Sed Exam 2: Depositional Environments
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
glaciers
A large accumulation of ice, snow, and debris that forms on land and moves down slope under its own weight and gravity
from compression of snow → granular ice → firn → glacial ice
dependent on latitude of snowline
alpine glaciers
ice that forms in mountainous areas and flow downhill
valley glaciers
form in valley areas
piedmont glaciers
spread out into lowlands
ice caps
dome-shaped mass of glacier ice that spreads out in all directions
forms in high latitudes/ polar regions
ice sheets
dome-shaped mass of glacier ice that is greater than 50,000 km²
glacier flow
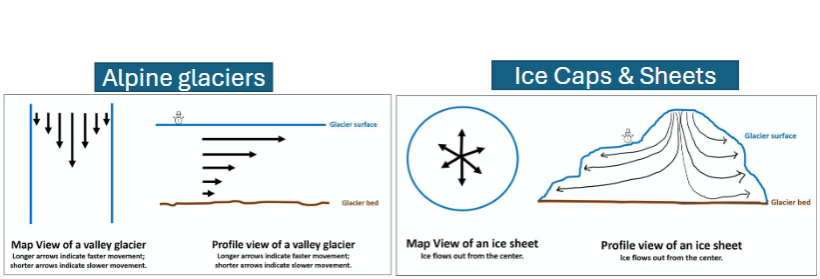
mass balance
balance between accumulation and ablation
accumulation zone: gaining mass
ablation zone: losing mass (melting, calving icebergs, sublimation)
equilibrium line evelation
warmer temperatures have ELA at higher elevations and glacier retreat
colder temperatures have ELA at lower elevations and glaciers expands

last glacial maximum
30 percent of land to 10 percent currently
supraglacial zone
on top of glacier

ice contact zone
ice in contact with bedrock
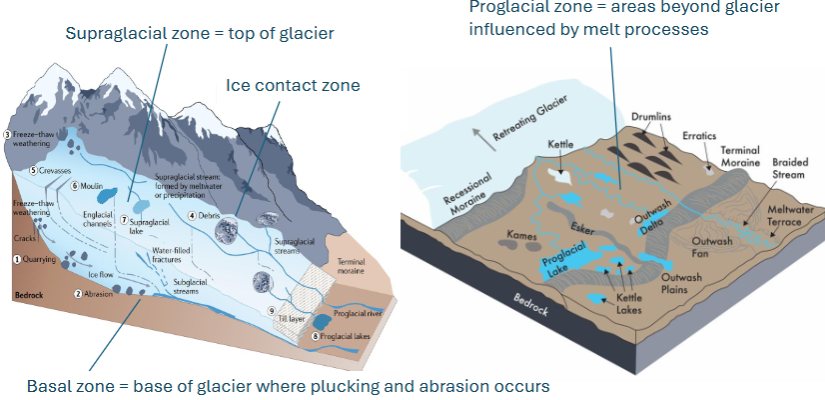
basal zone
base of glacier where plucking and abrasion occur

proglacial zone
areas beyond glacier influenced by melt processes
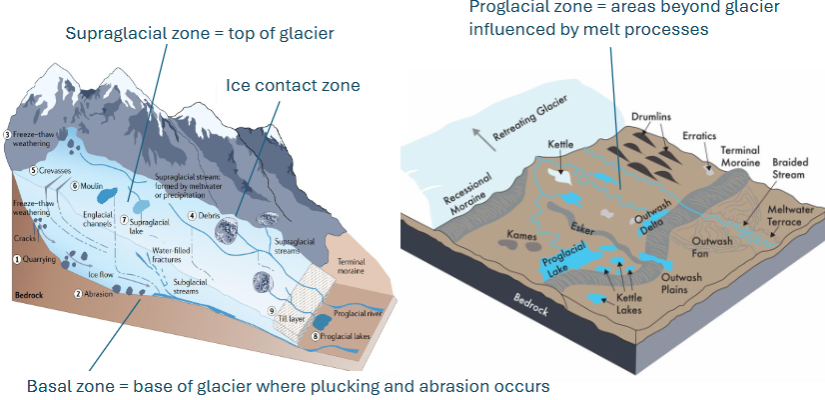
till
general term for unconsolidated sediment from glacial melt (very poorly sorted, clays-boulders)
generated from plucking via freeze-thaw at the surface and abrasion at the base and sides
tillite
a type of diamcitite from till becoming rock
glacial erratics
boulders carried far from source
glacial polish
smooth surface from abrasion
giant loofah (glacier) exfoliates face (land)
chatter marks
concentric gouges from boulder in basal ice pressed into bed
indicates flow direction
glacial grooves and striations
grooves scratched into cobbles and boulders transported by ice
rock flour
pulverized silt- to clay sized particles
occurs at mouths of braided streams that drain glaciers
grey, sticky, contribute to bright blue lakes
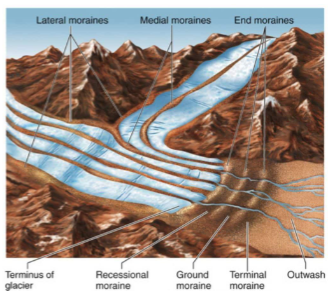
moraines
ridges, mounds, or sheets of unsorted, unstratified glacial sediment
combination of glacial till and roc flour
deposits classified as unstratified diamicts
types of moraines
terminal, recessional, lateral moraines
marine-terminating glaciers/tidewater glaciers
edge of glacier terminates in the sea instead of on land
sediment dumped and reworked by tides/waves, icebergs can form and carry debris, dropstones in marine cores
eskers
narrow sinuous ridges deposited parallel to glacial advance/retreat
formed by meltwater streams within glaciers
deposits classified as stratified diamicts
streams underneath glaciers deposit sed, occurs on top of topography, so land is not carved
kames
hill or ridges of till formed from meltwater deposits
unstratified heads of eskers
drumlins
ridges, mounds, or sheets of unsorted, unstratified glacial sediment
elongate part at ice edge, indicates direction of glacial flow
unclear how they form (erosional features from subglacial water flow, deposits infilling cavities under the ice, a combo, ice surges)
can contain stratified and/or unstratified till
kettle lakes
lakes that formed from depression created by a heavy block of ice
braided streams
create outwash plain deposits
finger lakes
elongated lake that forms in glacially incised valleys
proglacial lakes
form at edge of glaciers
expand like crazy when ice dams melt
glacial varves
seasonal laminations
bright summer layers
dark, thin winter layers
loess
windblown deposits of glacial flour
important deposits for agriculture and also for paleoclimate and paleoecology
proglacial example sequence
deformed substrate → lodgment till → ice-melt structure → braided-stream bar gravels → cross-bedded sands and gravelly sands → braided stream → glaciofluvial outwash → loess
demonstrates glacial retreat
river
body of flowing water that moves downhill via a channel
alluvial fan
fan-shaped mass of alluvium deposited when the flow of a river decreases in velocity
factors of channel form
channel slope, sediment transport processes, sediment characteristics
channel shape
number of channels and degree of sinuosity
straight, meandering, braided, anastomosing
sinuosity
the deviation of the channel from a straight line
degree (straight, low sinuous) and type (regular, irregular, and toruous)
meandering form
flows in a winding, snake-like pattern with numerous curves and bends, typically forming in flat areas
braided forms
streams with larger bedforms (bars) and accreting islands around which channels diverge and converge
anastomosing form
composed of two or more interconnected channels that enclose flood basin
“islands” but only form from flood flows and doesn’t deposit as often as braided streams
width to depth ratio
straight and meandering are deep and narrow
braided are wide and shallow
gradient
steep versus gentle
straight channels have gentle slopes while braided channels have higher slopes
flow velocity
discharge variability
sediment size, sediment load
stability of channel banks
meandering rivers
single channels, high degree of sinuosity, lower gradient, finer sed load, cohesive banks
meandering river sediments
ripples/dunes and trough cross-bedding
cutbanks (laterally migrating areas of erosion)
point bars (laterally accreting areas of deposition), characterized by cross-bedding, fining upward towards top of bar
oxbow lakes or abandoned meanders
floodplains have finer grained deposition (planar bedding) and deposition from overbank water (vertical accretion)
levees with coarse grained on river side, fine grained on floodplain side
crevasse splay when a stream breaks its natural levee creating a graded deposits and climbing ripples (similar to a bouma sequence)
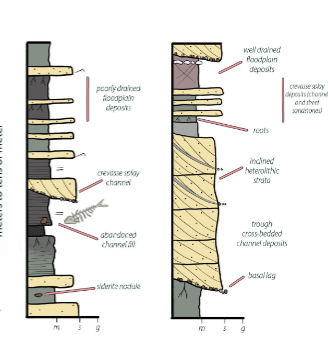
siderite (FeCO3)
forms through diagenesis in floodplainss under anaerobic, reducing conditions in areas with poor drainage
desiccation cracks and raindrop impressions
can be found in floodplain deposits
braided rivers environmental coditions
steep gradient, high relief areas, large/rapid fluctuations in river discharge, abundance of coarse sediment, noncohesive banks
braided river features
multiple channels that diverge and converge
point bars and mid-channel bars
mid-channel bars
accrete sediment on both sides
often submerged at high flow
longitudinal bars
parallel to flow
teardrop
coarse material on the upstream side and sand on the downstream side
usually form around an obstacle
can get more elongate through time
traverse bars
perpendicular to flow
wide and lobate shaped
sand size material
usually form in sandy streams when flow slows down
can migrate downstream through time
braided rivers stratigraphy
produce vertical stacking of bar deposits from episodes of channel shifting
cross-bedding in sand units (traverse bedding)
coarse material in longitudinal bars
planar and trough cross-bedding in channel deposits

factors controlling river system dynamics
sediment supply vs accommodation, hydrologic conditions (climate), base level, tectonics (uplift/subsidence)
effects from changes in river system dynamics
channel form adjustments (incision, downcutting, widening, aggradation, progradation)
sediment transfer
incision/downcutting
if a river is above base level, it will down cut and erode it’s bed
base level
lowest level to which water can flow and erode
local base level but also ultimate base level of sea level
widening
a river near base level will start eroding its banks (valley widening and river meandering)
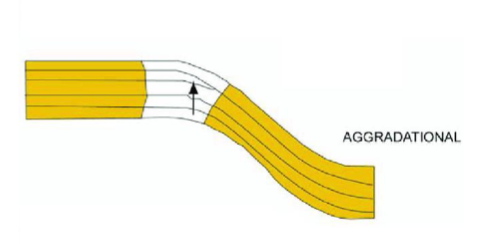
aggradation
vertical accumulation of sediments in the riverbed or floodplain
when the long-term rate of accommodation closely matches the long-term rate of sedimentation
relative balance between sediment supply and accommodation space
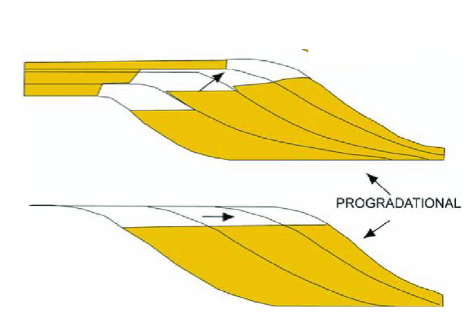
progradation
sediment sequence that build forward/outward from a source region (ex. seaward)
when the long-term rate of sedimentation exceeds long-term rate of accommodation
imbalance between sediment supple and accommodation space
impacts of sediment load and transfer
infrastructure (bridges, dams, reservoirs, navigability), river health and ecology, soil erosion from poor agricultural practices and deforestation, uplift and weathering over geologic time (basin infill, continental margin evolution), ocean sediment supply, pollution, hypoxia
suspended sediment discharge
Qs = kQC
Q is discharge
C is suspended sediment
k is conversion factor
Qs is suspended sediment discharge
the total amount of sediment transported by a river given points (as weight per unit volume)
alluvial fans
cone or wedge-shaped, consisting of poorly sorted sediment
form at a break in slope (water velocity = 0)
common in areas of high relief, where there is an abundant sediment supply
sediment transport typically associated with infrequent mass movements or flash flooding
debris-flow dominated fans
characterized by gravity flows of high density, and high viscosity
gullies, levees, lobes (active and abandoned lobes)
stream-flow dominated fans
deposition occurs by fluvial activity (by ephemeral streams)
active depositional lobe/channel occasionally shifts laterally to produce fan shaped cone of sediment
fan stratigraphy
proximal: landslides and gravity flow deposits
mid fan: poorly sorted deposits interbedded with cross-bedded sand
distal: foreset cross strata and trough filled cross strata to just trough fill corss strata
Debris flow vs Stream flow fans
debris flows have lobes of coarse sediment in mud matrix, poorly sorted
stream flow has gravel, sand, and mud and can be well-sorted and cross-bedded
hyperconcentrated flows
mixture of water and sediment in a channel which has properties intermediate between fluvial flow and debris flow
optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating
provides measure of time since sediment grains were buried (shielded from light/heat)
OSL methods
quartz and feldspar contain defects in crystal lattices that trap electrons
background radiation in sediment from radioactive decay generate those electrons that get trapped
sunlight/heat releases trapped electrons and zeros/bleaches luminescence signal
like a battery- quartz/feldspar grains are charged by radition (burial) and then depleted by sunlight (exposure)
pros/cons of OSL dating
pros: when radiocarbon is not possible (ex. sediment lack organic matter, sediments are older than 40ka)
cons: requires complete bleaching/zeroing of samples prior to burial, sediment may undergo multiple bleaching/burial cycles
OSL Age calculation
OSL Age (yr) = total dose (Gy) / Dose Rate (Gy/yr)
total dose
the luminescence signal in a sample
or how much radiation was trapped by minerals
dose rate
the radiation the sample was exposed to in the sedimentary environment (measured in the background sediment)
marginal marine environments
boundary between continental and marine depositional
riverine, wave, and tidal processes
clastics, carbonates, and evaporitic material
delta
any deposit (subaerial or subaqueous) formed by fluvial (river) sediments that build out (prograde) into a body of water
reworking of sediments at the river mouth by marine processes
delta formation
occur where rivers slow and drop their sediment load
influenced by sediment carried vs. accommodation and base level
retrogradation
marine transgression
landward migration of delta/shoreline
rate of sediment supply is greater than rate of sea level rise
aggradation
vertical increase in delta
rate of sediment supply - rate of sea level change
progradation
marine regression
seaward migration of a delta/shoreline
rate of sediment supply > rate of sea level rise
delta plain
where river meets ocean (distributary channels, floodplains, interchannel marshes)
delta front
slope down from sea level to ocean floor
(turbidites, slumps, grading)
Prodelta
subtidal to deep shelf
(fine grade, laminated)
topset deposits
gently dipping, delta plain
foreset ndeposits
delta front
steeply dipping
coarse nearshore to fine offshore
bottomset deposits
nearly flat, fine grained clays/muds, farther from shore
factors influencing sediment delivery to deltas
type/amount of sediment delivered AND density contrast between sediment laden outflow and basin water
hypopycnal
density of river water is less than density of basin water
homopycnal
density of river water is equal to the density of basin water
hyperpycnal
density of river water is greater than density of basin water
three types of deltas
fluvial dominated, tide dominated, wave dominated
fluvial dominated deltas
bird’s foot deltas
occurs when the river discharge and sediment transport is strong than reworking by waves/tides
form big delta lobes into the sea
distributaries with marshes, bays, or tidal flats
tide dominated deltas
large tidal ranges or high tidal current speeds
looks like an estuarine bay filled with many stretched island parallel to the main tidal flow
wave dominated deltas
high wave energy is the dominate factor
geometry is more lobate with smooth, arcuate to sharp margins
longshore drift can rework sediment to form barrier islands, bars, spits
delta types and sed supply
river and tide dominated deltas have high sed input
wave dominated deltas have low sed input