Chapter 23, Lesson 3: Glomerular Filtration
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 23, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
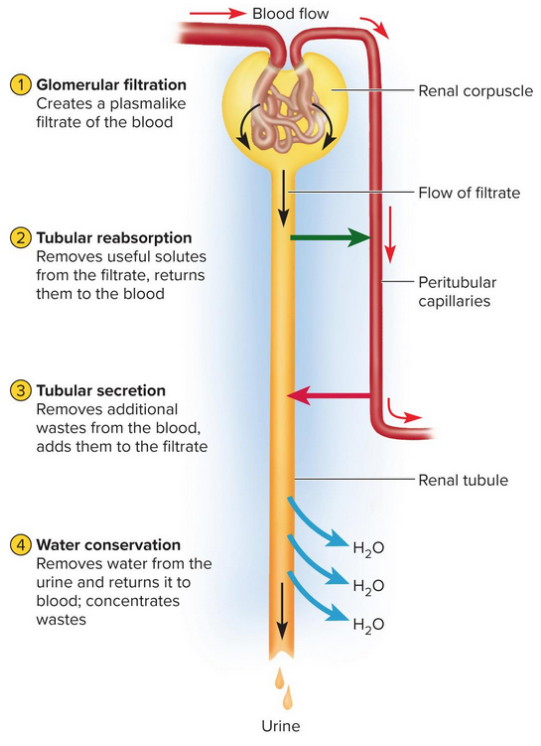
Urine formation stages
Glomerular filtration
Tubular reabsorption
Tubular secretion
Water conservation
Glomerular filtrate
Fluid in the capsular space, similar to blood plasma but without protein
Tubular fluid
Fluid from the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) to the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), with substances being removed or added by tubules
Urine
Fluid within the collecting duct and beyond, undergoes little alteration beyond this point except for water content changes
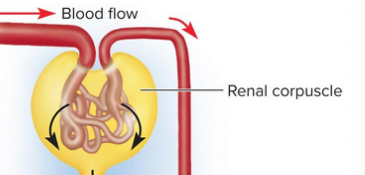
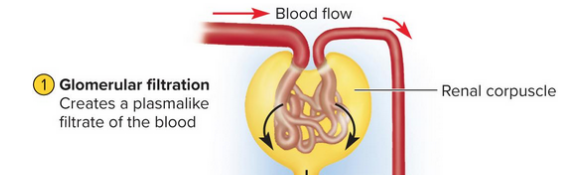
Glomerular filtration
The creation of a plasmalike filtrate of the blood; water and some solutes pass from within the glomerulus to the capsular space of the nephron
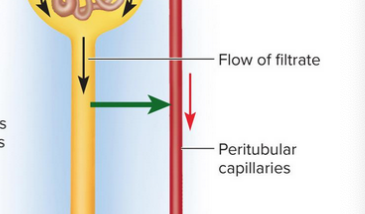
Tubular reabsorption
Removal of useful solutes from the filtrate to return to the blood
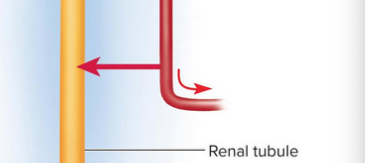
Tubular secretion
Removal of additional wastes from the blood to add to the filtrate
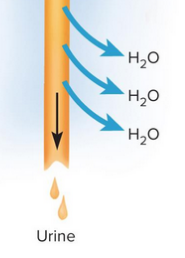
Water conservation
Water removal from the urine to return to the blood
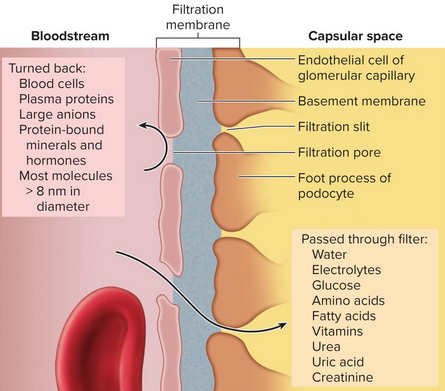
Filtration membrane
Barrier through which filtered fluid passes in the glomerulus with three components:
Fenestrated endothelium (pores that exclude blood)
Basement membrane
Filtration slits (has podocytes for filtration)
Fenestrated endothelium
Part of the filtration membrane that contains large filtration pores that are highly permeable but exclude blood cells
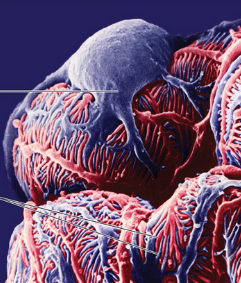
Filtration slits
Slits created by podocyte foot processes wrapping around the capillaries
Proteinuria (albuinuria)
Albumin in the urine
Hematuria
Blood in the urine
Hydrostatic pressure
Pressure that is high in glomerular capillaries to allow for molecule passage
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Amount of filtrate formed by the two kidneys, combined; equals about 50 to 60 times the amount of blood today with 99% reabsorption
Renal autoregulation
The ability of the nephrons ot adjust their own blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) without external control for stability, regulated through:
Myogenic mechanism (stretch stabilizer)
Tubuloglomerular feedback (filtration rate adjustment)
Myogenic mechanism
Stabilizing GFR based on smooth muscle contraction upon stretching
Higher blood pressure causes arteriole to constrict to prevent flow
Lower blood pressure causes arteriole to relax to allow for more flow
Tubuloglomerular feedback
Feedback on the glomerulus on the status of downstream fluid to adjust filtration rates
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
Complex structure found at the end of the nephron loop reentering the renal cortex as it comes in contact to the arterioles; uses macula densa and granular cells
Macula densa
A patch of slender, closely spaced sensory cells in the nephron loop that detects filtrate to stimulate granular cells
Granular cells
Modified smooth muscle cells that wrap around arteries close to the macula densa for constriction to correct GFR
Sympathetic control
Constriction of the arterioles by the sympathetic nervous system, adrenal epinephrine during times of shock or strain to redirect blood