A Lec Study Guide: Chapters 1, 2, 4, 6
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
**The study of body structure __________.
ex. size, shape, appearance
anatomy
What is gross anatomy?
study of large body structures visible to the naked eye
What is regional anatomy?
the study of all the structures in a particular region of the body
What is systemic anatomy?
all the organs with related functions are studied together (organ systems)
What is surface anatomy?
the study of shapes and markings (landmarks) on the surface of the body
What is microscopic anatomy?
the study of structures that are too small to be seen with the naked eye
**The study of body function or explaining how an organ or system(s) work is called __________.
physiology
Chemical Level of Organization
most simple level, atoms combine to form molecules
Cellular Level of Organization
cells and their functional subunits
Tissue Level of Organization
a group of cells performing a common functions
Organ Level of Organization
a discrete structure made up of more than one tissue performing a specific function
Organ System Level of Organization
organs working together for a common purpose
Organismal Level of Organization
highest level of structural organization, results from all simpler levels working in unison
Levels of organization from simplest to most complex.
chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
Function of the integumentary system
1. Forms the external body covering 2. Protects deeper tissue from injury 3. Helps regulate body temperature 4. Location of cutaneous nerve receptors
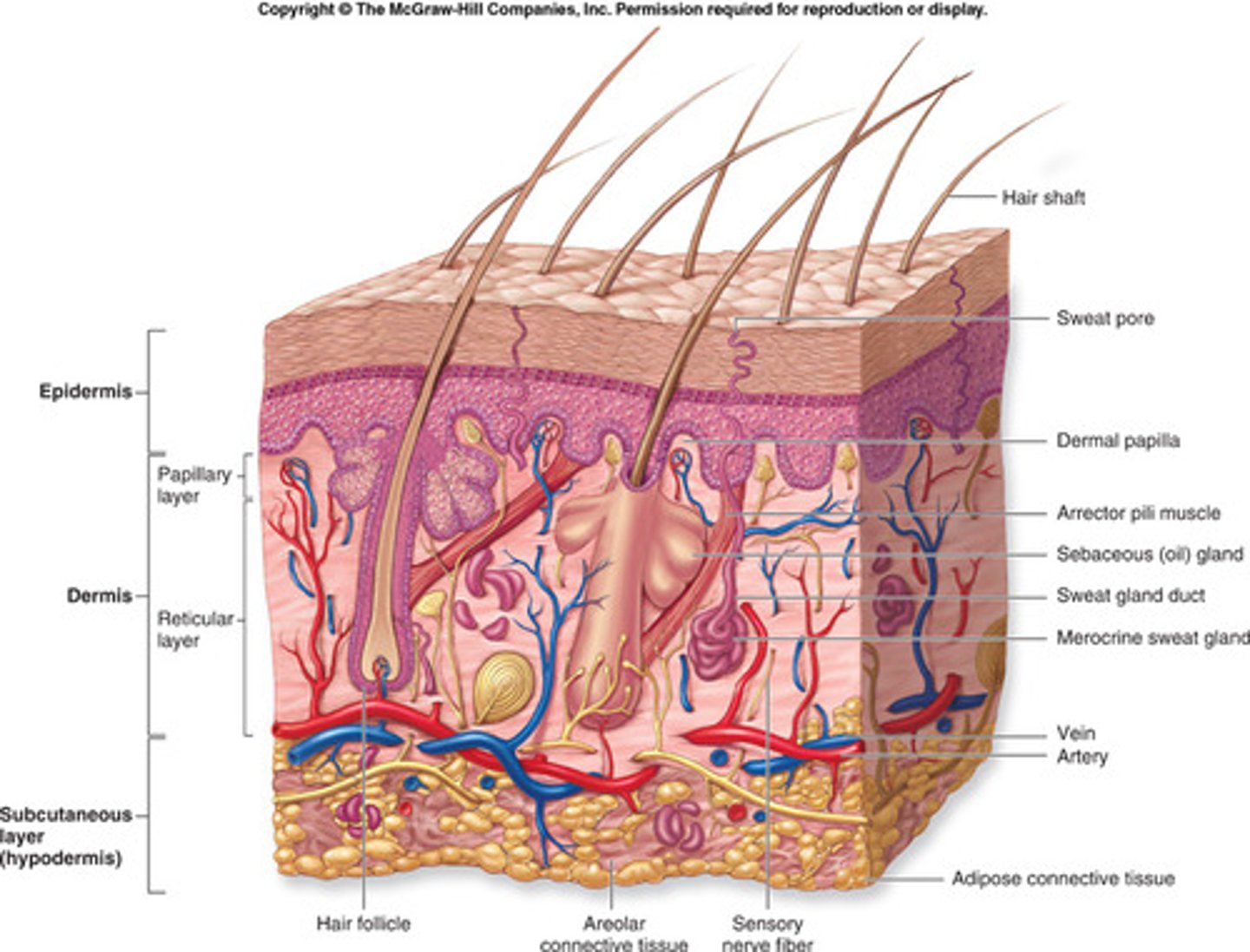
Function of the skeletal system
1. Protects and supports body organs
2. Provides a framework for muscle attachment for movement
3. Site of blood cell formation
4. Stores minerals
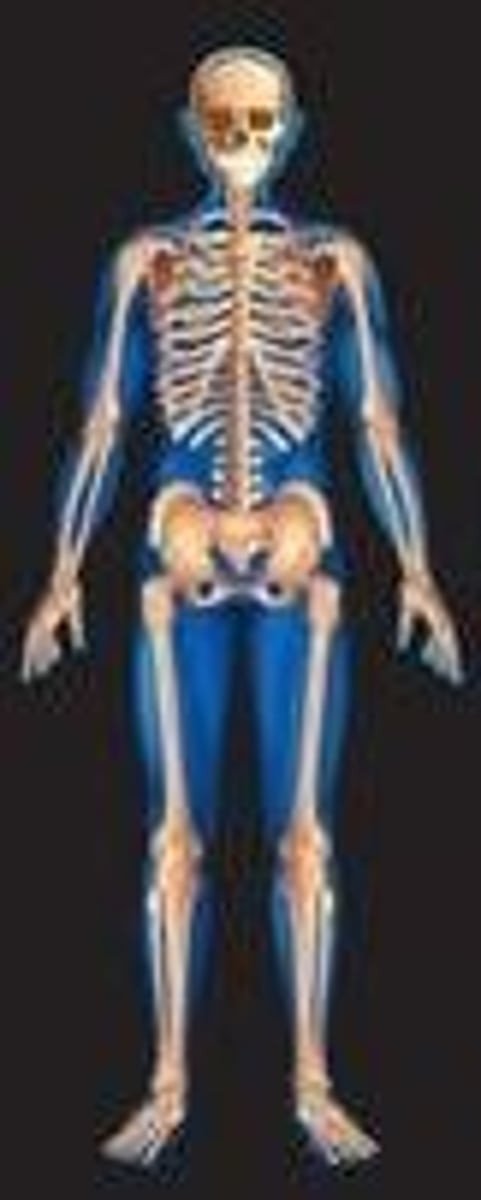
Function of the muscular system
1. Produces movement
2. Maintains posture
3. Produces heat
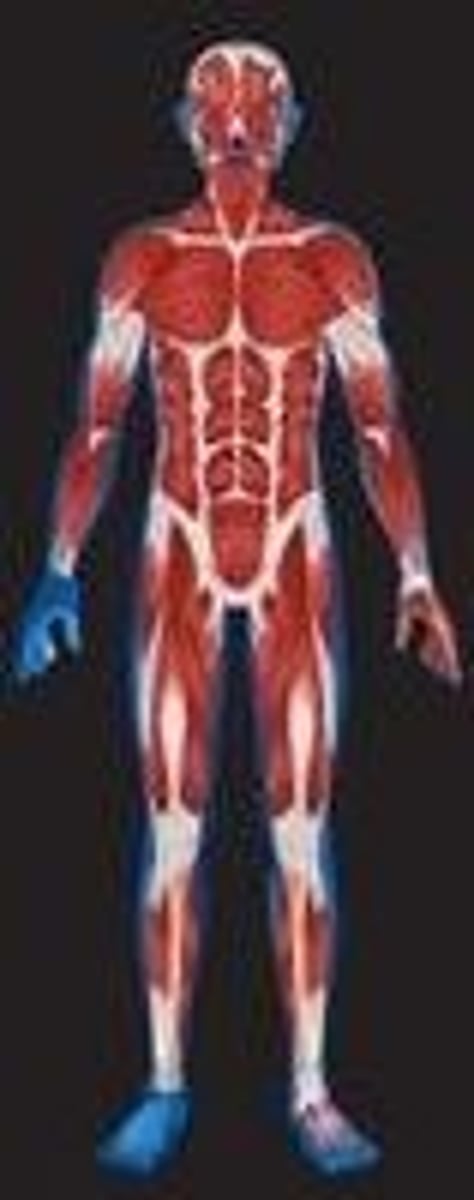
Function of the nervous system
1. Fast-acting control system
2. Responds to internal and external change
3. Activates muscles and glands
Function of the endocrine system
1. Secretes hormones that regulate (homeostasis):
a. Growth
b. Reproduction
c. Metabolism
Function of the cardiovascular system
1. Heart pumps blood via blood vessels which transports: oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes
Function of the lymphatic system
1. Returns fluids to blood vessels
2. Cleanses the blood by disposing of debris in the lymphatic stream
3. Houses WBC involved in immunity
Function of the respiratory system
1. Keeps blood supplied with oxygen
2. Removes carbon dioxide

Function of the digestive system
1. Breaks down food
2. Allows for nutrient absorption into blood
3. Eliminates indigestible material
Function of the urinary system
1. Eliminates nitrogenous wastes
2. Maintains acid-base balance
3. Regulates water and electrolytes
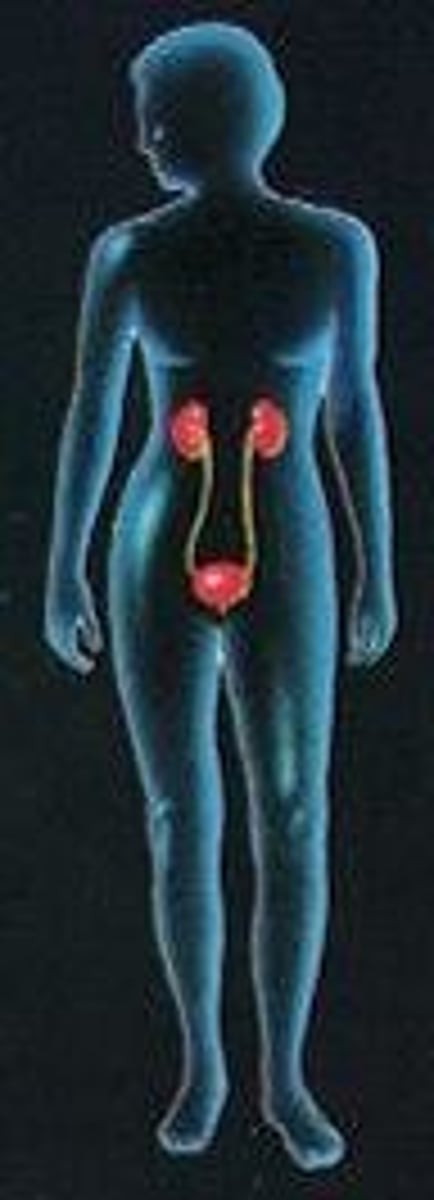
Which body system produces offspring?
reproductive system
What organ makes up the integumentary system?
skin
What organs make up the skeletal system?
bones, cartilage, joints
What organs make up the muscular system?
skeletal muscles
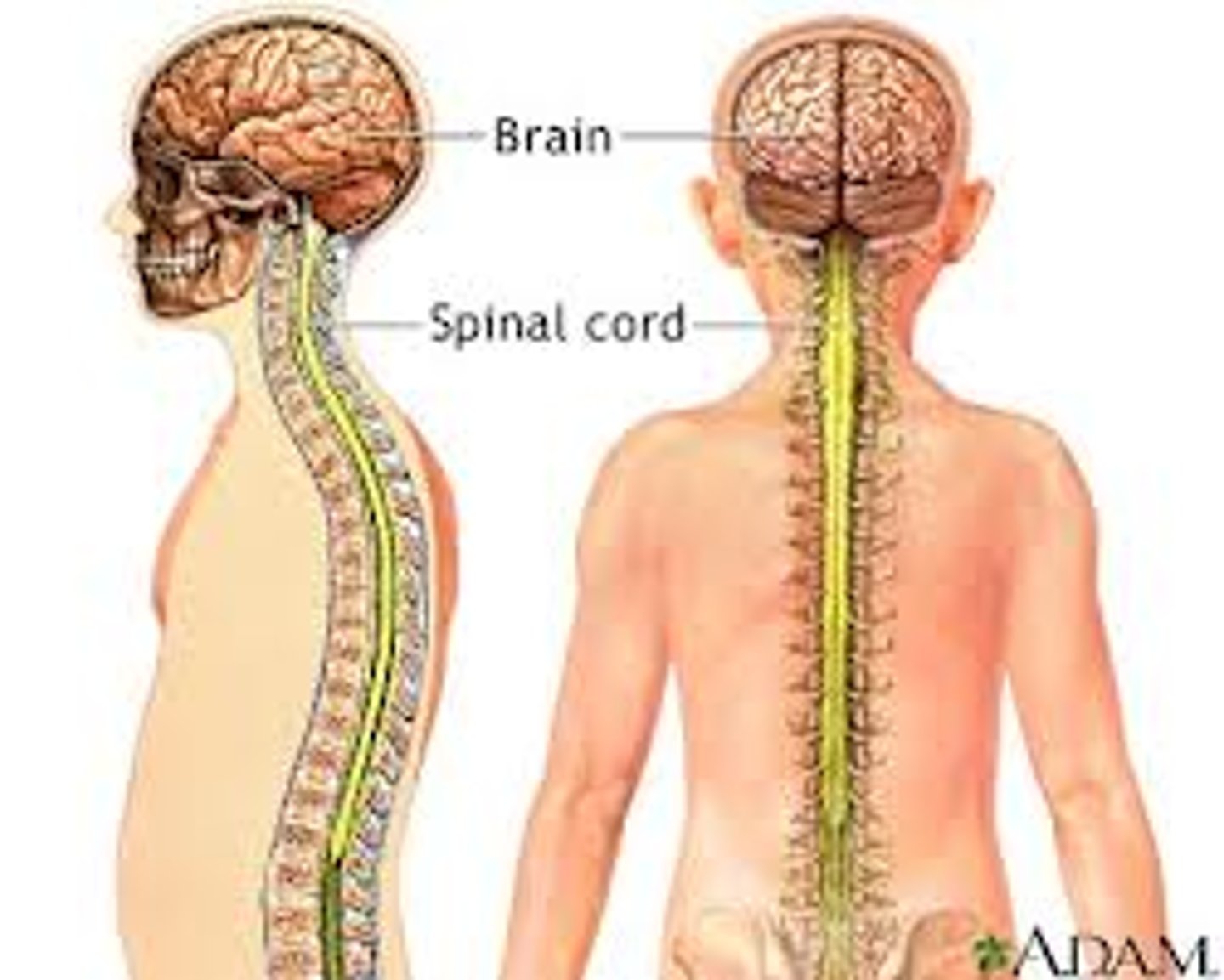
What organs make up the nervous system?
brain, spinal cord, nerves
The endocrine system is made up of __________.
glands
The cardiovascular system is made up of _________.
heart, blood vessels
The lymphatic system is made up of _________.
lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels
What organs make up the respiratory system?
nasal cavity, lungs, trachea
Organs of the digestive system are: ___________.
stomach, intestines, esophagus, oral cavity
The urinary system is made of _____________.
kidneys, ureters, bladder
The reproductive systems for females and males are made up of the following organs: ____________.
ovaries, uterus (female) & testes (male)
The skeletal system functions in storing mineral, such as _____.
calcium
The muscular system is involved in _______.
heat production
Which elements of a control system detect a change?
receptor
The survival need of _________ is required in order to release energy from foods.
oxygen
This body system responds to stimuli (internal and external).
the nervous system
This system is the site for hematopoiesis (blood cell formation).
the skeletal system
This system houses blood cells involved in immunity. It picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood.
the lymphatic system
The __________ is a slow-acting body control system.
endocrine system
In the __________, the body is erect with feet parallel and the arms hanging at the sides with the palms facing forward.
anatomical position
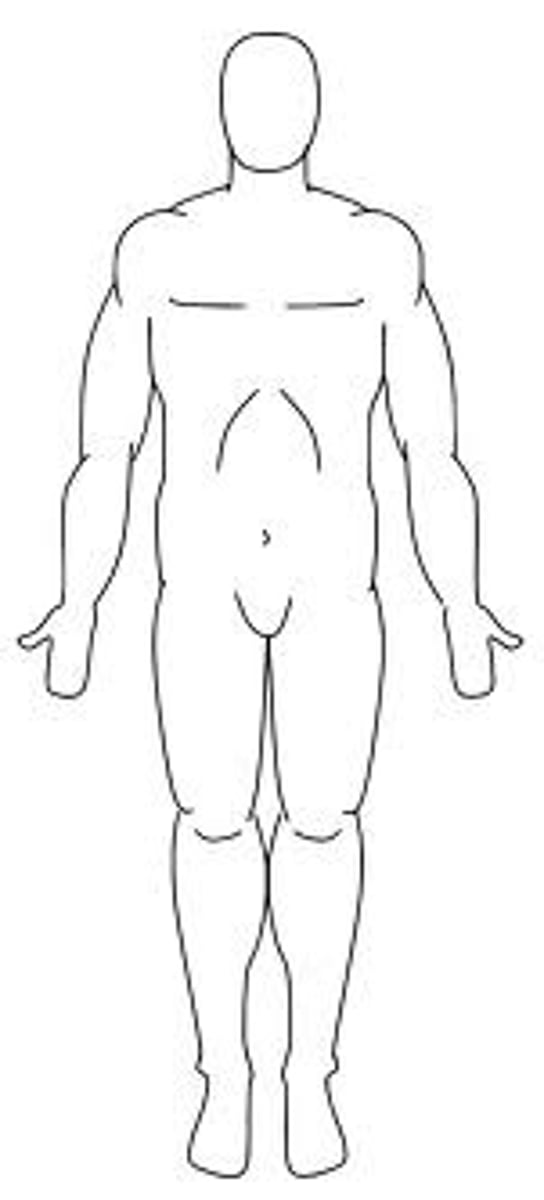
A section that divides the body on the longitudinal plane into right and left parts is called a(n) _________.
sagittal plane
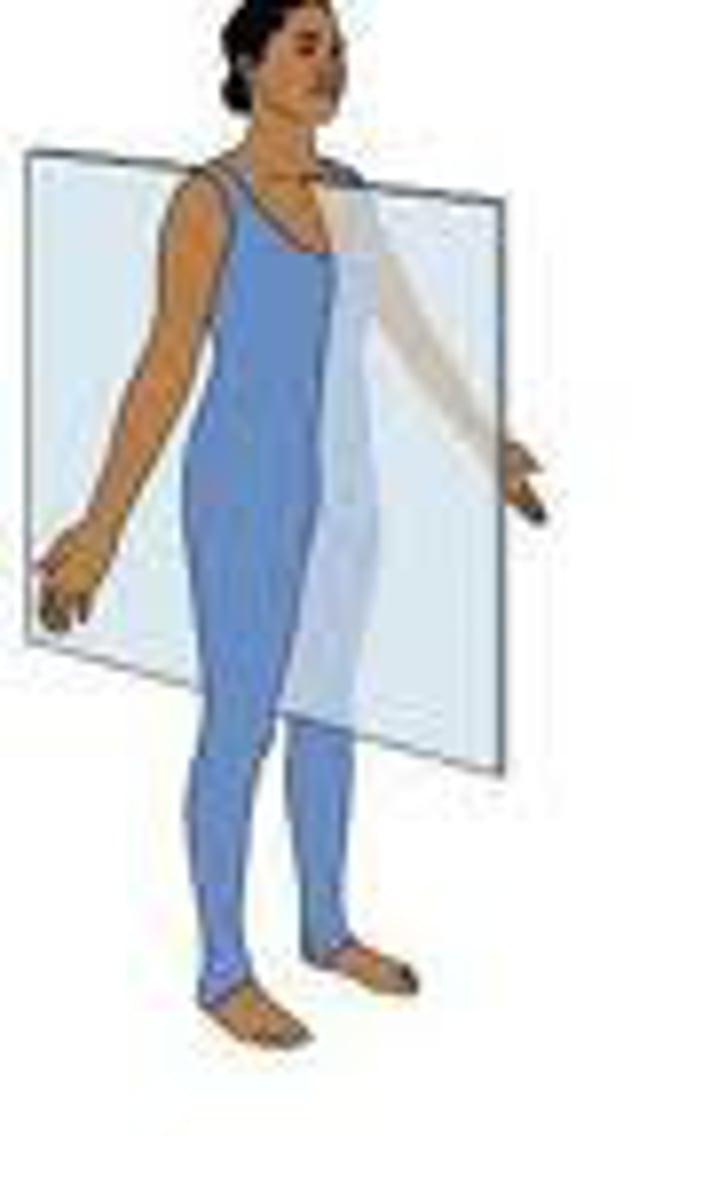
A section that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions is called
frontal plane
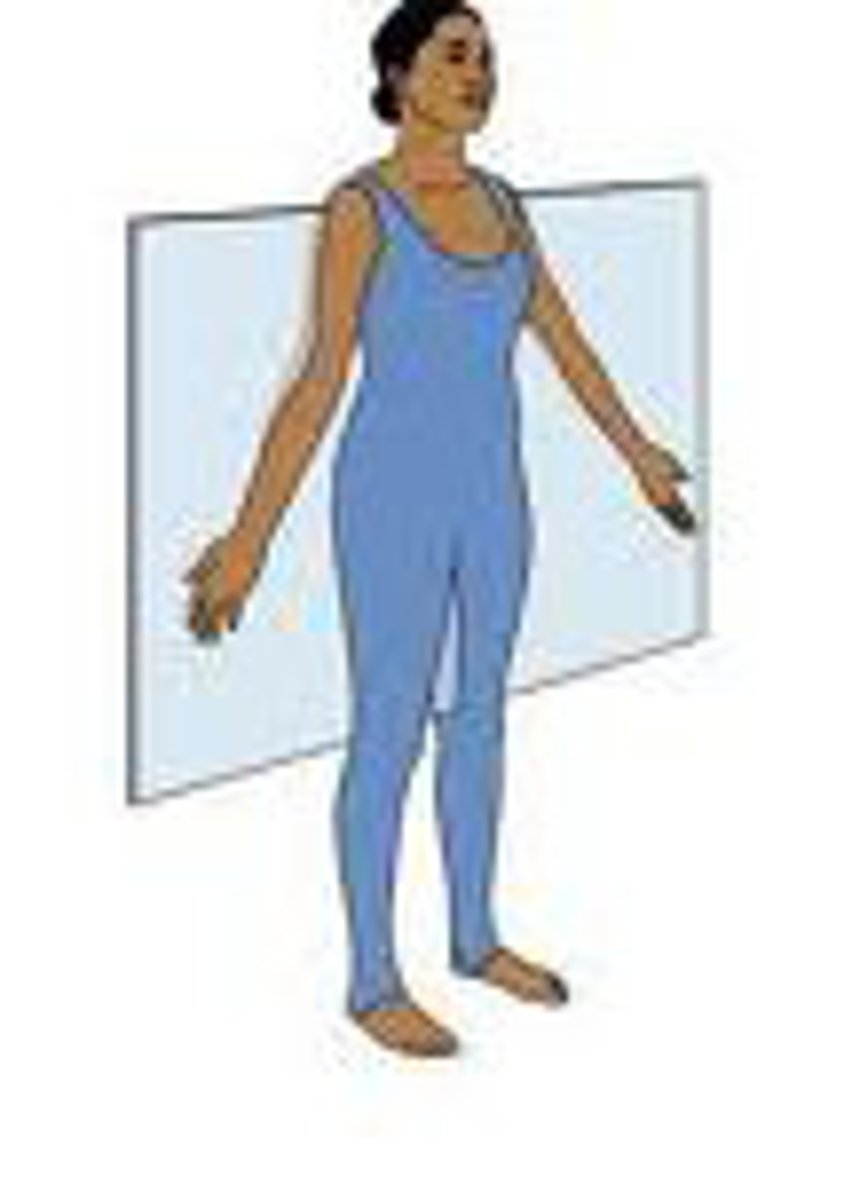

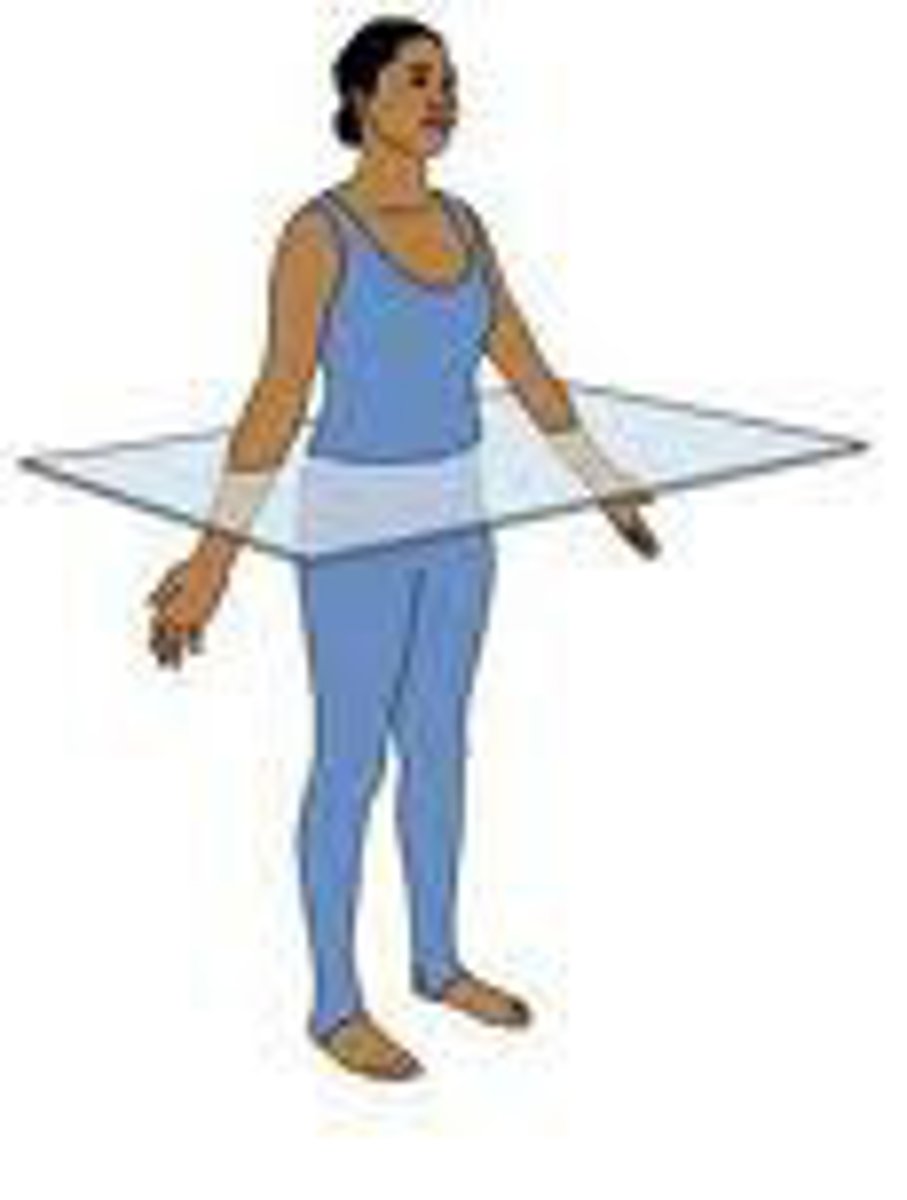
A section that divides the body into superior and inferior parts is called a(n) _________.
transverse plane
The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are subdivisions of the ____________.
ventral cavity (anterior)
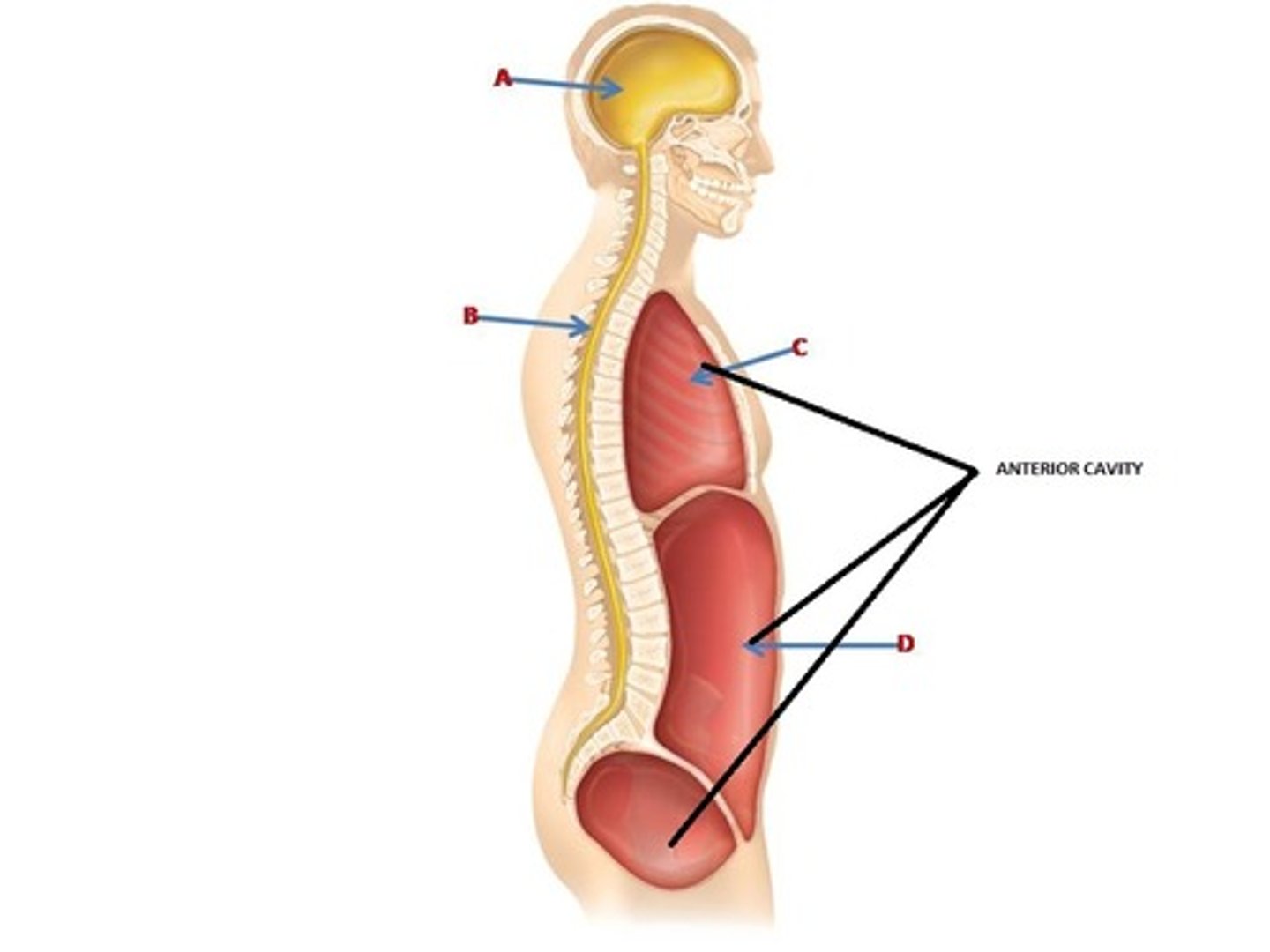
Thoracic Cavity
contains heart and lungs
The central region of the thoracic cavity containing the heart is called the ____________.
mediastinum
The two lateral regions of the thoracic cavity containing the lungs are called the ____________ .
pleural cavities
Abdominopelvic Cavity
contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities
Abdominal Cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
Pelvic Cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
The cranial and vertebral cavities are subdivisions of the _____________.
dorsal cavity (posterior)
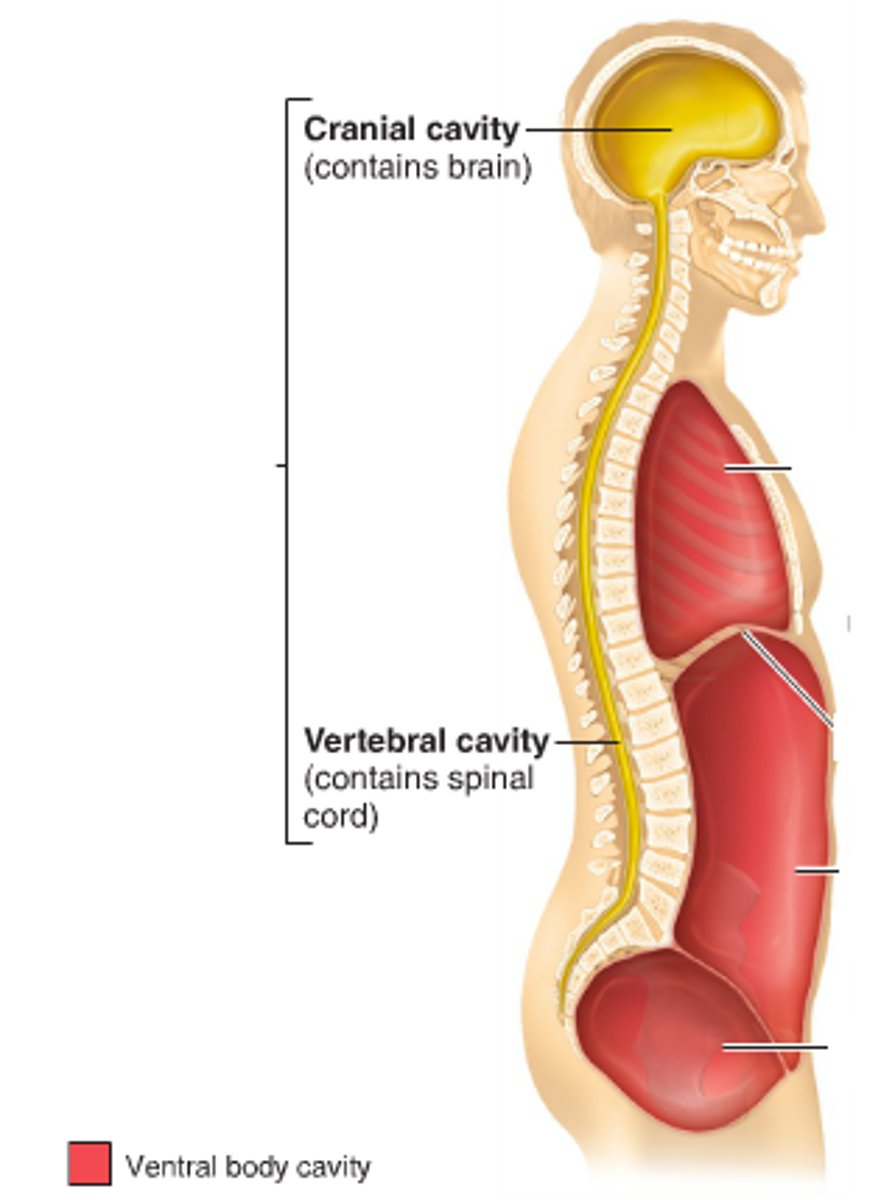
Cranial Cavity
contains the brain
Vertebral Cavity
contains the spinal cord
Serous Cavity
space between membranes lined by a serous membrane
Parietal Serosa
the outer membrane that lines the internal body cavity walls
Visceral Serosa
covers the internal organs
Serous Fluid
a clear, watery fluid secreted by the cells of a serous membrane
The right upper quadrant contains
liver and gallbladder
The left upper quadrant contains
diaphragm, spleen, stomach, transverse colon of large intestine
The right lower quadrant contains
cecum, appendix, ascending colon of large interesting, small intestine
The left lower quadrant contains
urinary bladder, initial part of sigmoid colon, descending colon of large intestine
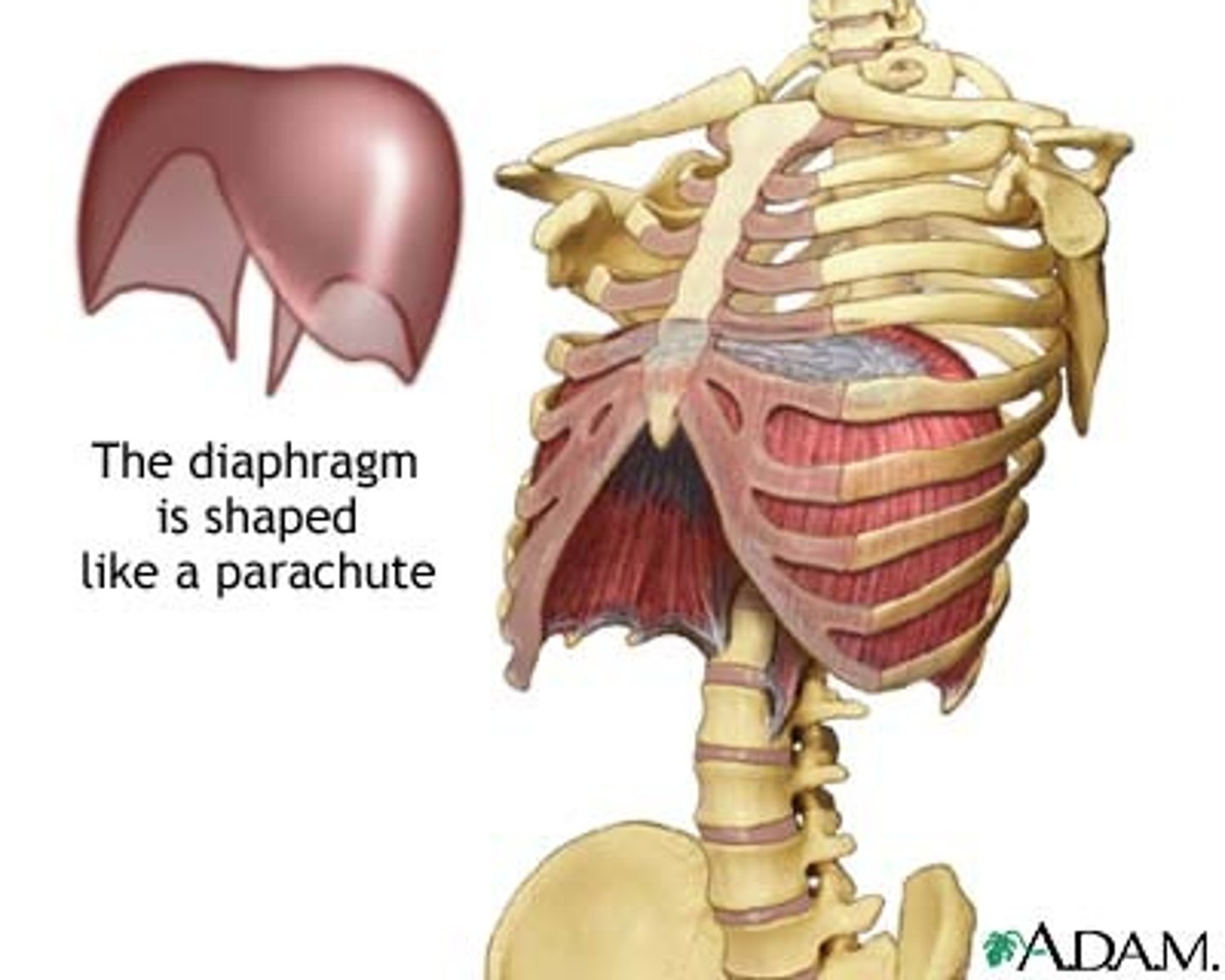
The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominopelvic cavity by the ____________.
diaphragm
What are the 3 major regions of a cell
- plasma membrane: the outer membrane
- cytoplasm: contains most organelles
- nucleus: controls cellular activities
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
fluid mosaic model (lipid bilayer), two types of proteins (integral and peripheral)
Integral Proteins
firmly imbedded in or attached to the lipid bilayer
Peripheral Proteins
attach to the surface of the membrane
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
mechanical barrier, selective permeability, and cell communication
Simple Diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Facilitated Diffusion (passive transport)
movement of molecules across a membrane via integral proteins without energy from ATP
Active Transport
energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a conc. gradient
Osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Endocytosis
process in which a cell takes material into the cell
Phagocytosis
"cell eating" specific in what enters the cell
Pinocytosis
"cell drinking" not specific in what enters the cell
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
the uptake of specific molecules based on a cell's receptor proteins
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane
Cytoplasm
lies internal to plasma membrane; consists of cytosol, organelles, and inclusions
Cytosol
jellylike fluid in which other cellular elements are suspended; consists of water, ions, and enzymes
Ribosomes
- site of protein synthesis
- free (in cytosol) or attached (to rough endoplasmic reticulum) ribosomes
- constructed of proteins and ribosomal RNA
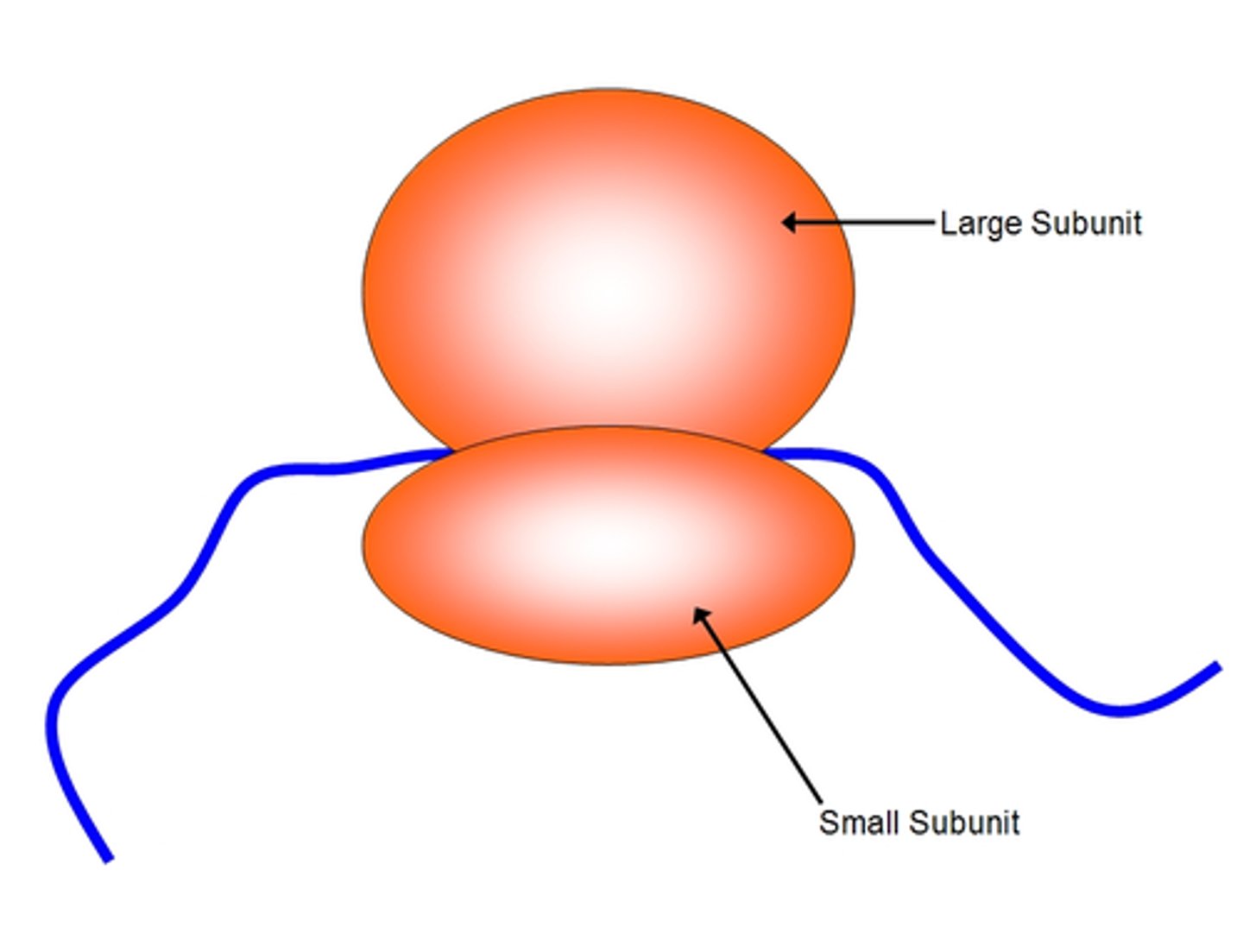
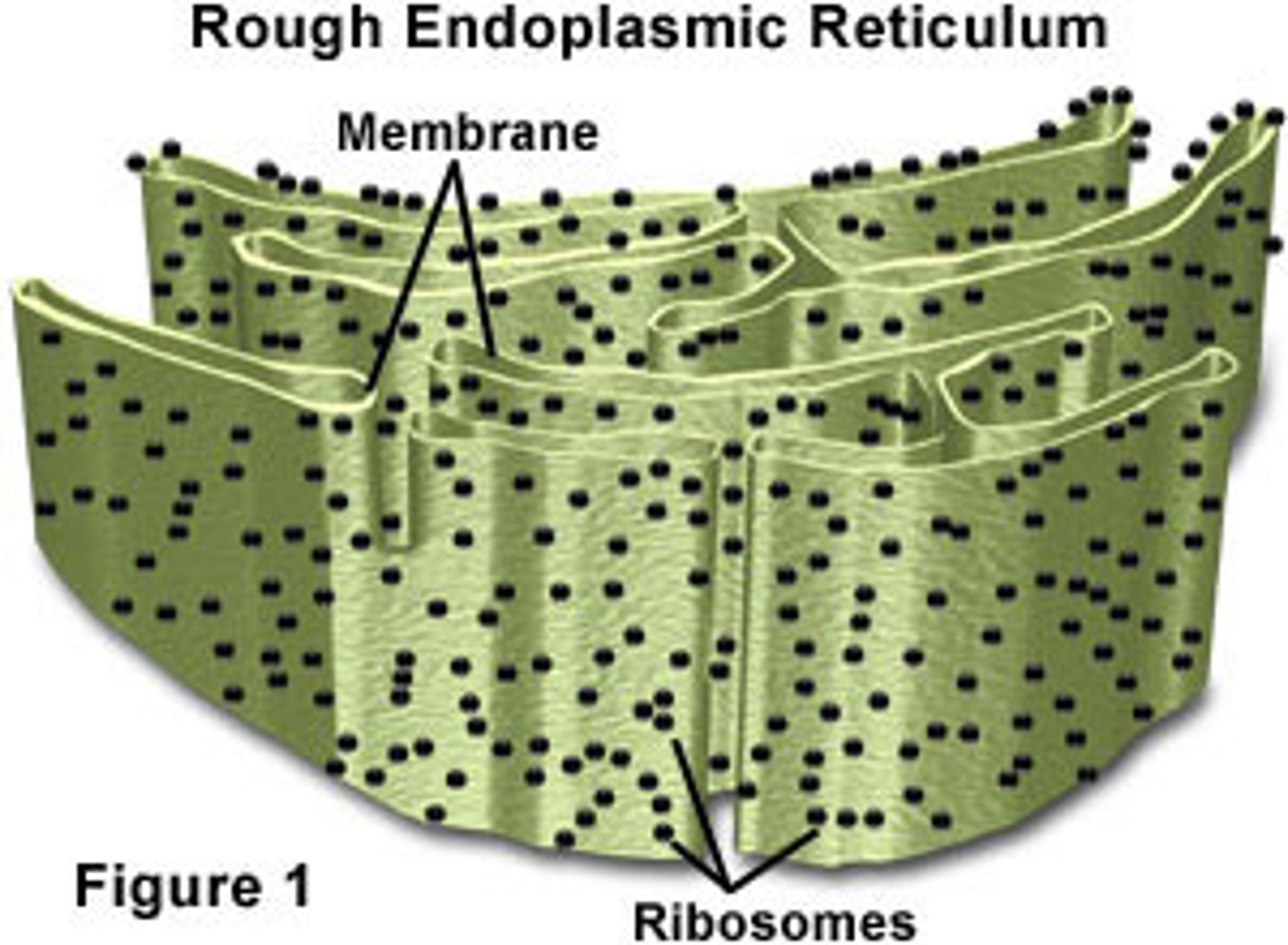
Endoplasmic Reticulum
a system of membrane-walled envelops and tubes throughout the cytoplasm
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
ribosomes attached to the external surfaces and are a part of protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
ribosomes aren't attached to the external surfaces and are a part of lipid synthesis
Golgi Apparatus
- a stack of 3 to 10 disc shaped cisterns
- sorts products of Rough ER and dictates where it's sent to

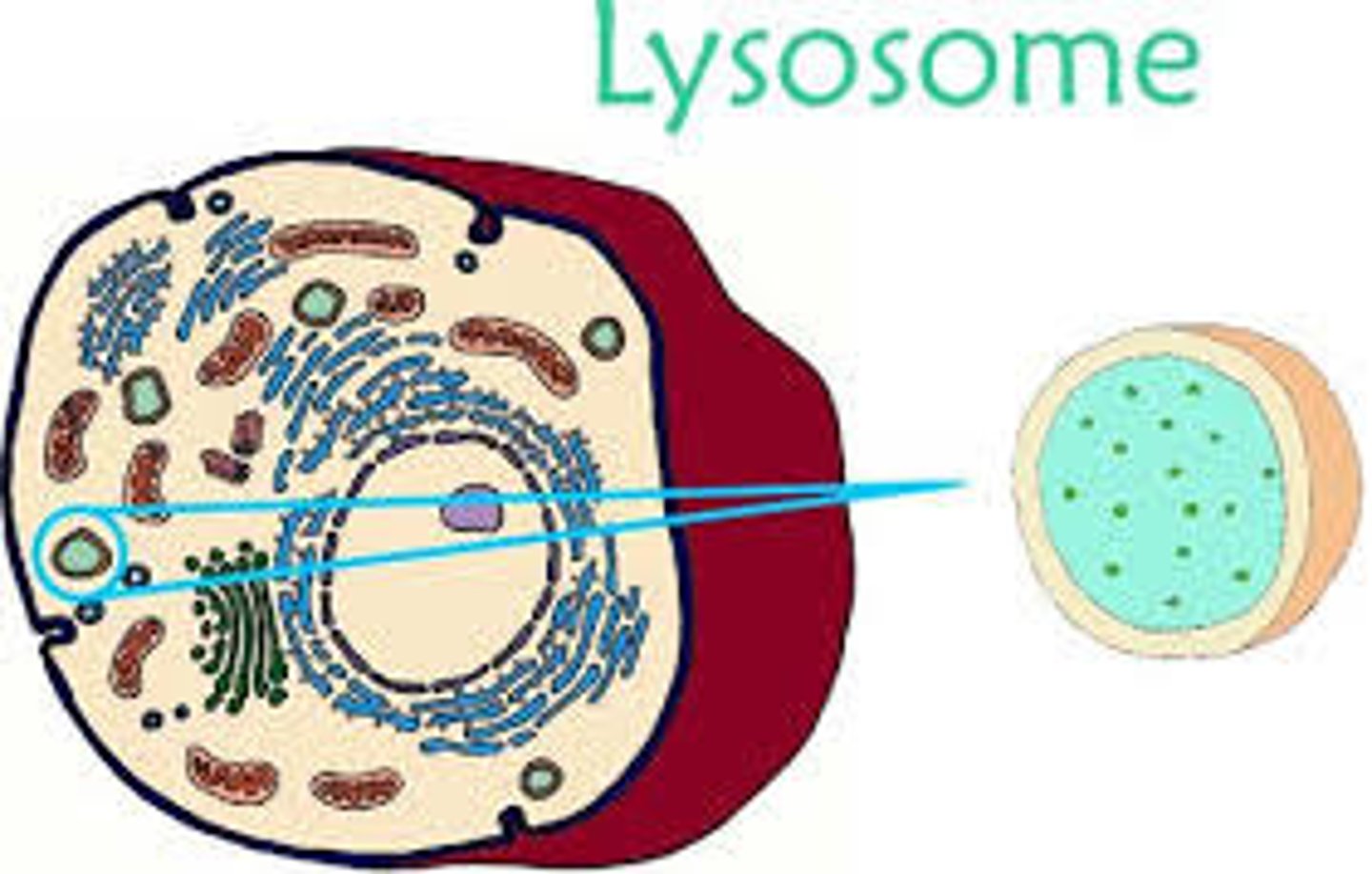
Lysosomes
- membrane walled sacs containing digestive enzymes (clears the debris we don't want)
- sites of intracellular digestion
Mitochondria
- surrounded by double walled membrane
- powerhouse of the cell
- site of ATP synthesis
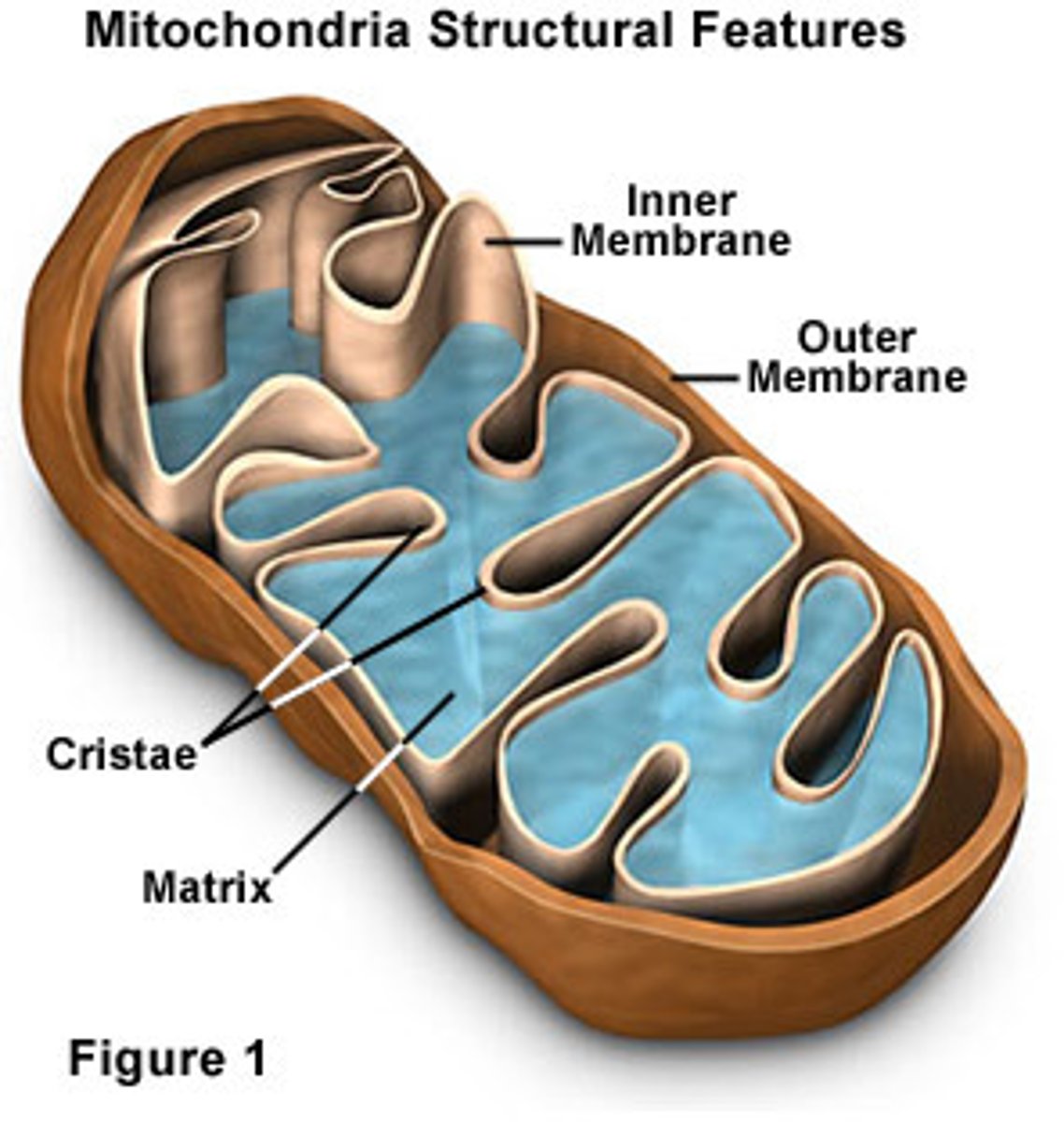
Peroxisomes
- membrane walled sacs of oxidase or catalase enzymes
- helps remove/filter the toxic waste in the cell
- enzymes neutralize free radicals and break down poisions

Cytoskeleton "cell skeleton"
an elaborate network of rods (microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules)
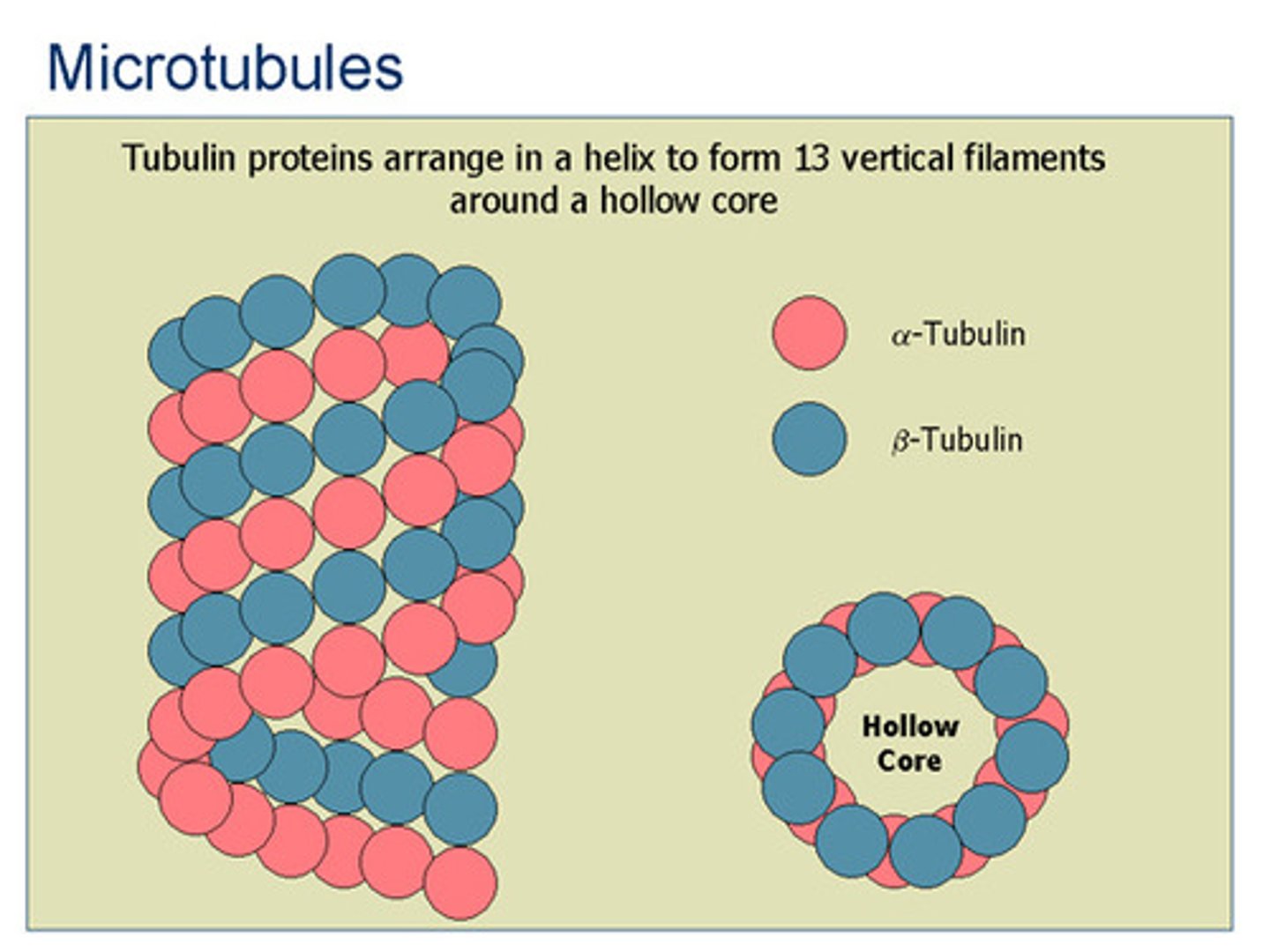
Microtubules
- cylindrical structures made of proteins
- support the cell and give it shape
- largest of the 3 rods
Intermediate Filaments
- protein fibers
- the stable cytoskeleton elements; resist mechanical forces acting on the cell
- middle size of the 3 rods
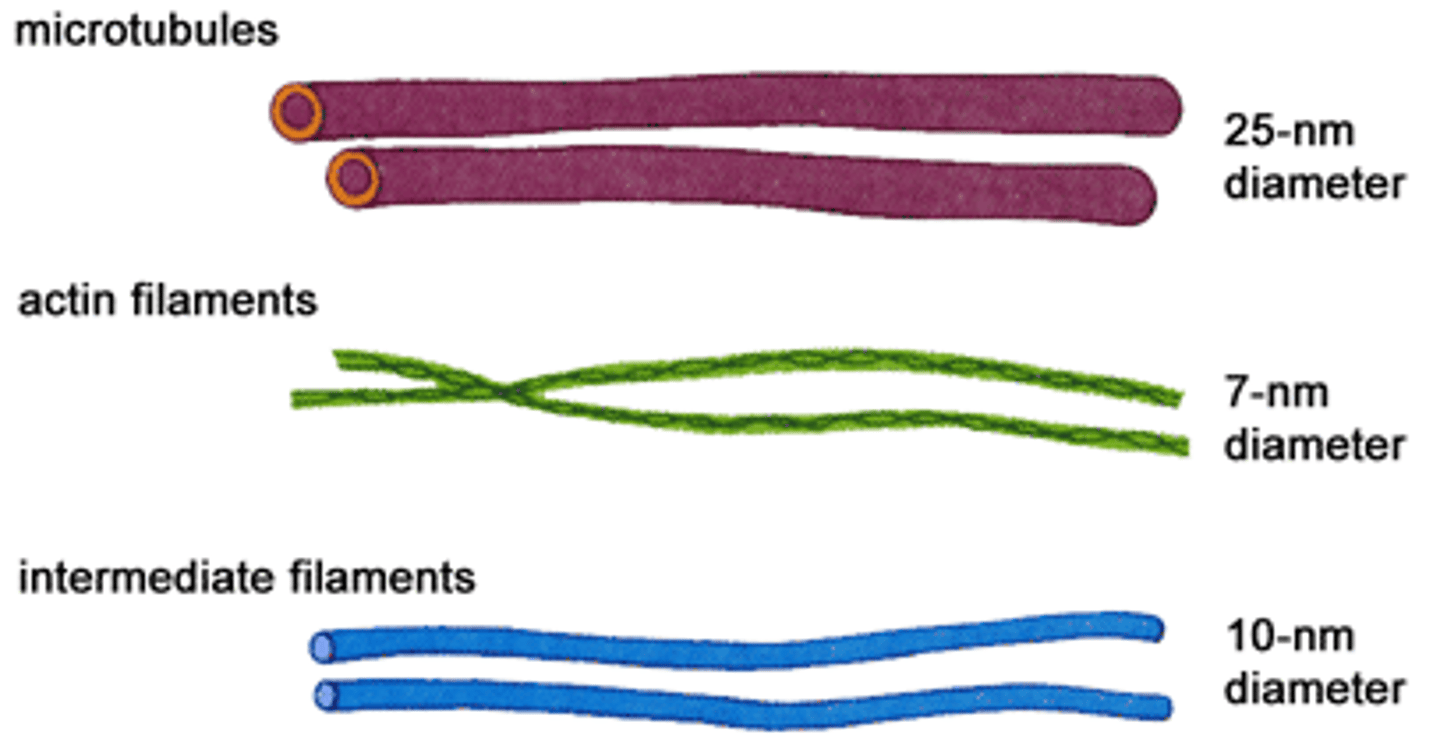
Microfilaments
-fine filaments composed of the contractile protein actin
- involved in muscle contraction and other types of intracellular movement
- smallest of the 3 rods
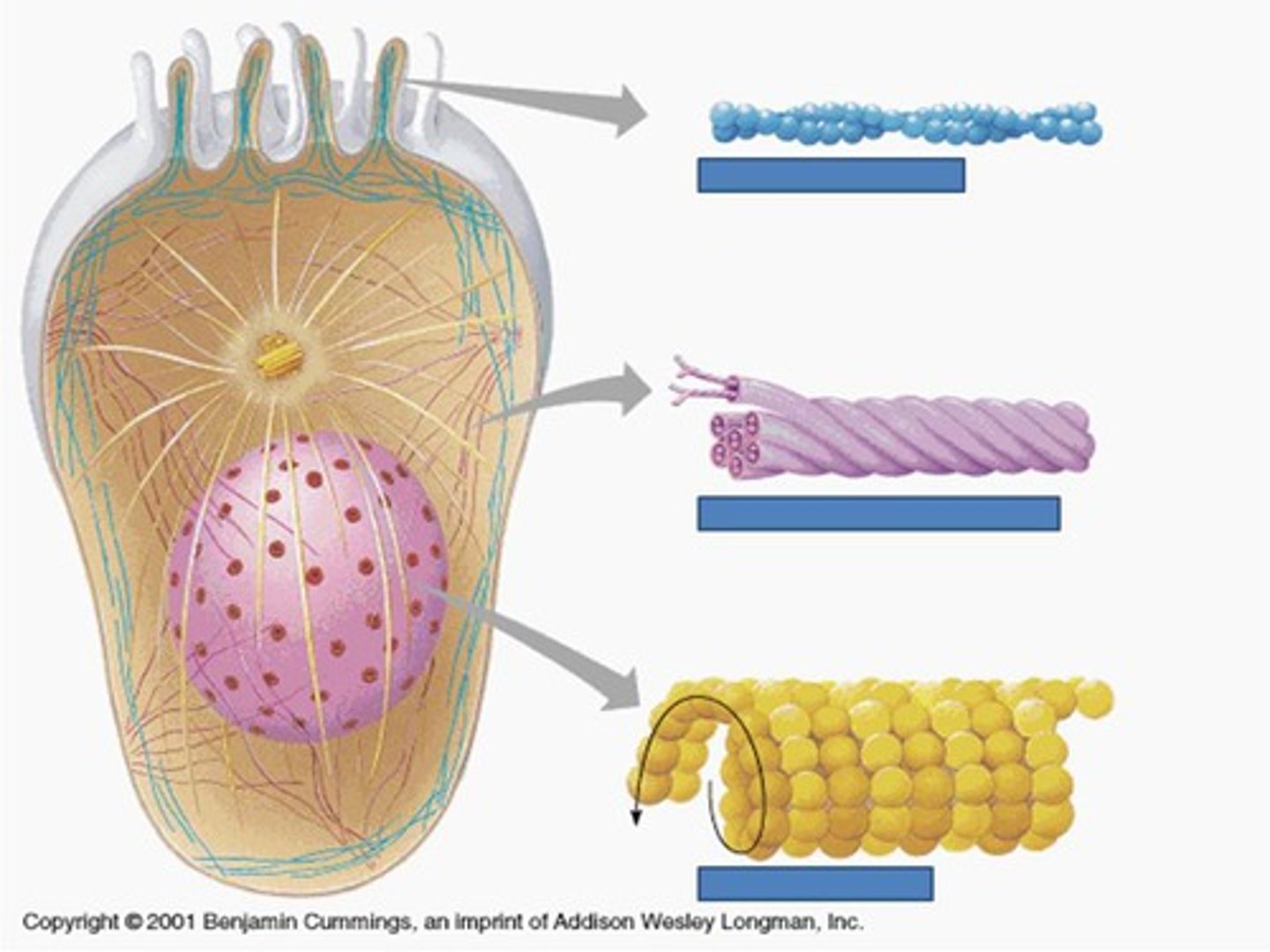
Centrosome
- a spherical structure in the cytoplasm
- composed of centrosome matrix and centrioles
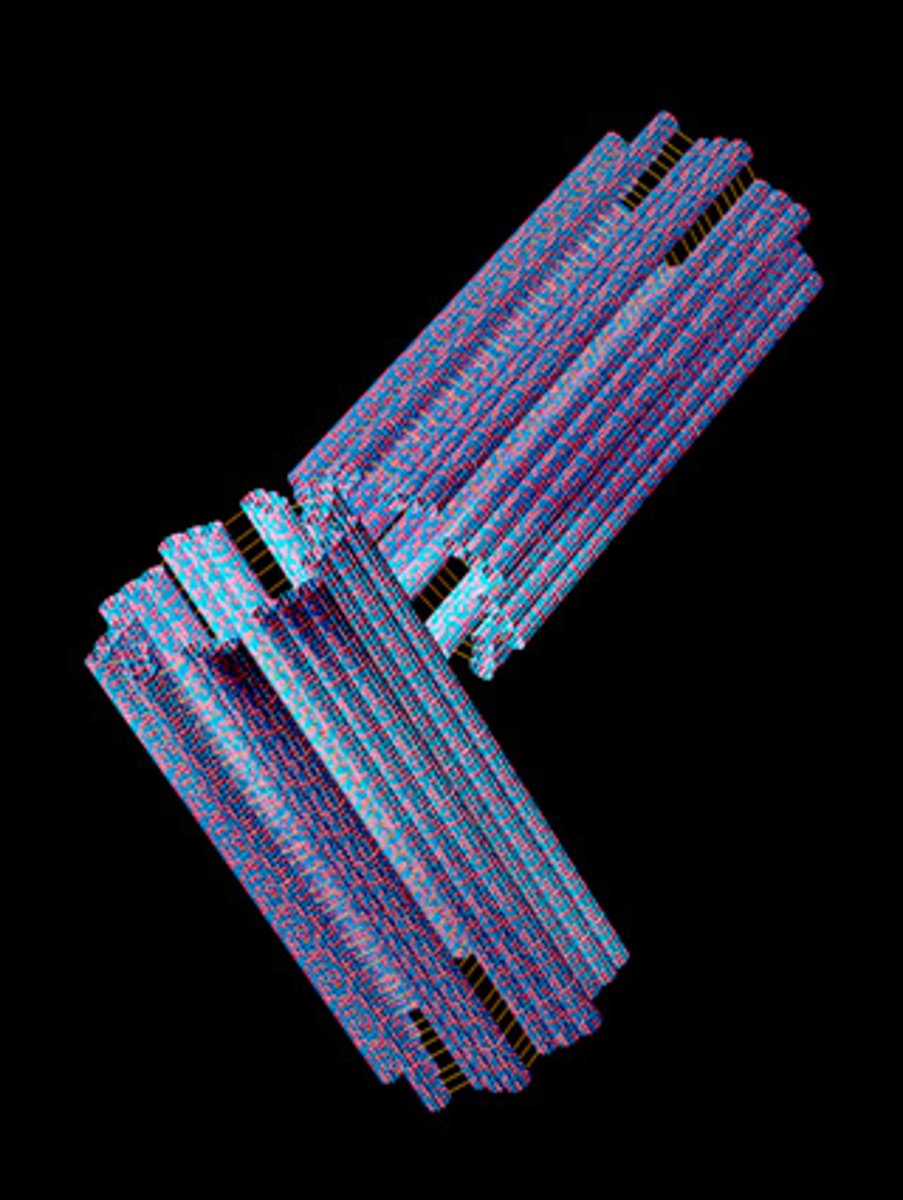
Centrioles
- paired cylindrical bodies
- act in forming cilia, flagella, and the mitotic spindle
Nucleus
- largest organelle
- control center of the cell
- responsible for transmitting genetic information
- provide instructions for protein synthesis
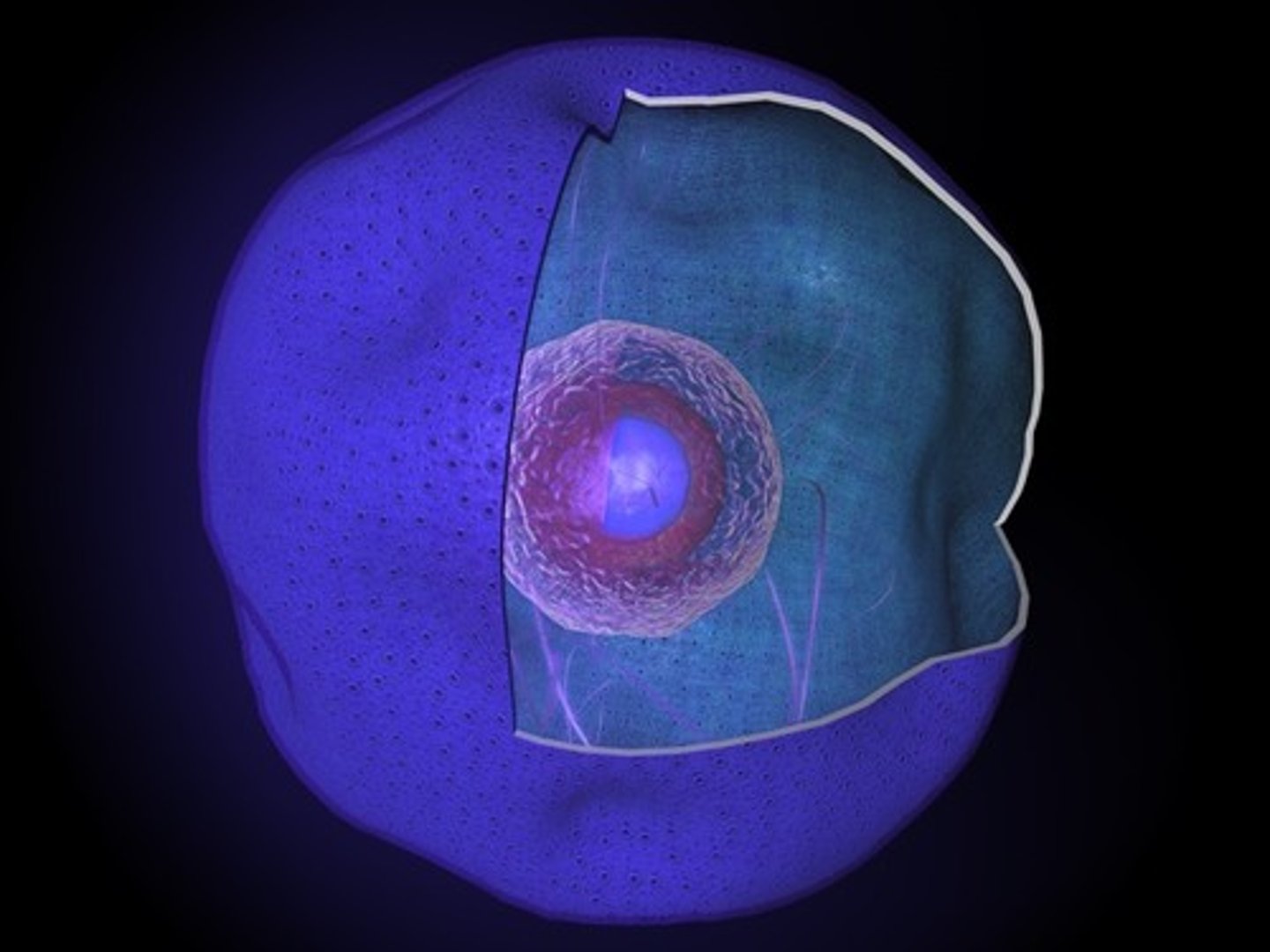
What are the 3 major portions of the nucleus?
Nuclear envelope: outer boundary
Nucleolus: site of ribosome subunit manufacture
Chromatin: packaged DNA
Nuclear Envelope
double membrane perforated with nuclear pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus