(CIE A2 Biology) Respiratory experiments - methylene blue + respirometers (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Redox Indicator
A substance that changes color when it is reduced or oxidized, such as DCPIP and methylene blue.
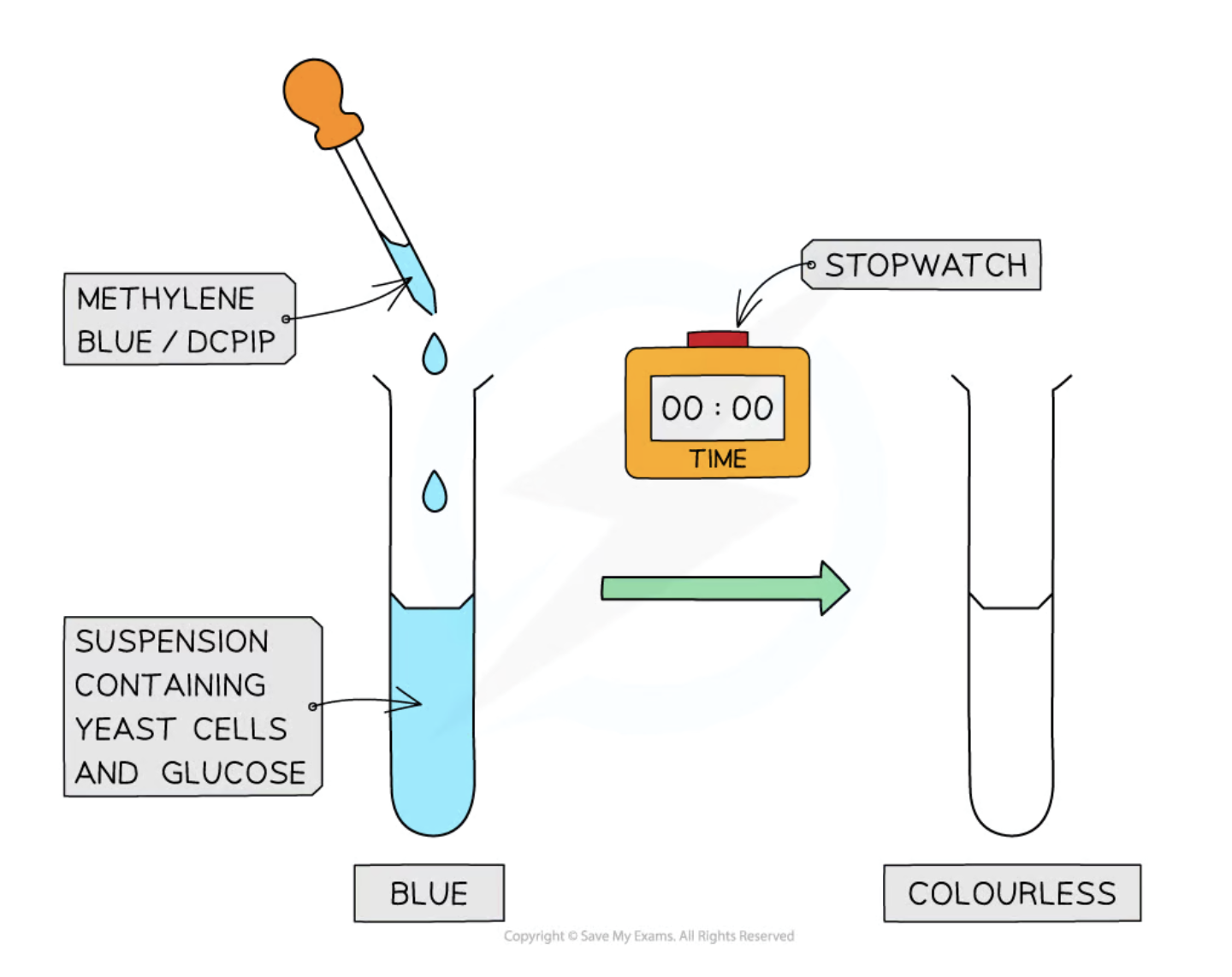
DCPIP/Methylene Blue
A redox indicator used to investigate the rate of respiration in yeast by changing color from blue to colorless when reduced.
Dehydrogenation
The removal of hydrogen atoms from substrate molecules during different stages of aerobic respiration, facilitating energy production.
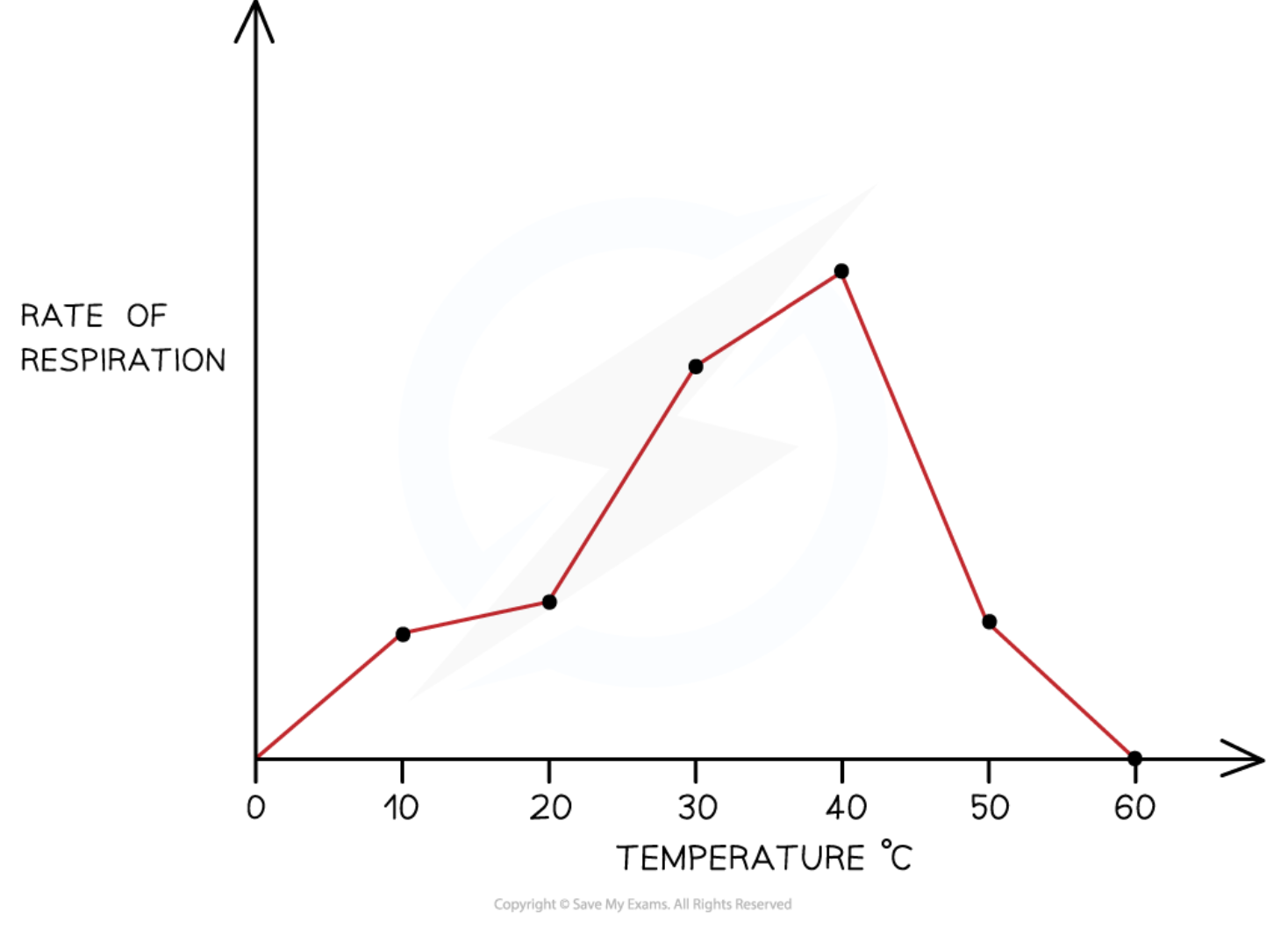
Effect of Temperature on Respiration
The rate of respiration in organisms can change with temperature (usually peaking at a specific optimum temperature), and is investigated by altering water bath temperatures.
Substrate Concentration
The amount of substrate present in a reaction, which can influence the rate of respiration in organisms like yeast.
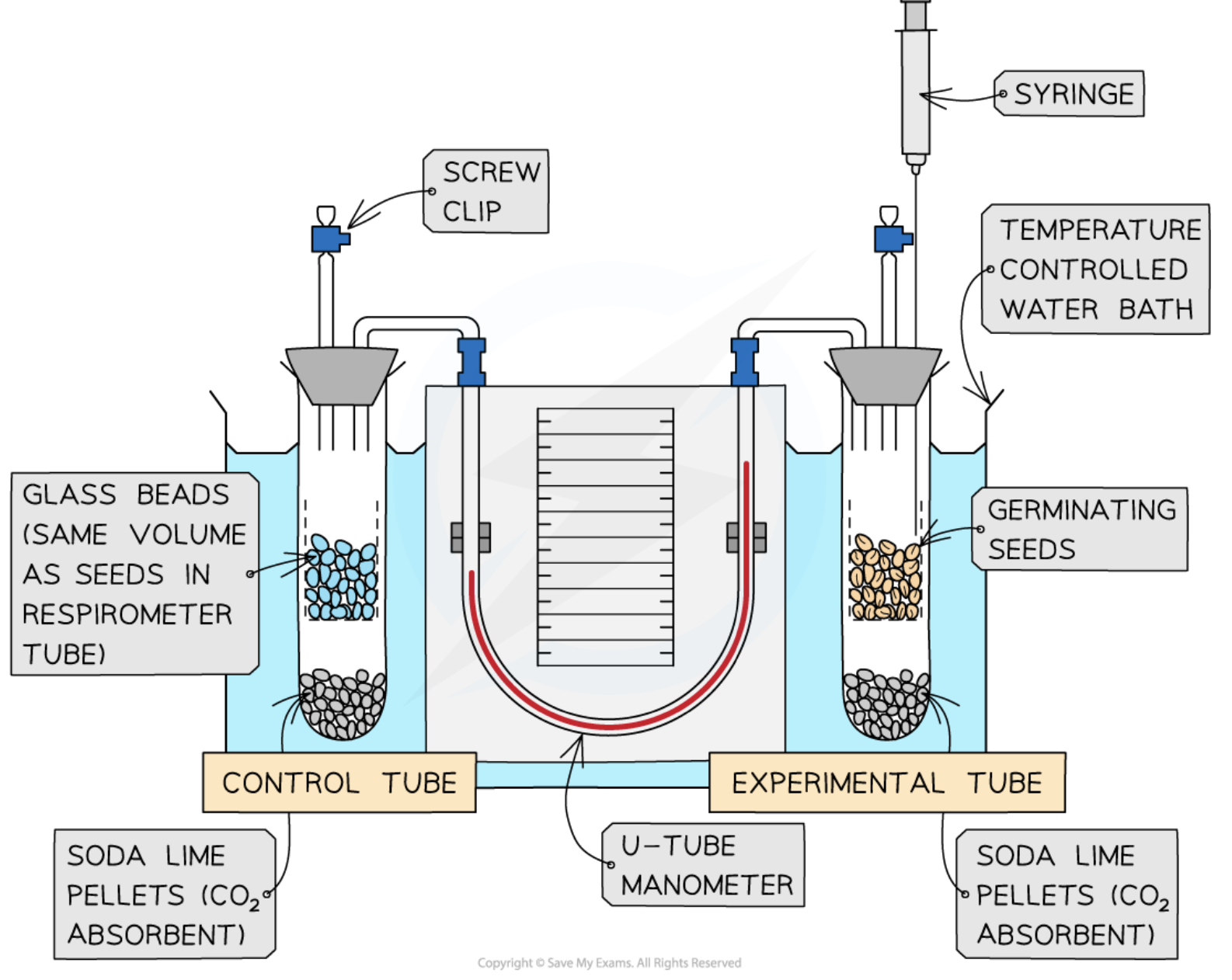
Respirometer
An apparatus used to measure the rate of oxygen consumption during aerobic respiration.
Rate of Respiration
A measurement of how quickly an organism consumes oxygen or releases carbon dioxide during respiration.

Control Variables
Factors that are kept constant in an experiment to ensure that the results are valid and due to the variable being tested.
Denaturation
The process in which proteins lose their three-dimensional structure due to high temperatures, affecting their function.
Enzymes
Proteins that act as catalysts to accelerate biochemical reactions, including those involved in respiration.
Color Change in Respiration Experiment
The change from blue to colorless in DCPIP or methylene blue indicates the rate of respiration by reflecting hydrogen release.
Formula for Oxygen Consumption
Volume of oxygen consumed can be calculated using πr²h, where 'r' is the radius of the capillary tube and 'h' is the distance moved by manometer fluid.
