other professions
Governance
Governed by a board of directors who are elected members
Accountable to the members of the association
Membership
Voluntary
Membership is based on professional designation
Proof of competency not required (membership fees only)
Roles
Advocates with policy makers and the interest of members.
Markets and promotes the profession
Represents the member’s interest by monitoring developments, which may impact scope of practice, employment opportunities and enhancing relationships with related professions
College of Kinesiologists of Ontario
Regulatory body that oversees kinesiologists working in Ontario.
Exists to protect the public.
Receives its authority from the Kinesiology Act, 2007 and the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991.
Sets the requirements for entry-level practice
Maintains a list of individuals qualified to practice kinesiology (public register)
Develops rules and guidelines for kinesiologists’ practice and conduct (including code of ethics)
Investigates complaints about kinesiologists and disciplines when necessary
Requires kinesiologists to participate in a program that helps ensure that their knowledge and skills are up-to-date, and monitors that participation
Ontario Kinesiology Association (OKA)
OKA's Vision
To have kinesiologists recognized as the authority on exercise and human movement and the preferred provider of practical, applied and effective exercise and physical activity solutions for the prevention and management of injury, disability and chronic disease, and the improvement of overall health and performance.
OKA's Mission
To be the voice for kinesiologists in Ontario
Assist in the growth and development of kinesiology and kinesiologists in Ontario
College vs Association

Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
A federal statute that governs the collection, use and disclosure of personal information in the course of commercial activities. This statute applies to all physiotherapists engaged in private practice and for some physiotherapists working in the public sector.
Created in 2004 and revised in 2019
“People have the right to access their personal information held by an organization. They also have the right to challenge its accuracy. Personal information can only be used for the purposes for which it was collected. If an organization is going to use it for another purpose, they must obtain consent again. Personal information must be protected by appropriate safeguards.”
Substantially Similar
Provincial laws that may apply instead of an act - Legally, "substantially similar" means that two things are alike enough to be considered the same for a legal purpose, but the exact meaning is context-dependent and not a bright-line rule.
PIPEDA - 10 Fair information principles
Accountability
Identifying purposes
Consent
Limiting Collection
Limiting Use, Disclosure, and Retention
Accuracy
Safeguards
Openness
Individual Access
Challenging Compliance
Federal Privacy Act
Created in 1985 and amended in 2019
Purpose: “is to extend the present laws of Canada that protect the privacy of individuals with respect to personal information about themselves held by a government institution and that provide individuals with a right of access to that information.”
The federal government does run health care in a few selected domains
Department of National Defence
Correctional Service of Canada
Canada’s anti-spam legislation (CASL)
Title of Act: An Act to promote the efficiency and adaptability of the Canadian economy by regulating certain activities that discourage reliance on electronic means of carrying out commercial activities, and to amend the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission Act, the Competition Act, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act and the Telecommunications Act
Aim of the Act:
To protect consumers and businesses from the misuse of digital technology, including spam and other electronic threats.
To help businesses stay competitive in a global digital marketplace
Don’t be a spammer, get consent!
Don't send messages without consent.
Make sure you provide an opportunity for clients to say no to your commercial electronic messages.
Clearly identify yourself and your organization.
Your business name and the name anyone on whose behalf you’re sending the message
A current mailing address and either a phone number, email or website address
An unsubscribe mechanism in accordance with subsection 11(1) of CASL
Be truthful in advertising (for example, specify whether or not taxes are included)
Personal Health Information Protection Act of Ontario (PHIPA)
Ontario’s health-specific privacy legislation.
Ontarians have the right to privacy.
Governs how personal health information may be collected, used and disclosed within the health sector (such as identifying information about an individual that relates to their physical or mental health) by Health Information Custodians (HICs).
Regulates health information custodians.
Creates a consistent approach to protecting personal health information across the health sector.
Designed to give individuals greater control over how their personal health information is collected, used or disclosed.
Patients have the right to know the purpose of collection, use or disclosures of their personal health information and have the ability to withhold or withdraw their consent for a particular purpose, including for the provision of health care.
PHIPA: Terms
Collect
Gather, acquire, receive, or obtain the information by any means from any source.
Use
View, handle or otherwise deal with the information.
Disclose
Make the information available to another health information custodian or another person.
PHIPA: Requirements & Provisions
Requires health information custodians to obtain consent before personal health information is collected, used or disclosed.
Provides individuals with the right to access and request a correction to their personal health information.
Provides a means for independent review and resolution of complaints through the Office of the Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario (IPC) when privacy rights relating to personal health information have been violated.
Health Information Custodian (HIC)
A person who operates an organization that delivers healthcare as a solo practice, group practice, or organization (e.g., a hospital or long-term care home) that has a reason to know personal health information.
Responsible for collecting, using and disclosing personal health information on behalf of clients. A HIC is generally the institution, facility, private practice or health practitioner that provides health care.
Each health facility must have a HIC appointed, who is responsible for the privacy policies of the facility. If you are a sole practitioner, you are the HIC for your patient’s health records.
Agent of a HIC
"a person that, with the authorization of the custodian, acts for or on behalf of the custodian in respect of personal health information for the purposes of the custodian, and not the agent’s own purposes..."

HIC Exceptions
An Aboriginal healer who provides traditional healing services to Aboriginal persons or members of an Aboriginal community.
An Aboriginal midwife who provides traditional midwifery services to Aboriginal persons or members of an Aboriginal community.
A person who provides treatment solely by spiritual means or by prayer.
PHIPA - Personal Health Information (PHI)
Information that can identify an individual (or can be combined with other information to identify an individual) and that relates to:
The physical or mental health of the individual, including the individual’s family health history
The health care provided to the individual (including identifying the individual’s health care provider).
Payment for the health service or eligibility for health care services
An individual’s health card number
The donation or testing of an individual's body part or bodily substance
The identification of the individual’s substituted decision-maker
Non-health care information (e.g., home contact information) mixed in with other personal health information (“mixed records).
PHIPA Principle #1: Accountability
HICs must take reasonable steps to ensure a number of things, including that records are kept in a manner that ensures that legislation and professional standards are respected
PHIPA Principle #2: Identifying purpose
HICs and their agents must ensure that the purpose for which they routinely collect, use, disclose, or retain PHI is clear to the individuals whose PHI they are managing.
PHIPA Principle #3: Informed consent
When PHI is being collected, used or disclosed, there must be informed consent, either by the individual whose PHI it is, or by their substitute decision-maker (SDM) if the individual is not capable of making the decision autonomously.
PHIPA Principle #4: Limiting collection
HICs must ensure that all forms of PHI are only collected for:
the purposes for which they are required
the purposes for which individuals provide consent.
PHIPA Principle #5: limiting, use, disclosure and retention
The legally permitted uses of the PHI are:
for the purposes for which the PHI was created or collected
for planning, delivering or monitoring services for which the custodian allocates funding or other resources
for risk management or other activities to maintain quality of care
for educating agents to provide health care
for obtaining payment, verifying or reimbursing claims, etc.
for research conducted by the custodian, subject to specific restrictions
The legally permitted disclosures of the PHI are:
within the circle of care
outside the circle of care with the consent of the patient
to the SDM of an incapable person
within the organization for certain audit or accreditation purposes
to a "successor" (the person taking over as HIC), with an attempt to gain consent if a planned succession and otherwise, with an attempt to contact patients as soon as possible to inform them of the succession
HICs are responsible for ensuring that retention policies and standards are followed (and are reasonable, legal, etc.).
PHIPA Principle #6: Accuracy
HICs are responsible for ensuring that reasonable steps are taken to ensure records are accurate, complete and up-to-date.
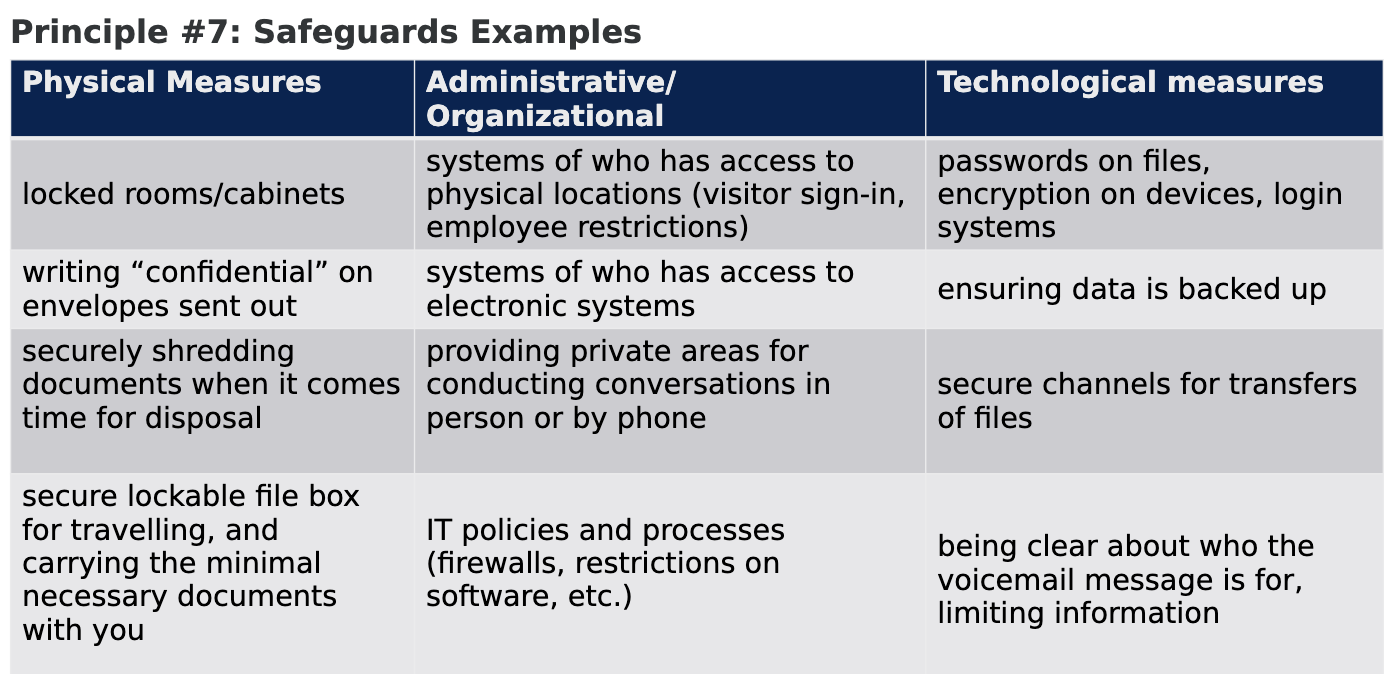
PHIPA Principle #7: Safeguards
HICs must take reasonable steps against theft, loss and unauthorized use or disclosure and to ensure that the records containing the information are protected against unauthorized copying, modification or disposal.
PHIPA Principle #8: Transparency
HICs must display or make available a written public statement about their privacy policies and patients'/clients' rights.
Obligations under PHIPA - Examples of privacy breaches:
Records are seen by someone who should not see them
Email, text messages, or phone messages are sent to the wrong person or are intercepted.
Paper records are stolen
Electronic records are accessed by people who should not have access.
Conversations are overheard by people outside the 'circle of care'
PHIPA Principle #9: Individual Access
Custodian must provide individuals with access to their personal health information upon request, with rare exceptions, and a valid request for access can be oral or in writing.
PHIPA Principle #10: Challenging Compliance
There are multiple powers granted to the Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario (IPC-O) and regulatory health colleges to investigate complaints from the public and to enforce penalties on practitioners who fall short of the expectations under the law.
Kinesiologists are expected to know and understand their obligations in the event of a privacy breach, including (but not limited to):
Notifying the individual whose information has been stolen, lost, used or disclosed inappropriately;
Notifying the Information Privacy Commissioner of Ontario when required
Informing the Health Information Custodian at your earliest convenience if the kinesiologist who caused the privacy breach is an agent of a Health Information
Custodian.
As per section 17.1 of PHIPA, 2004, kinesiologists who are Health Information Custodians are required to make a report to the appropriate regulatory College if:
Disciplinary action is taken against a member of a College, who is an employee or an agent of the Health Information Custodian, for a privacy breach; OR
The employee or agent of the Health Information Custodian resigns and the Health Information Custodian has reasonable grounds to believe that the resignation is related to investigation or other action relating to a privacy breach.
The objectives of record keeping are to:
Facilitate the safe and quality care and treatment of patients/clients.
Ensure patients/clients have access to up-to-date, accurate information about their health.
Ensure continuity of care for patients/clients from successive members or other treating health professionals.
Ensure accountability to patients/clients, payers, the College, the profession and other healthcare providers.
Demonstrate judgement, reasoning and adherence to the standards of the profession.
Meet any other requirements mandated by the organizations they are associated with, and, where required by law.
Records must be:
Identifiable;
Legible and understandable;
Comprehensive;
Accurate and timely;
Accessible and retrievable;
Secure and confidential.
Members of COKO will maintain the following records:
equipment service record
financial record
patient/client health record
Members of COKO will ensure that every patient/client health record and every financial record will be retained for the following periods of time:
For patients/clients who are 18 years of age or older at the time of the last contact: a period of at least 10 years.
For patients/clients who are less than 18 years of age at the time of the last contact: a period of at least 10 years following the date at which the patient/client would have become 18 years of age.
Equipment service records must be retained for a minimum of 5 years
SOAP Notes
SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Analysis, and Plan) is a widely used acronym in health care that represents a documentation method for clinical notes.
A well-written SOAP note should be easy to understand by other healthcare providers involved in the patient's care and should give a complete and precise overview of the patient's condition and management.
Subjective Data
The information received from the patient/client. This information may include the patient's/client's opinions, goals, concerns, feelings and perceptions of their own health.
Objective Data
Objective data refers to observable information that the clinician gathers during their assessment and treatment sessions.
Objective data is based on what can be seen, measured, or verified through testing.
The objective section must be stated in overt terms and does not include opinions.
Objective data includes clinical tests and measurements that are observable and repeatable. Treatment provided may also be written in this section.
E.g. vital signs, range of motion (ROM), strength tests, musculoskeletal special tests, functional mobility, and ambulation.
Analysis
A summary statement based on the subjective and objective findings.
This statement is the clinician’s interpretation of the client's input and the data gathered. This statement may indicate progression, regression or no change in the client’s functional status or condition.
Your initial analysis statement will be comprehensive - includes five components
Unless there is a significant change in the client’s status (for example, a change in condition or discharge from care) in your follow-up progress notes, your analysis statement may not need to include all five components
Plan
A concise statement of the overall intervention plan and follow-up proposal for the next session. This section helps the kinesiologist determine the next steps.
What is the treatment intervention plan? How do we achieve the patient and clinician goals? What will you do at the next appointment?
Five main components of an analysis statement
Client profile/summary
Present condition/diagnosis
Any risks
Prognosis and rationale
Potential for kinesiology or referral to other services
Client profile/summary
Includes the client’s name, date of birth, sex, pronouns, and significant presentation.
Present condition/diagnosis
May include the client’s current medical diagnosis or working differential diagnoses or physical diagnosis, or potential differential diagnoses (MD/Nurse Practitioner/Physiotherapist) and/or present condition.
Any risks
May include the condition's acuity/chronicity/stability and any risks – including the clinician’s primary concerns, precautions, contraindications, or assessment of the patient’s/client’s primary concerns/goals.
Prognosis and rationale
Attempts to answer: what is/are the possible etiology(ies) of the diagnosis(es) and/or impairments (the ‘why?’), and what potential ramifications there may be for interventions &/or for the future.
Prognosis - do they have the necessary support to achieve their goals? Do they express high or low self-efficacy and/or motivation levels?
Potential for kinesiology or referral to other services
The likelihood that a R Kin has something to offer and that the client is likely to, or not to, benefit from R Kin.
If a referral to other services is warranted (e.g., med, PT, OT, dietician, etc.)
Problem list
Present the client's problem list in order of importance that can be addressed by kinesiology interventions and/or requires consultation or referral to another healthcare practitioner.
The problem list will form the basis of your treatment/exercise plan, and may include impairments, activity limitations, or participation limitations.
Problems can be actual or potential (e.g., at risk for…) and should be related to the underlying cause or treatable issues.
SMART Goals
SMART goals are specific, measurable, action-oriented, realistic and time-bound.
Help create concise goals that clearly describe the actions your client will need to take to achieve their desired outcomes.
Short-term Goals
Steps or milestones along the way to achieving outcomes
Short-term goals are those that will be accomplished in 1 to 3 weeks.
Short-term goals can address function, impairments and/or education.
Aim to create 2-3 SMART short-term goals after completing your initial assessment.
Long-term Goals
Outcomes that are often linked to optimizing health and well-being and are aimed at resolving the client's problem list.
Long-term goals have a much longer duration. These goals could be accomplished in the next 6 weeks, the next 6 months or by the end of the year.
May relate to returning to performing a meaningful activity/role or attaining a level of health and/or wellness.
Aim for 2- 3 SMART long-term goals, prioritized by importance.
S.M.A.R.T.
Specific: The goal should be very precise with no room for misinterpretation.
Measurable: The goal should be quantifiable, and progress should be easy to track.
Action-oriented: The goal should indicate what needs to be done.
Realistic/Relevant: Considering your client's current fitness level and environment, the goal should be achievable and meaningful to the client.
Time-bound: The goal should have a defined start and end date. Goals should have a specific and realistic time frame.
Capable
A person is capable of giving consent to treatment if he or she:
Understands the information needed to make a decision concerning the treatment
Appreciates the reasonably possible consequences of giving consent to the treatment or refusing to consent to the treatment.
Capacity to consent to treatment can vary over time. For example, the capacity of an elderly patient with dementia to give consent can change throughout the course of the treatment plan. The physiotherapist should therefore continuously re-evaluate the patient’s capacity.
Substitute decision-maker
The substitute decision-maker is expected to make decisions based on the patient’s known wishes expressed when he or she was 16 years of age or older and capable of providing consent. The hierarchy of substitute decision-makers is:
Guardian of the person—appointed by the court
Someone who has been named as the person’s power of attorney for personal care
Someone appointed as a representative by the Consent and Capacity Board
Spouse, partner, or relative of the patient in the following order:
Spouse or partner
Child, parent or a children’s aid society or other person who is lawfully entitled to give or refuse consent in place of the parent
Parent who has only a right of access
Brother or sister
Any other relative (related by blood, marriage or adoption)
Public Guardian and Trustee
Health Care Consent Act (HCCA)
Provides explicit rules about when consent is required for treatment, who can give consent, and the roles of substitute decision-makers in the consent process.
The intent of the Health Care Consent Act is to:
Provide rules with respect to consent to treatment
Facilitate treatment for persons lacking the capacity to make those decisions
Promote an individual’s autonomy
What is common law?
Common law is the system of law that is based on previous legal decisions, rather than written laws
When is Consent Required?
Treatment
Admission to a care facility
Personal assistance services
What are the requirements for consent?
Relate to the proposed treatment
Be properly informed
Be given voluntarily
Not be obtained through misrepresentation or fraud
Patient has the capacity to consent
What is “informed” consent?
Informed consent means that the patient or SDM has received the information that a reasonable person, in the same circumstances, would require to make a decision about the treatment.
The nature of the recommended assessment/examination or treatment
Why the patient/client should have the assessment/examination or treatment
The alternatives to the assessment/examination or treatment
The effects, material risks and side effects of the proposed assessment/examination or treatment and alternative assessment/examinations or treatments
What might happen if the patient/client chooses not to have the assessment/examination or treatment
Initiating Individual Treatments
Must discuss or review individual treatments or procedures with the patient prior to initiating an individual treatment.
It would not be necessary to go through each part of the treatment in the same detail as was done to obtain consent initially, but this review allows the patient an opportunity to ask additional questions or withdraw their consent.
Informed consent, without a doubt
Confirm that consent was obtained, and the patient is aware of the treatment to be performed.
If uncertain about whether consent to treatment was obtained, the patient refuses treatment or does not seem aware of the treatment, do not proceed. In this situation, document their actions and notify the individual who proposed treatment and obtained consent.
Informed v. Implied Consent
Valid consent may be express or implied. You must determine if the patient’s action indicates that the patient has truly understood the information provided and made an informed choice.
Express consent can be communicated orally or when a patient provides written consent.
Implied consent is demonstrated through the patient’s actions and/or responses to questions asked.
Be cautious when acting on implied consent. If for any reason the patient’s actions are unclear, you should obtain confirmation of the informed consent verbally or in writing.
Withdrawing Consent
Consent is not everlasting. As part of the consent conversation, ensure that the patient knows that they have the right to refuse or withdraw consent at any time. One must respect that decision.
Minimum Age for Consent
There is no minimum age for giving consent.
Must consider the patient’s capability to understand the implications of their decisions rather than their age.
Must use professional judgement to determine capacity to provide informed consent.
This would include the patient demonstrating that they have an understanding and appreciation of the information relevant to making a decision. It is possible that a child could have the capacity to make some but not all decisions related to treatment.
Treatment - HCCA definition
Anything done for a therapeutic, preventive, palliative, diagnostic, cosmetic or other health-related purpose.
Includes a course of treatment, plan of treatment or community treatment plan.
If an individual treatment is part of a course of treatment, a plan of treatment, or a community treatment plan, separate consent for each individual treatment component may not be required as long as the patient is capable to understand and provide consent for the range of treatments that are part of the plan or course of treatment.
Consent Exceptions
An emergency occurs when a person for whom treatment is proposed is apparently experiencing severe suffering or is at risk of sustaining serious harm if treatment is not done immediately
Capacity
The ability to understand the nature and effect of treatment, different options and appreciate the consequence of such options including refusal.
The health care practitioner who is proposing treatment is responsible for forming an opinion about the patient’s capacity to either consent to or refuse treatment.
A person is presumed to be capable unless a professional reasonable grounds to believe otherwise.
If you believe that a patient does not have the capacity to consent to proposed treatment, you must inform the patient. They should be included in the decision-making process to the extent that is reasonably possible.
It is possible for a patient to be capable of providing consent for some treatments, but not others.
It can fluctuate day to day.
How is Incapacity Defined?
A patient is deemed incapable of making decisions about their personal care if:
They are unable to understand information that is relevant to making decisions about health care, nutrition, shelter, clothing, hygiene or safety
They are unable to appreciate the reasonably foreseeable consequences of a decision or lack of a decision
Laws Related to Capacity
The HCCA is concerned with the capacity to make decisions in relation to health care treatments, while the Substitute Decisions Act is concerned with the formal appointment of legal decision-makers in circumstances where the individual’s capacity to make decisions or manage their affairs is expected to be compromised on an ongoing basis.
Substitute decision-makers may have full decision-making authority, or they may be limited in scope and only able to make certain decisions.
If the patient’s capacity returns, the substitute decision-maker’s authority can be revoked.
Substitute Decisions Act
Allows an individual (16+) to designate a specific person to make decisions about personal care or treatment if the individual becomes incapable.
The designated person may be asked to follow certain wishes or instructions that the person had expressed while capable.
Defines the hierarchy
The substitute decision-maker would need to be designated prior to the patient becoming incapable.
Determining Capacity for Treatment
Capacity for treatment should not be based solely on the following circumstances, although they may be considerations in making a determination:
Psychiatric or neurological conditions
Disability
Refusal of the proposed treatment
Age (for example, a patient who is very young or an elderly patient)
Communication style
Lack of education about a decision or situation
Clinical diagnosis
Other health condition
Do not assume that these circumstances equal incapacity. These circumstances may or may not impact a patient’s ability to consent to treatment.
When determining if a patient is incapable of providing consent, some possible indicators to consider are:
Evidence of confused or delusional thinking
Appearance of an inability to make a settled choice about treatment
Severe pain or acute fear or anxiety
Appearance of severe depression
Appearance of impairment by alcohol or drugs (illegal or prescribed)
Any other observations that make you question the patient’s behaviour or communication
Autonomy
Autonomy is the right of a capable individual to make informed decisions about their care.
For patients who are deemed to be incapable, the Health Care Consent Act enhances autonomy by:
Allowing persons found incapable to challenge the finding by applying to the Consent and Capacity Board
Allowing persons to select the individual who will make decisions on their behalf should they become incapable
Requiring that their treatment wishes expressed while capable and after reaching the age of 16 be adhered to
Accessing Substitute Decision-Makers
Health care practitioners can rely on a person’s assertion that they are the substitute decision maker.
Family members are not required to provide a formal statement confirming their status as substitute decision maker.
To be a substitute decision maker, an individual must meet the following qualifications:
Be capable of consenting to or refusing treatment
Be willing to assume the responsibility of consenting to or refusing treatment
Be available
Be at least 16 years old or the parent of the person who is incapable
Not prohibited by any legal reasons to provide consent on behalf of the person who is incapable
What if there is more than one substitute decision-maker?
As per Ontario family law, generally, where parents are separated or divorced, and custody arrangements have not been clarified you should be aware that:
Parents with sole custody have full parental rights and can give consent for care.
Parents with access arrangements have the right to receive health information BUT do not have the right to give or withhold consent.
If the person accompanying the child reports they have the authority to provide consent, the PT can rely on the consent of that person unless they have reasonable grounds to be concerned.
What does a PT need to document to show they obtained informed consent?
A short summary of the discussion that took place including the risks, benefits, alternatives and consequences of not having treatment, and any questions the patient asked and how you responded.