GEO 004 Midterm #1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
1
New cards
The 4 A's of Migitation
Avoid, Accept, Anticipate, and Alter.
2
New cards
Calculating Slope
Slope \= rise/run
3
New cards
Find Contour Interval
Determine elevation difference between contours, Count \# of spaces between contours, elevation difference/ \# of spaces.
4
New cards
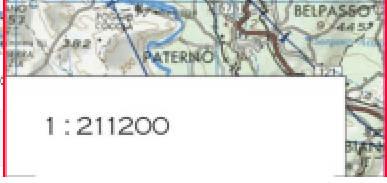
Numeric Scale
1:24,000
5
New cards
Verbal Scale
One inch equal four miles

6
New cards
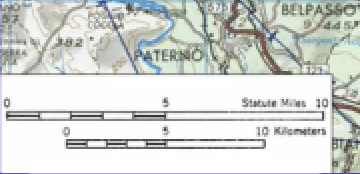
Graphical Scale
Small ruler that can be used to convert distances covered on a map to real
7
New cards
3 things to find location on earth
Longitude, Latitude, and Elevation.
8
New cards
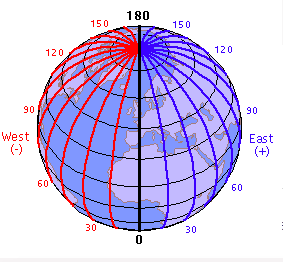
Longitude
Distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees.
9
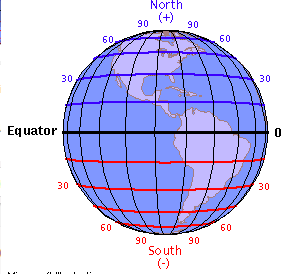
New cards
Lattitude
Lines that run east and west dividing the earth.
10
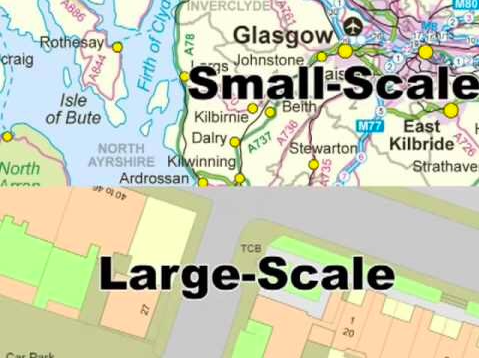
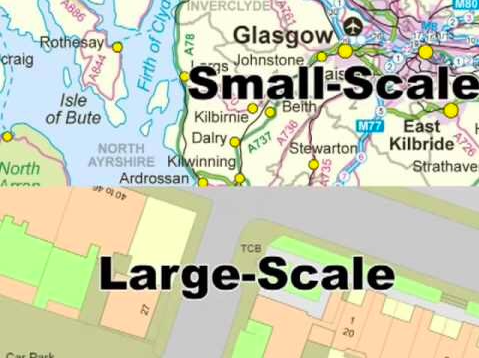
New cards
Large Scale Map
Relatively zoomed in, shows more detail.
11
New cards
Small Scale Map
Relatively zoomed out, shows less detail.
12
New cards
Topographic map
A map that shows the surface features of an area. Gives information on our location and elevation. The study of the surface of the Earth.
13
New cards
Radioactive Decay
A spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation. As they repeat decay they emit energy, energy loss happens gradually.
14
New cards
Sources of Internal Heat Energy
Impacts of asteroids and comets, gravitational energy, differentiation layers and decay of radioactive isotopes.
15
New cards
Types of Plate Boundaries
Divergent, Convergent, and Transform. Immense friction between plates, stress results in earthquakes.
16
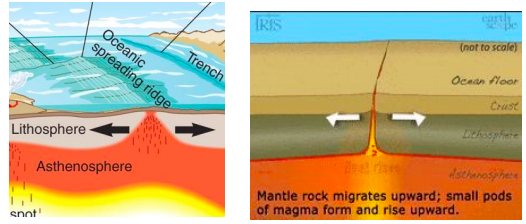
New cards
Divergent Boundary
A boundary where plates pull away/ apart from each other, occurs in oceans mostly.
17
New cards
Convergent Boundary
A boundary where two plates push together, plates collide, a subduction zone.
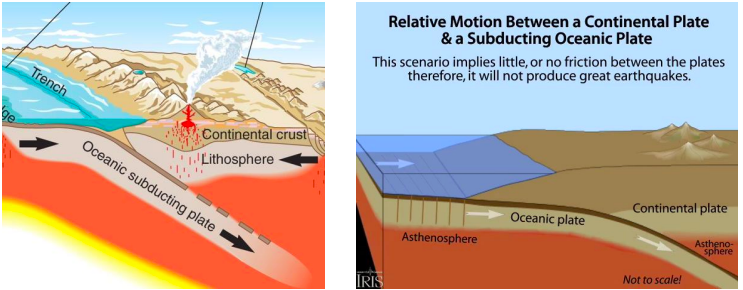
18
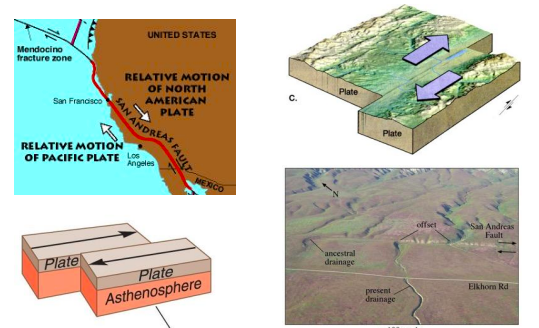
New cards
Transform Boundary
A plate boundary is where two plates move in opposite directions and slide past each other. The most rare plate boundaries and our type of fault; San Andreas fault.
19
New cards
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
\-Shape of continents, Pangea
\-Rocks matching mountain belts
\-Location of found fossils
\-Seafloor magnetization
\-Earthquake locations correspond to plate boundaries
\-Volcanoes locations occur along plate boundaries
\-Rocks matching mountain belts
\-Location of found fossils
\-Seafloor magnetization
\-Earthquake locations correspond to plate boundaries
\-Volcanoes locations occur along plate boundaries
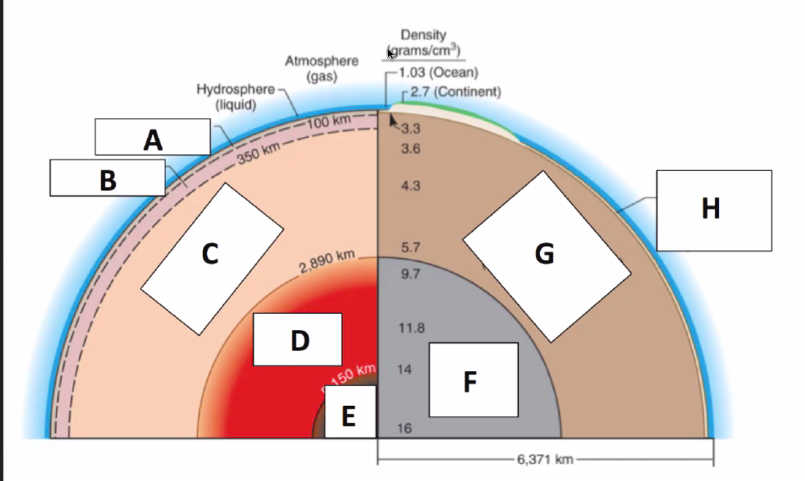
20
New cards
Volcanoes Hot Spots
Volcanic centers NOT near plate boundaries. Locations where narrow plumes of magma rise through the mantle in a fixed place over a long period of time. ex) Hawaii
21
New cards
Spreading Center
Lower viscosity, low volatility, large volume. A divergent boundary, marked by a rift at the crest of a mid-ocean ridge, where new oceanic crust is formed by seafloor spreading.
22
New cards
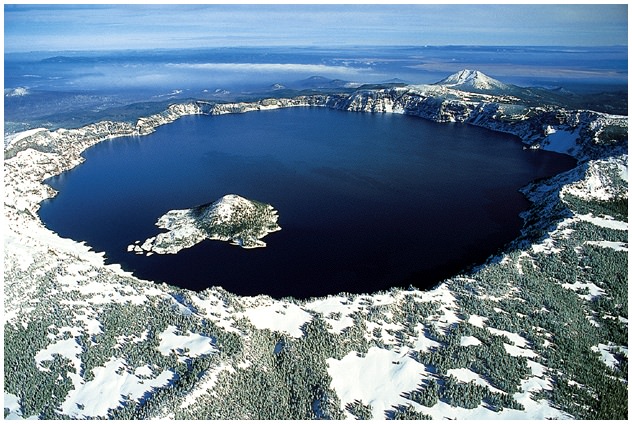

Calderas Volcano
Type of volcano:
High Viscosity
High Volatility
Very Large Volume.
Injection of magmas causes doming on surface, and dome collapses. Massive pyroclastic flows and lava flows. A large volcanic crater ex) Yellowstone.
High Viscosity
High Volatility
Very Large Volume.
Injection of magmas causes doming on surface, and dome collapses. Massive pyroclastic flows and lava flows. A large volcanic crater ex) Yellowstone.
23
New cards
Formation of Calderas Volcano
1) Injection of magma domes on surface
2) Fractures form, gas escapes, major ash falls
3) Dome collapses, caldera/ crater forms, lava flows
4) Injection of more magma, dome forms
2) Fractures form, gas escapes, major ash falls
3) Dome collapses, caldera/ crater forms, lava flows
4) Injection of more magma, dome forms
24
New cards
Flood Basalts
Form when lava flows out of long cracks in Earth's crust. Low viscosity, high volatility, very large volume. Characterized by massive volume of magma, stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava.
25
New cards
Viscosity
Resistance to flow, higher viscosity, the lower the flow \= more explosive eruption. In volcanic rocks viscosity is a function of silica, SiCO2.
26
New cards
Volatility
Dissolves gas in magma, the more dissolved water \= more explosive eruption. The tendency of a substance to vaporize.
27
New cards
Volume
Refers to the amount of magma being stored inside the volcano. Size of magma chamber, more magma \= more erupted material.
28
New cards
Matters for eruption type
\-Location
\-Way you melt (depressurize, temperature, water)
\-What you melt (crust with low or high SiCO2)
\-Determine chemistry and eruption type
\-Are both functions of tectonics in a region
\-Way you melt (depressurize, temperature, water)
\-What you melt (crust with low or high SiCO2)
\-Determine chemistry and eruption type
\-Are both functions of tectonics in a region
29
New cards
Prediction/ Mitigation
Recording and learning from past volcanic eruptions to help determine when the next eruption will happen.
30
New cards
How to predict volcanic eruptions
\-Monitoring gas emissions
\-Ground deformation
\-Presence of earthquakes/ seismic activity
\-Ground deformation
\-Presence of earthquakes/ seismic activity
31
New cards
Volcano Watch vs Warning
Watch - Volcano is exhibiting increased potential but poses limited hazards. Warning - Hazardous eruption is imminent, underway, or suspected. ex) Ingredients for a taco vs making and assembling a taco
32
New cards
What kind of plates do we live?
We live in the vicinity of the boundary between the North American and Pacific plates. It is transform plate boundary. San Andreas fault.
33
New cards
Types of faults
Normal, Reverse, and Strike-slip.
34
New cards
Normal fault
A type of fault where the hanging wall slides downward; caused by tension in the crust. Extensional setting, hanging wall moves down.
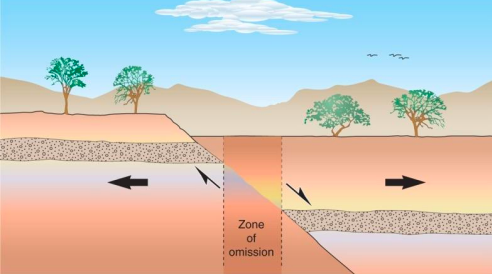
35
New cards
Reverse fault
A fault in which the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. Compressional setting, hanging wall moves up.
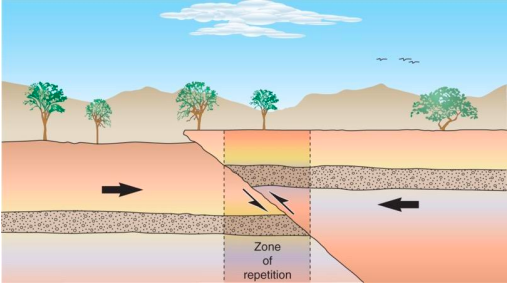
36
New cards
Strike-slip fault
Due to Shear. A type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up or down motion. Push together: creates hills/ mountains. Pull apart: creates holes, basins.

37
New cards
Right lateral Strike-slip fault
Strike-slip fault. As you face the fault, the opposite side of the fault moves to the right.
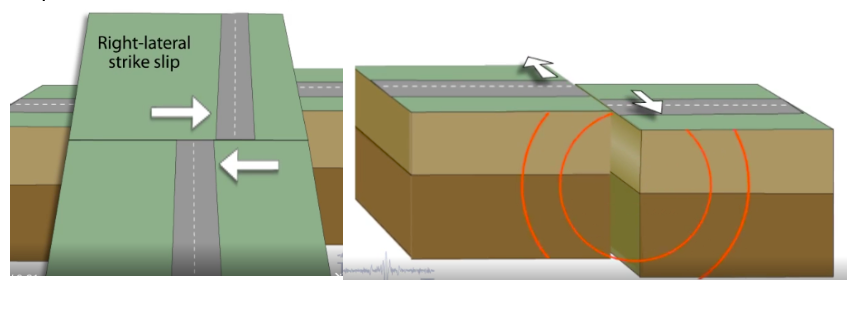
38
New cards
Left lateral Strike-slip fault
Strike-slip fault. As you face the fault, the opposite side of the fault moves to the left.
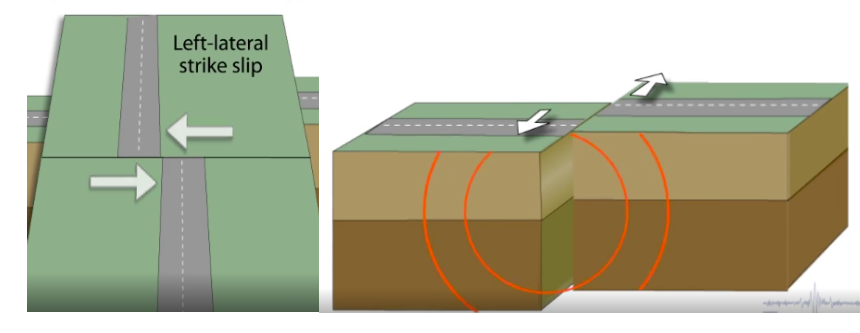
39
New cards
Dip Slip Fault
Due to Tension/ Compression. A fault in which the movement is parallel to the dip of the fault. Vertical movement.

40
New cards
Seismic waves
Travel from where earthquakes happen, rupture releases energy waves through the earth. Wavelength, Travel direction, and Amplitude.
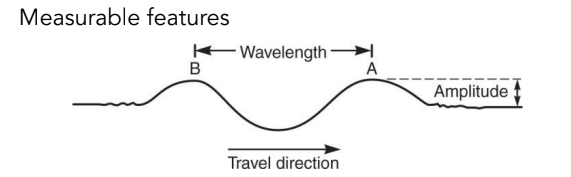
41
New cards
Seismometer/ Seismograph/ Seismogram
Seismic waves are measured with a Seismometer.
The recorder used to measure waves is referred to as a Seismograph.
The recording made is called a Seismogram.
The recorder used to measure waves is referred to as a Seismograph.
The recording made is called a Seismogram.
42
New cards
Amplitude
Height of seismic wave. Related to the strength of shaking.
43
New cards
Wave length
Distance between waves.
44
New cards
Period
Time between waves, measured in seconds.
45
New cards
Frequency
Number of waves passing through a fixed point during 1 seconds time, measured in hertz, period \= 1/frequency.
46
New cards
P waves
A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground. Always arrive first.
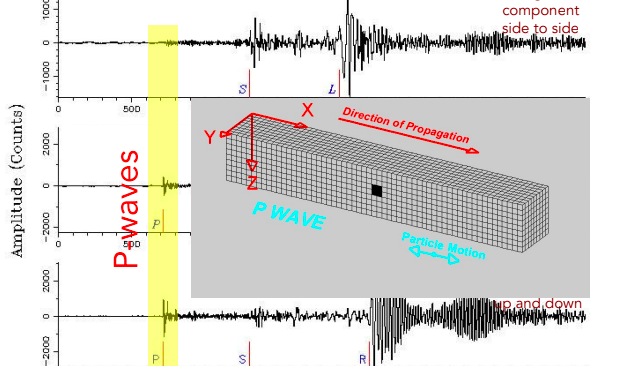
47
New cards
S waves
A type of seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side. Same rest as p waves, secondary waves.
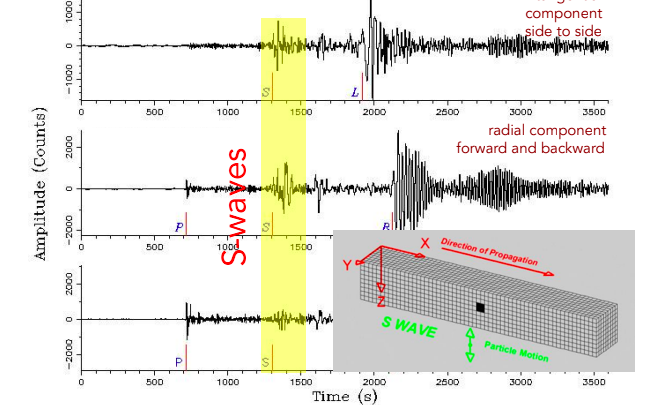
48
New cards
Love waves
Surface waves that shear the ground in a horizontal direction. Can only travel through solids. Third to arrive.
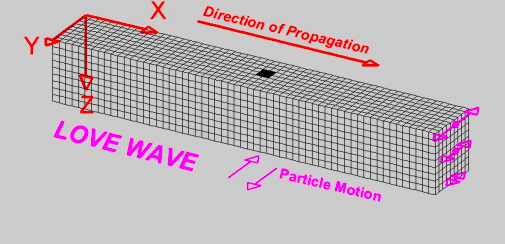
49
New cards
Rayleigh waves
Surface waves that travel in a backward
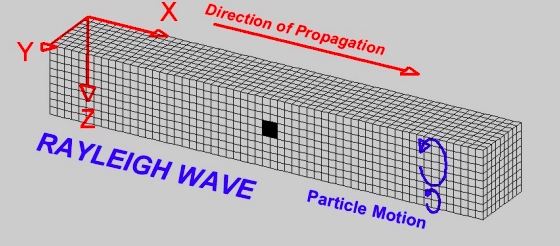
50
New cards
Why do earthquakes vary?
Propogation/ changes in amplitude is realted to:
\-Geometrical spreading
\-Attenuation
\-Rock Type
\-Earthquake magnitude
\-Geometrical spreading
\-Attenuation
\-Rock Type
\-Earthquake magnitude
51
New cards
Geometrical Spreading
Energy has to be spread over larger era as the distance from the source increases.
52
New cards
Attenuation
Loss of energy with distance due to scattering and friction. Friction between mineral grains dissipate energy and reduce amplitude. The longer wave travels the more energy is lost.
53
New cards
Rock Types
Different rocks have different frictional properties. East coast felt larger distance. Sediment or soil? Sediment: Soft, ground easily moves. Bedrock: Hard, ground does not move a lot.
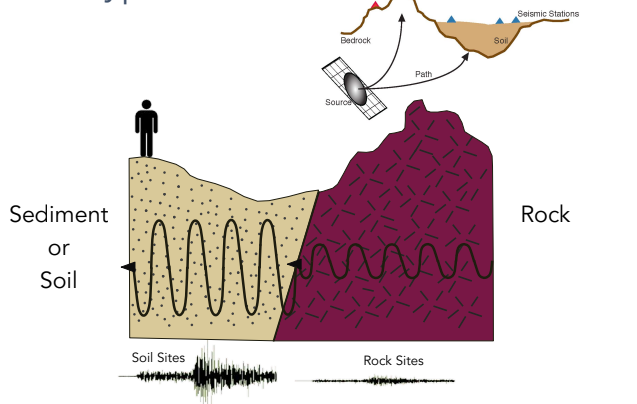
54
New cards
Site effects
Properties of soil and rock around you. Sediment sites amplify seismic waves. Ex) Bowl of Jello
55
New cards
Liquefaction
The process by which an earthquake's violent movement suddenly turns loose soil into liquid mud. 3 Factors
1) Loose granular sediment
2) Water saturated
3) Strong shaking
1) Loose granular sediment
2) Water saturated
3) Strong shaking
56
New cards
Magnitude
Measure of the energy released during an earthquake. Bigger the earthquake, the more energy emitted, and the rarer it is. Measured on the richter scale.
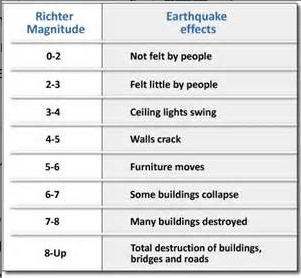
57
New cards
Seismic Hazard Steps
Step #1: Consult map to determine risk for shaking
Step #2: Design buildings and structure to withstand shaking
Step #3: Preventing injuries from falling contents Step #4: Plan and prepare.
Step #2: Design buildings and structure to withstand shaking
Step #3: Preventing injuries from falling contents Step #4: Plan and prepare.
58
New cards
Subduction Zone
Occurs at Convergent Plate Boundary. The region where oceanic plates sink down into the asthenosphere.
59
New cards
Types of Magma
Basalt, Andesite, and Rhyolite.
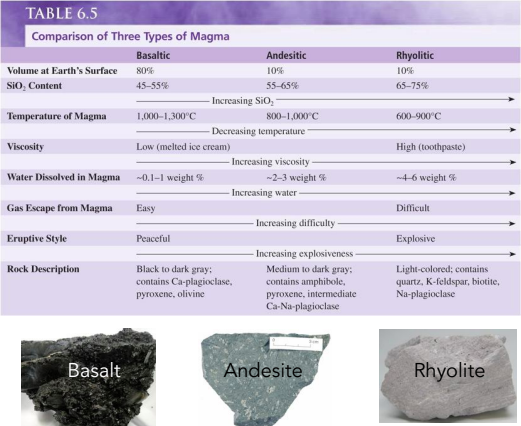
60
New cards
Igneous Rock Types SiCO2
Decreasing Silica content increasing dark, heavy minerals.
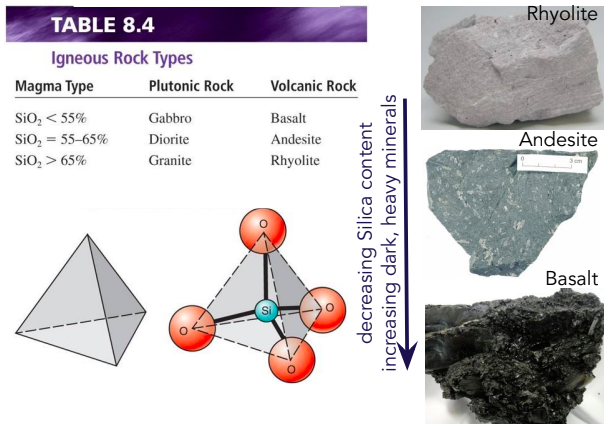
61
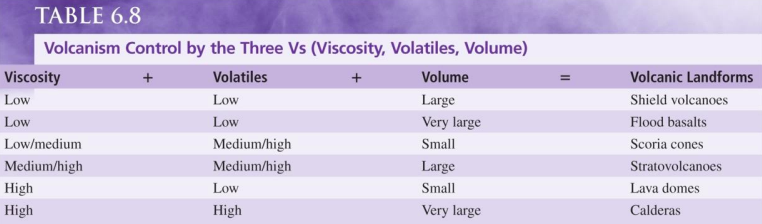
New cards
Volcanism Control by the Three V’s
Viscosity + Volatiles + Volume = Volcanic Landforms.
62
New cards
Released
As radioactive atoms decay, energy is __?
63
New cards
Chemical; Physical
The Earth's innermost layer is known as the core when considering ___ properties, but is broken into 2 layers, outer core and inner core, when discussing ___ properties.
64
New cards
Subduction Zone
When oceanic lithosphere collides with another plate, the older, colder plate goes beneath the younger, warmer plate This is known as the __?
65
New cards
Seafloor spreading
After lava cools, atoms in iron-bearing minerals on the seafloor become magnetized in the direction of the Earth's magnetic field at that time and place.
66
New cards
Rates of plate movement
Movement comparable to those of human fingernail growth?
67
New cards
Hot spots
_____ have active volcanoes above them on the Earth's surface and moving plates carry the volcanoes away from their hot-spot source.
68
New cards
True
T/F: The movements of the lithospheric plates are directly responsible for the vast majority of the earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountains on Earth.
69
New cards
True
T/F: A graphical scale is a small ruler included on a map that can be used to convert distances covered on a map to real-world distances. A numeric scale is a ratio defining the conversion factor between distance measured on a map and real-world distance.
70
New cards
3 Elements; Longitude, Latitude and Elevation.
How many elements (1, 2, 3, 4, etc) do you need to define your location on the Earth's surface?
71
New cards
Contour Lines
Flat, two-dimensional maps are great for showing your location in terms of north-south and east-west directions. What map features are used to show your vertical (up-down) position?
72
New cards
False
T/F: ALL Volcanoes tend to occur mostly along plate boundaries. (Hot spots do not)
73
New cards
Intraplate Volcanoes
“Intraplate” means within the interior of a tectonic plate. Volcanoes that takes place away from the margins of tectonic plates.
74
New cards
Yellowstone
When a mantle plume rises up through a continental plate, it may form a continental caldera/ Super Volcano such as _____.
75
New cards
**Volatile-rich**
Subducting plates bring water saturated sediments into the mantle , which results in partial melting and generation of ____ melt.
76
New cards
Increasing
As magma rises through continental crust, partial melting of the continental crust ______ing the SiO2 content and viscosity of the magma, eventually forming andesitic-rhyolitic magmas.
77
New cards
Divergent and Convergent
Volcanos occur at ___ plate boundaries?
78
New cards
False
T/F: The three Vs of volcanology are viscosity, volatiles, velocity
79
New cards
False
**T/F:** Shield volcanoes are steep-sided, symmetrical volcanic peaks built of alternating layers of pyroclastic debris capped by high-viscosity andesitic to rhyolitic lava flows.
80
New cards
True
T/F: A caldera collapse occurs after the magma chamber is mostly empty
81
New cards
True
T/F: The most peaceful eruptions are Icelandic type eruptions
82
New cards
True
T/F: Slow flowing, more viscous basaltic lava commonly has a rough, blocky texture called A’a.
83
New cards
True
T/F: In addition to lava flows, volcanic processes can cause tsunamis, debris avalanches, and lahars.
84
New cards
False
T/F: The primary cause(s) of death from explosive volcanic eruptions is lava flows.
85
New cards
Pyroclastic flows
Destructive mass of very hot ash, lava fragments, and gases ejected explosively from a volcano at great speed. Primary cause of death from volcanic eruptions.
86
New cards
Precursors of volcano eruption
Several geologic phenomena are considered precursors of an impending volcanic eruption. These include seismic waves, ground deformation, and the release of gases.
87
New cards
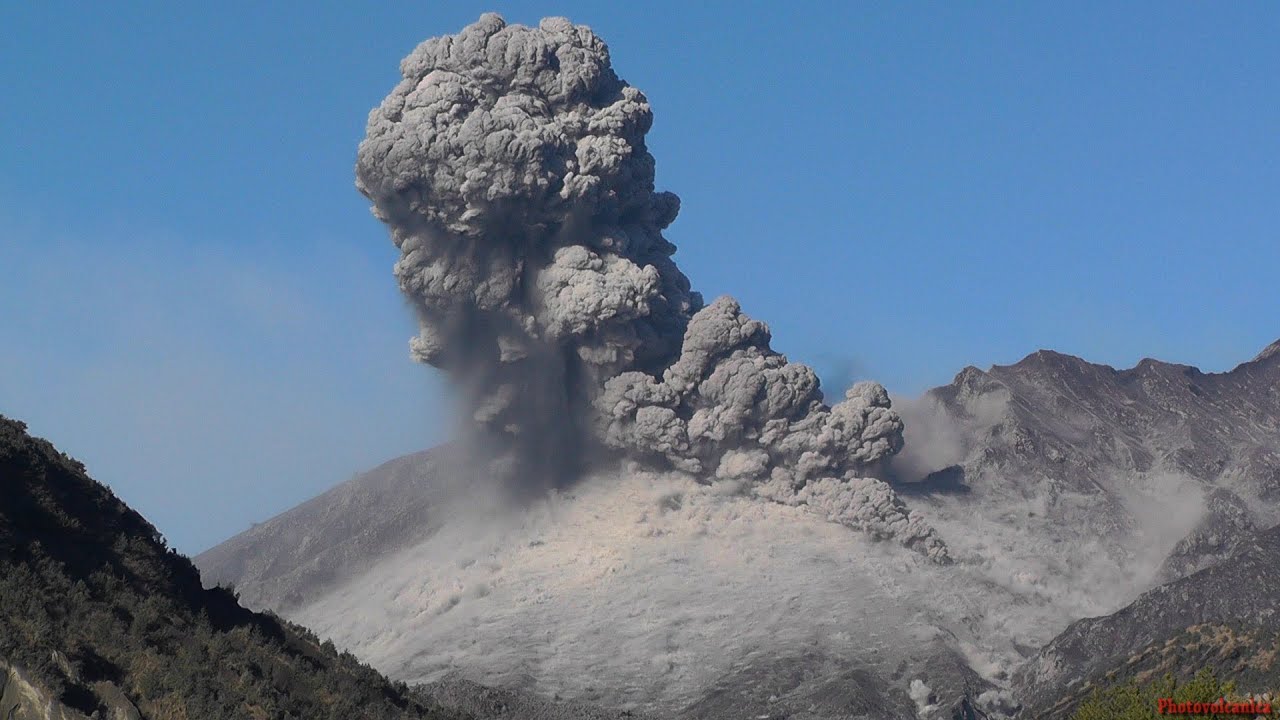

Vulcanian Eruptions
Type of Erruption:
Occur at convergent boundary.
Moderate-high viscosity lava
Moderate-high volatiles
Moderate volume (ash falls, etc.) Dangerous!
Occur at convergent boundary.
Moderate-high viscosity lava
Moderate-high volatiles
Moderate volume (ash falls, etc.) Dangerous!
88
New cards

Plinian Eruptions
Type of Erruption:
Occur at convergent boundary or continental-hot spot
High viscosity lava
High volatiles
High volume
Large stratovolano or supervolcano major ash falls, pyroclastic flows, Gooey lava, lahars. Very dangerous!
Occur at convergent boundary or continental-hot spot
High viscosity lava
High volatiles
High volume
Large stratovolano or supervolcano major ash falls, pyroclastic flows, Gooey lava, lahars. Very dangerous!
89
New cards

Hawaiian Eruptions
Type of Erruption:
Occur at hot spots erupting through oceanic crust
Low viscosity lava
Low volatiles (dissolved water).
Relatively high volume
Runny, erupt continuously at low rate known for extensive lava flows “not very dangerous”.
Occur at hot spots erupting through oceanic crust
Low viscosity lava
Low volatiles (dissolved water).
Relatively high volume
Runny, erupt continuously at low rate known for extensive lava flows “not very dangerous”.
90
New cards

Strombolian Eruptions
Type of Erruption:
Occur at convergent boundary
Moderate viscosity lava
Moderate volatiles (dissolved water)
Low-moderate volume
Somewhat runny, erupt nearly continuously at low rate known for volcanic bombs not especially dangerous.
Occur at convergent boundary
Moderate viscosity lava
Moderate volatiles (dissolved water)
Low-moderate volume
Somewhat runny, erupt nearly continuously at low rate known for volcanic bombs not especially dangerous.
91
New cards

Stratovolcano
Type of Volcano:
Med/high Viscosity, med/high
Volatility, large Volume. Also known as composite
volcanoes. High viscosity lava flows --> This is what
gives them their steep sides.
Med/high Viscosity, med/high
Volatility, large Volume. Also known as composite
volcanoes. High viscosity lava flows --> This is what
gives them their steep sides.
92
New cards

Shield Volcano
Type of Volcano:
Built up in from low viscosity, low volatility, large volume flows--> This is what gives them their gentle slopes, large size.
Built up in from low viscosity, low volatility, large volume flows--> This is what gives them their gentle slopes, large size.
93
New cards
True
T/F: Due to the tilt of the Earth on its axis, differential heating occurs resulting in the equatorial regions of Earth receiving more solar energy than the polar regions.
94
New cards
How to make magma?
Lowering pressure, Raising temperature, Adding water. Melt/ magma travels through rock with little SiO2, magma contains low SiO2.
95
New cards
Resistance to flow,
Dissolved gases,
Explosive
Dissolved gases,
Explosive
Viscosity refers to a materials _____. While volatiles refers to the _____. Higher viscosity and more volatiles lead to more ____ erruptions.
96
New cards
Solar Radiation
Which of the following is NOT a primary source for plate tectonics?
Solar Radiation
Radioactive Decay
Impact Energy
Gravitational energy from earth differentiation
Solar Radiation
Radioactive Decay
Impact Energy
Gravitational energy from earth differentiation
97
New cards
Inner Core
(Solid)
(Solid)
Identify Layers of the Earth:
What is E?
What is E?
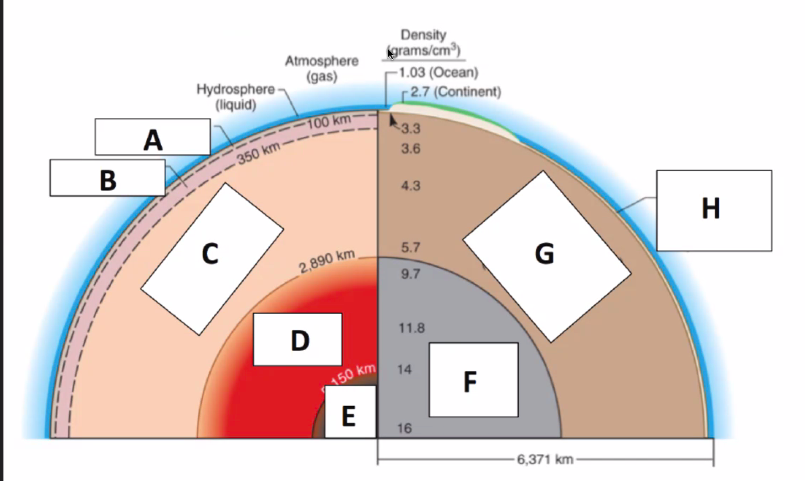
98
New cards
Outer Core
(Liquid)
(Liquid)
Identify Layers of the Earth:
What is D?
What is D?
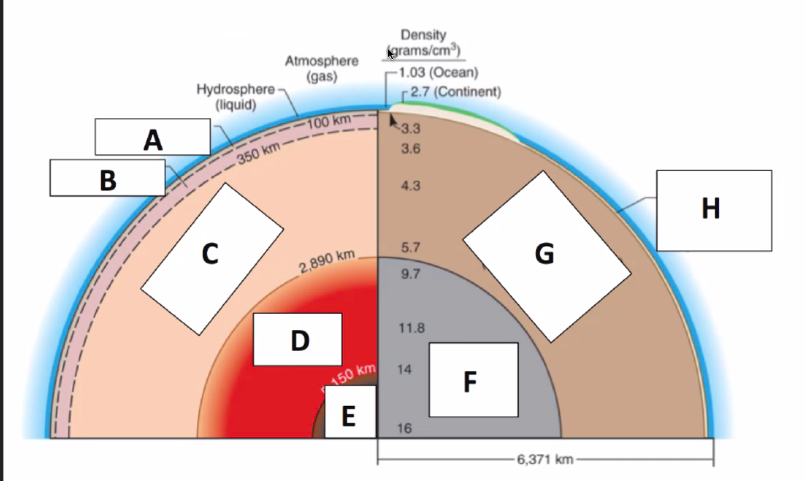
99
New cards
Mesosphere
(stiff plastic)
(stiff plastic)
Identify Layers of the Earth:
What is C?
What is C?
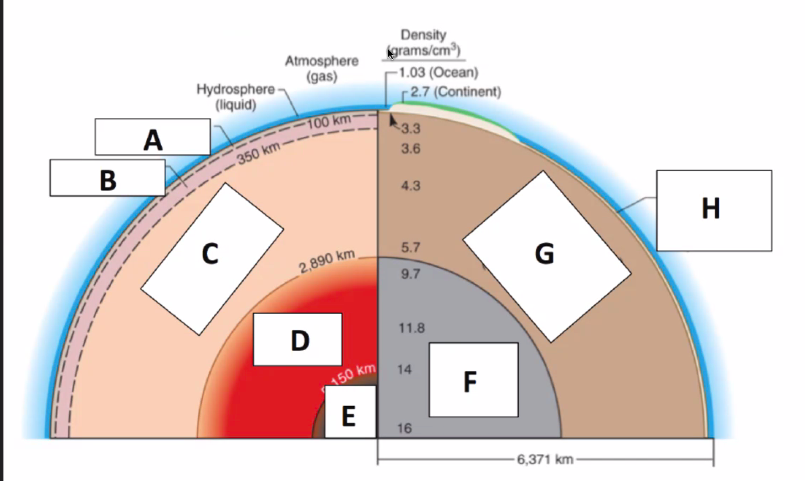
100
New cards
Athenosphere
(Ductile, soft plastic)
(Ductile, soft plastic)
Identify Layers of the Earth:
What is B?
What is B?