Exam 2 A&P
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
homeostasis
the body’s ability to maintain a constant environment
loops
series of reactions involving molecules, cells and tissues
negative feedback loops
body senses change and reacts to negate or reverse the condition
positive feedback loops
self-amplifying cycles in which an initial change leads to a greater change
positive feedback example
blood clotting formation
negative feedback example
temperature regulation
nervous system
nervous tissue, fast, electrical currents and chemical messages (neurotransmitters)
endocrine system
glandular tissue (secretes), slow, chemical messages (hormones)
cell body/soma
contains one nucleus
dendrites
short extensions off of the cell body, receives signals from other neurons
axon
extension away from the cell body, can be myelinated
synapse
site of communication between neurons or neuron to a tissue
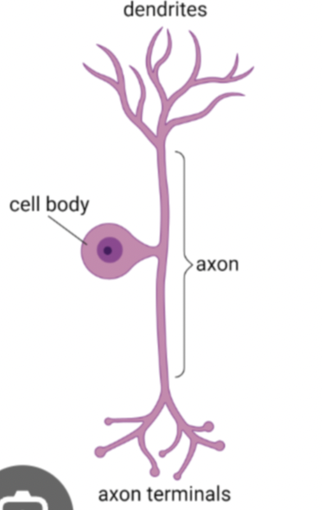
what neuron is this?
psudounipolar
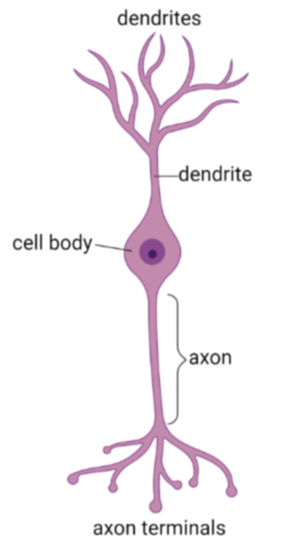
what neuron is this?
bipolar
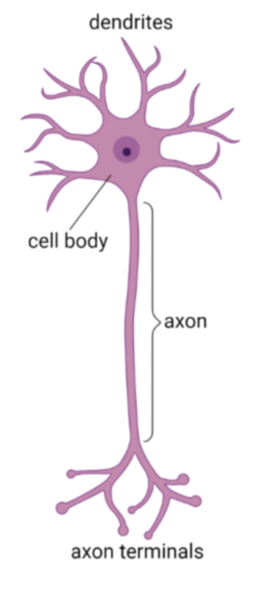
what neuron is this?
multipolar
sensory (Afferent neurons)
start in PNS and travel to CNS, detect stimuli, deliver info about environment or condition of body to CNS
motor (Efferent neuron)
sends signals from CNS to effectors (muscles, organs)
interneuron
in CNS, receives and integrates information
CNS
brain and spinal cord, major site of integration, cell bodies and axons
PNS
nerves travel to or from CNS, communication for sensory and outgoing motor information
endoneurium
surrounds individual neurons
perineurium
bundles neurons into fascicles
epineurium
tough outer layer
multipolar neuron
motor neurons and interneurons
bipolar neurons
special sensory neurons
pseudounipolar
sensory neurons
myelination
a fatty insulating layer of myelin wraps around axon to help with insulation, speed, and protection
oligodendrocytes
glial cell in CNS, produces and maintains myelin sheath facilitating saltatory conduction
schwann cells
glial cells that support and protect nerve cells in PNS, insulate axons with myelin sheath
cranial nerves
originate from brain, control head and neck functions
spinal nerves
emerge from spinal cord and connect to rest of body
ganglion
group of nerve cell bodies in PNS, synaptic relay station between neurons
dorsal
posterior
ventral
anterior
white matter
neuronal axons
grey matter
cell bodies
arachnoid mater
cobweby, middle membrane
subarachnoid space
between pia and arachnoid mater where CSF circulates
meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
cerebrospinal fluid
watery fluid that surrounds and protects CNS
dura mater
thick outermost layer
pia mater
innermost layer
dorsal horn
part of grey matter, receives sensory information from dorsal roots
lateral horn
contains visceral motor neurons, sense signals
ventral horn
sends out motor signals, contains cell bodies
dorsal root
posterior root, afferent nerve fibers, contains dorsal root ganglion, TO spinal cord
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
ventral root
anterior root, efferent nerve fiber, AWAY from spinal cord
current
flow of charged particles from one point to another
potential (voltage)
different in electrical charge between two points
charged particles (ions)
have chemical concentration gradient, uneven distribution of molecules
electrical gradients have an…
uneven distribution of charge, combination of ion permeability, pump function, and anions
electrochemical gradient
determines which way ions flow
membrane potential
charge inside cell - charge outside cell
resting membrane potential
membrane potential when neuron is at rest
what is resting membrane potential?
-70mV
Na+/K+ protein pump create __
chemical gradient of the ions
Potassium diffuses out of cell
inside of cell membrane more negative than outside
chemical gradient for chloride CI-
ECF>ICF
sodium cation concentrated ECF
extracellular fluid, outside cell
potassium cations concentrated
ICF (intracellular fluid, inside cell)
inside of cell membrane is more - than outside (electrical gradient)
K+ can diffuse easily than sodium, large anion trapped inside
RMP (difference in charge across membrane surface when neuron is at rest)
movement of ions along electrochemical gradients and pumps counteractive those movements
graded (local) potential
change of RMP created by movement of ions near stimulus
chemically gated channel
open when a specific molecule binds to the channel protein
voltage-gated channel
open when the membrane potential (voltage) changes
mechanically gated channels
open when a physical force changes the shape of the channel protein
depolarization (excitatory potential)
Na+ channels open and Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, membrane potential becomes + (closer to 0)
hyperpolarization (inhibitory potential)
CI- channels open and enters cell or K+ channels open and diffuse out of cell, membrane potential becomes more negative
afferent
graded potentials are typically excitatory, created by stimuli in environment or organs
interneurons and efferent
local potentials are excitatory OR inhibitory, created by neurotransmitters
threshold potential
minimum membrane potential that must be reached to trigger an action potential in a neuron (-55mV)
stimulus
electrical signal generated within a cell when it receives a stimulus that reaches threshold causing a rapid change in membrane potential