
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what is personality?
Personality is “regularities in feeling, thought, and action that are characteristic of an individual.” personality traits predict employee behaviors, affect a persons work habits, and how we behave in relationships at work.
Functions of personality
Function of: demographic, competency Characteristics, psychological characteristics
Two Aspects of Self
Self Efficacy: refers to an individual’s belief in his or her capacity to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific performance attainments
Self Monitoring: changing behavior to suit the situation
Locus of Control
Locus of Control refers to the degree to which individuals believe they have control over the events that influence their lives. It can be categorized as internal (belief in personal control) or external (belief in outside forces controlling outcomes).
Dark Triad
A personality model that encompasses three negative traits: narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy. These traits are associated with manipulative behavior and a lack of empathy.
Myers Briggs
A personality assessment that categorizes individuals into 16 distinct personality types based on their preferences in four dichotomies: introversion vs. extraversion, sensing vs. intuition, thinking vs. feeling, and judging vs. perceiving.
The Big 5
Personality could be summarized using five factors: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, neuroticism.
Psychological Capital
Four characteristics:Hope, Efficacy, Resiliency, and Optimism.
Important for human development, but also related to an organization’s competitive advantage.
3 aspects of Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness, Emotional-regulation, and Other awareness(social skills).
Diversity Approaches(why is it important)

Surface-Level and Deep-Level Diversity
Surface-level diversity refers to observable differences such as race, gender, and age, while deep-level diversity includes differences in values, beliefs, and personality traits.
“relief” in Discrimination
Refers to legal remedies or compensatory measures provided to individuals who have experienced discrimination in the workplace. ex. back pay, hiring, promotion, reinstatement, front pay, reasonable accommodation.
Generations in the Workplace
What is Mental Health
A state of well-being where a person is able to cope with the normal stresses of life.
This state permits productive work output and allows for meaningful contributions to society.
Understanding Mental Health
Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood.
Over the course of your life, if you experience mental health problems, your thinking, mood, and behavior could be affected. Many factors contribute to mental health problems, including:
Biological factors, such as genes or brain chemistry
Life experiences, such as trauma or abuse
Family history of mental health problems
Why it Matters - It determines your ability to function psychologically, emotionally, and socially.
Risk Factors
Abuse
Weather
Environment
Genetics
Diet
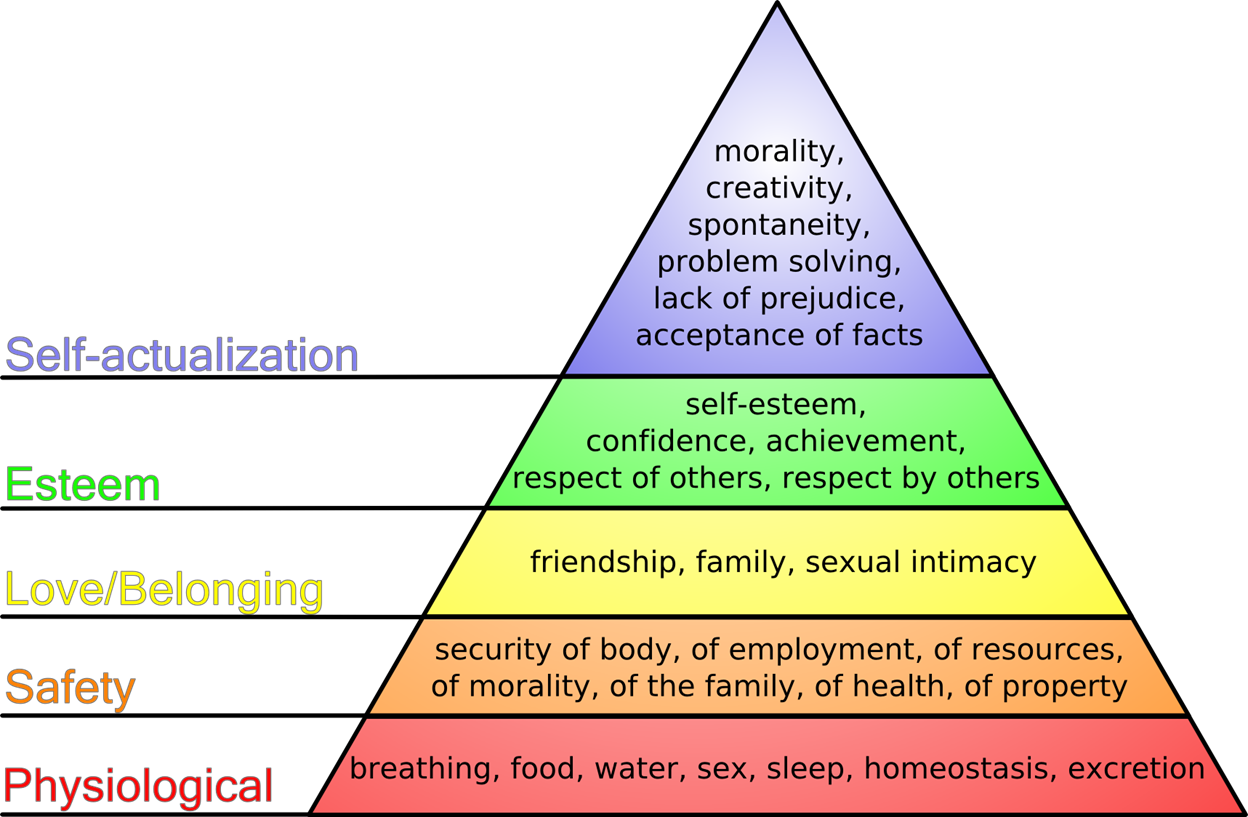
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Based on two types of needs: deficiency needs(lower levels that must be met first) and growth needs
Mccelland’s Need Theory
Need for Achievement (nACH) – people with higher needs for achievement perform at higher levels and may be more successful entrepreneurs
Does not mean you will be an effective leader (less of a coach/narcissistic)
Work better alone or with other high achievers
Need a lot of feedback and seek to improve
Engage in situations that offer personal accountability
Need for Affiliation (nAFF)- The need for relationships
Work best in teams, build strong relationships
Value belonging to a group
Want to be accepted & respected
Feedback should be provided in a personal way and in private
They want to know the relationship with the manager is important
Need for Power (nPOW) – The need to have influence over others and have status
Like to take charge & feel authoritative
Love to compete with other and win
Thrive on projects with challenging goals
Natural persuaders
Sales/Negotiations
Pillars of success
Resouces, Menoring
What is Mentoring
A professional relationship in which an experienced person assists another in developing specific skills and knowledge that will enhance the less-experienced person’s professional and personal growth.
How is Coaching Different than Mentoring
Relationship of finite duration, with a focus on strengthening or eliminating specific behaviors in the here and now.
