IMOS Module 4 - Copper/Bronze
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UF IDS2935: Impacts of Material Science Quest Fall 2023
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Properties of Copper and Bronze
metals
malleable
opaque
electrical conductor
thermall conductor
shiny, hard appearance
Copper v. Bronze
pure element v. alloy of copper and impurity (arsenic or tin)
melting point at 1084C v. 950C
hardness of 80 MPa v. 700 MPa
yield strength of 70 MPa v. 220 MPa
methods to strengthen bronze
plastic deformation (permanent)
elastic deformation (temporary) (dislocations → plastic deformation)
work hardening (add dislocations)
cold-rolling (increase tensile strength)
impurtities (block disolations)
Copper reaction
CuCO3 + heat = 2Cu + CO2
2CuCo2 + O2 = 2CO
CuO + CO = Cu + CO2
Smelting process
calls for mixing of ore with charchoal
resource intensive
140 lbs of wood = 20 lbs of charchol
2 lbs of CuCo2 (malachite) = 1lb copper
crucible and furnace
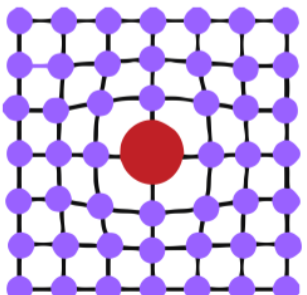
Phase diagram of Arsenic
x-axis = composition (As)
y-axis = temp.
6.8% at 685C is max solubility in copper
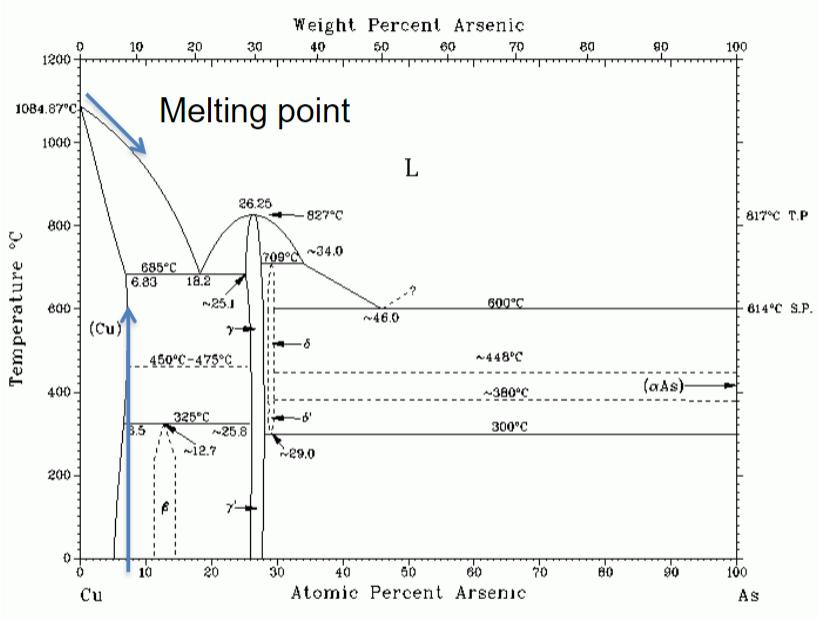
Arsenic alloy
produces altered color
increases the hardness of copper
lower melting point
oxidizes during smelting
produces AsO3 bi-product (toxic)
Tin alloy
increases strength
heat treat ment changes strength
adding too much tin can cause copper to be weaker
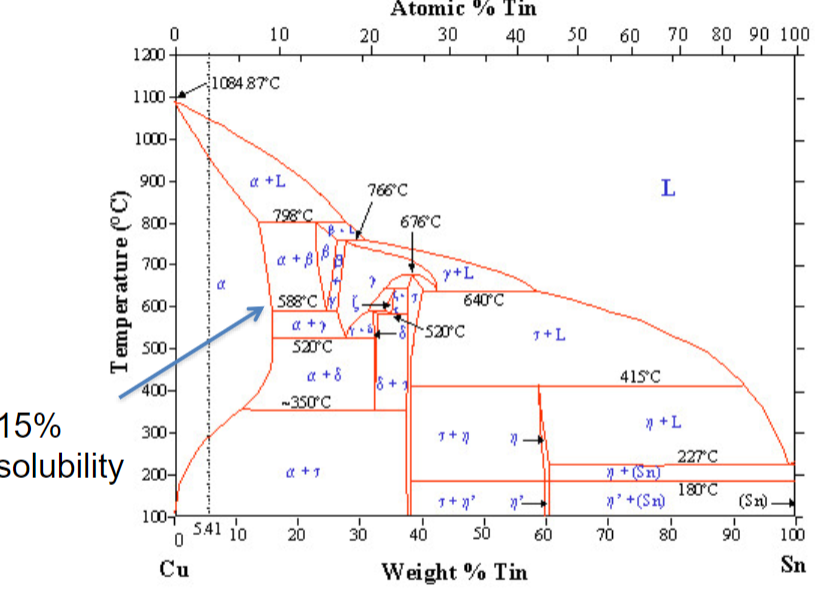
Tin v. Arsenic alloy
dissolve more tin than arsenic (<15%)
less toxic
harder to find than arsenic
Copper Age
5500-3000 BC
coppersmiths drew correlations between sources, conditions, and properties of copper
deposits’ purity depends on the region
used arsenic and tin as impurities
Bronze Age
3300-1200 BC
process of smelting
Otzi mummy is proof of copper smelting
King Solomon’s temple
parallel discoveries of copper around the world
social impacts (health, mining, exploration, and experimentation)
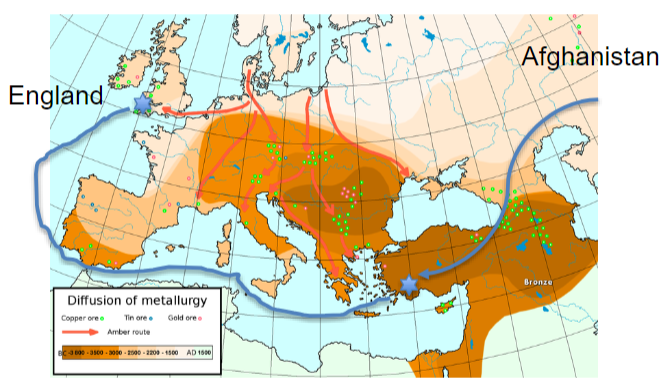
Trade developed around copper
England was the source of tin for Europe
Afghanistan also developed
casting technology created productino of art, tools, and weapons
Trade of Bronze Age
Egypt had gold
Afghanistan had tin (tin was precious metal)
Turkey had good metallurgists
very entangled society
End of Bronze Age
200 yrs. of drought, mass starvation, and earthquakes
ports shut down, centers are not used, and the tin supply chain stops
sea people attack Egypt and Hittites
society breaks down
iron and Phencians rise
Annealing
cold treatment (less brittle, more efficient)
Copper ingots
circular shaped (England); ox-hide shaped (Mediterranean)
Copper ores
mMalachite (oxidized), Fahlerz (sulphides)
Pure Copper v. 10% Tin Copper Alloy
melting point 1083C v. 1000C
cast hardness: 50 HB v. 100 HB
cold-worked hardness: 100 HB v. 230 HB
Metallurgy importance
technological: new skills became necessary and common
economic: raw and finished materials became abundant
social: introduces new scales of value and social divisions
Coppersmiths
Germany
Spain
mythological smiths (Dwarfs)
Solar cells/Photovoltaic material
something that converts light into electricity; needs to beable to break bonds and create electrons and holes
Impacts of photovoltaics and solar cells
50% of CO2 comes from electricity generation
50-70% of the world relies of fossil fuels
solar energy produces 50x less CO2 than fossil fuels
solar energy is 300x cheaper than 40 years ago
industry growth is making solar energy cheaper
some regions need >9% of land area to produce enough energy
hard to recycle Si at the end of life
Grid parity
new energy cost = grid cost
Semiconductor materials
Si
CdTe
CIGS
Pervoskites