OPT 223 Macula 3 & 4
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is choroidal rupture and what causes it?
break in Bruch's membrane secondary to eye trauma (can be longstanding)
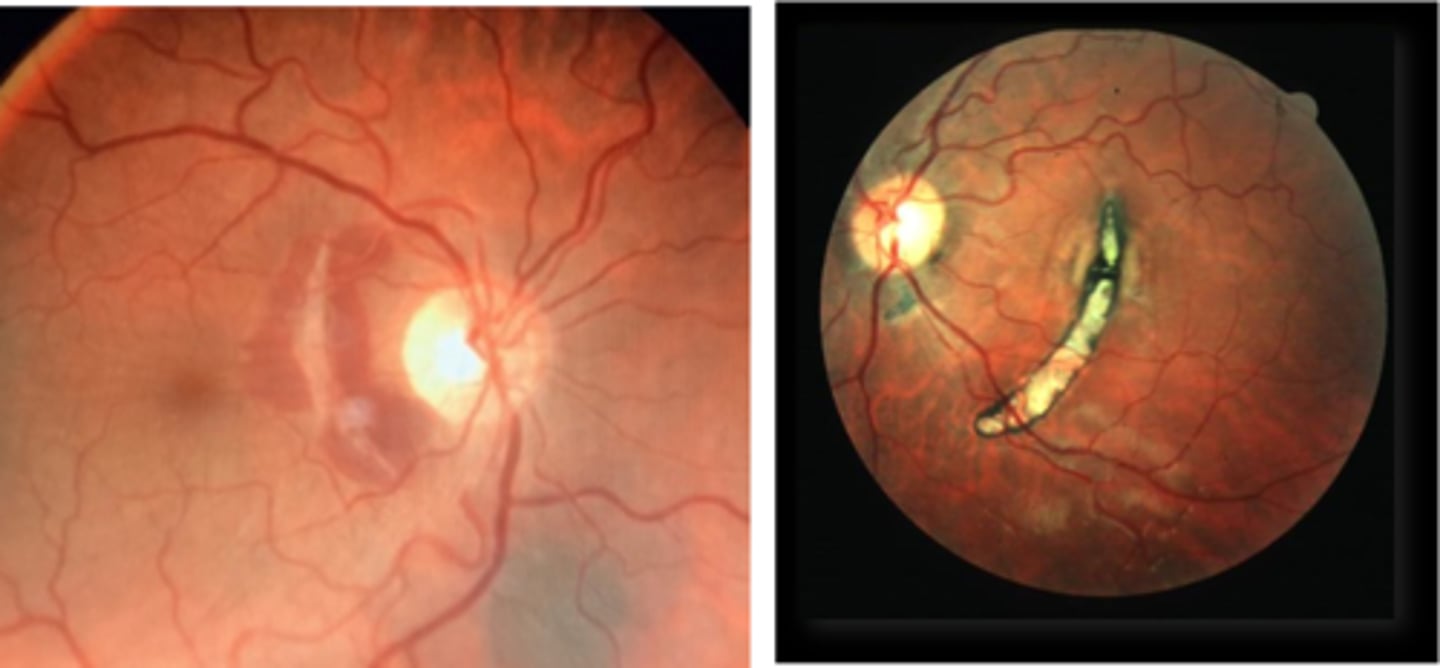
How does choroidal rupture appear on fundoscopy?
curvilinear or crescent-shaped streak, sometimes concentric to ONH
+/- subretinal /subRPE hemorrhage (acute)
Bruch's/Choriocapillaris/RPE damage
overlying neurosensory retina is intact
+/- RPE hyperplasia (chronic)
+/- CNV over time
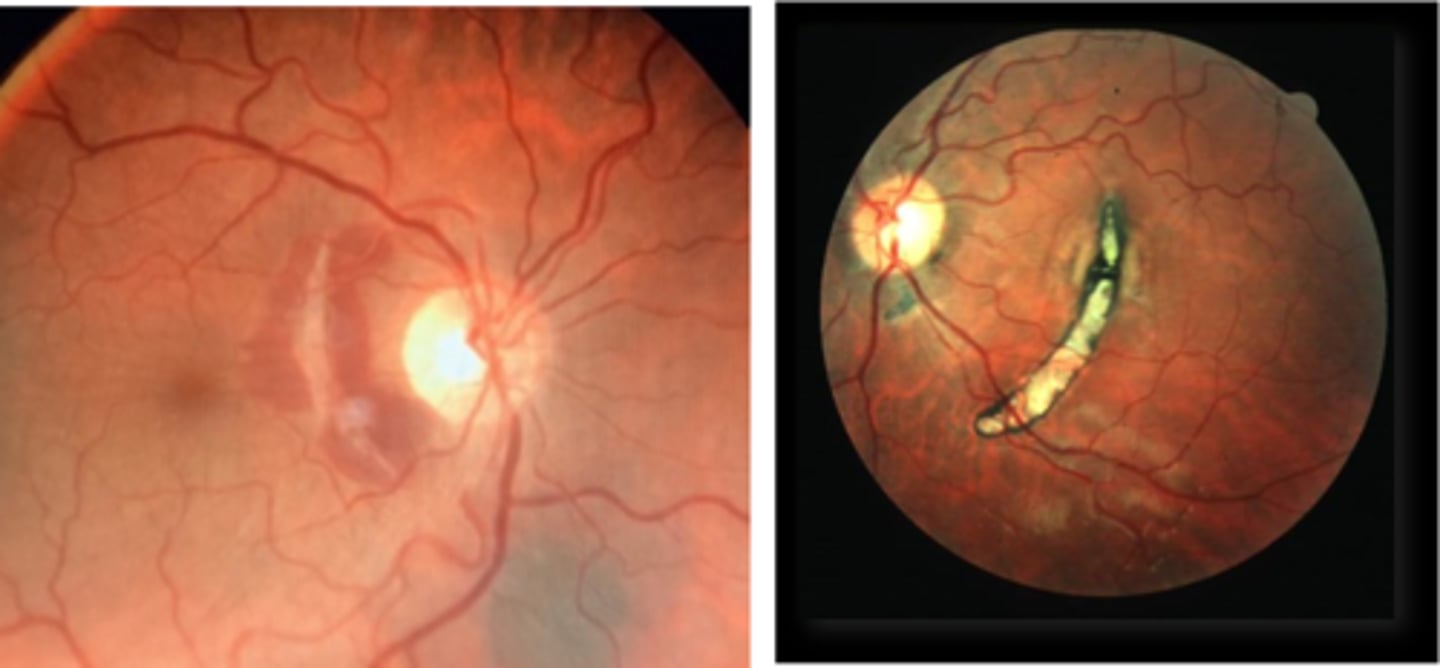
What are the symptoms of choroidal rupture?
asymptomatic if macula avoided
absolute scotoma if macula affected
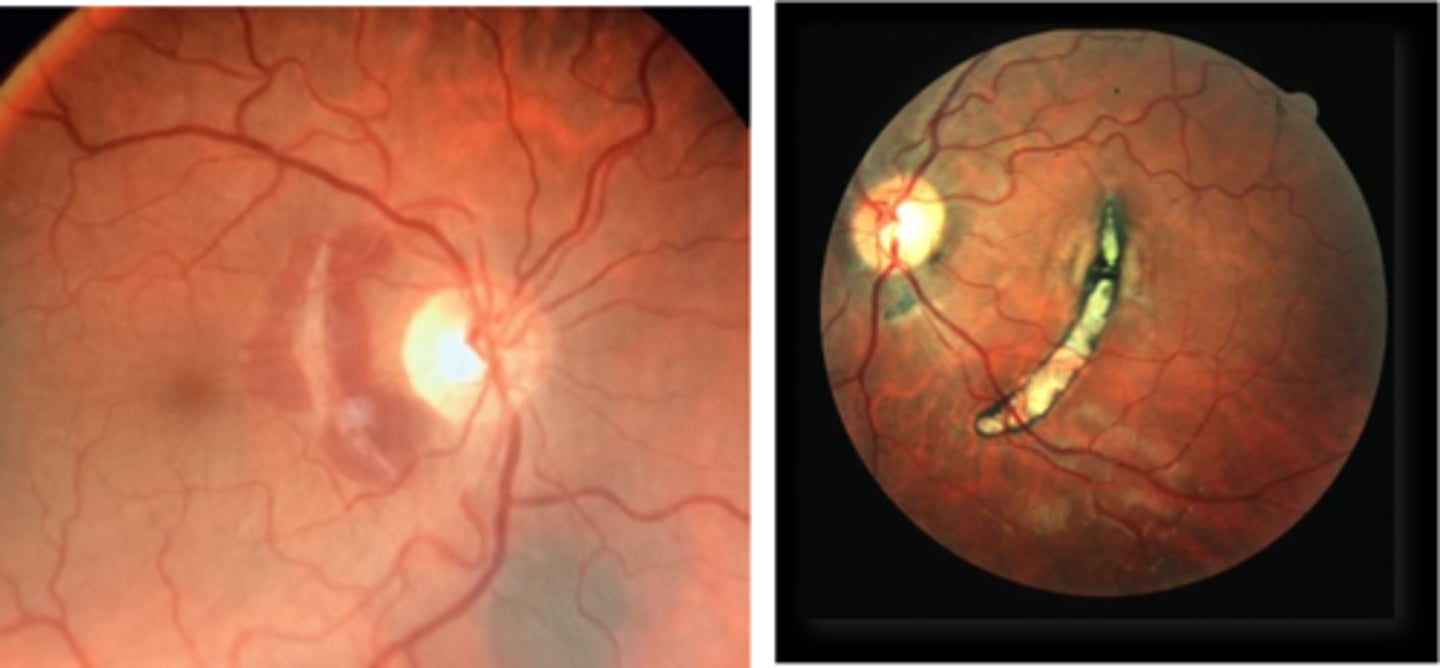
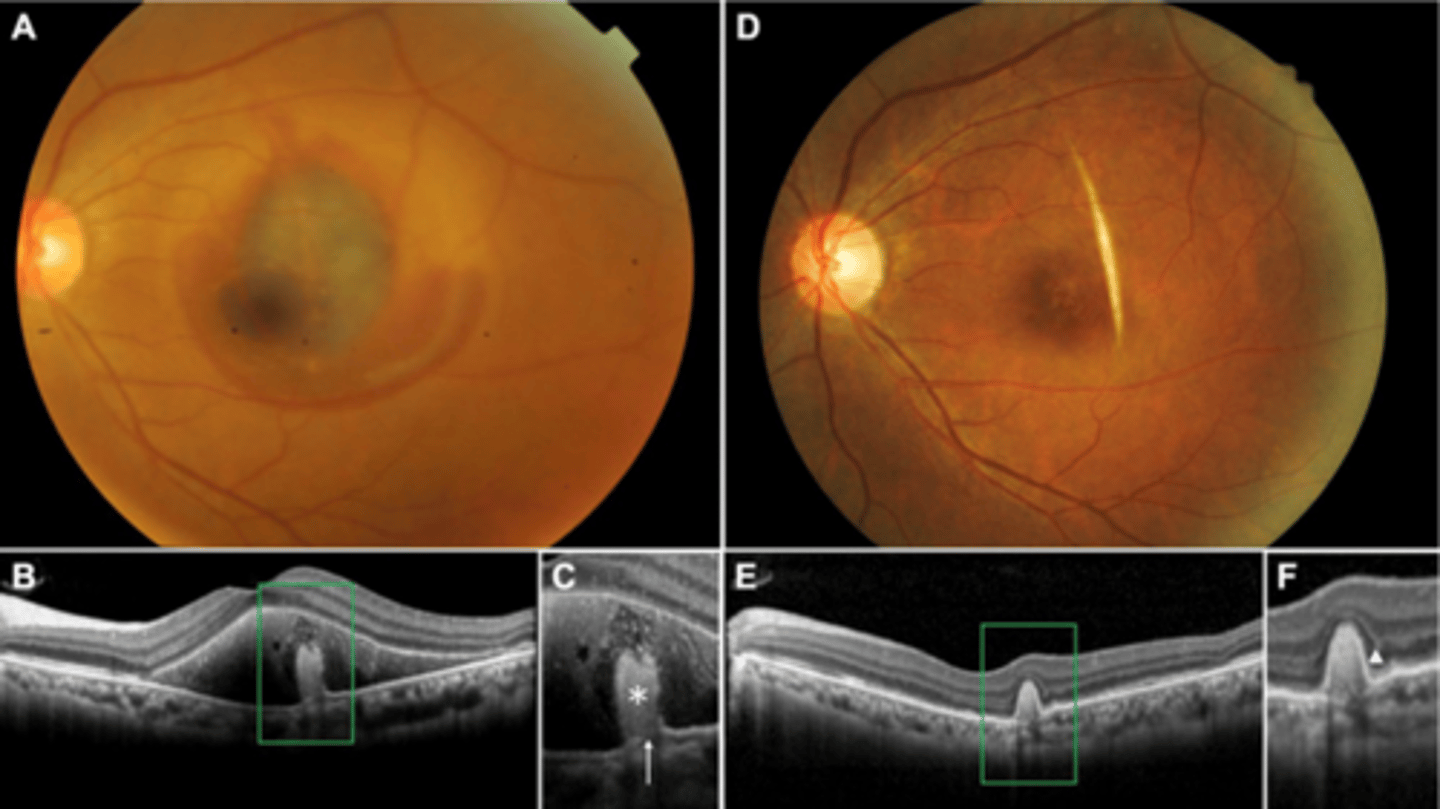
How does choroidal rupture appear on OCT here?
loss of RPE continuity at site of rupture = inner choroid atrophy
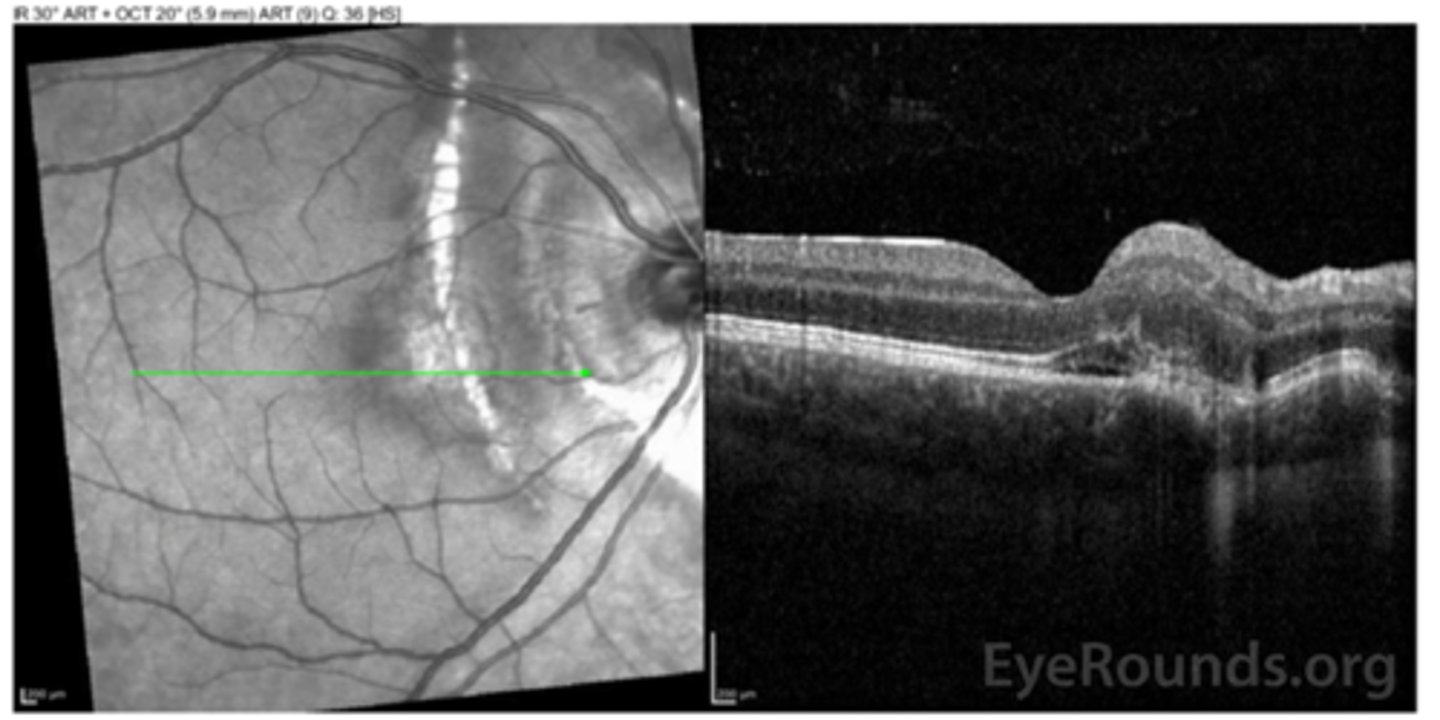
How does choroidal rupture appear on OCT here?
RPE disruption
+/- hemorrhage
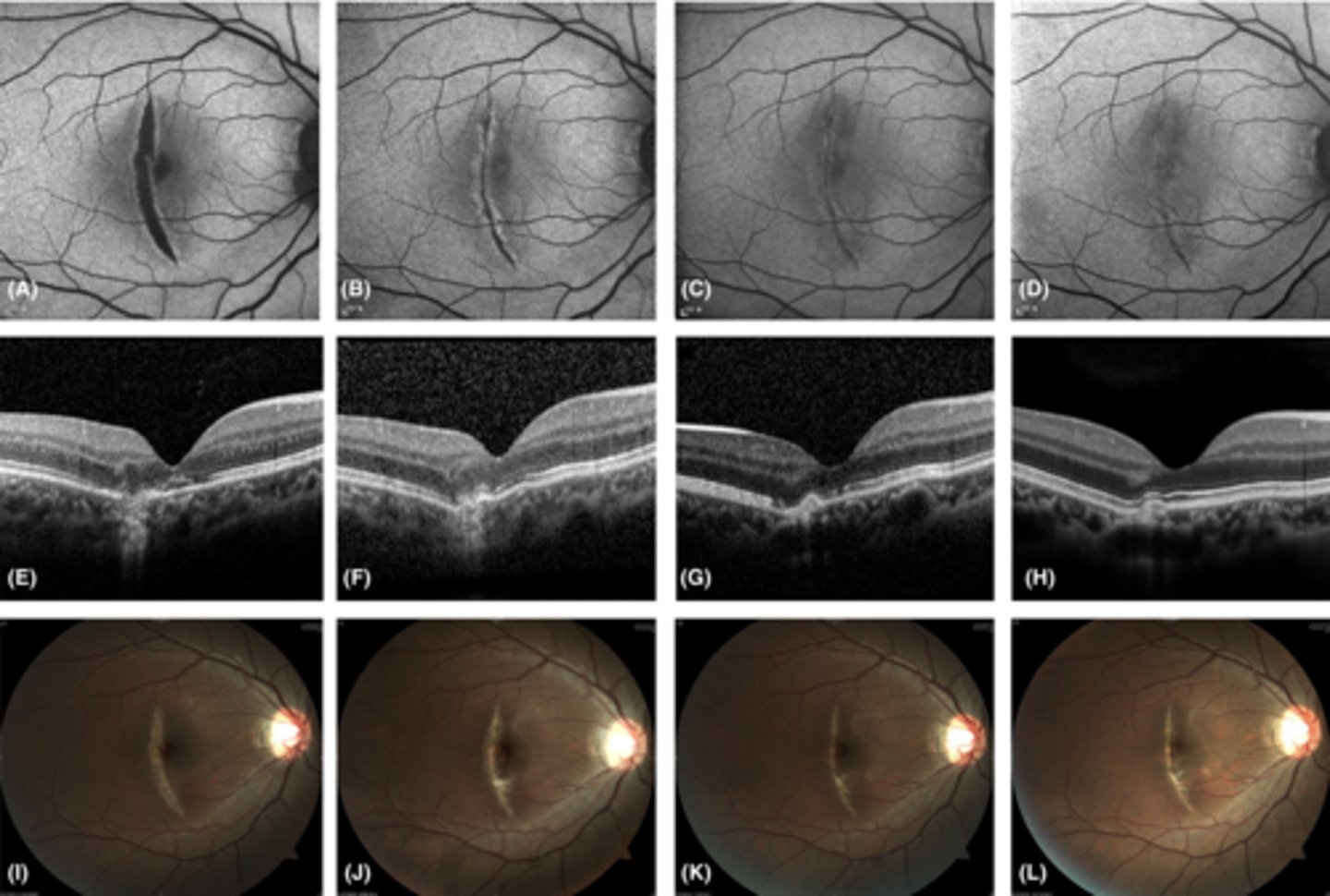
How does choroidal rupture appear on FAF?
hypoAF where RPE is atrophied
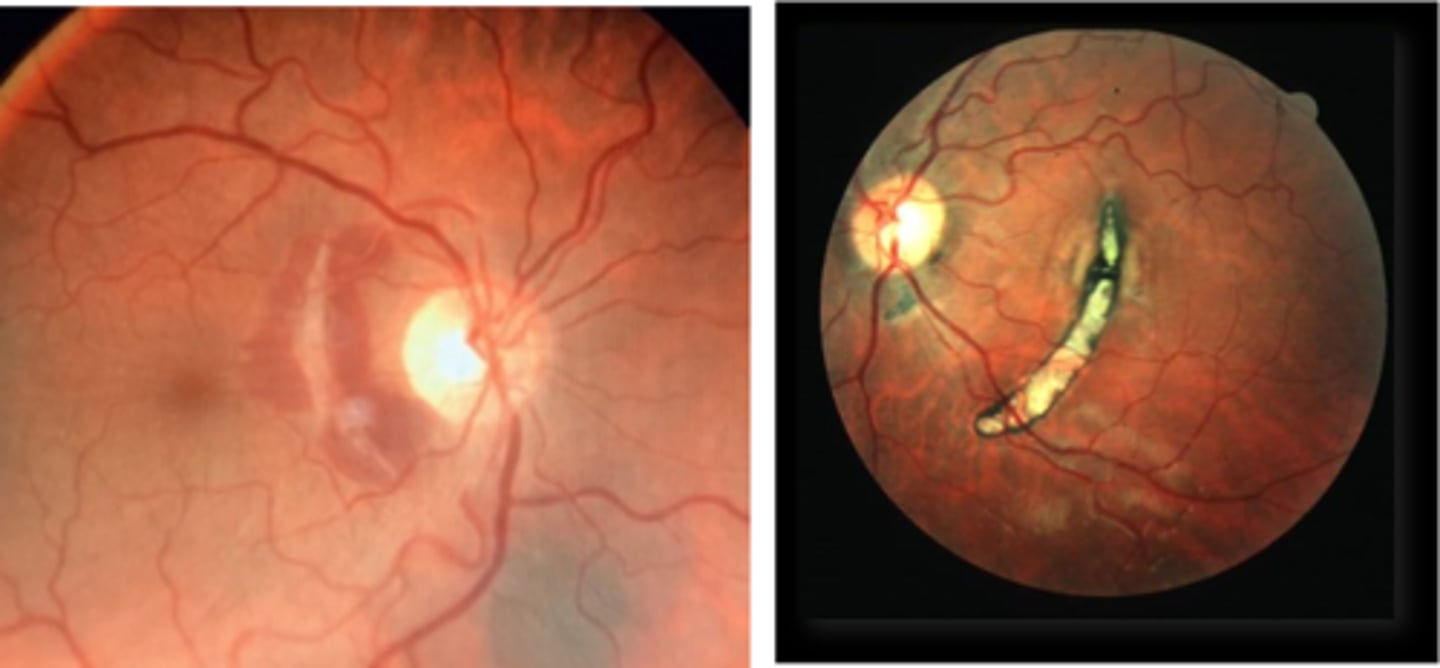
How do we manage choroidal rupture?
monitor q12 mos
monitor with at-home Amsler
What is degenerative myopia?
progressive and irreversible axial elongation and ocular stretching = thinning of the retina, choroid, and sclera
especially during childhood and adolescence
What are 3 risk factors for degenerative myopia?
high myopia of Rx > -6.00 SEQ or axial length > 26.5mm
excess near tasks
genetics
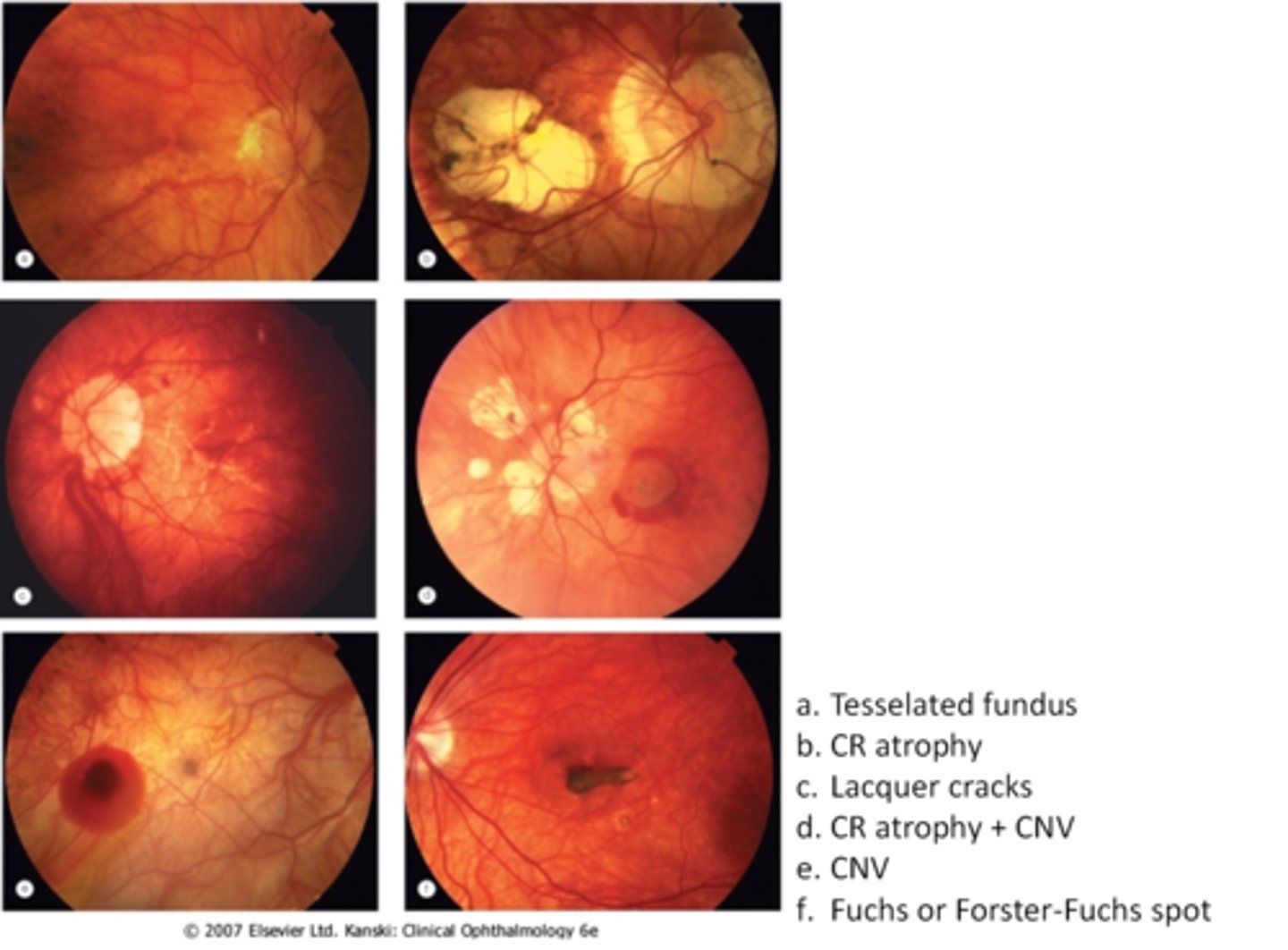
What are some common findings in high myopia?
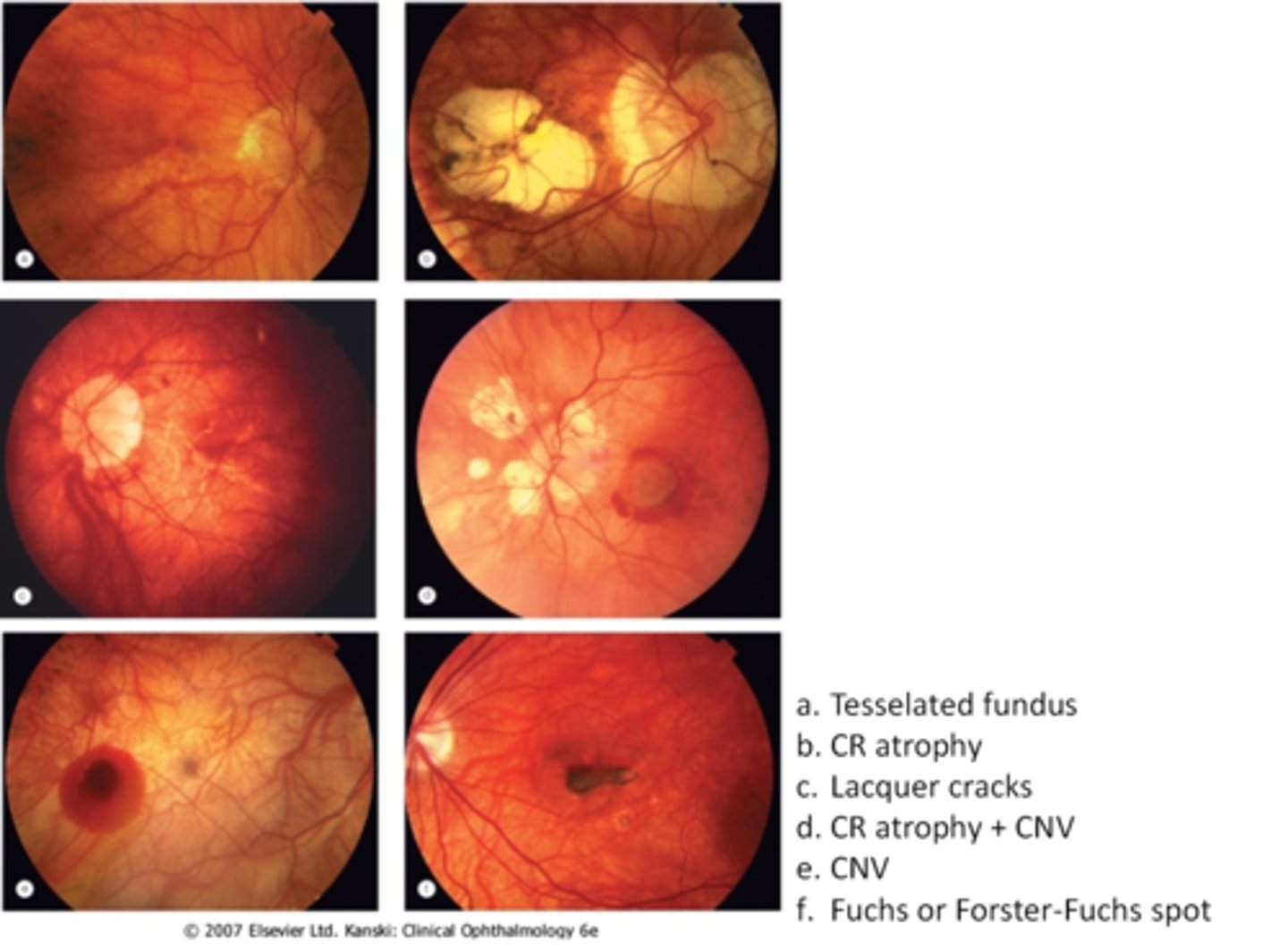
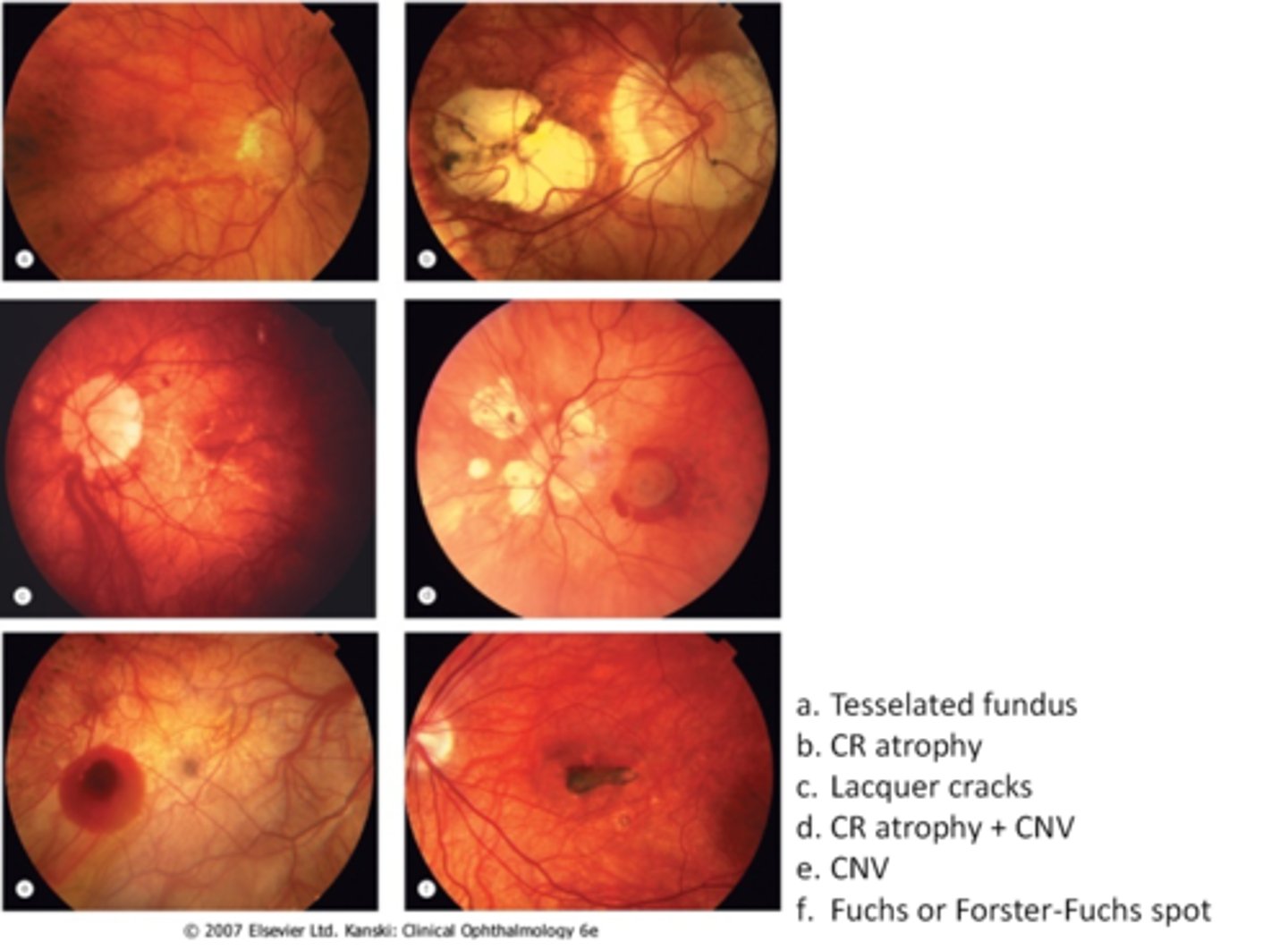
tesselated or tigroid fundus = visibility of choroidal vasculature (A)
malinserted, tilted, or oblique ONH insertion
large disc sizes (therefore larger C/Ds)
peripapillary atrophy, scleral or choroidal crescents
temporal wedge defects on visual field
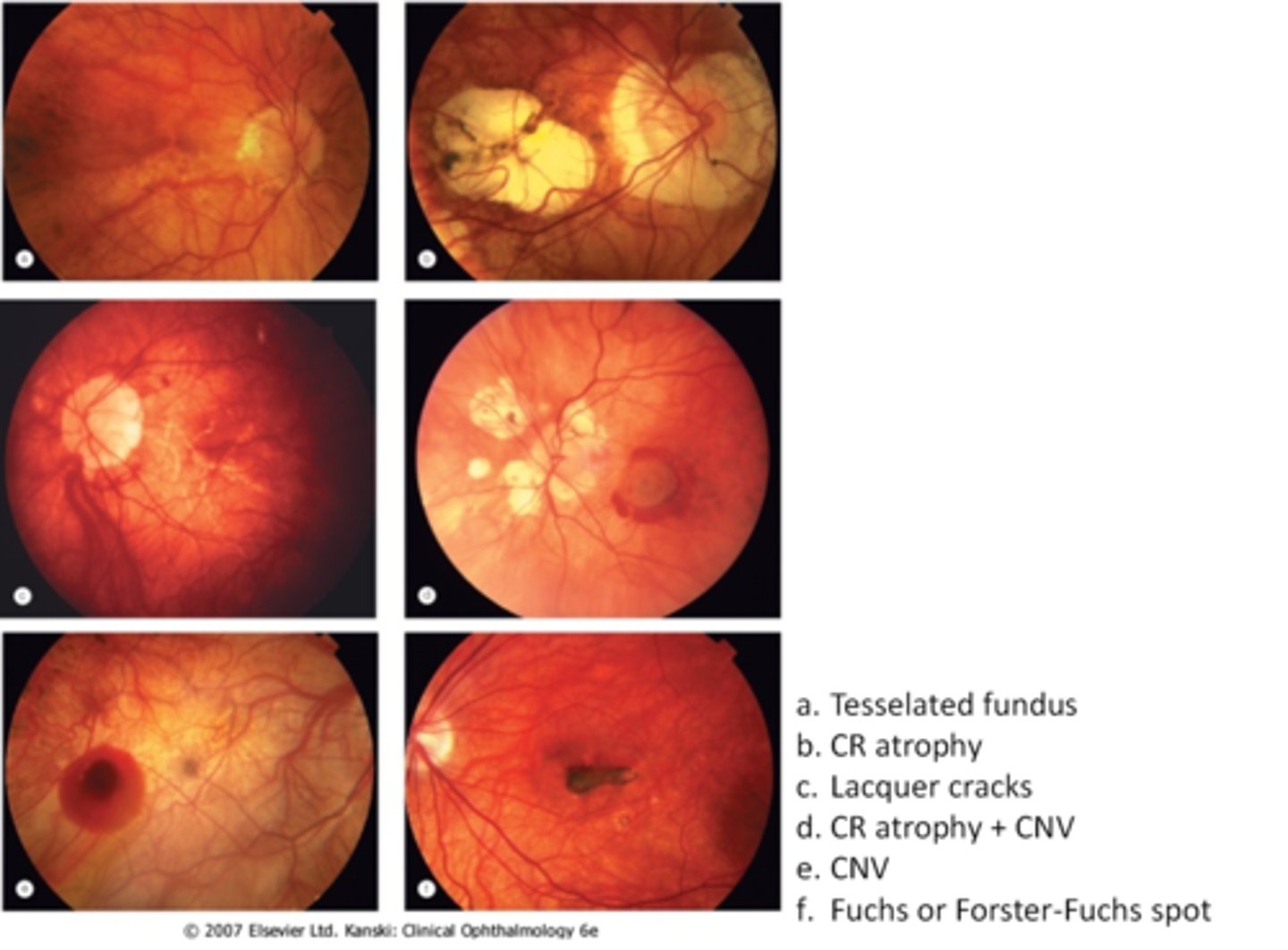
What are some common findings in degenerative myopia?
lattice degeneration
holes/tears
posterior staphyloma
lacquer cracks (C)
myopic retinoschisis
glaucoma
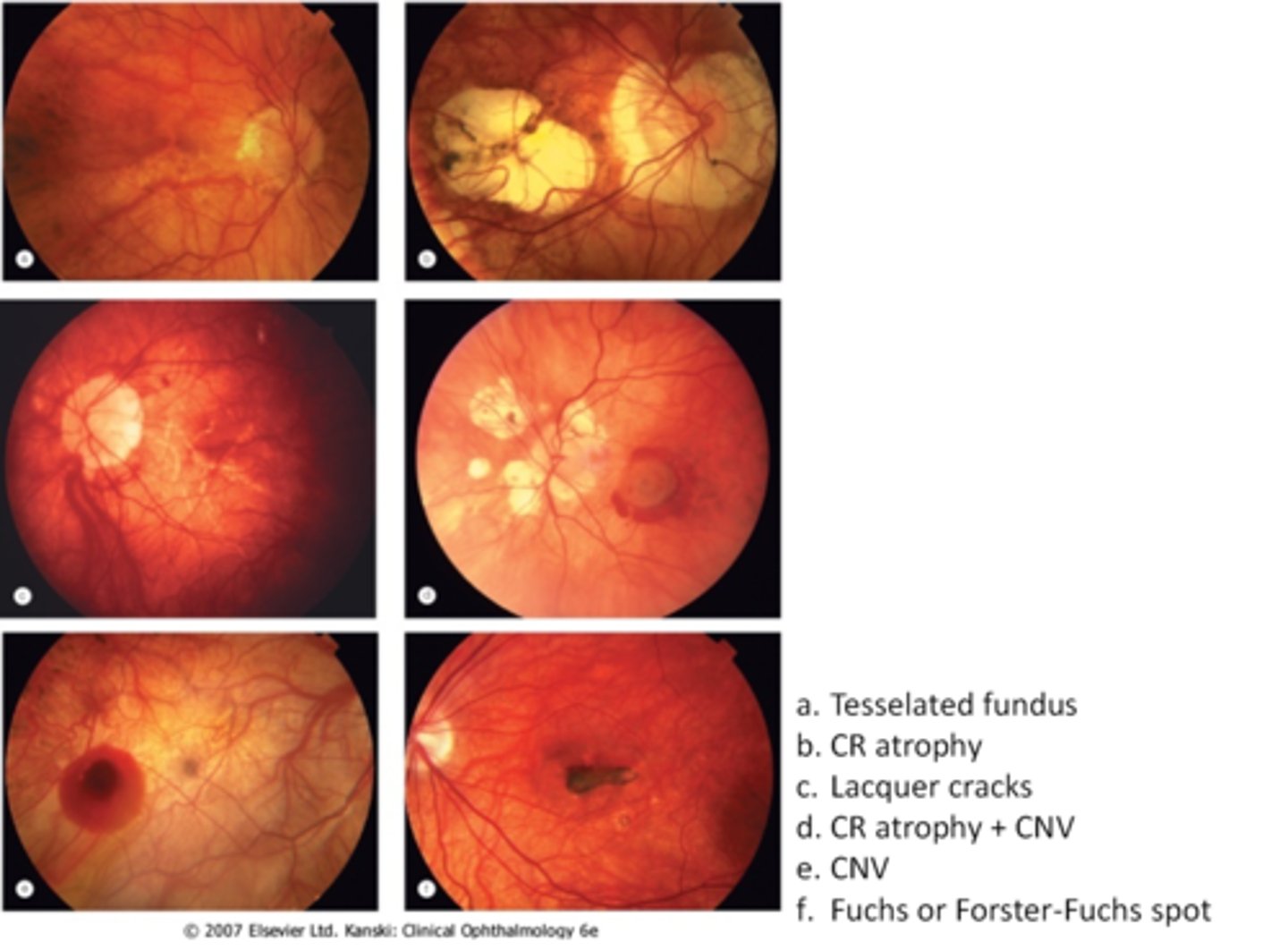
What are 3 possible complications of degenerative myopia?
RD
CNV (E)
chorioretinal atrophy (B)
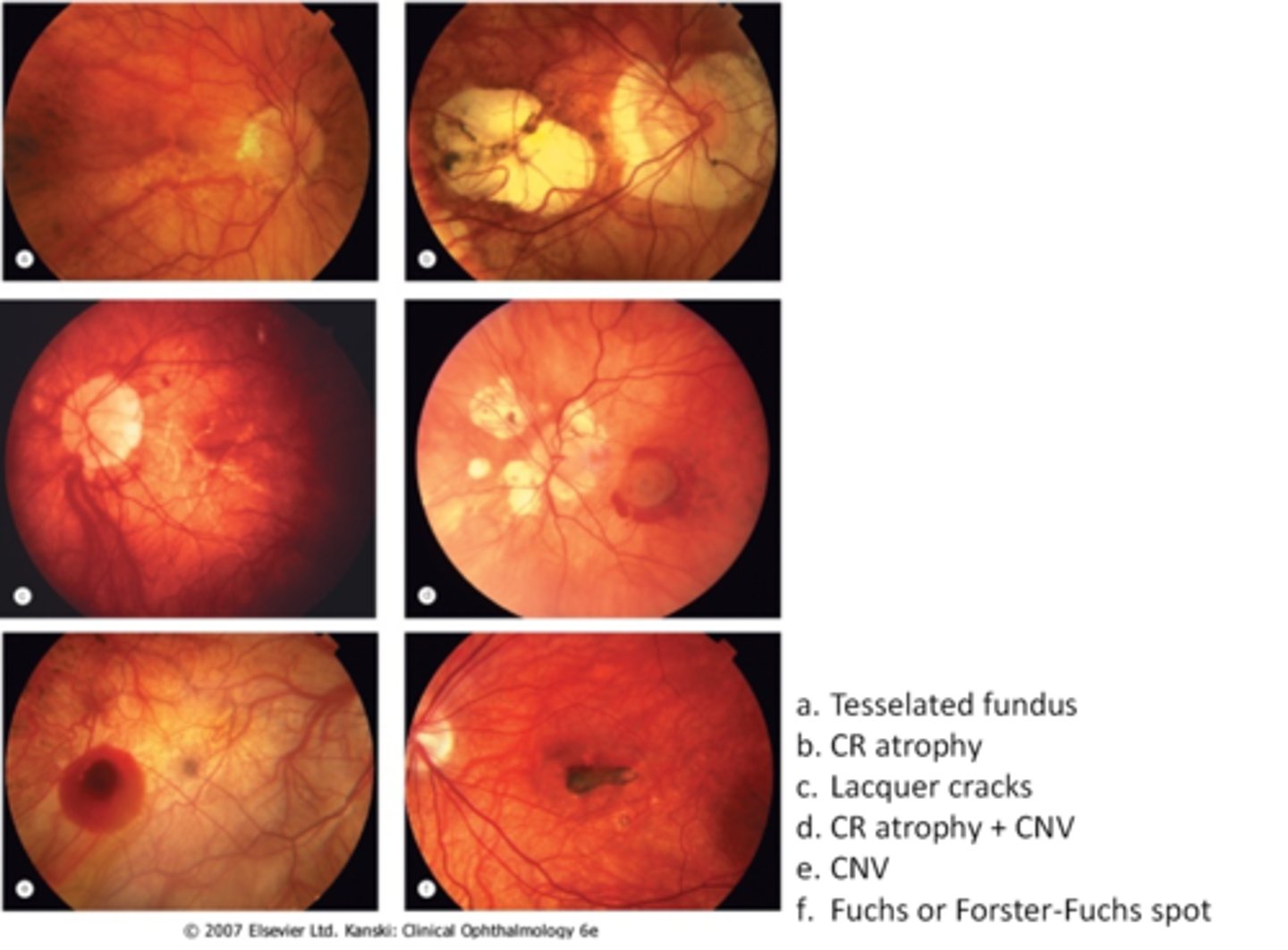
How do we manage degenerative myopia?
annual exam with DFE
home Amsler monitoring
environmental alterations of less near work, wearing protective eyewear
full correction = avoid under or over minus
refer to retina if RD, CNV
What are 3 possible ways to prevent degenerative myopia via myopia control?
1. MiSight MF CL's = add provides peripheral defocus = slows progression
2. low-dose atropine to inhibit accom
3. orthokeratology to reshape cornea overnight
What findings of degenerative myopia are seen here?
PPA
crescent
lacquer cracks
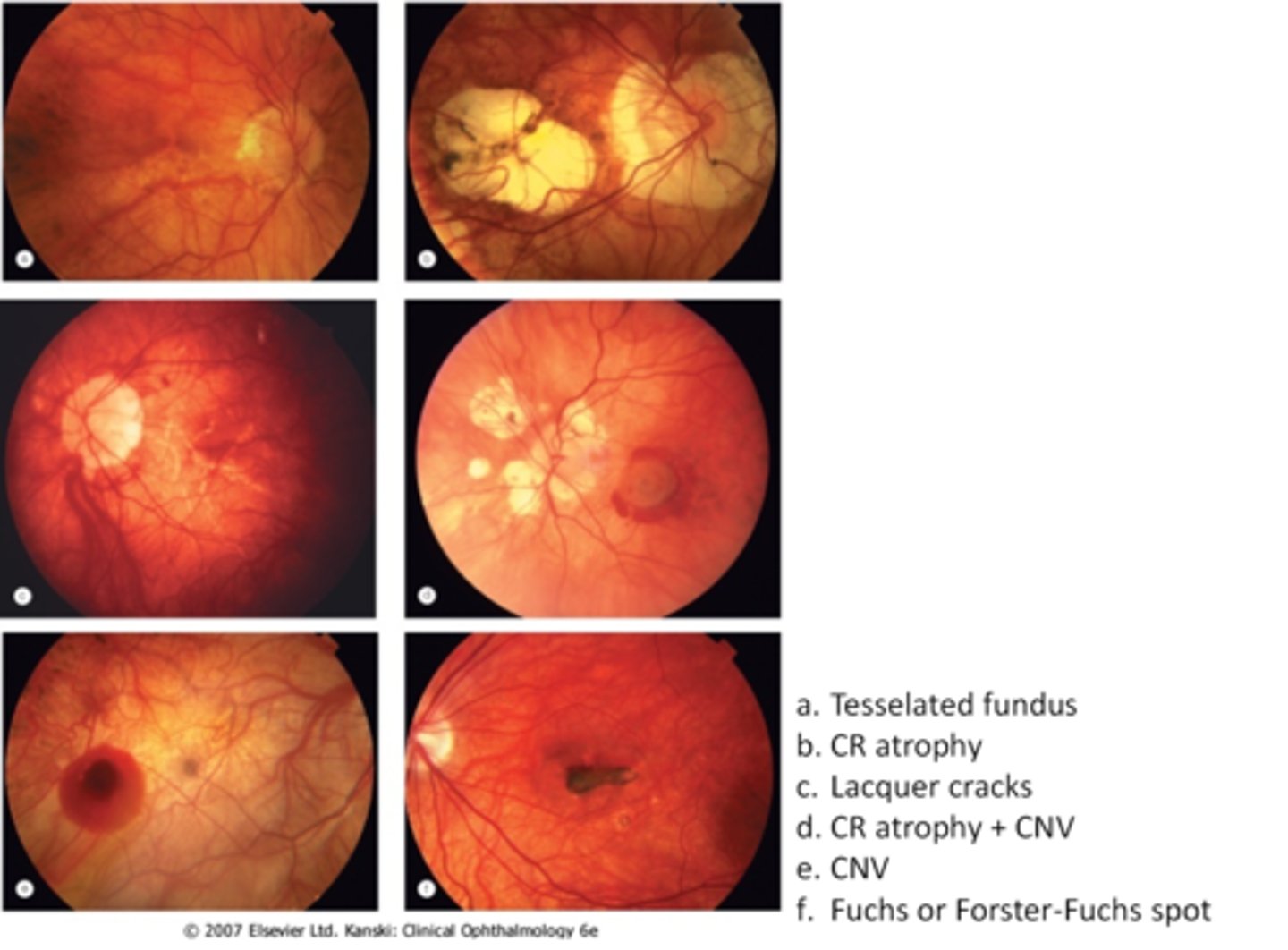
What are lacquer cracks and what causes them?
breaks in Bruch's membrane that can expand and contract, mostly seen in degenerative myopia
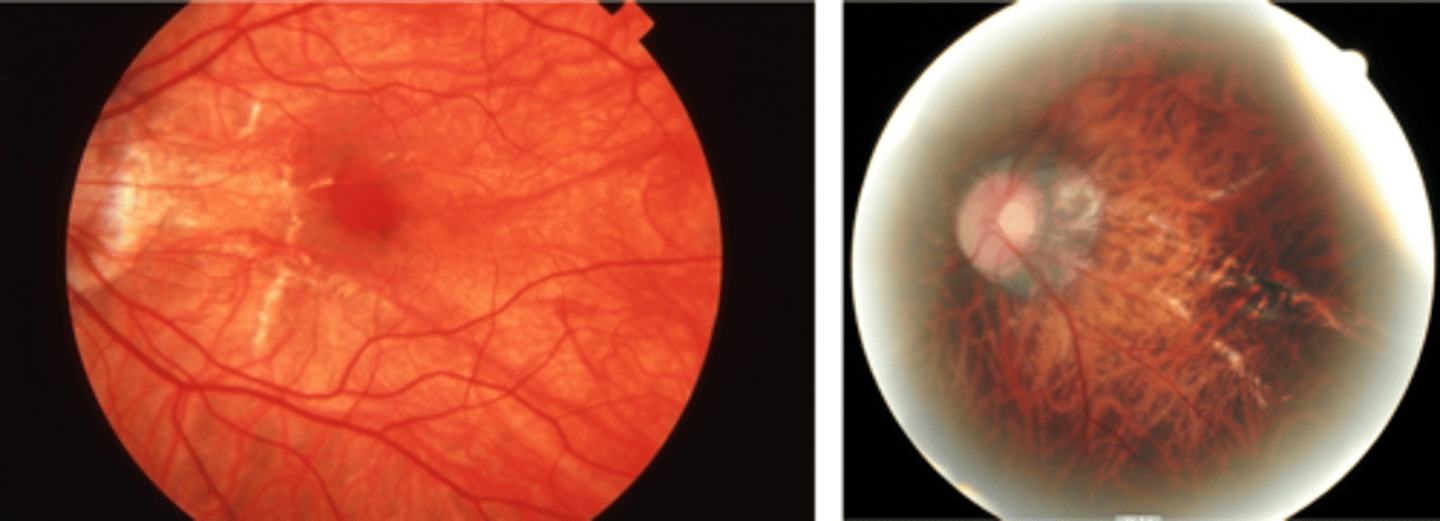
How do lacquer cracks appear on fundoscopy?
jagged, irregular yellow lines showing sclera in the posterior pole
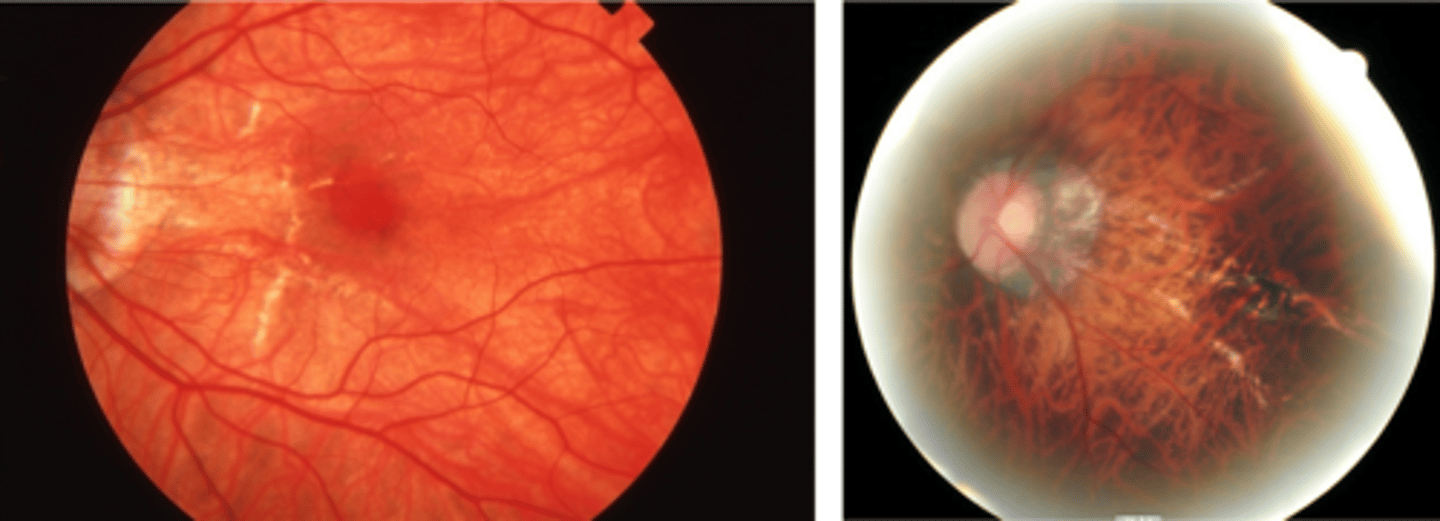
What is the main complication of lacquer cracks?
CNV in 29% of pt's
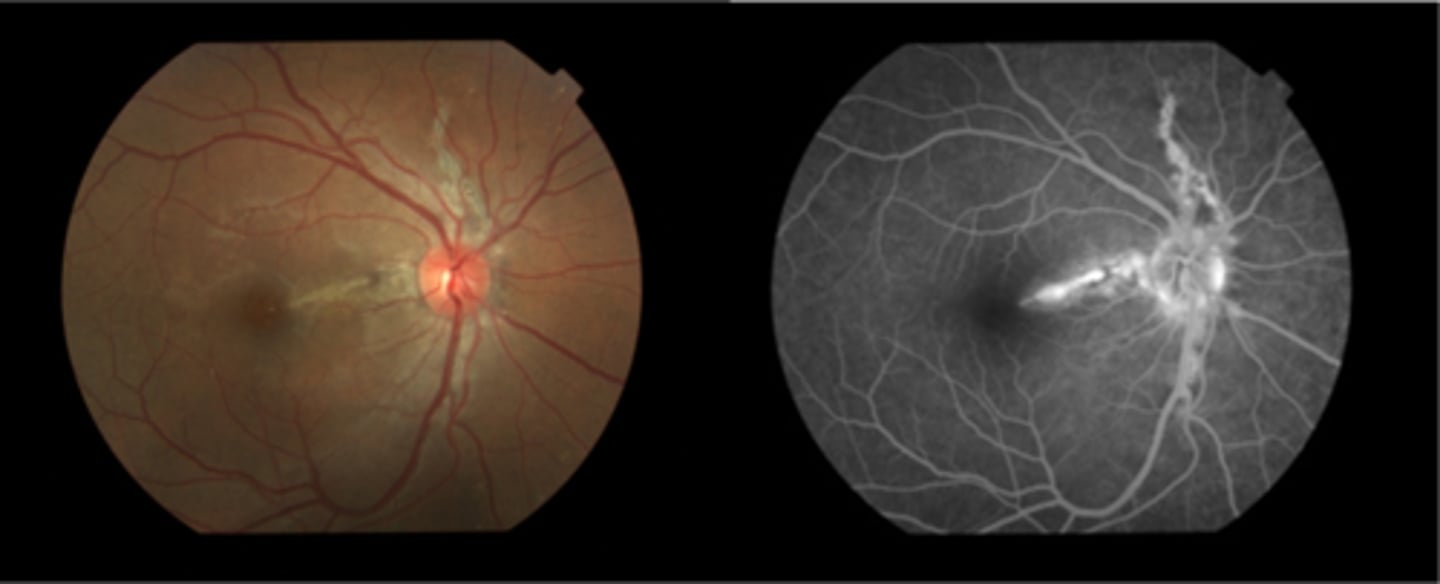
What are angioid streaks and what type of atrophy do they lead to?
breaks in Bruch's membrane in a radiating fashion emanating from the ONH = leads to RPE, PR's, choriocapillaris atrophy
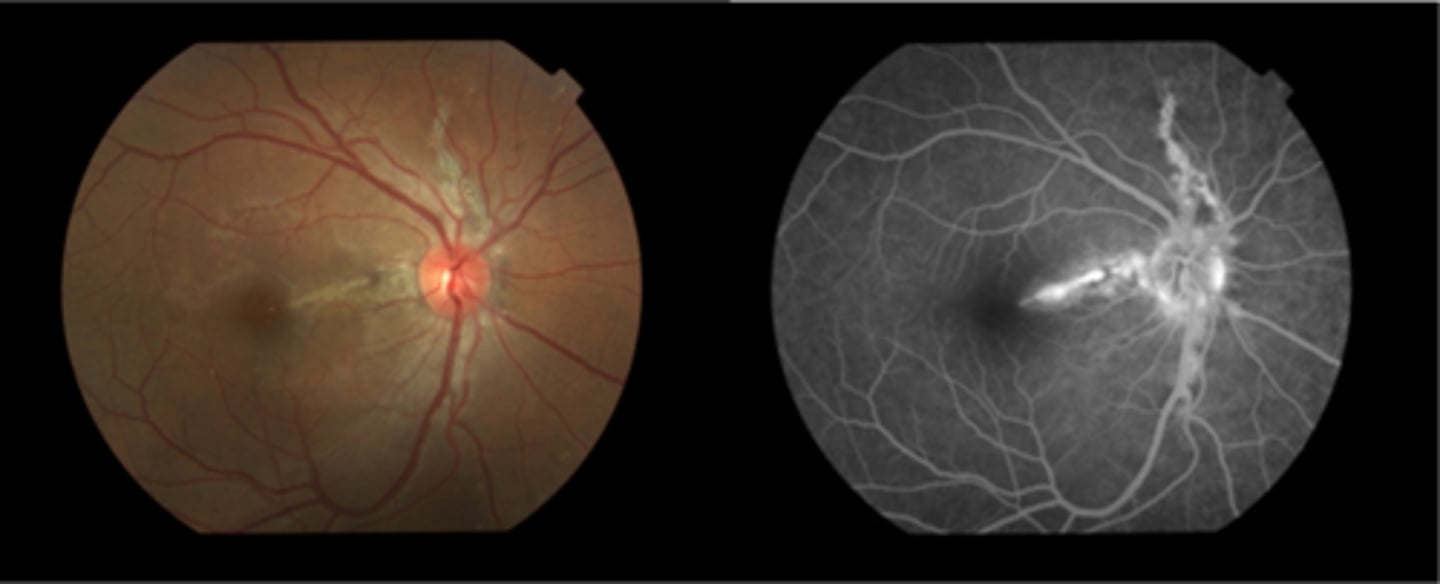
What causes angioid streaks?
weakened, calcified Bruch's membrane, often in connective tissue disease = bilateral
What are the 5 CT diseases associated with angioid streaks?
PEPSI:
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Paget's disease (of bone)
Sickle cell disease (and other hemoglobinopathies)
Idiopathic
THINK: Angie likes to drink PEPSI
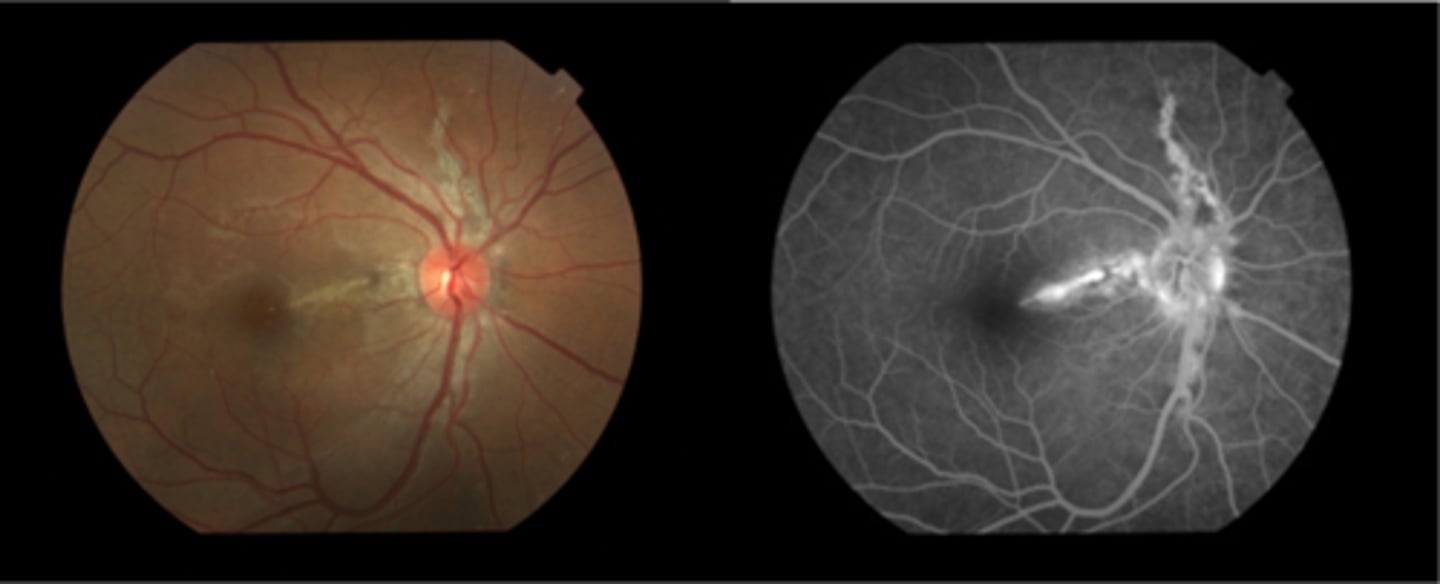
How do angioid streaks affect VA?
often asymptomatic as does not involve macula
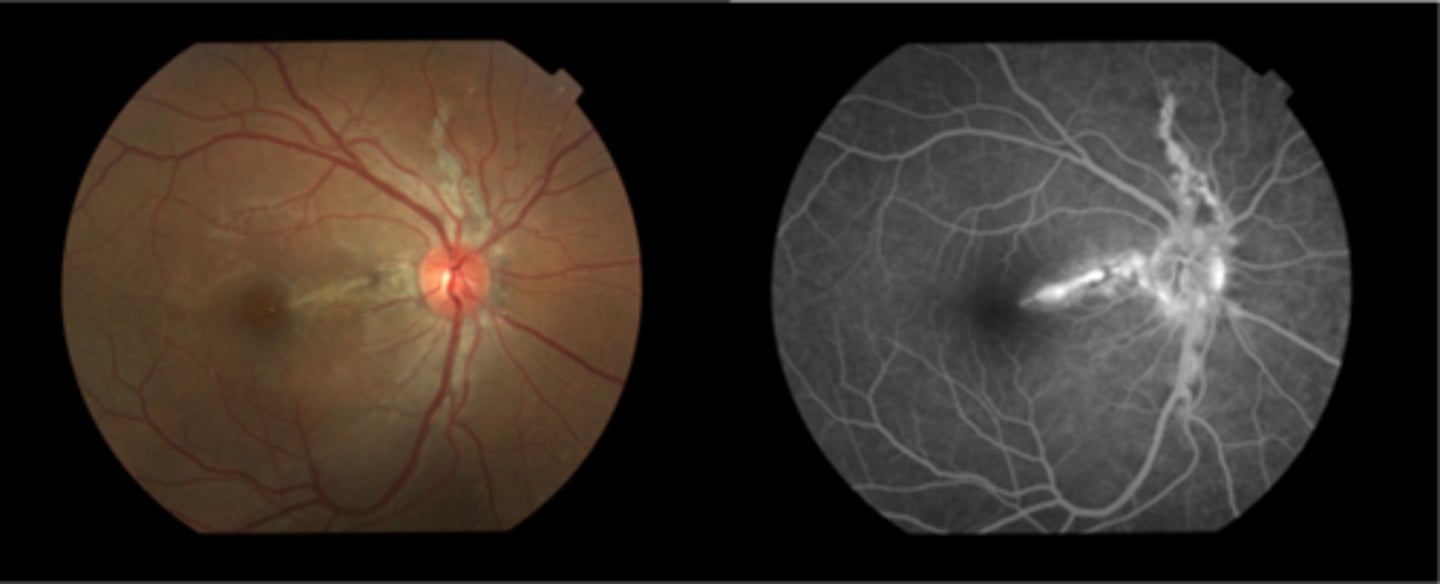
What are 2 possible complications of angioid streaks?
CNV
choroidal rupture
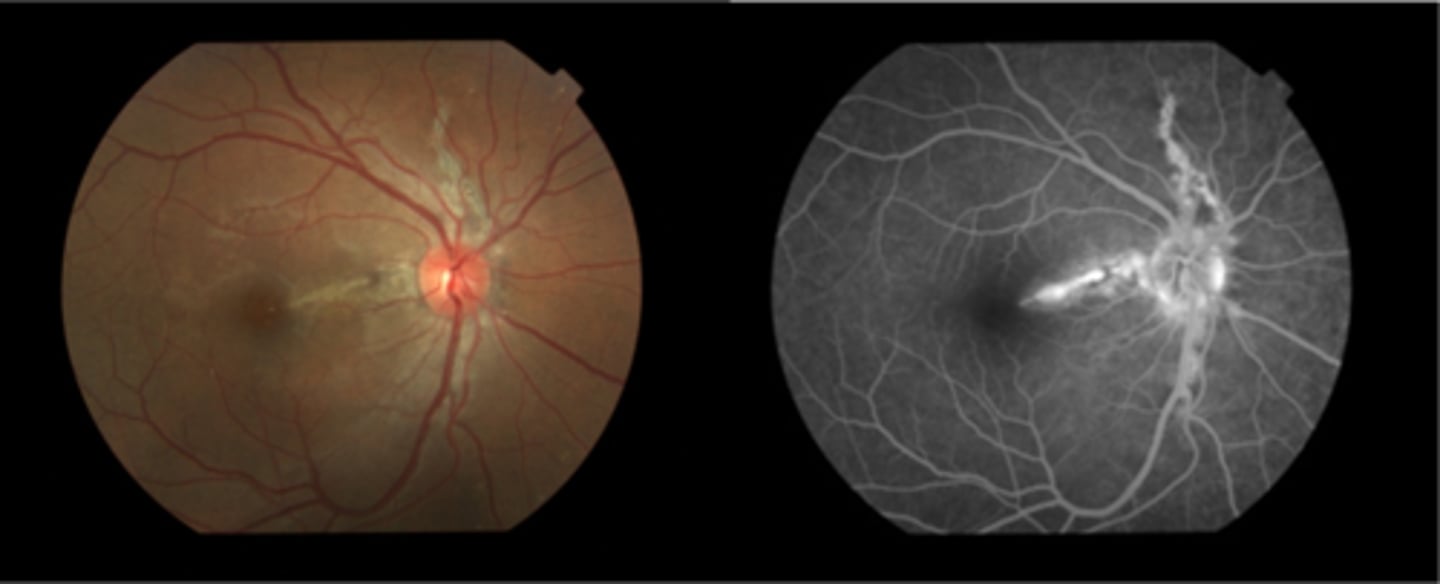
How do we manage angioid streaks?
educate on potential CNV or choroidal rupture, esp with injury = polycarbonate, reduced contact sports
Amsler for home monitoring
refer for CT disease workup if not already diagnosed
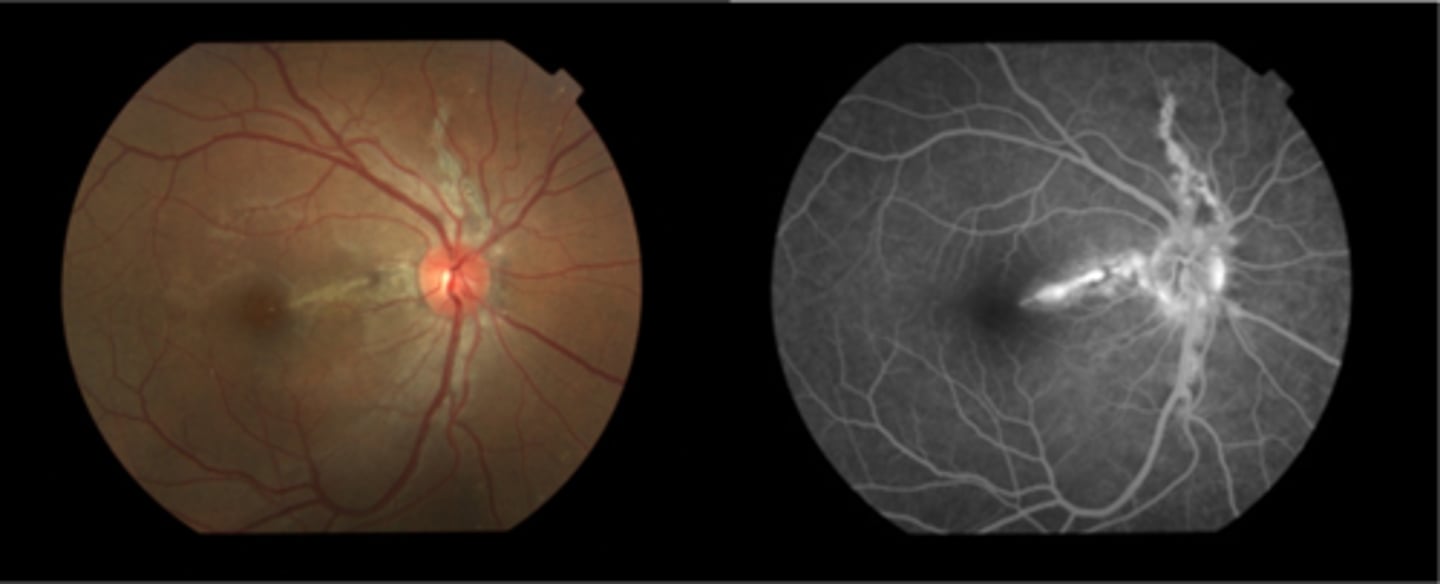
How does angioid streaks appear on IVFA?
hyperF bc loss of RPE = can see choroid better
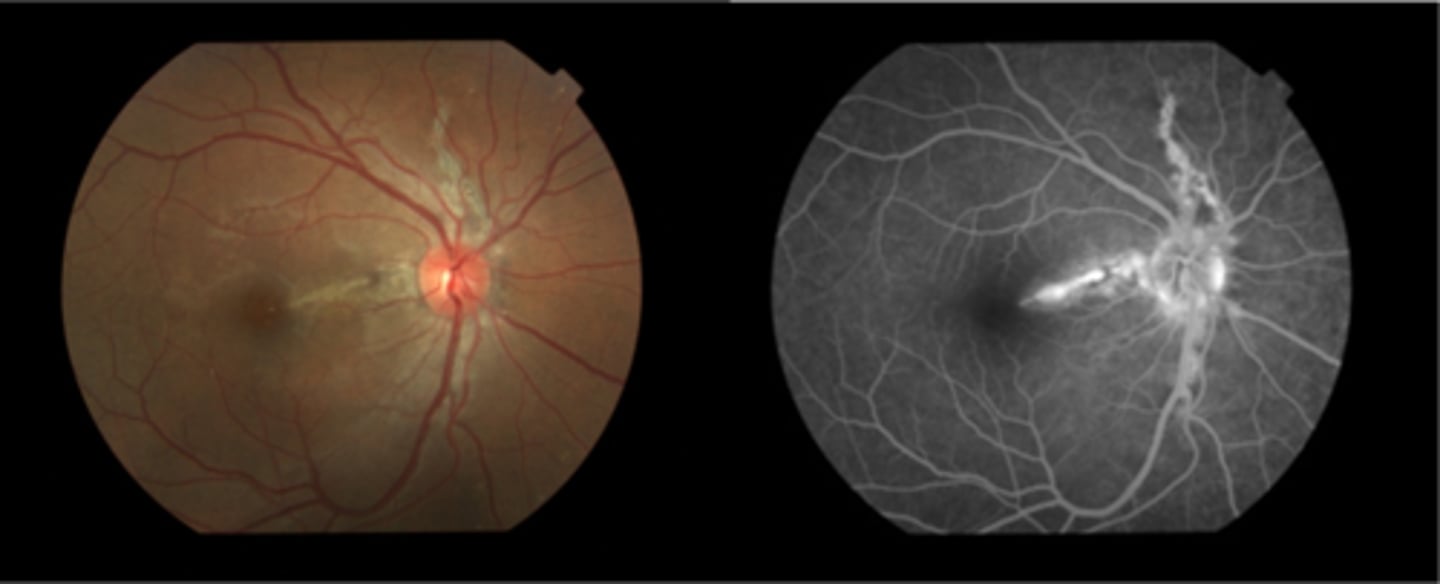
How does angioid streaks appear on FAF?
hypoAF bc RPE loss/damage
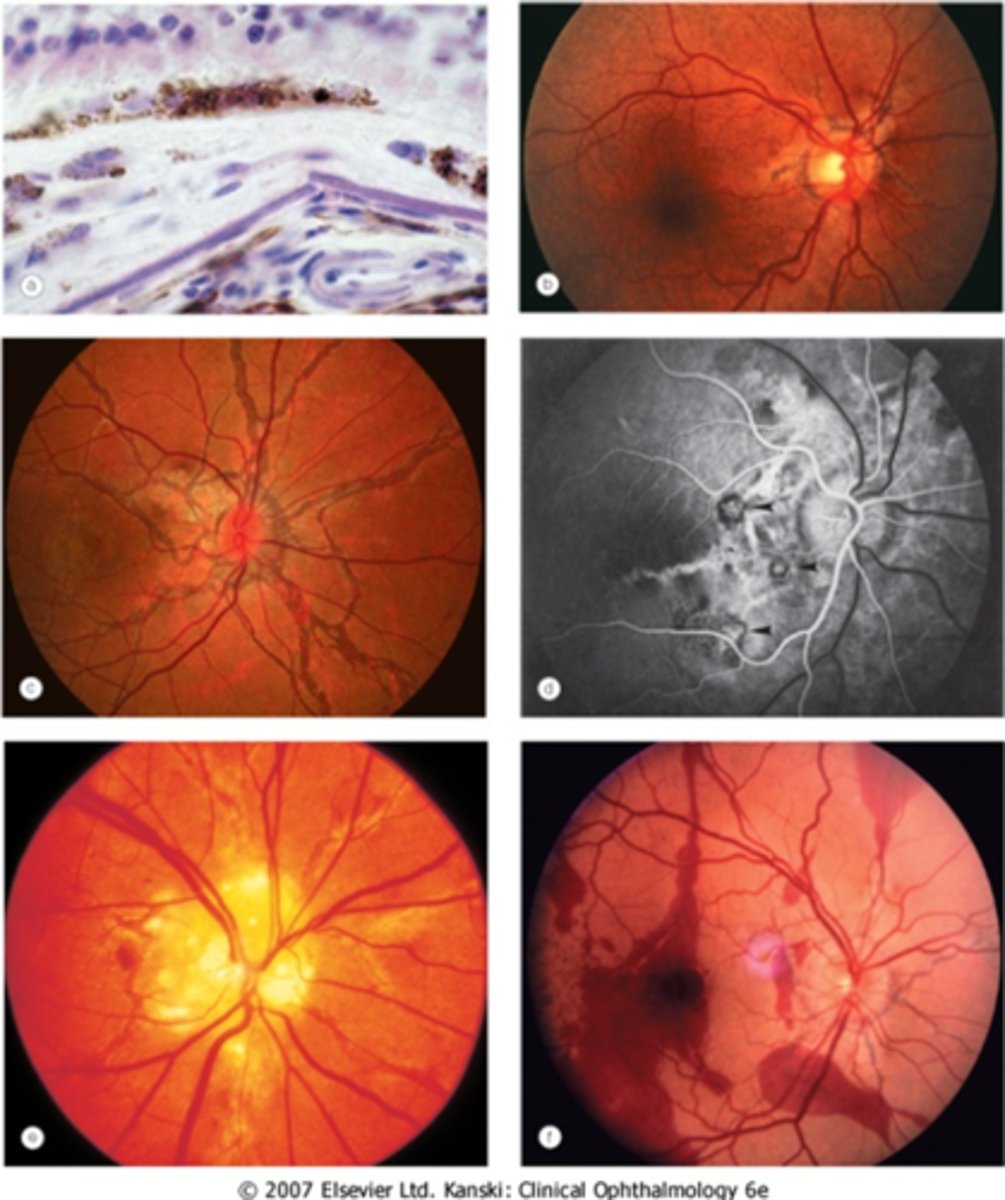
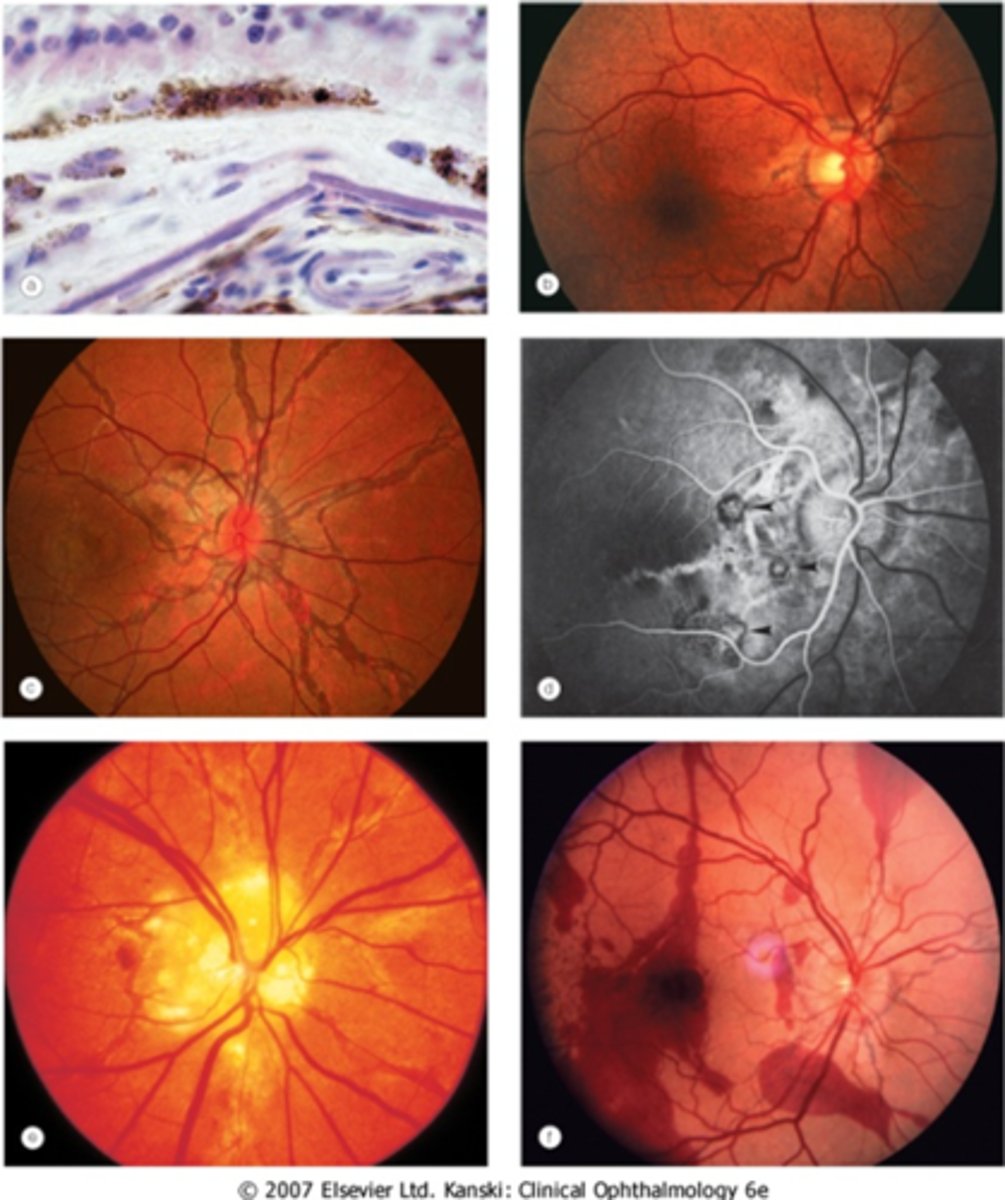
What ONH finding is sometimes seen with angioid streaks?
disc drusen
What is solar maculopathy?
photochemical toxicity (retinal burn) from excessive UV exposure (sungazing, eclipse viewing, lasers, welding)
How does solar maculopathy affect vision?
reduced VA
central/paracentral scotoma
distortions
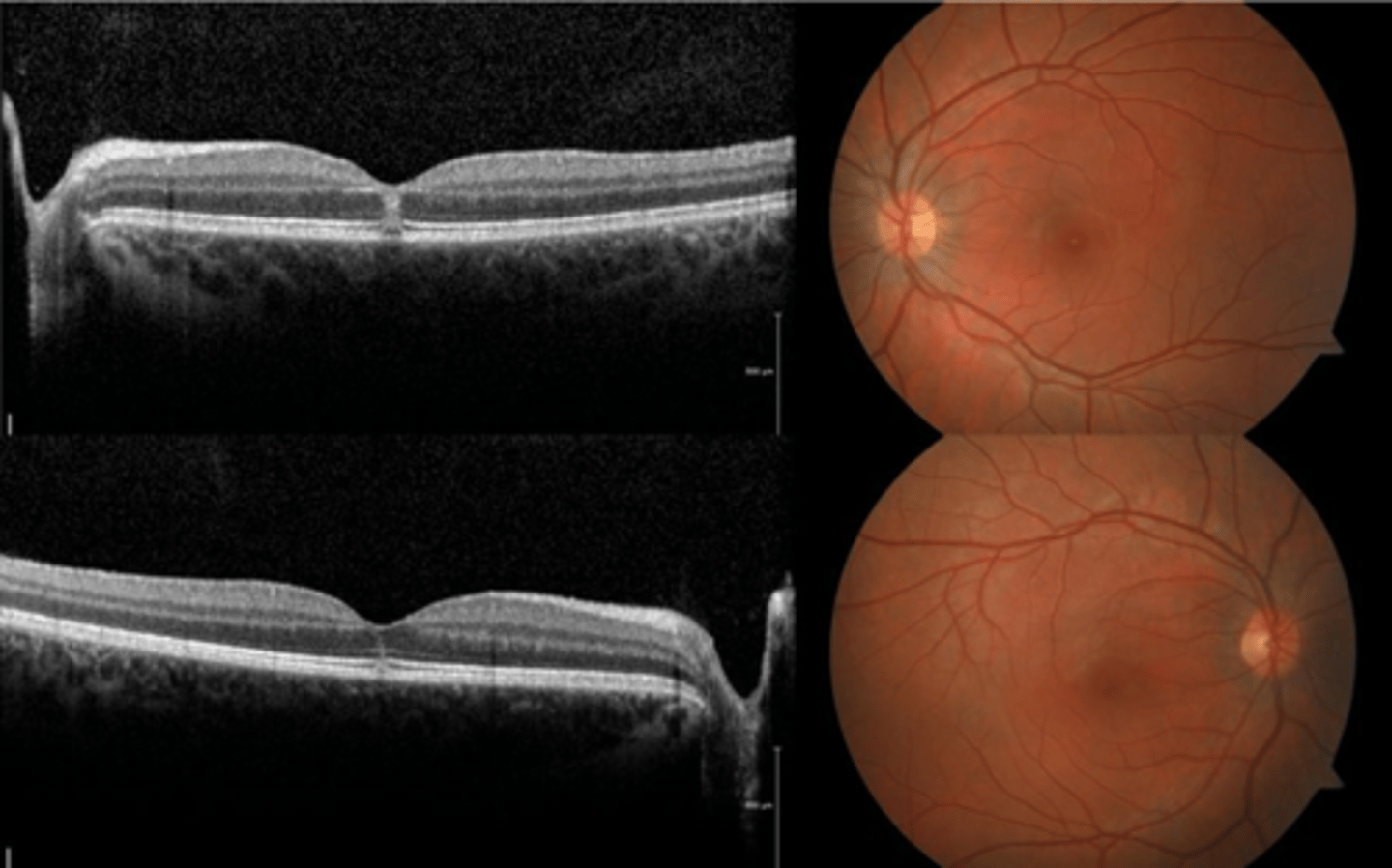
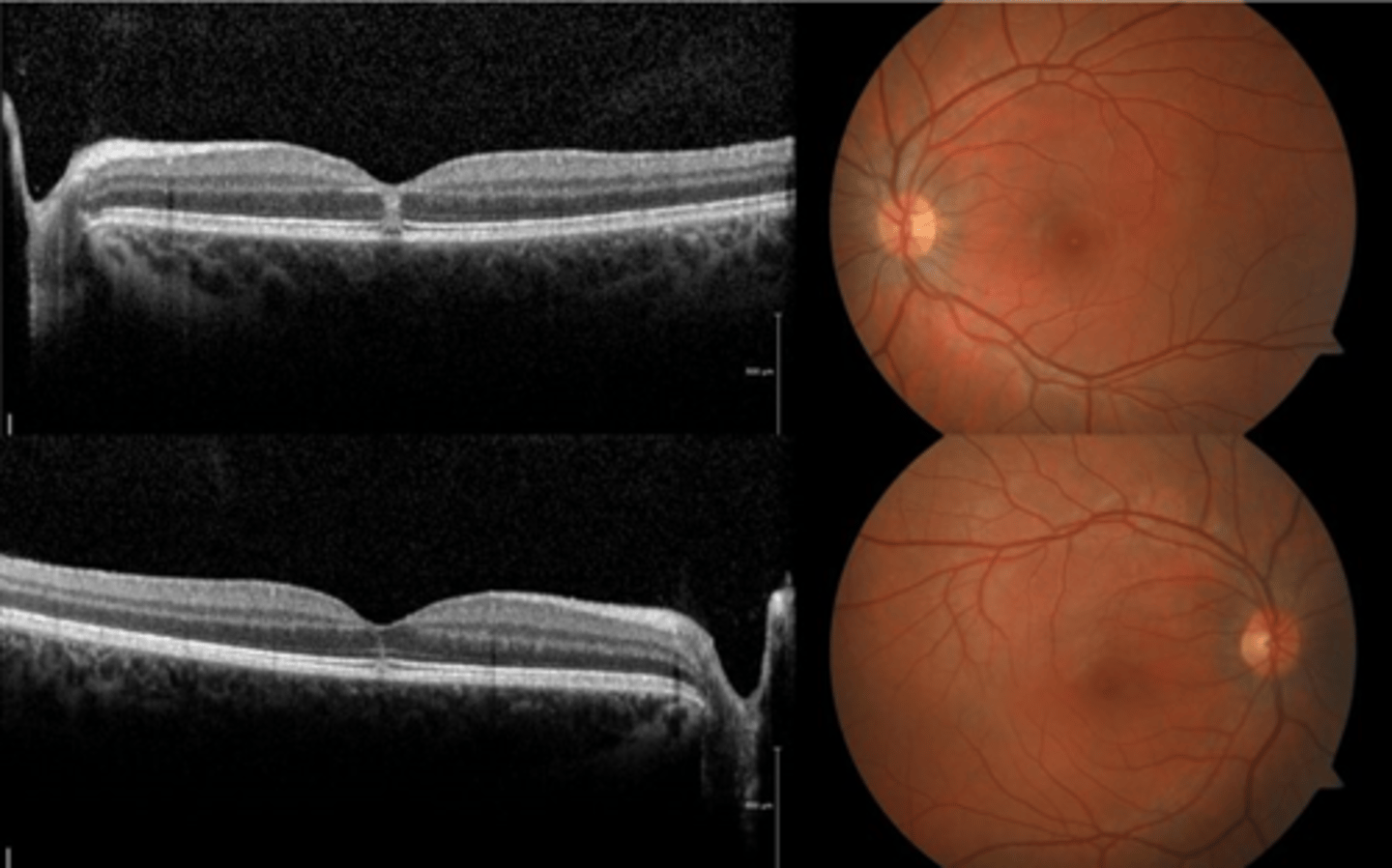
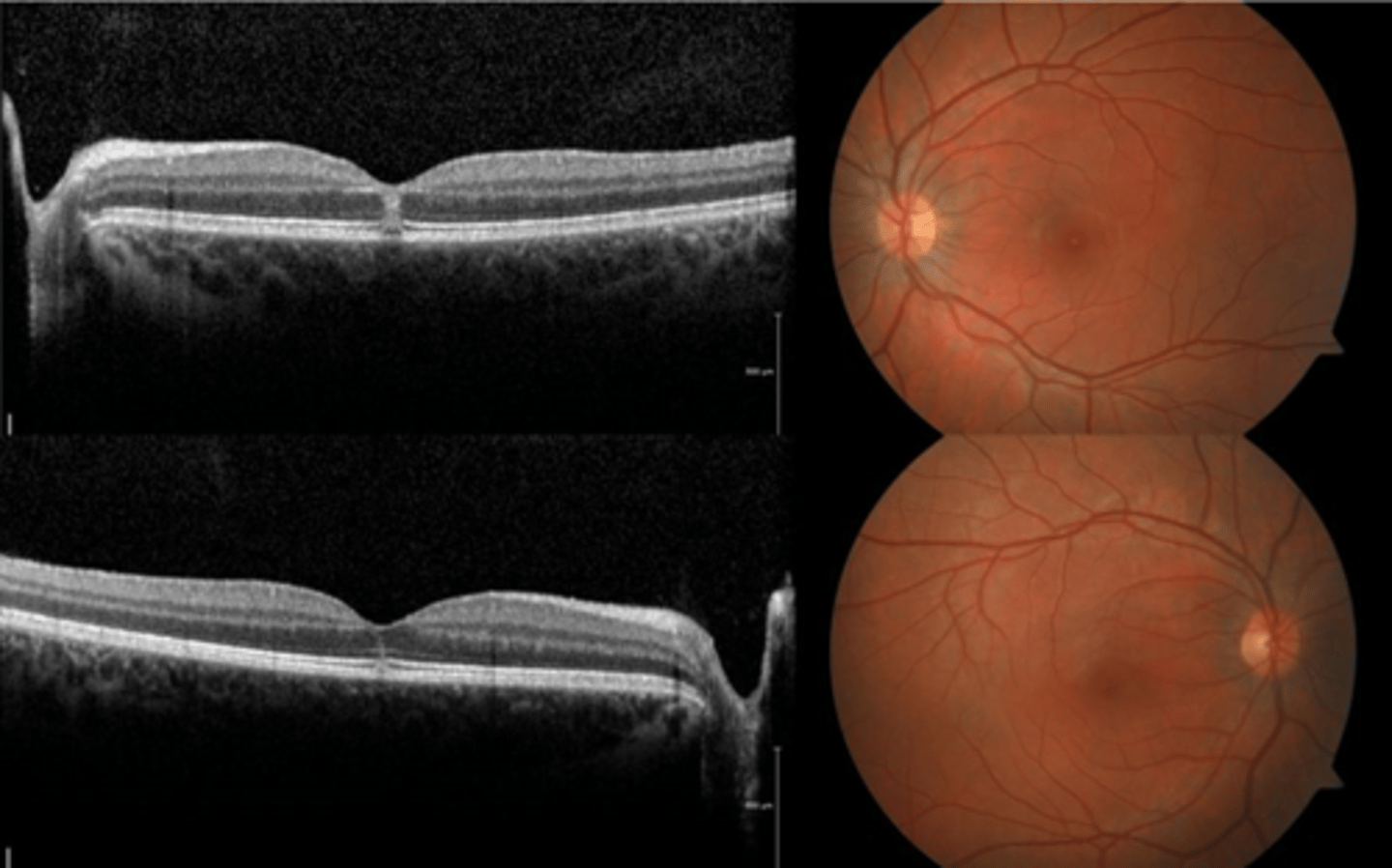
How does solar maculopathy appear on fundoscopy?
either no abnormalities
OR
yellow-white spot at fovea (acute)
OR
reddish spot at fovea w/ pigment halo (2-3 wks)
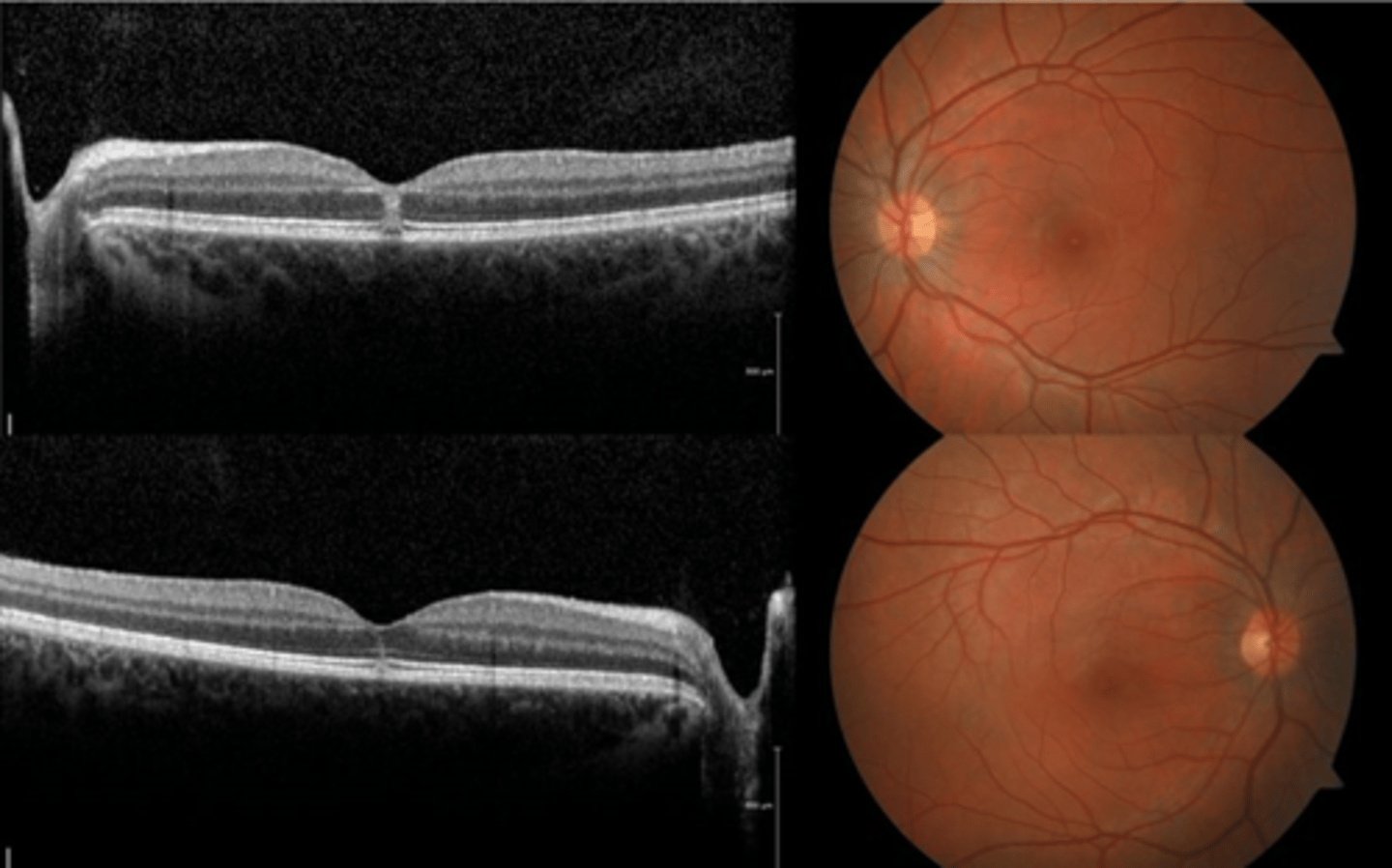
How does solar maculopathy appear on OCT?
hyperR of outer retinal layers at fovea (acute)
outer retina/subfoveal PIL disruption
100-200 micron lamellar hole
What is the management for solar maculopathy?
NONE - no possible tx
mostly focus on prevention
What is the prognosis of solar maculopathy?
depends on length/intensity of exposure = spontaneous recovery over 1-6 mos but visual recovery can be incomplete
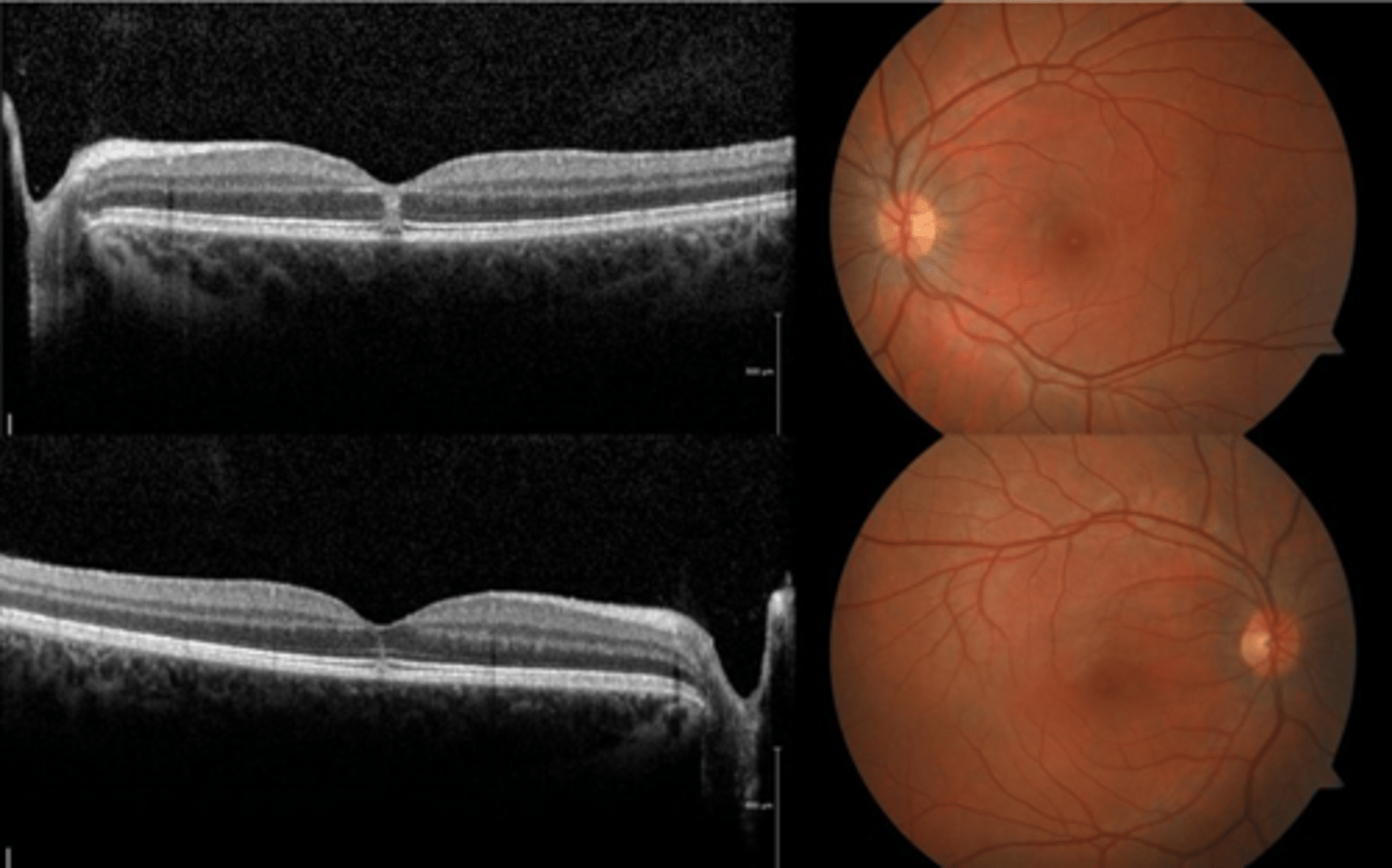
What is ocular histoplasmosis?
multifocal, bilateral chorioretinitis
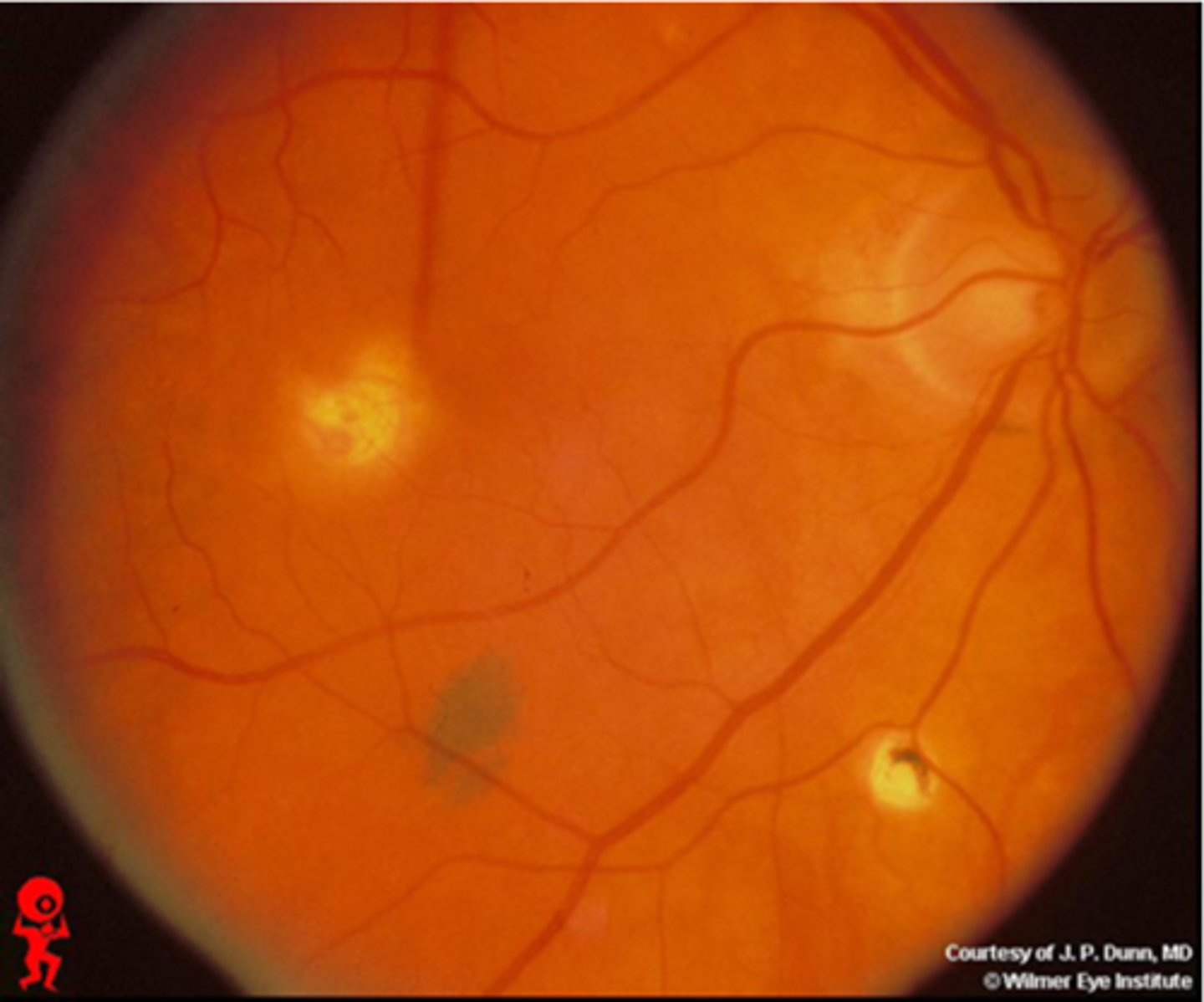
What causes ocular histoplasmosis?
Histoplasma capsulatum soil fungi or mold = carried by birds or bats, esp seen in the Ohio-Mississippi River Valley = humans inhale spores in poop = affects lungs, other organs
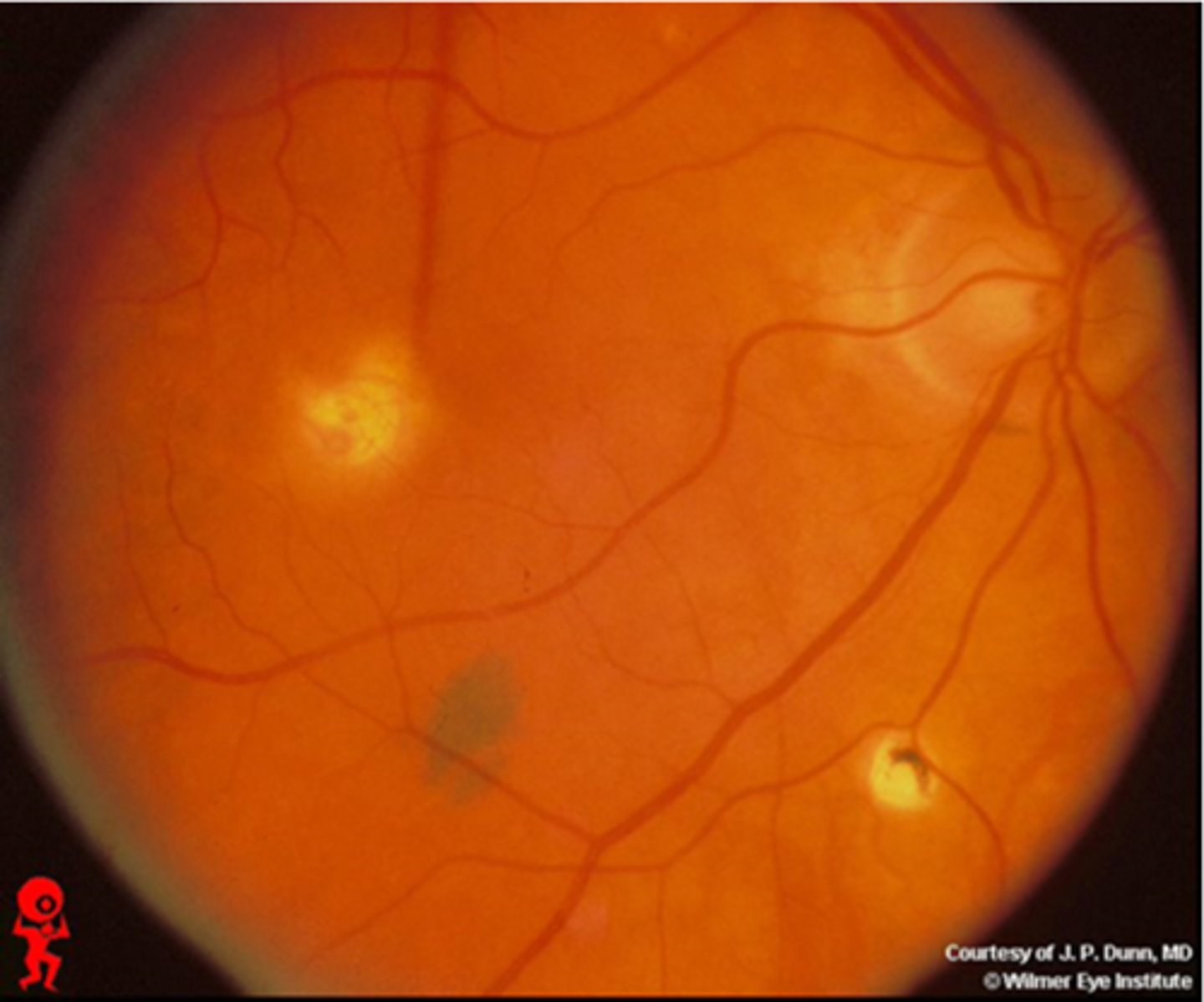
What is the classic triad of signs in ocular histoplasmosis?
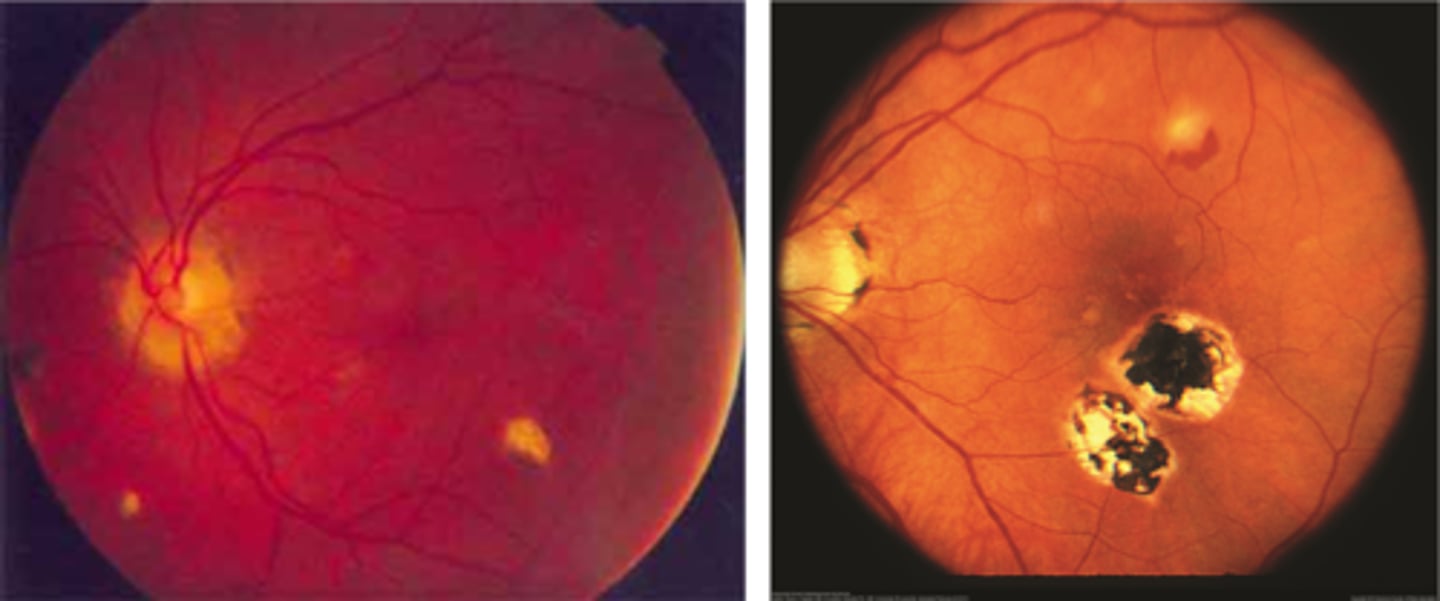
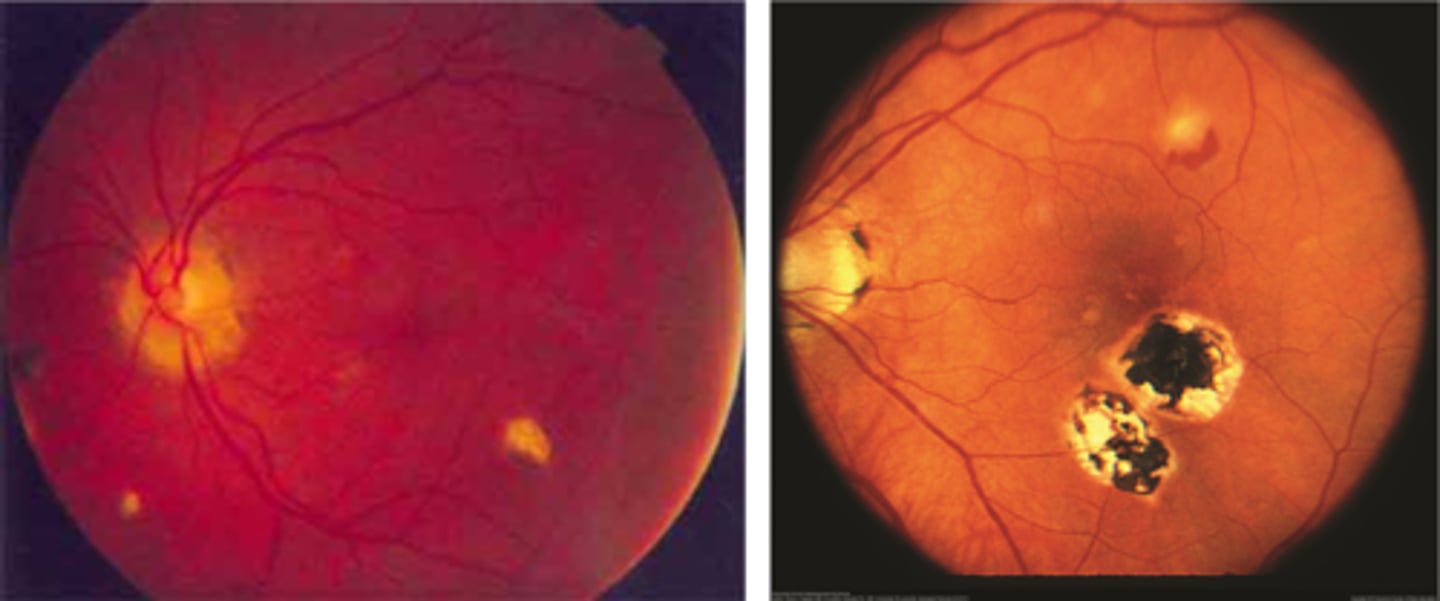
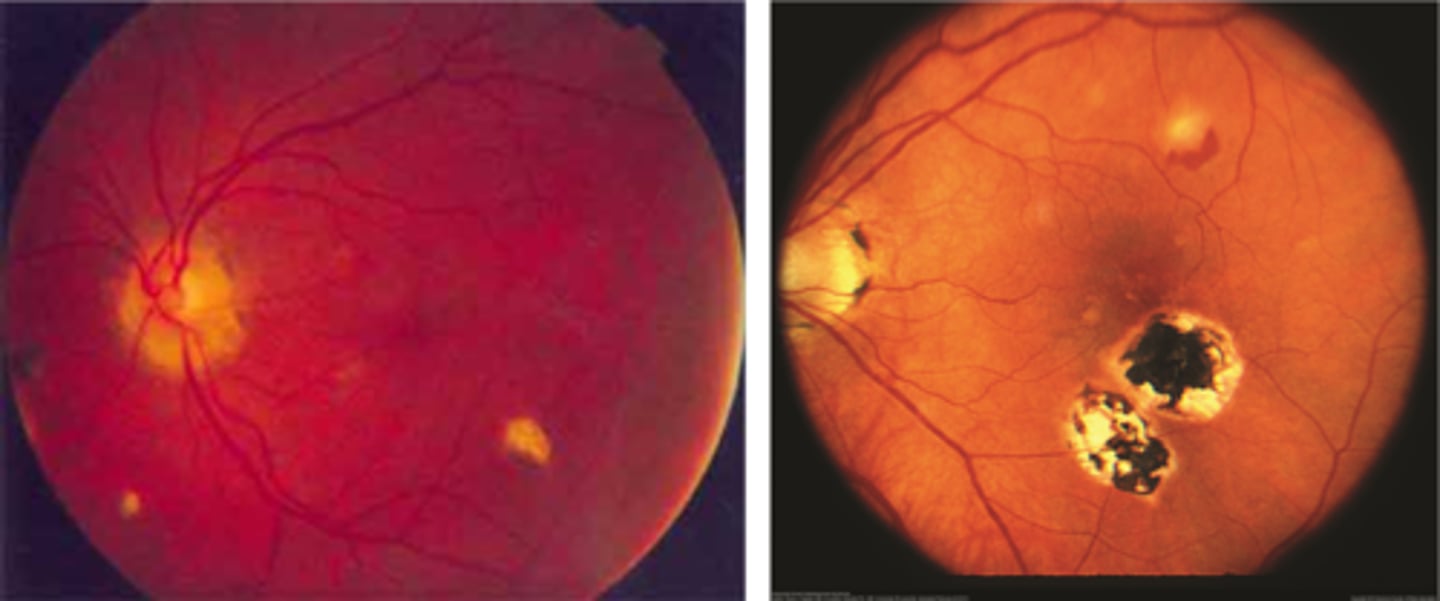
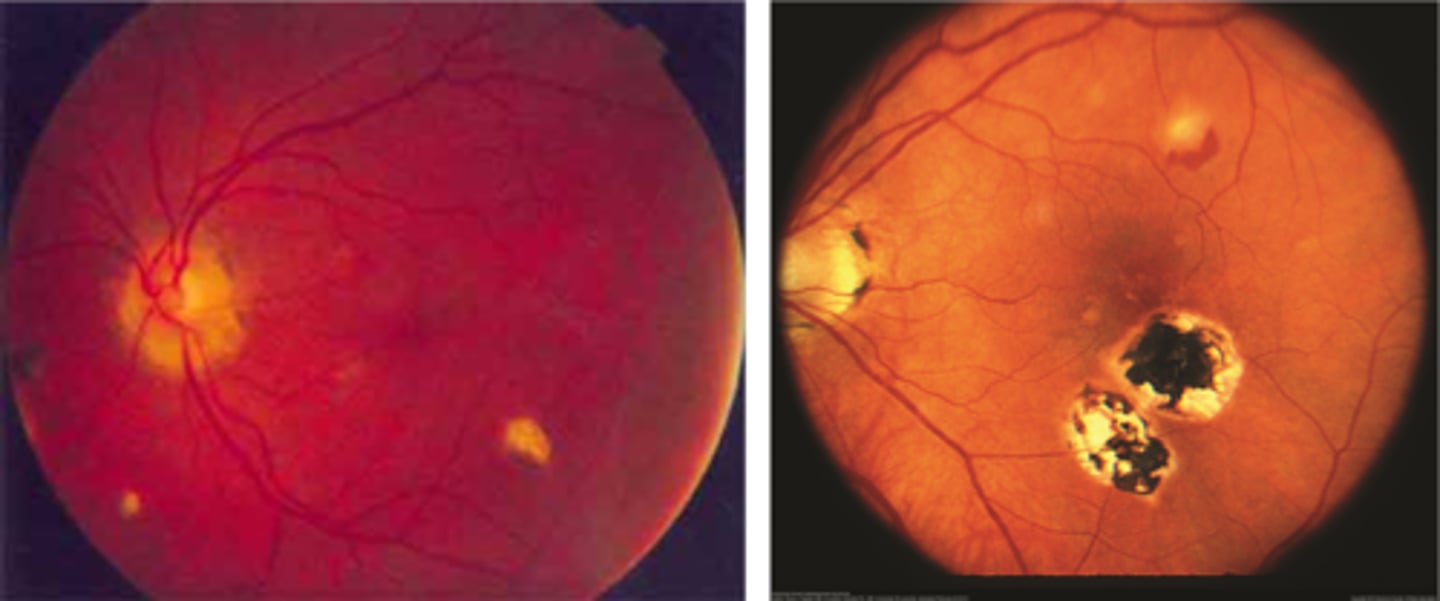
"punched-out" chorioretinal scars aka "histo spots" = outer retinal atrophy of ONL, PR's, RPE = scarring = yellow-white sclera or darker RPE hyperplasia
PPA = often further out, more irregular that crescents
absence of vitritis = white translucent dots floating in vitreous
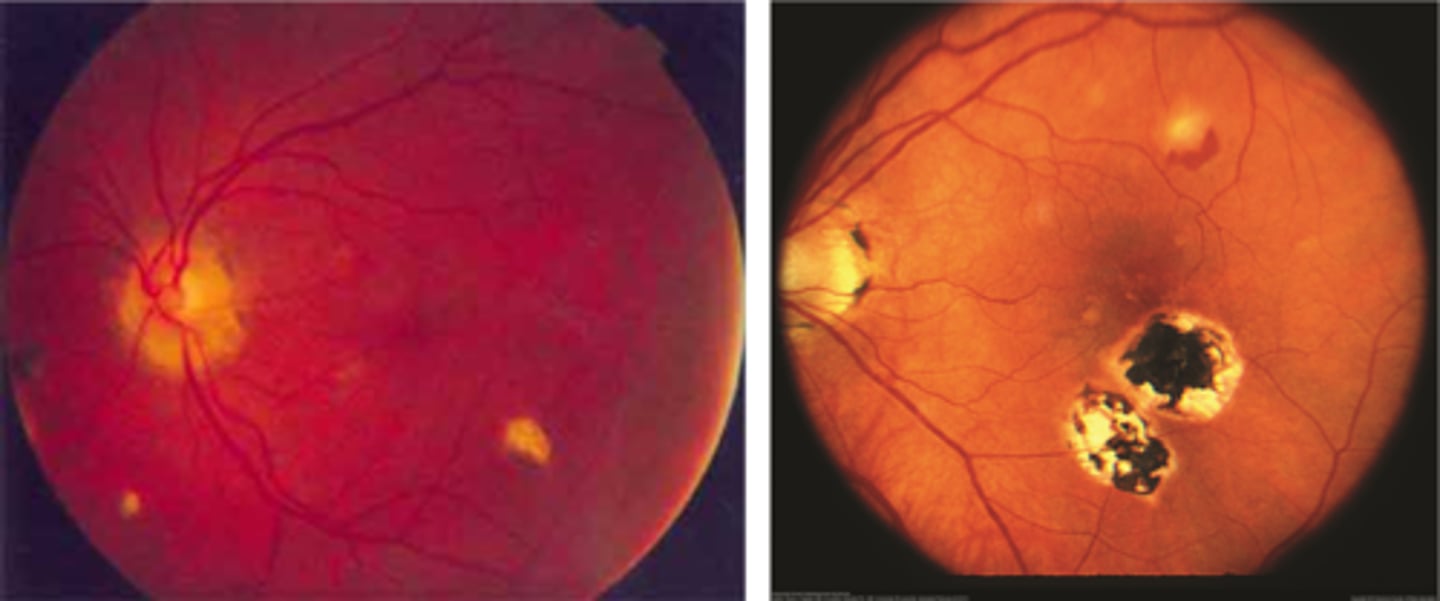
How long does it take for histoplasmosis fungal spores (exposure) in lungs/CV to reach retinal BV and choroid (ocular disease)?
can take up to years
What are the symptoms of ocular histoplasmosis?
often asymptomatic
What is the main complication of ocular histoplasmosis?
CNV = must monitor with Amsler
NOTE: subretinal heme by histo spot may be a sign of CNV
How do we manage ocular histoplasmosis?
observe, refer if CNV
How do ocular histoplasmosis spots appear on FAF?
hypoAF bc loss of retina/RPE = no lipofuscin
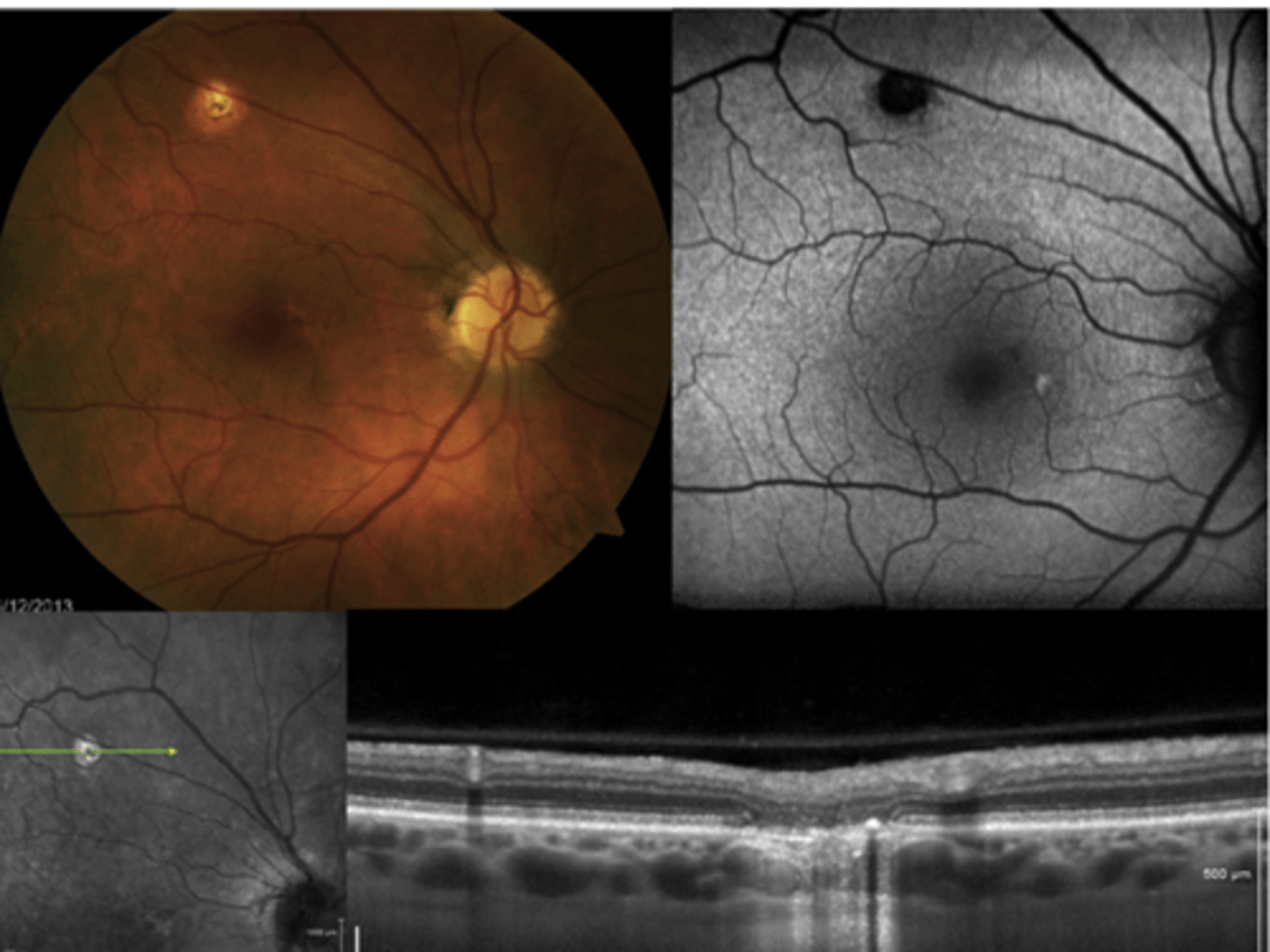
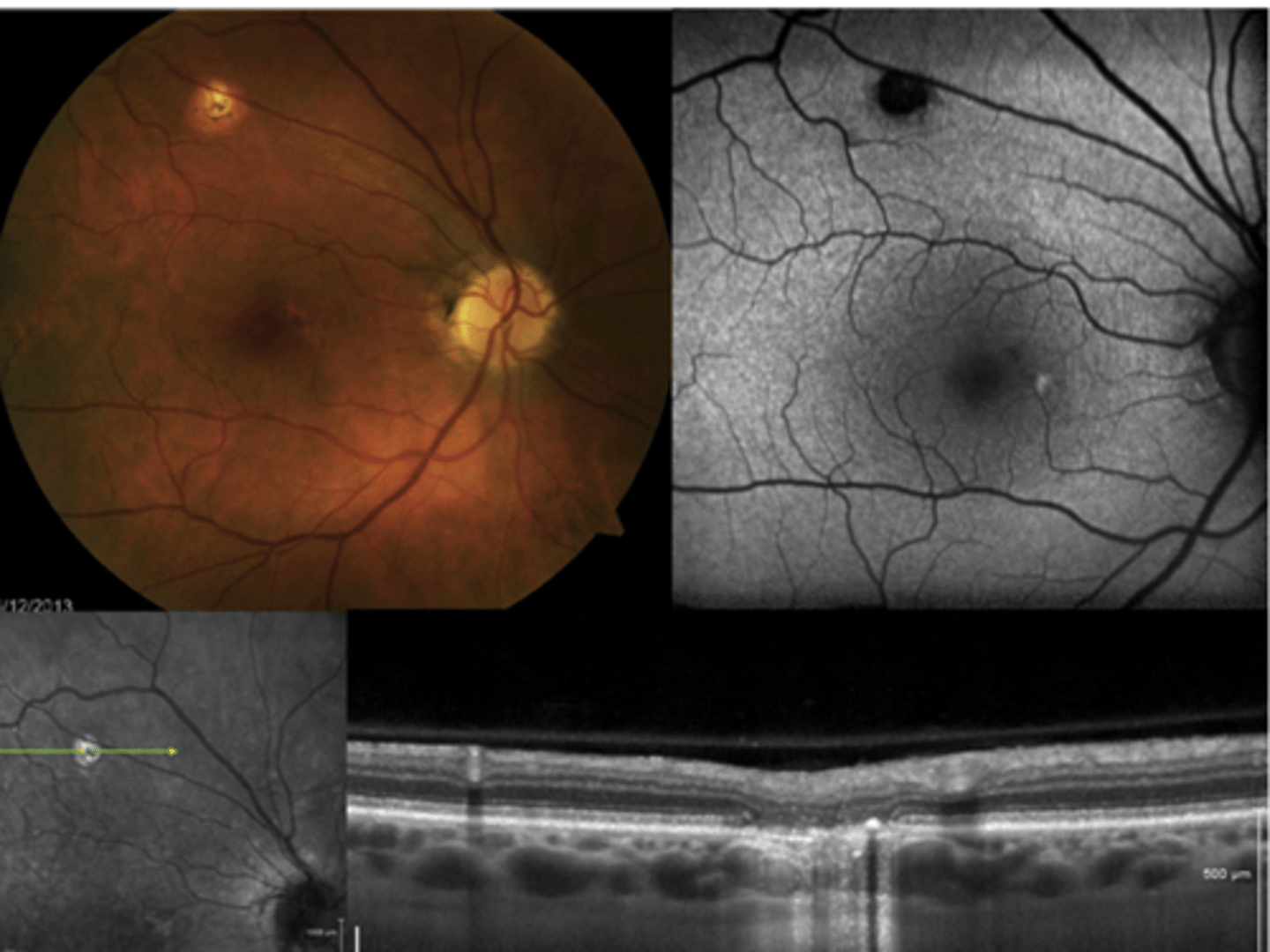
How do ocular histoplasmosis spots appear on IVFA?
hyperF bc loss of RPE = can see choroid blood below
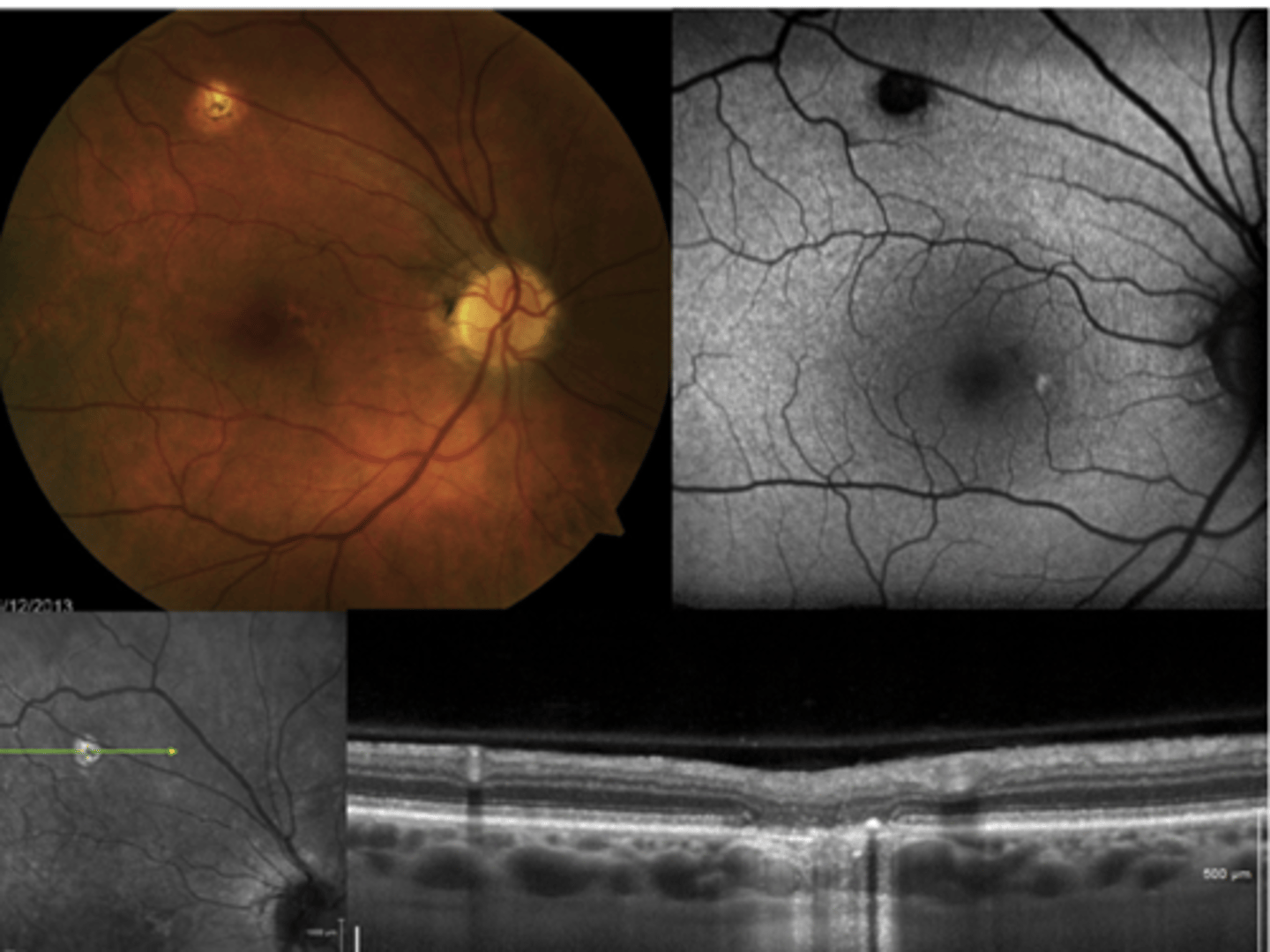
How do ocular histoplasmosis spots appear on OCT?
histo spots correspond to loss of ONL, PR's RPE, Bruch's
What is ocular toxoplasmosis?
focal, full-thickness retinochoroiditis
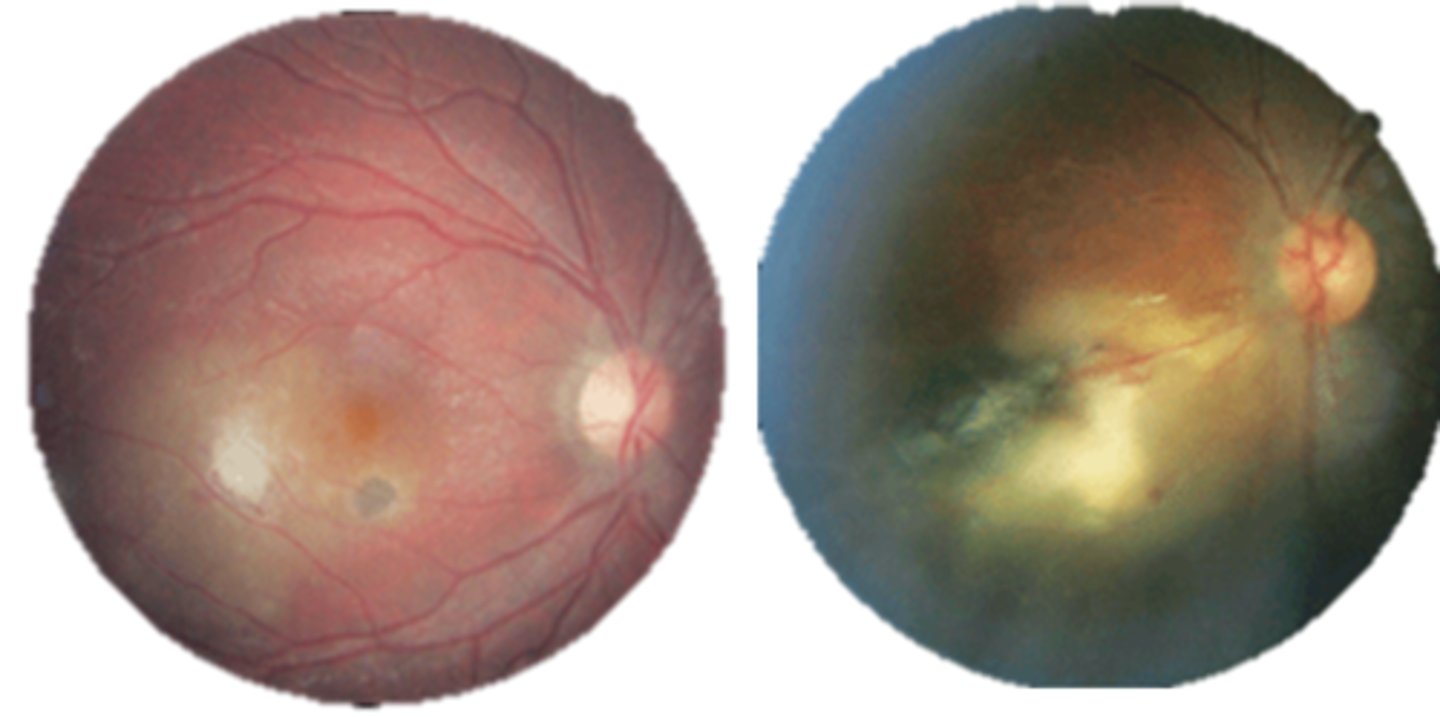
What causes ocular toxoplasmosis?
Toxoplasma gondii protozoan parasite = carried by cats (definitive host) but also other humans, mammals, birds, or reptiles (intermediate hosts)
What is the congenital form of ocular toxoplasmosis?
transplacental transmission at birth = bilateral
What is the acquired form of ocular toxoplasmosis?
breathing in particles from contaminated litter box, or eating undercooked meat with parasite = unilateral
How long does it take for the initial systemic toxoplasmosis parasitic infection (1-2 weeks of flu S/S) to have ocular involvement?
weeks to years
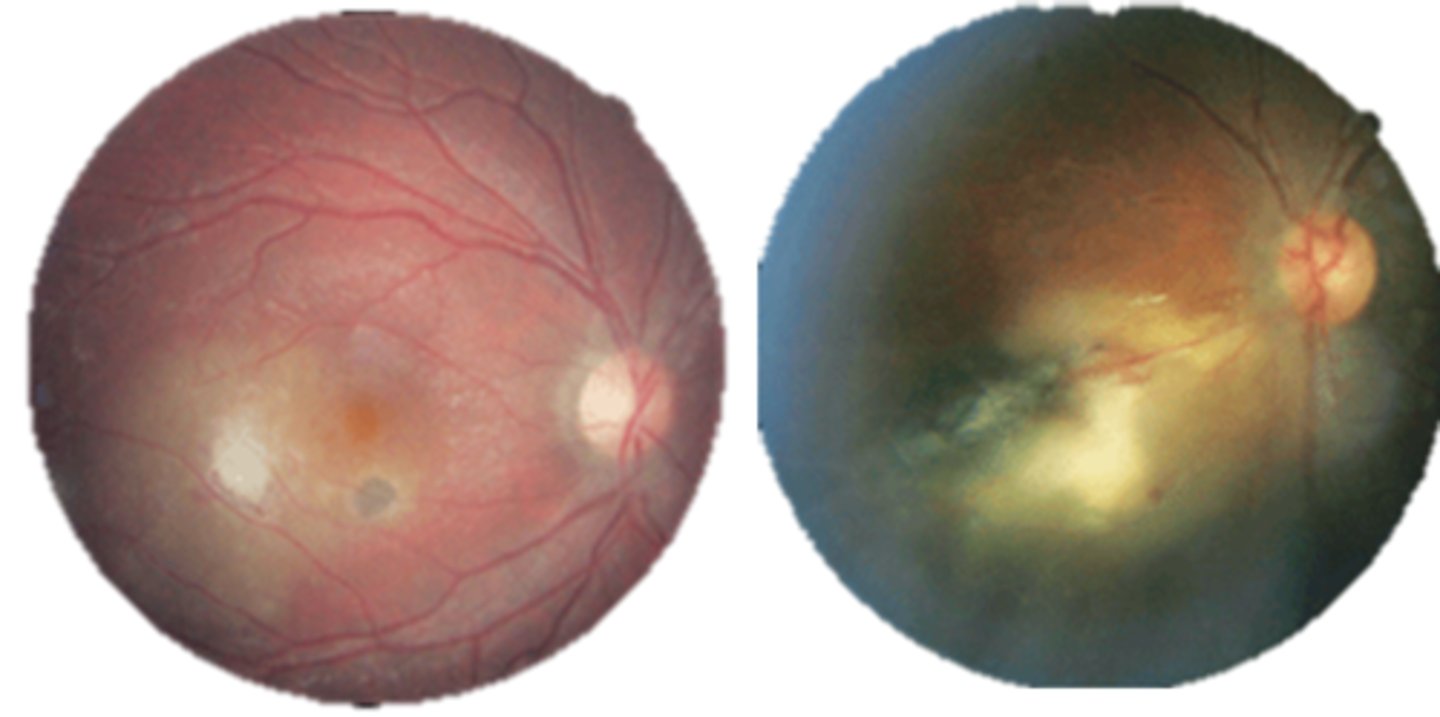
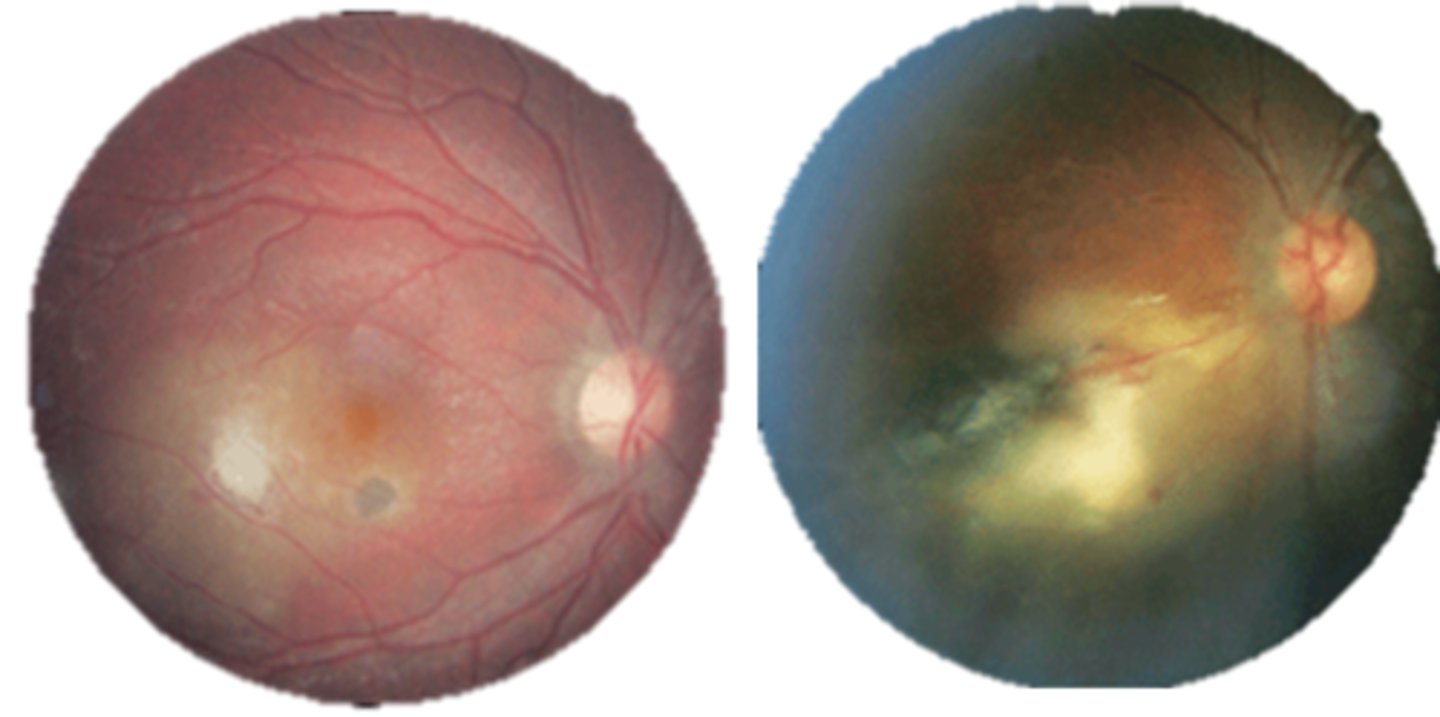
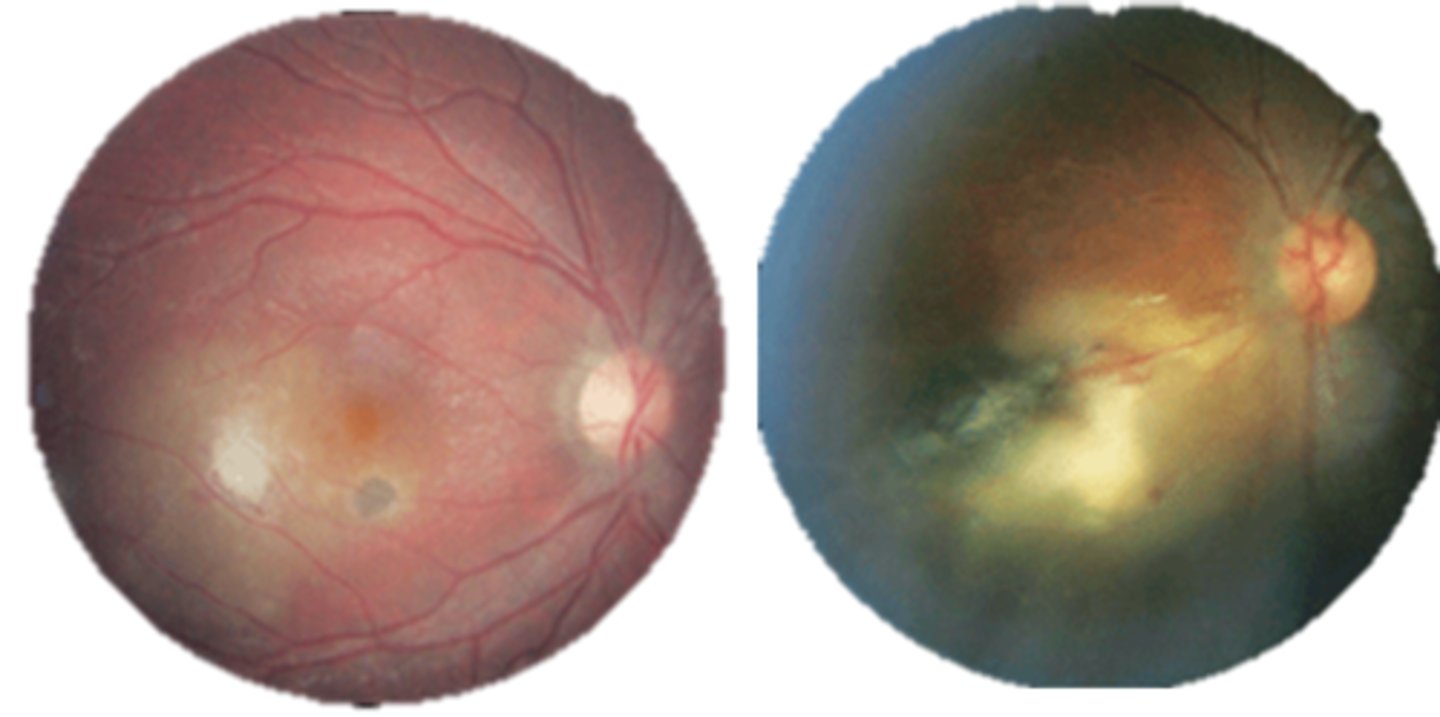
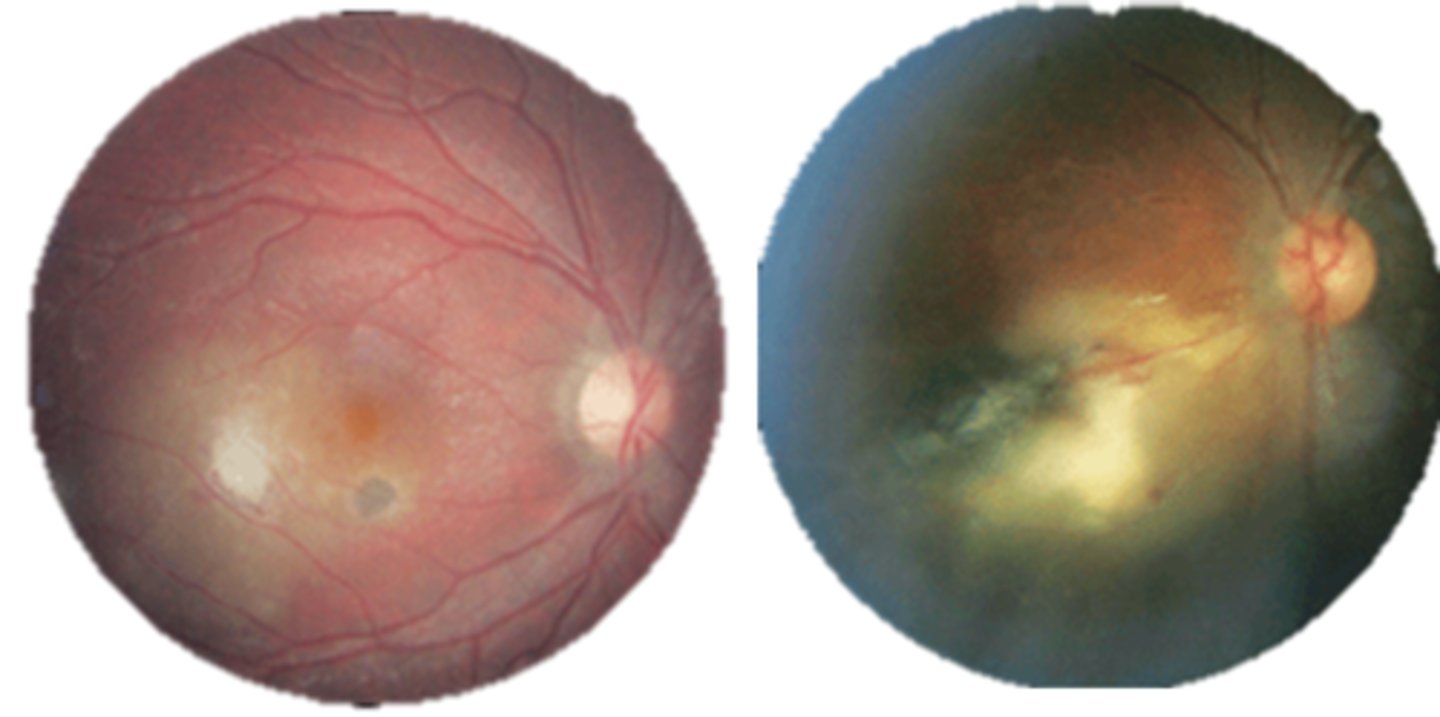
What are the 3 main ocular findings of ocular toxoplasmosis? Differentiate which are active vs latent.
white focal retinitis = active only
overlying vitritis = "headlight in the fog" = active only
nearby large pigmented retinochoroidal scar = active and latent
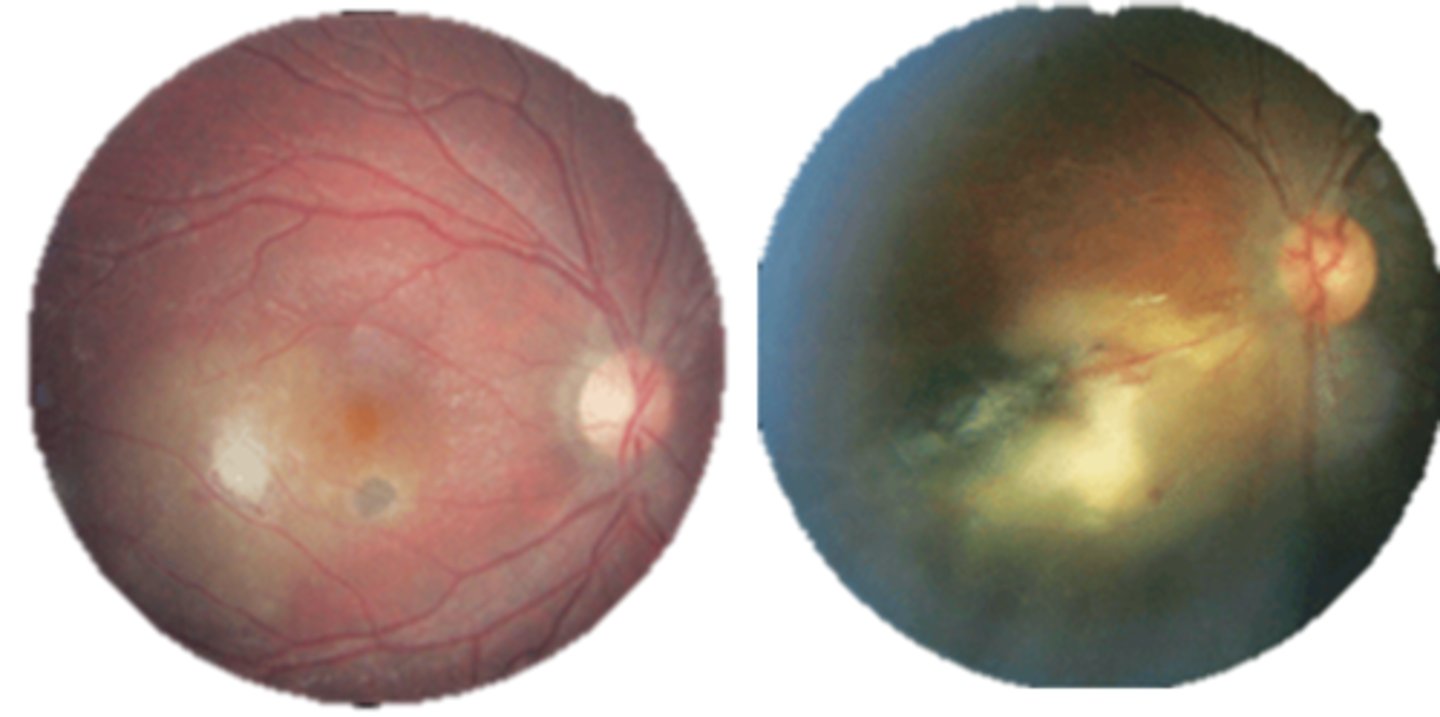
What are some other possible necrotizing retinitis-related findings of ocular toxoplasmosis?
+/- nearby retinal vasculitis
+/- secondary iridocyclitis
+/- papillitis, neuroretinitis, retrobulbar neuritis, scleritis, retinal detachment, punctate outer retinitis, branch retinal artery occlusion
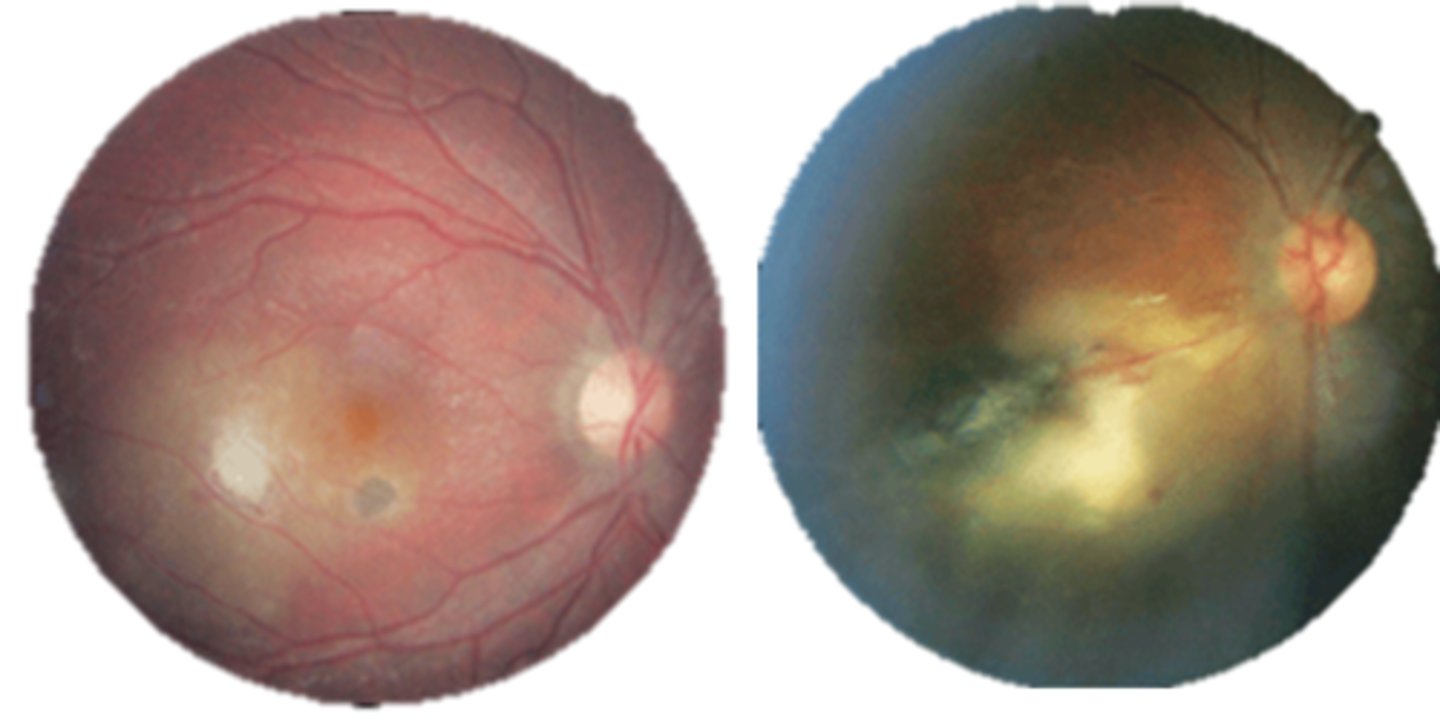
Aside from findings on fundoscopy, what else can we use to dx ocular toxoplasmosis?
IgG and IgM Ab tests BUT not very sensitive for ocular disease
PCR of aqueous/vitreous BUT only if hard to dx
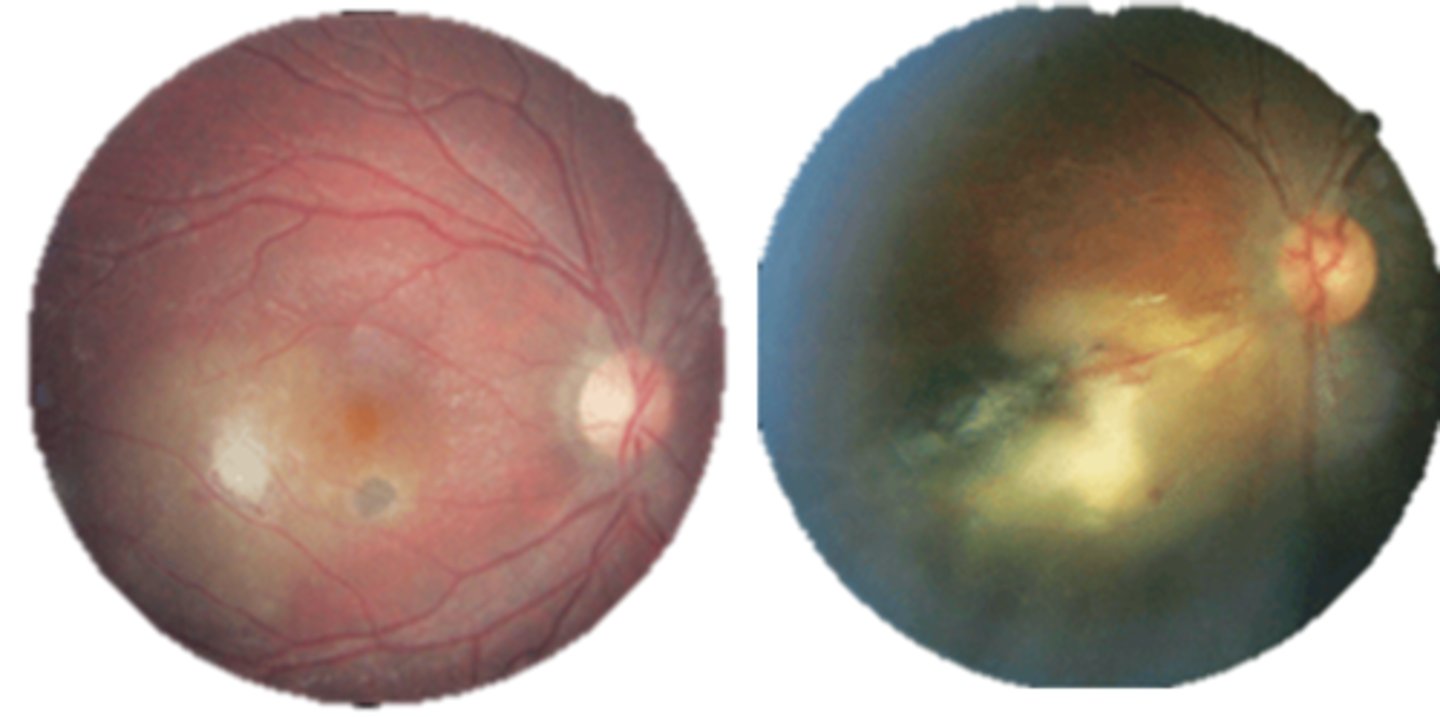
What is the main tx for ocular toxoplasmosis?
classic triple therapy (oral):
pyrimethamine w/ folic acid
sulfadiazine
corticosteroids
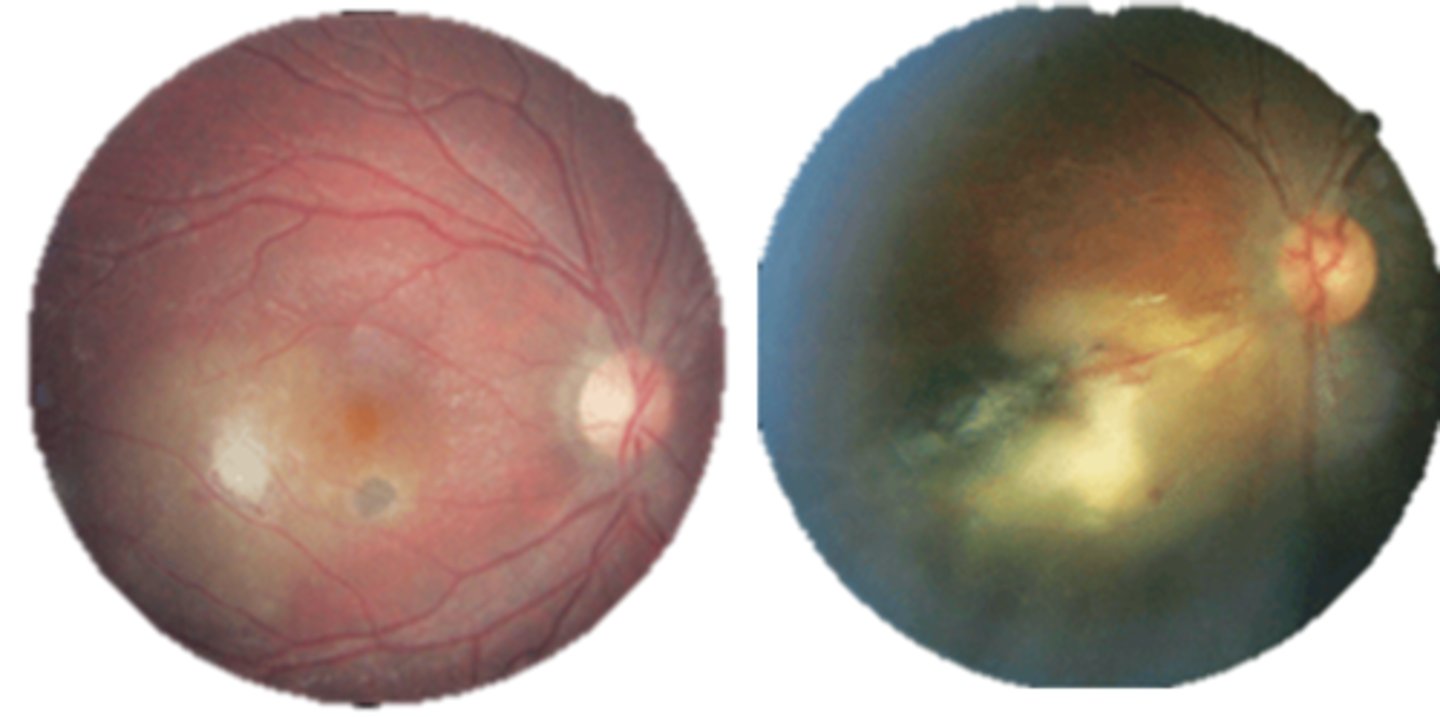
What is the prognosis for ocular toxoplasmosis?
4-6 weeks until lesion resolves
macular scarring = vision loss
risk of recurrence is high within 1st year of initial episode (esp at edge of initial scar where Bruch's is compromised)
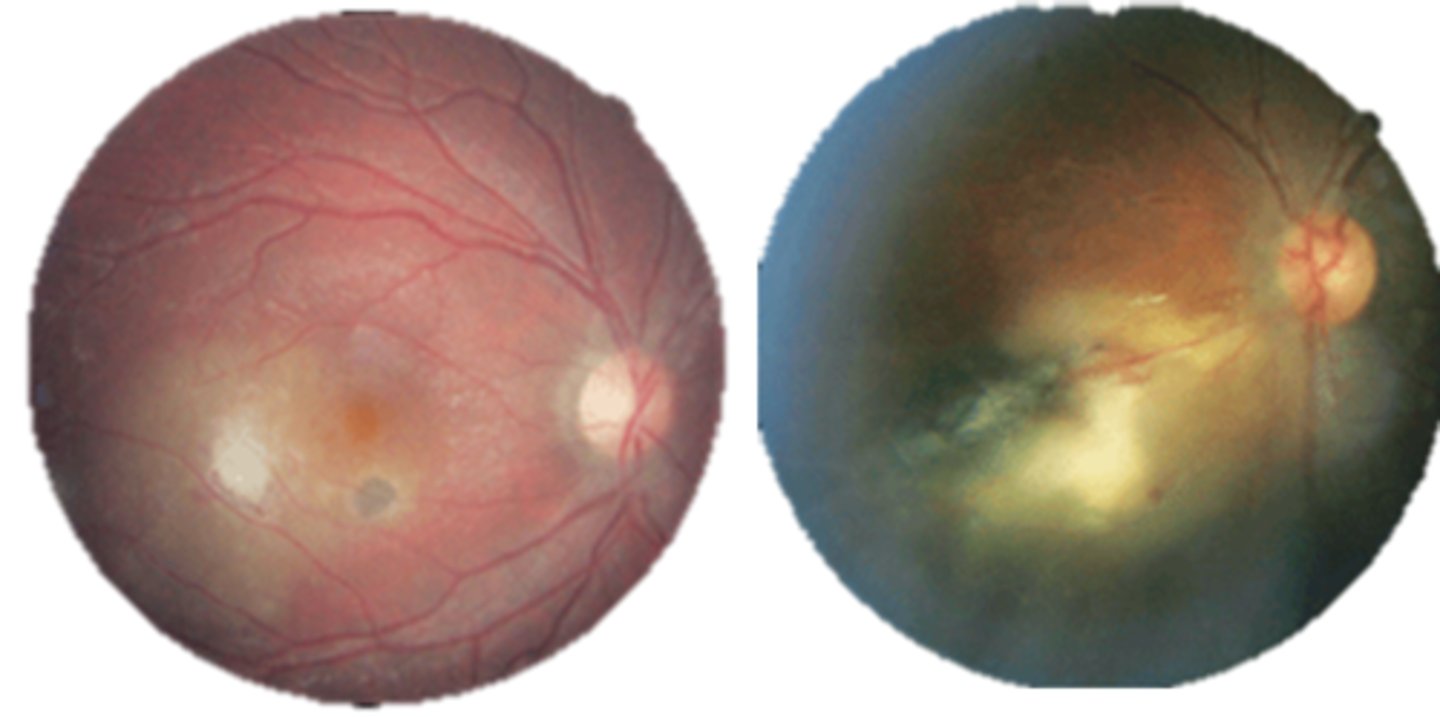
How often do we monitor ocular toxoplasmosis?
1st active = monitor every few mos, Amsler
otherwise = monitor q12 mos
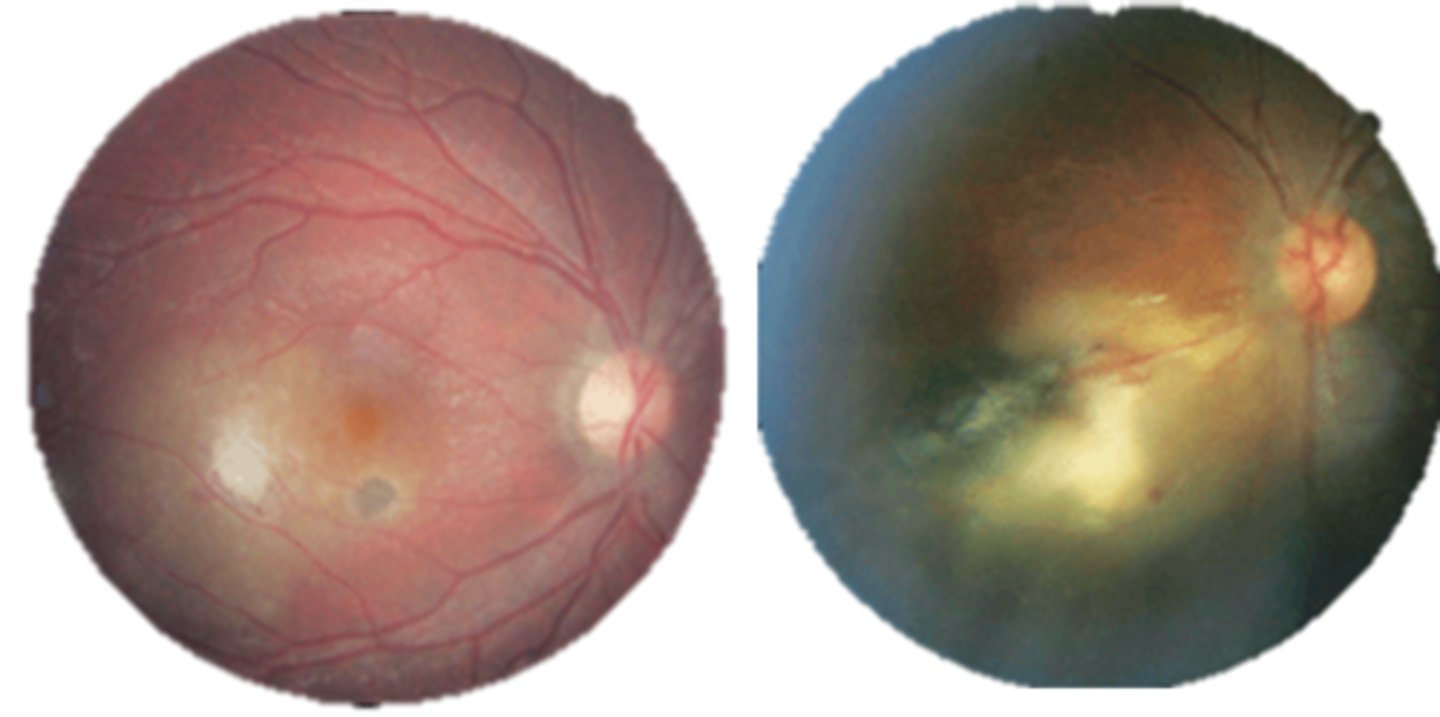
How can we prevent ocular toxoplasmosis?
avoid raw/undercooked meat
wash hands
clean fruits/veggies thoroughly
wear a mask when changing litter box (especially if pregnant)
bactrim q3 days prophylactically to prevent vision loss in fellow eye and prevent recurrence
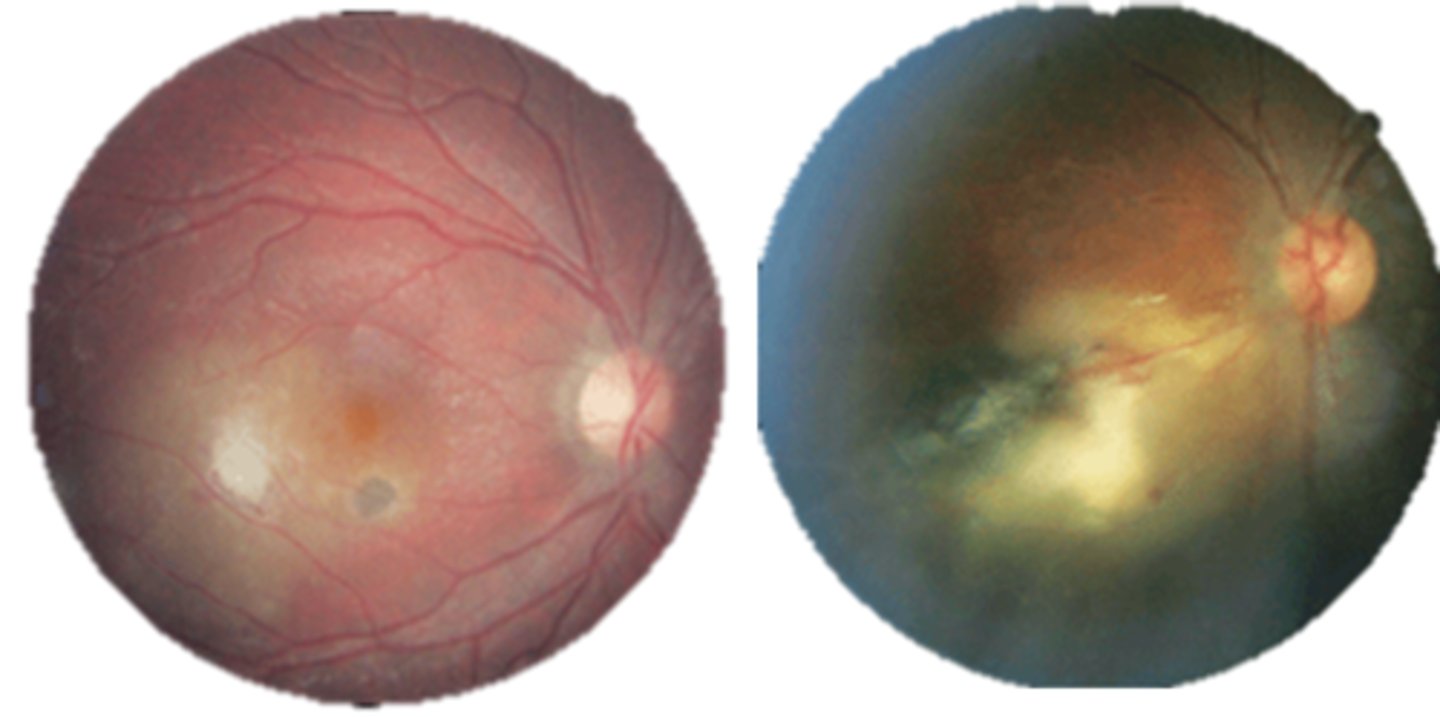
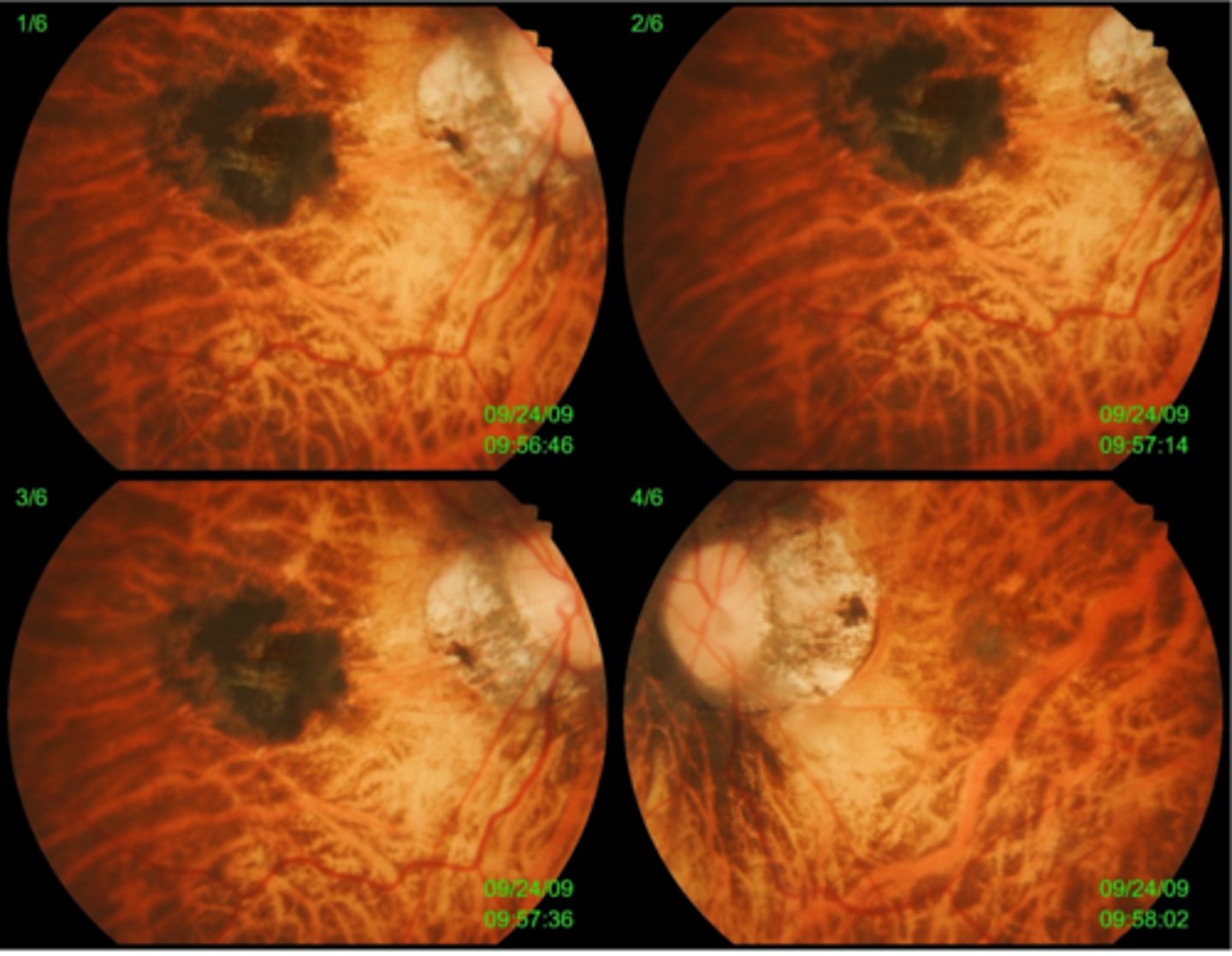
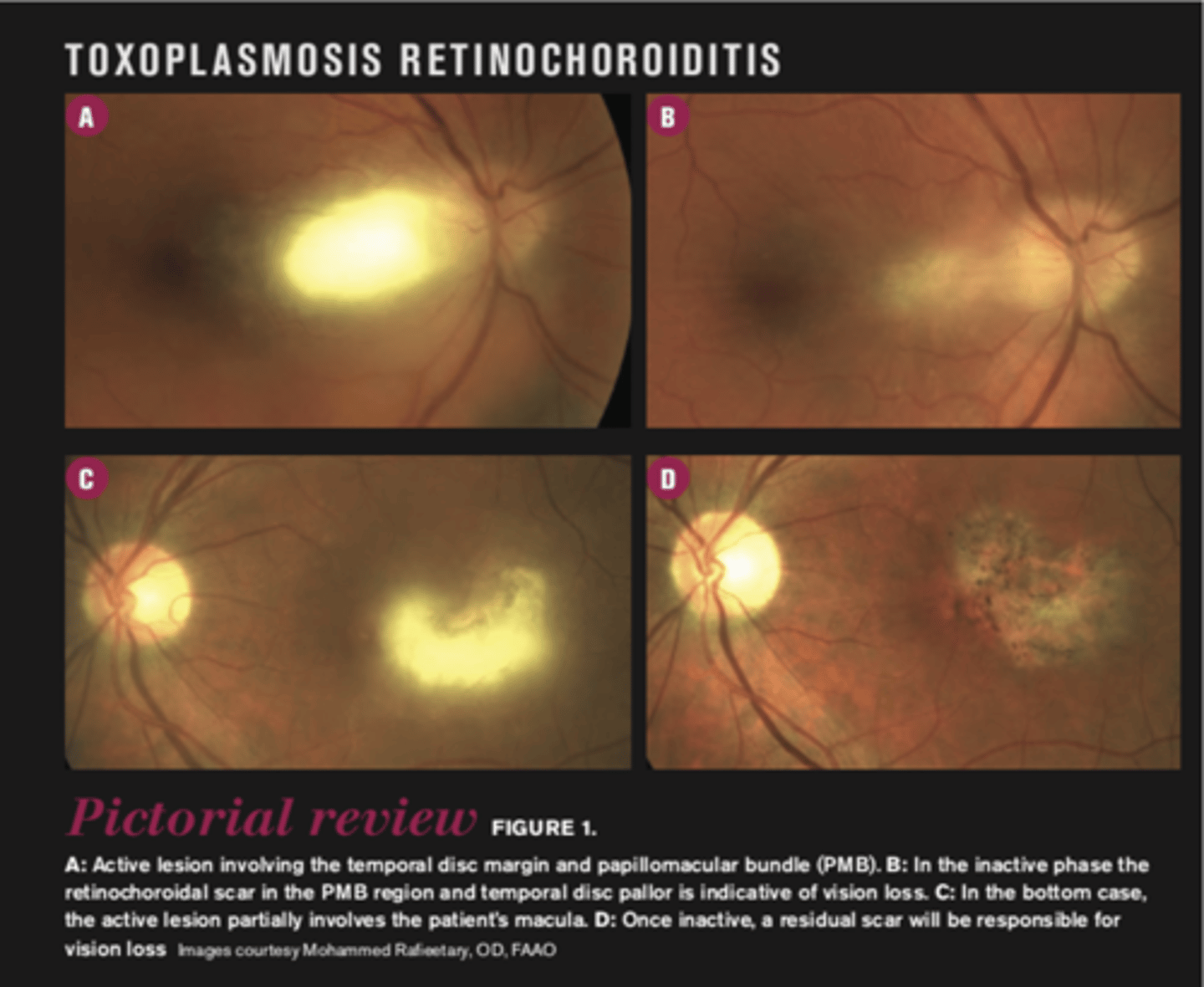
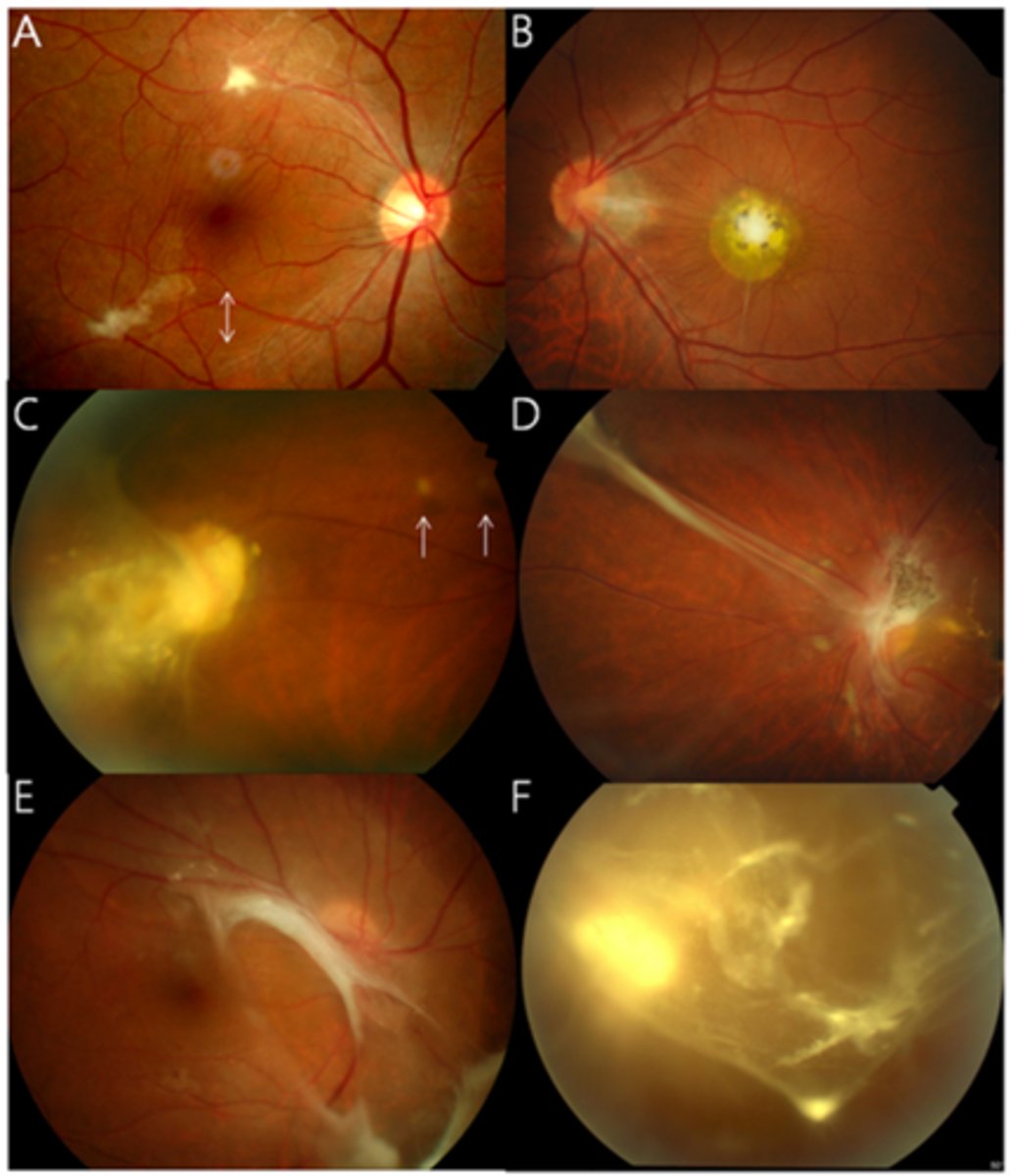
What finding of toxoplasmosis is seen in A/B?
retinitis turns into hazy scar with nerve pallor
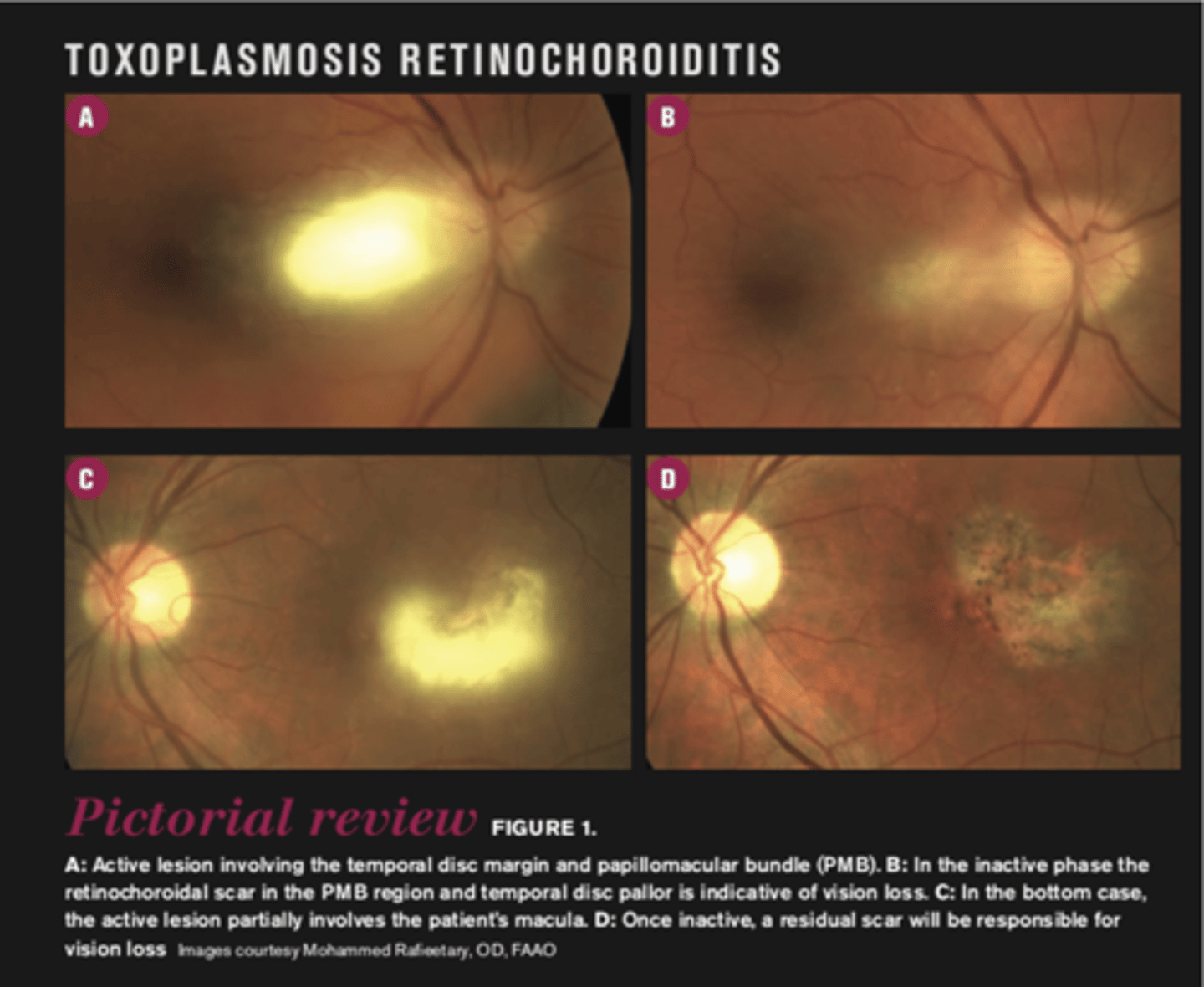
What finding of toxoplasmosis is seen in C/D?
scarring overtime with VA loss/scotoma
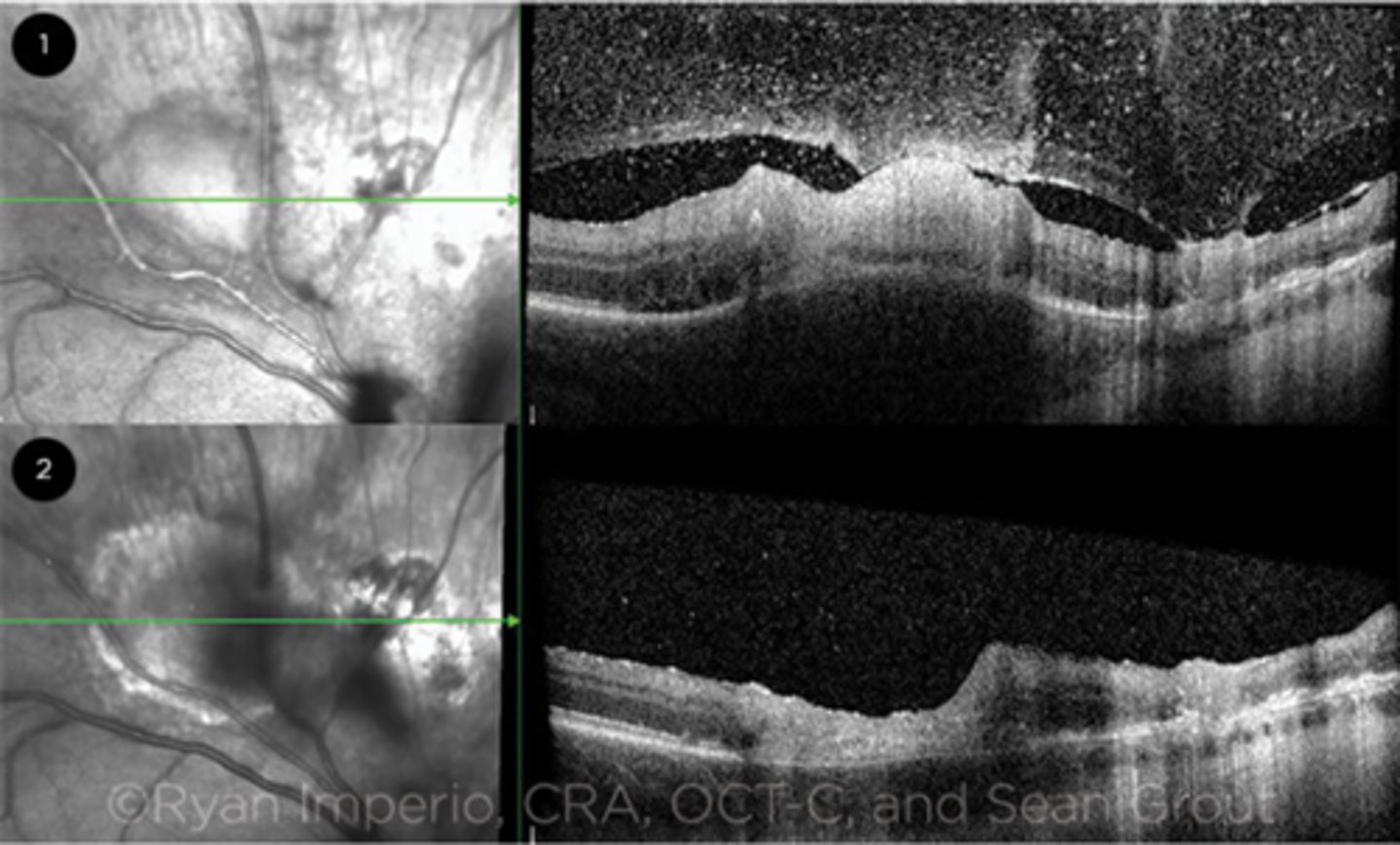
What is seen in toxoplasmosis with OCT?
acute = retinitis = inflam, thickening of layers
acute = vitritis = dots and haze vitreous
chronic = necrotizing atrophy = scarring, thinning
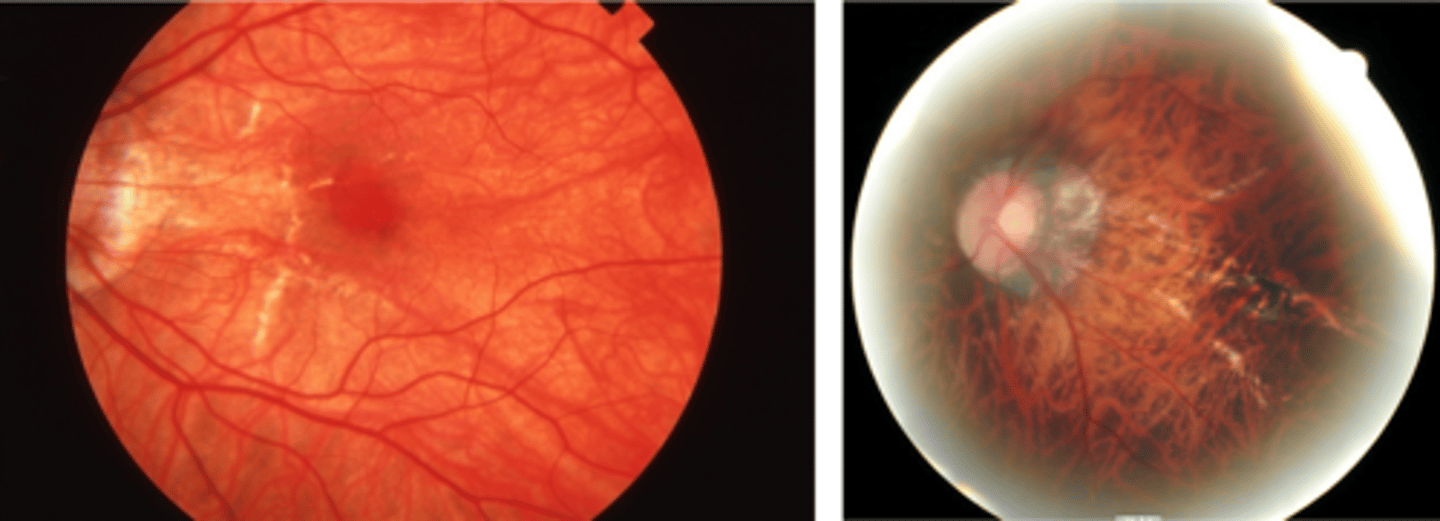
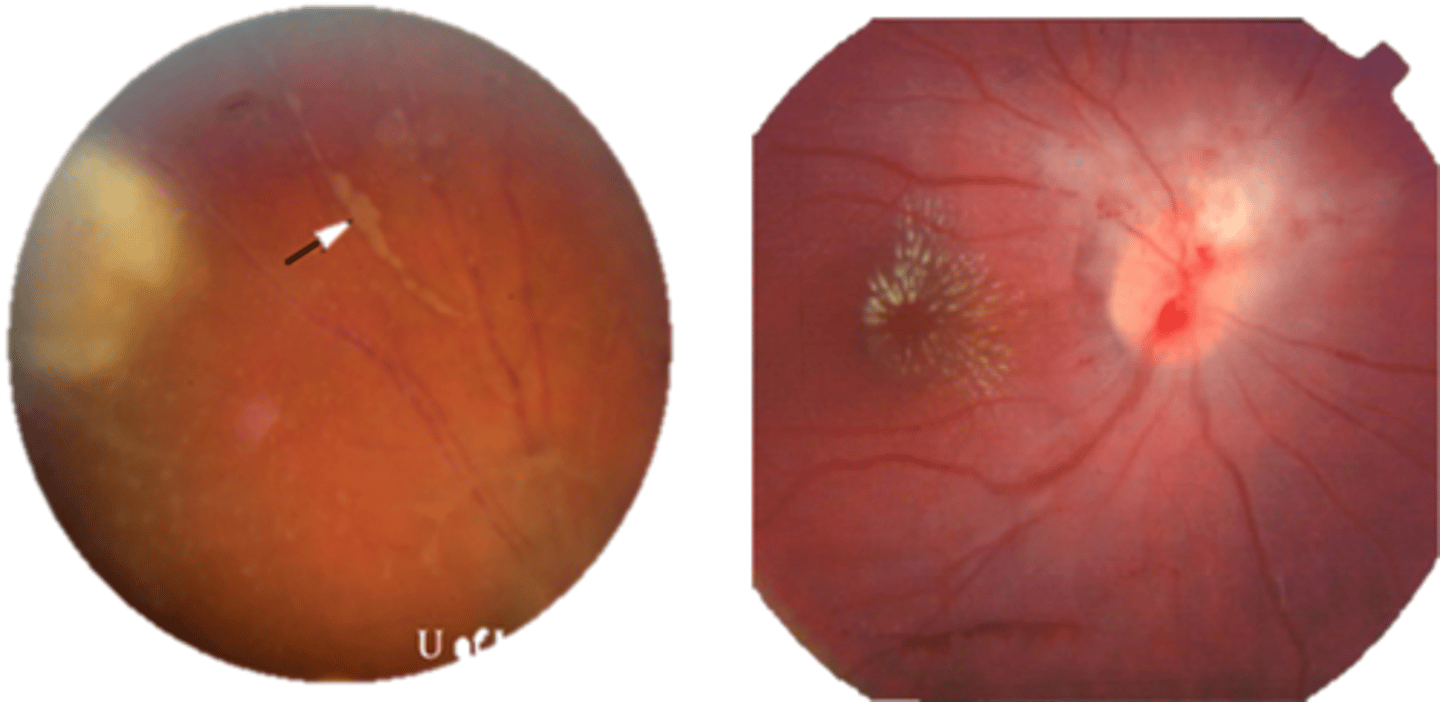
What findings of toxoplasmosis are seen here?
retinal vasculitis
exudative scar
focal, hazy vitritis and retinitis
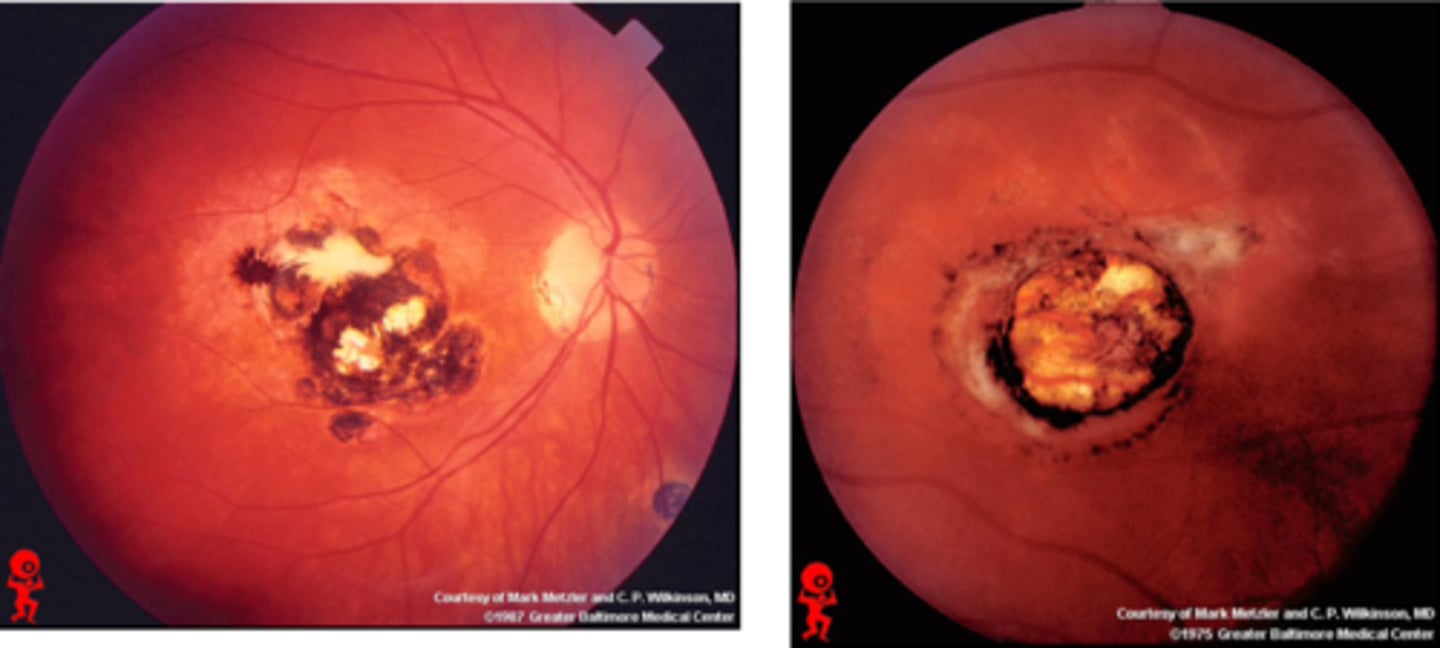
What findings of toxoplasmosis are seen here?
latent scars
What causes ocular toxocariasis?
nematode roundworms in dogs and cats (Toxocara canis or Toxocara cati) = live in dog/cat stomach and release eggs in stool that enters soil, causing...
visceral larva migrans (VLM) = systemic
ocular larva migrans (OLM) = posterior uveitis
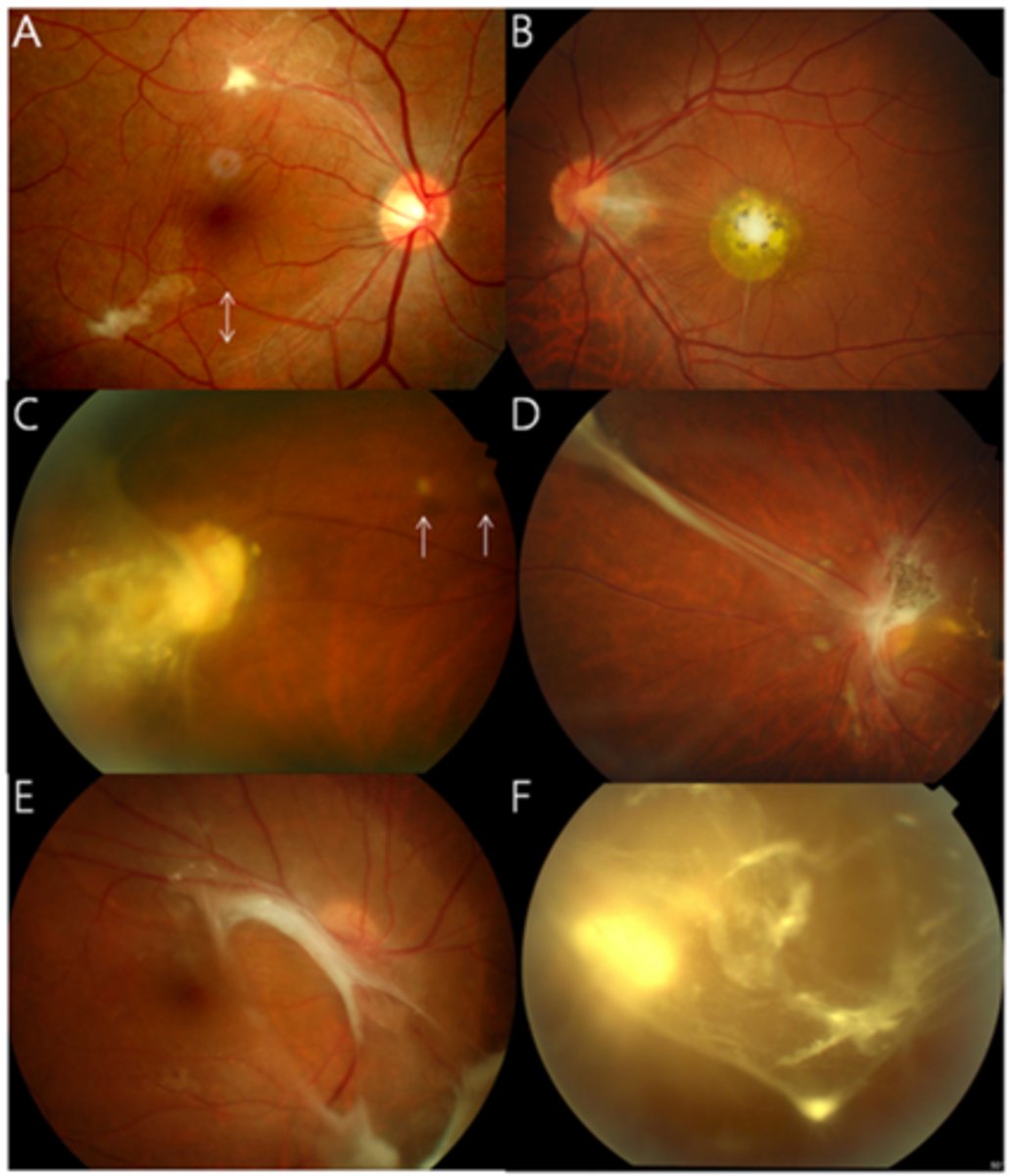
What are 3 subtypes of ocular toxocariasis?
central posterior granuloma
peripheral granuloma
chronic endophthalmitis
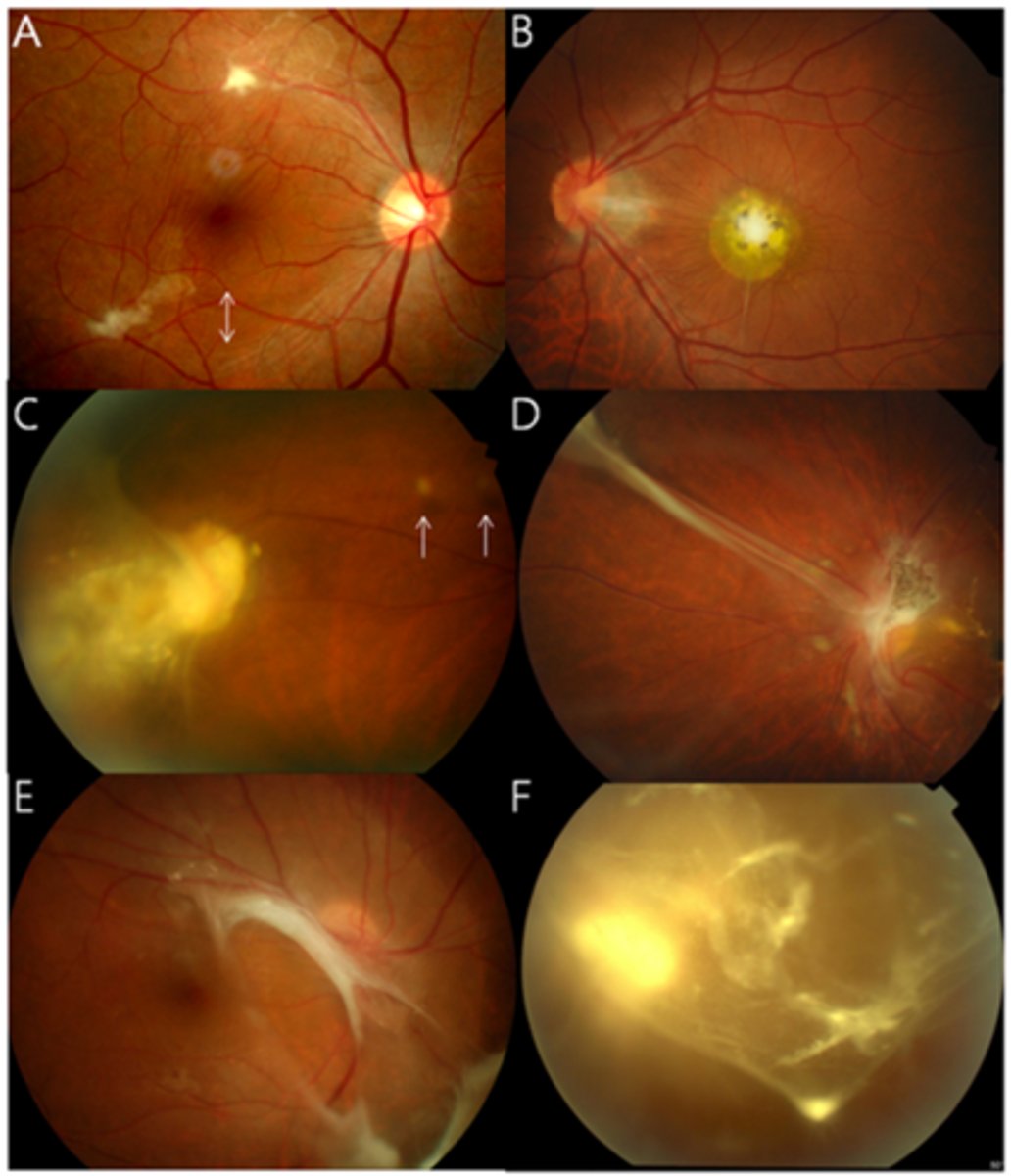
What are some signs of ocular toxocariasis?
UNILATERAL
granuloma = hazy white lesion made up of inflam debris
vitritis that can mimic endophthalmitis
fibrocellular stalks made up of inflam debris can contract = tugs on retina = retinal folds
NO chorioretinal scar
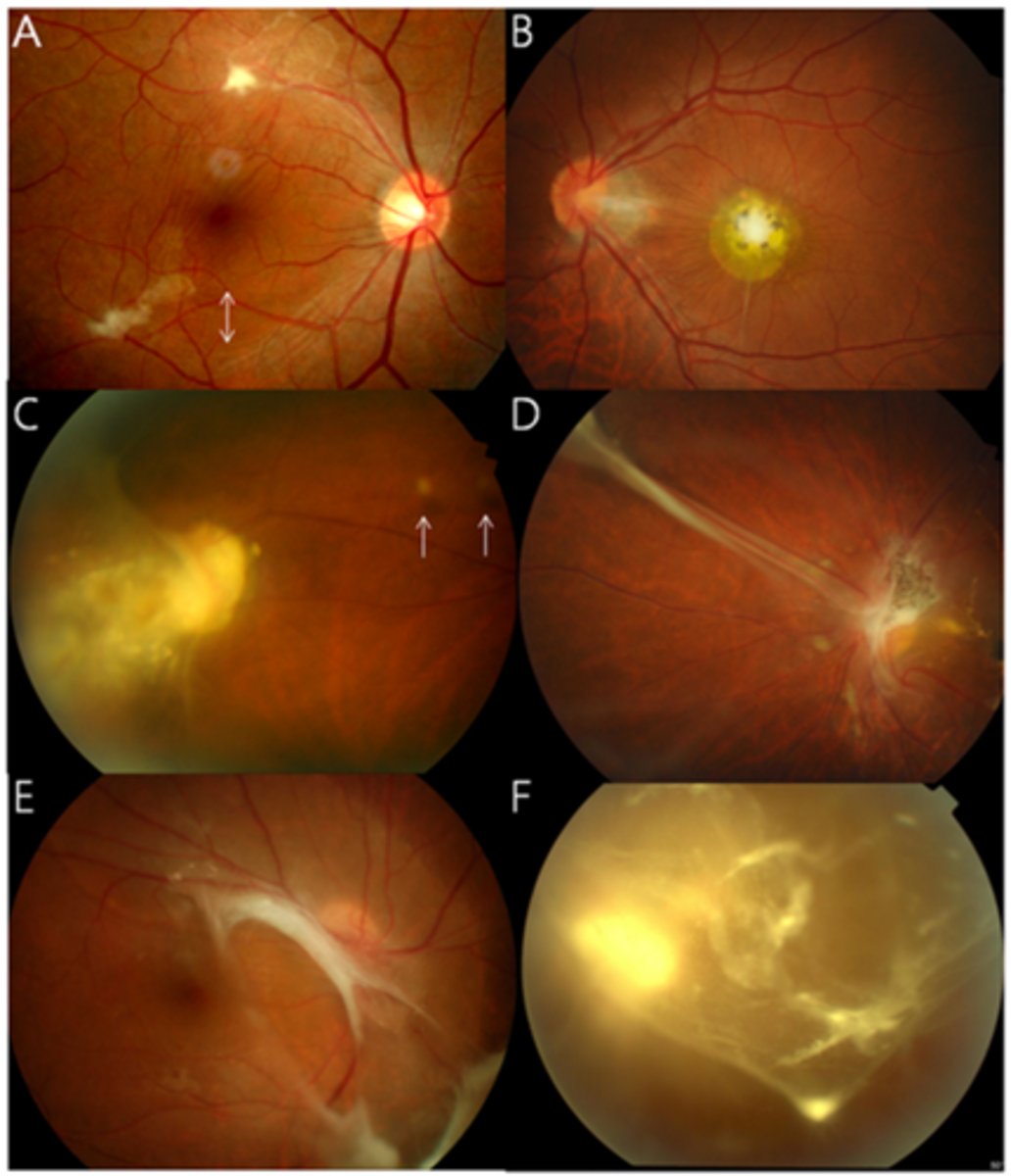
Aside from findings, how else can we dx ocular toxocariasis?
eosinophil tests
ELISA TES antigen
aq/vitreous sample
NOTE: these are only sometimes positive with ocular involvement
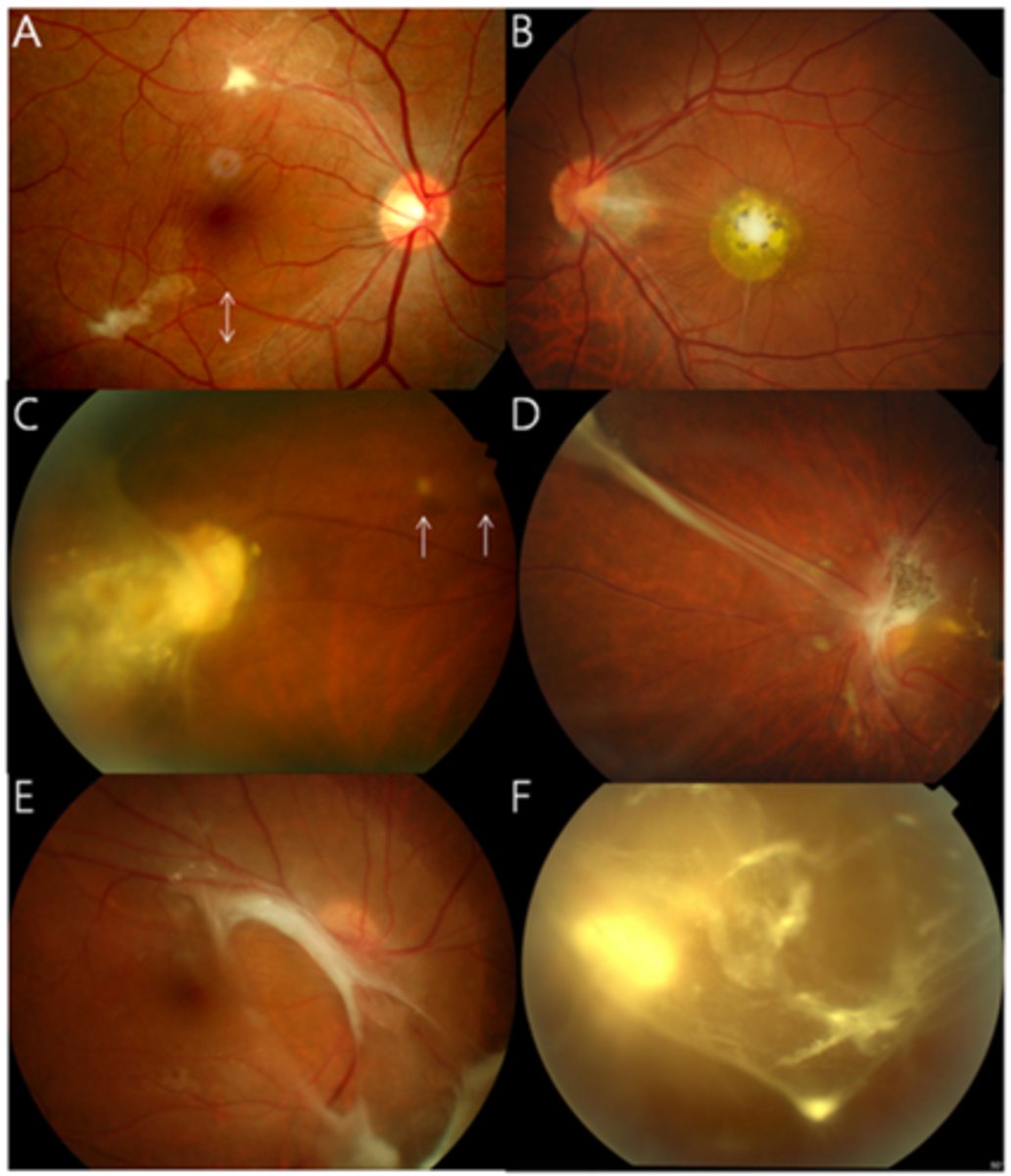
What is the tx for ocular toxocariasis?
anti-inflam like topical/injection/oral steroids, cycloplegic = avoid RD
anti-parasite but unproven
surgery for vitreous opacification or heme, RD, ERM = vitrectomy, laser, photocoagulation, cryotherapy
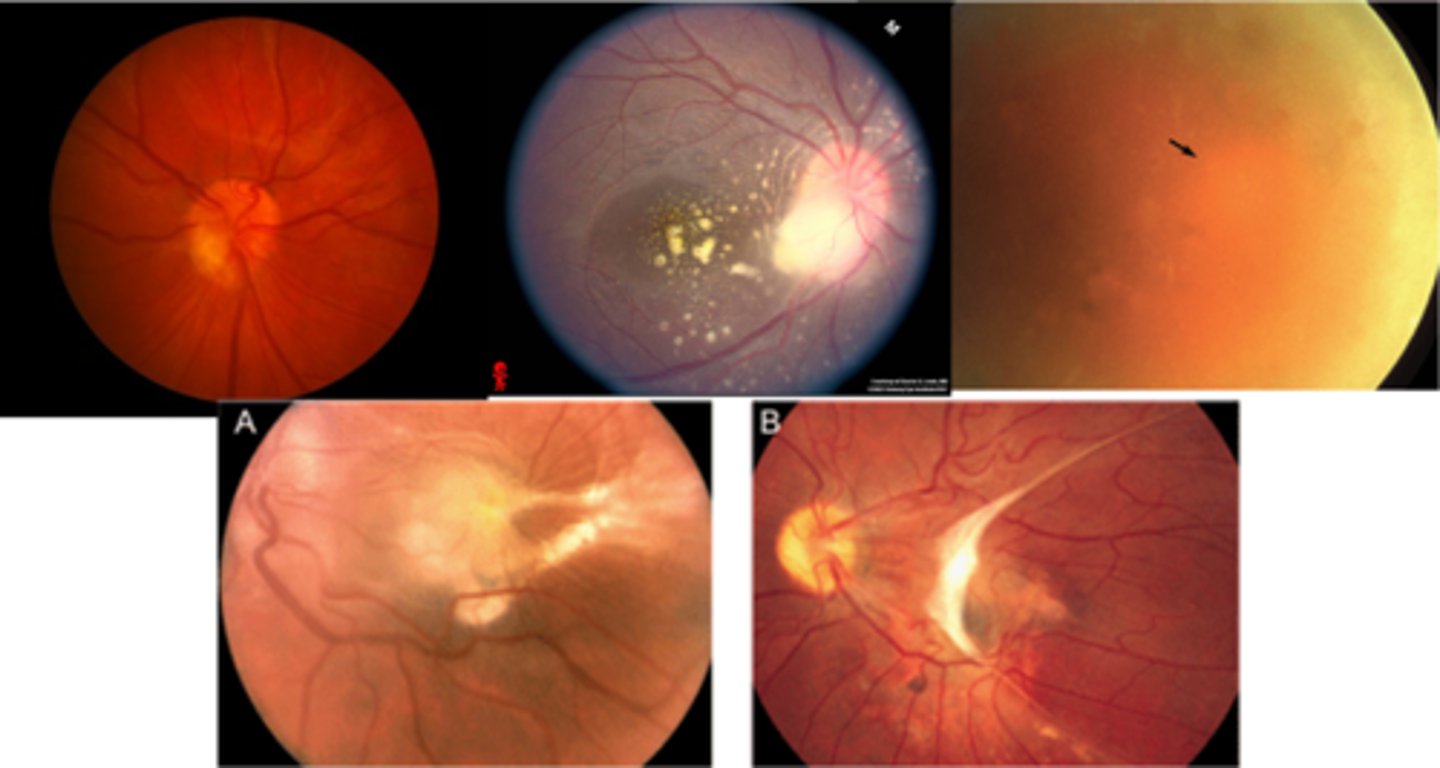
What is the prognosis for ocular toxocariasis?
depends on lesion location
if presenting vision poor, outcomes typically poor
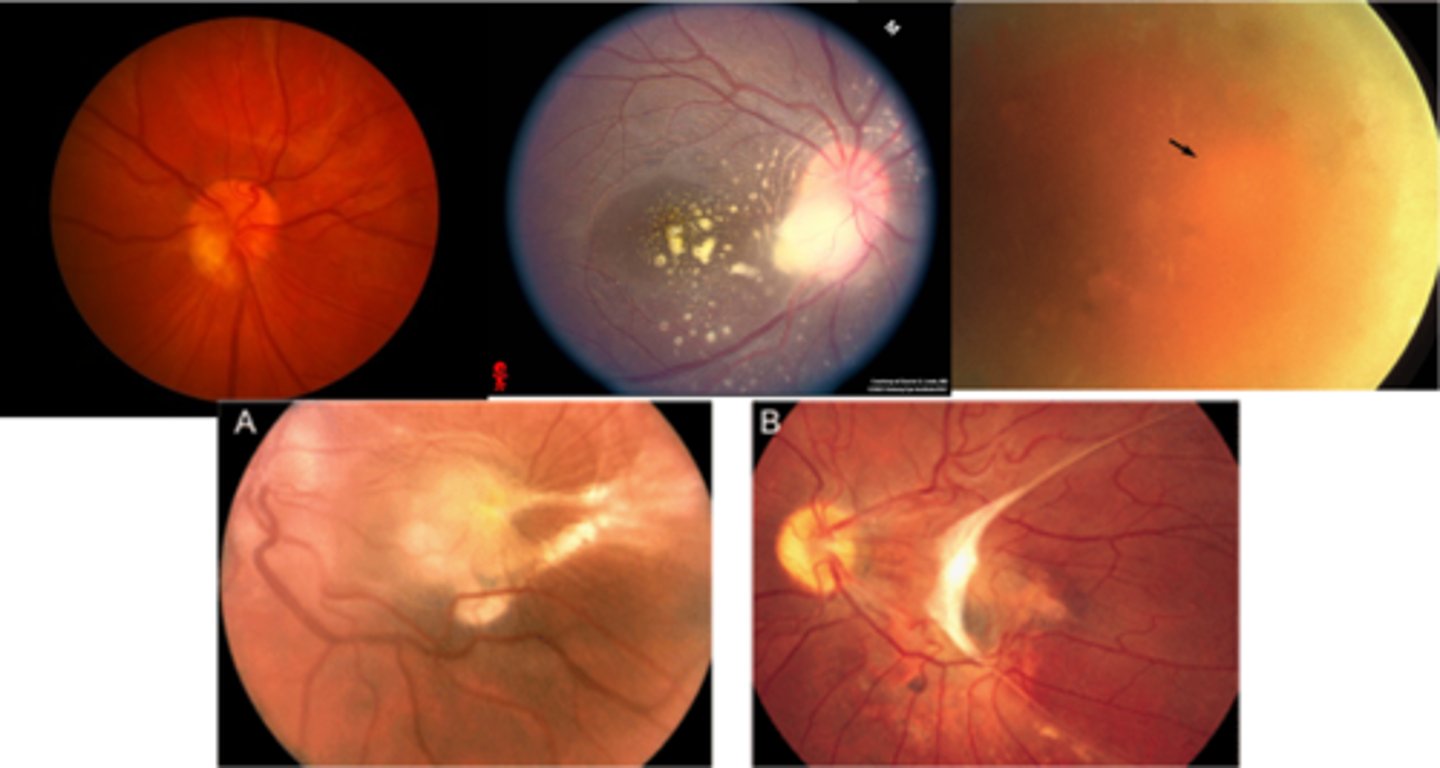
What is the prevention for ocular toxocariasis?
deworm pets
dispose litter appropriately
wash hands
clean produce properly
avoid raw meat
good water conditions
avoid dirt
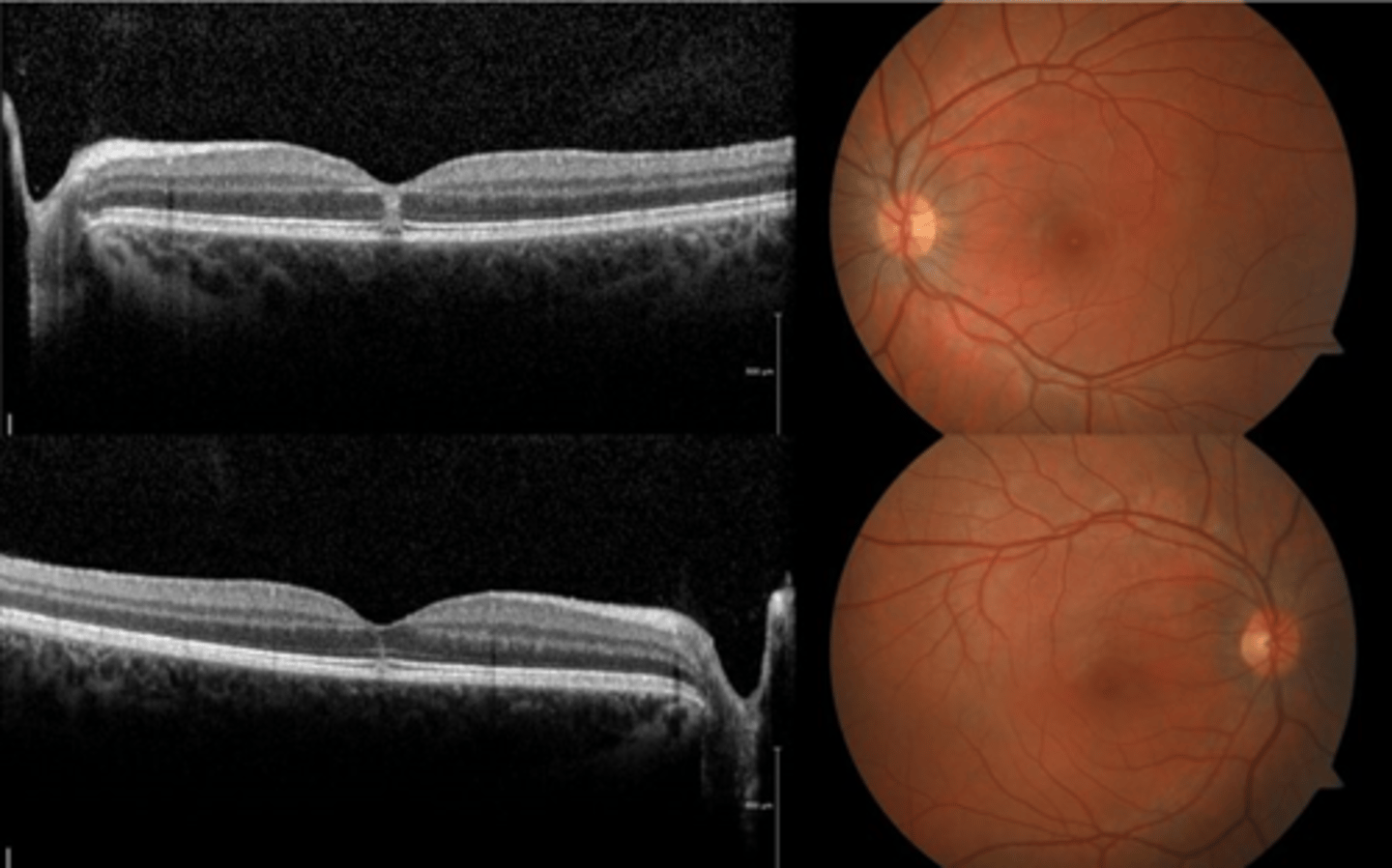
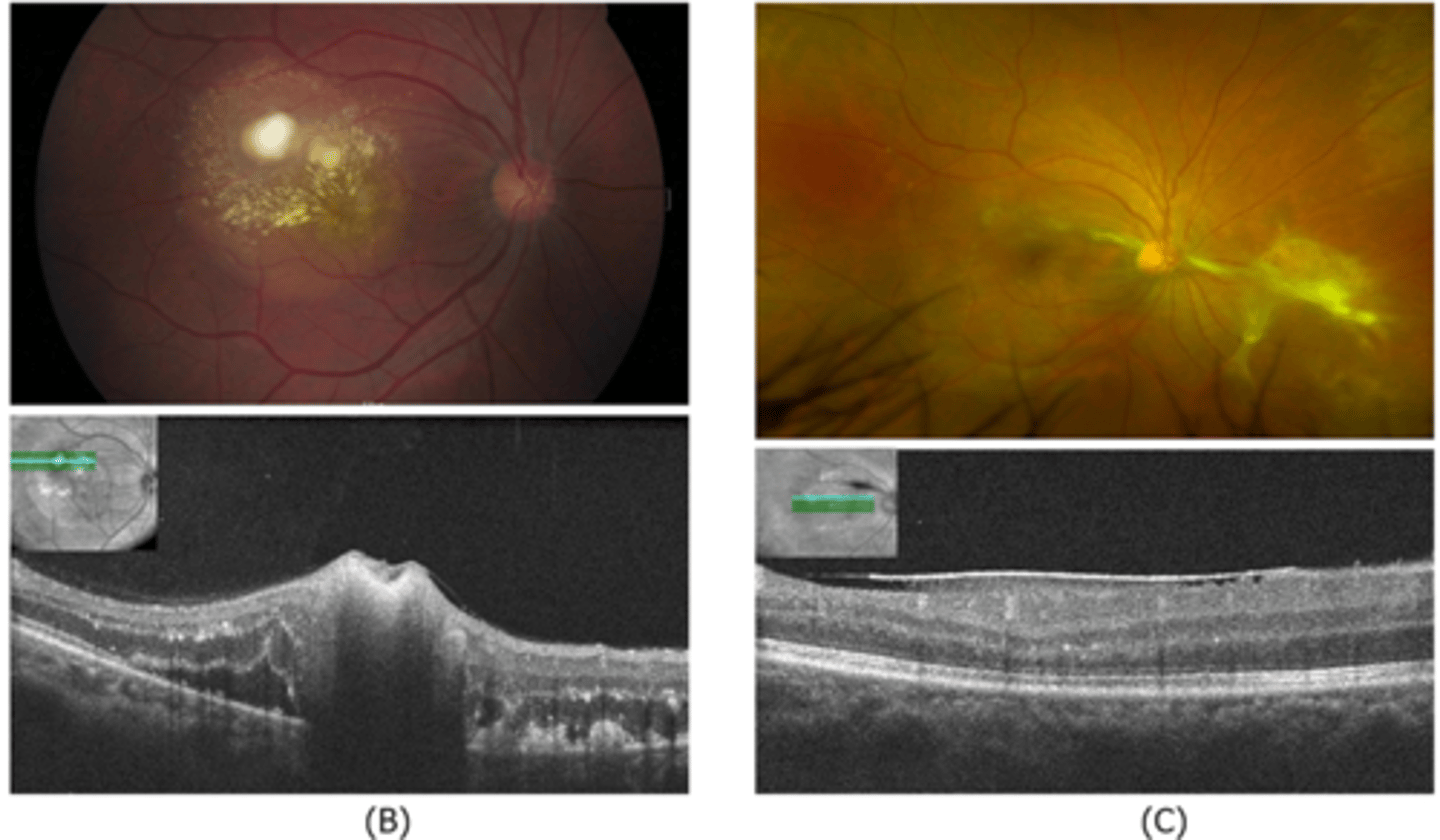
How does ocular toxocariasis appear on OCT, as seen here in patient A?
multiple light granulomas = hyperR
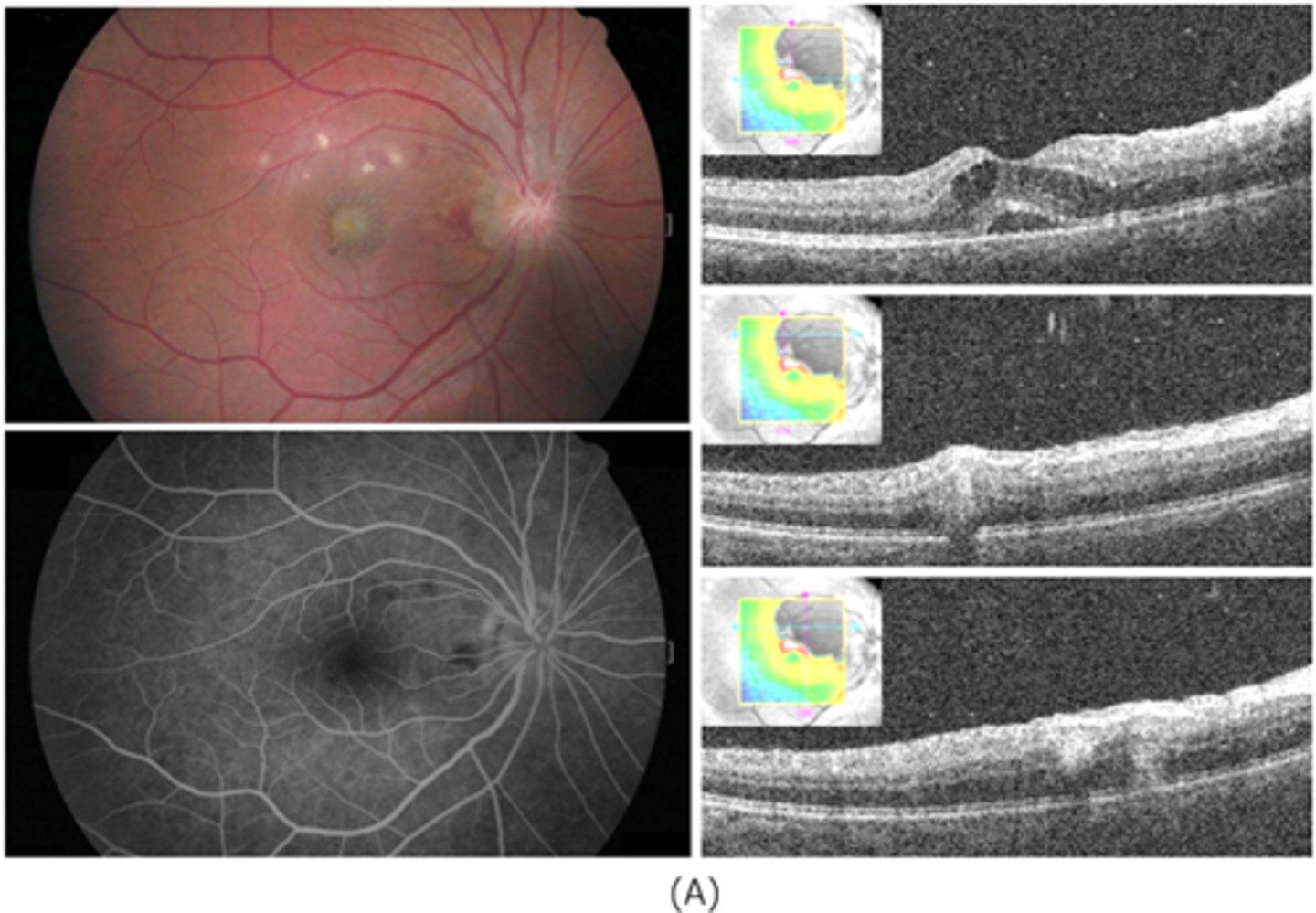
How does ocular toxocariasis appear on OCT, as seen here in patient B?
recurrence = granulomas with exudates, edema
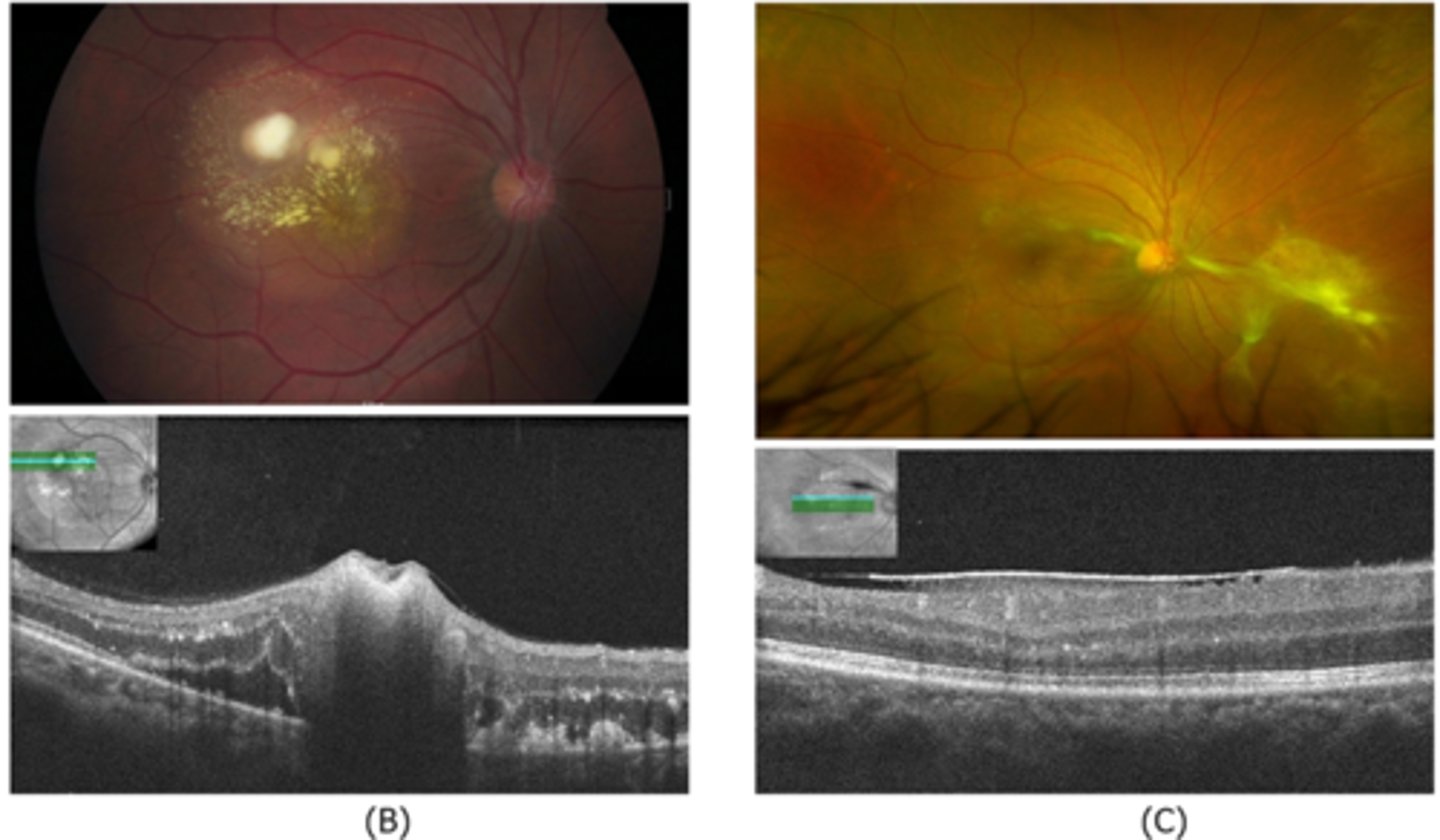
How does ocular toxocariasis appear on OCT, as seen here in patient C?
granuloma now in nasal retina, fibrous memb where granuloma once was (looks like ERM)
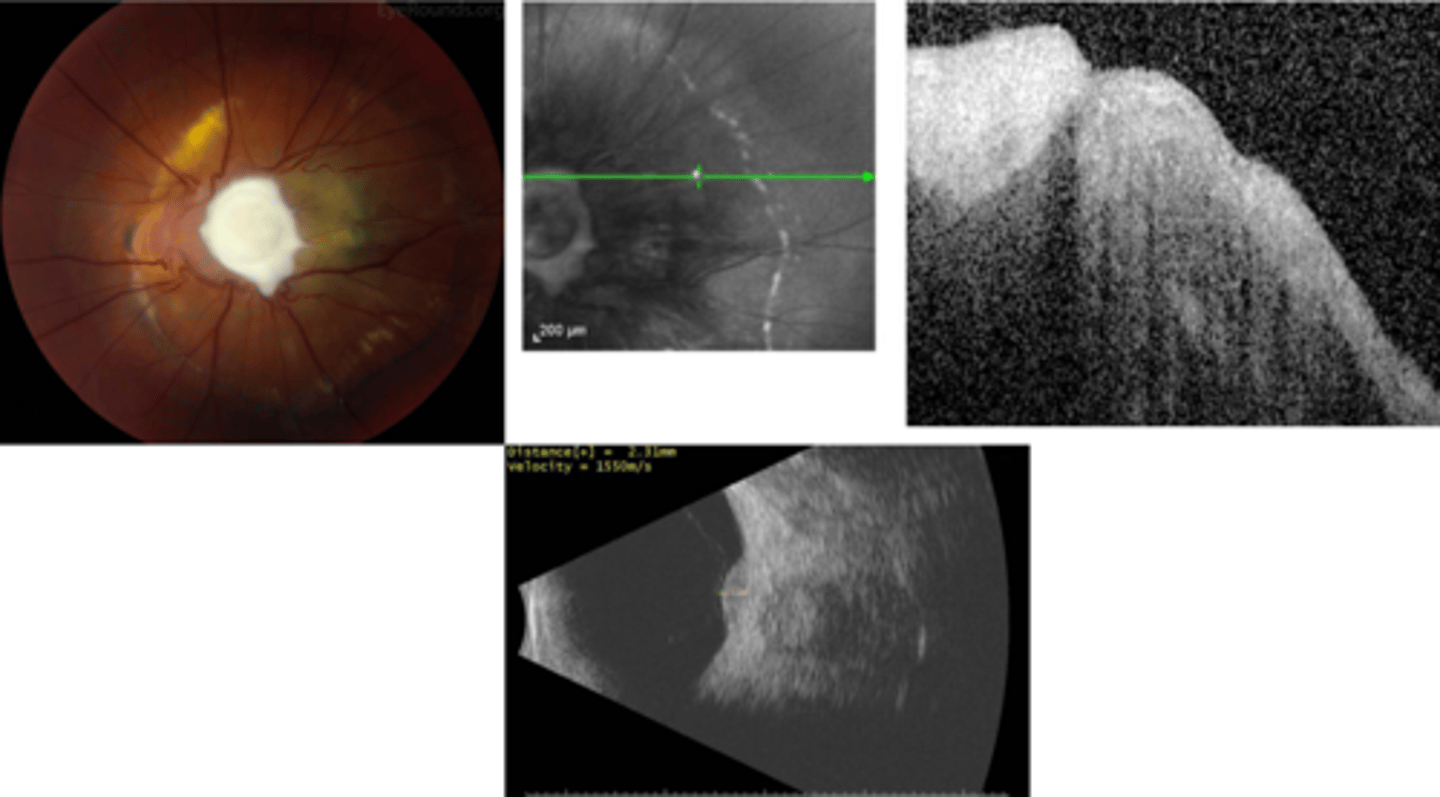
How does ocular toxocariasis appear on B-scan here?
granuloma mass over ONH = high-reflectivity
What is the most common cause of infectious posterior uveitis in non-immune compromised pt's?
ocular toxoplasmosis