Muscle Tissue
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Muscles makeup how much of our body mass?
Nearly half
Muscles convert chemical energy into
Mechanical energy for movement
What are the 5 main muscle properties?
-Electrical excitability
-Conductivity
-Contractility
-Extensibility
-Elasticity
Since muscles have conductivity, what does this mean?
They can conduct electrical currents in the body
Extensibility gives muscles the ability to
Stretch without damage
The ability for muscles to return to their original shape after contraction or extension is...
Elasticity
What are the 6 main characteristics of skeletal muscle?
-Form muscular system
-Attached to skeleton
-Striated
-Voluntary
-Multinuclear
-Stimulated by nerve impulses
What are the 6 main functions of skeletal muscle?
-Speech
-Voluntary movement
-Maintain posture
-Control body openings (ie. mouth)
-Body temperature regulation
-Blood sugar levels
What are the 5 main smooth muscle characteristics?
-Found in internal organs
-Involuntary
-Non-striated
-1 nucleus
-Excited by nerve stimuli AND self-excitable
What are the 4 main functions of smooth muscle?
-Movement for internal organs
-Control blood flow & blood pressure
-Act as valves (sphincters)
-Piloerection (skin)
What are the 9 main distinct things to remember about cardiac muscle?
-Has cardiocytes
-Produce blood flow
-Involuntary
-Intercalated discs
-Striated
-1 nucleus
-Cells connected laterally
-Self-excitable
-Has own pacemaker
What type of muscle forms the muscular system?
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle has _______ tissue and _______ ________
Nerve tissue and blood supply
Fascicles are...
Bundles of muscle fibers
The Epimysium is...
The membrane around the ENTIRE muscle
The Perimysium is...
The membrane around the Fascicles
The Endomysium is...
The membrane that surrounds the muscle fibers
How are muscle fibers arranged?
In parallel bundles called fascicles
The sarcolemma is...
The plasma membrane of the skeletal muscle fiber
Sarcoplasmic reticulum has...
Ca2+ ions
Transverse tubules (t-tubules)...
Carry impulses for contraction (like electrical wiring!)
Sarcomeres are...
Contractile units
Sarcomeres make up...
Myofibrils
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is...
A network of membranous channels surrounding each myofibril
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR) stores...
Calcium
What are terminal cisternae?
Expanded ends on either side of a transverse tubule (found in SR)
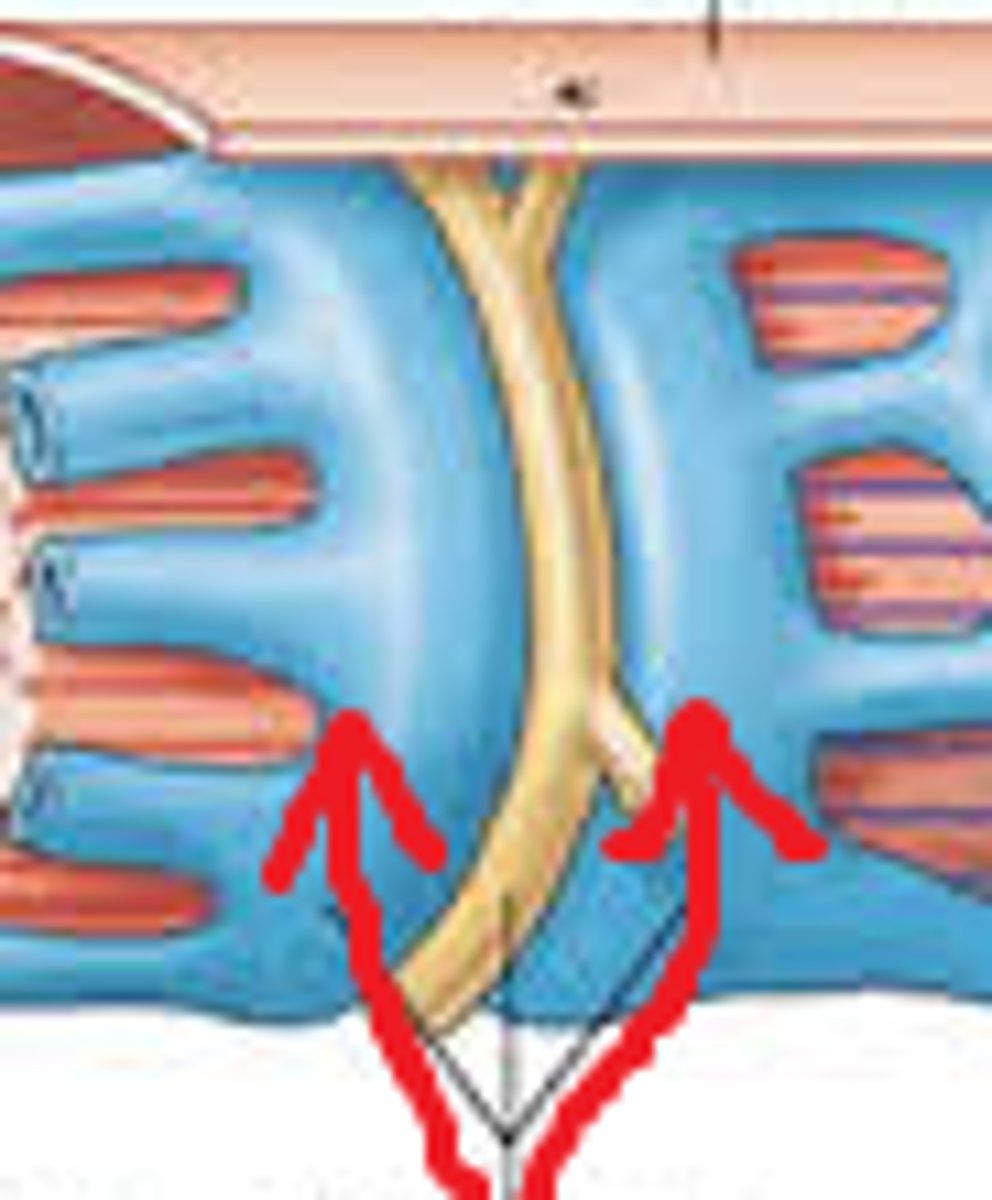
What is a triad?
2 terminal cisternae + 1 transverse tubule in between
Myofibrils make up (are found within)
Muscle fibers
Myofibrils are made of...
Bundles of thick and thin myofilaments
What are the end to end contractile units that make up myofibrils called?
Sarcomeres!
What are the lines that separate one sarcomere from the next?
Z-lines
What bands are between Z bands and appear light?
I bands
A bands appear _______ and _______________ thick and thin myofilaments
dark; overlap
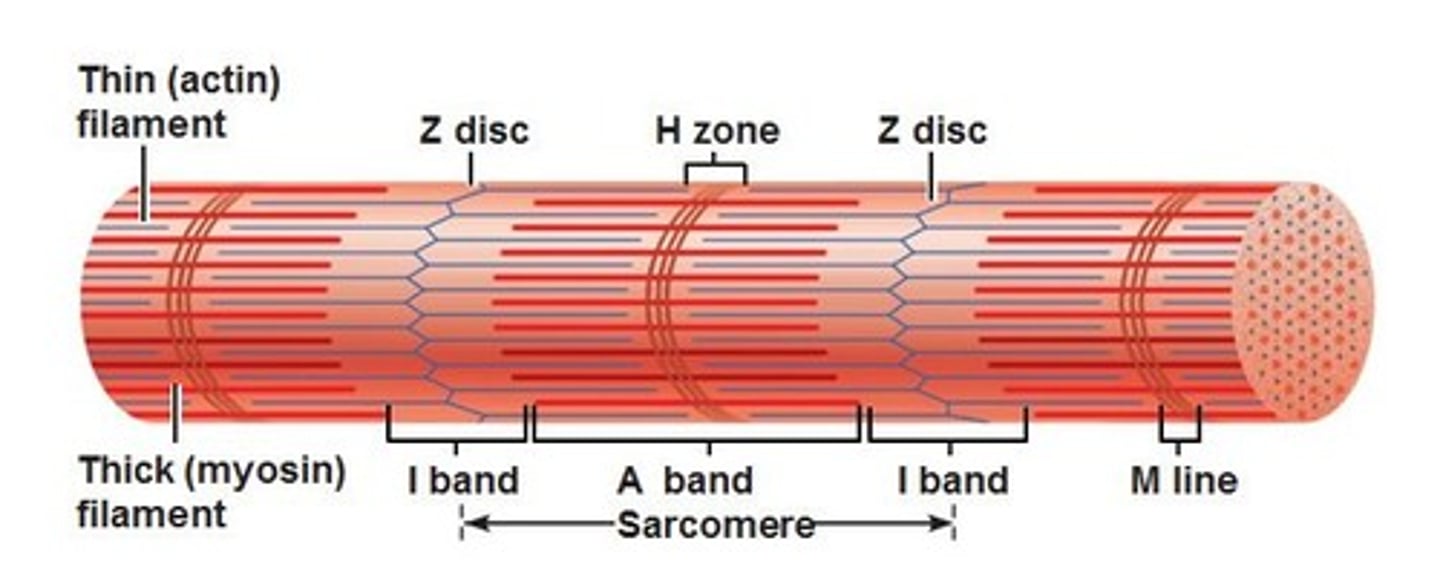
M lines are _____ ______ __________ of sarcomeres
in the middle
In relaxed sarcomeres, H bands only have ________ filaments
thick
When thin (actin) myofilaments slide along thick (myosin) myofilaments toward the middle of each sarcomere...
a muscle contraction occurs
What happens to Z-lines during muscle contraction?
They're pulled toward the middle of the sarcomere
During contraction, all sarcomeres ________
Shorten
During contraction, all myofibrils ________
Shorten
Thick myofilaments are arranged _____ to _____
Tail to tail (heads face in both directions)
Thick myofilaments are made of _______ myosin molecules and have _______ heads
300 ; flexible
Thin myofilaments are mostly ______
Actin
In thin myofilaments, actin is wrapped by thin filaments of _______________
Tropomyosin
The troponin complex is made of...
Globular protein of 3 subunits
What 2 things does Dystrophin do?
-Attaches peripheral actin to endomysium via linking proteins
-Transfers force of sarcomere contraction to endomysium, then to tendon
Muscle dystrophy is caused by...
Lack of dystrophin
When a sarcomere contracts, the I bands and H bands get smaller. True or False?
True
When a sarcomere contracts, the A band gets smaller. True or False?
False
What are the 4 things needed for muscle contraction?
-Nerve impulses to release calcium
-Calcium for binding myosin heads to actin
-ATP
-Anaerobic and Aerobic respiration to produce ATP
What make up nerves?
Axons
Nerve impulses travel down...
T-tubules
What is the nerve transmitter released from synaptic knobs?
Acetylcholine (ACH)
What energizes and cocks myosin heads?
ATP
Nerve impulses release...
Calcium
What are the strands of protein that cover actin active sites called?
Tropomyosin
The sarcomere can't contract until calcium...
Uncovers actin active sites
Sarcomere contraction is also called...
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
How many steps of Excitation-Contraction Coupling are there?
6
What is in Step 1 of sarcomere contraction?
The Myosin heads are energized & cocked, but the actin active sites are still covered by tropomyosin (there's no Ca2+ available)
What is in Step 2 of sarcomere contraction?
The binding sites become uncovered as nerve impulses spread down t-tubules and Ca2+ is released from SR and bonded to the Troponin complex. Troponin flexes and pulls tropomyosin off actin active sites
What happens in Step 3 of sarcomere contraction?
The Myosin heads bind to actin & a CROSS-BRIDGE is formed
What happens in Step 4 of sarcomere contraction?
The Myosin heads pivot (flex), pulling thin myofilaments from each end of sarcomere to the middle
What happens in Step 5 of sarcomere contraction?
Cross-Bridge detachment as ATP is added and makes the myosin heads release their grip with actin
If Ca2+ can be thought of as glue for the binding, then ________ can be thought of as the opposite of glue.
ATP
What happens in Step 6 of sarcomere contraction?
Myosin reactivation (repeating until full contraction)
-The ATP that was just added becomes hydrolyzed and re-energizes the myosin heads causes them to re-cock and bind to next actin active sites
What 4 things happen causing sarcomere contraction to stop (relax)?
-Nerve impulses stop
-Ca2+ gets pumped back into SR
-Troponin complex unflexes, allowing tropomyosin to cover the actin sites again
-Repeating cycle stops bc cross-bridge can't be formed anymore
What composes a motor unit?
A motor neuron and the many skeletal muscle fibers it stimulates
Motor neurons branch into...
Several motor nerve endings
A motor neuron can stimulate many ____________ __________ fibers simultaneously
Skeletal muscle
How many muscle fibers are found in a motor unit?
10-100s
Heavier items require a greater number of _________ _________ to pickup
Motor units
A single rapid contraction is called a...
Muscle twitch
Desired muscle contractions require (2)...
-Sustained, relatively smooth contractions
-Ability to increase contraction strength
Myograms are...
Recordings of muscle twitches
Do twitches have increasing strengths?
Yes
Low frequency stimuli produce...
Identical twitches
Higher frequency stimuli produce...
Temporal (wave) summation
Temporal (wave) summation is how many stimuli per sec?
20-40 stimuli per sec
Incomplete tetanus is...
Only partial relaxation between stimuli
Fluttering is found in Complete tetanus. True or False?
False. Fluttering is found in incomplete tetanus
Complete tetanus is...
No relaxation between stimuli
______________ makes muscle contraction stronger
Tetanus
The more motor units recruited, the ___________ the contraction
Stronger
Fewer and smaller motor units are used when...
Minimal contraction strength is required
More larger motor units are used when...
Maximum strength is required
Individual motor units _________, meaning they can't keep contracting without resting to recover
Fatigue
During longer periods of sustained contraction...
Not all motor units contract at the same time
When some motor units are contracting while others are relaxing & recovering, this is called...
Asynchronous contraction
Contractions are sustained and made stronger by... (2)
Temporal Summation & Motor unit recruitment
What is Temporal summation?
Varying degrees of stimulus frequency which doesn't allow muscle to relax
What are the benefits of muscles always being partially contracted (muscle tone)?
-Posture maintenance
-Better muscle coordination
-Readies muscle for faster action when needed
-Prevents muscle atrophy
Isotonic (literally) means...
Equal tension
Iso=
equal
What are the 2 types of Isotonic muscle contraction?
Concentric & Eccentric
Isotonic muscle contractions are used for...
Body movements and moving objects
When a muscle shortens and pulls on another structure to produce movement and reduce the angle at a joint, this is...
Concentric Isotonic Contraction
When tension exerted by myosin cross-bridges resists movement of a load and slows the lengthening process, this is...
Eccentric Isotonic Contraction
Pulling a dumbbell UP is
Concentric
Slowly bringing a dumbbell down is
Eccentric
Angle getting bigger at joint is
Eccentric